Ergotamine Derivatives: Comprehensive Guide to Migraine Treatment and International Trade
What are ergotamine derivatives and how are they used to treat migraines. How do these medications work and what are their potential side effects. What is the global trade landscape for ergot alkaloids and their derivatives.
Understanding Ergotamine Derivatives and Their Role in Migraine Treatment
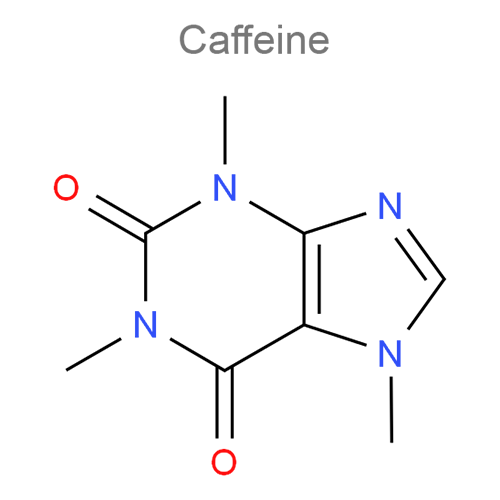
Ergotamine derivatives are a class of medications primarily used in the treatment of migraines and cluster headaches. These compounds are derived from ergot alkaloids, which are naturally occurring substances produced by fungi. Two of the most commonly used ergotamine derivatives in clinical practice are ergotamine itself and dihydroergotamine.
How do ergotamine derivatives work?
Ergotamine derivatives exert their therapeutic effects through multiple mechanisms:
- Vasoconstriction of cranial blood vessels
- Activation of serotonin receptors
- Modulation of pain signaling pathways
By targeting these various pathways, ergotamine derivatives can help alleviate the intense pain and associated symptoms of migraines and cluster headaches.

Pharmacological Properties of Key Ergotamine Derivatives
Ergotamine
Ergotamine is an alpha-1 selective adrenergic agonist and vasoconstrictor. It is primarily used for:
- Acute treatment of migraines with or without aura
- Management of cluster headaches
Ergotamine interacts with multiple receptor targets in the body, including:
- 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptors: 1A, 1B, 1D, 1F, 2A, 2B, 2C
- Alpha adrenergic receptors: 1A, 1B, 1D, 2A, 2C
- Dopamine receptors: D1, D2
Dihydroergotamine
Dihydroergotamine is a semisynthetic ergot alkaloid used in the acute treatment of migraine and cluster headaches. Its pharmacological profile is similar to that of ergotamine, but with some distinct differences:
- Greater affinity for 5-HT1D and 5-HT1B receptors
- Improved oral bioavailability compared to ergotamine
- Potentially fewer peripheral vasoconstrictive effects
Dihydroergotamine also interacts with a wide range of receptors, including:
- 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors: 1A, 1B, 1D, 1E, 1F, 2A, 2B, 2C, 4
- Alpha adrenergic receptors: 1, 2, 2A
- Dopamine receptors: D2, D3, D4
- Beta-3 adrenergic receptors
Therapeutic Applications and Administration of Ergotamine Derivatives
Ergotamine derivatives are primarily indicated for the acute treatment of migraine attacks. They are most effective when administered early in the course of a migraine episode. Common routes of administration include:
- Oral tablets or sublingual formulations
- Nasal sprays
- Suppositories
- Injectable formulations (typically reserved for severe cases or in clinical settings)
Are ergotamine derivatives suitable for all migraine sufferers? While these medications can be highly effective, they are not recommended for everyone. Contraindications include:
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding
- Coronary artery disease
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Liver or kidney dysfunction
Healthcare providers must carefully assess a patient’s medical history and risk factors before prescribing ergotamine derivatives.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Considerations
While ergotamine derivatives can be effective in treating migraines, they are associated with a range of potential side effects. Common adverse reactions include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness
- Tingling or numbness in extremities
- Muscle pain or weakness
- Chest tightness
More serious complications can occur with long-term or excessive use of ergotamine derivatives. These may include:
- Ergotism: a severe vascular condition characterized by intense vasoconstriction
- Fibrosis of heart valves or other tissues
- Increased risk of stroke or heart attack
To minimize the risk of adverse effects, it is crucial to adhere to recommended dosing guidelines and avoid overuse. Patients should be educated about the potential for medication overuse headaches, which can occur with frequent use of ergotamine derivatives.
