Does tramadol make you sleepy or awake. Tramadol Effects: Understanding the Impacts of This Prescription Painkiller
How does tramadol affect your body and mind. What are the potential side effects of tramadol use. Can tramadol lead to addiction and withdrawal symptoms. How is tramadol classified legally and what are the consequences of misuse.
What is Tramadol and How Does It Work?
Tramadol is a prescription painkiller used to treat moderate to severe pain. It belongs to a class of drugs known as opioid analgesics. While not as potent as some other opioids like heroin, tramadol shares similar effects and carries a risk of addiction.
How does tramadol relieve pain? Tramadol works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, altering the way the body perceives and responds to pain signals. Additionally, it increases levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, which can further contribute to its pain-relieving and mood-altering effects.
Common Forms of Tramadol
- White pills or tablets (most common)
- Colored capsules
- Liquid formulations
Tramadol is typically prescribed in pill or capsule form for oral consumption. However, some individuals who misuse the drug may crush the tablets and snort them, seeking a more rapid and intense effect.
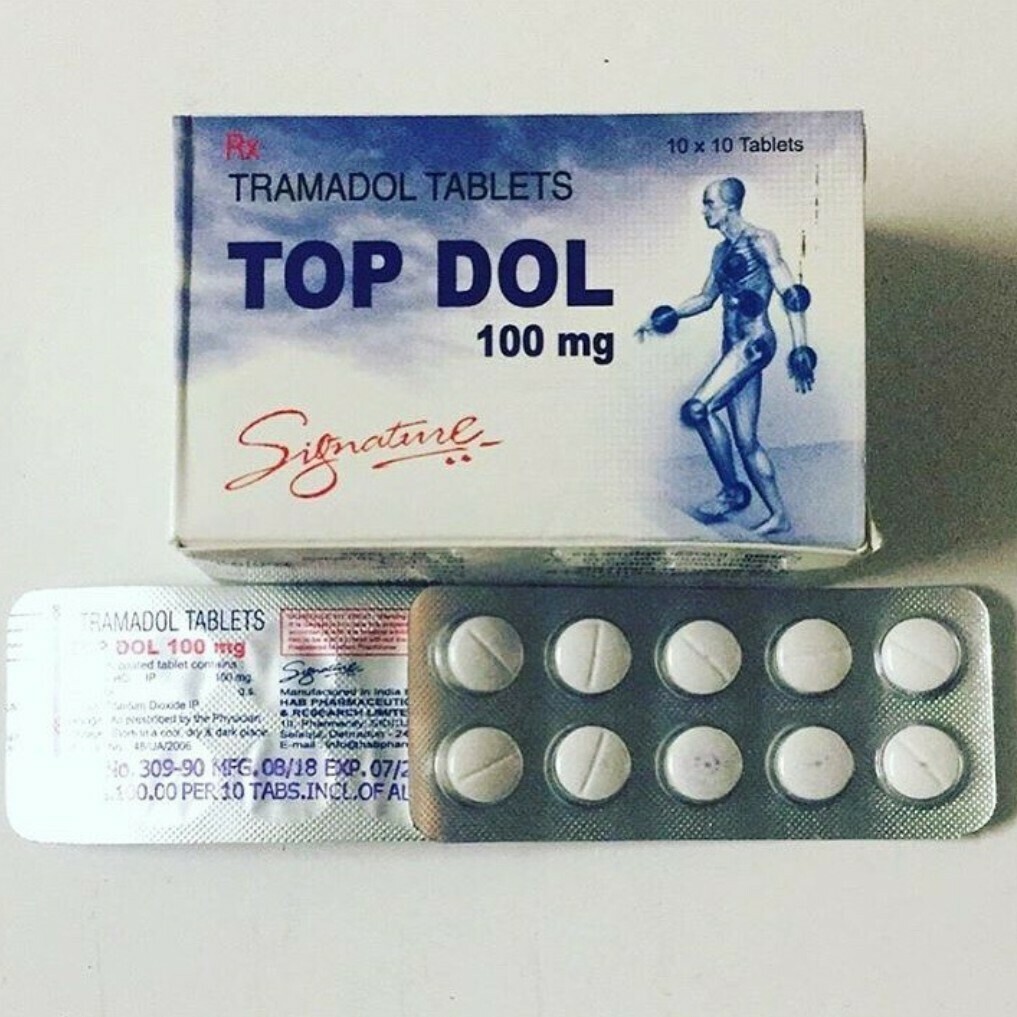
The Effects of Tramadol on Body and Mind
When used as prescribed, tramadol can effectively manage pain. However, it also produces a range of other effects on the body and mind, some of which may be desirable to those who misuse the drug.
Common Effects of Tramadol
- Pain relief
- Feelings of calmness and relaxation
- Mild euphoria
- Increased alertness (in some cases)
- Drowsiness and sedation (in other cases)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Reduced appetite
- Sweating
- Itching
- Mood changes, including irritability
Do the effects of tramadol vary from person to person? Indeed, the way tramadol affects an individual can depend on various factors, including dosage, body chemistry, and whether it’s being used in combination with other substances.
Less Common Side Effects
While less frequent, some users may experience more severe side effects from tramadol use:
- Diarrhea
- Fainting
- Excessive sweating
- Increased blood pressure
- Respiratory difficulties
- Muscle weakness
- Sensory disturbances
- Hallucinations
- Seizures
- Blood disorders
The Impact of Tramadol on Behavior and Cognition
Tramadol can significantly affect a person’s behavior and cognitive function. Users may appear drowsy, confused, or “out of it.” In some cases, individuals might seem to be on the verge of falling asleep.

How long do tramadol’s effects last? The duration of tramadol’s effects can vary based on several factors, including:
- The dosage taken
- The individual’s body size and metabolism
- Whether other drugs were consumed simultaneously
- The person’s tolerance level
Tramadol can typically be detected in urine tests for 2 to 6 days after use. However, this is only a general guideline, as detection times can vary based on individual factors and the specific testing method used.
Physical Health Risks Associated with Tramadol Use
While tramadol is less potent than some other opioids, it still carries significant health risks, especially when misused or taken in large doses.
