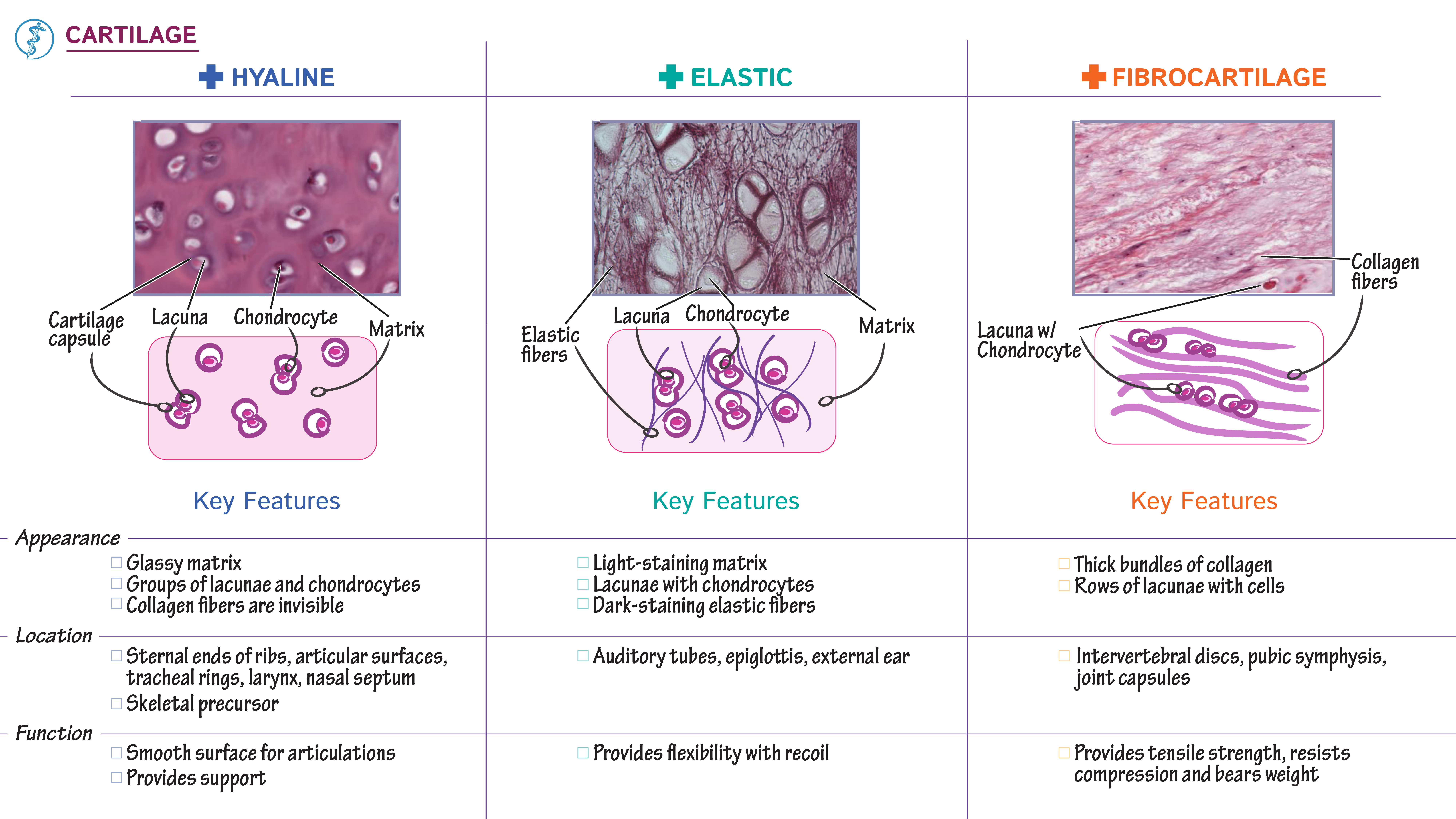
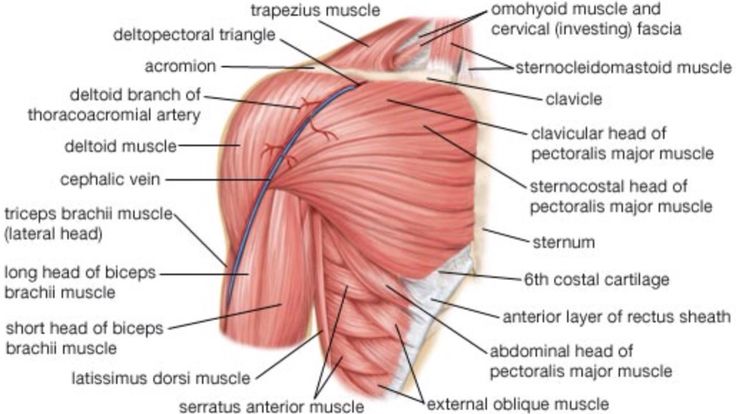
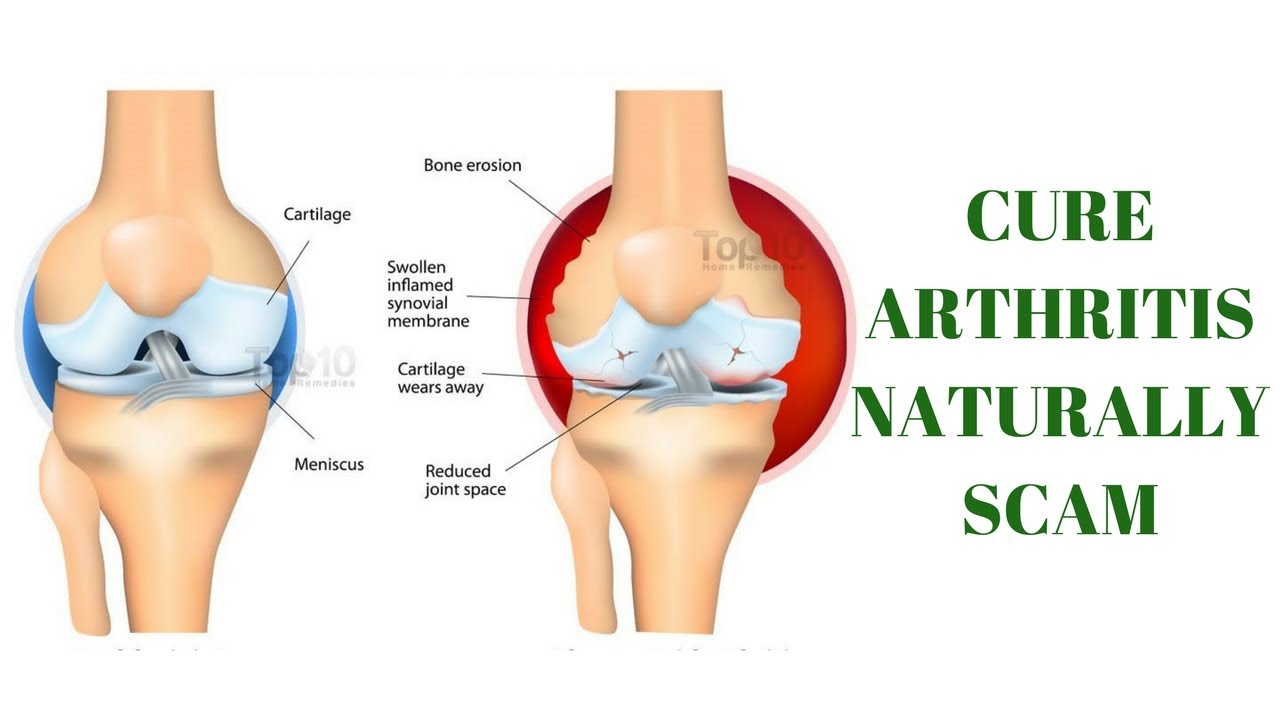
Cartilage around the heart. Costochondritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment of Cartilage Inflammation Around the Heart
What are the common symptoms of costochondritis. How is costochondritis diagnosed and treated. Can costochondritis be prevented. What is the outlook for people with costochondritis.
