I have a ringing in my right ear. Tinnitus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options for Ringing in the Ears
What are the main types of tinnitus. How common is occasional tinnitus. What are effective treatments for persistent tinnitus. Can hearing aids help manage tinnitus symptoms. What lifestyle changes can reduce tinnitus.
Understanding Tinnitus: More Than Just Ringing in the Ears
Tinnitus is a condition characterized by the perception of sound in the absence of an external source. While often described as a ringing in the ears, tinnitus can manifest as a variety of sounds, including buzzing, humming, whistling, or even music-like tones. This auditory phenomenon affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact quality of life when persistent.
What Exactly is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is not a disease itself, but rather a symptom that can be associated with various underlying conditions. It occurs when the brain interprets certain neural signals as sound, even when no external sound is present. This can happen in one ear, both ears, or seem to originate from within the head itself.

The Two Main Types of Tinnitus: Pulsatile and Non-Pulsatile
Tinnitus is generally classified into two main categories: pulsatile and non-pulsatile. Understanding the difference between these types can provide insights into potential causes and treatment approaches.
Pulsatile Tinnitus: Rhythmic Sounds
Pulsatile tinnitus is characterized by rhythmic sounds that often sync with the heartbeat. This type of tinnitus is usually caused by:
- Changes in blood flow near the ears
- Muscle movements around the ear
- Changes in the ear canal
People experiencing pulsatile tinnitus often describe hearing their own pulse or heartbeat. This form of tinnitus is less common and may be indicative of underlying vascular issues or increased awareness of normal body sounds.
Non-Pulsatile Tinnitus: Constant or Intermittent Sounds
Non-pulsatile tinnitus is more common and is typically described as a constant or intermittent sound that seems to originate from within the head or ears. This type of tinnitus is often associated with:
- Damage to the auditory system
- Exposure to loud noises
- Age-related hearing loss
- Certain medications
Non-pulsatile tinnitus can vary in pitch and volume, and may be perceived differently by each individual.

The Prevalence of Occasional Tinnitus: Is It Normal?
Many people experience brief episodes of tinnitus from time to time, and this is generally considered normal. These temporary bouts of ringing or buzzing in the ears typically last only a few minutes and often resolve on their own. But how common is this phenomenon?
Research suggests that up to 25-30% of the population experiences occasional tinnitus. These fleeting episodes are usually not a cause for concern and may be triggered by various factors such as:
- Exposure to loud noises
- Changes in air pressure (e.g., during air travel)
- Stress or fatigue
- Certain medications
- Consumption of caffeine or alcohol
While occasional tinnitus is generally harmless, persistent or recurring tinnitus that lasts for extended periods may warrant medical attention.
When Tinnitus Becomes a Concern: Persistent Symptoms
While occasional tinnitus is usually nothing to worry about, persistent tinnitus can significantly impact daily life and may be indicative of underlying health issues. So, when should you be concerned about tinnitus?

Consider seeking medical attention if:
- Tinnitus persists for more than a week
- The sound is accompanied by dizziness or balance problems
- You experience sudden hearing loss along with tinnitus
- Tinnitus is severely affecting your quality of life or sleep
- The sound is pulsatile (in sync with your heartbeat)
A healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause of persistent tinnitus and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Exploring the Causes of Tinnitus: From Age-Related Hearing Loss to Medical Conditions
Tinnitus can have a wide range of causes, some of which are easily identifiable while others may require more in-depth medical investigation. Understanding these potential causes can help in managing the condition and seeking appropriate treatment.
Common Causes of Tinnitus
Some of the most frequent causes of tinnitus include:
- Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis)
- Exposure to loud noises
- Earwax blockage
- Certain medications (ototoxic drugs)
- Head or neck injuries
- Cardiovascular problems
- Stress and anxiety
- Meniere’s disease
- Acoustic neuroma
It’s important to note that in many cases, the exact cause of tinnitus may remain unknown. However, identifying potential triggers can still be helpful in managing symptoms.

The Link Between Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
There is a strong correlation between hearing loss and tinnitus. As we age, the delicate hair cells in our inner ear can become damaged or die off, leading to age-related hearing loss. This type of hearing loss is often accompanied by tinnitus. In fact, about 90% of people with tinnitus also have some degree of hearing loss.
The relationship between hearing loss and tinnitus is thought to be due to the brain’s attempt to compensate for the loss of certain sound frequencies. As the brain receives less external auditory input, it may begin to generate its own phantom sounds, leading to the perception of tinnitus.
Treatment Options for Tinnitus: From Lifestyle Changes to Medical Interventions
While there is no cure for tinnitus, there are numerous treatment options available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The most effective approach often involves a combination of strategies tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Lifestyle Modifications for Tinnitus Management
Simple lifestyle changes can often make a significant difference in managing tinnitus symptoms:
- Stress reduction techniques (meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises)
- Improving sleep habits
- Limiting consumption of caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine
- Regular exercise
- Avoiding exposure to loud noises
These lifestyle modifications can help reduce the perceived intensity of tinnitus and improve overall well-being.

