How many 500mg tylenol should i take. Acetaminophen Dosage Guide: Safe Usage and Overdose Prevention
How much acetaminophen is safe to take. What are the symptoms of an acetaminophen overdose. When should you seek medical help for acetaminophen toxicity. How is an acetaminophen overdose treated.
Understanding Acetaminophen: Uses and Formulations
Acetaminophen, commonly known by the brand name Tylenol, is a widely used over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer. It’s found in numerous medications, both prescription and non-prescription. While generally considered safe when used as directed, it’s crucial to understand proper dosing to prevent potentially dangerous overdoses.
Acetaminophen comes in various forms and strengths:
- Suppositories: 120 mg, 125 mg, 325 mg, 650 mg
- Chewable tablets: 80 mg
- Junior tablets: 160 mg
- Regular strength tablets: 325 mg
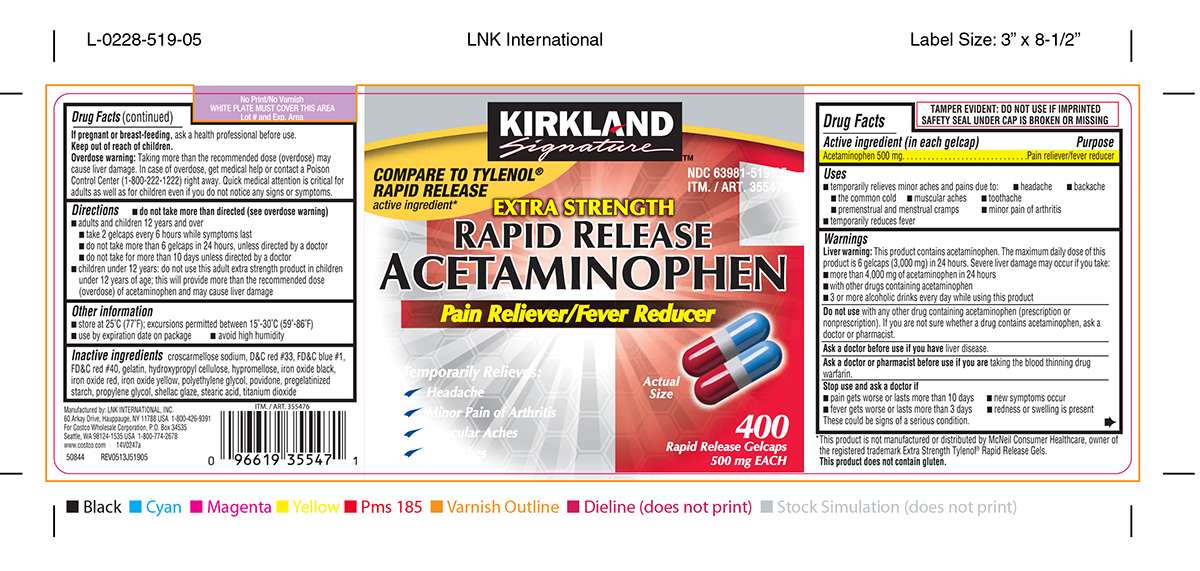
- Extra strength tablets: 500 mg
- Liquid: 160 mg/teaspoon (5 milliliters)
- Drops: 100 mg/mL, 120 mg/2.5 mL
It’s also an ingredient in many combination medications for colds, flu, and pain management. Always check labels carefully to avoid unintentionally doubling up on acetaminophen from multiple sources.

Recommended Dosage for Adults
What is the maximum safe dose of acetaminophen for adults? The general guideline is that adults should not exceed 3,000 mg of single-ingredient acetaminophen in a 24-hour period. This equates to:
- 6 extra-strength (500 mg) tablets
- 9 regular-strength (325 mg) tablets
However, there are important considerations:
- Adults over 65 should take lower doses due to decreased liver function
- Individuals with liver or kidney disease should consult their healthcare provider before using acetaminophen
- Never exceed 4,000 mg in 24 hours, as this significantly increases the risk of liver damage
It’s crucial to space out doses appropriately. For 500 mg tablets, wait at least 6 hours between doses. For 325 mg tablets, wait at least 4 hours.
Recognizing Acetaminophen Overdose Symptoms
What are the signs of acetaminophen toxicity? Symptoms may not appear immediately, often taking 12 hours or more to manifest. Early symptoms can include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Sweating
- Irritability
As liver damage progresses, more severe symptoms may develop:
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Confusion
- Severe abdominal pain
- Seizures
- Coma
It’s important to note that the absence of early symptoms doesn’t rule out a potentially dangerous overdose. If you suspect an overdose, seek medical attention immediately, even if no symptoms are present.