Understanding Costochondritis: An Overview of Cartilage Inflammation
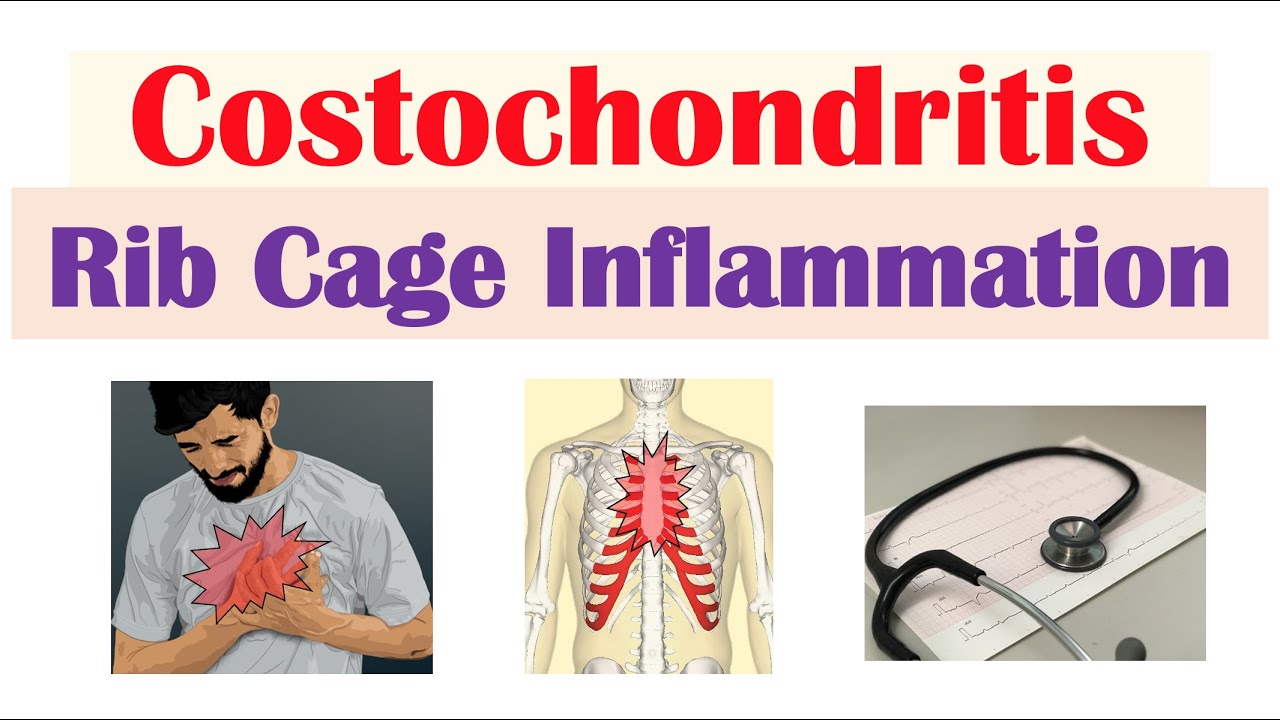
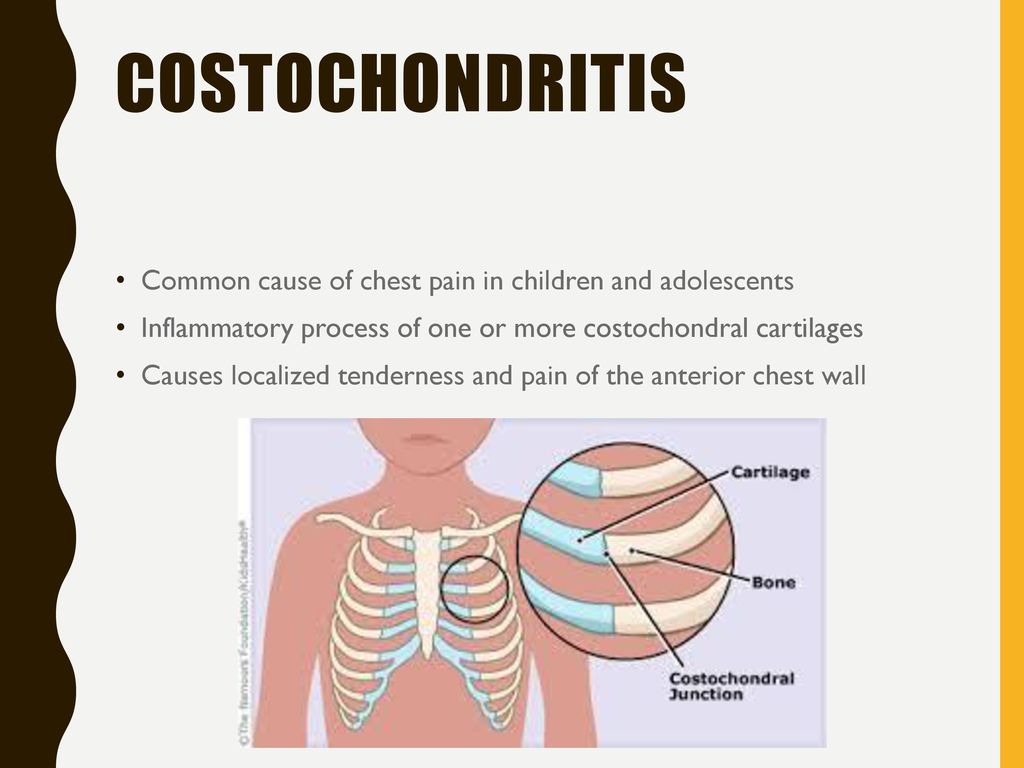
Costochondritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the cartilage connecting the upper ribs to the breastbone (sternum). This area, known as the costochondral junction, can become painful and tender, often mimicking the symptoms of a heart attack. While the condition can be distressing, it is generally harmless and typically resolves on its own without long-term complications.