Sound Therapy and Masking Devices
Sound therapy involves the use of external noises to alter the perception of tinnitus. This can be achieved through:
- White noise machines
- Tinnitus masking devices
- Hearing aids with built-in sound generators
- Smartphone apps that produce soothing sounds
The goal of sound therapy is to provide a more pleasant or neutral sound that can help mask or distract from the tinnitus.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Tinnitus
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a type of psychotherapy that has shown promise in helping individuals cope with tinnitus. CBT focuses on:
- Changing negative thought patterns associated with tinnitus
- Developing coping strategies
- Reducing anxiety and depression related to tinnitus
- Improving overall quality of life
While CBT doesn’t eliminate tinnitus, it can significantly reduce its impact on daily life and emotional well-being.
The Role of Hearing Aids in Tinnitus Management
Hearing aids can play a crucial role in managing tinnitus, especially for individuals who also experience hearing loss. But how exactly do hearing aids help with tinnitus?

How Hearing Aids Can Alleviate Tinnitus Symptoms
Hearing aids can benefit individuals with tinnitus in several ways:
- Amplifying external sounds: By increasing the volume of ambient sounds, hearing aids can help mask the perception of tinnitus.
- Reducing listening effort: With improved hearing, the brain may focus less on internal sounds (tinnitus) and more on external stimuli.
- Sound therapy features: Many modern hearing aids come with built-in sound generators that can provide customized sound therapy for tinnitus relief.
- Stress reduction: By improving communication and reducing hearing-related stress, hearing aids can indirectly help manage tinnitus symptoms.
For many individuals with both hearing loss and tinnitus, hearing aids can provide significant relief and improve overall quality of life.
Choosing the Right Hearing Aid for Tinnitus
When considering hearing aids for tinnitus management, it’s important to work with an experienced audiologist who can help select the most appropriate device. Factors to consider include:
- The severity and characteristics of your tinnitus
- The degree and type of hearing loss
- Lifestyle and daily activities
- Budget and insurance coverage
- Personal preferences for style and features
Modern hearing aids offer a wide range of features and styles, making it possible to find a solution that addresses both hearing loss and tinnitus effectively.

Emerging Treatments and Research in Tinnitus Management
The field of tinnitus research is constantly evolving, with new treatments and management strategies being developed and tested. While some of these approaches are still in the experimental stages, they offer hope for improved tinnitus management in the future.
Neuromodulation Techniques
Neuromodulation involves the use of various stimulation techniques to alter neural activity in the brain. Some promising neuromodulation approaches for tinnitus include:
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
- Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)
- Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)
These techniques aim to disrupt the abnormal neural activity associated with tinnitus perception.
Pharmacological Interventions
While there is currently no FDA-approved medication specifically for tinnitus, research is ongoing to identify potential drug therapies. Some areas of investigation include:
- NMDA receptor antagonists
- Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications
- Anticonvulsants
- Hormone therapies
It’s important to note that any potential medications would likely be used as part of a comprehensive treatment approach rather than as a standalone cure for tinnitus.

Gene Therapy and Regenerative Medicine
Advances in gene therapy and regenerative medicine offer exciting possibilities for treating the underlying causes of tinnitus, particularly when related to hearing loss. Research in this area focuses on:
- Regenerating damaged hair cells in the inner ear
- Repairing or replacing damaged auditory neurons
- Gene therapies to prevent or reverse age-related hearing loss
While these approaches are still in the early stages of development, they hold promise for future tinnitus treatments.
As research in tinnitus management continues to advance, it’s essential for individuals experiencing persistent tinnitus to stay informed about new treatment options and work closely with healthcare professionals to find the most effective management strategies for their specific situation.
Is It Normal to Have Occasional Tinnitus?
There are things that go on in our bodies where we’re always a little curious or concerned about it. For the most part, they’re nothing to be worried about, but with anything that concerns you, you should always get checked out. Tinnitus is a type of ringing in the ears, and some of us might experience occasional bouts of it. But is this something to be worried about or not?
Types of tinnitus
There are two types of tinnitus that are worth knowing about. The first is a pulsatile, and this is like a heartbeat. It’s caused by sound created by the muscle movements around your ear, changes in the ear canal or blood flow problems. These problems are usually located in the face or neck and is why you’ll likely hear sounds like your own pulse.
The second is called no pulsatile tinnitus and is often caused by problems in the nerves. This results in sounds in one or both ears and can often be described as a sound that comes from inside your head.
Is it normal to have occasional tinnitus?
Most people experience the occasional ringing in their ear, and it usually will last just a few minutes. It’s actually fairly normal to have this ringing in your ears so long as it doesn’t last for long. As we age, the most common form of hearing loss is due to old age, and that’s something none of us can avoid.
So, although you might have the occasional ringing sound, it’s nothing that’s serious as long as you’re taking good care of your hearing and doing everything possible to protect it.
For those times where you experience, you don’t need to go looking for any medical treatment unless it doesn’t stop. If it doesn’t stop, then that’s when you need to be looked at by a professional.