Respiratory Depression
One of the most serious risks associated with tramadol use is respiratory depression. This condition, where breathing becomes dangerously slow and shallow, can be life-threatening. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may be at higher risk.

Serotonin Syndrome
Tramadol use has been linked to serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition resulting from excessive serotonin activity in the body. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome may include:
- High fever
- Rapid pulse
- Shivering and sweating
- Muscle twitches
- Agitation and confusion
Risks During Pregnancy
Pregnant women should avoid tramadol use, as it can be toxic to the developing fetus. The drug can cross the placental barrier and affect the unborn child, potentially leading to withdrawal symptoms in newborns.
Epilepsy and Seizure Risk
Individuals with epilepsy should only take tramadol under close medical supervision due to the increased risk of seizures associated with the drug.
Mental Health Implications of Tramadol Use
Tramadol can have significant effects on mental health, both during use and when attempting to discontinue the drug.
Interactions with Antidepressants
Individuals taking certain antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), should use tramadol only under careful medical supervision. The combination can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome and other adverse effects.

Mood Changes and Emotional Instability
Tramadol use can lead to mood swings, irritability, and emotional instability. In some cases, it may exacerbate existing mental health conditions or trigger new ones.
Cognitive Impairment
Long-term or heavy use of tramadol can impair cognitive function, affecting memory, attention, and decision-making abilities.
The Addictive Potential of Tramadol
Despite being less potent than some other opioids, tramadol carries a significant risk of addiction. Over time, regular use can lead to physical dependence and psychological cravings.
Factors Contributing to Tramadol Addiction
- Prolonged use, even when prescribed
- Misuse or abuse of the drug
- Genetic predisposition to addiction
- Co-occurring mental health conditions
- Environmental and social factors
Why do some people become addicted to tramadol after medical use? In some cases, individuals prescribed tramadol for legitimate pain management may develop dependence over time. As tolerance builds, they may need higher doses to achieve the same pain-relieving effects, potentially leading to a cycle of increased use and dependence.

Signs of Tramadol Addiction
- Inability to stop or reduce tramadol use despite wanting to
- Spending significant time obtaining, using, or recovering from tramadol use
- Neglecting responsibilities due to tramadol use
- Continuing to use tramadol despite negative consequences
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when attempting to stop
Withdrawal Symptoms and Detoxification
When a person who has developed dependence on tramadol attempts to stop or reduce their use, they may experience withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can be uncomfortable and potentially dangerous, highlighting the importance of medical supervision during detoxification.
Common Tramadol Withdrawal Symptoms
- Anxiety and restlessness
- Muscle aches and spasms
- Sweating and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Insomnia
- Runny nose and teary eyes
- Goosebumps
- Abdominal cramps
How long does tramadol withdrawal typically last? The duration and severity of withdrawal symptoms can vary, but they often begin within 12-24 hours after the last dose and may persist for several days to weeks. The exact timeline depends on factors such as the duration of use, dosage, and individual physiology.
Managing Tramadol Withdrawal
Medically supervised detoxification is often recommended for individuals withdrawing from tramadol. This may involve:
- Gradual tapering of the drug to minimize withdrawal symptoms
- Use of medications to manage specific symptoms
- Close monitoring for complications
- Psychological support and counseling
Legal Status and Consequences of Tramadol Misuse
Tramadol is classified as a controlled substance in many countries due to its potential for abuse and addiction. In the United Kingdom, for example, it is a Class C drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971.
Legal Consequences of Tramadol Misuse in the UK
- Possession: Up to 2 years in prison, an unlimited fine, or both
- Supply or intent to supply: Up to 14 years in prison, an unlimited fine, or both
- Driving under the influence: Heavy fines, driving ban, or prison sentence
Can landlords or venue owners be held responsible for tramadol use on their premises? Yes, if police catch individuals supplying illegal drugs in a home, club, bar, or hostel, they may prosecute the landlord, club owner, or any other person involved in managing the premises.

Prescription Requirements
Tramadol is only legally available with a valid prescription from a licensed healthcare professional. Obtaining or using tramadol without a prescription is illegal and can result in significant legal consequences.
Harm Reduction and Safe Use of Tramadol
While the safest approach is to use tramadol only as prescribed by a healthcare professional, there are harm reduction strategies for those who choose to use the drug:
- Never mix tramadol with other substances, especially alcohol or other depressants
- Start with a low dose and gradually increase if necessary
- Be aware of the signs of overdose and seek immediate medical attention if they occur
- Do not crush or snort tramadol tablets, as this increases the risk of overdose and addiction
- If using tramadol for pain management, explore alternative pain relief methods with a healthcare provider
How can one minimize the risk of tramadol addiction? If prescribed tramadol, follow the dosage instructions carefully, communicate openly with your healthcare provider about any concerns, and explore non-opioid pain management strategies when possible.

Seeking Help for Tramadol Addiction
If you or someone you know is struggling with tramadol addiction, it’s crucial to seek professional help. Treatment options may include:
- Medically supervised detoxification
- Inpatient or outpatient rehabilitation programs
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Support groups and peer counseling
- Medication-assisted treatment
Remember, recovery from tramadol addiction is possible with the right support and treatment approach. Don’t hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals or addiction specialists for guidance and assistance.
Tramadol | Effects of Tramadol
A prescription painkiller that people can get addicted to and abuse
Also called:
What does it look like?
- White pills or tablets (the most common type)
- Coloured capsules
- A liquid
Tramadol is used to treat moderate to severe pain. People usually swallow it in pills or capsules.
On its own, tramadol is a prescription-only painkiller. It’s used to treat pain that can’t be stopped by more common painkillers. This means you can’t buy it legally without a prescription.
People who take tramadol illegally, or abuse their prescription, sometimes crush up the tablets and snort them.
How does it make you feel?
Although tramadol is not as strong as heroin, it shares many of the same effects and both are addictive.
