Is banana acid or alkaline. Bananas for Acid Reflux: Benefits, pH Levels, and Safe Fruit Options for GERD
Are bananas acidic or alkaline. How do bananas affect acid reflux. Which fruits are safe to eat with GERD. What is the pH level of different banana varieties. How can certain fruits help reduce gastric acid.
Understanding the pH Scale and Acidity of Bananas
To properly evaluate whether bananas are beneficial for acid reflux, it’s crucial to understand the pH scale and how it relates to banana acidity. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Any value below 7 is considered acidic, while values above 7 are alkaline.
Interestingly, the acidity of bananas can vary based on their ripeness:
- Unripe bananas: pH around 5.6 (acidic)
- Ripe bananas: pH around 6.5 (mildly acidic)
Despite having a pH slightly below 7, ripe bananas are often considered alkaline foods. This is due to their high potassium content, which can have an alkalizing effect on the body after digestion.
pH Levels of Different Banana Varieties
The acidity of bananas can also vary depending on the specific variety:

- Red banana: pH 6.2
- Cavendish banana: pH 5.5
- Burro banana: pH 7.6
- Baby banana: pH 7.3
- Apple banana: pH 5.8
As we can see, some banana varieties like the Burro and Baby banana actually have a pH above 7, making them truly alkaline.
The Impact of Bananas on Acid Reflux
For those suffering from acid reflux or GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease), bananas are generally considered a safe and beneficial fruit option. Here’s why:
- Low acidity: Ripe bananas have a relatively low acidity compared to many other fruits.
- High fiber content: The fiber in bananas can help promote healthy digestion and prevent acid reflux symptoms.
- Stomach coating properties: Bananas may help create a protective coating on the stomach lining, potentially reducing irritation from stomach acid.
- Alkalizing effect: Due to their high potassium content, bananas can have an alkalizing effect on the body, potentially helping to neutralize excess stomach acid.
While bananas are generally safe for those with acid reflux, it’s important to note that individual reactions can vary. Some people may find that even mildly acidic foods trigger their symptoms.

Other Fruits Safe for Acid Reflux Sufferers
In addition to bananas, several other fruits are considered safe options for those with acid reflux or GERD:
- Melons (honeydew, cantaloupe, watermelon)
- Apples
- Pears
- Coconut
These fruits are generally low in acid and high in fiber, making them good choices for managing acid reflux symptoms.
Why Are These Fruits Beneficial?
Melons, apples, pears, and coconut offer various benefits for those with acid reflux:
- Alkaline properties: Many of these fruits have alkaline-forming properties in the body.
- Low acidity: They have a lower acid content compared to citrus fruits and tomatoes.
- High water content: Fruits like melons and coconut have high water content, which can help dilute stomach acid.
- Nutrient-rich: These fruits provide essential vitamins and minerals that support overall digestive health.
Fruits to Avoid with Acid Reflux
While some fruits can be beneficial for those with acid reflux, others may exacerbate symptoms. Fruits to avoid include:

- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits)
- Pineapple
- Tomatoes (technically a fruit)
These fruits are highly acidic and can trigger or worsen acid reflux symptoms in many individuals. It’s also advisable to avoid fruit juices made from these fruits, as they can be even more concentrated in acidity.
The Role of Fruit Ripeness in Acid Reflux Management
The ripeness of fruit can significantly impact its acidity and potential effects on acid reflux. Generally, riper fruits tend to be less acidic and better tolerated by those with GERD. This is particularly true for bananas:
- Unripe (green) bananas: More acidic and may contain higher levels of resistant starch, which can be harder to digest.
- Ripe (yellow with brown spots) bananas: Less acidic and easier to digest, often better tolerated by those with acid reflux.
When selecting fruits for an acid reflux-friendly diet, opt for fully ripe options whenever possible.
Incorporating Fruits into an Acid Reflux Diet
While certain fruits can be beneficial for those with acid reflux, it’s important to incorporate them thoughtfully into your diet:

- Portion control: Even safe fruits should be consumed in moderation to avoid overloading the digestive system.
- Timing: Avoid eating fruits close to bedtime, as lying down shortly after eating can increase the risk of acid reflux.
- Preparation: Consider blending fruits into smoothies or cooking them, which may make them easier to digest for some individuals.
- Combine with other foods: Eating fruits alongside other non-acidic foods can help buffer their effects and may improve tolerance.
Remember that everyone’s digestive system is unique, so it’s essential to pay attention to your body’s reactions and adjust your diet accordingly.
Beyond Fruits: Other Dietary Considerations for Acid Reflux
While focusing on fruit choices is important, managing acid reflux involves a comprehensive approach to diet. Consider these additional dietary tips:
- Avoid trigger foods: Common triggers include spicy foods, fatty foods, chocolate, and caffeine.
- Eat smaller meals: Large meals can put pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter, increasing the risk of acid reflux.
- Stay upright after eating: Wait at least three hours after a meal before lying down.
- Limit alcohol and carbonated beverages: These can relax the lower esophageal sphincter and increase acid production.
- Choose lean proteins: Opt for fish, poultry, and plant-based proteins over fatty meats.
- Incorporate whole grains: These can help absorb stomach acid and provide beneficial fiber.
