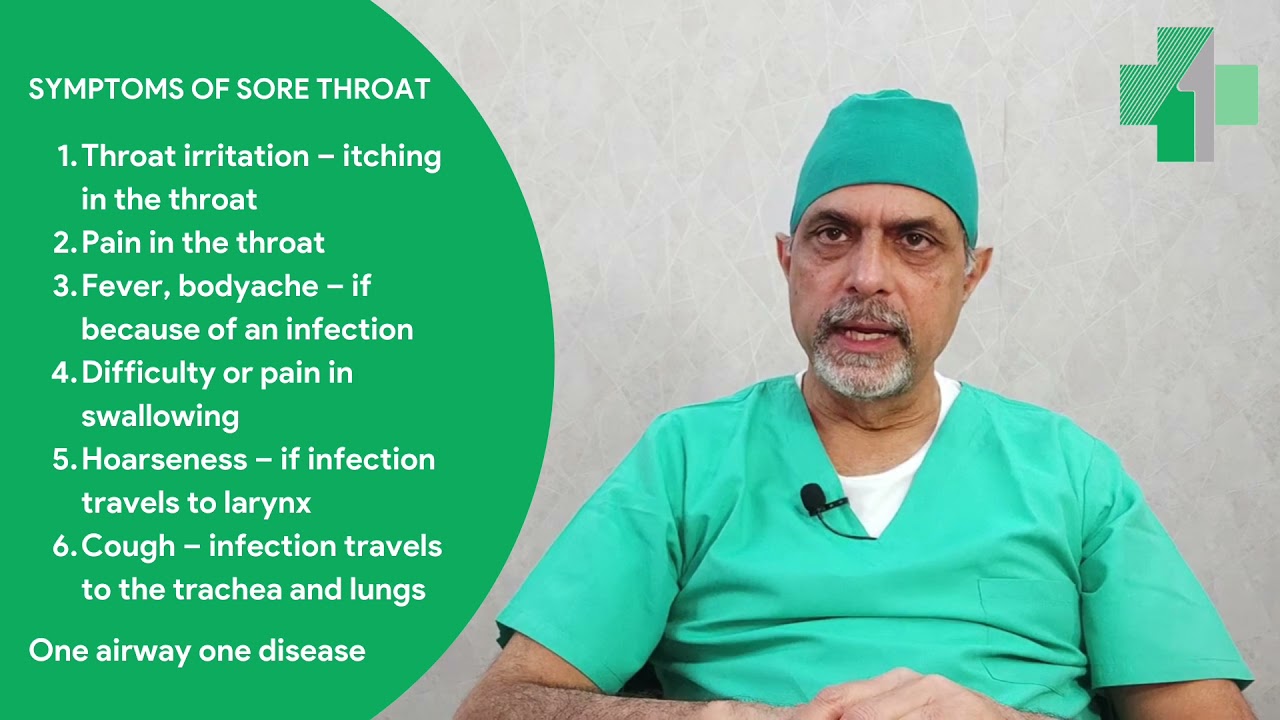
Itchy ears inside and throat. Itchy Ears and Throat: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
What causes itchy ears and throat. How to identify common triggers for ear and throat irritation. When should you see a doctor for itchy ears and throat. What are effective treatments for relieving ear and throat itchiness.
Common Causes of Itchy Ears and Throat
Experiencing itchiness in your ears and throat can be uncomfortable and concerning. While often harmless, these symptoms may indicate an underlying condition that requires attention. Let’s explore some of the most common causes:
Allergies and Hay Fever
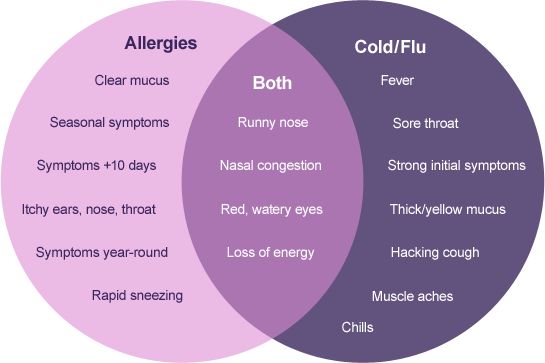
Allergic reactions are a frequent trigger for itchy ears and throat. Allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, can cause irritation in these areas. What are the typical allergens responsible? Pollen, dust mites, and animal dander top the list. During allergy seasons, particularly in spring and summer, many people experience increased itchiness along with other symptoms like sneezing and watery eyes.
Infections: Bacterial and Viral
Various infections can lead to itchy sensations in the ears and throat. Viral infections like the common cold or flu often cause these symptoms in their early stages. Bacterial infections, such as strep throat or tonsillitis, may also present with itchiness before developing into more severe pain. How can you differentiate between viral and bacterial infections? Bacterial infections often come with more intense symptoms and may require antibiotic treatment, while viral infections typically resolve on their own.
Ear Infections
Ear infections deserve special mention as they frequently cause itching sensations. These can be caused by bacteria or viruses, often as a complication of upper respiratory infections. In some cases, excess ear wax or trapped water can create an environment conducive to infection. Chronic ear infections may indicate a more serious underlying ear health issue that requires professional evaluation.
Skin Conditions Affecting the Ears and Throat
Several skin conditions can manifest in the ear and throat areas, leading to persistent itchiness:
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Dermatitis
These conditions often cause dry, flaky skin and itchiness. If you experience similar symptoms on other parts of your body, it’s possible that the same condition is affecting your ears and throat. How should you approach treatment for these skin conditions in sensitive areas? It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before applying any topical treatments to ensure safety and effectiveness.

Allergic Reactions to Medications and Foods
Allergies aren’t limited to environmental factors. Both medications and foods can trigger allergic reactions that manifest as itchy ears and throat.
Medication Allergies
If you’ve recently started a new medication and notice itching in your ears or throat, you may be experiencing an allergic reaction. These reactions can develop even if you’ve taken the medication before without issues. What should you do if you suspect a medication allergy? Contact your healthcare provider immediately to discuss alternative options.
Food Allergies
Food allergies can cause a range of symptoms, including itchiness in the mouth, throat, and sometimes ears. Common food allergens include:
- Nuts
- Shellfish
- Eggs
- Milk
- Soy
In severe cases, food allergies can lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction. If you suspect a food allergy, it’s essential to undergo proper allergy testing and develop a management plan with an allergist.
Environmental Factors and Lifestyle Habits
Sometimes, the cause of itchy ears and throat lies in our environment or daily habits:
Dry Air
Low humidity environments can dry out the delicate tissues in our ears and throat, leading to itchiness. This is particularly common during winter months when indoor heating further reduces air moisture. How can you combat dry air? Consider using a humidifier in your living spaces to maintain optimal humidity levels.
Excessive Ear Cleaning
Ironically, overzealous ear cleaning can lead to itchiness. Removing too much earwax strips the ear canal of its natural protective coating, leading to dryness and irritation. What’s the proper way to clean your ears? Generally, the ears are self-cleaning, and you should only clean the outer part with a damp cloth. Avoid inserting any objects into the ear canal.
Smoking and Second-hand Smoke
Tobacco smoke is a significant irritant to the throat and can indirectly affect the ears. Regular exposure to smoke can lead to chronic irritation and itchiness. Quitting smoking or avoiding second-hand smoke can significantly improve these symptoms.

When to Seek Medical Attention
While many causes of itchy ears and throat are benign, certain situations warrant professional medical evaluation:
- Persistent symptoms lasting more than a week
- Severe pain or discomfort
- Discharge from the ears
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears
- Difficulty swallowing
- High fever
If you experience any of these symptoms along with itchiness, it’s crucial to consult with an ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialist or your primary care physician. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment.
Diagnostic Approaches for Itchy Ears and Throat
When you visit a healthcare provider for itchy ears and throat, they may employ several diagnostic methods:
Physical Examination
A thorough examination of the ears, throat, and surrounding areas is typically the first step. The doctor will look for signs of infection, inflammation, or structural abnormalities.
Medical History
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, their duration, and any potential triggers you’ve noticed. Information about your overall health, medications, and lifestyle can provide valuable clues.
Allergy Testing
If an allergy is suspected, your doctor may recommend skin prick tests or blood tests to identify specific allergens.
Imaging Studies
In some cases, imaging techniques like CT scans or MRI may be used to get a detailed view of the ear and throat structures.
Treatment Options for Itchy Ears and Throat
The treatment for itchy ears and throat depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common approaches:
Medications
- Antihistamines: For allergy-related itchiness
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is present
- Antifungal medications: For fungal infections in the ear
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation
Topical Treatments
Ear drops or throat sprays may be prescribed to provide localized relief. These can contain antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, or anesthetics depending on the specific condition.
Lifestyle Modifications
Simple changes can often make a big difference:
- Using a humidifier to combat dry air
- Avoiding known allergens
- Proper ear cleaning techniques
- Quitting smoking
Immunotherapy
For severe allergies, immunotherapy (allergy shots or sublingual tablets) may be recommended to desensitize the immune system to specific allergens over time.

Prevention Strategies for Itchy Ears and Throat
While not all causes of itchy ears and throat can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
Maintain Good Hygiene
Proper hand washing and avoiding touching your face can help prevent the spread of infections that may cause itchiness.
Manage Allergies
If you know you have allergies, work with your doctor to develop an effective management plan. This may include taking medications preemptively during high-risk seasons.
Protect Your Ears
When swimming or bathing, use earplugs or a swim cap to prevent water from entering your ears, which can lead to infections.
Avoid Irritants
Minimize exposure to smoke, strong perfumes, and other known irritants that can trigger itchiness in sensitive individuals.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps keep mucous membranes moist, potentially reducing irritation in the throat and ears.
Understanding the various causes of itchy ears and throat empowers you to take appropriate action, whether it’s making simple lifestyle changes or seeking medical attention. By staying informed and attentive to your body’s signals, you can effectively manage these uncomfortable symptoms and maintain optimal ear and throat health.

What Causes Itchy Ears and Throat?
Have questions? Use our contact form to get in touch with us today! Contact Us
Itchy ears and throat can be caused by a number of different things. In most cases, it may be something minor like the common cold or allergies, which are not a cause for concern. However, these symptoms could be an indication of a more serious problem, so you may need to seek the advice of an ENT doctor. These are some of the potential causes of itchy ears and throat.
Ear infections
If you notice an itching sensation in your ear, this could be an indication that you have an ear infection or you are developing one. Ear infections can be caused by the bacteria and viruses in people that have the common cold. In some cases, it may also be because the ear is blocked with excess wax or you have water trapped in your ear. If you see an ENT doctor, they will be able to identify the cause of the ear infection and suggest a course of treatment to clear it up.
Usually, this will be enough to solve the problem. However, some people experience chronic ear infections that keep recurring, and that is a sign that you have a more serious ear health issue. If this is the case, you need to see an ENT doctor so they can identify the underlying reason behind your recurring ear infections.
