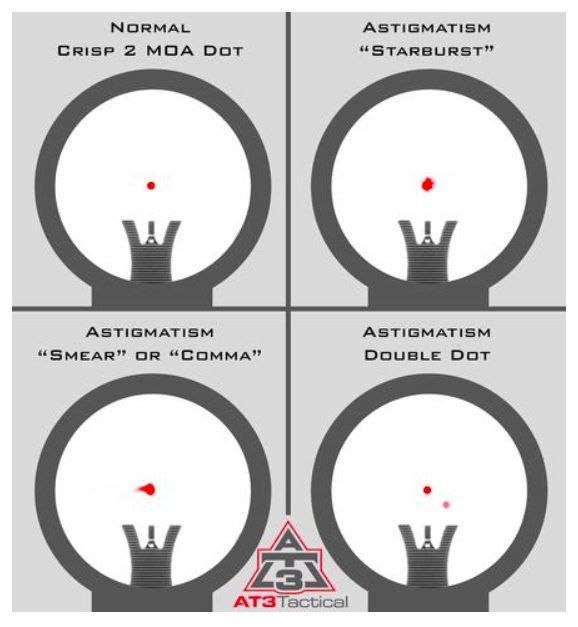
How is astigmatism diagnosed. Astigmatism: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
How is astigmatism diagnosed. What are the common symptoms of astigmatism. What treatment options are available for astigmatism. How does astigmatism affect vision. Who is at higher risk of developing astigmatism.
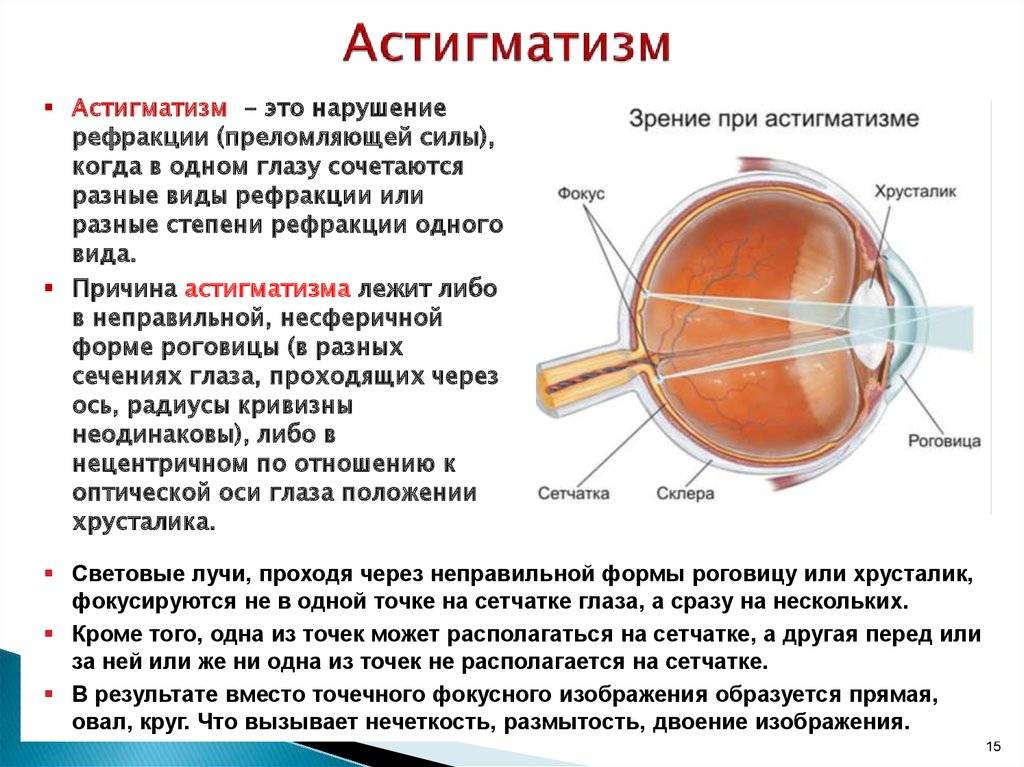
Understanding Astigmatism: Causes and Types
Astigmatism is a common vision problem that occurs when the cornea or lens of the eye has an irregular shape. This irregularity affects how light reaches the retina, resulting in blurred or distorted vision. There are two main types of astigmatism:
- Corneal astigmatism: This occurs when the cornea has an irregular curvature
- Lenticular astigmatism: This happens when the lens inside the eye has an abnormal curve
The exact cause of astigmatism remains unclear, but research suggests it may have a genetic component. It can be present at birth, develop later in life, or result from an eye injury.
Risk Factors for Astigmatism
Several factors can increase your risk of developing astigmatism:

- Family history of astigmatism or other eye conditions like keratoconus
- Corneal scarring
- Corneal thinning
- Severe myopia (nearsightedness) or hyperopia (farsightedness)
- Previous eye surgeries, such as cataract removal
Recognizing Astigmatism Symptoms
Astigmatism can manifest in various ways, and the severity of symptoms can differ from person to person. Some individuals may have astigmatism without experiencing any noticeable symptoms. Common signs of astigmatism include:
- Blurry or distorted vision at any distance
- Difficulty seeing clearly at night
- Eye discomfort and strain
- Frequent squinting
- Irritated eyes
- Recurring headaches
Is it possible to have these symptoms without having astigmatism? Yes, it’s important to note that experiencing these symptoms doesn’t necessarily mean you have astigmatism. Other eye conditions can cause similar issues, which is why a comprehensive eye examination is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Procedures for Astigmatism
Diagnosing astigmatism is typically done during a routine comprehensive eye exam. Eye care professionals use several tests and devices to obtain accurate results:

Visual Acuity Assessment
This basic test measures how well you can see at various distances using an eye chart.
Refraction Test
During a refraction test, the eye doctor places different lenses in front of your eye and uses light to measure how it bends through the cornea. A phoropter may then be used to assess your eyes’ focusing ability, helping the optometrist determine the lens that provides the clearest vision.
Keratometry
Keratometry helps your eye doctor evaluate the curvature of your cornea. This test is performed by focusing a circle of light on the curve of your eyes and measuring the reflection.
Corneal Topography
Corneal topography is becoming an increasingly popular method for diagnosing astigmatism. This computerized diagnostic tool creates a contour map of the cornea, providing your eye doctor with precise data about its shape.
Effective Treatment Options for Astigmatism
Not every patient with astigmatism experiences vision problems, but treatment is available if your vision is impaired. The goal of astigmatism treatment is to improve visual acuity and reduce eye strain.

Corrective Eyewear
Eyeglasses and contact lenses are the most common and non-invasive treatments for astigmatism. Your eye doctor can correct vision problems associated with astigmatism by providing glasses and contact lenses with a special cylindrical lens. This lens helps compensate by adding extra power to a specific area in the field of vision.
Many patients are interested in frame-free vision correction, and initially, optometrists could only use rigid contact lenses to correct astigmatism. However, soft lenses called toric contact lenses are now available.
Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) Lenses
Ortho-K lenses are typically worn at night. These lenses are designed to reshape the cornea to its ideal form. This corneal reshaping helps light focus correctly on the retina, providing clear vision throughout the day without the need for contact lenses or glasses.
Surgical Interventions for Astigmatism
For those seeking a more permanent solution, several surgical options are available to correct astigmatism:
LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis)
LASIK is a popular refractive surgery that can correct astigmatism, nearsightedness, and farsightedness. During the procedure, a laser is used to reshape the cornea, allowing light to focus properly on the retina.
PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy)
PRK is another type of laser eye surgery that can correct astigmatism. It differs from LASIK in that no flap is created in the cornea. Instead, the outer layer of the cornea is removed before the laser reshaping takes place.
SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction)
SMILE is a newer, minimally invasive laser vision correction procedure that can treat astigmatism and myopia. It involves creating a small lens-shaped piece of tissue within the cornea, which is then removed through a tiny incision.
Living with Astigmatism: Lifestyle Considerations
While astigmatism can’t be prevented, there are ways to manage it effectively and maintain good eye health:
- Regular eye exams: Schedule comprehensive eye exams at least every two years, or more frequently if recommended by your eye doctor
- Proper lighting: Ensure adequate lighting when reading or working to reduce eye strain
- Screen time management: Follow the 20-20-20 rule when using digital devices: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds
- UV protection: Wear sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays to protect your eyes from harmful solar radiation
- Healthy diet: Consume foods rich in vitamins A, C, and E, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for eye health
Innovations in Astigmatism Treatment
The field of ophthalmology is continually evolving, with new technologies and treatments emerging to address astigmatism and other vision problems. Some recent innovations include:

Wavefront-Guided LASIK
This advanced form of LASIK uses wavefront technology to create a detailed map of the eye’s optical system, allowing for more precise correction of astigmatism and other refractive errors.
Corneal Cross-Linking
While primarily used to treat keratoconus, corneal cross-linking is being explored as a potential treatment for certain types of astigmatism, particularly those associated with corneal irregularities.
Implantable Collamer Lenses (ICLs)
ICLs are an alternative to LASIK for correcting high degrees of astigmatism. These lenses are surgically implanted in the eye, working in conjunction with the eye’s natural lens to improve vision.
Astigmatism in Children: Special Considerations
Astigmatism can affect people of all ages, including children. Early detection and treatment of astigmatism in children are crucial for proper visual development and academic success.
Signs of Astigmatism in Children
Parents and caregivers should be aware of potential signs of astigmatism in children, which may include:
- Squinting or tilting the head to see clearly
- Difficulty reading or focusing on near tasks
- Frequent eye rubbing
- Complaints of headaches or eye strain
- Poor performance in school, especially with visual tasks
How often should children have their eyes examined? The American Optometric Association recommends that children have their first comprehensive eye exam at 6 months of age, followed by another at age 3, and then annually once they start school.
Treatment Options for Children with Astigmatism
Treatment for astigmatism in children is similar to that for adults, with some considerations:
- Eyeglasses: Often the first line of treatment, with special attention to frame fit and durability
- Contact lenses: May be an option for older children and teenagers, under proper supervision
- Orthokeratology: Can be particularly beneficial for children, as it may help slow the progression of myopia
Is it possible for children to outgrow astigmatism? In some cases, mild astigmatism in young children may resolve on its own as the eye develops. However, regular eye exams are essential to monitor any changes and ensure proper treatment if needed.

The Impact of Astigmatism on Daily Life
Astigmatism can affect various aspects of daily life, beyond just vision. Understanding these impacts can help individuals better manage their condition:
Work and Productivity
Uncorrected astigmatism can lead to decreased productivity at work, especially in jobs that require detailed visual tasks or prolonged computer use. Proper correction can significantly improve work performance and comfort.
Sports and Physical Activities
Astigmatism can affect depth perception and spatial awareness, which may impact performance in sports and other physical activities. Corrective lenses designed for sports or activities can help maintain clear vision during these pursuits.
Driving
Night driving can be particularly challenging for those with astigmatism due to increased glare from headlights and street lamps. Proper correction and anti-reflective coatings on glasses can help improve night driving vision.
Digital Device Use
With the increasing use of smartphones, tablets, and computers, individuals with astigmatism may experience more eye strain and fatigue. Regular breaks, proper lighting, and correctly prescribed corrective lenses can help alleviate these issues.

How can individuals with astigmatism optimize their workspace for better vision? Some tips include:
- Positioning computer screens at arm’s length and slightly below eye level
- Using proper lighting to reduce glare
- Taking regular breaks using the 20-20-20 rule
- Adjusting screen brightness and contrast for comfort
- Using larger font sizes when possible
Astigmatism and Other Eye Conditions
Astigmatism often coexists with other refractive errors or eye conditions. Understanding these relationships can help in managing overall eye health:
Astigmatism and Myopia/Hyperopia
Astigmatism frequently occurs alongside nearsightedness (myopia) or farsightedness (hyperopia). This combination of refractive errors is often referred to as “compound astigmatism” and requires specific corrective approaches.
Astigmatism and Presbyopia
As individuals age, they may develop presbyopia, a condition that affects the eye’s ability to focus on close objects. When combined with astigmatism, this can result in the need for multifocal lenses or separate glasses for different distances.

Astigmatism and Keratoconus
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disease that causes the cornea to thin and bulge into a cone-like shape. This condition can lead to significant astigmatism and may require specialized treatment approaches, such as rigid gas permeable contact lenses or corneal cross-linking.
Can astigmatism worsen over time? Astigmatism can change as you age, sometimes improving and other times worsening. Regular eye exams are crucial to monitor these changes and adjust treatment as necessary.
The Future of Astigmatism Treatment
As technology advances, new treatments and diagnostic tools for astigmatism continue to emerge. Some promising areas of research and development include:
Adaptive Optics
This technology, originally developed for astronomy, is being adapted for use in eye care. It allows for extremely precise measurements of the eye’s optical system, potentially leading to more accurate diagnoses and treatments for astigmatism.
Gene Therapy
While still in early stages, researchers are exploring the potential of gene therapy to correct the underlying causes of certain types of astigmatism, particularly those with a strong genetic component.

Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis
AI algorithms are being developed to assist in the diagnosis and monitoring of astigmatism and other eye conditions, potentially improving accuracy and efficiency in eye care.
Advanced Contact Lens Materials
Ongoing research into new contact lens materials may lead to more comfortable and effective options for correcting astigmatism, including lenses that can adapt to changing light conditions or provide extended wear times.
What can we expect in the near future for astigmatism treatment? While it’s difficult to predict exact developments, it’s likely that we’ll see continued improvements in surgical techniques, more personalized treatment options, and enhanced integration of technology in both diagnosis and treatment of astigmatism.
In conclusion, astigmatism is a common vision problem that can significantly impact daily life. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, most individuals with astigmatism can achieve clear, comfortable vision. Regular eye exams, awareness of symptoms, and open communication with eye care professionals are key to managing this condition effectively. As research continues and technology advances, we can look forward to even more effective and personalized approaches to treating astigmatism in the future.

Как диагностируется астигматизм? | Команда офтальмолога
Объяснение астигматизма
Вы, вероятно, слышали термин астигматизм или знаете кого-то с этой распространенной проблемой зрения, но вы можете не знать подробностей этого состояния или того, как оно диагностируется.
Астигматизм может быть следствием неправильной формы роговицы или неправильной формы хрусталика внутри глаза. Эти условия изменяют то, как свет достигает сетчатки, светочувствительной поверхности, расположенной в задней части глаза.
Люди с астигматизмом часто сталкиваются с размытым или искаженным зрением. Проблемы со зрением могут увеличиваться или уменьшаться из-за изменения кривизны хрусталика внутри глаза.
Оптометристы не могут предотвратить астигматизм, потому что это аномалия глаза, но существуют различные методы лечения, помогающие пациентам добиться четкого зрения.
Существует 2 типа астигматизма:
- Роговичный астигматизм : Это состояние возникает, когда роговица имеет неправильный изгиб.

- Лентикулярный астигматизм : Это состояние возникает при неправильном искривлении хрусталика.
Что вызывает астигматизм?
Эксперты не могут прийти к единому мнению о том, почему формы роговицы и хрусталика различаются у разных людей, но исследования показывают, что это состояние может быть генетическим. Астигматизм может проявиться при рождении, развиться в более позднем возрасте или возникнуть из-за травмы глаза.
Близорукость (миопия) и дальнозоркость (гиперметропия) часто идут рука об руку с астигматизмом. Эти состояния называются аномалиями рефракции, потому что они влияют на то, как глаз преломляет свет.
Вы подвержены более высокому риску развития астигматизма, если:
- У вас есть семейная история астигматизма.
- Имеют семейный анамнез глазных заболеваний, таких как кератоконус.
- Имеются рубцы на роговице.
- Имеют истончение роговицы.