When to Seek Medical Help
When should you contact emergency services for a potential acetaminophen overdose? Immediate medical attention is crucial in the following situations:
- Known or suspected ingestion of more than the recommended dose
- Accidental ingestion by a child
- Presence of any overdose symptoms, even if mild
- Uncertainty about the amount taken, especially if it might exceed the maximum daily dose
Do not wait for symptoms to appear or worsen before seeking help. Early treatment is key to preventing severe liver damage. Contact your local poison control center or emergency services immediately if you suspect an overdose.
Treatment Approaches for Acetaminophen Overdose
How is an acetaminophen overdose treated? The approach depends on the severity and timing of the overdose. Treatment may include:

- Activated charcoal: Given orally to absorb remaining acetaminophen in the stomach
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC): An antidote that helps protect the liver from damage
- IV fluids: To support hydration and organ function
- Blood tests: To monitor acetaminophen levels and liver function
- Supportive care: Including oxygen therapy and management of symptoms
In severe cases, liver transplantation may be necessary. The effectiveness of treatment is highly dependent on how quickly it’s initiated after the overdose occurs. If treatment begins within 8 hours of ingestion, the prognosis is generally good.
Preventing Accidental Overdose
How can you safeguard against unintentional acetaminophen overdose? Follow these key guidelines:
- Always read medication labels carefully
- Keep a log of all medications taken, including over-the-counter drugs
- Use a dosing chart or pill organizer to track intake
- Never exceed the recommended dose or frequency
- Be cautious with combination medications that contain acetaminophen
- Store medications safely out of reach of children
- Consult a healthcare provider or pharmacist if unsure about proper dosing
Remember, what seems like a small increase in dose can potentially lead to serious consequences. When in doubt, err on the side of caution and seek professional advice.

Special Considerations for At-Risk Groups
Who is at higher risk for acetaminophen toxicity? Certain populations need to be especially cautious:
Elderly Individuals
Older adults may have decreased liver function and should generally take lower doses. They should consult their healthcare provider for personalized dosing recommendations.
People with Liver Disease
Those with existing liver conditions are at higher risk for complications from acetaminophen use. They should discuss safe usage with their doctor and may need to avoid the medication entirely.
Chronic Alcohol Users
Regular alcohol consumption can increase the liver’s susceptibility to acetaminophen-induced damage. These individuals should be extremely cautious and may need to limit their acetaminophen intake.
Children
Pediatric dosing is weight-based and differs significantly from adult dosing. Always use child-specific formulations and follow dosing instructions carefully.
Alternatives to Acetaminophen
What are some alternative pain relief options if acetaminophen isn’t suitable? Consider these alternatives:

- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen
- Topical pain relievers for localized pain
- Non-pharmacological approaches such as heat/cold therapy, massage, or physical therapy
- Prescription pain medications (under medical supervision)
Always consult with a healthcare provider before switching pain management strategies, especially if you have ongoing health conditions or take other medications.
Understanding proper acetaminophen use is crucial for safe pain management. By following recommended dosages, recognizing potential overdose symptoms, and seeking prompt medical attention when needed, you can effectively use this common medication while minimizing risks. Remember, when it comes to medication use, knowledge and caution are your best safeguards against potential complications.
Acetaminophen overdose: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
URL of this page: //medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002598.htm
To use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript.
Acetaminophen (most common brand name Tylenol) is a pain medicine. Acetaminophen overdose occurs when someone takes more than the recommended amount of this medicine.
Acetaminophen overdose is one of the most common poisonings. People often think that this medicine is very safe. However, it can be deadly if taken in large doses.
This article is for information only. DO NOT use it to treat or manage an actual overdose. If you or someone you are with overdoses, call the local emergency number (such as 911), or the local poison control center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States.
Acetaminophen is found in a variety of over-the-counter and prescription pain relievers.
Tylenol is a brand name for acetaminophen. Other medicines that contain acetaminophen include:
- Anacin-3
- Liquiprin
- Panadol
- Percocet
- Tempra
- Various cold and flu medicines
Note: This list is not all inclusive.
Common dosage forms and strengths:
- Suppository: 120 mg, 125 mg, 325 mg, 650 mg
- Chewable tablets: 80 mg
- Junior tablets: 160 mg
- Regular strength: 325 mg
- Extra strength: 500 mg
- Liquid: 160 mg/teaspoon (5 milliliters)
- Drops: 100 mg/mL, 120 mg/2.5 mL
Adults should not take more than 3,000 mg of single-ingredient acetaminophen a day. You should take less if you are 65 or more years old. Taking more, especially 7,000 mg or more, can lead to a severe overdose problems. If you have liver or kidney disease, you should discuss the use of this drug with your health care provider.