Dry ears
Oil and wax in the ear play a very important role as it helps to keep your ears clean and healthy. But a lot of people make the mistake of cleaning out their ears too often and removing the oil and wax. This then leads to dry ears that get very itchy. If you have dry ears, you will notice flaky skin on the outside of the ear, as well as an itching sensation. Changing your cleaning habits should rectify this problem but if it persists, you should see an ENT doctor.
Skin conditions
Certain skin conditions may also cause itchy ears. Things like psoriasis, eczema and dermatitis all lead to dry flaky skin and itchiness.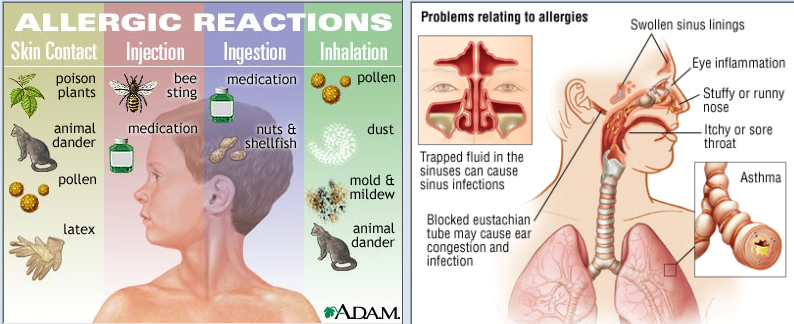 If these conditions affect other areas of your body, it is possible that they are the cause of your ear health problems as well. The standard treatments that you normally use should work around the ear area as well, but you should always seek the advice of an ENT doctor before applying treatment to the area.
If these conditions affect other areas of your body, it is possible that they are the cause of your ear health problems as well. The standard treatments that you normally use should work around the ear area as well, but you should always seek the advice of an ENT doctor before applying treatment to the area.
Allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, more commonly known as hay fever, can cause itching in the ear and also affect your throat health. It is caused by an allergic reaction to things like pollen, dust mites or animal fur. Symptoms include itchy ears and throat as well as watery eyes, a runny nose, headaches and sneezing. It is particularly bad in the summer so if you notice that you have itchy ears and an itchy throat when the weather is warm, that may be a sign that you have hay fever. If you take some over the counter medication, this should alleviate the problem but if you do not notice a change then you should see an ENT doctor.
Food allergies
Food allergies are another common cause of throat health issue and they can also cause itchy ears in some cases. A mild food allergy will cause itchiness in the throat, mouth or ears but more serious allergies can be life-threatening. Allergies can also develop over time so if you notice a reaction after eating certain foods, it is important that you seek medical advice and have yourself tested.
A mild food allergy will cause itchiness in the throat, mouth or ears but more serious allergies can be life-threatening. Allergies can also develop over time so if you notice a reaction after eating certain foods, it is important that you seek medical advice and have yourself tested.
Medication allergies
If you are on a new medication and you notice that you have itchy ears or an itchy throat, there is a possibility that you are having an allergic reaction to the drugs. If this is the case, speak with your doctor and see whether there are any alternatives to the medication that you could take instead.
Bacterial and viral infections
Bacterial and viral infections have a big impact on your throat health. In the early stages of an infection, you will notice an itching sensation in your throat, which will develop into a more severe sore throat. In some cases, you may have a common cold or the flu, which will pass in their own time. But itchy and sore throats can also be caused by more serious bacterial and viral infections such as strep throat and tonsillitis. In this case, it is best to see an ENT doctor for treatment.
In this case, it is best to see an ENT doctor for treatment.
If you notice itchiness in your ears and throat, it may be a symptom of a more serious problem that requires treatment, so you should see an ENT doctor. You can get in touch with Mountain Ear, Nose & Throat Associates today using the following numbers at Sylva: 828-586-7474 Franklin: 828-524-5599, Murphy: 828-835-1014 and New Asheville: 828-458-8100
3 Causes and Remedies for Itchy Ears – Cleveland Clinic
When it comes to itchy ears, you may be your own worst enemy. So put down that cotton swab (or whatever you were about to stick in there) and think about that for a minute.
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Now let’s talk about what you should — and shouldn’t — do for your ears.
Itchy ears are quite common and aren’t usually a sign of a serious condition. But sometimes the things you do, or forget to do, can cause them to itch — or make the problem worse.
But sometimes the things you do, or forget to do, can cause them to itch — or make the problem worse.
Ear surgeon Erika Woodson, MD, says itchy ears are a universal experience. “It’s part of the human condition, but it’s not generally something to be concerned about,” she says.
She traces the most likely causes to these three problems:
1. Getting your ears ‘too clean’
Dr. Woodson says nearly half the patients she treats have ear conditions they caused themselves. The biggest culprit? Excessive or intrusive cleaning.
“The purpose of earwax is to waterproof and protect your ears,” she explains. “It has both antifungal and antibacterial properties to help prevent infection.”
Over-cleaning can remove that protection. While it may provide temporary relief, it leaves you open to bigger problems than that tickle in your ear.
Sticking objects in your ear canal to clean it (or to scratch an itch) often just makes matters worse. You’ll likely just push the wax farther in. And that can lead to earwax buildup.
And that can lead to earwax buildup.
Itchiness is often a symptom of wax buildup, but you’ll likely notice other signs — pain or an odor coming from the ear, for instance.
“Most of us don’t need to clean our ears at all,” says Dr. Woodson. Earwax generally comes out of the ear canal on its own. And you can wash it away from your outer ear when you bathe.
What to do: You can typically treat earwax buildup at home. Use ear drops to break up the wax, but don’t try to clean out the ear canal with anything else, Dr. Woodson advises. See your doctor if drops aren’t effective.
2. Underlying skin conditions
Dermatologic conditions like eczema and psoriasis can surface on various areas of the skin — and make you itch.
But the rashes or plaques can also develop in places the eye can’t see.
“Your ear canal is lined with skin, so eczema and psoriasis may also show up there,” Dr. Woodson explains.
What to do: If your ears itch and you have a condition like eczema or psoriasis, see your dermatologist, or an ear, nose and throat specialist. “Get your ears checked out — your itch may be caused by a treatable dermatologic condition,” says Dr. Woodson.
“Get your ears checked out — your itch may be caused by a treatable dermatologic condition,” says Dr. Woodson.
3. Ear infections
Itchiness is one early symptom of an ear infection. But you’ll typically see other symptoms as well.
“If you feel pain in the ear or there’s discharge from the ear, it’s time to call your doctor,” Dr. Woodson says.
These are signs of an infection, which can harm your ears or damage your hearing.
Dr. Woodson notes that those who use hearing aids are sometimes more prone to fungal ear infections.
What to do: Don’t hesitate to call your doctor about an ear infection. And if you wear a hearing aid, clean it regularly to avoid itchiness and infection, following the manufacturer’s directions.
The bottom line
Mild ear itchiness is usually temporary and goes away on its own. If your itch lasts more than a few days, or if you have other symptoms, see the doctor. And remember, cleaning your ears the right way will help you avoid problems.
Why Do My Ears Itch? 7 Causes of Itchy Ears & How to Treat Them
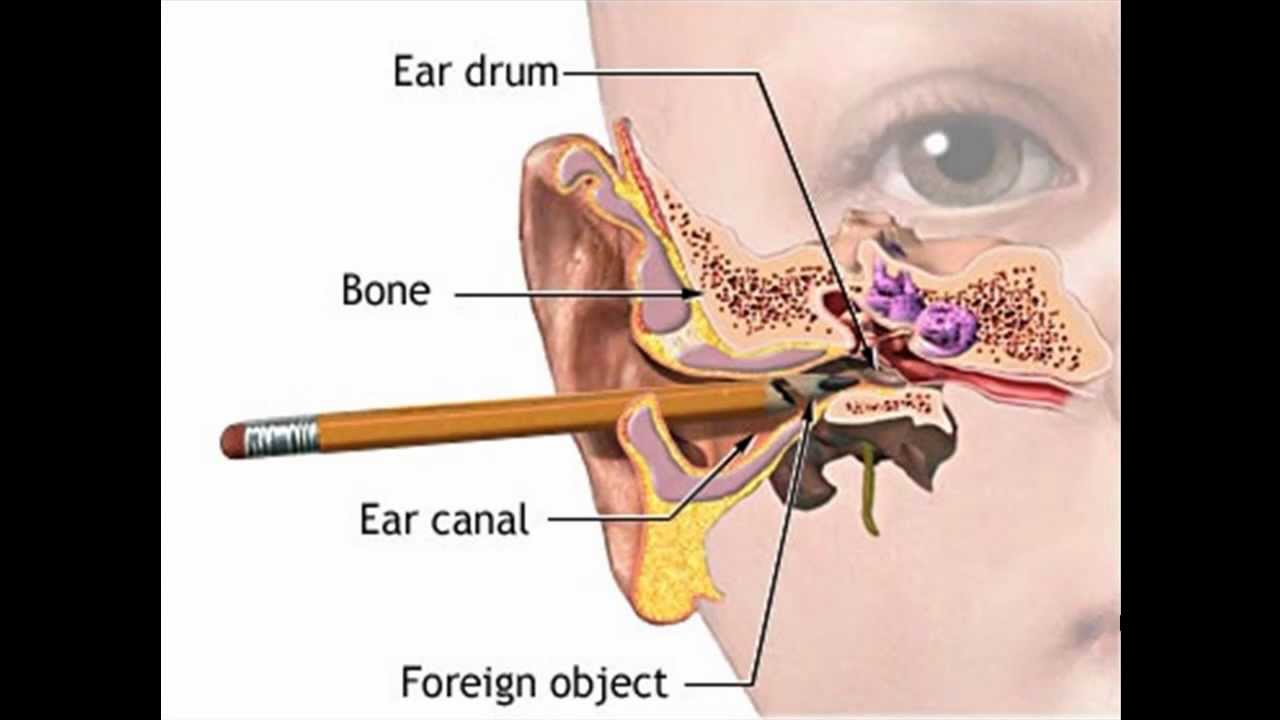
Can’t stop scratching your ears? An itchy ear canal (the tube that connects your outer ear to your eardrum) happens to people of all ages. How you can get relief will depend on what’s making you scratch.
No matter the cause of your itch, it’s never a good idea to stick any objects in your ears. You could damage your inner ear, including the tiny bones that help you hear.
Some reasons for itchy ears include:
Earwax buildup. Wax is your body’s way of cleaning dead skin cells and dirt out of your ears, but too much of it can make them itch.
Don’t be tempted to try to remove the buildup with a cotton swab. That pushes the wax deeper inside, where it can get stuck. Instead, try over-the-counter ear drops that break up the wax. If that doesn’t help, see your doctor. They can use a special tool to safely remove built-up wax.