Despite its benign nature, costochondritis warrants attention due to its potential to cause significant discomfort and anxiety. The condition affects people of all ages, with a higher prevalence among children and adolescents. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for proper management and peace of mind.
Identifying the Symptoms of Costochondritis
Recognizing the symptoms of costochondritis is essential for early detection and appropriate management. The primary symptom is chest pain, which can be alarming due to its similarity to cardiac-related discomfort. However, several distinguishing features can help identify costochondritis:
- Sharp, localized pain in the front of the chest, typically on the left side
- Pain that worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or physical activity
- Tenderness when pressure is applied to the affected rib joints
- Pain that may radiate to the back or abdomen
- Discomfort that improves with rest or shallow breathing
Is the pain associated with costochondritis constant? The intensity of costochondritis pain can vary. Some individuals experience persistent discomfort, while others may have intermittent pain that flares up with certain activities or movements.
Exploring the Causes and Risk Factors of Costochondritis
The exact cause of costochondritis often remains unclear, but several factors have been identified as potential contributors to its development:
- Physical trauma or injury to the chest wall
- Overuse or strain of the upper body muscles
- Respiratory infections, particularly those caused by viruses
- Certain types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
- Rare cases of bacterial or fungal infections
- Tumors (in extremely rare instances)
Are certain individuals more susceptible to developing costochondritis? While the condition can affect anyone, some factors may increase the risk:
- Age: Children and adolescents, particularly between 12-14 years old, are more commonly affected
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop costochondritis than men
- Physical strain: Activities involving repetitive arm movements or carrying heavy loads (such as backpacks) may increase risk
- Medical history: Individuals with a history of chest injuries or certain medical conditions may be more prone to costochondritis
Diagnosing Costochondritis: Challenges and Approaches
Diagnosing costochondritis can be challenging, as there is no specific test to confirm the condition. Healthcare providers typically employ a process of elimination to rule out more serious causes of chest pain. The diagnostic approach may include:
- Physical examination: Checking for tenderness in the costochondral junctions
- Medical history review: Assessing symptoms, risk factors, and recent activities
- Imaging studies: Chest X-rays or CT scans to exclude other conditions
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To rule out cardiac issues
- Blood tests: To check for signs of inflammation or infection
How do doctors differentiate costochondritis from other conditions causing chest pain? Physicians rely on a combination of symptom presentation, physical examination findings, and the absence of other concerning features to distinguish costochondritis from more serious conditions like heart attacks or pulmonary embolisms.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies for Costochondritis
While costochondritis often resolves on its own, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and promote recovery:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation
- Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms
- Heat or cold therapy: Applying heat or ice to the affected area may provide relief
- Gentle stretching exercises: To improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension
- Topical anti-inflammatory creams: For localized pain relief
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS): A therapy that uses low-voltage electrical currents to alleviate pain
In more severe or persistent cases, healthcare providers may recommend additional treatments:
- Corticosteroid injections: To reduce inflammation in the affected area
- Physical therapy: To improve posture, strengthen chest muscles, and promote healing
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy: To manage pain perception and reduce anxiety associated with the condition
Can costochondritis be treated effectively at home? Many cases of costochondritis can be managed successfully with home remedies and over-the-counter treatments. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and guidance, especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
Preventing Costochondritis: Strategies for Reducing Risk
While it may not always be possible to prevent costochondritis, certain measures can help reduce the risk of developing the condition or experiencing recurrences:
- Practice good posture: Maintaining proper alignment can reduce stress on the chest wall
- Use proper lifting techniques: Avoid straining the chest muscles when lifting heavy objects
- Warm up before exercise: Gentle stretching can prepare the muscles and reduce the risk of injury
- Manage underlying conditions: Keeping arthritis or other inflammatory conditions under control may help prevent costochondritis
- Avoid overexertion: Gradually increase the intensity of physical activities to prevent strain
Is it possible to completely eliminate the risk of developing costochondritis? While these preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk, it’s not always possible to completely prevent costochondritis, especially in cases where the underlying cause is unclear or related to factors beyond an individual’s control.

Costochondritis in Special Populations: Children, Adolescents, and Adults
Costochondritis affects different age groups in unique ways, requiring tailored approaches to diagnosis and management:
Costochondritis in Children and Adolescents
Costochondritis is particularly common in young people, accounting for a significant proportion of chest pain cases in pediatric settings. Key considerations for this age group include:
- Higher prevalence in ages 12-14
- Potential link to carrying heavy school bags
- Importance of reassurance and education for both children and parents
- Need for activity modification in school and sports settings
Costochondritis in Adults
While less common in adults, costochondritis can still occur and may present unique challenges:
- Higher likelihood of misdiagnosis due to concerns about cardiac issues
- Potential impact on work and daily activities
- Increased risk in women compared to men
- Possible association with occupational factors or repetitive movements
How does the management of costochondritis differ between children and adults? The fundamental principles of treatment remain similar, but approaches may be tailored to address age-specific concerns, such as growth and development in children or occupational factors in adults.

Long-term Outlook and Quality of Life with Costochondritis
Understanding the prognosis and potential impact of costochondritis on daily life is crucial for individuals affected by the condition:
- Duration of symptoms: Costochondritis typically resolves within a few weeks to months, though some cases may persist longer
- Recurrence: Some individuals may experience recurrent episodes of costochondritis
- Impact on activities: The condition may temporarily limit physical activities but rarely causes long-term disability
- Emotional aspects: Managing anxiety related to chest pain is an important aspect of care
- Follow-up care: Regular check-ups may be necessary to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed
Can costochondritis lead to long-term complications? In most cases, costochondritis does not cause lasting damage or complications. However, chronic pain can impact quality of life, emphasizing the importance of proper management and support.