Treating Tinnitus
As much as the occasional tinnitus is harmless, there are ways to treat tinnitus and to prevent it from occurring again. In order to prevent it from happening too often, you can try to relax and find something that brings you that calm feeling.
You should also look at ways to improve your sleeping pattern so that you’re getting a good night’s sleep. You can also join a support group if that helps to talk to people about your experience in tinnitus and to be with people who are going through the same thing.
Some common causes of tinnitus can be from the build-up of earwax and so if you find you get a lot of earwax, try to get this removed professionally every once in a while. Certain medicines can cause tinnitus, which can be hard to avoid if the medication is very much necessary. Drinking too much alcohol or caffeine can contribute to it so it’s worth trying to limit this where possible.
You can get tinnitus from dental problems or other areas of the mouth as well as from other injuries you’ve had previously. Any injury to the ear and also blood flow problems can contribute to it too. There’s obviously plenty of factors you can control, but then there are others you can’t. If you can work on the things you can change, then this will hopefully make a difference overall.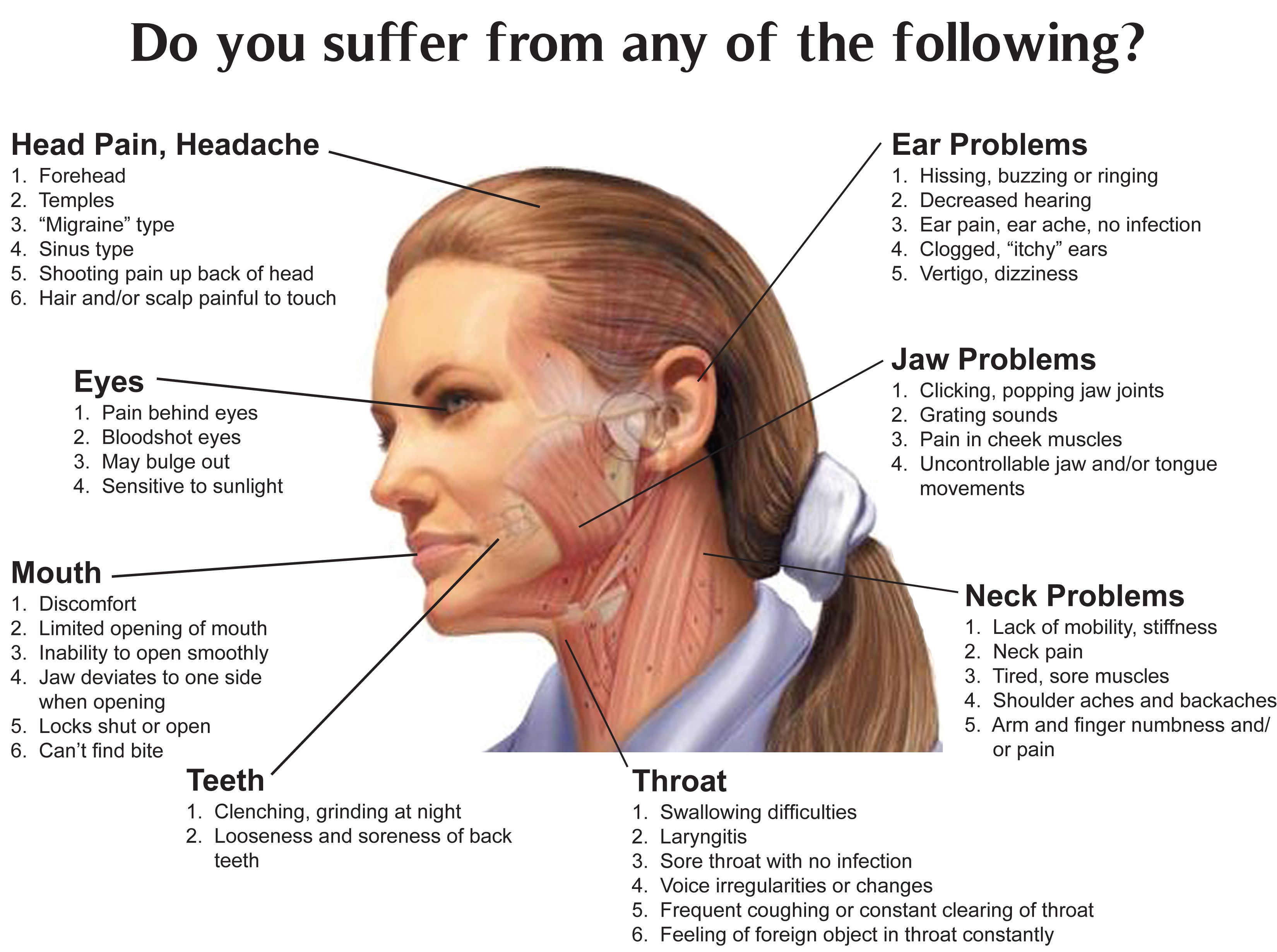
Hearing aids for Tinnitus
Hearing aids are something that people with tinnitus will tend to consider because it can be a great way of helping minimize the ringing whilst helping with any hearing loss. It’s worth looking into hearing aids if it’s something that’s already been suggested to you or that you’re still exploring when it comes to treating tinnitus.