But don’t overdo it. Ears can also get itchy if they don’t have enough wax inside them.
Infections. Itchy ears can sometimes be a sign of an ear infection. Bacteria and viruses cause them, usually when you have a cold, the flu, or allergies. One kind, swimmer’s ear, can happen when water stays in your ear after you swim. Too much moisture wears away your ear canal’s natural layer of defense against germs.
To stop the itch, you’ll need to treat the infection. Some may go away on their own, but your doctor could prescribe ear drops. You may need to take them a few times a day for a week. Other infections may need a course of antibiotics. Learn more about ear infection symptoms.
Skin allergies. The skin inside your ears can itch because of an allergic reaction. A beauty product like hair spray or shampoo could be the culprit. So can products that have nickel, like earrings. Plastic, rubber, or metal you put inside your ears, like earbuds or a hearing aid, can also cause a rash called contact dermatitis.
To get relief, you’ll need to figure out what you’re allergic to and stop using it. Until then, your doctor may prescribe a steroid cream to stop your urge to scratch. Learn more about skin allergies and contact dermatitis.
Until then, your doctor may prescribe a steroid cream to stop your urge to scratch. Learn more about skin allergies and contact dermatitis.
Eczema or psoriasis. If you have these skin conditions, you may be prone to itchy ear canals. You can usually treat these problems with ear drops. In severe cases, you may also need to take steroid pills. Learn more about psoriasis in your ears.
Cleaning your ears. Putting cotton swabs into your ears can inflame your ear canal and leave you itching. Bobby pins, paper clips, matchsticks, and your fingers can also scratch the skin inside your ears, making it easy for bacteria to enter and cause an infection. Learn more about how to clean your ears.
Food allergies. If you have hay fever or a pollen allergy, your ears may itch when you eat certain fruits, vegetables, or tree nuts. Known as oral allergy syndrome, you may notice this most during allergy season.
The prickly feeling in your ears should stop as soon as you swallow the food or take it out of your mouth. In most cases, you don’t need treatment. Still, speak to your doctor. She may test you to see how severe your allergy is. People with extreme food allergies may need to carry an epinephrine auto-injector. Learn more about food allergies and your skin.
In most cases, you don’t need treatment. Still, speak to your doctor. She may test you to see how severe your allergy is. People with extreme food allergies may need to carry an epinephrine auto-injector. Learn more about food allergies and your skin.
Itchy ears – Why do my ears itch, what causes it and what can I do?
Contributed by Debbie Clason, staff writer, Healthy Hearing
Last updated 2021-03-08T00:00:00-06:00
Are your ears itchy? Fighting off the urge to scratch deep inside your ear canal? Forget the folktale you learned as a child. It has nothing to do with whether or not someone is talking about you and everything to do with how the delicate skin in your inner ear is reacting to your environment.
What can cause itchy ears?
Your ears may itch on the external part of your ear (known as the pinna), or your ears may itch deep inside your ear canal, which is still considered the outer ear. Both are aggravating and annoying problems. Your itchy ears are most likely caused by a mild case of dermatitis, but it’s best to have a doctor take a look. Here are the top reasons your ears might itch, and what do about it:
Both are aggravating and annoying problems. Your itchy ears are most likely caused by a mild case of dermatitis, but it’s best to have a doctor take a look. Here are the top reasons your ears might itch, and what do about it:
Seborrheic dermatitis of the ear
The most common reason for itchy ears is a condition called seborrheic dermatitis, a type of rash that affects the sebaceous glands, which produce oil. It can occur on the scalp and eyebrows, and in the ears. A mild case of seborrheic dermatitis causes the skin to flake, known as dandruff. When dermatitis is severe, the skin also may be red and intensely itchy.
Your risk of seborrheic dermatitis increases with age, according to Dr. Steve Daveluy, associate professor and program director at Wayne State University School of Dermatology.
Other common reasons your ears may itch
- Irritation from hearing aids or earbuds (more on that below)
- Earwax blockage
- Contact dermatitis caused by irritants such as hydrogen peroxide, rubbing alcohol, water, ear drops (both prescribed and over-the-counter), or excessive ear cleaning
- Food and seasonal allergies
- Eczema, the name for a group of conditions that cause patches of the skin to become red, itchy and inflamed
- Psoriasis, a chronic, genetic, disease of the immune system characterized by a red, itchy rash on the skin
Hearing aids can aggravate the problem
If your ears are itchy, be careful!
Scratching can make the problem worse.
Hearing aids sometimes create itching because the domes or earmolds cause irritation by rubbing against the skin. They also block the ear canal, which can cause moisture buildup. Rarely, some people become allergic to a component of the hearing aid.
If your hearing devices cause your ears to itch, talk to your hearing health professional. They’ll examine the fit to make sure your devices are seated correctly. If the skin in your ears is dry, they may recommend using a product such as MiraCell ProEar, which makes hearing devices easier to insert and more comfortable to wear. Also be sure to clean your hearing aids regularly. Ask your hearing care provider for guidance if you’re not sure about how to clean hearing aids.
Earbuds also can lead to ear irritation, itchiness and infection
If you frequently wear earbuds (a type of headphone that sits just inside the ear canal), keep in mind that overuse can lead to ear irritation, including swelling and itchiness.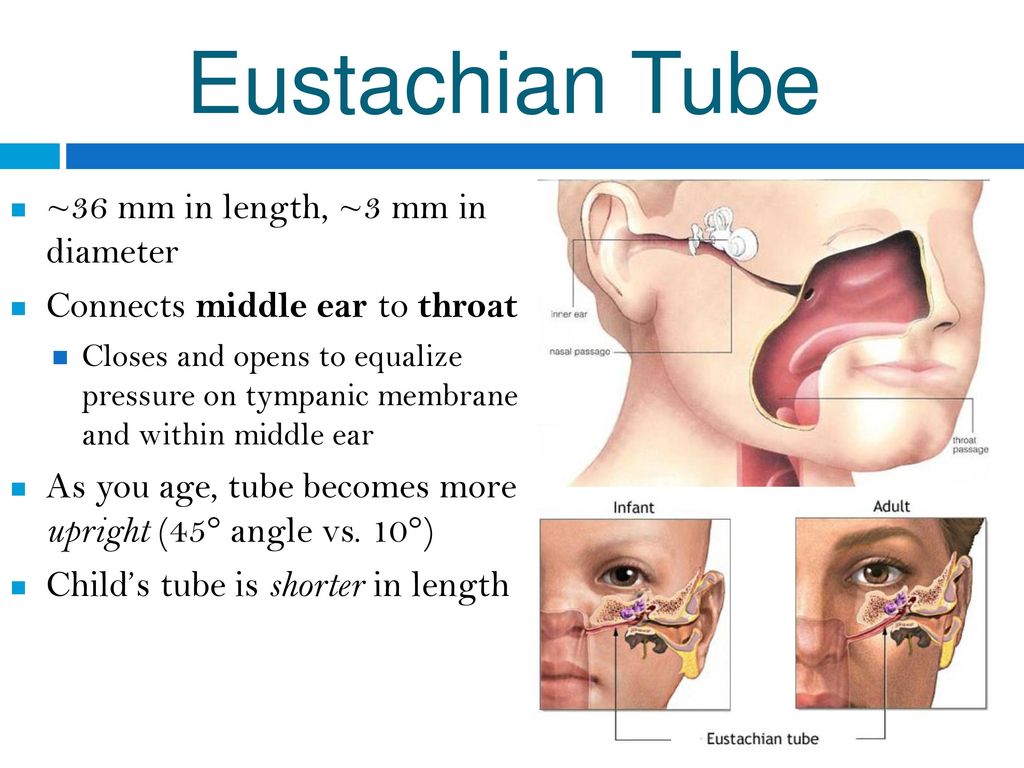 In severe cases, unclean earbuds can trigger an outer ear infection (otitis externa), more commonly known as swimmer’s ear.
In severe cases, unclean earbuds can trigger an outer ear infection (otitis externa), more commonly known as swimmer’s ear.
How to treat itchy ears
First, don’t put anything in your ears. While it’s tempting to insert something into your ear canal to scratch the itch, that’s exactly what you shouldn’t do. Not only do you risk damaging the eardrum and scratching the delicate skin of the inner ear, you also increase your urge to itch.
“Try not to scratch at all,” Dr. Daveluy said. “For any skin, scratching makes the nerves that feel itch grow. So the more you scratch, the more you’ll itch.”
The more you scratch, the more you’ll itch.
Instead, try treating the underlying problem. If you have dandruff, try switching to a dandruff shampoo. If your itching flares up along with seasonal allergies, try taking an antihistamine. To alleviate dryness associated with over-cleaning the ears or earwax blockage, apply a few drops of baby oil or olive oil before you go to bed at night.
Can you prevent itchy ears?
Yes, and prevention is important. To reduce your risk of developing itchy ears, resist the urge to insert items such as cotton swabs, bobby pins, twisted cloths or ear candles into the ear canal. These items can remove protective earwax or push earwax deeper into the ear canal. They can also break the skin or puncture the eardrum, which increases your risk for infection.
Why are ears so sensitive?
The environment in your inner ear is unique and faces some “special challenges,”
“Because of the warmth and moisture, the ear canal is at a higher risk of infection by bacteria,” Dr. Daveluy said. “To protect against this, the skin of the ear canal has specialized oil glands (called ceruminous glands) that secrete earwax. Much like the nose, the ear canal also grows small hairs to help prevent debris from entering the ear.”
Another unique attribute of inner ear skin is that it doesn’t contain eccrine sweat glands, the kind the rest of our body uses to secrete sweat when we’re warm or stressed. This, along with the waxy nature of cerumen, helps prevent moisture buildup in the canal.
This, along with the waxy nature of cerumen, helps prevent moisture buildup in the canal.
When to seek medical treatment
If you don’t know the cause of your itching, have tried a home remedy that didn’t help, have any breakdown of the skin or are experiencing pain and swelling, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately as infections in the ear can be dangerous.
Your family doctor can discuss your symptoms, examine your skin and determine the proper diagnosis to formulate an effective treatment plan. If you have a complicated case, you may be referred to a dermatologist or an ear, nose and throat physician.
Don’t let itchy ears prevent you from wearing your hearing aids
Itchy ears can be annoying, but they shouldn’t prevent you from wearing your hearing aids as prescribed. So often this condition is easily resolved, leaving you free to be part of every conversation—no matter what people happen to be saying.
If your hearing aids are causing problems or if you aren’t hearing your best, schedule an appointment with a hearing care professional. For a complete list of hearing centers in your community, visit our online directory of consumer-reviewed clinics.
For a complete list of hearing centers in your community, visit our online directory of consumer-reviewed clinics.
