Liver function levels normal range. Liver Function Tests: Understanding Normal Ranges and Interpreting Results
What are liver function tests. How do doctors interpret liver function test results. What do abnormal liver function test results indicate. How can you prepare for a liver function test. What substances do liver function tests measure.
What Are Liver Function Tests?
Liver function tests, also known as liver panels, are blood tests that measure various substances produced by the liver. These tests provide valuable information about the health and functioning of this vital organ. Doctors use liver function tests to:
- Evaluate overall liver health
- Detect liver inflammation or damage
- Diagnose liver diseases
- Monitor the progression of liver conditions
- Assess the effectiveness of treatments
Liver function tests are crucial because liver disease often progresses silently without obvious symptoms in its early stages. By the time noticeable symptoms appear, significant liver damage may have already occurred. Regular testing can help detect problems early when they are most treatable.
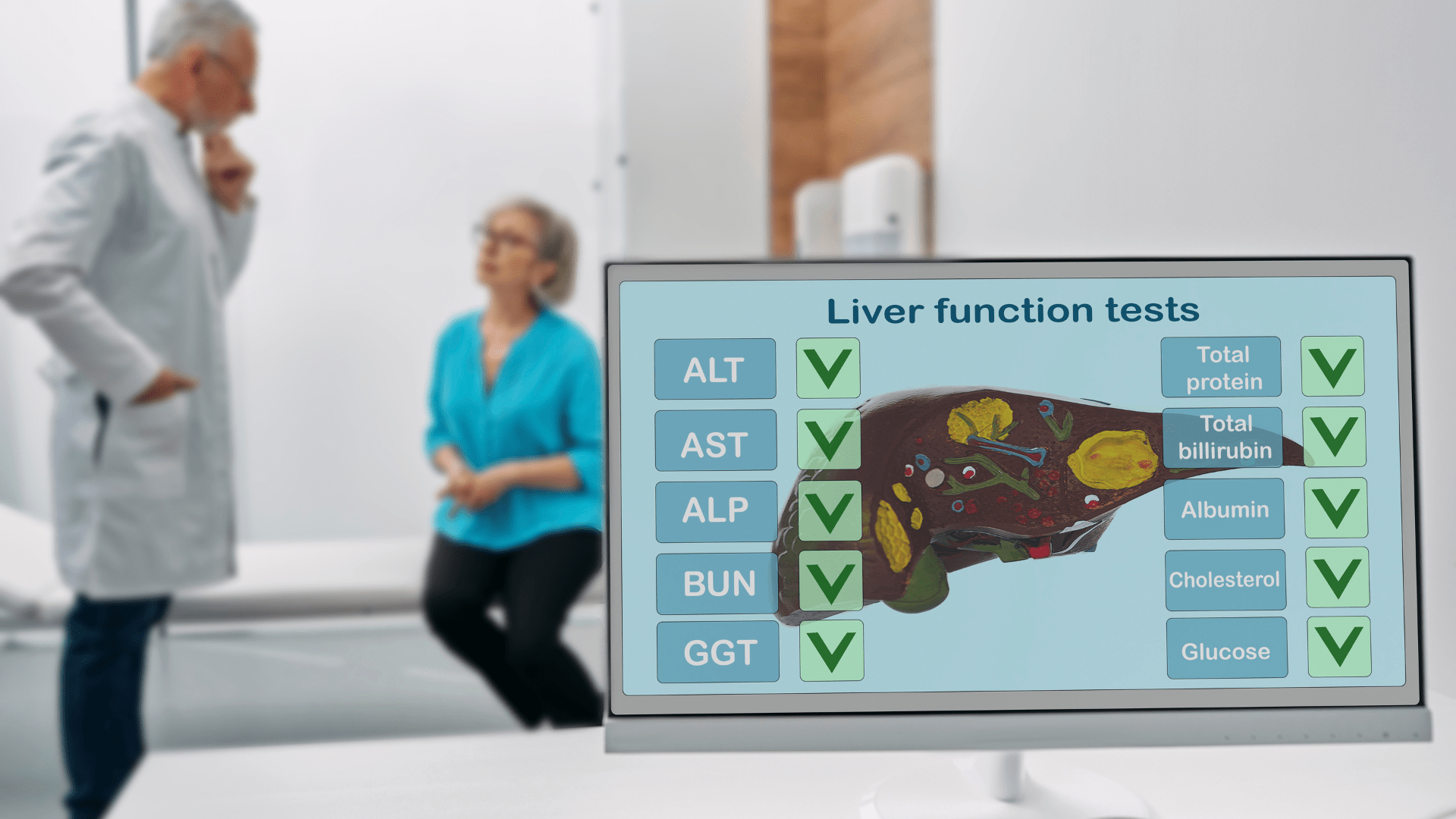
Key Components of Liver Function Tests
A comprehensive liver panel typically measures several different substances in the blood. The main components include:
Liver Enzymes
- Alanine transaminase (ALT): An enzyme found primarily in liver cells
- Aspartate transaminase (AST): An enzyme found in the liver, heart, and muscles
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): An enzyme present in various tissues, including the liver and bones
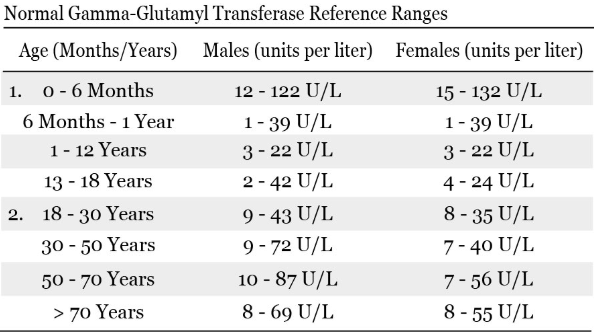
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT): An enzyme found mainly in the liver
Proteins
- Albumin: The main protein produced by the liver
- Total protein: The sum of all proteins in the blood
Other Substances
- Bilirubin: A waste product from the breakdown of red blood cells
- Prothrombin time (PT): A measure of blood clotting ability
Understanding Normal Ranges for Liver Function Tests
Interpreting liver function test results requires comparing the measured values to established normal ranges. However, it’s important to note that these ranges can vary slightly between laboratories and may be influenced by factors such as age, sex, and overall health.