Symptoms may include:
- Abdominal pain, upset stomach
- Appetite loss
- Coma
- Seizures
-
Diarrhea - Irritability
- Jaundice (yellow skin and whites of the eyes)
-
Nausea, vomiting -
Sweating
Note: Symptoms may not occur until 12 or more hours after the acetaminophen was swallowed.
There is no home treatment. Seek medical help right away.
The following information is helpful for emergency assistance:
- Person’s age, weight, and condition
- Name of the product (ingredients and strength, if known)
- Time it was swallowed
- Amount swallowed
However, DO NOT delay calling for help if this information is not immediately available.
Your local poison control center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States. This national hotline will let you talk to experts in poisoning. They will give you further instructions.
This is a free and confidential service. All local poison control centers in the United States use this national number. You should call if you have any questions about poisoning or poison prevention. It does NOT need to be an emergency. You can call for any reason, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
The provider will measure and monitor the person’s vital signs, including temperature, pulse, breathing rate, and blood pressure. Blood tests will be done to check how much acetaminophen is in the blood. The person may receive:
Blood tests will be done to check how much acetaminophen is in the blood. The person may receive:
- Activated charcoal
- Airway support, including oxygen, breathing tube through the mouth (intubation), and ventilator (breathing machine)
- Blood and urine tests
- Chest x-ray
- CT (computerized axial tomography) scan
- ECG (electrocardiogram, or heart tracing)
- Fluids through the vein (intravenous or IV)
- Laxative
- Medicines to treat symptoms, including an antidote, n-acetylcysteine (NAC), to counteract the effects of the drug
People with liver disease are more likely to develop serious complications of acetaminophen overdose. Overdose may be either acute (sudden or short-term) or chronic (long-term), depending on the doses taken, and symptoms may therefore vary.
If treatment is received within 8 hours of the overdose, there is a very good chance of recovery.
However, without rapid treatment, a very large overdose of acetaminophen can lead to liver failure and death in a few days.
Tylenol overdose; Paracetamol overdose
Aronson JK. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) and combinations. In: Aronson JK, ed. Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs. 16th ed. Waltham, MA: Elsevier; 2016:474-493.
Ganetsky M. Acetaminophen. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 138.
Updated by: Jesse Borke, MD, CPE, FAAEM, FACEP, Attending Physician at Kaiser Permanente, Orange County, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Dosage Chart: Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
Dosage Chart: Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- New to the Area?
- Well Care / Annual Check-Ups
- “Get Acquainted” Visits
- Lab Work
- Recommended Health Maintenance Schedule
- Dosage Chart: Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Dosage Chart: Ibuprofen (Motrin/Advil)
- Vaccination Policy
Ped*I*Care
Should my child be seen during Ped*I*Care Hours?
Acetaminophen may be less upsetting to the stomach than ibuprofen. Therefore, in general, use of acetaminophen is preferable to ibuprofen if the patient has stomach upset or is not drinking well.
Therefore, in general, use of acetaminophen is preferable to ibuprofen if the patient has stomach upset or is not drinking well.
In case of doubt: First, read the package label. If uncertainty still exists, call the office.
| Age | 0-3 mos | 4-11 mos | 12-23 mos | 2-3 yrs | 4-5 yrs | 6-8 yrs | 9-10 yrs | 11-12 yrs | 12+ yrs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight in pounds | 6-11 | 12-17 | 18-23 | 24-35 | 36-47 | 48-59 | 60-71 | 72-95 | 96+ | |
| Concentration | ||||||||||
| 5 ml = 160 mg | Children’s Tylenol Suspension mL | 1. 25 25 | 2.5 | 3.75 | 5 | 7.5 | 10 | 12.5 | 15 | 20 |
| 1 tab = 80 mg | Children’s Tylenol Melt-aways # of tabs | – | – | 1 ½ | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 |
| 1 tab = 160 mg | Junior Tylenol Melt-aways # of tabs | – | – | – | 1 | 1 ½ | 2 | 2 ½ | 3 | 4 |
| 1 tab = 325 mg | Tylenol (regular adult) # tabs | – | – | – | – | ½ | 1 | 1 | 1 ½ | 2 |
| 1 tab = 500 mg | Tylenol (extra strength adult) # tabs | – | – | – | – | ½ | ½ | 1 | 1 | 1 ½ |
| 1 tab = 650 mg | Tylenol (extended release adult) # tabs | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 1 |
- Check dosage form and concentration carefully!