By combining these strategies with careful fruit selection, you can create a comprehensive dietary approach to managing acid reflux symptoms.

The Importance of Individualized Approaches to Acid Reflux Management
While general guidelines about fruit consumption and acid reflux can be helpful, it’s crucial to remember that every individual’s experience with GERD is unique. Factors that can influence how fruits and other foods affect your acid reflux symptoms include:
- Severity of GERD
- Individual food sensitivities
- Overall diet composition
- Stress levels
- Eating habits and timing
- Other medical conditions
Given these variables, it’s advisable to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized diet plan. They can help you identify your specific triggers and create a balanced diet that manages your symptoms while ensuring you get all necessary nutrients.
Keeping a Food Diary
One effective way to identify your personal acid reflux triggers is to keep a detailed food diary. Here’s how to do it:
- Record everything you eat and drink, including portion sizes and timing.
- Note any symptoms you experience and when they occur.
- Look for patterns between certain foods or eating habits and your symptoms.
- Use this information to guide your food choices and discuss findings with your healthcare provider.
By maintaining a food diary, you can gain valuable insights into how different fruits and other foods affect your acid reflux symptoms, allowing for a more tailored approach to dietary management.
/high-angle-view-of-apples-and-bananas-arranged-593452887-5962e42d3df78cdc68bb1d5d.jpg)
Non-Dietary Approaches to Managing Acid Reflux
While diet plays a crucial role in managing acid reflux, it’s not the only factor to consider. Several lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can complement dietary changes:
Lifestyle Changes
- Elevate the head of your bed: This can help prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus during sleep.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter, exacerbating GERD symptoms.
- Manage stress: Stress can increase stomach acid production and exacerbate symptoms.
- Wear loose-fitting clothes: Tight clothing can put pressure on the stomach and lower esophageal sphincter.
Medical Interventions
In some cases, dietary and lifestyle changes may not be sufficient to manage acid reflux symptoms. Medical interventions may include:
- Over-the-counter antacids
- H2 receptor blockers
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- Prescription medications
- In severe cases, surgical options may be considered
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication or treatment regimen for acid reflux.
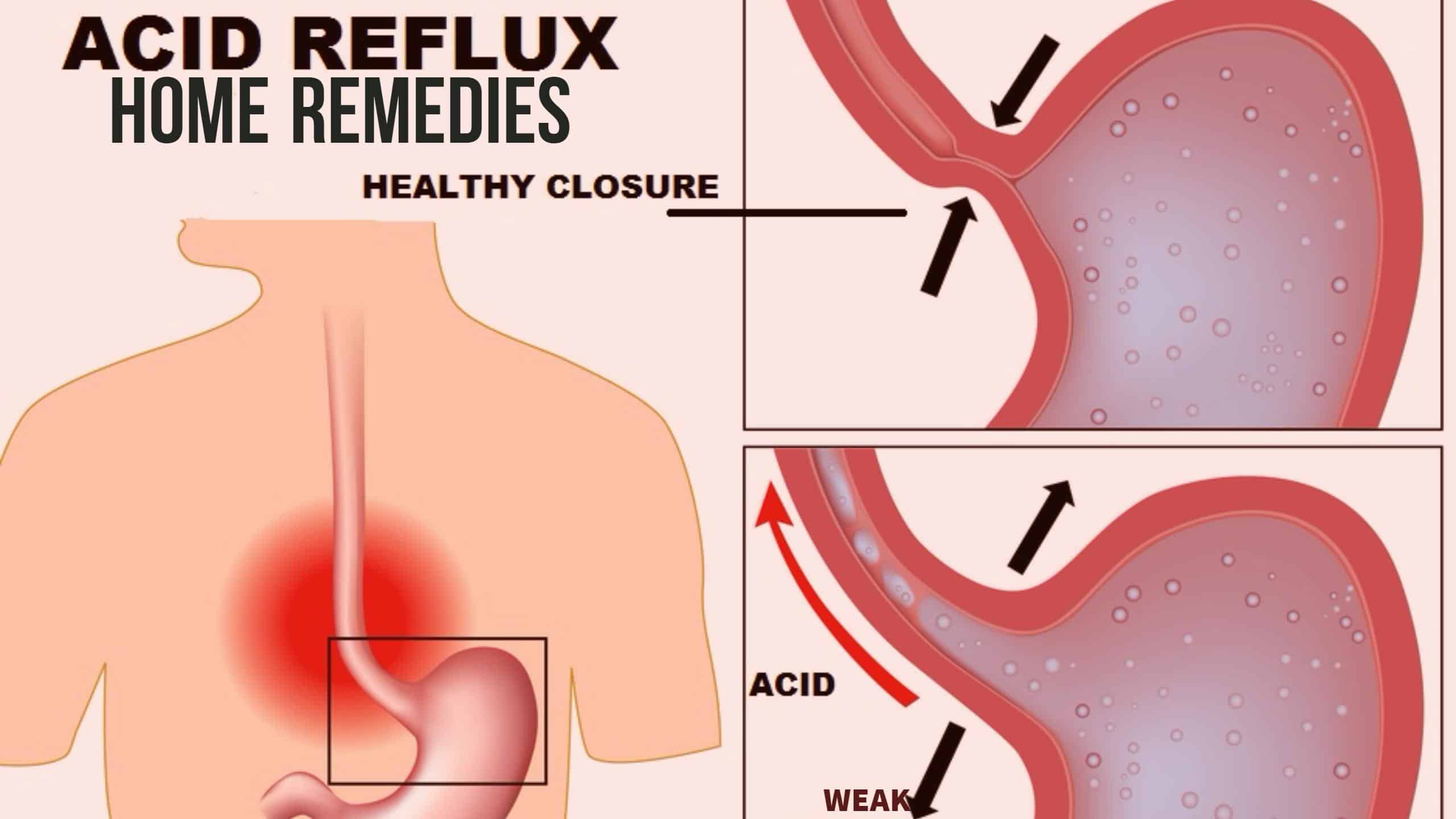
By combining appropriate fruit choices with other dietary considerations, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions as needed, most individuals can effectively manage their acid reflux symptoms and enjoy a better quality of life.