There are lots of helpful advice and tips out there as well as many companies that can help treat your tinnitus through hearing aids. It’s worth exploring it, and you can do so by speaking to your local audiologist.
An audiologist can be helpful in conducting a hearing test and then discussing with you all the options you have available. By picking out a hearing aid, you could see a huge improvement to the tinnitus and how it impacts your life generally, overall.
If you want to learn more about tinnitus and how hearing aids can help treat it, then it’s worth getting in touch with The Hearing and Tinnitus Center. We can give you the best guidance when it comes to hearing aids and their benefits for tinnitus. You can give our team a call at 303-534-016. Who knows, it might benefit you to discuss your options.
We can give you the best guidance when it comes to hearing aids and their benefits for tinnitus. You can give our team a call at 303-534-016. Who knows, it might benefit you to discuss your options.
Ringing in ears after COVID-19? 5 tinnitus causes, what it sounds like and how to get some relief
Do you ever hear what sounds like ringing, humming or noise in your ears or head? If so, you may be experiencing tinnitus. At times, everyone hears tinnitus noise but may not pay much attention to it until it’s brought into focus. There is always internal information coming into our brain, but the noise may not be at the forefront until we’re conscious of it. Thankfully, tinnitus is a symptom, not a disease, and it’s very common.
What does tinnitus feel like?
Tinnitus is more than just ear ringing. It may be in one ear, both ears or alternating from side to side. The noise you hear may come in different forms, including ringing, scratching, pulsating, hearing your heartbeat, chimes, crickets, clicking, static, humming or whooshing.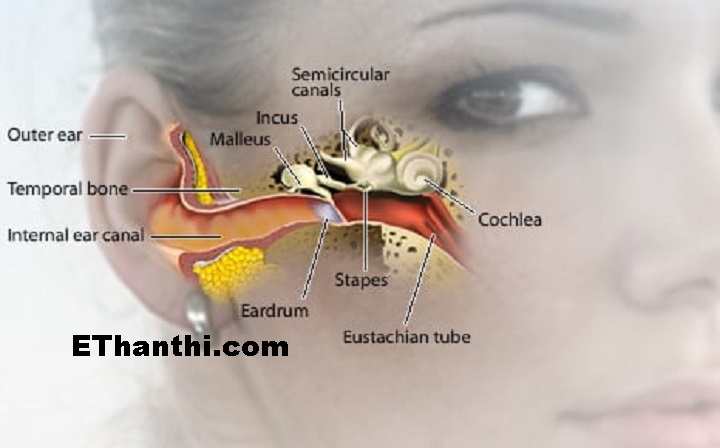
What causes tinnitus?
Anything that causes hearing loss can cause tinnitus,” says Geoffrey Casazza, MD, Nebraska Medicine otolaryngologist and head and neck surgeon. “Many patients think it will lead to deafness, which is extremely unlikely. They may worry it could be due to a tumor, which is possible but also unlikely. They may wonder it is due to an inner ear infection, which is possible, but not likely without other additional symptoms.”
While we’re not certain what is going on physically to cause tinnitus, much of the time (about 99%), certain types of stress are at play.
Five types of stress can have a significant impact, including:
- Chemical Stress: Excess coffee, nicotine, alcohol, high doses of over-the-counter (OTC) pain medication or a side effect of certain prescription medications.
- Acoustic Stress: Noise input or exposure. Very loud or prolonged noise, such as high volume concerts, firearms or noisy work environments like factory work.

- Pathologic Stress: Hearing loss, ear infection, wax impaction or other diseases of the ear.
- Physical Stress: Your heart pumps 60 to 100 times per minute for your entire life. You may hear this when you are exercising, performing a strenuous activity or when you lie down – especially if you have an illness or fever.
- Emotional Stress: Anxiety or depression are common reasons tinnitus may become noticeable or seem worse.
Can COVID-19 cause tinnitus?
The relationship between COVID-19 and tinnitus is unclear
“Since tinnitus is so common, the answer is a challenging one,” says Dr. Casazza. “While there have been reports of sudden hearing loss, tinnitus is so common it’s difficult to see if there’s a relationship between the two. It is not always clear if studies report an actual change, development of a new symptom or simply more awareness of an already existing issue.”
Social consequences of COVID-19 may be a factor
The pandemic’s increased stress and anxiety, social isolation and restrictions may also exacerbate a person’s already existing tinnitus and bring it to the foreground.
Certain proposed treatments for COVID-19 may contribute
“Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, interferon and ivermectin, are known to be ototoxic and could cause someone to develop hearing loss, which may lead to tinnitus,” adds Dr. Casazza. “Available evidence suggests that the ototoxic effects may be improved or mitigated by stopping the offending agents. Therefore, recognizing hearing loss, tinnitus or vertigo is crucial to facilitate early intervention and prevent long-term damage.”