Differentiating Costochondritis from Similar Conditions
Accurately diagnosing costochondritis involves distinguishing it from other conditions that may present with similar symptoms:
Tietze Syndrome
Often confused with costochondritis, Tietze syndrome has some distinct characteristics:
- Sudden onset of chest pain that may radiate to the arms or shoulders
- Visible swelling at the affected costochondral junction
- Typically affects the upper ribs, particularly the second or third rib
- Less common than costochondritis
Other Conditions to Consider
Healthcare providers must also rule out more serious conditions that can mimic costochondritis symptoms:
- Cardiac issues: Including angina or myocardial infarction
- Pulmonary conditions: Such as pneumonia or pulmonary embolism
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Including acid reflux or peptic ulcer disease
- Musculoskeletal problems: Such as rib fractures or intercostal muscle strain
How do healthcare providers ensure they don’t miss a more serious condition when diagnosing costochondritis? A thorough medical history, physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic tests are crucial in differentiating costochondritis from potentially life-threatening conditions. When in doubt, further investigation is always warranted.
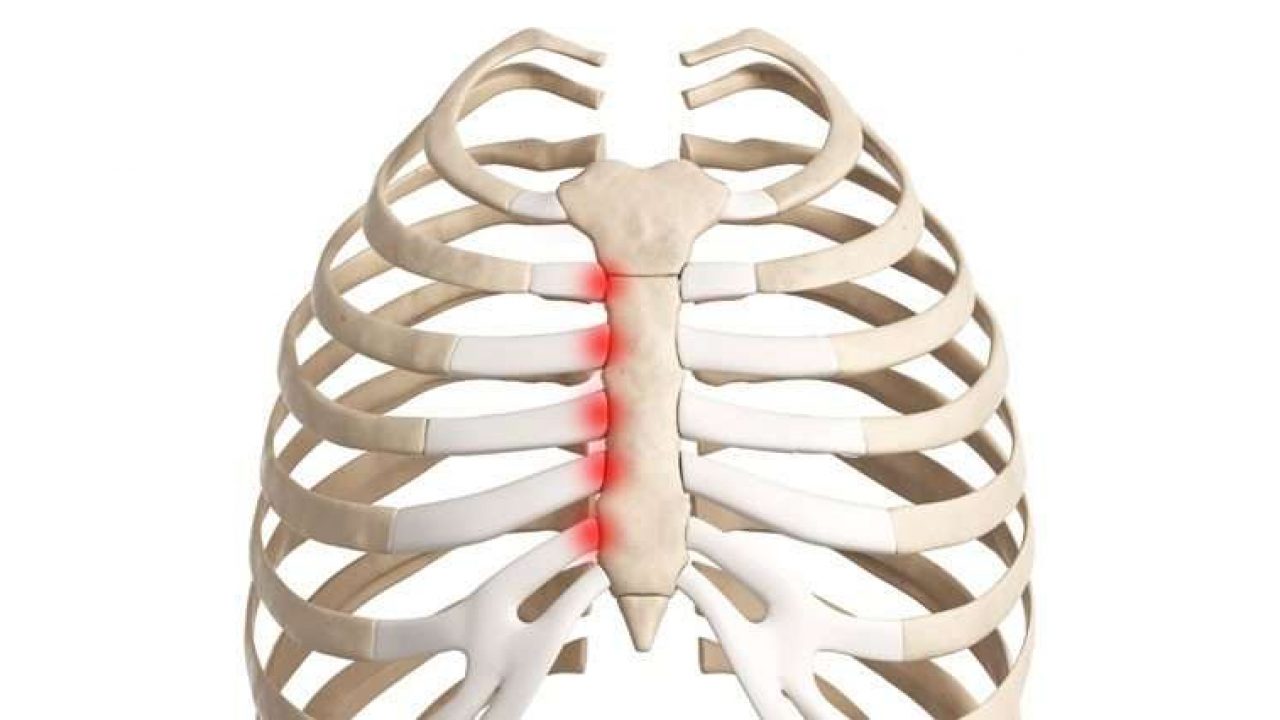
Emerging Research and Future Directions in Costochondritis Management
As medical understanding of costochondritis continues to evolve, new avenues for research and treatment are emerging:
- Improved diagnostic techniques: Development of more specific imaging or biomarker tests for costochondritis
- Novel treatment approaches: Exploration of alternative therapies or targeted medications
- Understanding risk factors: Further research into genetic or environmental factors that may predispose individuals to costochondritis
- Long-term outcomes: Studies on the natural history and potential long-term effects of recurrent costochondritis
- Prevention strategies: Development of evidence-based guidelines for preventing costochondritis in high-risk populations
What potential breakthroughs might we see in costochondritis research in the coming years? While it’s difficult to predict specific advancements, ongoing research may lead to more precise diagnostic tools, targeted treatments, and improved strategies for prevention and management of costochondritis.
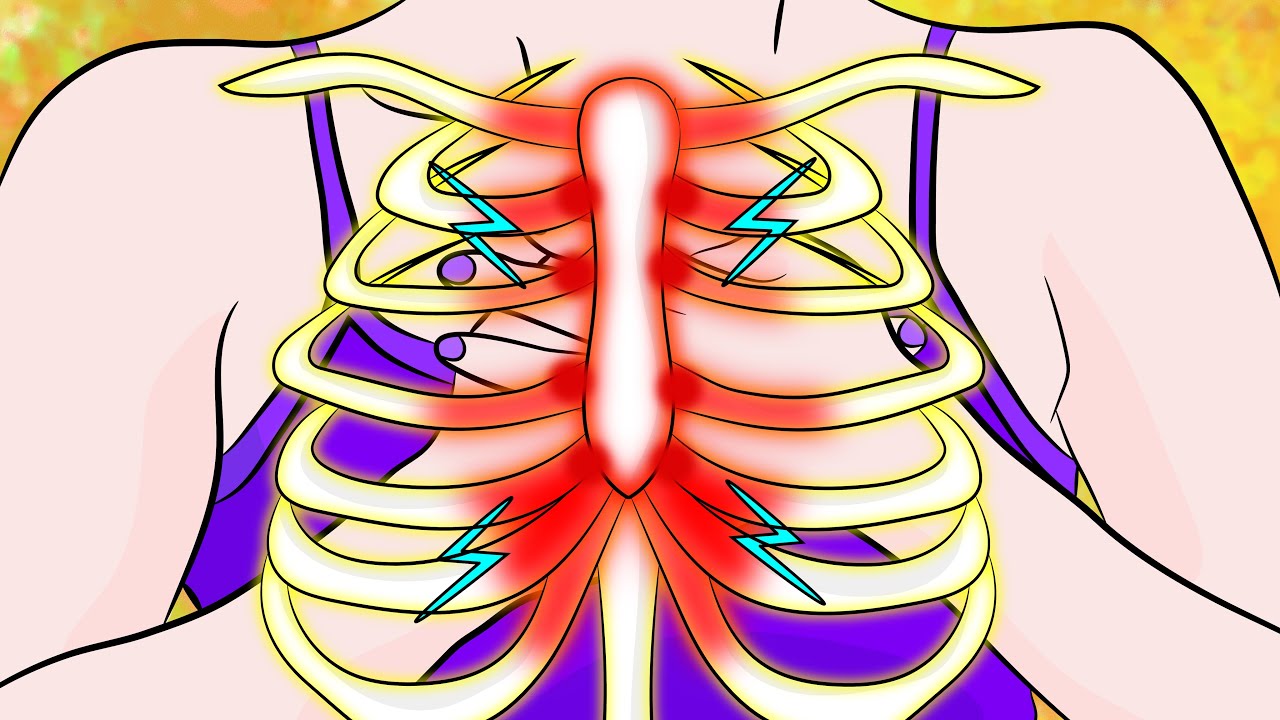
In conclusion, costochondritis, while often benign, can be a source of significant discomfort and concern for those affected. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and management strategies, individuals can navigate this condition more effectively. As research continues to advance our knowledge of costochondritis, we can look forward to improved diagnostic and treatment options in the future. For anyone experiencing persistent or concerning chest pain, it remains crucial to seek prompt medical evaluation to ensure proper diagnosis and care.