Typical normal ranges for common liver function tests include:
- ALT: 7-55 units per liter (U/L)
- AST: 8-48 U/L
- ALP: 45-115 U/L
- GGT: 8-61 U/L
- Albumin: 3.5-5.0 grams per deciliter (g/dL)
- Total protein: 6.0-8.3 g/dL
- Total bilirubin: 0.1-1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
- Prothrombin time: 11-13.5 seconds
What do these numbers mean? Normal ranges indicate the values typically seen in healthy individuals. Results falling outside these ranges may suggest liver dysfunction or other health issues. However, it’s crucial to interpret results in the context of an individual’s overall health and other factors.
Interpreting Abnormal Liver Function Test Results
When liver function test results fall outside the normal range, it doesn’t always indicate a serious problem. Various factors can influence these values, including:
- Medications
- Recent alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Certain genetic conditions
- Intense exercise
- Pregnancy
However, persistently abnormal results may suggest liver dysfunction or disease. Here’s what different abnormal results might indicate:
Elevated Liver Enzymes
Increased levels of ALT, AST, ALP, or GGT can suggest liver cell damage or inflammation. Common causes include:
- Viral hepatitis
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Drug-induced liver injury
- Autoimmune liver diseases
Low Albumin or Total Protein
Decreased levels of these proteins may indicate:
- Chronic liver disease
- Malnutrition
- Kidney disease
Elevated Bilirubin
High bilirubin levels can cause jaundice and may suggest:
- Liver disease
- Bile duct obstruction
- Certain genetic disorders
Prolonged Prothrombin Time
An extended PT may indicate:
- Liver damage affecting clotting factor production
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Use of blood-thinning medications
Preparing for a Liver Function Test
Proper preparation can help ensure accurate liver function test results. How should you prepare for a liver function test? Follow these guidelines:
- Fast for 8-12 hours before the test, unless otherwise instructed by your doctor
- Drink only water during the fasting period
- Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal products you’re taking
- Avoid alcohol for at least 24 hours before the test
- Refrain from strenuous exercise for 24 hours prior to testing
What happens during the test itself? A healthcare professional will draw a small amount of blood from a vein in your arm using a needle. The procedure is quick and generally causes minimal discomfort.
When Are Liver Function Tests Recommended?
Doctors may order liver function tests in various situations. When might you need a liver function test? Common reasons include:
- Evaluating unexplained symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, or abdominal pain
- Monitoring known liver conditions
- Screening for liver disease in high-risk individuals
- Assessing liver health before starting certain medications
- Investigating abnormal results from other tests
- Evaluating the effectiveness of liver disease treatments
How often should liver function tests be performed? The frequency depends on individual circumstances. People with chronic liver conditions may need regular testing, while those without known liver issues might only require occasional screening.
Beyond Liver Function Tests: Additional Diagnostic Tools
While liver function tests provide valuable information, they are just one tool in diagnosing and managing liver conditions. What other tests might be used to evaluate liver health?
Imaging Studies
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the liver
- CT scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the liver
- MRI: Offers high-resolution images without radiation exposure
- Fibroscan: Measures liver stiffness to assess fibrosis
Additional Blood Tests
- Hepatitis virus tests: Detect viral hepatitis infections
- Autoimmune markers: Identify autoimmune liver diseases
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP): Screens for liver cancer
Liver Biopsy
In some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis or assess the severity of liver damage. This procedure involves removing a small sample of liver tissue for microscopic examination.
How do these additional tests complement liver function tests? They provide a more comprehensive picture of liver health, helping doctors pinpoint specific conditions and determine the most appropriate treatment strategies.
Maintaining Healthy Liver Function
While regular liver function tests are important for monitoring liver health, there are several steps you can take to support your liver and maintain optimal function:
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can lead to liver damage and disease
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and supports liver function
- Avoid unnecessary medications: Some drugs can stress the liver, so use medications only as directed
- Practice safe sex and avoid sharing needles: These behaviors reduce the risk of hepatitis B and C infections
- Get vaccinated: Hepatitis A and B vaccines can protect against these viral liver infections
- Limit exposure to toxins: Use protective equipment when working with chemicals or pesticides
How effective are these lifestyle measures in promoting liver health? Research shows that adopting these habits can significantly reduce the risk of liver disease and improve overall liver function.
The Future of Liver Function Testing
As medical science advances, new approaches to liver function testing are emerging. What innovations are on the horizon for liver health assessment?