Long-term Ergotamine Derivative Therapy: Benefits and Risks
The case study mentioned in the title, “Long-term Ergotamine Derivative Therapy for Migraine Associated with Pachymeningitis and Sixth Cranial Nerve Palsy,” highlights potential complications of prolonged ergotamine use. While the specific details of this case are not provided, it raises important questions about the long-term safety of these medications.
Pachymeningitis refers to inflammation of the dura mater, the outermost layer of the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Sixth cranial nerve palsy can result in double vision due to impaired eye movement. The association of these conditions with long-term ergotamine use underscores the need for careful monitoring and periodic reassessment of patients on these medications.
Are there alternatives to long-term ergotamine derivative therapy for chronic migraine sufferers? Several options exist, including:
- Preventive medications (e.g., beta-blockers, anticonvulsants, CGRP antagonists)
- Botulinum toxin injections
- Neuromodulation techniques
- Lifestyle modifications and trigger avoidance
Healthcare providers should work closely with patients to develop individualized treatment plans that balance efficacy and safety considerations.
Global Trade and Market Dynamics of Ergot Alkaloids and Derivatives
The international trade of ergot alkaloids and their derivatives, including ergotamine and dihydroergotamine, involves a complex network of exporters and importers. Key points regarding the global market include:
- Major exporting countries (as of 2020):
- Czech Republic (US$44.7 million)
- Italy (US$27.1 million)
- India (US$3.71 million)
- Primary importing countries (as of 2020):
- China (US$20.3 million)
- Japan (US$10.6 million)
- Romania (US$6.9 million)
In the context of Mexico’s trade balance for ergot alkaloids and derivatives:

- As of June 2020, Mexico reported international purchases of US$5.74 million, with no recorded international sales, resulting in a trade deficit.
- In 2022, the state of Ciudad de México was the primary importer, with purchases totaling US$110,000.
- Major countries exporting to Mexico in 2022 included:
- Czech Republic (US$33,500)
- India (US$30,000)
- Italy (US$29,000)
- Germany (US$16,600)
- France (US$1,000)
What factors influence the global trade of ergot alkaloids and their derivatives? Several key considerations include:
- Regulatory policies and drug approval processes in different countries
- Agricultural production of ergot-containing plants
- Advancements in synthetic chemistry and pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Shifting treatment paradigms in migraine management
- Economic factors and healthcare spending patterns
Future Perspectives and Research Directions
As our understanding of migraine pathophysiology continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of treatment options. While ergotamine derivatives have been a mainstay of acute migraine therapy for decades, ongoing research is exploring novel approaches and refining existing treatments.
Areas of active investigation include:
- Development of new ergotamine formulations with improved bioavailability and reduced side effect profiles
- Exploration of combination therapies that leverage the synergistic effects of ergotamine derivatives with other antimigraine agents
- Investigation of the long-term safety and efficacy of ergotamine derivatives in various patient populations
- Elucidation of the complex receptor pharmacology of ergotamine derivatives to guide the development of more targeted therapies
- Assessment of the potential applications of ergotamine derivatives in other headache disorders or neurological conditions
As research progresses, it is likely that the role of ergotamine derivatives in migraine management will continue to evolve. Healthcare providers and patients alike must stay informed about the latest developments to make well-informed treatment decisions.
In conclusion, ergotamine derivatives remain an important tool in the management of acute migraine attacks. However, their use must be carefully balanced against potential risks, particularly in the context of long-term therapy. As the global market for these medications continues to evolve, ongoing research and pharmacovigilance efforts will be crucial in optimizing their therapeutic potential while minimizing adverse effects.
Ergotamine Derivative | DrugBank Online
All categories
- Name
- Ergotamine Derivative
- Accession Number
- DBCAT003327
- Description
Not Available
- Drugs
Drug Drug Description Dihydroergotamine An ergot alkaloid used in the acute treatment of migraine headache and cluster headache. Ergotamine An alpha-1 selective adrenergic agonist vasoconstrictor used to treat migraines with or without aura and cluster headaches. Dihydroergotoxine Not Annotated - Drugs & Drug Targets
Drug Target Type Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1D target Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1B target Dihydroergotamine Cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme Dihydroergotamine Alpha-2A adrenergic receptor target Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B target Dihydroergotamine P-glycoprotein 1 transporter Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A target Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1E target Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A target Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2C target Dihydroergotamine Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors target Dihydroergotamine Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors target Dihydroergotamine Dopamine D2 receptor target Dihydroergotamine Dopamine D3 receptor target Dihydroergotamine Dopamine D4 receptor target Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1F target Dihydroergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 target Dihydroergotamine Beta-3 adrenergic receptor target Ergotamine Alpha-1A adrenergic receptor target Ergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1D target Ergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1B target Ergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A target Ergotamine Alpha-2A adrenergic receptor target Ergotamine Dopamine D2 receptor target Ergotamine Cytochrome P450 3A4 enzyme Ergotamine Alpha-1B adrenergic receptor target Ergotamine Alpha-1D adrenergic receptor target Ergotamine P-glycoprotein 1 transporter Ergotamine D(1) dopamine receptor target Ergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A target Ergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1F target Ergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2C target Ergotamine 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B target Ergotamine Alpha-2C adrenergic receptor target
Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl.
 Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof): Commercial exchange, international purchases and sales, market and specialization
Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof): Commercial exchange, international purchases and sales, market and specialization
About
#permalink to section
The states with the most international purchases in 2022 were Ciudad de México (US$110k).
The main commercial origins of Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) in 2022 were Czech Republic (US$33.5k), India (US$30k), Italy (US$29k), Germany (US$16.6k), and France (US$1k).
In the global context, the main exporting countries of Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) in 2020 were Czech Republic (US$44.7M), Italy (US$27.1M), and India (US$3.71M). In the same year, the main importing countries of Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) were China (US$20. 3M), Japan (US$10.6M), and Romania (US$6.9M).
3M), Japan (US$10.6M), and Romania (US$6.9M).
Trade Balance of Mexico
#permalink to section
Net Trade Balance
#permalink to section
Year20222021202020192018201720162015201420132012201120102009200820072006
The visualizations show the net balance of Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) at the level of states and countries. Colors more similar to blue, indicate that the territory presented a higher level of international sales. Colors more similar to red, indicate that the territory presented a higher level of international purchases.
Net International Trade
#permalink to section
June, 2020: US$5.74M, International Purchases
In June 2020, international sales of Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) were US$0, while international purchases reached US$5. 74M. The above results in a trade balance of -US$5.74M.
74M. The above results in a trade balance of -US$5.74M.
Exchange by Territory
#permalink to section
International Purchases
#permalink to section
Year20222021202020192018201720162015201420132012201120102009200820072006
In 2022, the states with the highest international in Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) were Ciudad de México (US$110k).
The countries with the most international sales to Mexico in 2022 were Czech Republic (US$33.5k), India (US$30k), Italy (US$29k), Germany (US$16.6k), and France (US$1k).
Specialization
#permalink to section
Specialization by State
#permalink to section
The RCA-Complexity diagram compares the Revelead Comparative Advantages of states in Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) and the Economic Complexity Index of each state.
RCA values greater than 1 indicate that the state has comparative advantages in Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof). On the other hand, high levels of complexity (ECI) are associated with higher levels of income, potential for economic growth, lower income inequality and lower emissions.
Global Market
#permalink to section
Origins and Trade Destinations
#permalink to section
20202019201820172016201520142013
The visualizations show the global market for Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof). In both charts, Mexico stands out in order to identify its participation in the export and import market.
In 2020, the main exporting countries of Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) were Czech Republic (US$44.7M), Italy (US$27.1M), and India (US$3.71M). In the same year, the main importing countries for Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) were China (US$20.3M), Japan (US$10.6M), and Romania (US$6.9M).
Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) were Czech Republic (US$44.7M), Italy (US$27.1M), and India (US$3.71M). In the same year, the main importing countries for Ergot Alkaloids of Rye and its Derivatives; Salts Thereof (Excl. Ergometrine, Ergotamine, Lysergic Acid and Salts Thereof) were China (US$20.3M), Japan (US$10.6M), and Romania (US$6.9M).
TN VED code 2939620000. Online service
TN VED
Online service
Ergotamine (INN) and its salts
TN VED position
|
Position OKPD 2
|
Customs fees
Import
| Basic rate of customs duty | 3% sol.  80 80 |
| VAT | Life-saving medical equipment Alkaloids of plant origin. (VAT Medicines): Decree 688 of September 15, 2008 of the Government of the Russian Federation 10% – Medicines (Marketing Authorization) 20% – Other Exemptions and benefits Organic chemical compounds (VAT Prod. Decree 908 of December 31, 2004 of the Government of the Russian Federation 10% – sweeteners for people with diabetes mellitus, for use in food and feed purposes (including intended for certification tests, checks, experiments) 20% – other |
Export
| Basic rate of customs duty | Duty free |
| Excise | Is not a subject to a tax |
Calculate contract
Product Features
Consequences of misuse of painkillers
Pain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAIDs, ergotamine derivatives, analgesics) are the most popular and widely used over-the-counter drugs.