Costochondritis — Symptoms, Causes, Tests, and Treatment for Costochondritis — from WebMD
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
- What Is Costochondritis?
- Costochondritis Causes
- Costochondritis Symptoms
- Costochondritis Risk Factors
- Costochondritis Diagnosis
- Costochondritis Treatment and Home Remedies
- Costochondritis Prevention
- Costochondritis Outlook
- More
Costochondritis is inflammation of the areas where your upper ribs join with the cartilage that holds them to your breastbone. These areas are called costochondral junctions. The condition causes chest pain, but it’s typically harmless and usually goes away without any treatment. But any chest pain in adults should be taken seriously, so you should be examined and tested for heart disease.
A rare condition called Tietze syndrome is often referred to as costochondritis, but the two are distinct conditions. You can tell the difference by the following:
You can tell the difference by the following:
Tietze syndrome usually comes on all of a sudden, with chest pain spreading to your arms or shoulder and lasting several weeks.
Tietze syndrome causes swelling at the painful area (where your ribs and breastbone meet).
Doctors don’t know exactly why costochondritis happens, but they do know that some things can lead to it:
- Repeated minor trauma to your chest wall
- Overuse of your arms
- Arthritis. Costochondritis can sometimes be a sign of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, or other conditions that affect your cartilage.
- Tumors. These can move from joints and other parts of your body and settle in your chest.
- Respiratory infections caused by viruses
- Bacterial infections, especially in people who use IV drugs or have had surgery near their upper chest
- Fungal infections (in rare cases)
Chest pain linked to costochondritis usually comes on after exercise, minor trauma, or an upper respiratory infection.
- Sharp pain in the front of your chest, near where your breastbone and ribs meet, typically on the left side. It may spread to your back or belly.
- Pain when you take a deep breath or cough. It gets better when you stop moving or your breathing is quieter.
- Tenderness when you press on your rib joints. If you don’t have this tenderness, you probably don’t have costochondritis.
- If costochondritis happens because of an infection after surgery, you’ll have redness, swelling, or pus discharge at the site of the surgery.
Call your doctor if you have any of the following:
- Trouble breathing
- High fever
- Signs of infection such as redness, pus, and increased swelling at the rib joints
- Continuing or worsening pain despite medication
- Nausea
- Sweating
- Dizziness
Go to a hospital’s emergency room if you have a hard time breathing or any of the following. They’re not usually caused by costochondritis:
They’re not usually caused by costochondritis:
- High fever that doesn’t get better with fever reducers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Signs of infection at the tender spot, such as pus, redness, increased pain, and swelling
- Persistent chest pain of any type when you also have nausea, sweating, or pain in your left arm. These may be signs of a heart attack. If you’re not sure what’s causing your chest pain, go to the emergency room.
Costochondritis is a common cause of chest pain in children and adolescents. It accounts for 10% to 30% of all chest pain in children. Annually, doctors see about 650,000 cases of chest pain in people ages 10 to 21. The peak age for the condition is ages 12-14.
Kids who often carry heavy book bags over one shoulder can be more likely to develop costochondritis.
In adults, costochondritis affects women more than men (70% vs. 30%).
30%).
There is no specific test for diagnosing costochondritis. To rule out a more serious cause of your chest pain related to your heart or lungs, your doctor will probably start with tests like an echocardiogram (ECG), chest X-rays, and blood test for heart damage, among others.
If those tests come back normal, they’ll likely see if you have tenderness in any of your rib joints, usually over the fourth to sixth ribs.
If you’ve had sternum (breastbone) surgery or are at risk for heart disease, they may recommend getting a test to see if infection is the cause of your chest pain. Doctors will:
- Look for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, pus, and drainage at the site of surgery
- Recommend a more sophisticated imaging study of the chest called a gallium scan, which will show an increase in the radioactive material gallium
- Check your white blood cell count to see if it is high, a sign of infection
- Recommend a chest X-ray if pneumonia might be a cause of your chest pain
Home Remedies for Costochondritis
These home remedies may provide relief from costochondritis:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen as needed
- Using local heat or ice to relieve pain
- Avoiding unnecessary exercise or activities that make the symptoms worse; avoiding contact sports until there is improvement in symptoms, and then returning to normal activities only as tolerated
- Doing stretching exercises
Medications for Costochondritis
Your doctor may suggest the following:
- Prescription-strength NSAIDs.

- A local anesthetic and steroid injection in the area that is tender if normal activities become very painful and the pain doesn’t get better with medicine.
- Narcotics like hydrocodone/acetaminophen (Norco, Vicodin) or oxycodone/acetaminophen (Percocet, Roxicet, Tylox) can help with extreme pain, but, as with any narcotics, there’s danger of becoming addicted to them.
- Steroids. Your doctor can give you a corticosteroid shot directly into a painful joint, but that’s considered something of a last resort.
- Tricyclic antidepressants or cyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline can help ease pain, but they also can have side effects, like weight gain and drowsiness.
- Antiseizure drugs, usually gabapentin (Neurontin), are typically used to treat epilepsy, but they also may help with costochondritis.
- Infectious (bacterial or fungal) costochondritis should be treated with IV antibiotics.
 Afterward, antibiotics by mouth or by IV should be continued for another 2 to 3 weeks. You should see a doctor during recovery, and then once a year.
Afterward, antibiotics by mouth or by IV should be continued for another 2 to 3 weeks. You should see a doctor during recovery, and then once a year.