- Non-invasive biomarkers: Researchers are investigating new blood-based markers that may provide more specific information about liver health and disease progression
- Advanced imaging techniques: Improved imaging technologies may offer more detailed views of liver structure and function without the need for invasive procedures
- Genetic testing: Identifying genetic markers associated with liver disease risk could enable earlier interventions and personalized treatment strategies
- Artificial intelligence: Machine learning algorithms may help interpret complex liver test results and imaging studies more accurately
How might these advancements impact liver disease diagnosis and management? By providing more precise and comprehensive information about liver health, these innovations could lead to earlier detection of liver problems, more targeted treatments, and improved patient outcomes.
In conclusion, liver function tests play a crucial role in assessing and monitoring liver health. By understanding what these tests measure and how to interpret the results, individuals can take a more active role in maintaining their liver health and overall well-being. Regular check-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and staying informed about advancements in liver health assessment can contribute to better liver function and a reduced risk of liver disease.
Liver Function Tests | Kaiser Permanente
Skip Navigation
Test Overview
Some blood tests are used to determine whether your liver is damaged or inflamed. Although these tests help your doctor evaluate how well your liver is working, they cannot tell if you have hepatitis C.
Tests that assess liver function
Your doctor may do tests to measure certain chemicals produced by the liver. These tests can help your doctor check how well your liver is working.
Tests may measure:
- Bilirubin.
- Albumin.
- Total serum protein.
Tests that check for inflammation of the liver (liver enzyme studies)
Your liver may be damaged if you have increased levels of:
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT or SGPT).

- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST or SGOT).
An increased level of alkaline phosphatase (AP) may indicate blockage of bile ducts.
Why It Is Done
Liver tests are done when a medical history or physical exam suggests that something may be wrong with your liver.
These tests can also help diagnose long-term (chronic) infection. If liver enzymes are high, a test for hepatitis C antibodies may be done to see if you have hepatitis C.
If you are being treated with antiviral therapy, you may have liver tests from time to time to see whether treatment is working.
How To Prepare
In general, there’s nothing you have to do before this test, unless your doctor tells you to.
How It Is Done
A health professional uses a needle to take a blood sample, usually from the arm.
Results
Normal
All levels are within the normal range.
Abnormal
One or more levels are outside the normal range. Abnormal liver function tests may mean that your liver is inflamed or is not working normally. This can be a sign that you have a viral infection.
Credits
- Top of the page
Next Section:
Why It Is Done
Liver function tests: Uses, results, and more
Liver function tests are blood tests that measure substances that the liver produces. Doctors can use these results to evaluate the health of a person’s liver. Abnormal results can indicate liver disease, even when a person does not have symptoms.
Doctors can use these results to evaluate the health of a person’s liver. Abnormal results can indicate liver disease, even when a person does not have symptoms.
The liver serves several essential functions that support a person’s overall health and well-being. It removes toxins from the blood, metabolizes fats and proteins, and regulates blood clotting.
Viral infections, medications, genetic disorders, heavy alcohol consumption, and obesity can cause inflammation and damage in the liver. Continuous liver damage can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which can progress into a severe condition called cirrhosis.
Liver disease causes nearly 2 million deaths each year globally. However, early stage liver disease does not always cause symptoms.
Continue reading this article to learn more about liver function tests, including their uses and how to interpret the results.
Share on PinterestA doctor may order a blood test to measure liver function.
Liver function tests, or liver panels, measure the levels of proteins, enzymes, and waste materials (bilirubin) in a person’s blood.
Doctors use these tests when they want to evaluate the health of a person’s liver or identify the cause of liver damage.
Liver function tests measure the following compounds:
- Alanine transaminase (ALT) is an enzyme found in liver and kidneys cells. ALT helps create energy for liver cells. Damaged liver cells release ALT into the bloodstream, which can elevate ALT levels in the blood.
- Aspartate transaminase (AST) is an enzyme in the liver and muscles that helps metabolizes amino acids. Similarly to ALT, elevated AST levels may be a sign of liver damage or liver disease.
- Alkaline phosphate (ALP) is an enzyme present in the blood. ALP contributes to numerous vital bodily functions, such as supplying nutrients to the liver, promoting bone growth, and metabolizing fat in the intestines.
- Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) is an enzyme that occurs primarily in the liver, but it is also present in the kidneys, pancreas, gallbladder, and spleen.
 Higher than normal concentrations of GGT in the blood may indicate alcohol-related liver damage. Elevated GGT levels can also increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Higher than normal concentrations of GGT in the blood may indicate alcohol-related liver damage. Elevated GGT levels can also increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. - Bilirubin is a waste product that forms when the liver breaks down red blood cells. Bilirubin exits the body as bile in stool. High levels of bilirubin can cause jaundice — a condition in which the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow — and may indicate liver damage.
- Albumin is a protein that the liver produces. The liver releases albumin into the bloodstream, where it helps fight infections and transport vitamins, hormones, and enzymes throughout the body. Liver damage can cause abnormally low albumin levels.
- Prothrombin time (PT) measures how long it takes for the blood to clot. A prolonged PT may be a sign of certain blood clotting disorders related to liver damage.
Doctors use liver function tests to evaluate the health of a person’s liver. If a doctor suspects someone has liver disease or liver damage, they may perform one or more liver function tests to identify the underlying cause.
If a doctor suspects someone has liver disease or liver damage, they may perform one or more liver function tests to identify the underlying cause.