COVID-19 vaccines or post-COVID-19 syndrome
There is no definite correlation between COVID-19 vaccination and new or worsened otologic symptoms. Further studies are needed. “While there may be some evidence that those who have persistent COVID symptoms, such as loss of taste or smell, fatigue and the like may also develop tinnitus,” says Dr. Casazza. “But if this is a true development of the tinnitus or an exacerbation of a prior symptom is unclear.”
What can I do to manage tinnitus symptoms? Does it go away on its own?
The brain prefers to listen to external noise, so use this to your advantage. Having some baseline noise level, even low enough to be subconscious can be helpful to mask tinnitus. Over time, most will see improvement.
Having some baseline noise level, even low enough to be subconscious can be helpful to mask tinnitus. Over time, most will see improvement.
Management tips:
- Turn on a fan, open a window, turn the TV on low or use a sound machine
- If you have associated hearing loss, hearing aids or amplifiers may help
- Tinnitus retraining therapy or cognitive behavioral therapy has been shown to be effective
- OTC treatments or vitamin supplements are not recommended
Can seeing a doctor help?
If the tinnitus is only on one side, if you’re hearing your heartbeat while at rest, if you’re distressed or not sleeping, it’s a good idea to see a doctor. Also, make an appointment if there are other neurological symptoms like numbness, facial weakness, trouble swallowing or hearing loss. A doctor can help rule out potential physical causes of tinnitus and if needed, perform hearing tests, order imaging tests, initiate treatment or give therapy referrals.
“Most patients who struggle with tinnitus don’t realize that there is help to manage it,” says Dr. Casazza. “Don’t be afraid to reach out to your doctor and have a discussion about it.”
The Nebraska Medicine ear, nose and throat team treats patients from birth through adulthood. From basic conditions to the most complex, our experts are here to help. Call 800.922.0000 to make an appointment.
Noise in the right ear – causes and treatment. How to cure a noise in the right ear
14 Oct 2017 Causes, Causes and symptoms Buzzing in the ears, Noise in the head, Noise in the ears patients, middle age. The fact is that this symptom is far from always the usual consequence of the gradual destruction of the auditory analyzer, which takes place in old age.
If you are young, but you are pestered by an outsider hum that no one else hears, there is a reason to see a doctor. It happens that the cause is a disease of one or another organ. Do not start noise in the right ear – only a specialist can determine causes and treatment .
It happens that the cause is a disease of one or another organ. Do not start noise in the right ear – only a specialist can determine causes and treatment .
Contents of the article:
- 1 Tinnitus: etiology
- 1.1 Symptoms
- 1.2 Diagnosis
- 1.3 Treatment
- 1.3.1 Where can you treat right-sided tinnitus?
If there is a violation – illness, injury, foreign body, etc. – fluctuations of hairs are produced chaotically, randomly. Mixed signals enter the brain, resulting in a different type of noise, similar to:
- Surf.
- Mosquito squeak.
- Bell ringing.
- Bubbling stream.
- Strong wind.
Patients may associate such discomfort with different types of sounds – it will be good if you can give it the most accurate definition at the doctor’s appointment.
If the noise is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, pain, the causes may be diseases:
- Tumor-like formation on the right.

- Acoustic neuritis.
- Right-sided otitis.
- Tympanic membrane injury.
- Head injuries – violation of the integrity of the skull, concussion.
For the timely detection and elimination of a pathology that poses a danger to human life, it is important not to wait and consult a doctor as soon as the symptoms make themselves felt.
Noise in one ear may be purely physiological. In this case, it does not interfere with sleep and do business, read, work. It is heard only in complete silence, provided that there are no distractions and you can concentrate on your own feelings. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that the blood passes through the section of the inner ear, hitting the walls of the vessels that are located there – a resonant effect occurs.
If you listened to loud music for a long time using a headset in one earphone, visited a construction site where a jackhammer was working to your right, or were subjected to a one-sided sound “attack” of a different nature – the echoes of this situation will disturb you in the form of noisy discomfort for several hours .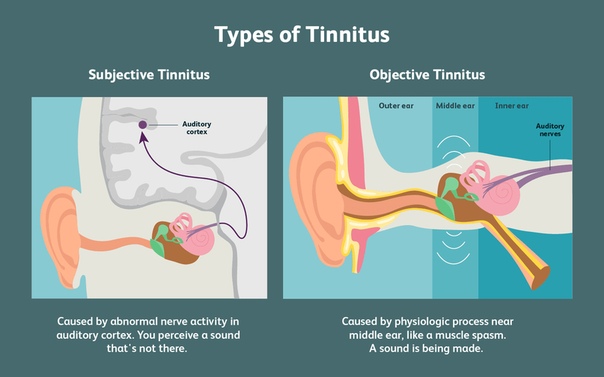
In addition, the cause may be an air flight, a long trip in transport and other cases when the body finds itself in unusual conditions for it.
Don’t worry if water gets into your right ear, you just need to tilt your head to remove it.