Hermina Hospitals | Five fruits you can eat to reduce gastric acid
- Posted On: 22 August 2022
- Posted By: Hermina Padang
- 3 min read
- Reviewed By: Prof.Dr.dr.Nasrul Zubir,Sp.PD, KGEH
Five fruits you can eat to reduce gastric acid
Hello, Hermina’s friends. Have you ever experienced stomach acid? Of course, stomach acid pain really makes Hermina’s friend uncomfortable during activities when experiencing stomach acid.
Surely Hermina’s friend is wondering if there are fruits that can prevent stomach acid. Of course, there is Hermina’s friend. Let’s read the article below to find out what fruits can prevent stomach acid.
Patients with gastric acid reflux disease, or GERD, need to be careful when eating fruit. Because there are a number of fruits that are high in acid and have the potential to make stomach acid recur. So, what are the fruits for stomach acid that are safe to eat?
From bananas to coconuts, here are a variety of fruits that are great for acid reflux.
1. Banana
Bananas are one of the delicious fruits for stomach acid.
banana, a yellow fruit that tastes delicious.
Bananas for stomach acid are considered safe because they have alkaline (alkaline) properties.
In addition, this fruit is also considered to help balance the acid in the stomach so that symptoms of acid reflux or GERD can be prevented.
2. Melon
Just like bananas, the benefits of melon for stomach acid come from its alkaline nature.
According to reports from Johns Hopkins Medicine, this sweet-tasting fruit is believed to relieve stomach acid and prevent irritation due to gastric acid reflux.
There are various types of melons that are safe for people with stomach acid reflux to consume, including honeydew melon, cantaloupe (cantaloupe), and watermelon (watermelon).
3. Apple
Apples for stomach acid are believed to be safe because they contain alkaline minerals, such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which are claimed to relieve stomach acid reflux symptoms.
4. Pears
Because it does not contain as much acid as citrus fruits and tomatoes, you can eat pears for stomach acid.
Thanks to this low acid content, pears are considered not to trigger the recurrence of stomach acid reflux symptoms.
5. Coconut
Coconut can be a safe choice for people with stomach acid because it is considered one of the fruits with the lowest acid content.
What’s more, this fruit that contains a lot of water is believed to improve brain function, potentially prevent heart disease, and reduce the risk of stroke.
Stomach acid is a taboo fruit that needs to be avoided.
There are a number of stomach acid taboos that need to be avoided.
- Orange
- Lime
- Grapefruit
- Lemon
- Pineapple
- Tomatoes.
Furthermore, there are a number of fruit juices for people with stomach acid that should not be consumed first, such as tomato juice and orange juice, because they are considered to cause stomach acid to rise.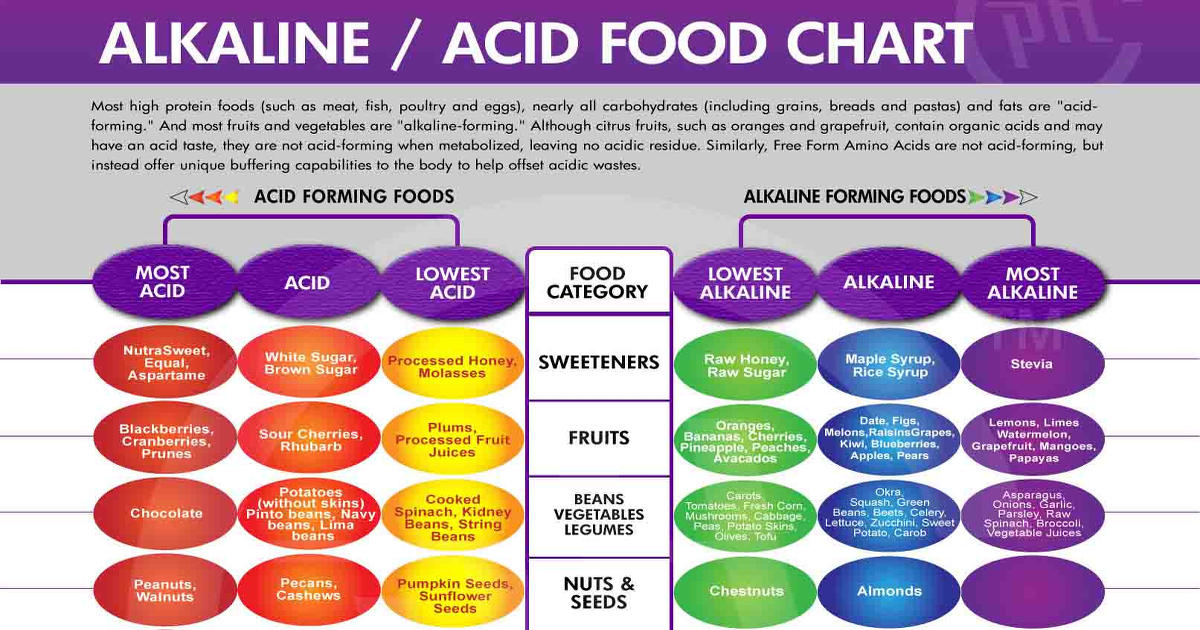
Processed tomatoes in the form of sauce or foods with tomato sauce, such as pizza and lasagna, should also be avoided because they have the potential to cause stomach acid to rise.