It is prescribed as a painkiller, but it can make you feel:
- calm
- happy
- relaxed
- awake – it may stop you from sleeping
- sick – you may need to vomit
- dizzy
- tired and lethargic – you may feel like you have no energy
- constipated
- uninterested in food
- drowsy
- confused
- sweaty
- itchy
- moody and irritable
Other, less common, side effects include:
- diarrhoea
- dizziness or fainting
- excessive sweating
- itching
- raised blood pressure
- tightness in the airways
- muscle weakness
- sensory disturbances
- hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren’t there)
- fits
- blood disorders
How does it make people behave?
Tramadol can make people feel drowsy or confused. People may look out of it or look like they’re falling asleep.
People may look out of it or look like they’re falling asleep.
How long the effects last and the drug stays in your system depends on how much you’ve taken, your size and what other drugs you may have also taken.
How long will it be detectable?
Tramadol can show up in a urine test for 2 to 6 days after using.
How long a drug can be detected for depends on how much is taken and which testing kit is used. This is only a general guide.
Physical health risks
Although tramadol isn’t as strong as some of the other opioid drugs (such as heroin), it can still cause some of the same problems and, like other opoid drugs, overdosing can kill.
Tramadol can depress breathing and may be risky for people with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Tramadol use has been linked with serotonin syndrome. This is a potentially life-threatening condition where the serotonin receptors are overstimulated. Serotonin syndrome can lead to high fever, rapid pulse, shivering, sweating, trembling, muscle twitches, agitation and confusion.

Pregnant women should not use tramadol as it can be toxic to the developing foetus.
If you have epilepsy you should only take tramadol with clear medical advice because of the known risks.
Mental health risks
- If you are on certain antidepressants you should only take tramadol with clear medical advice because of the known risks.
What is tramadol cut with?
Nothing harmful – so long as it’s prescribed by a doctor.
Although most tramadol is made by pharmaceutical companies to a high standard, tramadol bought from a dealer of from the internet can sometimes be cut with other substances or be counterfeit (fake).
If you’re not sure where the tablets have come from, there’s no way of knowing what’s inside them. Even testing kits may not find everything.
Is it dangerous to mix with other drugs?
Mixing drugs is always risky but some mixtures are more dangerous than others.
What happens if I mix Tramadol and
Select a drug
Can you get addicted?
Yes, tramadol is addictive.
Over time, tramadol can produce cravings and a psychological desire to keep on using.
Some people get addicted to tramadol after being prescribed it to treat a physical pain. They experience withdrawal symptoms after stopping to take it, so carry on taking it instead. So long as you take tramadol as prescribed by your doctor, this shouldn’t happen.
Tolerance can also build, so that users have to take more just to get the same effects or to avoid an unpleasant withdrawal.
Withdrawal symptoms include:
- nervous tremors
- anxiety
- yawning
- sweating
- runny nose
- sleep disturbance
- nausea
- diarrhoea
- goosebumps
- restlessness
- abdominal cramps and muscle spasms
Class: C
This is a Class C drug, which means it’s illegal to have for yourself, give away or sell.
Possession can get you up to 2 years in prison, an unlimited fine or both.

Supplying someone else, even your friends, can get you up to 14 years in prison, an unlimited fine or both.
Like drink-driving, driving when high is dangerous and illegal. If you’re caught driving under the influence, you may receive a heavy fine, driving ban, or prison sentence.
If the police catch people supplying illegal drugs in a home, club, bar or hostel, they can potentially prosecute the landlord, club owner or any other person concerned in the management of the premises.
Additional law details
Tramadol is a class C drug and is only available with a prescription from a doctor or other healthcare professional that is qualified to prescribe.
Was this information useful?
Does Tramadol Make Your Sleepy? How It Affects Your Sleep
Tramadol is a synthetic opioid that acts in the central nervous system (CNS) to relieve pain. Even when used as prescribed, tramadol can cause side effects, including disturbances in sleep patterns. Like other opioids, tramadol can make you tired, lightheaded, dizzy, and even sleepy. These are relatively common effects of tramadol. Because of this, it’s not recommended to drive or perform machinery immediately after taking tramadol.
Like other opioids, tramadol can make you tired, lightheaded, dizzy, and even sleepy. These are relatively common effects of tramadol. Because of this, it’s not recommended to drive or perform machinery immediately after taking tramadol.
Does Tramadol Make You Sleepy or Awake?
While the side effects of tramadol can make you sleepy and tired, tramadol use is more associated with insomnia. In a short study, people taking tramadol exhibit shorter stage 2 sleep and significantly shorter stage 4 sleep. Tramadol may also cause sleep-related problems such as sleep apnea, leading to sleep disturbances and changing healthy sleeping patterns.
Although tramadol is a depressant, mainly calming and relaxing effects, higher doses can also produce euphoric feelings. People who abuse tramadol or mix it with other substances can make tramadol act as a stimulant, having mild euphoric effects comparable to heroin.
What Are The Side Effects of Tramadol
Some people may experience adverse side effects while taking tramadol. These side effects can occur due to interactions with other medications or not taking the medicines according to prescription instructions. The most common side effects include:
These side effects can occur due to interactions with other medications or not taking the medicines according to prescription instructions. The most common side effects include:
- Drowsiness
- Dry mouth
- Heartburn
- Sleepiness
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Constipation
- Bodyache
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
How Long Do Tramadol Side Effects Last
Generally, tramadol side effects occur when you first introduce the substance to the system. As your body adjusts to the medicine, many of these side effects may go away. If side effects continue or become too bothersome, you should talk with your primary doctor to discuss your symptoms.
Long-term side effects of tramadol use, such as dependence, difficulty sleeping, muscle spasms, stomachaches, and serotonin syndrome, can be challenging to manage. Without proper medical attention, long-term side effects of continued tramadol misuse can last for years. In this case, speaking with your doctor about your tolerance and dependence on tramadol may be helpful. Some people might need to seek a medical detox program to safely and comfortably withdraw from tramadol without experiencing severe withdrawal effects.
In this case, speaking with your doctor about your tolerance and dependence on tramadol may be helpful. Some people might need to seek a medical detox program to safely and comfortably withdraw from tramadol without experiencing severe withdrawal effects.
Why Does Tramadol Affect Sleep
Although the effects of analgesic medications on sleep aren’t fully understood, the short-term effects of tramadol on sleep are being discovered. In a small study, participants received a single oral dose of tramadol. During the study, researchers found that lower doses of tramadol kept participants awake in the first hour. However, higher doses promoted sleep at first but induced wakefulness later, disturbing participants’ night sleep.