If a foreign object gets inside – often small flying insects – it is necessary to consult a doctor. You should not try to remove the “violator” yourself – with careless movements you can only push it further, injure the eardrum.
Wax plug can form on the right side – in this case, a doctor’s intervention is necessary to remove it and treat the ear with a special antiseptic solution. Signs of cork:
- Feeling of heaviness.
- Ear congestion.
- Hearing loss or hearing loss, on the one hand.
It is best to have the cork removed by a doctor, as only he will be able to do it as carefully as possible, without injuries and properly treat the internal cavity with an antiseptic. The procedure is short and does not take much time – the specialist will wash the inside of the ear with a special syringe and saline.
The procedure is short and does not take much time – the specialist will wash the inside of the ear with a special syringe and saline.
Symptoms
Noise effects – pulsating , severe , constant – may be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- head, ear, neck, spine.
- The head is spinning, coordination of movements is disturbed.
- Decreased general tone, depression.
- Impaired hearing, vision, speech.
- Nausea , vomiting.
Symptoms that drastically disrupt the general condition of the body, cause pain, interfere with sleep – this is a direct sign of a serious illness that needs to be treated urgently.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic measures are a mandatory procedure that must be completed to determine the exact nature of the disease. The task of the patient at this stage is to take each prescribed direction seriously and pass all the necessary examinations.![]() Even the usual delivery of urine and blood for a general analysis can help detect inflammation or other pathology.
Even the usual delivery of urine and blood for a general analysis can help detect inflammation or other pathology.
The main work is laboratory research of biomaterial and hardware examination of internal organs. The last group includes the brain, cranial bones, hearing aid.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures are the final stage of the doctor’s work aimed at eliminating the disease and restoring the body. The classic methods are the appointment of medicines, which must be taken strictly according to the instructions – unless otherwise indicated by the attending specialist.
If the disease is advanced, the patient can be referred for hardware procedures that will help to cope with the disease faster. Surgical intervention is performed only as a last resort.
Where can right-sided tinnitus be treated?
Tinnitus Neuro Medical Center has everything you need for effective assistance:
- High-tech equipment.
- Modern techniques.

- Experienced and qualified staff.
It’s easy to get your health back – contact Tinnitus Neuro!
Was this article helpful?
Yes
You can subscribe to our newsletter and learn a lot of interesting things about tinnitus, ways to fight and scientific advances:
Your e-mail
No
We’re sorry!
How can this article be improved?
Ringing in the ears – symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Contents
- Mechanism of the phenomenon
- Causes
- Common combinations of symptoms
- Diagnosis
- Treatment of tinnitus
- Relief measures
We often ignore problems with our health until they cause us severe discomfort and persistent pain. Therefore, many do not pay attention to the obsessive whistle that they constantly hear. What does this ringing in the ears mean? Is it possible and worth it to endure or should one immediately turn to lore?
Contents
Mechanism of the phenomenon
In the professional community, tinnitus is called tinnitus. This phenomenon never occurs by itself, but is a clear symptom of many pathologies and conditions. Ringing can be single or combined with other negative auditory manifestations: crackling, humming and buzzing.
This phenomenon never occurs by itself, but is a clear symptom of many pathologies and conditions. Ringing can be single or combined with other negative auditory manifestations: crackling, humming and buzzing.
Not every tinnitus can indicate a pathological condition of a person. In a room devoid of sounds, any healthy person will hear a characteristic noise. “Ringing silence” is a manifestation of a transient hum, which is absolutely normal and physiological. In a normal environment, we do not notice it because of the abundance of noise around.
If the ringing accompanies you constantly, the symptom may indicate a pathology – both in the auditory organs, and in the nervous and skeletal systems.
To understand why the ears are ringing, you need to understand the structure of the auditory organ:
- Sound (or rather, air vibration) acts on the eardrum, forcing it to vibrate.
- The vibration of the tympanic membrane is transmitted to the malleus, anvil and stapes located near it, which also begin to move.

- Their vibrations are transmitted to the snail filled with liquid and having special cilia on the surface.
- The fluid moves under the influence of vibrations, forcing the cilia to move.
- Cilia transmit a nerve impulse to the brain, where it is processed and perceived by us as sound.
A failure may occur in one of these steps and cause the patient to hear a steady, maddening ringing that is not actually there.
Causes
Noise
A common cause of ringing is loud noises. Sharp unbearable noise, watching a movie in a cinema, going to a nightclub or a concert often lead to an overstrain of the conductive nerve endings. In order for the ringing to pass, it is enough to sleep or spend some time surrounded by quiet, unobtrusive sounds.