Symptoms of liver disease can include:
- nausea and vomiting
- loss of appetite
- unintentional weight loss
- pain in the upper right part of the abdomen
- swelling in the feet, ankles, or calves
- jaundice, or yellowing eyes and skin
- dark urine
Doctors may recommend one or more liver function tests for people who:
- have been exposed to or have a history of hepatitis A, B, or C infections
- are currently receiving treatment for liver disease
- currently take medications that affect the liver
- show signs of liver damage
- have alcohol use disorder
- have a family history of liver disease
- have a history of intravenous drug use
- have overweight or obese
Healthcare professionals perform liver function tests on blood samples.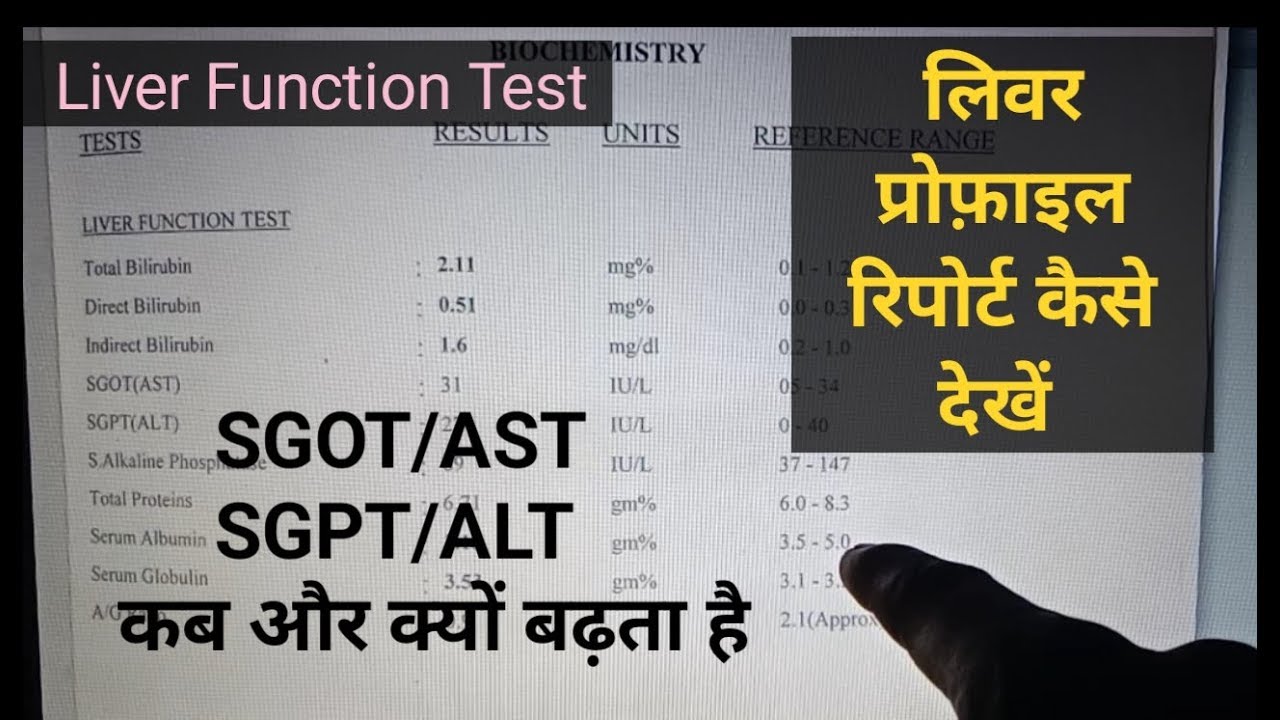 A blood draw is a quick and straightforward procedure.
A blood draw is a quick and straightforward procedure.
During a blood draw, a healthcare professional will disinfect the skin above a large vein in the arm. They may tie an elastic band, called a tourniquet, a few inches above the puncture site, which will increase the pressure inside the vein.
Once the healthcare professional can see the vein under the skin, they will insert a hollow needle at a 30-degree angle. They will attach a collection tube to the other end of the needle.
After collecting the blood sample, they will release the tourniquet, remove the needle, and press a cotton ball or gauze strip on the puncture site.
The healthcare professional will replace the cotton ball or gauze with a new one and apply an adhesive bandage over the puncture site. People can go home after having their blood drawn.
The blood sample will go to a laboratory for analysis. A doctor may discuss a person’s results over the phone or schedule a follow-up appointment.
Liver function tests reveal different information about the liver, depending on the specific substance a doctor is testing for.
The table below contains the normal ranges for different liver function tests and possible interpretations of abnormal test results.
| Test | Normal levels | Abnormal results |
| alanine transaminase (ALT) | 0–45 international units per liter (iu/l) | Higher than normal results are a sign of:
|
| aspartate transaminase (AST) | 0–35 iu/l | Higher than normal results are a sign of:
|
| alkaline phosphate (ALP) | 30–120 iu/l | Higher than normal results are a sign of:
Lower than normal results are a sign of:
|
| gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) | 0–30 iu/l | Higher than normal results are a sign of:
|
| bilirubin | 2–17 micromoles per liter (mcmol/l) | Higher than normal results are a sign of:
|
| albumin | 40–60 grams(g)/l | Higher than normal results are a sign of:
Lower than normal results are a sign of:
|
| prothrombin time (PT) | 10. 9–12.5 seconds 9–12.5 seconds | Longer than normal results are a sign of:
|
Doctors use liver function tests to evaluate the health of a person’s liver. Abnormal results may indicate liver damage or
liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis.