Unfortunately, there aren’t many studies looking at the connection between tramadol and sleep disturbances to understand what’s happening. It’s known that opioids disrupt sleep patterns by blocking access to rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep and the deeper restorative stages of sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions While Taking Tramadol
While taking tramadol, most patients have questions about what they can and cannot do. Here are some of the most common precautions while taking tramadol.
Can I drink while taking tramadol? No. Since tramadol and alcohol are both central nervous system depressants, combining these substances dramatically increases the risk of overdose. Extreme drowsiness, respiratory depression, and even death can occur. Other medications to avoid include other opioids, benzodiazepines, tranquilizers, antipsychotics, and muscle relaxants.
How long after taking tramadol can I drive? Tramadol affects everyone very differently. You should avoid driving, operating machinery, or engaging in activities that require mental alertness after taking tramadol. Because tramadol causes drowsiness and sleepiness, you should avoid these activities after taking it until you know how your body reacts to the drug.
Is tramadol addictive? Yes. Even when used as prescribed, tramadol is a habit-forming synthetic opioid medication that’s been linked to abuse and addiction. If you have a history of mental health disorders or substance use disorders, you should let your doctor know. Ask for non-opioid pain medicine that has less risk for addiction.
Bottom Line
Tramadol can make you feel sleepy after taking it. Drowsiness and sleepiness are common side effects about 25% of tramadol users experience. However, long-term use of tramadol can affect your sleep patterns. While the medication makes you sleepy and drowsy during the date, it tends to disrupt your REM sleep stage and keep you awake at night, potentially causing insomnia.
If you experience any side effects while on tramadol, consult your doctor to find the root cause. Interactions with other medications, misuse, or dosage can be contributing to the side effects. Discuss any questions about tramadol with your healthcare provider to determine if it’s the right medication for your symptoms.
Sources:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11270008/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/tramadol-oral-route/side-effects/drg-20068050?p=1
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34064349/
Sleep and wakefulness. Insomnia and sleeping pills
In all living beings (from protozoa to humans), all organs and systems of the body function in accordance with circadian (from the Latin words “circa” – about and “dies” – day) or circadian rhythms. Fluctuations in circadian rhythms are most pronounced during the transition of the body from sleep to wakefulness, and they also appear during sleep. The physiological significance of circadian rhythms in humans and animals lies not only in the regulation of the rhythmic activity of physiological functions and metabolism, but also in the interaction of the body with the environment.
A waking person actively interacts with the environment. In the state of sleep, this interaction does not disappear, but has a number of physiological differences.
Physiological (normal) sleep proceeds in several stages. In a healthy person, it starts from the so-called “relaxed wakefulness” (stage A), which corresponds to the transition from wakefulness to sleep. The person is in bed and getting ready for bed. Alpha waves are recorded on the encephalogram. Then comes the latent period of sleep (stage B, falling asleep and the most superficial sleep), characterized by the appearance of delta waves on the encephalogram. This is followed by superficial sleep (stage C), when the sleeping person no longer responds to weak external stimuli. On the encephalogram, high-amplitude “vertex teeth” lasting 3-5 s appear, as well as spindle-shaped bursts of rhythm – beta waves (“sleepy spindles”). Stage D (moderately deep sleep) is characterized by the appearance of fast beta waves on the encephalogram. In stage E (deep sleep), slow beta waves are episodically superimposed by slow alpha waves. In stages D and B, there is a complete loss of consciousness, a significant decrease in pain sensitivity and tone of the striated muscles, as well as a lack of response to strong stimuli.
Before awakening, a sleeping person usually goes through another, special phase of sleep, characterized by desynchronization of the encephalogram, as well as episodes of rapid eye movements with atony of the remaining striated muscles.
It must be emphasized that during the night there are four cycles of changes in sleep phases.
Another feature of the physiology of sleep has been established – during sleep, some centers of the brain are in a state of rest (inhibition), while others are in a state of excitation.