Some people with GERD also find it difficult to tolerate garlic and onions, as well as foods processed with these ingredients.
Hermina’s friend, after reading the article above, knows that there are fruits that can prevent stomach acid. With us, we have done prevention against gastric acid disease. We can avoid chronic gastric acid disease.
Are Bananas Acidic? Bananas for Acid Reflux [Good or Bad]
Latest Posts
report this ad
Bananas are considered the most beneficial fruit for acid reflux, but is it that efficient? To know that, you must dig into the inner facts about whether bananas are acidic or alkaline.
Banana is considered an alkaline food because of their high potassium content. While the pH fluctuates with the ripeness and species, the perfectly ripe, creamy bananas are alkaline. The unripe bananas are acidic as they have a pH of around 5.6. However, ripe bananas have a pH of about 6.5, which is less acidic.
The unripe bananas are acidic as they have a pH of around 5.6. However, ripe bananas have a pH of about 6.5, which is less acidic.
However, there is much more to it! Read on to find out if you should consume bananas when suffering from acid reflux.
Why Are Bananas Acidic or Alkaline?
To understand the basis of the alkalinity of bananas, you first need to know the basics of the pH scale. Anything on a pH scale less than 7 is acidic, and above 7 is alkaline.
The ripe banana’s pH is 6.5, which is mildly acidic. But due to high potassium, ripe bananas show alkalinity in nature.
Image sources: usgs.gov
Also, most banana species are non-acidic, but a few, such as green bananas, may show a certain level of acidity.
| Banana species | pH |
| Red banana | 6.2 |
| Cavendish banana | 5.5 |
| Burro banana | 7.6 |
| Baby banana | 7. 3 3 |
| Apple banana | 5.8 |
pH of Bananas
Also Read: Are Mangoes Acidic? [Mango And Acid Reflux Good Or Bad]
Bananas for acid reflux [good or bad]
Unripe bananas contain the highest concentrations of oxalic, malic, and citric acid. So, if you suffer from acid reflux, it might intensify your stomach acidity after eating.
On the other side, in ripe bananas, the concentration of oxalic acid drops, leading to alkalinity in the fruit. Due to the alkalinity of ripe bananas, it works as a natural antacid, significantly reducing acid reflux.
But how does it work?
The banana’s high potassium content contributes to pH, making it alkaline. Also, ripe bananas contain probiotics, minerals, and vitamins, which help reduce symptoms of acid reflux. However, since your stomach already has an acidic pH, you need foods that do not amplify it. And ripe bananas are exactly what you need!
Low acidic and alkaline ripe bananas prevent acid reflux by shielding the stomach lining from the acids.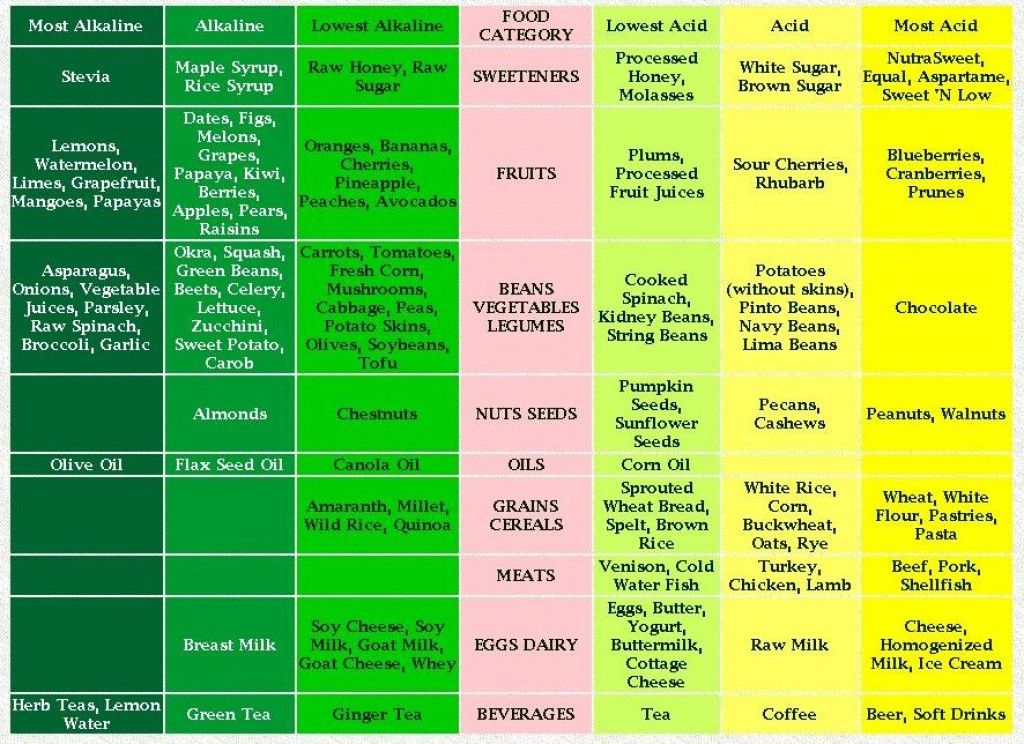
Also, ripe bananas contain beneficial digestive enzymes amylases and glucosidases. These enzymes help to strengthen your gut and esophagus and prevent acid reflux.