However, certain medications, lifestyle factors, and other underlying medical conditions can influence liver function test results.
Doctors may choose to investigate abnormal test results using:
- imaging tests, such as a CT scan or ultrasound
- a liver biopsy
- a blood count test
- tests for viral infections
- cholesterol and triglyceride testing
- genetic testing
- autoimmune tests
The exact type of treatment a person receives will vary depending on the underlying cause.
For example, people who have liver damage due to alcohol use disorder may need a doctor’s help to stop drinking.
A doctor might recommend dietary and lifestyle changes to people who have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Doctors can prescribe medications that treat viral hepatitis infections, autoimmune hepatitis, and conditions that damage the bile ducts.
Severe liver damage can cause complications, such as portal hypertension, that may require surgery or a liver transplant.
Liver disease presents a significant global health risk. Cirrhosis ranks as the 11th leading cause of death around the world.
Many people do not realize they have liver disease until they have significant liver damage. As a result, doctors may order liver function tests as part of a regular health screening. These tests measure the levels of liver proteins, enzymes, and bilirubin in a person’s blood.
Abnormal liver function test results may provide the first indications of liver disease. However, abnormal results can also occur as a result of taking certain medications, viral illnesses, lifestyle factors, and other health conditions.
However, abnormal results can also occur as a result of taking certain medications, viral illnesses, lifestyle factors, and other health conditions.
These tests do not often identify the underlying cause, but doctors can use them to plan their next steps.
blood test norms and correct interpretation
Contents
- give
- 1.3 List of basic samples for checking liver function
- 1.3.1 1. ALT and AST
- 1.3.2 2. Albumin
- 1.3.3 3. Total bilirubin
- 1.3.4 4. GGTP
- 1.4 What do liver test results mean?
- 1.5 What indicators can be detected during the examination of the liver?
- 1.6 Liver test norms in adults and children
- 1.7 Why does the liver level change?
- 1.8 What diseases can be associated with abnormal liver function tests?
- 1.9 What to do if the level of indicators is outside the norm?
- 1.10 How do I properly prepare for liver tests?
- 1.
 10.1 Rules for preparing for tests
10.1 Rules for preparing for tests - 1.10.2 How to pass tests for liver tests?
- 1.
- 1.11 Frequency of liver checks
- 1.12 Conclusion
- 1.13 Helpful tips for maintaining a healthy liver
- 1.13.1 1. Moderation in alcohol consumption
- 1. 13.2 2. Proper nutrition
- 1.13.3 3. Active image life
- 1.13.4 4. Rational use of drugs
- 1.13.5 5. Refusal of bad habits
- 1.14 Where can I get a liver test?
- 1.15 List of Liver Samples
- 1.16 Why is it necessary to check the level of liver samples?
- 1.17 Related videos:
- 1.18 Q&A:
- 1.18.0.1 What values are normal in liver tests?
- 1.18.0.2 How to prepare for liver tests?
- 1.18.0.3 How to interpret abnormal liver tests?
- 1.18.0.4 Can drugs affect liver tests?
- 1.18.0.5 What symptoms can signal problems in the liver?
A liver test is a blood test that measures the function of the liver. Deciphering the results allows you to identify the presence of liver diseases and determine their severity. Find out how a blood test for the liver goes, how to correctly decipher the results and what is the norm of liver tests.
Deciphering the results allows you to identify the presence of liver diseases and determine their severity. Find out how a blood test for the liver goes, how to correctly decipher the results and what is the norm of liver tests.
The liver performs many important functions in the human body, it is involved in metabolism and blood purification from toxins. Because of this, any violation of its work can lead to serious illness and even death.
Diagnosis of liver diseases requires appropriate tests, including liver tests. Their results help the doctor determine how well the liver is functioning and whether the patient has malfunctions of the organ.
In this article, we’ll talk about the norms of liver tests and the correct interpretation of their results, so that everyone can more fully understand the importance of this test and take the necessary measures to maintain liver health.
Liver: main functions
The liver is one of the most important organs of the human body, located in the right upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. It performs many functions, including:
It performs many functions, including:
- Metabolism of fats and carbohydrates;
- Production of bile necessary for digestion;
- Synthesis of proteins and globulins necessary for the immune system;
- Removal of slag substances and toxins from the body;
Due to the fact that the liver performs so many functions, its performance can be impaired in various diseases or as a result of negative factors. In this regard, special liver tests are often carried out, which allow assessing the state of this organ and identifying possible malfunctions.