It is well known that sleep is a physiological state of the body and vital for a person. During sleep, a person rests, restores his strength, just during sleep, the processes of growth and normalization of metabolism are accelerated. There is a relationship between growth and sleep of a child. During sleep, growth hormone is released. The longer the baby sleeps, the better he grows. If we add to this that a person spends a third of his life in a dream, then the vital need for sleep becomes clear.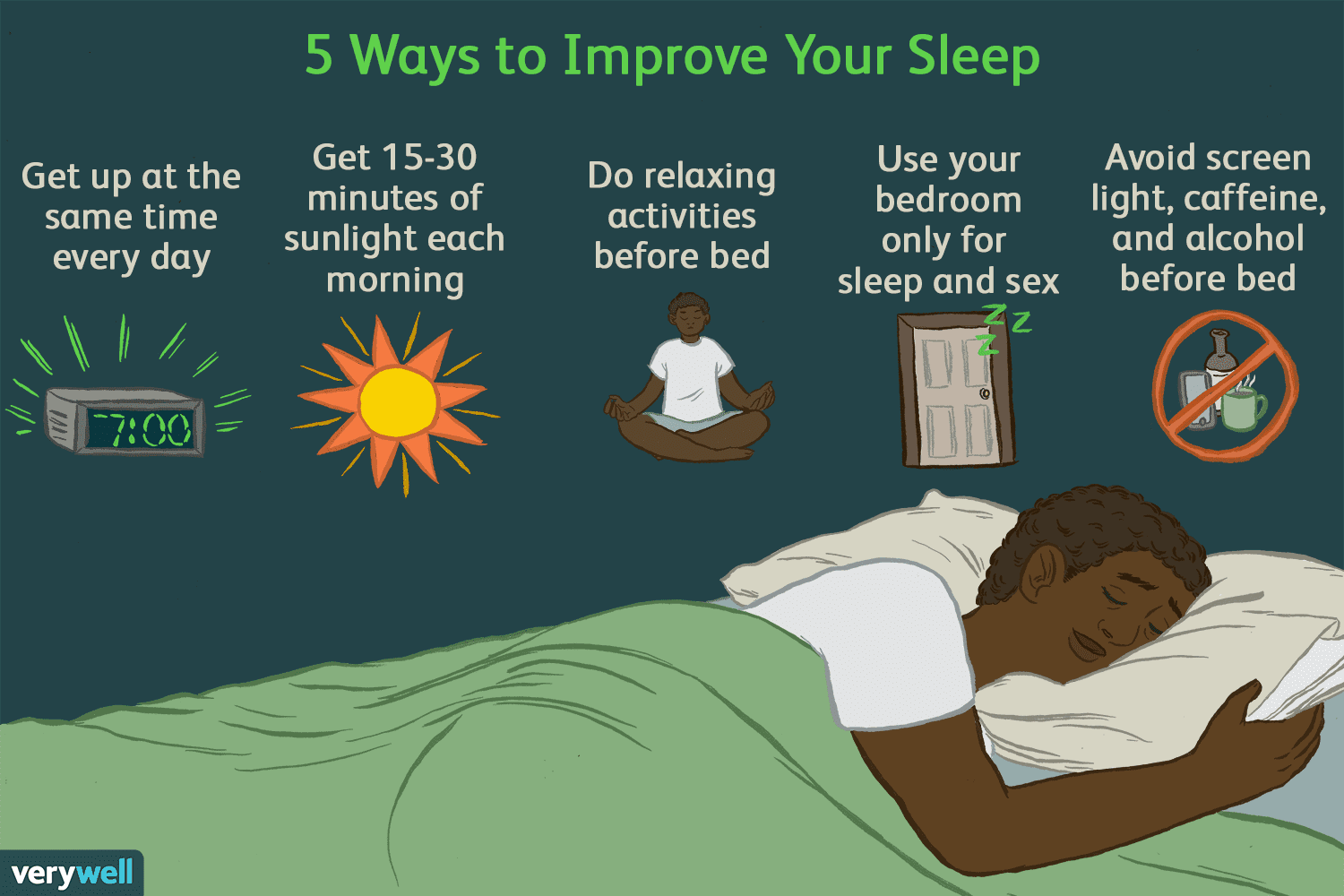
Studies conducted on animals have shown that depriving them of sleep for three days or more leads not only to dysfunction of the nervous, cardiovascular, urinary systems, digestive organs, metabolism, but also to the development of degenerative (necrotic) changes in the structure of nerve cells.
Insomnia negatively affects the general condition of the human body, reduces its ability to work, causes fatigue, increased irritability, mental imbalance, leads to the development of a state of constant stress, slows down the healing process in diseases of internal organs. Insomnia is one of the risk factors for the development of hypertension or ischemic disease, hypertensive crisis, angina attack. Without a doubt, insomnia reduces the ability to work, the mental activity of a person, and negatively affects the communication of a person in a team.
Therefore, sleep disorders are so difficult for patients to endure, and this requires the use of hypnotic drugs that are capable of inducing normal physiological sleep.
Restoration of physiological sleep is the main purpose of sleeping pills. Insomnia remedies can not only normalize a patient’s sleep, but also improve a person’s general condition.
Scientists around the world have long been searching for effective and safe sleeping pills. The first synthetic hypnotic drug was chloral hydrate, which began to be used from the middle of the 19th century. The drug, in addition to sleeping pills, has a calming effect. Chloral hydrate induces sleep close to physiological, lasting 6–8 hours. However, a pronounced irritant effect on the skin and mucous membranes, as well as the development of a state of drug dependence, sharply reduces the value of chloral hydrate as a hypnotic. This drug is currently not used for this purpose.
A significant success in the search for sleeping pills was the synthesis in 1902 by the German chemist E. Fischer of barbituric acid derivatives – barbital and phenobarbital, which had a pronounced hypnotic effect. This was no doubt a significant achievement in the search for new drugs for insomnia. Therefore, already in 1904, E. Fischer received the Nobel Prize for this discovery. Then they began to synthesize new derivatives not only of barbituric acid, but also of other chemical groups.
This was no doubt a significant achievement in the search for new drugs for insomnia. Therefore, already in 1904, E. Fischer received the Nobel Prize for this discovery. Then they began to synthesize new derivatives not only of barbituric acid, but also of other chemical groups.
Unfortunately, the first success was somewhat overshadowed by the side effects caused by barbiturates. In the morning, a person did not feel vivacity, freshness, there was a general (albeit insignificant) fatigue, a decrease in working capacity, a deterioration in mood. Research began to study the mechanism of such action.
One of the disadvantages of the action of barbiturates on the human body was that the sleep caused by these drugs does not “fit” into the phases of normal sleep. If we add to this that drug dependence develops due to the use of barbiturates, it becomes clear why these drugs have not been practically used in the treatment of insomnia in recent years.
At the end of the 60s, a new group of hypnotics appeared – benzodiazepine derivatives (diazepam, phenazepam, chlordiadepoxide, etc. ), which have not only hypnotic, but also a calming (tranquilizing) effect. The hypnotic effect of benzodiazepine derivatives is more physiological and resembles natural normal sleep, so they have become widely used to treat various forms of insomnia.
), which have not only hypnotic, but also a calming (tranquilizing) effect. The hypnotic effect of benzodiazepine derivatives is more physiological and resembles natural normal sleep, so they have become widely used to treat various forms of insomnia.
However, the use of benzodiazepines may also cause undesirable effects, such as: slight daytime sleepiness, fatigue, headache, incoordination, muscle weakness. They should not be prescribed to pregnant women due to the adverse effect on the fetus (mental retardation, muscle hypotension). Unfortunately, it turned out that drugs of this group can cause even more pronounced drug dependence than barbiturates. This has significantly limited the use of benzodiazepine derivatives for insomnia.
Imidazopyridine derivatives include zolpidem hemisuccinate. In addition to the hypnotic effect, the drug has a sedative, as well as a slightly pronounced anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and central muscle relaxant effect. Zolpidem hemisuccinate is prescribed at a dose of 10-20 mg for situational, short-term and chronic sleep disorders, including difficulty falling asleep, nocturnal and early awakenings. In a review article on the pharmacotherapy of insomnia, J.L. Goren et al (1999), note that zolpiden, interacting with benzodiazepine receptors, can cause drug dependence.