Surgery for Costochondritis
You may need surgery to remove the sore cartilage if other treatments don’t help. Your doctor can refer you to a surgeon.
Because inflammatory costochondritis has no definite cause, there is no good way to prevent it.
Noninfectious costochondritis will go away on its own, with or without anti-inflammatory treatment. Most people will recover fully.
Infectious costochondritis responds well to IV antibiotics and surgery, but recovery may take a long time.
Top Picks
Costochondritis and Arthritis: Understanding Symptoms and Treatment
If you’re like me, you probably won’t have heard of costochondritis until you or someone you know is diagnosed with it. I speak from experience because costochondritis, an inflammation of the segments of cartilage — called costosternal joints — that connect the ribs to the breastbone, wasn’t even on my radar when I went to the emergency room late one recent night with pain and tightness in my chest.
I speak from experience because costochondritis, an inflammation of the segments of cartilage — called costosternal joints — that connect the ribs to the breastbone, wasn’t even on my radar when I went to the emergency room late one recent night with pain and tightness in my chest.
Turns out I’m far from the first person with costochondritis to show up in the ER thinking they might be having a heart attack. According to one study, 30 percent of patients who went to the ER with chest pain had costochondritis.
Costochondritis and Arthritis: What’s the Link?
Costochondritis is not as common as inflammation in the joints of the hands, elbows, knees, or feet, but if you have inflammatory arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, or psoriatic arthritis, you may also be more likely to get costochondritis.
“When you have a condition that predisposes you to inflammation over multiple joints, you have increased susceptibility to developing it,” says Vinicius Domingues, MD, a rheumatologist in Daytona Beach, Florida, and medical advisor for CreakyJoints.
Though costochondritis can happen at any age, it is more common in people over 40 and, like inflammatory arthritis, it affects women more than men — 70 percent versus 30 percent.
Symptoms of Costochondritis
The most common symptom of costochondritis is pain and tenderness in the chest that’s typically described as sharp, aching, or pressure-like.
The ribs and breastbone connect in seven different places and pain can occur at any of them or even at more than one location. Costochondritis often occurs on just one side and frequently on the left side, which is why it’s often mistaken as a symptom of a heart attack.
One tipoff that it’s not a cardiac event is that your chest is painful to the touch (something that doesn’t happen when you’re having a heart attack). My doctor diagnosed my costochondritis by pressing on my chest, which hurt like hell.
Other clues it’s costochondritis: Pain is often exacerbated by upper body movement and deep breathing, even if it’s just reaching up into a high cupboard or blow-drying your hair (yes, again, I speak from experience). Moving the arm on the affected side will usually also cause pain.
Moving the arm on the affected side will usually also cause pain.
But remember: Any time you experience chest pain, you should seek medical attention. Don’t attempt to assess for yourself whether or not you may be having costochondritis, a heart attack, or something else.
Causes of Costochondritis
If you live with a form of inflammatory arthritis, that may be all it takes for the costochondral joint to become inflamed. Other reasons for costochondritis include:
- Strain from coughing
- Injury to your chest
- Infections, including respiratory tract infections or post-op infections
- Physical strain from repeated exercise or sudden exertion
According to my doctor it doesn’t take much to develop costochondritis from exertion. Because I developed costochondritis around the holidays, she asked if I’d recently lifted a turkey. I traced it to a vigorous workout on the elliptical machine followed the next day by some strenuous yardwork.
Treatment for Costochondritis
The pain from costochondritis often goes away on its own in a few days or weeks, but it can also take up to a few months or longer. It’s unusual for costochondritis to become chronic, says Dr. Domingues.
Treatment includes rest, ice or moist heat (if you can stand the cold, Dr. Domingues suggests alternating each for 20 minutes a few times a day), and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin. Here are answers to common patient questions about taking NSAIDs.
Of course, refrain from any physical activity that makes the pain worse. I found the pain from costochondritis to be exhausting so I laid quietly in bed on my stomach as much as possible (laying on my back seemed to exacerbate the pain). It took about a week for my pain to go away completely. If yours persists, physical therapy and/or steroid injections can help. The good news: By all accounts, these remedies are rarely necessary.
Track Your Arthritis Symptoms
Use our ArthritisPower app to track your symptoms and disease activity and share your results with your doctor. Learn more and sign up here.
Keep Reading
- Back Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Causes It, and How to Treat It
- How Inflammatory Arthritis Affects Your Lungs
- 11 Ways to Describe Arthritis So Other People Get What It Really Feels Like
symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Day hospital (surgery)
Malykhin
Sergey Alexandrovich
Experience 13 years
First qualification category
Make an appointment
Hygroma is a neoplasm in the form of an encysted tumor, which is filled with serous-mucous or serous-fibrous liquid mass. Favorite hygroma placements are located near the joints or tendons. In the normal state, the biggest discomfort is brought by the unsightly appearance of the tumor. When the neoplasm grows or is located near the nerve endings, the hygroma hurts or, conversely, impaired sensitivity is observed.
When the neoplasm grows or is located near the nerve endings, the hygroma hurts or, conversely, impaired sensitivity is observed.
Diagnosis of pathology includes an analysis of the anamnesis and physical examination. At the same time, classical methods of treatment are of little benefit, the most effective is removal by surgical intervention.
The word hygroma in Greek means a liquid tumor. In medicine, this word denotes a pathology in the form of a benign tumor, which consists of dense walls formed by connective tissues and a viscous filler.
Outwardly, the contents look like a transparent or yellow jelly. Chemically, the content consists of serous fluid with the addition of fibrin or mucus. The density of the tumor can be different, so the hygromas are soft and elastic, hard like cartilage or bone.
This pathology accounts for about half of all benign neoplasms in the wrist joint. Despite the favorable prognosis, a high percentage of the probability of recurrence of the disease remains. At risk are women aged 20 to 30 years, while men, children and the elderly practically do not have such a pathology.
At risk are women aged 20 to 30 years, while men, children and the elderly practically do not have such a pathology.
The most common hygromas are on the wrist or other areas of the wrist joint. The rarest case of manifestation is a hygroma of the brain, which is a consequence of a traumatic brain injury.
Symptoms and signs
The initial symptom of hygroma is the appearance of a small tumor in the area of the joints or tendons, which is clearly visible under the skin. In most cases, the pathology is single, but sometimes several neoplasms appear at once. Whatever the tumor, it always has clear boundaries. The main part of it is tightly attached to the underlying tissues, while other surfaces remain mobile and are not connected to the skin or subcutaneous tissues, so the skin can move freely.
When you click on the site of the hygroma, an adult experiences an acute attack of pain. In a calm state, the symptoms depend on the location and size of the formation, these can be:
- constant dull pain;
- pain under heavy exertion;
- radiating pain.