Itchy Ears | Find Out Why Your Ears Are Constantly Itching
Have you ever had an itch in your ear and gone to someone older in your family to find out why? If the answer is yes, you may have heard that itching ears mean that someone is talking about you.
With all due respect to those spreaders of old wives’ tales, there is probably a more credible medical reason why our ears itch on occasion. The hard part is figuring out which of the many possible conditions or habits is causing this reaction.
Identifying the culprit can lead to appropriate treatment for itchy ears. Here are some potential causes:
- Psoriasis – Pain or itching on the skin on or around your ear might be an indication of psoriasis, a relatively common skin condition. If this is the case, you might notice a buildup of rough, dry, red patches or scales in the external area of your ear that can itch or hurt.
 There are a variety of treatment options including topical medications or steroids.
There are a variety of treatment options including topical medications or steroids. - Skin allergies – The skin inside your ears can itch because of an allergic reaction to something that is applied in or near your ear. A new hair product may be the culprit and earrings that contain nickel have also been known to cause an allergic reaction. Be mindful whenever introducing anything new to your skin and stop using it if you believe it is the cause.
- Food allergies – Similar to reactions from skin contact, some might have an allergic reaction to something they ate, causing their ears to itch. Certain fruits, vegetables, or tree nuts are the most common sources of food allergies. A doctor can test for the source of a food allergy, determine the severity and prescribe the appropriate medication.
- Hay fever – This condition, also known as allergic rhinitis, occurs when individuals have allergic reactions to particles commonly found in the atmosphere.
 These particles range from animal fur to dust mites and pollen. Experiencing itchy ears along with watery eyes and a runny nose is not uncommon among hay fever sufferers.
These particles range from animal fur to dust mites and pollen. Experiencing itchy ears along with watery eyes and a runny nose is not uncommon among hay fever sufferers. - Infections – Itchy ears can sometimes be a sign of an ear infection. Bacteria and viruses cause them, usually when you have a cold or the flu. One kind of infection, swimmer’s ear, can happen when water stays in your ear after you swim. To stop the itch, you’ll need to treat the infection, possibly with ear drops or antibiotics.
- Improper cleaning – Placing cotton swabs into your ears can inflame your ear canal and leave you itching. Pins, paper clips, matchsticks, and your fingers can also scratch the skin inside your ears, making it easy for bacteria to enter and cause an infection. Excessive ear wax build-up can also cause your ears to itch. Your doctor can remove excessive wax using special instruments.
Regardless of the reason you are experiencing itchy ears, it is important to be mindful of any changes in your diet or environment and share that information with your doctor so he or she can prescribe the correct course of treatment. Our Department of Internal Medicine offers allergy and immunology services to help in diagnosing allergies.
Our Department of Internal Medicine offers allergy and immunology services to help in diagnosing allergies.
To make an appointment at Flushing Hospital’s Ambulatory Care Center, please call 718-670-5486. We’ll help you to get to the bottom of your problem with itchy ears so that you can feel your best—and hear your best—from one day to the next.
All content of this newsletter is intended for general information purposes only and is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Please consult a medical professional before adopting any of the suggestions on this page. You must never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment based upon any content of this newsletter. PROMPTLY CONSULT YOUR PHYSICIAN OR CALL 911 IF YOU BELIEVE YOU HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY.
This entry was posted in General Health and tagged #psoriasis, Ear Infection, flushing hospital, food allergy, itchy ear, skin allergy, swimmer’s ear by Michael Hinck.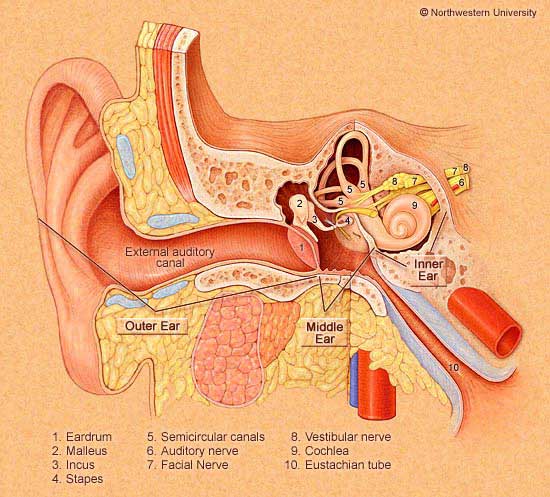 Bookmark the permalink.
Bookmark the permalink.
Ear, Nose & Throat Specialists
Have you ever had an itchy throat or itchy ears, and there doesn’t seem to be a reason for it? It doesn’t necessarily hurt, but it’s not the most comfortable feeling either. Some of you might be able to recognize it as the beginning of allergies making their presence known. It might even be a cold starting to settle in. Unfortunately, in some cases, it might mean something a little more serious. Here are a few reasons why your ears and throat are uncommonly itchy.
- Ear Infection: Ear infections happen when there’s either a buildup of ear wax or water in the ear. Usually, it doesn’t have the ability to drain because of allergies or other reasons. It can also be caused by bacteria and viruses that can accompany the common cold, allergies, or other ailments. It can be a recurring issue, especially if your allergies are severe. If you get chronic ear infections, your ENT specialist will be able to figure out the underlying issue.

- Dry Ears: While excessive ear wax is bad, not having enough can also be an issue. Naturally, your ears create ear wax and oils to help keep them healthy and clean. Not producing enough will cause your ears to become very itchy and the skin can start flaking around the outside of the ear. Usually, paying closer attention to your ears as you wash up should help, but if it persists your ENT can advise a treatment.
- Food Allergies: Food allergies can be a little tricky. Commonly mild food allergies affect the throat, but they can also cause itchy ears and the mouth as well. Allergies might develop over time. For example, you could have loved peaches growing up, but because your body changes as you get older, you might now develop an allergy to them. More serious allergies can be life-threatening and need immediate attention.
- Medication Allergies: Similar to food allergies, you might have or develop an allergic reaction to certain medications.
 They can cause an itchy, throat, ears, and mouth, hives, a rash, to more serious reactions. If this happens, you have to contact your doctor to get an alternative to the medication.
They can cause an itchy, throat, ears, and mouth, hives, a rash, to more serious reactions. If this happens, you have to contact your doctor to get an alternative to the medication. - Bacterial & Viral Infections: Several bacterial and viral infections start out as causing an itch in your throat which could develop into a sore throat. It’s similar to your ears as well. It could develop into something more serious like an ear infection, strep throat, or tonsillitis depending on where the issue is. You’ll need to contact your doctor for the appropriate treatment.
Feeling the discomfort of itchy ears or throat? Give us a call today to help provide the best remedy for you!
The Causes of Itchy Ears and Throat
The Causes of Itchy Ears and Throat
Are you facing itchy ears and throat? If so, you’re not alone. This is a common issue that many people experience at some point in their lives. In most cases, itchy ears and throat aren’t a big deal. Other times, however, they may be a sign of a more serious problem and warrant the attention of an ENT doctor. Here’s a closer look at some of the reasons you may be suffering from itchy ears and throat.
Other times, however, they may be a sign of a more serious problem and warrant the attention of an ENT doctor. Here’s a closer look at some of the reasons you may be suffering from itchy ears and throat.
Ear Infections
You may have an ear infection if you’re facing itching in your ear. At its core, an ear infection is the result of bacteria and viruses in anyone who has the common cold. It may also arise if your ear is obstructed with too much wax or water has been trapped in your ear. An ENT can help pinpoint the cause of an ear infection and recommend a viable treatment. In the event your ear infection persists, you may have a serious complication that you can trust an ENT to diagnose.
Dry Ears
Your ears stay healthy and clean due to the wax and oil found inside of them. But if you clean out your ear too frequently and remove the wax and oil, you can put yourself at risk for dry, itchy ears. If your ears are too dry, you’ll probably find dry, flaky skin outside of your ear and an uncomfortable urge to itch.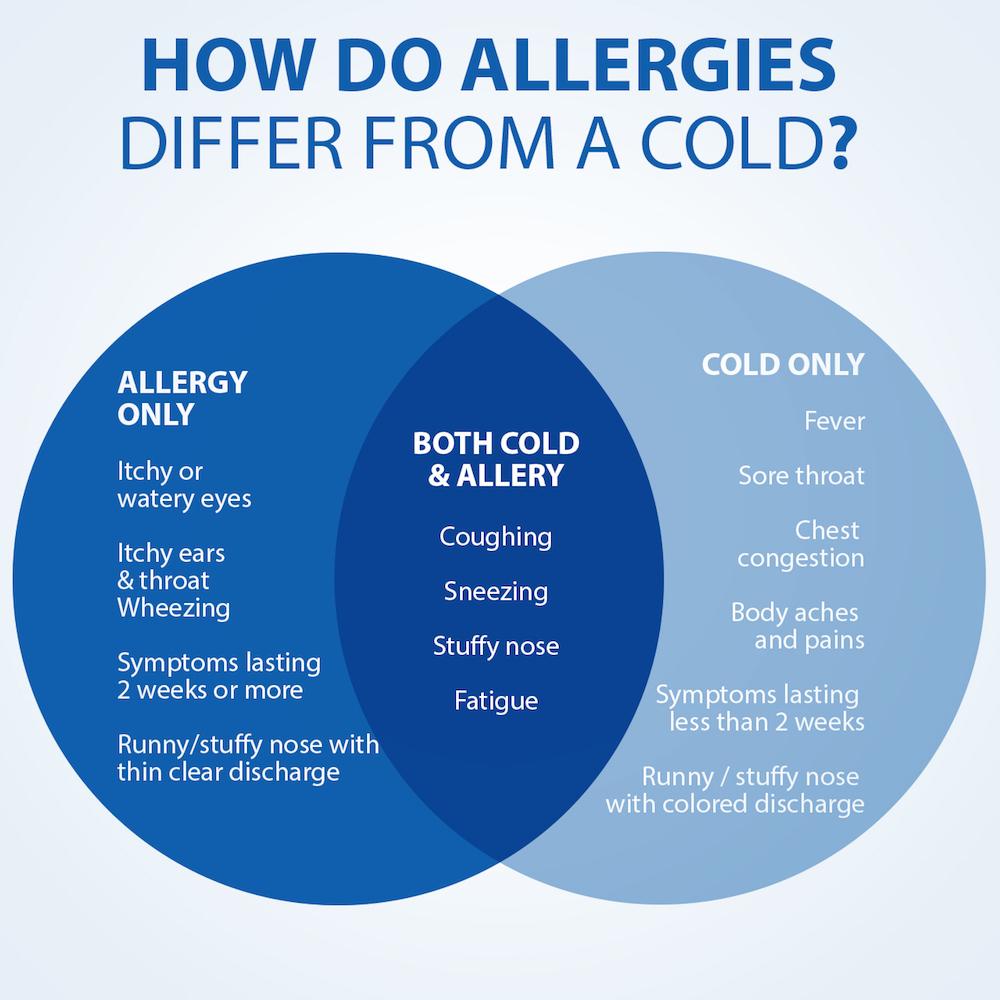 Cleaning your ears less often should resolve this problem. If it doesn’t, however, visit an ENT doctor.