However, remember that it works when taken in moderation, so do not overeat it.
Are Bananas Bad for Acid Reflux?
Bananas are one of the safest foods to consume for chronic cases of acid reflux and GERD. The high alkalizing properties help reduce the acidity in the stomach and promote the growth of mucous around the stomach. Furthermore, it also ensures proper functioning of the esophageal sphincter, thus, preventing reflux.
Why Do Bananas Give Me Heartburn?
Is it possible that instead of preventing acid reflux, bananas trigger it for some people? Unfortunately, yes! But this is no reason to consider bananas among foods to avoid with acid reflux.
There could be two reasons if bananas are not working for you. Let’s have a closer look.
Some people have an exceptionally low tolerance for acidic food. Thus, you must closely monitor your diet for any signs of discomfort to rule out if bananas are triggering heartburn.
Thus, you must closely monitor your diet for any signs of discomfort to rule out if bananas are triggering heartburn.
But wait, there is one more reason! You might be eating unripe bananas, causing acid reflux. Why does that happen? Do bananas cause acid reflux? Unlike ripe bananas, unripe ones have a higher percentage of potassium nitrate, making them comparatively more acidic.
Besides, a few species of bananas are naturally less alkaline, owing to higher starch content. A higher starch content thus contributes to higher gut fermentation, leading to bloating and heartburn.
What Kind of Banana Is Good for Acid Reflux?
Essentially, all kinds of bananas work well for acid reflux. However, a few species are comparatively more alkaline and have a better chance of relieving symptoms. This includes the “Burro bananas” and the “Baby bananas.”
With a pH of 7.6 and 7.3, these species promote mucous formation around the stomach and the proper functioning of LES (Lower Esophageal Sphincter).
Are Ripe Bananas Acidic?
Are bananas alkaline or acidic? Well, ripe bananas are alkaline, with a maximum pH of 7.6. But here’s the catch! Some species of bananas, namely the cavendish and red bananas, are acidic even when perfectly ripe.
This is because of their natural starch content, resulting in a lower pH. However, for the most part, ripe bananas are non-acidic, and patients suffering from acid reflux can easily consume them.
Are Green Bananas Acidic?
Have you noticed a tangy, grassy taste in unripe or green bananas? This is due to a greater starch content in unripe bananas, leading to higher acidity.
While it essentially depends on how ripe the bananas are and the species, unripe bananas usually have a pH ranging from 4.5 to 5.2. The level of enzymes and oxalic acid also affect the pH balance, making green bananas acidic compared to ripe ones.
Are Overripe Bananas Acidic?
Just as unripe bananas are acidic, overripe bananas are also acidic, although for completely different reasons. Hence, it is important you choose perfectly ripe bananas to ensure optimum alkalinity and help with gastric problems. An overripe banana means breaking down more carbs and producing alcohol. This affects the pH, making them acidic.
Hence, it is important you choose perfectly ripe bananas to ensure optimum alkalinity and help with gastric problems. An overripe banana means breaking down more carbs and producing alcohol. This affects the pH, making them acidic.
| Ripeness | Alkalinity |
| Unripe | Acidic |
| Ripe | Alkaline |
| Overripe | Acidic |
Are Cooked Bananas Acidic?
Cooking the bananas breaks down some of the starch, decreasing the alkalinity. This makes them slightly less alkaline than raw bananas; however, they are still not acidic. The alkalinity also depends on how you cook the bananas, whether you bake, boil, or fry them. Boiling or frying the bananas reduces the potassium content to 40%, resulting in a decline in alkalinity.
| Boiled bananas | Alkaline |
| Baked bananas | Slightly alkaline |
| Fried bananas | Least alkaline |
What Are the Benefits of Eating Bananas?
There are many health benefits of eating banana. Some of the core health benefits are described below.
Some of the core health benefits are described below.