In a review article on the pharmacotherapy of insomnia, J.L. Goren et al (1999), note that zolpiden, interacting with benzodiazepine receptors, can cause drug dependence.
In recent years, a new hypnotic drug, an ethanolamine derivative, DONORMIL (doxylamine succinate) has been used in medical practice.
DONORMIL is available in the form of coated tablets and effervescent tablets. One tablet, both effervescent and coated, contains 15 mg of doxylamine succinate.
DONORMIL is widely used in the countries of Western and Central Europe, the Middle East, etc., and in most countries DONORMIL is included in the group of over-the-counter drugs.
The pharmacokinetic properties of DONORMILA are characterized by the fact that the active substance, doxylamine succinate, is well absorbed from the intestine. Its plasma half-life is comparable to that of benzodiazepines. Biotransformation of doxylamine succinate is carried out in the liver only partially. The main part of the drug (about 60%) is excreted unchanged in the urine, partly in the feces.
In the pharmacodynamics of DONORMILA, one can distinguish: 1) features of the mechanism of action; 2) the physiological nature of the hypnotic effect.
1. A feature of the mechanism of the hypnotic action of DONORMILA is that the active substance of the drug – doxylamine succinate acts simultaneously on M-cholinergic (which resembles central anticholinergics) and H 1 -histamine (which resembles the antihistamine drug – dimedrol (diphenylhydramine)) receptors in the central nervous system (CNS). Such a combined effect on receptors in the central nervous system enhances the hypnotic effect, as well as the development of the sedative effect of the drug.
2. Unlike other hypnotic drugs, DONORMIL not only increases the duration and improves the quality of sleep, but also does not disturb the physiological phases of normal sleep and circadian rhythms. This is one of the most important features of the new hypnotic drug DONORMIL.
Indications for its use are sleep disorders and insomnia of various origins in patients aged 15 years and older.
Usually the drug is prescribed in a dose of 1/2-1 tablet 15-30 minutes before bedtime. However, depending on the individual response of the patient, the dose of the drug can be reduced to 1/4 tablet or increased to 2 tablets. The effervescent tablet is dissolved in 150 ml of water, and the film-coated tablet is washed down with water. At the same time, the patient should know that the duration of sleep will be at least 7-8 hours, if the expected period of sleep is less, then after waking up for a short time, a decrease in psycho-emotional activity is possible. The drug is prescribed in courses: the first course lasting 10 days. This is enough to normalize sleep. If necessary, repeat 10-day courses are carried out with a break of 10-15 days.
At the Department of Dermatology and Venereology of the National Medical University, clinical studies were conducted to study the effectiveness of DONORMILA as a sleeping pill. The study compared the effects of DONORMILA and Dimedrol in patients with dermatological profile (eczema, pemphigus, mycosis, psoriasis) suffering from insomnia. The results of the study convincingly indicate that DONORMIL is significantly superior to Diphenhydramine in terms of the effectiveness of hypnotic action, and at the same time, it has practically no antihistamine effect.
The results of the study convincingly indicate that DONORMIL is significantly superior to Diphenhydramine in terms of the effectiveness of hypnotic action, and at the same time, it has practically no antihistamine effect.
At the Center for Somnological Research of the Russian Federation (Moscow) and at the Department of Nervous Diseases of the Moscow Medical Academy (headed by Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Prof. A.M. Vein), the hypnotic effect of DONORMILA was studied in patients with various types of insomnia. We studied the effect of the drug on the duration of sleep and its latent period. The duration of various stages of sleep was determined in accordance with international requirements according to the data of the encephalogram, electrooculogram, electromyogram, as well as on the basis of subjective and objective data. The results of the study convincingly indicate that DONORMIL has a pronounced hypnotic effect and normalizes the structure of sleep, usually without causing the development of side effects. At the same time, the effective therapeutic effect of Donormil on patients with severe sleep disorders was noted. DONORMIL reduced the duration of falling asleep, the duration of sleep, and also increased the duration of non-REM sleep phases.
At the same time, the effective therapeutic effect of Donormil on patients with severe sleep disorders was noted. DONORMIL reduced the duration of falling asleep, the duration of sleep, and also increased the duration of non-REM sleep phases.
In 1996, Schadeck B. et al. completed a multicenter, randomized, double-blind study involving 338 patients, comparing the hypnotic effect and safety of doxylamine succinate and zolpidem. The study revealed high activity of both drugs without significant differences in their safety and efficacy. However, side effects in the group of patients taking doxylamine succinate were observed less frequently. Thus, the results of the study indicate that doxylamine succinate is an effective and safe non-addictive drug that, due to its pharmacological properties, does not require special accounting and storage conditions and is available to the widest range of people with sleep disorders.
Side effects are noted only when the drug is used in high doses, in these cases, daytime drowsiness, dry mouth may occur, accommodation disturbances and constipation are even more rarely observed.
Contraindications to prescription: glaucoma, age under 15 years, hypersensitivity to the drug, lactation period.
It should be remembered that with the simultaneous use of DONORMILA with barbiturates, benzodiazepines, clonidine, opiate analgesics, neuroleptics, tranquilizers, there is an increase in the inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.
While taking DONORMILA with atropine or other blockers of M-cholinergic receptors, the risk of developing anticholinergic side effects increases: dry mouth, urinary retention is possible. Alcohol enhances the sedative effect of DONORMILA. As already noted, after taking DONORMILA, you should take 7-9 hours to sleep, if the duration of sleep is insufficient, then attention may be weakened, which can complicate driving or working with various mechanisms.
Overdose is possible only when taking the drug in very high doses.
Symptoms: mydriasis, flushing of the facial skin, hyperthermia, impaired coordination of movements, tremor, convulsions are possible. In the absence of treatment, severe hypotension may occur, accompanied by the development of collapse. The phase of excitation and development of seizures may be preceded by a state of CNS depression.
In the absence of treatment, severe hypotension may occur, accompanied by the development of collapse. The phase of excitation and development of seizures may be preceded by a state of CNS depression.