Cleaning your ears less often should resolve this problem. If it doesn’t, however, visit an ENT doctor.
Skin Conditions
You may be surprised to learn that there are a number of skin conditions that can lead to itchy ears. These include eczema, dermatitis, and psoriasis. They may be the reason behind your ear health issues, especially if they impact other areas of your body as well. Before you treat them, make sure you check with an ENT doctor.
Allergic Rhinitis
Also known as hay fever, allergic rhinitis can lead to ear itching and throat discomfort. It’s usually caused by animal fur, pollen, and dust mites and may also result in headaches, watery eyes, and sneezing. Since allergic rhinitis tends to be at its worst when it’s warm outside, you may notice it more often in the summer. Fortunately, it can be treated with an over-the-counter medication. If your condition continues despite taking an over-the-counter drug, visit an ENT.
Viral and Bacterial Infections
Viral and bacterial infections and throat health go hand-in-hand. If you’re in the early stages of an infection, you may experience itching in your throat which may eventually turn into a more severe sore throat. You may also face the common cold or flu which will disappear on its own. Due to the fact that viral and bacterial infections can lead to strep throat and tonsillitis, it’s wise to go to an ENT doctor for treatment.
If you’re in the early stages of an infection, you may experience itching in your throat which may eventually turn into a more severe sore throat. You may also face the common cold or flu which will disappear on its own. Due to the fact that viral and bacterial infections can lead to strep throat and tonsillitis, it’s wise to go to an ENT doctor for treatment.
If you have itchy ears or throat, visit an ENT doctor as soon as possible to determine whether it’s a sign of a more serious issue.
90,000 What causes itchy ears and throat
Itchy ears and the feeling that something is scratching your throat can be signs of several different conditions, including allergies and the common cold. These symptoms are usually not bothersome and you can treat them at home.
However, some of the symptoms that accompany itchy ears and throat indicate more serious conditions.
Should I worry if my ears and throat itch? Here are some possible causes of itchy ears, tips to relieve symptoms, and information on when to see your doctor.
Possible Cause-1: Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is the main symptom of a disease such as hay fever . It occurs when your immune system reacts to pollen and fungal spores in the environment that are actually harmless.
AR symptoms can also be caused by pet dandruff and dust mites.
During the reaction to an irritant, chemicals are produced, in particular histamine, which cause allergy symptoms.
Besides the fact that allergic rhinitis causes itching in the ears and throat, the following symptoms may occur:
How to treat allergic rhinitis
An allergist may give you a skin prick test or blood sample to determine which allergens are molecularly causing the symptoms.
You can prevent the onset of symptoms by avoiding their factors:
- Use special materials and acaricides to prevent mites from growing in upholstered furniture and bedding.
- Wash duvets and linens above + 60 ° C.

- Vacuum upholstered furniture, carpets and curtains.
- Stay indoors when there are high concentrations of pollen outside.
- Keep windows closed and do not turn off the air conditioner.
- Do not smoke and keep as far away from smokers as possible.
- Don’t let your pets in your bedroom.
- Maintain humidity in your home at or below 50% to prevent fungal growth.Clean up any moldy areas you find with antifungal agents.
To eliminate allergy symptoms, your doctor will prescribe the necessary medications and may recommend allergen-specific immunotherapy, which will gradually stop your body’s reaction.
Another name for this method is allergenic immunotherapy (AIT). After a course of treatment, the allergy usually recedes for many years, or even forever.
For AIT to be effective, it needs high quality drugs.In particular, such are the allergens of the Spanish company Inmunotek, available in Ukraine: the Oraltek spray and the Alxoid injectable drug.
Possible Cause-2: Food Allergy
An estimated 4 to 6% of children and up to 4% of adults have food allergies. Like seasonal allergies, food allergies occur when the immune system is exposed to allergens such as peanuts, eggs, or other foods.
Symptoms of food allergies range from mild to severe.These include:
Some allergies are severe enough to cause a life-threatening reaction called anaphylaxis.
Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
- shortness of breath,
- wheezing,
- swelling of the mouth,
- swallowing problems,
- dizziness,
- fainting,
- heaviness in the throat,
- heart palpitations.
If you think you are having an anaphylactic reaction, call your local emergency room or go to the emergency room yourself immediately.
Some fruits, vegetables and nuts contain proteins similar to pollen allergens. If you are sensitive to the latter, these foods can trigger a reaction called Oral Allergy Syndrome (OA).
Oral allergy syndrome can also cause itchy ears and throat.
SOA trigger products:
In addition to itchy ears, symptoms of OSA are itchy mouth, stabbing sore throat, swelling of the walls of the mouth, tongue and throat.
Some children outgrow allergies to foods such as eggs, soy and cow’s milk proteins.Other food allergies, such as peanuts and tree nuts, can persist throughout your life.
How to Treat Food Allergies
If you frequently react to certain foods, contact your allergist. Skin tests, especially molecular tests and prick-to-prick tests with certain foods can reveal which foods are causing your allergies.
After identifying the causal food, you will need to avoid it. Check the ingredient list for every product you buy.
If you are severely allergic to any food, carry an automatic epinephrine dispenser with you to prevent a severe reaction.
Possible Cause-3: Drug Allergy
Many drugs can cause side effects, but only about 5-10% of drug reactions are true allergies..jpg) Like other allergies, drug allergies happen when your immune system reacts to drugs in the same way as germs.
Like other allergies, drug allergies happen when your immune system reacts to drugs in the same way as germs.
Most allergic reactions develop within hours or days after taking medication.
Drug allergy symptoms:
- skin rash,
- urticaria,
- itching,
- shortness of breath,
- wheezing,
- edema.
Severe drug allergies can cause anaphylaxis with symptoms such as:
- urticaria,
- swelling of the face or throat,
- wheezing,
- dizziness,
- shock.
Contact your doctor if you have symptoms of a drug allergy. If you are allergic, you may need to stop using the drug.
Possible Cause-4: Cold
Colds are one of the most common.Most adults get two to three colds a year.
The common cold is caused by many different viruses. They are spread when an infected person coughs or sneezes and droplets of liquid containing the virus fly into the air.
The common cold is not a serious illness. But in pandemics, especially new viruses, the same coronavirus, when the body does not have natural defense against an aggressive agent, the consequences can be threatening, until death.
However, usually a cold unsettles for a few days with the following symptoms:
- runny nose,
- cough,
- sneeze,
- sore throat,
- weakness,
- headache.
Prolonged or more severe symptoms require medical attention.
How to treat colds
There are no specific medicines for the common cold. However, you can relieve painful symptoms by consuming plenty of warm liquids and vitamins.Most colds go away on their own within 7-10 days.
If symptoms persist for more than two weeks or get worse, you will need medical attention.
When to see a doctor
So, see your family doctor if your symptoms last more than 10 days or get worse over time. Call emergency medical help for more serious symptoms:
Call emergency medical help for more serious symptoms:
- shortness of breath,
- wheezing,
- urticaria,
- severe headache,
- sore throat,
- swelling of the face,
90,037 difficulty swallowing.
Your doctor may do a blood test or throat swab to see if you have a bacterial infection that needs antibiotic treatment.
If the doctor determines that your symptoms are of an allergic nature, he will refer you to an allergist.
90,000 We treat itching in the throat, we help with ENT diseases
Navigation on page :
Itching in the throat is a feeling of unpleasant tickling and burning sensation that usually appears with various ENT pathologies.This symptom can be constant or recurrent – for example, itching in the throat at night, before coughing, when allergens get on the mucous membranes, etc. Let’s find out what it is connected with and why you cannot ignore it!
Types of disease
Itching in the throat is classified for the reasons that it is caused by:
- Prritoceptive – associated with inflammatory processes, foreign bodies and mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the throat.

- Allergic itching in the throat – occurs when a mediator of allergic reactions (histamine) acts on the mucous membrane.
- Neuropathic – associated with lesions of the central system, for example, vascular pathologies, hemorrhages, brain tumors.
- Psychogenic – is a reaction to stress, overwork, anxiety and other psycho-emotional disorders.
Causes of itchy throat
Why does the throat itch? This symptom can be associated with pathologies of the throat and larynx, as well as other causes.
ENT pathology
- Inflammatory diseases – pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis and other pathologies are a common cause of itching.
- Neoplasms of the larynx and pharynx are a dangerous disease that can be of a malignant nature. As the tissue develops and spreads, the symptoms intensify – the throat itches from the inside, it becomes difficult to swallow and breathe.
- Injuries, foreign bodies, insect bites – May cause itching, swelling and perspiration.

- Vocal fatigue – for singers, presenters, teachers, etc.
Other reasons
When a person is worried about itching in the throat, the reasons may be as follows: causes a protective reaction of the cells of the body.
When to see a doctor
Even the slightest sore throat and itching are reasons for an examination by an ENT doctor. It is especially important to seek help if symptoms worsen – the throat is scratched, it hurts, breathing and swallowing are difficult. All these are signs of diseases that need treatment. If you pay attention to the problem in time, you can cure the pathology, avoiding serious complications.
It is especially important to seek help if symptoms worsen – the throat is scratched, it hurts, breathing and swallowing are difficult. All these are signs of diseases that need treatment. If you pay attention to the problem in time, you can cure the pathology, avoiding serious complications.
How to get rid of itchy throat
If a person has an itchy throat, treatment depends on the cause. Allergies are treated with antihistamines and specific immunotherapy. For inflammatory diseases, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, as well as medical procedures. It is recommended that tumors be removed surgically.
How to get rid of itchy throat – our doctors know. They will carry out comprehensive diagnostics, help to understand the causes of the problem and solve it.Make an appointment if your throat itches!
What can cause an itchy throat
Itchy throat? This symptom can be a sign of a tumor, including cancer. It is very important to detect and eliminate the disease in the early stages, while it is amenable to conservative treatment. In advanced cases, it is necessary to remove the entire organ, and the patient loses his voice.
In advanced cases, it is necessary to remove the entire organ, and the patient loses his voice.
Prophylaxis
To prevent the throat from itching, it is recommended to protect it from too hot and cold, treat ENT diseases in time, and be regularly monitored by an otolaryngologist.Also, doctors advise to give up smoking and alcohol.
Appointment for a consultation
Itching in the ear and throat at the same time – Question to ENT will be on the topic of the main question. You can also ask a new question, and after a while our doctors will answer it. It’s free. You can also search for the information you need in similar questions on this page or through the site search page.We will be very grateful if you recommend us to your friends on social networks.