Tests to be done
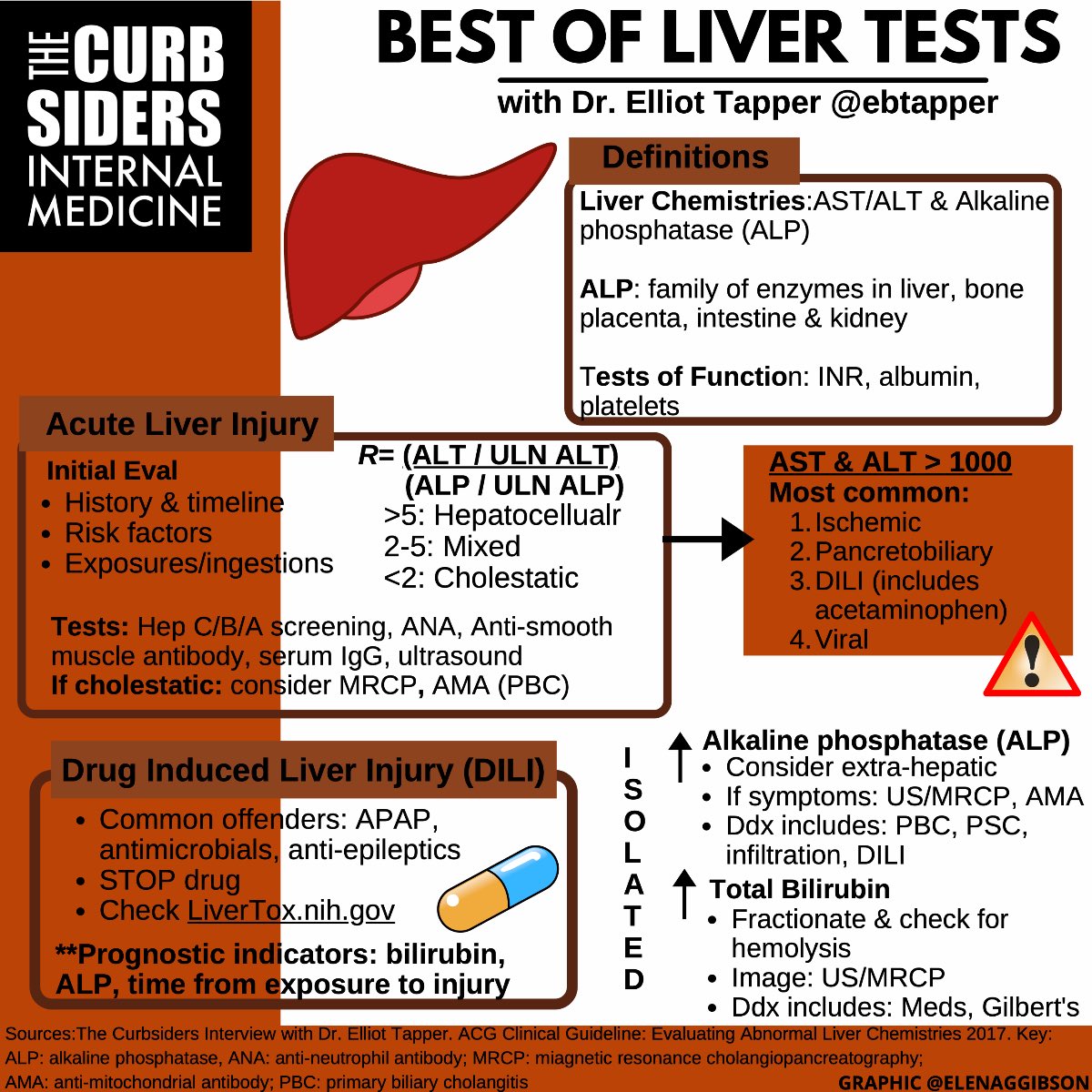
When liver disease is suspected, doctors usually recommend several basic tests: ALT, AST, ALP, GGTP, and bilirubin.
ALT (alanine aminotransferase) is an enzyme found in the liver and other organs. When the liver is damaged, ALT is released into the blood. High levels of ALT may indicate hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver.
AST (aspartate aminotransferase) is similar to ALT and is another indicator of liver damage.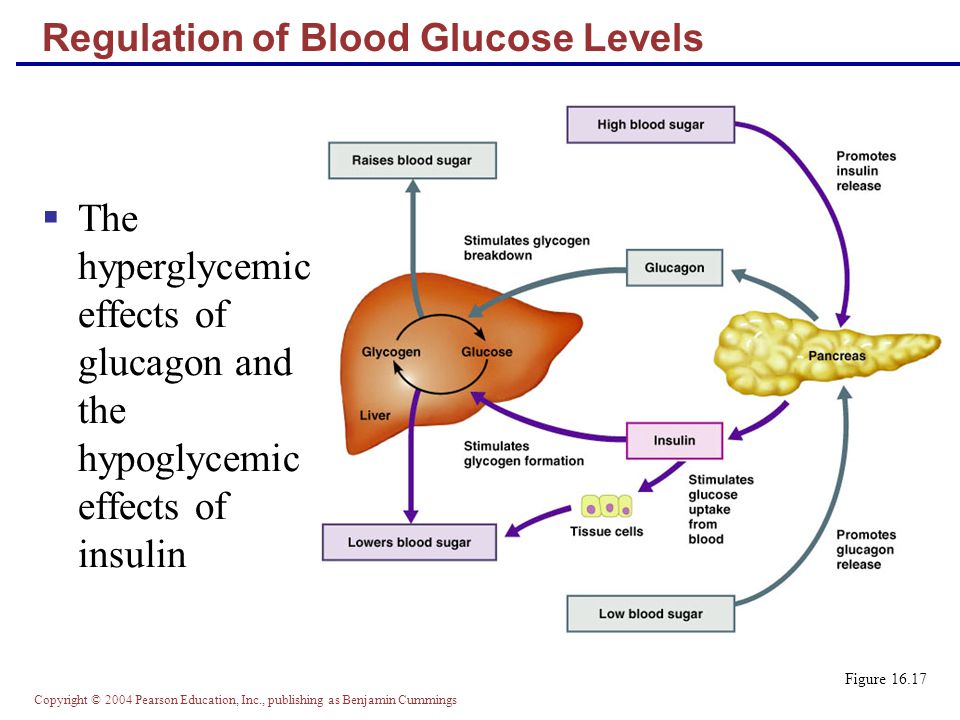 However, AST levels can also be elevated when muscles or the heart are damaged.