About a third of cases of pathology have no symptoms at all. If the defect is localized under the ligaments, then outwardly it will be invisible for a long time. In this case, the symptom is unpleasant pain at the time of bending the hand or grasping objects with the hands.
The skin can become rough, flaky and redden, or remain unchanged. At the moment of active movement, the tumor usually grows, and at rest it returns to its size. Education increases in size over time, sometimes transiently. Usually the maximum size reaches a diameter of 3 cm, but there have been cases of 6 cm.
Causes of emergence and development
The causes of the hygroma have not been definitively established. Traumatology and orthopedics distinguish several of the most likely causes of the appearance, established in a static way:
- hereditary predisposition – most often occurs in relatives close by blood;
- single injury – about a third of patients initially received a single injury, then they simply overloaded the injury site with excessive load.

The most popular places for the development of pathology are also one of the causes of hygroma. In theory, pathology can appear wherever there are connective tissues, but in practice, the distal extremities have become its favorite place:
- dorsum of wrist joint;
- palmar surface of the same joint – this also includes hygroma of the hand;
- hygroma on the foot or ankle, as well as hygroma on the finger.
Routes of infection and risk factors
What does a hygroma look like? Many believe that this is just a protruding joint capsule or tendon, in which, due to the restrained isthmus, a tumor has appeared, located separately. In fact, this opinion is not entirely accurate. Hygroma joints also affect tendons, but the cells of the capsule are degeneratively changed, as they develop in the process of degeneration of connective tissues. It is difficult to treat hygroma, standard methods do not bring any effect, and surgery is replete with a high percentage of relapses due to the processes of degeneration of connective tissue cells./the-heart-wall-4022792-FINAL-ff0aca97377c4fe9aeef72b044138011.png) The removed hygroma, while maintaining even the smallest part of the degenerative cells, will reappear.
The removed hygroma, while maintaining even the smallest part of the degenerative cells, will reappear.
Complications
Why is hygroma dangerous? The most common complication is purulent tendovaginitis, which leads to dysfunction of the affected area.
Damage to the shell of the formation leads to leakage of the liquid filling to the outside or nearby tissues. Subsequently, the shell will recover and entail the appearance of new formations, most often in larger numbers.
When to see a doctor
A traumatologist-orthopedist or a surgeon is engaged in the treatment of hygroma. You can make an appointment with any of these specialists at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitberg) in the center of Moscow near the Mayakovskaya metro station. The clinic has a wealth of experience and treats each patient individually. Reception is conducted only by first-class specialists of international level. You can make an appointment by calling +7 (495) 775-73-60, using the feedback form on the social network or with the administrators at the clinic: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskoy pereulok, 10.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of “hygroma”, the doctor collects an anamnesis and clinical signs. In some cases, to exclude the possibility of error in the diagnosis, the following examinations are carried out:
- x-ray hygroma – excludes the pathology of the bone-articular property;
- MRI is performed in case of suspicion of nodular tumors to determine the structure of the walls and the contents of the formation;
- hygroma puncture;
- hygroma on ultrasound shows the cyst itself, the uniformity of the structure, the fullness of the liquid, the presence of blood vessel formation in the walls, and other important aspects.
The main task of diagnosis is to distinguish between hygroma and other tumors and soft tissue formations, for example, lipomas, traumatic cysts, atheromas and others. This takes into account the localization, the nature of the patient’s complaints and the consistency of education. Hygromas on the arm must be distinguished from bone and cartilage neoplasms.
JSC “Medicina” (clinic of academician Roitberg) can undergo any diagnostic study with high accuracy of results.
Treatment
Hygroma treatment is divided into two types – conservative and surgical. Moreover, the first type is less effective than the second.
Conservative methods include:
- crushing or kneading – the very first methods from the past;
- punctures – introduction of sclerotics or enzymes into the formation cavity;
- physiotherapy – therapeutic mud and dressings with ointments.
The operation to remove the hygroma is more effective. The return of the disease occurs in no more than 20% of cases, while conservative therapy reaches 90% of cases.
Indications for the operation of hygroma:
- pain at rest and in motion;
- limitation of movements in the joints;
- unaesthetic appearance;
- a high rate of tumor growth is the most obvious sign for the removal of a hygroma, since the larger the size, the more difficult the operation.

The complexity of the hygroma operation increases in the presence of the following factors:
- location near vessels and ligaments, as well as nerves – the difficulty lies in the displacement of these formations;
- tendon opening – involves an operation in a hospital, while most removals are performed on an outpatient basis;
- complex localizations or large sizes – anesthesia or conduction anesthesia is used.
What to do with hygroma? Go to the surgeon and remove. Operations are performed under local anesthesia, as this, together with the application of a rubber tourniquet, makes it possible to clearly distinguish between healthy and damaged tissues due to bleeding and the introduction of an anesthetic. This distinction is of great importance during the operation, because the smallest parts of the altered tissues left lead to a new formation of hygroma.
How to remove hygroma forever? During the removal process, it is necessary to completely excise the degenerative tissues and carefully examine the base for the presence of small cysts, which also need to be removed.
How to treat hygroma surgically? After complete excision of damaged tissues, the cavity is washed, which is sutured. The wound must be drained. The limb is fixed with a plaster splint after applying a pressure bandage. Hard fixation is especially necessary in the following cases:
- hygroma of the joints;
- hygroma on the finger;
- hygroma on the arm.
Seams no later than on the tenth day.
Today, laser removal of hygroma is becoming widespread. The advantages of laser hygroma removal are:
- small cut area;
- minor tissue trauma;
- shorter recovery period.
The prognosis of treatment is favorable, since the formation is benign and must be completely removed during the treatment.
Folk recipes
Alternative recipes for hygroma of the hand can only have an additional effect aimed at relieving symptoms – reducing inflammation and pain, as well as reducing the level of discomfort. For these purposes, apply:
For these purposes, apply:
- cabbage leaf – as a compress with honey or as food;
- freshly squeezed cabbage juice twice a day for half a glass for a month on an empty stomach;
- wormwood juice – as a compress, it is necessary to rub into the site of the tumor.
Prophylaxis
Preventive measures are:
- exclusion of injuries of the wrist and hand;
- the timeliness of the treatment of inflammation in the joints, such as bursitis and tendovaginitis.