Medportal 03online.com carries out medical consultations in the mode of correspondence with doctors on the website. Here you get answers from real practitioners in their field. At the moment, on the site you can get advice in 71 areas: a COVID-19 specialist, an allergist, an anesthesiologist-resuscitator, a venereologist, a gastroenterologist, a hematologist, a geneticist, a hepatologist, a geriatrician, a gynecologist, a gynecologist-endocrinologist, a homeopathologist, a pediatrician, a pediatrician , pediatric dermatologist, pediatric infectious disease specialist, pediatric cardiologist, pediatric ENT, pediatric neurologist, pediatric nephrologist, pediatric ophthalmologist, child psychologist, pediatric pulmonologist, pediatric rheumatologist, pediatric urologist, pediatric surgeon, pediatric endocrinologist, defectologist, nutritionist, nutritionist clinical psychologist, cosmetologist, speech therapist, ENT specialist, mammologist, medical lawyer, narcologist, neuropathologist, neurosurgeon, neonatologist, nephrologist, nutritionist, oncologist, urologist oncologist, orthopedist-traumatologist, psychologist, parasitologist, proctiatrist, pediatrician , rheumatologist, radiologist, reproductologist, sexologist-andrologist, dentist, trichologist, urologist, pharmacist, physiotherapist, phytotherapist, phlebologist, phthisiatrician, surgeon, endocrinologist.
We answer 97.48% of questions .
Stay with us and be healthy!
“Itching in the ears: causes, treatment” – Yandex.Q
Contents:
The appearance of an unpleasant, itchy sensation in the ears is a fairly common problem that everyone can face. The presence of natural itching is allowed, which occurs due to the accumulation of sulfur. In this case, increased discomfort occurs after taking a bath, due to the fact that water enters the ear, thereby softening the sulfur masses.
To get rid of these sensations, it is enough to observe hygiene – often clean and wash the ear canal. But there are situations in which the unpleasant itching persists for a longer time. It is then that a visit to the otorhinolaryngologist is necessary.
In this course of circumstances, itching is a symptom of a medical condition that can have a very negative effect on the health of the hearing aid. In addition to this symptom, others may appear, for example, purulent discharge, congestion, peeling of the ear canals, fever, and even hearing loss.
Severe itching in the ears is an indicator of systemic diseases that form in the body. With a rare manifestation and no discomfort, this symptom can be easily ignored. However, do not forget that psoriasis, otitis media, eczema and dermatitis most often begin to manifest themselves with just such a symptom.
In addition to diseases, itching in the ears can occur due to mechanical damage to the ear canal by any foreign object, for example, a cotton swab. This is due to the ingress of sulfur into the resulting microtrauma.
Causes of itchy ears
The main causes of itching in the ears are:
abundant accumulation of sulfur mass;
- irritation caused by unclear origin;
- Intense hairline in the ear opening;
- increased dryness;
- hypothermia of the whole organism;
- allergic reaction;
- otitis media caused by microorganisms;
- diabetes mellitus;
- the appearance of a boil in the ear canal;
- metabolic failure;
- ear mite.

90,037 old age;
90,037 injuries;
90,037 diseases of the outer ear skin;
Activation of pathogenic microorganisms, which show their activity due to severe hypothermia, can also occur.
Otitis
Inflammatory process in the ear, which is characterized by an acute or chronic course – otitis media. The main symptoms of the disease are redness of the auricle, pain and burning sensation, severe itching. The penetration of pathogenic microflora occurs from the nasopharynx region directly into the tympanic cavity. Passing through the Eustachian tube, they quickly penetrate the inner ear.In addition, it is possible from the external environment.
- Mild inflammation of the ear canal and concha – otitis externa. With this type, pain of a different nature appears (dull, pressing, sharp), which intensifies when trying to touch the ears. There is also a weakening of hearing and the appearance of persistent subfebrile condition.
- With inflammation of the middle ear, the auditory tube is damaged, and there is also an accumulation of exudate in the tympanic cavity.
 The patient suffers from ear congestion, hearing loss, fever, intoxication, and severe pain.As soon as purulent discharge appears, there is a decrease in pain and an improvement in well-being.
The patient suffers from ear congestion, hearing loss, fever, intoxication, and severe pain.As soon as purulent discharge appears, there is a decrease in pain and an improvement in well-being. - Labyrinthitis is characterized by impaired hearing and balance. Vestibular disorders occur in the body, as a result of which dizziness and loss of coordination begin. After this, hearing impairment occurs, the formation of noise and severe itching. The painful sensations increase when the head is turned to the side.
Otomycosis
The development of the inflammatory process due to damage to the ear by the fungus occurs against the background of the development of chronic otitis media.Due to the influence of unfavorable factors, there is an increase in fungi of the genus Candida, which are normal inhabitants of the skin. In this case, severe itching appears, white flakes of skin, a whitish crust in the outer ear. With a severe form of the disease, fungi can penetrate deeper, affecting not only the labyrinth, but also the bones of the skull.
Allergy
An allergic reaction can develop to a large number of products of the food, industrial and cosmetic industries.In most cases, allergies are accompanied by itchy ears. In this case, the treatment is agreed between two specialists – an otolaryngologist and an allergist.
Skin diseases
Since the appearance of itching in the ears is considered one of the first symptoms of the development of skin diseases, with the development of this symptom, the development of ear dermatitis can be suspected. This disease is characterized by itching of varying intensity, redness, and the formation of nodules.
In eczematous dermatitis, in addition to itching, severe peeling appears, as well as hyperemia of the skin, on which small bubbles are located.
If the outer ear is damaged by pathogenic fungi, then seborrheic dermatitis develops. In addition to the characteristic plaques, oily yellow spots appear on the skin.
Mechanical damage
Damage to the ear canal can occur due to improper cleaning of the ears, as a result of which microtrauma appears.It is in these small lesions that an infection can penetrate, which will begin to spread to neighboring organs.
In rare cases, an insect can enter the ear and cause itching and discomfort.
Symptoms that may accompany itchy ears
With the addition of painful sensations, we can talk about the development of an inflammatory process in the ear cavity. In this case, a visit to a specialist is considered mandatory.
With the localization of sore throat and itching in the ears, we can talk about the development of angina, these symptoms disappear immediately after treatment.
If, in addition to the main symptom, discharge appears, then this is talking about the presence of a fungal infection.
The development of desquamation is the main symptom of dermatitis, vitamin deficiency and allergies.
Formation of a boil – purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, indicates the development of staphylococcus.
Itchy ears: treatment
You can start therapy only after a diagnosis has been made.In the future, complex treatment may be required:
- Use of medicines: antibiotics in the form of drops are prescribed for the development of otitis media. If intoxication occurs in the body, then a direct intake of antibiotics by mouth is prescribed. Drops that have anti-inflammatory effects are also widely used. If atomicosis develops, then an antimycotic drug is prescribed. The development of an allergic reaction is an indication for the use of antihistamines.
- Physiotherapy. In certain cases, heating of the ear canals is allowed, as well as flushing and disposal of sulfur masses.
- Traditional medicine is also widely used to combat itchy ears. But do not forget that first of all you need to get expert advice.
 They have proven themselves very well: tea tree oil, salicylic alcohol, calendula tincture, propolis alcohol tincture.
They have proven themselves very well: tea tree oil, salicylic alcohol, calendula tincture, propolis alcohol tincture.
In order to avoid the development of itching in the ears, it is necessary to observe careful personal hygiene, avoid hypothermia and increase the general immunity of the body.
Material provided
bezboleznej.ru
Allergic diseases of the ear, throat, nose
Allergic diseases are inherent in many people today. The mucous membrane of the nose, its paranasal sinuses, as well as the pharynx, larynx and trachea is the first barrier on the way of air to the lungs, and therefore it is it that first of all reacts to the allergens contained in it. The ears are directly connected to the nasopharynx through the auditory tube, and this explains the allergic nature of some ear diseases.The constant presence of a variety of microbial flora on the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, as well as in the lacunae of the tonsils, is also important./throatpainfinal-01-5c3ba1dd46e0fb0001061529.png) In addition, allergens that have entered the body in other ways, in particular through the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and the skin, can also cause allergic diseases of the ear, throat and nose.
In addition, allergens that have entered the body in other ways, in particular through the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and the skin, can also cause allergic diseases of the ear, throat and nose.
Allergic diseases are known to be based on the interaction of allergens and specific antibodies produced by the body in response to their introduction.This increases the permeability of the walls of the smallest blood vessels. As a result, edema occurs – the main symptom of allergic diseases.
The allergic disease “HAIR SEASON” (spring or seasonal catarrh) is a typical example of such a disease. It begins during the flowering period of field grasses, cereals, some types of shrubs and trees. People with increased sensitivity to plant pollen suffer from it. Hay rhinitis is characterized by abundant watery nasal discharge, sneezing, lacrimation, itching in the nose and eyes, conjunctivitis, headache, nasal congestion up to the complete absence of nasal breathing.
Asthmatic attacks of suffocation can join hay rhinitis. Body temperature often remains normal, but can rise to 39 degrees.
Body temperature often remains normal, but can rise to 39 degrees.
An allergic disease usually begins in spring, summer or early autumn and almost on the same days of the same month, depending on the flowering period in a given climatic zone of plants, to the pollen of which the patient is hypersensitive. Starting suddenly, hay coryza is just as sudden and stops when the plants have faded.
Attacks of an allergic rhinitis, if it is caused by contact with one or another allergen at home or at work, are repeated throughout the year. Their duration can be different: from several hours to several days and even weeks, in some they are repeated daily and even several times a day, in others – every other day, once a week or less often.
Allergic disease “ALLERGIC PHARYNGOPATHY” (disease of the pharynx) can be independent or accompany other manifestations of allergic diseases of the skin, mucous membranes.It is characterized by swelling of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, in particular the palate and uvula. The patient feels a foreign body in the throat, a desire to push it out with coughing movements; the timbre of the voice changes.
The patient feels a foreign body in the throat, a desire to push it out with coughing movements; the timbre of the voice changes.
Allergic disease “ALLERGIC LARYNGITIS” (a disease of the larynx) begins with a feeling of awkwardness when swallowing, difficulty breathing of varying severity up to suffocation, hoarseness. All these symptoms are the result of swelling of the laryngeal mucosa.
Allergic disease “ALLERGIC TRACHEITIS” is accompanied by excruciating whooping cough, itching, scratching in the throat, hoarseness of the voice.
Allergic disease “ALLERGIC OTITIS”. In this allergic ear disease, there is a large amount of liquid discharge from the external auditory canal and swelling of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity. Often, with otitis media, there can be an allergic rhinitis and weeping eczema of the external auditory canal.
No matter how an allergic disease manifests itself, it is always a reaction of the whole organism. Therefore, most patients complain of poor sleep, general weakness, irritability, decreased performance, sweating.