However, AST levels can also be elevated when muscles or the heart are damaged.
Alkaline Phosphatase is an enzyme also found in the liver and other organs. Elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase may indicate diseases of the biliary tract or bones.
GGTP (gamma-glutamyltransferase) is another enzyme found in the liver and other organs. High levels of GGTP may also indicate biliary tract disease.
Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced by the breakdown of red blood cells. Elevated levels of bilirubin may indicate diseases of the liver or biliary tract.
In addition to these tests, your doctor may recommend additional tests, such as hepatitis virus, CBC, tumor markers, etc.
List of basic liver function tests
that are in the blood of any person. They monitor the functioning of the liver and can increase if it is damaged. Usually their rate depends on gender and age. A doctor orders a test when a patient suspects a liver disease or if the patient is taking medications that may affect liver function.

2. Albumin
Albumin is a protein produced by the liver. Its blood level may decrease with liver disease or if the patient does not get enough protein from food. Also, this analysis can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment of liver diseases.
3. Total bilirubin
Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced in the liver when red blood cells break down. Its level in the blood can increase if the liver is malfunctioning or if the production of bilirubin exceeds its processing by the liver. Elevated levels of total bilirubin may indicate jaundice.
4. GGTP
GGTP is an enzyme that is produced in the liver. Its blood level rises when the liver is damaged or when alcohol is consumed. The GGTP assay is used to diagnose liver disease and monitor treatment.
- ALT and AST – basic indicators, monitor the work of the liver;
- Albumin – reflects the level of protein in the blood and liver function;
- Total bilirubin – reflects the level of yellow pigment in the blood;
- GGTP – Produced in the liver and increased by injury or alcohol consumption.

What do liver test results mean?
Liver tests are used to evaluate a patient for liver disease. The results of such tests reflect not only the general condition of the liver, but also possible violations in its work.
Doctors can also view the level of bilirubin, which is a breakdown product of hemoglobin. Elevated levels of bilirubin may indicate a violation of the function of the liver or biliary tract.
It is worth noting that the results of liver tests can be increased not only in liver diseases, but also in other diseases. Based on this, they should only be used in combination with all types of surveys.
What indicators can be detected during the examination of the liver?
The liver is an organ that acts as a filter for the blood, carries out metabolism, is involved in the production of bile and the breakdown of lipids. When examining the liver, the greatest attention is paid to its functionality and the presence of pathological processes.
Liver tests can detect:
- ALT and AST levels are indicators that help determine the presence of liver cell damage. Elevated levels of ALT and AST may indicate the presence of hepatitis, cirrhosis, and other liver diseases.
- The level of bilirubin is an indicator that reflects the work of the liver to remove bile. An elevated level of bilirubin may indicate the presence of cholelithiasis, hepatitis, cirrhosis.
- The level of alkaline phosphatase is an indicator that reflects the course of the processes of production and excretion of bile. Its increase may indicate the presence of diseases of the biliary tract.
- Prothrombin index is an indicator that reflects the work of the liver in the production of thrombin. Its decrease may indicate the presence of liver disease.
In case of detection of violations of indicators, it is recommended to contact a specialist for additional examination and determination of the causes of pathological changes.
Norms of liver tests in adults and children
The liver plays a key role in ensuring human health, so the analysis of liver tests is very important for detecting diseases of this organ. The norms of liver tests in adults and children are different.
- Total bilirubin: in adults – 3.4-19.7 µmol/l, in children – 3-20 µmol/l;
- ALT: in adult women – up to 31 U/l, in adult men – up to 45 U/l, in children – up to 50 U/l;
- AST: in adult women – up to 31 U/l, in adult men – up to 47 U/l, in children – up to 140 U/l;
- Alkaline phosphatase: in adults – 45-125 U/l, in children – 200-600 U/l;
- GGT: in adults – up to 50 U/l, in children – up to 150 U/l;
- Total protein: adults 60-85 g/l, children 51-73 g/l.
In some cases, the norms may differ slightly depending on the laboratory, therefore, when interpreting the results, it is necessary to be guided by the recommendations of the doctor and conduct additional examinations if necessary.
Why does the level of indicators in the liver change?
Various processes take place in the liver related to metabolism, blood filtration, toxin utilization and protein synthesis. With some diseases or other adverse factors, these processes may be disturbed, which is reflected in the level of indicators in the blood.
In addition, non-disease factors, such as certain medications, alcohol consumption, nutritional deficiencies, etc., can influence the level of the liver test results. Therefore, all such factors must be taken into account when interpreting the results of liver tests.
In general, a change in the level of indicators in liver tests can be associated with both liver diseases and other adverse factors affecting the functionality of the body. For a more accurate interpretation of these samples, you need to contact an experienced doctor who will conduct additional diagnostics and select the appropriate treatment.
What diseases can be associated with abnormal liver function tests?
Abnormal levels of liver tests in a blood test can be an indicator of various liver diseases. For example, an elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level may be associated with hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease. At the same time, ALT is a more sensitive indicator of liver cell damage in comparison with Aspartate aminotransferase (AST).