High Nutritional Value
Bananas are capable of fulfilling your dietary needs while keeping your calories under control. You get a complete package without fat with a total calorie count of 112. From potassium and folate to vitamin C and fibers, it makes an ideal snack with high nutritional gains.
Better Digestion
Thanks to the prebiotics and fibers, such as pectin, your gut health stays top-notch. This prevents constipation and keeps your bowel movement in check to prevent risks of diverticulitis. The fibers also prevent chances of colon cancer, although more studies are required to attest to this observation.
Weight Loss
A medium-sized banana can easily keep your hunger at bay. The best part is that it keeps you full at only 126 calories. The fibers add bulk to your diet, which reduces the hunger pangs and helps maintain a steady weight. Dieticians around the world widely recommend the Banana diet due to its proven weight loss results.
Cardiovascular Health
Potassium has shown to significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disorders, such as blood pressure and stroke. What better way to incorporate potassium than the good old bananas? Additionally, the magnesium and folate in bananas contribute to the overall health benefits aiding their popularity.
Easily Accessible
Bananas are one fruit accessible throughout the year in almost all parts of the world. You can eat it as is, or add it to your smoothie, shake, or granola. Since it does not contain much protein, you might want to add it to yogurt or a high-protein source if you plan to add it to your diet.
FAQs
Is ripe banana good for acid reflux?
Ripe bananas are great for patients suffering from acid reflux, thanks to their 7.6 pH and high potassium levels. The alkaline nature of bananas helps against acidity by promoting mucous lining around the stomach. Besides, the natural probiotics and vitamins in bananas also help fight acid reflux symptoms.
Which foods neutralize stomach acid?
Foods that are high in alkalinity are good for neutralizing stomach acid. This includes bananas, apples, pears, avocados, and green vegetables. Ginger tea also helps tame down acidity with its anti-inflammatory properties.
What fruits have low acidity?
A few common fruits with low acidity include melons, bananas, avocados, olives, pears, and mangoes. Hence, people with acid reflux can consume these without fruits without any worries of triggering their symptoms.
What acid does a banana have in it?
Raw bananas have a high concentration of oxalic acid, malic acid, and citric acid. However, as the banana ripens, the level of oxalic acid falls, making it less acidic. Naturally cultivated bananas have more acids compared to treated ones.
Bottom Line
Now that you know the answer to “Are bananas acidic or alkaline?” you can incorporate these into your diet without any worries. However, do not consume them in excess as they can be triggering for some people with extremely low acidity tolerance.
However, do not consume them in excess as they can be triggering for some people with extremely low acidity tolerance.
Finding a high-alkalinity species such as the Burro bananas is better, but even the typical species in your local grocery stores work fine.
Latest Recipes
report this ad
More Recipes Like This
11 unusual ways to use bananas
Life
January 29
Skin care, gardening, cleaning – and that’s not all of their areas of application.
1. Make a face mask
A good alternative to store-bought products that moisturizes and softens the skin. Mash a ripe banana to make a paste and apply a thin layer on the face and neck. Hold the mask for 10-20 minutes and then rinse with cool water. For even more hydration, mix a banana with a quarter cup of unsweetened yogurt and two tablespoons of honey.
2. Polish silverware and leather shoes
Sounds like a joke, but banana skin really does help bring back the shine to silver and leather. Remove excess fibers from the inside of the peel and rub it on the surface of dishes or shoes. Then dry with a paper towel or soft cloth. The hack can also be used to bring back the shine of leather furniture.
Remove excess fibers from the inside of the peel and rub it on the surface of dishes or shoes. Then dry with a paper towel or soft cloth. The hack can also be used to bring back the shine of leather furniture.
3. Tenderize the meat
Simply add a ripe banana peel to the pan with this product and cook as usual. The enzymes contained in it will help break down the proteins in the meat and soften it during frying. The taste of the dish will not change.
4. Refresh indoor plants
If the leaves of house flowers are dull and dusty, do not rush to spray them with water: this will only smear dirt on them. Instead, rub each leaf with the inside of a banana peel and they will shine.
5. Drive away aphids in the garden
Bury dried banana peels 2 to 5 centimeters deep around the plant that the aphids have attacked and the pests will soon disappear. It is better not to use the whole peel and pulp: rodents and other animals can find them a tasty treat and dig them up.
6. Feed your crops
Bananas and their husks are high in potassium, an important nutrient that is good for you and your garden. Feeding can be done in two ways. First: dry the peel, grind in a blender and add to the ground when planting – just pour a pinch into the hole before lowering the plant into it. The second way is to puree fresh skins with water and use as a liquid fertilizer.
7. Soothe skin from burns and scratches
Banana peel has anti-inflammatory properties, which means it will be useful if you are bitten by an insect or if you are scratched, stinged with nettles or sunburned. Place the skin on the affected area and press lightly. Hold until you feel relief, changing the compress from time to time.
8. Speed up the ripening of fruits and vegetables
Ripe bananas produce ethylene gas, which induces ripening. Therefore, if you need a vegetable to ripen faster, put it in a paper bag along with a banana.
9. Brighten your teeth
After brushing your teeth, rub them for a couple of minutes with a banana peel. It contains citric acid, which gently whitens the enamel.
It contains citric acid, which gently whitens the enamel.