The main and most difficult thing in the treatment of an allergic disease is to find the allergen that caused it. If an allergen is identified and the patient stops contacting it, recovery is guaranteed. In those cases, when the detailed information collected does not allow identifying the “culprit” of the disease with sufficient accuracy, the doctor determines the sensitivity to allergens using skin tests.
Only an allergist can decide the question of what, how and where to treat an allergic disease.A wide network of allergy rooms is now being organized throughout the country at many polyclinics.
In the prevention of allergic diseases, an important role is played by medical examinations before employment in enterprises where contact with allergenic substances is possible. For people susceptible to certain substances, doctors may advise you to change jobs.
Experience shows that an allergic disease such as “drug allergy” is now quite widespread. And this is due to the fact that many take medications for a long time and uncontrollably, often without a doctor’s prescription. It happens that a patient has an allergic reaction to taking a medication recommended by a doctor. It is necessary to inform the doctor about this!
It happens that a patient has an allergic reaction to taking a medication recommended by a doctor. It is necessary to inform the doctor about this!
Some people use vasoconstrictors for an unreasonably long time for instillation into the nasal cavity with a cold. And this creates the prerequisites for an allergic reaction. They should be used strictly according to the doctor’s prescription!
To avoid an allergic disease, timely elimination of infectious foci in the mouth, nose, pharynx, ear, and dust control are important measures to prevent microbial allergization of the body.Try not to litter the apartment, do not scatter newspapers, magazines wherever you have – they especially collect dust. Store books in closed cabinets. Systematically do wet cleaning of the apartment and ventilate it more often.
Avoid hypothermia, excessive voice load, and chemical and mechanical irritation of the upper respiratory tract. Remember that tobacco, alcohol, spicy foods pose a direct threat to the development of allergic diseases.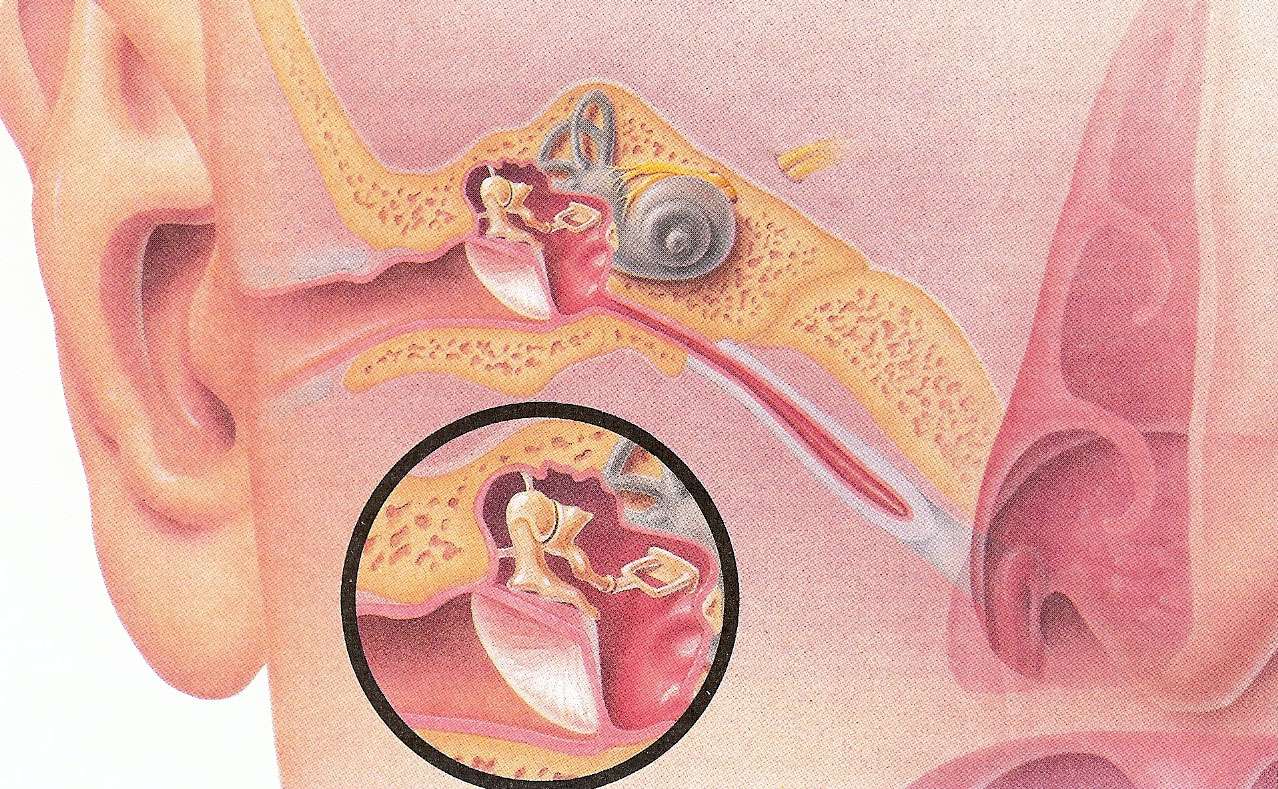 And be sure to temper your body.
And be sure to temper your body.
In case of food allergies, the main thing is to completely exclude from the diet a product that provokes an exacerbation, in a timely manner to treat metabolic diseases, vitamin deficiency, liver and endocrine gland diseases.Food should be complete, varied, and contain a sufficient amount of vitamins.
Hay rhinitis patients need to know which plant pollen is causing them the disease and when it blooms. If possible, for this period, it is advisable to take a vacation and travel to another climatogeographic zone where there are no such plants. If this fails, then during the period of aggravation, keep the windows in the apartment closed and tightened with gauze, try not to be in places with abundant vegetation.
# National Project Demography89
Itchy throat – causes, danger and treatment methods
Feel an unpleasant tickle in your throat? Do not postpone a visit to the doctor – this may be a sign of dangerous pathologies. Find out more about this symptom and how to get rid of it.
Find out more about this symptom and how to get rid of it.
If your throat itches, this is a reason for contacting an ENT doctor. This unpleasant sensation is very uncomfortable – as if someone were scratching inside.But the reasons causing it are much more dangerous – they can lead to serious complications. It’s time to figure out why the throat itches from the inside out, and how to get rid of itchy throat!
Page navigation:
Types and causes of the disease
When an itchy throat is worried about , the causes of can be associated with ENT diseases, allergies, irritation or nervous strain. This pathology is classified by origin.
Reasons
Quite a common cause of this symptom is angina, laryngitis, pharyngitis and other throat diseases.The disease causes an inflammatory process, due to which the tissues swell and begin to itch. Also, the cause may be a neoplasm of the larynx or pharynx – growing, it spreads to neighboring tissues and provokes itching in the throat.
Sometimes itching provokes pharyngomycosis – a fungal infection of the pharyngeal mucosa. It can develop against the background of immunodeficiency, severe chronic pathologies, taking aggressive drugs (antibiotics, immunosuppressants, chemotherapy).
There are other causes of this problem:
- Mechanical injuries to the neck;
- allergic reactions;
- vocal fatigue;
- diseases of the thyroid gland;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, namely reflux;
- stress and nervous strain.
90,037 violations of the central nervous system;
Views
Depending on the etiology, distinguish:
- allergic itching in the throat – occurs when irritating substances get on the mucous membrane;
- pruritoseptive – develops in inflammatory diseases, trauma or foreign bodies;
- psychogenic – manifests itself when a person is very nervous or very tired;
- neuropathic – caused by disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system.

Diagnostics
To understand why the throat itches, the doctor conducts a consultation and a visual examination, and then an endoscopic examination.Modern optical devices allow you to examine the condition of the mucous membranes, see inflammation, neoplasms, foreign bodies, injuries, etc. Digital endoscopes also record a video report of the examination – so that you can study everything in detail and track the development of pathology in dynamics. Additionally, smears of microflora, laboratory blood tests are taken. If the examination does not find any ENT pathologies, the doctor refers the patient to accompanying specialists for the diagnosis of the thyroid gland, reflux, etc.
What to do if you feel itchy throat
Are you worried about a feeling of unpleasant burning and tickling in your throat? In this case, you need to make an appointment with an ENT doctor. He will take a history and conduct an examination that will help to find out the cause of the problem.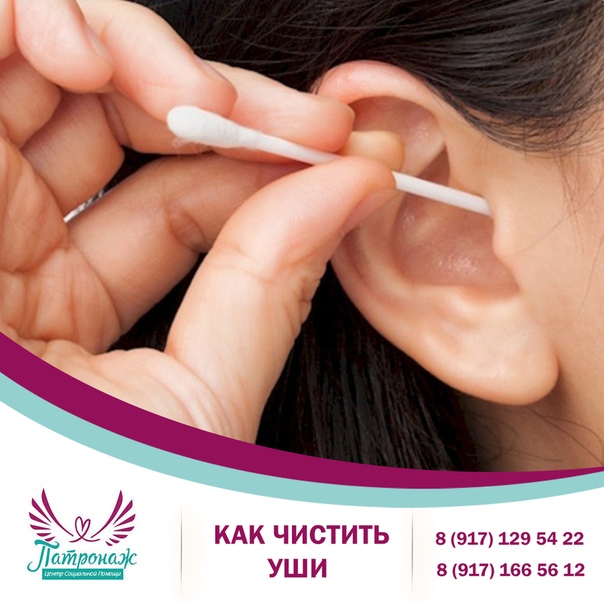 The sooner you notice this symptom, the more successful the treatment will be.
The sooner you notice this symptom, the more successful the treatment will be.
What not to do in case of itching in the larynx
If your throat is itchy , then in no case is it necessary:
- rinse it with self-prescribed drugs;
- put compresses;
- relieve itching with hot drinks or alcohol;
- there are lemons, ginger, honey, garlic, hot peppers;
- drink herbal teas recommended by traditional medicine;
- to do steam inhalation;
- to postpone the visit to the doctor.
90,037 smoking;
Sore throat and itching can be not only signs of inflammatory diseases, but also irritation, trauma, etc. In this case, lemon tea and inhalation can harm – for example, the acidic environment irritates the mucous membrane even more. There is no need to experiment with your health – it is better to find out the cause through professional diagnostics.
Treatment of itchy throat at Betterton
For patients who complain of itching in the throat, treatment is prescribed individually – according to the results of the examination. If it appears due to an inflammatory process, then our ENT doctors prescribe a course of drugs that eliminate the infection and relieve swelling. Symptomatic treatment is also prescribed – softening tablets, gargles or sprays to eliminate dryness and perspiration.
If it appears due to an inflammatory process, then our ENT doctors prescribe a course of drugs that eliminate the infection and relieve swelling. Symptomatic treatment is also prescribed – softening tablets, gargles or sprays to eliminate dryness and perspiration.
Allergies are treated with antihistamines and non-specific immunotherapy. It lies in the fact that an allergen is systematically introduced into the body in micro doses, as a result, it stops responding to histamine.