- When choosing dose, weight is more important than age.

- Acetaminophen doses may be repeated every four hours. 5 doses in 24 hours is a reasonable maximum.
- 1 tsp (teaspoon) = 5.0 ml
instructions for use, dosage, composition, analogues, side effects / Pillintrip
Page reviewed by pharmacist Kovalenko Svetlana Olegovna CodigesicPanadol Extraben-u-ron (Acetaminophen)ZaldiarPanacodSinutabAnalgilasaLonalgalDafalgan CodeineActifed Rhume Jour & Nuit Panadol
Top 20 drugs with the same use:
BuscofenIbucareAddaprinBrufenFevadolAlfenGofenDolvenActimol-FIbutinMigralineMinosetIbutenFaspic (Ibuprofen)DeponArtrilAdvilPedifenNurofenPar
Composition
9 0002 The information provided in section Composition of Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to clarify the information in section Composition
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Caffeine; Acetaminophen
Therapeutic Indications
The information provided in Therapeutic Indications Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to clarify the information in section Therapeutic indications
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Pain of mild to moderate intensity (including headache, toothache, sore throat and general malaise), fever.
Dosage and Administration
The information provided in section Dosage and Administration of Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as the medicine Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to check the information on section Dosage and administration
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Inside, 2 caplets 3-4 times a day, but not more than 8 caplets per day.
Contraindications
Provided in section Contraindications Tylenol The information is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the drug Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to check the information on section Contraindications
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Hypersensitivity, pronounced disorders of the liver and kidneys, deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, children’s age (up to 12 years).
Adverse effects
The information provided in section Adverse effects of Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as the drug Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to check the information in section Side effects
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
In rare cases, nausea, abdominal pain, allergic reactions (skin rash, itching, urticaria).
Overdose
The information provided in section Overdose Tylenol is based on data of another medicine with exactly the same composition as the Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to specify the information on section Overdose
in the instructions for the medicine Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Symptoms: pale skin, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, anorexia, hepatonecrosis (severity of necrosis directly depends on the degree of overdose). After a day or two, signs of liver damage are determined. In severe cases, liver failure and coma develop.
Treatment: stop taking the drug, do a gastric lavage, take activated charcoal. Further therapeutic measures should be carried out in a medical institution: the introduction of donators of SH-groups and precursors of the synthesis of glutathione – methionine – after 8–9h after an overdose and N-acetylcysteine - after 12 hours. The need for additional therapeutic measures (further administration of methionine, intravenous administration of N-acetylcysteine) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as on the time elapsed after its administration.
The need for additional therapeutic measures (further administration of methionine, intravenous administration of N-acetylcysteine) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as on the time elapsed after its administration.
Pharmacodynamics
The information provided in section Pharmacodynamics Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as medicine Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to specify the information on section Pharmacodynamics
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Combined preparation, the effect of which is determined by the components that make up its composition. Paracetamol, which has an analgesic and antipyretic effect, and caffeine, which reduces drowsiness and fatigue, has an effect on the cardiovascular system (increases heart rate, increases blood pressure).
Pharmacokinetics of
The information provided in section Pharmacokinetics of Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as the drug Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to specify the information on section Pharmacokinetics
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Film-coated tablets; Long release tablet; Soluble tablets
Powder for solution for oral administration
Paracetamol and caffeine are well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, evenly distributed throughout the tissues, penetrate into the brain, and are metabolized in the liver. Both substances and their metabolites are excreted mainly by the kidneys.
Paracetamol is rapidly absorbed in the upper intestines, metabolized in the liver with the formation of glucuronide and sulfate. It is excreted mainly by the kidneys.
It is excreted mainly by the kidneys.
Pharmacological group
The information provided in section Pharmacological group Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as the drug Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to specify the information on section Pharmacological group
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
- Anilides
Interactions
The information provided in section Interactions Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to check the information on section Interaction
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist in the pharmacy.
more…
Enhances the action of MAO inhibitors. Reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs. Caffeine accelerates the absorption of ergotamine. Under the influence of paracetamol, the elimination time of chloramphenicol increases by 5 times. With prolonged use, paracetamol can enhance the effect of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin and other coumarins). Simultaneous use of paracetamol and alcoholic beverages increases the risk of hepatotoxic effects and acute pancreatitis. Barbiturates, phenytoin, ethanol, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants and other stimulants of microsomal oxidation increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, causing the possibility of severe intoxication with small overdoses. Microsomal oxidation inhibitors (cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity. Metoclopramide and domperidone increase, and cholestyramine reduces the rate of absorption of paracetamol.