10. Remove the splinter
Apply a banana skin to the affected area for half an hour with its inner surface. The enzymes contained in it will destroy the bonds between the proteins of the upper layer of the skin (which is why the substances are used in facial exfoliating products), after which even deeply stuck splinters will be removed without problems.
11. Relieve Heartburn
Bananas are alkaline, and the alkali neutralizes stomach acid. If you suffer from heartburn, be sure to add these fruits to your daily diet. For example, eat a banana after breakfast to protect your stomach lining throughout the day.
Read also 🧐
- How to use citrus peel
- 8 ways to use ground coffee after brewing
- 20 unusual ways to use olive oil
Non-traditional soap making: making banana soap
I propose to spend a couple of bananas, a little courage, a little imagination and time to make incredibly tasty and delicate soap from scratch.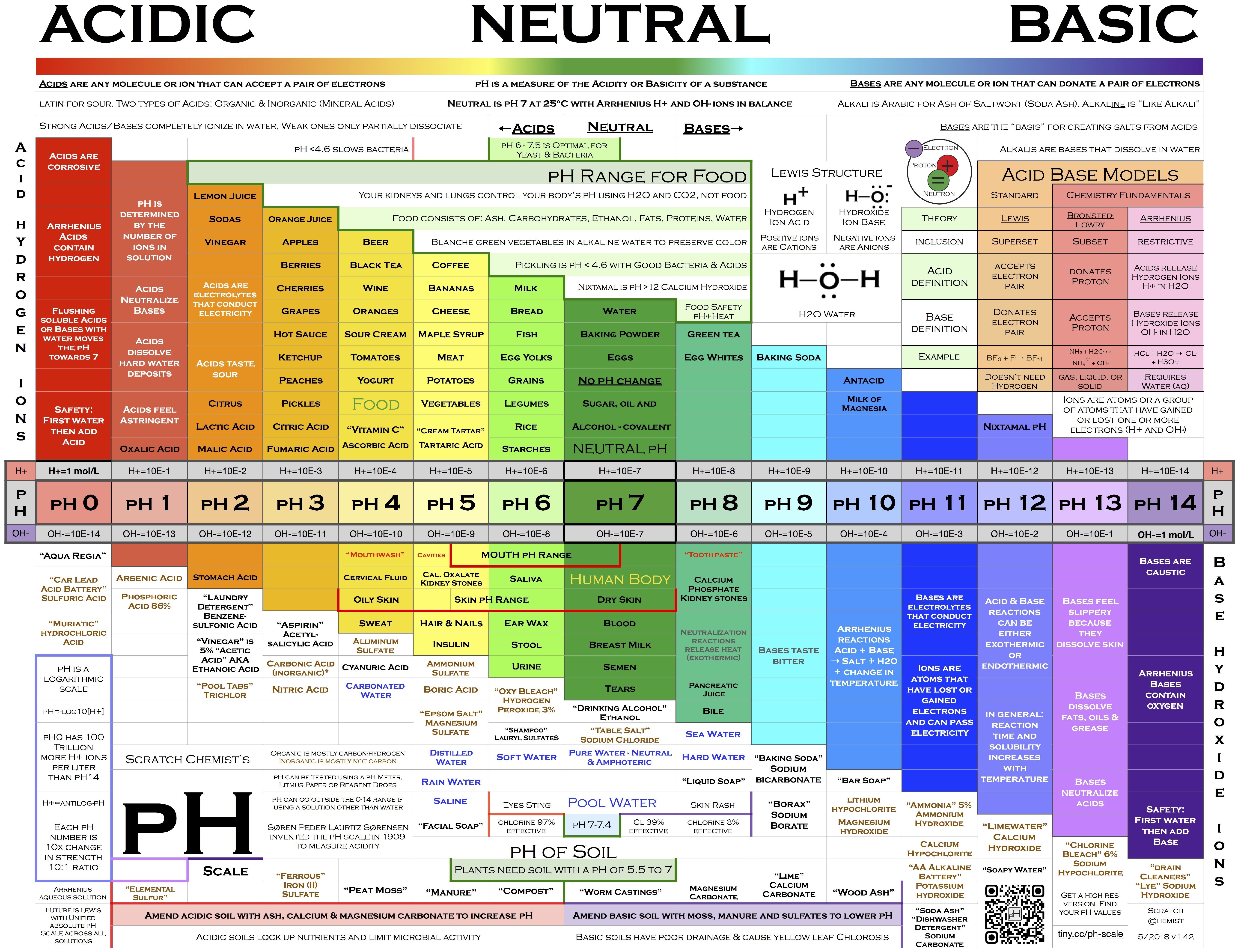
The master class is quite detailed, designed for those who have just started their soap-making journey and want to diversify their creativity with fruit variations. I’ll answer any questions you may have right away.
1. Will bananas go bad? But they won’t make it in time, because they will boil in alkali with oils. Chemical reactions will take place, and the bananas will be saponified, that is, they will become full-fledged parts of the soap bar. For the sake of the experiment, I left organic soap for a long shelf life. It behaves the same, and sometimes a little better, than the usual, cooked without additives. The scent lasts better and doesn’t dry out as quickly. No mold or other damage was observed.