Treatment: symptomatic. It is necessary to wash the stomach, prescribe sorbents, saline laxatives. According to indications, anticonvulsants are used.
Thus, DONORMIL has the following characteristic features of pharmacological action in clinical use:
day, as well as improving the quality of life.
2. DONORMIL is effective in almost all forms of sleep disorders, as it eliminates various pathological processes that lead to insomnia.
3. After taking DONORMILA in therapeutic (recommended) doses, patients do not experience an aftereffect (headache, weakness, general weakness, etc.).
4. The drug is well tolerated by patients. When DONORMILA is used in therapeutic doses, side effects are extremely rare.
5. DONORMIL does not cause drug dependence and withdrawal syndrome.
Thus, an effective hypnotic drug, DONORMIL, has appeared in the arsenal of doctors, which can be widely used in clinical practice to treat various forms of insomnia. An ethanolamine derivative – Donormil is one of the most effective and safe hypnotics, the use of which restores normal physiological sleep in a person suffering from insomnia.
Ivan Chekman, Corresponding Member
NAS and AMS of Ukraine, Honored Worker of Science and Technology of Ukraine, Professor, Head of the Department of Pharmacology with the Course of Clinical Pharmacology of the National Medical University. A.A. Bogomolets
| LITERATURE | |
|
Tramadol tablets for oncology – instructions for use, reviews, reaction in cancer patients to the drug
Tramadol is an effective pain reliever that belongs to soft drugs. It is difficult to get a prescription for it, but it is often impossible for cancer patients to do without this drug.
Oncology and pain syndrome
Drug therapy of pain syndrome in oncology is carried out in accordance with some fundamental principles: pain in 90% of patients;
Description and pharmacological effects of Tramadol
Tramadol is a weak opioid analgesic like morphine, only weaker. This compound is a derivative of cyclohexanol. Once in the body, it binds to opioid prescriptions and blocks the transmission of pain impulses to the spinal cord. In addition, this drug has a sedative (sedative) and antitussive effect. Thus, after the introduction of Tramadol, the patient not only ceases to experience pain, but also calms down, can sleep normally.
Indications for the use of Tramadol
Tramadol is prescribed for various conditions that are accompanied by very severe pain, with the ineffectiveness of drugs from the NSAID group:
- injuries;
- oncological diseases;
- myocardial infarction;
- postoperative period;
- neuralgia.

Tramadol in oncological practice
Tramadol according to the rules of the “anaesthesia ladder” recommended by WHO, is prescribed in the second line – after the use of nonsteroidal drugs (NSAIDs).
Long-term use of opiates is addictive. But cancer patients should not be afraid of this side effect – provided that they are used strictly according to indications, adequate dosage and regimen.
Pharmacokinetics
Tramadol enters the body in an inactive form and only in the liver is converted into ten inactive metabolites and one active, which reduces pain intensity and disrupts the transmission of pain impulses in the spinal cord.
Of the tablets and drops taken, 68% of the medicine reaches the “sore spot”, all 100% are delivered by blood when injected. The disintegrated drug is excreted by 90% by the kidneys and 10% through the intestines, therefore, with renal failure, it can linger in the blood and tissues for a long time.
After taking a tablet or drops, the analgesic effect will appear after a quarter of an hour, after a maximum of half an hour, and will last almost 6 hours, Tramadol-retard acts up to 12 hours.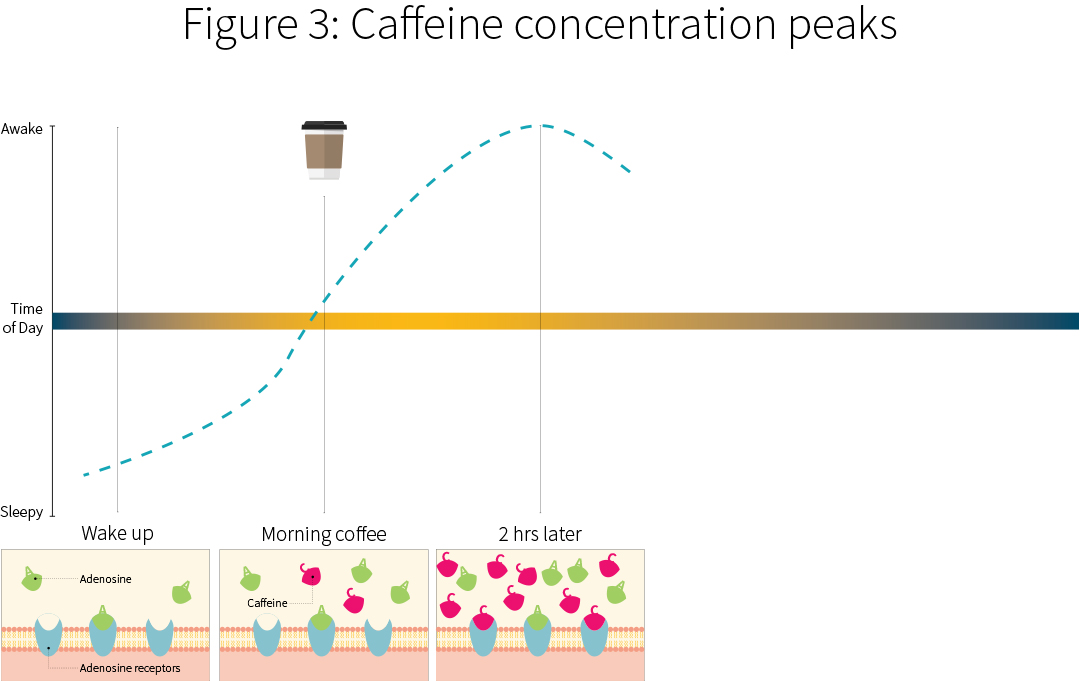 The drug is highly effective, but over time the body decomposes it more actively, which requires an increase in the dose. If tramadol does not help at all, then a transition to stronger narcotic analgesics is required.
The drug is highly effective, but over time the body decomposes it more actively, which requires an increase in the dose. If tramadol does not help at all, then a transition to stronger narcotic analgesics is required.
How to use the medicine?