Storage of
The information provided in section Storage of Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as Tylenol . Be
Be
carefully and be sure to specify the information on section Storage
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
At 15-30°C.
Shelf life of Tylenol ™ 4 years.
Do not use after the expiry date which is stated on the packaging.
Packaging and contents of
The information provided in section Packaging and contents of Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to clarify the information in section Packaging and contents
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
1 caplet contains paracetamol 500 mg; in a blister of 10 pcs. , in a box 1 blister or in strips of 2 pcs., in a box of 50 strips.
, in a box 1 blister or in strips of 2 pcs., in a box of 50 strips.
Pregnancy and lactation use, fertility
Provided under section Pregnancy and lactation use, fertility Tylenol information is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as medicine Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to check the information under section Use in pregnancy and lactation, fertility
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
Permissible, but only on prescription.
ATC – Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification
The information provided in section ATC – Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition as Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to specify the information on section ATC – Anatomical-Therapeutic-Chemical Classification
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TylenolPM-3c4148310a754069a9e5bc36d59370f5.jpg)
more…
N02BE01 Paracetamol
Nosological classification (ICD-10)
The information provided in section Nosological classification (ICD-10) Tylenol is based on data from another medicine with exactly the same composition om like medicine Tylenol . Be
carefully and be sure to clarify the information in section Nosological classification (ICD-10)
in the instructions for the drug Tylenol directly from the package or from the pharmacist at the pharmacy.
more…
- K08.8.0* Toothache
- R07.0 Sore throat
- R50 Fever of unknown origin
- R51 Other constant pain
Tylenol price
Medium the cost of Tylenol 325 mg per unit in online pharmacies is from $0.38 to $0.46, per pack from $37 to $44.
Sources:
- https://www.drugs.com/acetaminophen.html
- https://pubmed.
 ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=tylenol
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=tylenol
Find in the country:
90 002 A
B
C
D
E
E
C
I
J
K 90 003
L
M
H
O
R
R
C
T
U
F
X
Ch
Sh
E
Yu
I
likіv vіd UNIAN
Tylenol intake
Indication before zastosuvannya
Tylenol – warehouse and release form
Tylenol: how to take the drug
Tylenol – contraindications and side effects
Tylenol analogs
Tylenol – zasib that zastosovuєtsya with a cold. Tylenol is classified as a group of non-narcotic analgesics. The drug is injected into the center of thermoregulation, pain, and speech intoxication – paracetamol.
Tylenol congestion
Indication before congestion
Tylenol is effective for fever due to aphid infections, it helps with toothache, headache, as well as pain, arthralgia єyu, migraine, mialgієyu, which is blamed for algomenorrhea.
Tylenol – stock and product form
Stock and dispensing form
1 caplet for paracetamol 500 mg; in blister 10 pcs. in a box 1 blister or in strips of 2 pcs. in a box 50 strips.
Release form. Tablets
Tylenol: how to take the drug
How to take it
For children over 12 years of age, those over 40 kg, and adults, Tylenol is prescribed at a single dose of 500 mg. Take Tylenol about 4 times per day. Therapy lasts 5-7 days.
If the patient suffers from liver damage, either eg Gilbert’s syndrome, vin will require a dose adjustment to the lower side. Those are worth the cost and years of patients. Reducing the dose of Tylenol for such patients is practiced by reducing the interruption between doses.
For children up to birth, up to 7 kg, 350 mg Tylenol is prescribed.
Children under 1 year of age, up to 10 kg give 500 mg of Tylenol.
Children up to three years old, up to 15 kg give 750 mg.
Children up to 6 years old, up to 22 kg – 1 rub.
Children 9 years of age, up to 30 kg give 1.5 g Tylenol.
Children up to 12 years old – 2 rubles.
Tylenol – contraindications and side effects
Side effects internal congestion, confusion, tedium, pain in the epigastrium, agitation, hepatonecrosis, anemia, backache, cyanosis, baldness in the heart, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia. Tylenol can be nephrotoxic in a large number of people: nirk colic, papillary necrosis, or interstitial nephritis.
Contraindications
Tylenol is contraindicated in case of allergy to children under one month of age. Precautionary measures are taken when Tylenol is recognized in patients with nirk, liver failure, benign hyperbilirubinemia, viral hepatitis, who suffer from alcoholism, diabetes, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, and also lіt to them patients, women, pregnant women, children up to 3 months.


 ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=tylenol
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=tylenol