- Имеют выраженную близорукость (близорукость).
- Имеют выраженную дальнозоркость (дальнозоркость).
- В прошлом были операции на глазах, например операция по удалению катаракты.
Симптомы астигматизма
Некоторые пациенты имеют это состояние, но не испытывают никаких симптомов. Каждый человек индивидуален, и симптомы могут различаться по степени тяжести.
People with astigmatism may experience the following symptoms:
- Blurry vision at any distance
- Distorted vision at any distance
- Issues with seeing at night
- Eye discomfort
- Eyestrain
- Squinting
- Irritated eyes
- Frequent головные боли
Важно отметить, что даже при этих симптомах у вас может не быть астигматизма. Всегда говорите со своим офтальмологом для диагноза и вариантов лечения.
Диагностика астигматизма
Отличные новости! Ваш окулист может диагностировать астигматизм во время обычного комплексного осмотра глаз. Существует несколько тестов и устройств, которые помогут вашему врачу получить точные результаты:
Существует несколько тестов и устройств, которые помогут вашему врачу получить точные результаты:
Оценка остроты зрения
Проверка рефракции
При проверке рефракции врач помещает перед вашим глазом различные линзы и с помощью света измеряет, как она изгибается через роговицу. После этого можно использовать фороптер для оценки фокусирующей способности ваших глаз, помогая оптометристу подобрать линзу, обеспечивающую максимально четкое зрение.
Кератометрия
Кератометрия помогает вашему окулисту оценить кривизну вашей роговицы. Этот тест проводится путем фокусировки круга света на изгибе ваших глаз и измерения отражения.
Топография роговицы
Топография роговицы становится все более популярным методом диагностики астигматизма. Этот компьютеризированный диагностический инструмент создает контурную карту роговицы и предоставляет вашему окулисту точные данные о ее форме.
Лечение астигматизма
Не каждый пациент с астигматизмом испытывает проблемы со зрением, но лечение доступно, если ваше зрение нарушено.
Корригирующие очки и контактные линзы
Ваш окулист может исправить проблемы со зрением, связанные с астигматизмом, предоставив очки и контактные линзы со специальной цилиндрической линзой. Эта линза помогает компенсировать, придавая дополнительную силу определенной области в поле зрения.
Многие пациенты заинтересованы в безоправной коррекции зрения, и изначально оптометристы могли использовать только жесткие контактные линзы для коррекции астигматизма. Однако в настоящее время доступны мягкие линзы, называемые торическими контактными линзами.
Зрение у всех разное, и мы рекомендуем связаться с нашими экспертами из The Eye Care Team, чтобы обсудить оптимальные варианты линз для вашего зрения.
Ортокератологические линзы (Ortho-K)
Линзы Ortho-K обычно носят на ночь. Эти линзы предназначены для придания роговице идеальной формы. Это изменение формы роговицы помогает свету правильно фокусироваться на сетчатке, обеспечивая четкое зрение в течение дня без использования контактных линз или очков.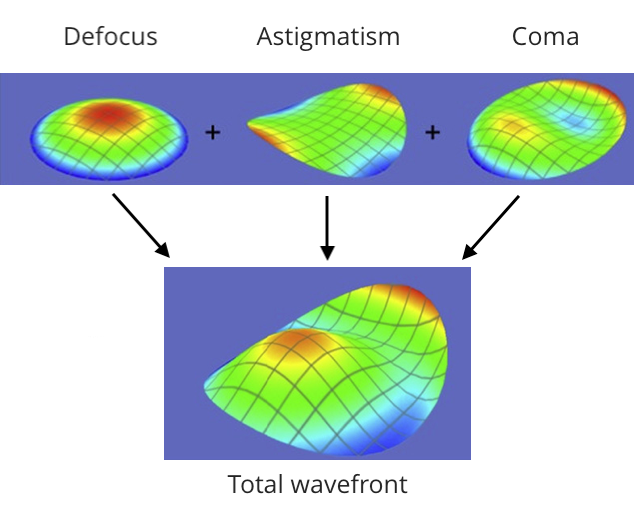
Коррекция зрения с помощью этих линз носит временный характер, но пациенты могут сохранять четкое зрение при регулярном использовании.
Хирургия
Пациентам с более тяжелыми случаями астигматизма окулист может порекомендовать такие процедуры, как LASIK или ФРК.
Лазерный кератомилез in situ (LASIK) — популярная операция по коррекции аномалий рефракции, при которой офтальмолог изменяет форму ткани роговицы с помощью предварительно запрограммированного лазера в соответствии с желаемым рецептом.
Фоторефракционная кератэктомия (ФРК) — еще один тип лазерной хирургии глаза. Основное различие между ФРК и LASIK заключается в том, как ваш врач получает доступ к ткани роговицы.
Жизнь с астигматизмом
Вы получили диагноз от окулиста, и что теперь?
Астигматизм — распространенная проблема со зрением, и исследования показали, что примерно каждый третий американец страдает этим заболеванием. Зрение каждого человека уникально, и у некоторых пациентов симптомы проявляются более ярко; другие вообще не заметят изменений.
Зрение каждого человека уникально, и у некоторых пациентов симптомы проявляются более ярко; другие вообще не заметят изменений.
Наиболее важным шагом является выбор лечения, которое лучше всего подходит для вашего зрения и вашего образа жизни.
Если у вас есть вопросы об астигматизме или вы хотите записаться на всестороннее обследование глаз, свяжитесь с одним из наших дружелюбных экспертов из группы по уходу за глазами. Мы можем помочь вам с вашим первоначальным диагнозом и помочь вам на пути к более четкому зрению.