Pain medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – NSAIDs, ergotamine derivatives, analgesics) are the most popular and widely used OTC drugs. At the same time, headaches (cephalgia) are very often the cause of their use. Most often it is the so-called tension headache and migraine.
The possibility of buying a drug without a doctor’s prescription in Ukraine leads to the fact that many people decide on their own which drug, at what dose and with what frequency to take. And therein lies the danger, since for each drug there are certain contraindications and restrictions for use.
First, the uncontrolled use of analgesics and NSAIDs often leads to the development of various side effects, including changes in blood composition, gastrointestinal bleeding, erosions and ulcers in the digestive tract.
And secondly, irrational (too frequent or exceeding the recommended dosage) use of painkillers for cephalalgia, including migraine, often causes the so-called drug-induced or abuse headache. Most often, such a headache occurs in chronic migraine as a result of chronic abuse of drugs for the treatment of attacks of cephalalgia. The development of overuse headache is indicated by the use of painkillers more than 2-3 times a week (10 times a month) for 3 or more months. At the same time, the severity of headache attacks and the frequency of their occurrence can progress against the background of excessive drug intake.
Most often, such a headache occurs in chronic migraine as a result of chronic abuse of drugs for the treatment of attacks of cephalalgia. The development of overuse headache is indicated by the use of painkillers more than 2-3 times a week (10 times a month) for 3 or more months. At the same time, the severity of headache attacks and the frequency of their occurrence can progress against the background of excessive drug intake.
Interestingly, analgesic-associated headache occurs only in patients with primary headache (80% of overbusy headache patients are migraine patients) and never develops as a result of taking the same drugs, but according to different indications (for example, osteoarthritis).
Theoretically, too frequent use of any migraine medications, including analgesics, NSAIDs, ergotamine derivatives, opioids, triptans, can lead to the development of “abuses”. However, since the fact of abuse (i.e., excessive frequency of use) of the drug is of greatest importance here, this problem most often occurs when taking NSAIDs and analgesics, given their greater availability and less effectiveness in moderate and severe forms of migraine. As for the mechanisms of development of abusus cephalgia, it is assumed that it is based on changes in the parts of the brain responsible for conducting pain impulses that arise as a result of regular use of headache medications.
As for the mechanisms of development of abusus cephalgia, it is assumed that it is based on changes in the parts of the brain responsible for conducting pain impulses that arise as a result of regular use of headache medications.
Diagnosis of overuse headache is not difficult – it is enough to analyze the entries in the headache diary of a patient who has addressed a doctor with complaints of progression of migraine or other primary headache, in which the time of onset of headache attacks and the number of pain medications taken for at least 3 months.
The superimposition of drug-induced headache on migraine symptoms significantly worsens the patient’s condition and requires proper treatment, the effectiveness of which depends on the patience and discipline of the patient. First of all, the doctor studies the treatment regimen, finds and cancels the “guilty” drug. Usually the complete withdrawal of such pain medication is sufficient intervention, however, in severe cases, inpatient treatment with antidepressants and detoxification therapy may be required. At the second stage, a correction of the migraine treatment regimen is carried out in order to effectively prevent attacks and most sparing pain relief in the event of the development of cephalalgia. Treatment regimens with alternating periods of frequent use of the drug and relatively long periods without treatment are preferred, since the regular use of painkillers is a major risk factor for the development of abuse headaches. A necessary condition for the effective treatment of “abuses” is the refusal to take the analgesic that caused the development of abuses headache, since any therapy will be much less effective if the patient continues to use such a drug on a regular basis.
At the second stage, a correction of the migraine treatment regimen is carried out in order to effectively prevent attacks and most sparing pain relief in the event of the development of cephalalgia. Treatment regimens with alternating periods of frequent use of the drug and relatively long periods without treatment are preferred, since the regular use of painkillers is a major risk factor for the development of abuse headaches. A necessary condition for the effective treatment of “abuses” is the refusal to take the analgesic that caused the development of abuses headache, since any therapy will be much less effective if the patient continues to use such a drug on a regular basis.
Prevention of the development of drug-induced headaches in people with migraine and other primary cephalalgias consists in refusing self-medication and strictly following the doctor’s recommendations. In particular, it is of great importance to abandon the uncontrolled increase in the doses and frequency of taking NSAIDs and analgesics, in case of their ineffectiveness, in favor of switching to triptans.

 ..
..  goods):
goods):