2. You have a big step, the calculation is wrong, and it’s unprofessional to do so! My soap is gentle, the skin does not dry out, friends and customers are satisfied. I propose an idea that I have been implementing for a year now (it’s been a year that I’ve been brewing such banana soap, and I don’t have it stale).
Those who don’t experiment don’t make soap either 🙂
First, let’s prepare a theoretical base. We will select the components for our magic soap.
Objective: to make a soap that is hard, long rinsing, lathers well and won’t dry out the skin.
Solution: we select oils: olive, coconut, palm, castor, stearic acid.
Olive oil – classics of the genre, gives the soap a little hardness, soft foam, washing properties, is used in almost any soap. There is a soap made from 100% olive oil – Castile.
Coconut – this oil is responsible for foaming, hardness, gives the soap the main washing properties. If you put a lot, this soap will dry the skin. There is soap made from coconut oil – Marseilles, sailors’ soap. It lathers even in salt water.
Palm oil – in my opinion, this is one of the best oils for soap making. It gives the piece smoothness, hardness, slightly softens the drying effect, lengthens the period of use.
Castor oil – softens well, while increasing foaming. The disadvantage is a high iodine number, that is, it contributes to rancidity of soap.
Stearic acid is a fatty acid widely used in soap making and cosmetics. Accelerates the onset of trace and gel, accelerates the hardening of soap, lengthens the rinsing period. Not recommended for glycerin.
We make a bookmark in grams on a soap calculator and calculate the recipe and other components.
I calculate the basic recipe for 800 grams of oils. This amount is enough to weld a brick of more than a kilogram into a standard form or into a milk carton + a couple of molds.
SF (overfat or maintenance part) I always put 0% and put it on top depending on the needs. Today, for the purity of the experiment, SF will be from bananas.
On the right you can see the preliminary properties of the future soap. As you can see, it fits well with our reference version. The iodine number let us down a little, but from practice I can say that up to 55, you don’t have to worry.
The calculator calculated the amount of water and sodium hydroxide for us.
So:
- castor oil – 100 grams;
- coconut oil – 200 grams;
- olive oil (pomas) – this is what with pomace, not the first pressing – 250 grams;
- palm oil – 200 grams;
- stearic acid – 50 grams;
- water (liquid) – 304 grams;
- sodium hydroxide – 118.8 grams.
Now let’s prepare the equipment.
We will need scales, a saucepan for a bath, a container for cooking heat-resistant soap, dishes for diluting alkali, a magic wand for stirring soap during the cooking process, an immersion blender (do not use for eating), gloves, old clothes, an apron, glasses (if necessary for eye protection), thermometer, who enjoy, good mood.
I will not dwell on the security measures and rules, without me they are written in every master class.
Let’s start the practical magic!
1. We take two ripe or very ripe magic bananas with peel and weigh them.
Since their weight exceeds the weight of the required liquid, this will suit us just fine.
Next, we cut our bananas with skin and pulp, excluding only the tough tips and roots.
Now measure out 204 grams of sliced bananas. This will be a partial fluid change. That is, our soap is directly called banana, we start it on bananas 🙂
2. Now let our bananas rest a bit while we prepare the water to dissolve the alkali. We measure out 100 grams of water in a heat-resistant dish.
3. Now measure out 118.8 grams of sodium hydroxide. Since my step is grams, then I measure 119 .
4. Pour alkali into water , and not vice versa!
5. Alkali solution is very corrosive and hot. We work carefully. We stir the lye in the water with our magic wand. When all the grains disperse, we pour our bananas into this terrible solution.
When all the grains disperse, we pour our bananas into this terrible solution.
They immediately begin to turn red, and then turn black. In order not to breathe alkaline fumes, I take the whole thing out onto the balcony. And the solution will cool faster.
6. We measure out the oils.
We put them in the bath and melt them. In the meantime, let’s check our bananas and stir.
When the oil mixture dissolves to a liquid state, combine the alkaline solution with the oil. With the hot method of soap making, it is not necessary to bring the oil and the alkaline solution to the same temperature. Pour the lye into the oil.
We have fiber in the solution, which has not completely dispersed. It won’t hurt, it’ll all work out.
This is how our solution of bananas with lye in oil looks like 🙂
7. Now take an immersion blender and knead until a trace appears. Stearic acid accelerates the onset of the trace. And the soap is ready for the bath in a couple of minutes.
And the soap is ready for the bath in a couple of minutes.
In addition, stearic acid makes our soap more characteristic 🙂 If the temperature of the oils and alkali is high, then the soap enters the gel instantly. And downright strives to escape from the pan. For me, it usually rises like dough, about twice.
Stir to keep from running away from the apartment. As soon as the gel stage comes and the soap settles, you can close the bath with a lid and take a break. We do not forget about soap, control the fire, stir after half an hour.
8. About an hour later, our soap looks like this.
The gel stage has passed. We thoroughly mixed the soap twice. Now you can put any care components that will no longer be eaten by alkali. I wait another half an hour, stir the soap again, and add the rest of the bananas. By reference, our soap will not dry the skin, so this time I will not add oils. And banana fiber, rich in magnesium, starchy substances and pectin, will make the soap very pleasant for our skin.