Possible complications
When the throat itches, it reduces the quality of life. For example, itchy throat at night interferes with sleep and leads to unnecessary strain on the nervous system. But the main danger is that the diseases that cause this symptom have severe complications. Inflammatory processes spread to adjacent tissues and lead to damage to the lower respiratory tract. They can also provoke a pharyngeal abscess and other dangerous conditions.
If itching is caused by an allergic reaction, the person may develop severe swelling that blocks the airway.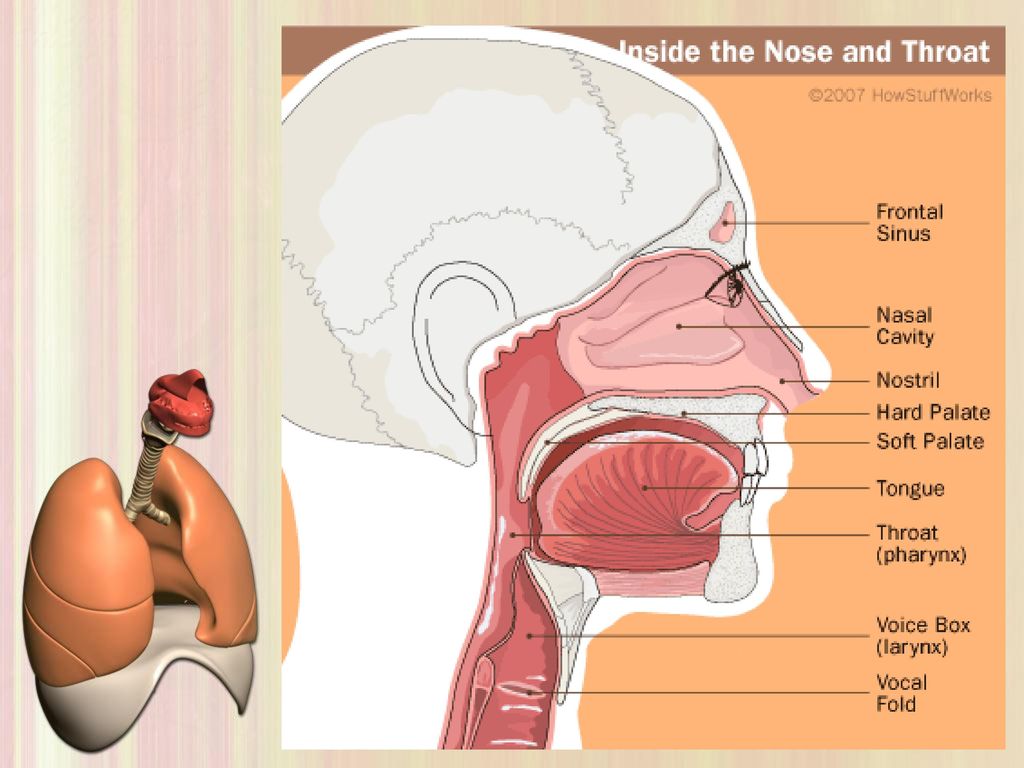 Because of this, there is a risk of suffocation. And with a sore throat associated with neoplasms in the throat, there is a risk of degeneration into life-threatening cancer.
Because of this, there is a risk of suffocation. And with a sore throat associated with neoplasms in the throat, there is a risk of degeneration into life-threatening cancer.
Prevention
In order not to be bothered by an itchy throat, treat ENT diseases in time, lead a healthy lifestyle, undergo preventive examinations with an otolaryngologist. It is also not recommended to eat too hot or cold, spicy, sour.
Make an appointment with a doctor:
Make an appointment with a doctor:
About the author:
Otolaryngologist (ENT) for children and adults
Dr. Antonevich S.S. treats all types of ENT diseases, conducts treatment procedures for the ear, nose and throat, tests hearing, and performs gentle outpatient surgeries.
Work experience:
over 12 years
Latest publications from the author
90,000 Otolaryngologists advise taking care of earwax – Rossiyskaya Gazeta
According to WHO, every fifth inhabitant of the planet suffers from fungal infections
In the fall, problems with the nose, throat, ears are not uncommon. They are not always caused by common colds. Sometimes the cause of the disease is Candida yeast fungi, Aspergillus mold fungi, and other fungi.
They are not always caused by common colds. Sometimes the cause of the disease is Candida yeast fungi, Aspergillus mold fungi, and other fungi.
Not the flu, but the mushroom?
Ears often suffer from fungi. In Russia, according to statistics, fungi cause 26% of all otitis media in children and 18% in adults. This disease is called otomycosis. This is what sets it apart from a common ear cold:
- Itching and burning in the ear. These are the main symptoms that distinguish fungal otitis media from normal bacterial otitis media.
- Discharge: green, yellowish, brown and even black – it depends on the type of the causative fungus. With otomycosis, discharge will be necessary, since fungi, during growth and reproduction, secrete waste products.
- Ears congestion, swelling. Formation of crusts, plugs in the external auditory canal is possible.
- Otomycosis is often accompanied by allergies.
It has been noticed that those who are engaged in swimming are at risk. Otolaryngologists even have such a term – bather’s ear.
Otolaryngologists even have such a term – bather’s ear.
Save the sulfur
Treatment of otomycosis is radically different from the treatment of common bacterial otitis media. Here are some rules:
- In no case should you use warming compresses, this only enhances the growth of fungi.
- We’ll have to give up regular ear drops. They usually contain antibiotics that do not affect the growth of fungi in any way, but only destroy bacteria – their natural antagonists.
- One important tip: When you wash your ears, don’t wash all the wax out of your ear canal. Sulfur is not dirt, but a natural ear protection against infection, it has a bactericidal and antifungal effect at the same time. Of course, if too much sulfur has accumulated, the excess can be wiped off with a soft swab. But this must be done carefully, trying not to injure the skin.
- Although with proper treatment, otomycosis recedes in almost 95% of cases, self-medication is unacceptable here.
 After all, it is important to use not a universal antifungal drug, but a specific, destructive for a certain fungus that caused the disease.And this can only be established by a doctor.
After all, it is important to use not a universal antifungal drug, but a specific, destructive for a certain fungus that caused the disease.And this can only be established by a doctor.
Where else do mushrooms live?
Nose. Mycosis in the sinuses is characterized by itching, constant congestion. The abundance and frequency of discharge depend on the stage of development of the fungal infection. The patient experiences unpleasant sensations of heaviness in the sinus affected by mycosis, and the mucous membrane becomes very painful.
Carious teeth become one of the common reasons for the development of this type of mycoses. Sometimes dental treatment can also lead to the introduction of fungal spores into this area of the paranasal sinuses.
Throat. Pharyngomycosis (sore throat caused by a fungus) can occur even after minor trauma to the mucous membrane (for example, due to unsuccessful dentures), against the background of a common inflammation of the throat and tonsils. It begins with a slight redness and dryness of the oral mucosa, then a whitish cheesy plaque appears, capturing the tonsils, soft palate, and the back of the pharynx. Frequent tonsillitis (up to ten times a year) is a serious reason to check for pathogenic fungi in the oral cavity.
It begins with a slight redness and dryness of the oral mucosa, then a whitish cheesy plaque appears, capturing the tonsils, soft palate, and the back of the pharynx. Frequent tonsillitis (up to ten times a year) is a serious reason to check for pathogenic fungi in the oral cavity.
Larynx. The characteristic symptoms of the disease are constant hoarseness and specific plaque. Often occur when dust, acid vapors, alkalis are inhaled. Sometimes laryngomycosis can occur if the larynx is burned by hot food. The risk group includes people who have acid reflux from the stomach into the esophagus, and then into the larynx.
Important to know
Most often, fungi parasitize on nails, skin and hair. You can get infected both in public places (in gyms, in a bathhouse, swimming pools, a manicure / pedicure salon, on the beach), and in your own home.Shared shoes at home, in the country or on a visit, walking barefoot, household items (towels, rugs, coverings) – and now all family members suffer from fungal diseases.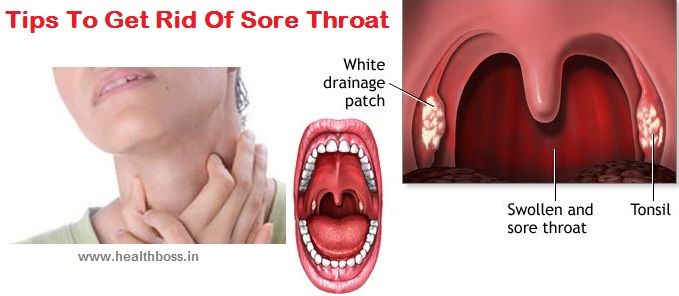

 There are a variety of treatment options including topical medications or steroids.
There are a variety of treatment options including topical medications or steroids.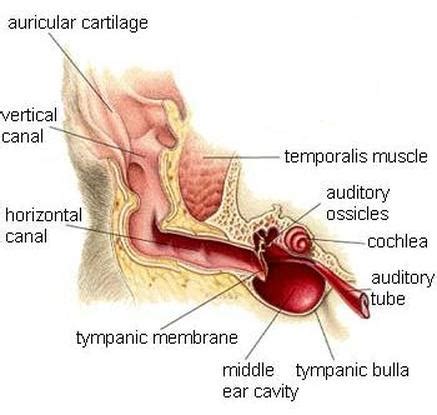 These particles range from animal fur to dust mites and pollen. Experiencing itchy ears along with watery eyes and a runny nose is not uncommon among hay fever sufferers.
These particles range from animal fur to dust mites and pollen. Experiencing itchy ears along with watery eyes and a runny nose is not uncommon among hay fever sufferers.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-530683730-57899b7b3df78c09e94ee299.jpg) They can cause an itchy, throat, ears, and mouth, hives, a rash, to more serious reactions. If this happens, you have to contact your doctor to get an alternative to the medication.
They can cause an itchy, throat, ears, and mouth, hives, a rash, to more serious reactions. If this happens, you have to contact your doctor to get an alternative to the medication.


 The patient suffers from ear congestion, hearing loss, fever, intoxication, and severe pain.As soon as purulent discharge appears, there is a decrease in pain and an improvement in well-being.
The patient suffers from ear congestion, hearing loss, fever, intoxication, and severe pain.As soon as purulent discharge appears, there is a decrease in pain and an improvement in well-being. They have proven themselves very well: tea tree oil, salicylic alcohol, calendula tincture, propolis alcohol tincture.
They have proven themselves very well: tea tree oil, salicylic alcohol, calendula tincture, propolis alcohol tincture.
 After all, it is important to use not a universal antifungal drug, but a specific, destructive for a certain fungus that caused the disease.And this can only be established by a doctor.
After all, it is important to use not a universal antifungal drug, but a specific, destructive for a certain fungus that caused the disease.And this can only be established by a doctor.