But ringing in the ears due to loud noise does not always go away without a trace. People who work for a long time in noisy industries, or patients who are fond of loud music or using headphones, over time note that rest no longer contributes to relief from discomfort.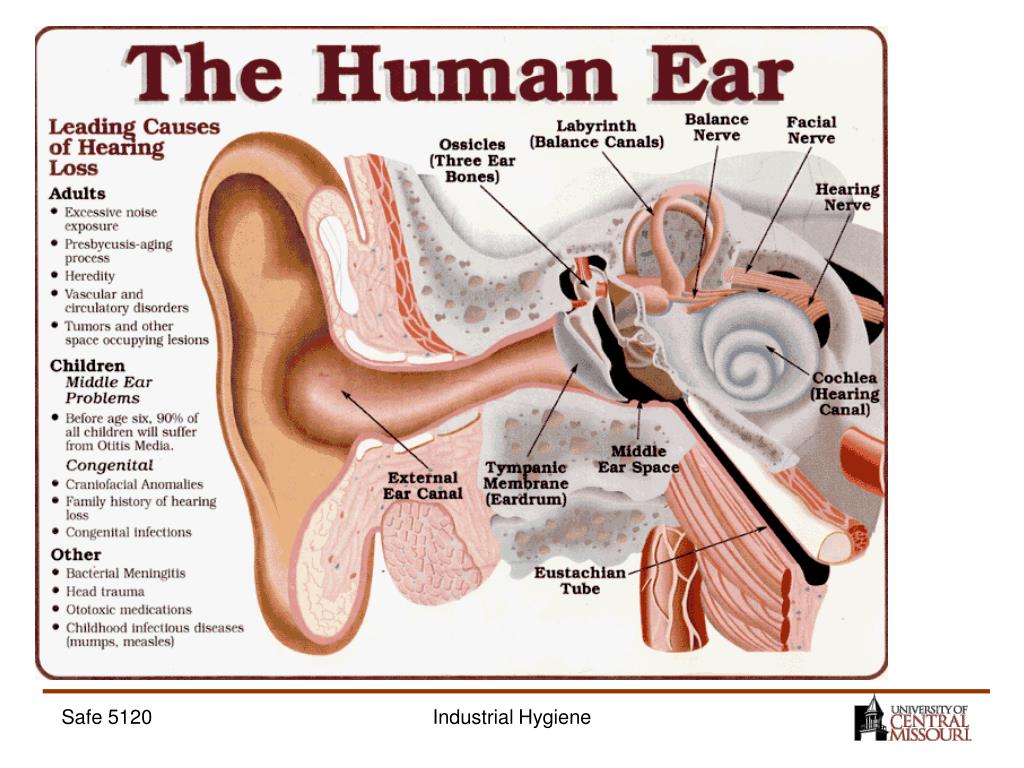 Along with the onset of deafness, they hear a constant hum and think about how to get rid of the ringing in their ears.
Along with the onset of deafness, they hear a constant hum and think about how to get rid of the ringing in their ears.
See also: How to relieve stuffy ears at home?
Otosclerosis
This age-related change, which is noticeably “younger” today, occurs when spongy bone tissue begins to grow on the surface of the dermis inside the ear. Regardless of which direction this formation begins to spread, it will still have a detrimental effect on the functionality of the organ.
At first the patient will hear ringing in the ear, and then gradually his hearing will noticeably decrease.
Substances
The cause of ringing in the ear is sometimes the abuse of certain substances: caffeine, nicotine and quinine. Frequent smoking, passion for energy drinks, coffee and even strong black tea can cause changes in the vessels, which will affect the internal parts of the auditory organ.
Puffiness
Patients with ARVI often note that their ear is blocked and ringing in it. This is due to the fact that stagnant mucus or swelling block the lumen of the auditory tube. A stuffy nose and ear canal cause a difference in pressure, causing the eardrum to bulge inwards. Unable to move from sound vibration, this film remains in place, and the patient, meanwhile, hears only a physiological ringing in the ear.
This is due to the fact that stagnant mucus or swelling block the lumen of the auditory tube. A stuffy nose and ear canal cause a difference in pressure, causing the eardrum to bulge inwards. Unable to move from sound vibration, this film remains in place, and the patient, meanwhile, hears only a physiological ringing in the ear.
High blood pressure
A sudden increase in blood pressure or hypertension in a patient can lead to spasm of the posterior auricular artery. At the same time, the ringing is characterized by a special tact – it is not constant, but seems to duplicate the heartbeat, pulsates.
Medicines
A number of medicines have tinnitus as a side effect. In particular, taking antibiotics that include gentomycin, as well as medicines containing aspirin, can cause temporary hearing loss.
As soon as you stop taking the culprit drug and it is completely removed from the plasma, the obsessive noise will also disappear.
Injuries
If the causes of tinnitus are injuries of the head or only the auditory organs, then its character will be pronouncedly pulsating, and sometimes resemble a whistle. This pathology is accompanied by hearing loss of varying degrees, as well as headaches, dizziness, nausea. With severe swelling of the brain, vomiting and severe coordination disorders may occur.
This pathology is accompanied by hearing loss of varying degrees, as well as headaches, dizziness, nausea. With severe swelling of the brain, vomiting and severe coordination disorders may occur.
Any of these symptoms following a head injury should be seen by a specialist as soon as possible.