Anatomy and physiology of the nose – Zelenin NV
The external nose has the shape of a trihedral pyramid. The bony part is represented by the nasal bones. Connecting along the midline, they form the back of the nose. Outside of the nasal bones are the frontal processes of the upper jaw, which are the lateral surfaces of the external nose. The nasal bones, the frontal processes of the upper jaw, the upper jaw form a pear-shaped opening, to the edges of which cartilaginous formations adjoin. Under the edge of the nasal bones in the form of a roof fit the upper lateral (triangular) cartilages. In the lateral direction, they pass into fibrous tissue, reaching the edges of the piriform opening. The triangular cartilages are adjacent to the lower lateral (wing) cartilages, which are located at the tip of the nose and nasal wings. Each of the cartilages forms two legs: the larger one, the lateral one, is located in the wing of the nose, and the narrower one, the medial one, goes in the skin septum. Between the triangular and alar cartilages is the quadrangular cartilage of the nasal septum. The outer nose is covered with skin. The skin covers not only the outer, but also the inner part of the surface of the wings, the nasal septum and its bottom.
Under the edge of the nasal bones in the form of a roof fit the upper lateral (triangular) cartilages. In the lateral direction, they pass into fibrous tissue, reaching the edges of the piriform opening. The triangular cartilages are adjacent to the lower lateral (wing) cartilages, which are located at the tip of the nose and nasal wings. Each of the cartilages forms two legs: the larger one, the lateral one, is located in the wing of the nose, and the narrower one, the medial one, goes in the skin septum. Between the triangular and alar cartilages is the quadrangular cartilage of the nasal septum. The outer nose is covered with skin. The skin covers not only the outer, but also the inner part of the surface of the wings, the nasal septum and its bottom.
The nasal cavity connects the body with the air. It is an air channel of various diameters, surrounded by the bones of the facial and cerebral parts of the skull, in front communicating through the nasal openings with the external environment, behind with the nasopharynx. The lateral wall of the nasal cavity is represented by: nasal bone, upper jaw, lacrimal bone, ethmoid bone, palatine bone, inferior nasal concha, pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. A feature of this wall is the presence of turbinates on it: lower, middle, upper, which delimit the corresponding nasal passages. The nasolacrimal canal opens in the lower nasal passage. Under the middle nasal passage, the fistula of the maxillary sinus, anterior and middle cells of the ethmoid bone open. The posterior ethmoid cells and the sphenoid sinus open into the superior nasal passage. The floor of the nasal cavity is formed by horizontal processes of the upper jaw and palatine bone, which simultaneously serve as the basis of the hard palate.
The lateral wall of the nasal cavity is represented by: nasal bone, upper jaw, lacrimal bone, ethmoid bone, palatine bone, inferior nasal concha, pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. A feature of this wall is the presence of turbinates on it: lower, middle, upper, which delimit the corresponding nasal passages. The nasolacrimal canal opens in the lower nasal passage. Under the middle nasal passage, the fistula of the maxillary sinus, anterior and middle cells of the ethmoid bone open. The posterior ethmoid cells and the sphenoid sinus open into the superior nasal passage. The floor of the nasal cavity is formed by horizontal processes of the upper jaw and palatine bone, which simultaneously serve as the basis of the hard palate.
The nasal septum divides the nasal cavity into two parts. It consists of bone and cartilage parts. The bone part is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and the vomer. The perpendicular plate from above in front adjoins the frontal bone and to the inner surface of the nasal bones, and behind and below it connects to the upper edge of the vomer. A quadrangular cartilage enters between the anterior edge of the perpendicular plate and the anterior third of the vomer. The upper edge of the cartilage forms the anterior part of the back of the nose. The medial pedicle of the greater alar cartilage adjoins the anterior edge of the quadrangular cartilage. Skin-cartilaginous, anterior, section of the nasal septum, in contrast to the bone, is mobile.
A quadrangular cartilage enters between the anterior edge of the perpendicular plate and the anterior third of the vomer. The upper edge of the cartilage forms the anterior part of the back of the nose. The medial pedicle of the greater alar cartilage adjoins the anterior edge of the quadrangular cartilage. Skin-cartilaginous, anterior, section of the nasal septum, in contrast to the bone, is mobile.
The nasal cavity performs the following functions: olfactory, respiratory, protective, speech.
The olfactory region is represented by olfactory, basal and supporting cells. It occupies the space above the middle of the middle turbinate. In the olfactory region there are tubular-alveolar glands that produce a serous secretion that moistens the olfactory hairs and promotes the perception of olfactory irritation.
The respiratory region is lined with a mucous membrane extending into the paranasal sinuses. The mucous membrane is supplied with cavernous tissue and mucous glands located mainly in the inferior turbinate.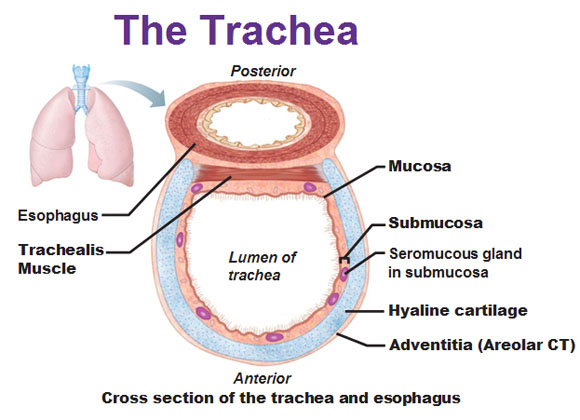 The mucous membrane is lined with ciliated epithelium, among the cells of which secretory cells are located. When breathing through the nose, the main mass of air is directed upward in an arcuate manner, from there it descends down to the choanae. When exhaling, the air rushes in the opposite direction along the same path, somewhat entering the olfactory region. Nasal breathing is a normal physiological act, and its violation causes various pathological conditions of the whole organism. Gas exchange in the lungs decreases, therefore, the alkaline reserve of the blood decreases. Oxygen metabolism is disturbed, causing a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells. Turning off nasal breathing and its difficulty is reflected in the work of the heart and blood pressure.
The mucous membrane is lined with ciliated epithelium, among the cells of which secretory cells are located. When breathing through the nose, the main mass of air is directed upward in an arcuate manner, from there it descends down to the choanae. When exhaling, the air rushes in the opposite direction along the same path, somewhat entering the olfactory region. Nasal breathing is a normal physiological act, and its violation causes various pathological conditions of the whole organism. Gas exchange in the lungs decreases, therefore, the alkaline reserve of the blood decreases. Oxygen metabolism is disturbed, causing a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells. Turning off nasal breathing and its difficulty is reflected in the work of the heart and blood pressure.
Protective nasal reflexes include: sneezing resulting from irritation of the trigeminal nerve endings by coarse suspended particles contained in the air; lacrimation that occurs when inhaling harmful air impurities.

 Afterward, antibiotics by mouth or by IV should be continued for another 2 to 3 weeks. You should see a doctor during recovery, and then once a year.
Afterward, antibiotics by mouth or by IV should be continued for another 2 to 3 weeks. You should see a doctor during recovery, and then once a year.