Что такое астигматизм? Симптомы, причины, диагностика, лечение
Астигматизм — это несовершенство кривизны роговицы или хрусталика глаза.
В этой статье:
- Видео: Что такое астигматизм?
- Что является основной причиной астигматизма?
- Как астигматизм влияет на зрение?
- Как узнать, есть ли у вас астигматизм?
- Диагностика астигматизма
- Как корректируется астигматизм?
- Видео: ЛАСИК при астигматизме
Чтобы понять астигматизм, полезно представить нормальный глаз как равномерно округлый, как баскетбольный мяч. При астигматизме глаз имеет яйцевидную или овальную форму, как мяч для американского футбола. Существует два основных типа астигматизма:
При астигматизме глаз имеет яйцевидную или овальную форму, как мяч для американского футбола. Существует два основных типа астигматизма:
- горизонтальный астигматизм (когда ширина глаза превышает его высоту) и
- вертикальный астигматизм (когда высота глаза превышает его ширину)
При любом типе астигматизма зрение вблизи и вдаль размыто из-за неправильной формы глаза.
Видео: Что такое астигматизм?
Что является основной причиной астигматизма?
Астигматизм возникает из-за того, что форма роговицы или хрусталика отличается от нормальной. Астигматизм встречается очень часто. Врачи не знают, почему форма роговицы или хрусталика варьируется от человека к человеку. Но они знают, что риск получить астигматизм передается по наследству (передается от родителей).
Люди также могут заболеть астигматизмом в результате:
- заболеваний глаз
- травма глаза
- или после операции
Это миф, что чтение при слабом освещении или сидение очень близко к телевизору вызывает астигматизм или усугубляет его.
Как астигматизм влияет на зрение?
В норме роговица и хрусталик в передней части глаза имеют равномерно круглую форму. Это помогает четко сфокусировать световые лучи на сетчатке, чтобы вы могли ясно видеть.
При астигматизме световые лучи не преломляются (или не преломляются) должным образом, когда попадают в переднюю часть глаза. Зрение размыто вблизи и вдали, потому что световые лучи либо не доходят до сетчатки, либо остаются позади нее.
Люди могут иметь астигматизм наряду с другими аномалиями рефракции, такими как:
- близорукость (близорукость) или
- дальнозоркость (гиперметропия).
В нормальном глазу роговица и хрусталик фокусируют световые лучи на сетчатке.
При астигматизме изображение фокусируется перед сетчаткой и за ее пределами. Близкие и удаленные объекты выглядят размытыми.
Как узнать, есть ли у вас астигматизм?
Симптомы астигматизма могут включать:
- нечеткое зрение или области искаженного зрения
- напряжение глаз
- головные боли
- щурится, пытаясь разглядеть ясно, или
- дискомфорт в глазах
Эти симптомы не всегда означают, что у вас астигматизм. Обратитесь к офтальмологу для всестороннего осмотра глаз, чтобы выяснить, что вызывает ваши симптомы.
Обратитесь к офтальмологу для всестороннего осмотра глаз, чтобы выяснить, что вызывает ваши симптомы.
Дети могут не осознавать, что у них нечеткое зрение . И вряд ли они будут жаловаться на размытое или искаженное зрение.
Но без лечения астигматизм может:
- повлиять на успеваемость ребенка в школе и спорте
- приводят к амблиопии (ленивому глазу) и потере зрения
Вот почему так важны проверки зрения в раннем детстве педиатром, семейным врачом или другим офтальмологом. Если обнаружен астигматизм или другая проблема с глазами, обратитесь к офтальмологу, чтобы получить правильное лечение.
Диагностика астигматизма
Офтальмологи могут диагностировать астигматизм во время комплексного обследования глаз. Тестирование может включать:
- Таблица для проверки зрения. Вам будет предложено прочитать буквы на таблице для проверки зрения. Это тест на остроту зрения или резкость вашего зрения на определенных расстояниях.

- Фороптер. Здесь вы смотрите в большое устройство, похожее на бинокль, и говорите своему врачу, какую букву вы видите лучше. Основываясь на ваших ответах, врач выписывает рецепт, чтобы обеспечить вам как можно более четкое зрение.
- Авторефрактор. Это устройство также помогает измерить астигматизм или другие аномалии рефракции. Он работает, направляя свет в глаз и измеряя, как он меняется, когда он отражается от задней части глаза.
- Кератометр измеряет изгиб вашей роговицы. Ваш врач-офтальмолог может также выполнить сканирование топографии роговицы, которое поможет найти дефекты и искажения на поверхности роговицы.
Фороптер поможет вашему окулисту узнать рецепт на очки или контактные линзы.
Как корректируется астигматизм?
- Очки или контактные линзы. Они работают, перефокусируя свет на сетчатке в задней части глаза, чтобы вы могли видеть более четко.