Atherosclerosis
This disease is characterized by narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels due to the growth of cholesterol plaques on their walls. Impaired blood flow causes a characteristic noise – a ringing appears in the ears.
Ringing may be constant or occur occasionally, intermittently. Often it is accompanied by dizziness, patients have a headache.
Read also: Causes of constant ringing in the ears
Neoplasms
Acoustic neuroma can cause ringing in the right or left ear. The tumor grows and begins to put pressure on the area where the cochlea is located and affect it. As a rule, if ringing in the left ear or right ear due to a neuroma, the noise will be heard in only one organ of hearing. It will not be very pronounced at first and resemble a squeak or even the sound of sea waves.
It will not be very pronounced at first and resemble a squeak or even the sound of sea waves.
Growing, the tumor begins to compress the brain stem and other parts of the auditory organ, which causes dizziness, impaired coordination and hearing loss.
Otitis media
Inflammation of the inner ear is a common cause of ringing. The swelling that accompanies the pathological process, as well as the accumulating fluid, reduce the mobility of the malleus and stirrup and keep them in a state of constant vibration. This causes false noise in one ear.
In addition to the above causes of tinnitus, it can manifest itself in:
- Meniere’s disease;
- diabetes mellitus;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- sulfur plug;
- anemia;
- osteochondrosis;
- overwork;
- schizophrenia.
As you can see, there is a fairly wide list of diseases and conditions that accompany tinnitus, their treatment should be timely and go under the supervision of specialists.
Frequent combinations of symptoms
Dizziness + ringing
Such symptoms can be caused by:
- Changes in the movement of nerve impulses after injuries, atherosclerosis and inflammatory processes in the internal parts of the auditory organ;
- changes in vascular patency with increased pressure, atherosclerosis and the influence of medicines and certain substances;
- overexertion of nerve fibers due to stress or fatigue.
Dizziness + ringing + visual symptoms
If dizziness becomes stronger when moving the head, the patient experiences pain in the neck, feels a knock in the temples and ringing in the ears, the appearance of stars in the eyes is often noted, then it is worth making an appointment with a neurologist. This set of symptoms, which means that a person has osteochondrosis of the cervical region, is a good reason to contact a neurologist.
If the ringing appeared abruptly, accompanied by a hum, dizziness and darkening of the eyes, such an attack may indicate a pressure surge.![]()
Ringing + tachycardia + dizziness
If the ringing appears in combination with dizziness, pre-syncope, a person has a faster heartbeat, he sweats profusely, and the limbs freeze during such attacks, then such symptoms will mean that the culprit is vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Dizziness + ringing + lethargy
If you have dizziness and ringing that does not go away, accompanied by lethargy, persistent unwillingness to work, severe irritability, as well as sudden changes in appetite and weight, then this spectrum of symptoms will signal the exhaustion of the nervous system and the occurrence of neurosis and depression.
Read also: Squeaking in the ears: causes and treatment of an unpleasant symptom
Diagnosis
Having determined which disease the general symptoms belong to, immediately contact the right specialist in order to start getting rid of the noise and its root causes as soon as possible.
If the noises are intrusive, but you have not identified specific symptoms, make an appointment with a general practitioner to go to a specific narrow doctor. The doctor will listen to you, examine you and redirect you to the specialist who should help you: tell you what causes tinnitus, what to do and how to treat the disease accompanied by this symptom.
The doctor will listen to you, examine you and redirect you to the specialist who should help you: tell you what causes tinnitus, what to do and how to treat the disease accompanied by this symptom.
Treatment of tinnitus
The treatment of this specific symptom will be to eliminate its root cause.
- If the symptom is caused by taking medications, they are replaced with others or they wait until the end of the course, observing the patient in dynamics.
- Ringing in the ear caused by vascular problems is treated by a surgeon. This therapy is very long-term, but very important. Perhaps the doctor will reveal a serious pathology in you thanks to the noise in the auditory organs and prescribe a course of drugs and measures to cure the disease.
- If your ears are stuffy and noisy due to stress or other neurological pathologies, a course of sedatives will help you, in serious cases, the doctor may prescribe strong antidepressants.
- In case of VVD, the neurologist will prescribe you treatment in the form of vascular strengthening drugs.

- If the cause of ringing in the ear is an inflammatory process, the ENT will prescribe you a complex antibacterial treatment, which must be strictly followed so that otitis media does not become chronic.
Measures to alleviate the condition
Before visiting a specialist in modern realities, it can take quite a long time, and until then you need to somehow relieve annoying obsessive symptoms:
- Tinnitus can be removed by listening to soft music – calm melodies will slightly alleviate your condition.
- If you have a blood pressure monitor at home, take your blood pressure first. If it is noticeably increased, and you have a prescription from a therapist or a cardiologist, take a pill to normalize it.
- Before visiting a doctor, a salt-free diet should be followed. Sodium can aggravate your condition, and ringing in your left ear or right ear will only get worse.
- If you have taken drugs containing aspirin, stop using them.



/earpainfinal-01-5c86a4ba46e0fb00015f8fca.png)