Unlike most narcotic analgesics, Tramadol has several dosage forms. You can swallow capsules and tablets, and two types of solutions are also available: in drops for oral administration and in ampoules for injection.
In all cases, oral forms are preferred: injections are painful and, in patients weakened by a long illness, are associated with the possibility of developing an abscess even if complete sterility is observed – immunity works at half strength.
Tramadol drops begin to work very quickly, but they are easy to overdose. It is necessary to drip 20 drops onto a piece of sugar or into water – this is a dose for one dose. The second 20 drops are taken in the absence of pain relief within an hour after the first dose.
Capsule and tablet contains a full single dose. They are taken regardless of food. With unbearable pain syndrome, it is allowed to swallow two at once.
Long-acting tablet – Tramadol retard contains a double, triple dose, and the largest one contains 4 single doses at once, which last up to 12 hours, but in especially difficult situations it can be taken after 6 hours.
Ampoules contain 1 or 2 milliliters of solution, i.e. 50 mg or 100 mg of the drug. How often can you inject tramadol? Injections under the skin, into a muscle or vein are repeated no earlier than 4 hours later.
Contraindications
Tramadol should not be used:
- if allergic to it;
- in case of alcohol and drug intoxication, overdose of psychotropic drugs;
- is incompatible with antidepressants from the group of MAO inhibitors due to the possibility of developing a severe serotonin syndrome;
- in severe renal failure, when the drug remains in the blood for a long time at a high concentration and an overdose may occur;
- in liver failure, the formation of the active metabolite is impaired.

Oncology and Pain
90% of cancer patients experience pain of varying intensity, but not necessarily unbearable. Intolerable excruciating pain usually accompanies metastatic cancer, again, not in everyone, but with severe complications.
Duration of use
How long tramadol can be taken depends on the purpose for which it is prescribed. For example, after injuries and operations, it is used in a short course for several days, a maximum of weeks. In oncological diseases, the drug is used for a long time. It is important to strictly follow the instructions of the attending physician and immediately report all side effects.
Special instructions
During pregnancy Tramadol is prescribed only in short courses. Otherwise, the fetus may become addictive, and then the newborn child may experience a withdrawal syndrome. During breastfeeding, it is also necessary to take into account that a certain amount of the drug passes into breast milk.
Tramadol should be used with caution in case of impaired liver and kidney function .
Do not use the drug in children under 1 year of age. At the age of 1-14 years, dosages of 1 to 2 mg/kg are used. At the same time, prolonged forms of Tramadol should not be used in children under 14 years of age.
Tramadol should be used with caution in case of hypersensitivity to other opioid analgesics, confusion, drug dependence, convulsions.
The drug is incompatible with alcohol, drugs from the group of MAO inhibitors.
Tramadol reduces attention and reaction speed, therefore, during the course of treatment, you can not drive a car and engage in certain activities.
Side effects
Tramadol at therapeutic doses is well tolerated but may cause nausea , which is usually treated with conventional antiemetics – antiemetics.
In long-term treatment, especially in bedridden patients, constipation is possible , which are fought with enemas and laxatives.
Drowsiness and drowsiness are not always unfavorable for severe patients, they even help to some extent, however, this is a side effect.
The drug is characterized by excitation due to changes in the metabolism of serotonin – the “hormone of joy”.
Some patients find over time that this medicine no longer helps them effectively relieve pain and ask the doctor: “why doesn’t tramadol work?”. First, it is one of the weakest opioids. Secondly, as we mentioned above, with prolonged use, the body “gets used” to it and does not respond as well. If the pain syndrome can no longer be effectively controlled, this is an occasion to reconsider the treatment regimen, to include more powerful drugs in it.
Overdose
The maximum dose of Tramadol per day is not more than 400 mg, that is, four times 40 drops, or 8 capsules and regular tablets, 4 suppositories or 4 painkillers injections of tramadol, 2 ml each.
Exceeding the dose is accompanied by a change in consciousness – workload and even coma, convulsions, respiratory depression against the background of a strong heartbeat and a decrease in blood pressure are not excluded. To stop the condition, naloxone is used, convulsions are relieved by an injection of diazepam. Serotonin syndrome is treated with cyproheptadine.
To stop the condition, naloxone is used, convulsions are relieved by an injection of diazepam. Serotonin syndrome is treated with cyproheptadine.
Tramadol analogues
Tramadol and Tramal are the same drug from different manufacturers.
The combination of Tramadol with paracetamol from the group of NSAIDs is available under the names zaldiar, ramleps, tramaceta and forsodol.
How to replace tramadol in oncology? This question is best answered by the attending physician, who knows how the disease proceeds in a particular individual patient.
Only a doctor knows what needs to be done to make the painkiller Tramadol work in full force and with minimal risk to the patient’s health. But it is also important for the patient himself to have information about the drug in order to better understand the goals of treatment, follow the doctor’s prescriptions correctly, and notice side effects in time. Euroonco clinics use only original drugs with proven efficacy, and they are always in stock. Our doctors prescribe treatment in accordance with modern international recommendations.
Our doctors prescribe treatment in accordance with modern international recommendations.
Appointment for a consultation around the clock
+7 (495) 668-82-28
References:
- Abuzarova G.R. /The role of tramadol in oncology and surgery// Abstracts X Ross. National congress “Man and medicine”; M.; 2003.
- Abuzarova G.R., Gallinger E.Yu. Pchelintsev M.V. / Algorithm for pharmacotherapy of chronic pain syndrome in an oncological clinic // Vrach; 2011.-№ 6.
- Pain ed. Yakhno N.N. / Guide for doctors / / Ed. Medpress info; 2009
- Kogonia L.M., Voloshin A.G., Novikov G.A., Sidorov A.V. /Practical recommendations for the treatment of chronic pain syndrome in cancer patients // Malignant tumors: Practical recommendations RUSSCO #3s2, 2018 (vol. 8 ).
- Osipova N.A., Abuzarova G.R. /Treatment of chronic pain in incurable patients at home// Doctor; 2002.-№ 4.
- Novikov G.A., Osipova N.A. /Treatment of chronic pain of oncological genesis//Ed.




 – L .: Nauka, 1971; 4–11.
– L .: Nauka, 1971; 4–11. 