For example, an elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level may be associated with hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease. At the same time, ALT is a more sensitive indicator of liver cell damage in comparison with Aspartate aminotransferase (AST).
In addition, an elevated Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) level can also indicate the presence of liver disease, such as gallstone disease or liver metastases.
However, to determine the exact liver disease, a comprehensive evaluation is required, including a medical history, physical examination, and additional tests and procedures. Therefore, contact your doctor if you have abnormal liver function tests in your blood.
What to do if the level of indicators is outside the norm?
If the results of liver tests are abnormal, you should consult a doctor for advice and order further tests.
If alcohol or drugs are the cause of high values, your doctor may recommend that you eliminate them from your diet.
It is important to remember that self-medication can be hazardous to health, so you should not take any medication without consulting a doctor.
How do I properly prepare for a liver test?
How to prepare for tests
Proper preparation for liver tests will help you get a more accurate result, which will allow your doctor to more accurately diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Before taking the test, it is important to remember a few rules:
- Refrain from drinking alcohol a few days before the test.
- Eliminate fatty, spicy, salty foods the day before the test.
- Fast 8-12 hours before testing.
- If you are taking any medications, ask your doctor if you can take them before the test.
How to do liver tests correctly?
Proper testing technique will allow you to get a more accurate result, which will then help the doctor to make a more effective treatment.
In order to pass the tests for liver tests correctly, you need to:
- Prepare for the test, following the above rules.
- Before taking the tests, it would not be harmful to visit the toilet in order to exclude the possibility of getting any side elements into the urine.
- Collect morning mid-stream urine in a clean, dry container.
- Safely deliver the collected urine to the laboratory.
Frequency of liver checks
Examination of the liver is very important for maintaining health, as it is one of the largest and most important organs in our body with many functions. Some people at risk of developing liver disease should have liver tests more frequently than others.
If you do not have risk factors for liver disease, you can have a liver exam once a year along with your annual health care. However, if you are at risk of developing liver disease, for example if you drink alcohol or have a family history of liver disease, you may be advised to be screened more frequently.
In all cases, it is best to see your doctor and find out how often you need to have your liver checked. This will help prevent the development of serious liver diseases that can lead to chronic health problems or even death.
Conclusion
Liver tests are important tools for assessing liver health. They help to detect the presence of functional or structural changes in the liver, such as diseases and injuries. Liver test results may indicate liver problems such as inflammation, cirrhosis, or cancer.
It must be understood that liver tests may be elevated for many reasons not necessarily related to liver disease, so full interpretation of the results must be made by the clinician, taking into account other factors.
If you see a doctor complaining of symptoms of liver disease or liver disease, liver tests can help your doctor make a diagnosis and choose the best course of treatment.
In general, regular check-ups of liver tests can help detect changes in the body before symptoms appear, which is essential for early detection of liver diseases and their effective treatment.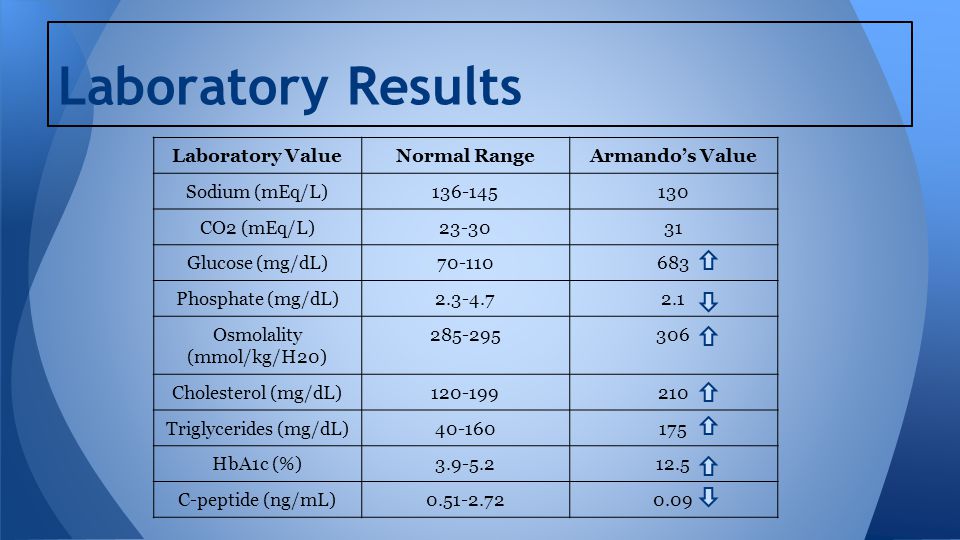
Tips for keeping your liver healthy
1. Moderation in alcohol consumption
Alcohol is the main enemy of the liver . It is better to abandon it completely. If this is not easy for you, try to drink alcohol within reasonable limits. No more than one standard drink for women and two for men per day is recommended.
2. Proper nutrition
The liver is the body’s filter that cleanses the blood of harmful substances. Proper nutrition will help reduce the burden on the liver. It is important to eat more vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and protein foods. It is also necessary to reduce the consumption of fatty, fried and salty foods.
3. Active lifestyle
To maintain a healthy liver, it is very important to be active. Physical activity helps improve blood circulation in the body and improves digestion. Choose sports activities that you enjoy, such as fitness classes or yoga.
4. Rational use of drugs
Some drugs can be toxic to the liver, so it is important to take them only as directed by your doctor and not exceed the recommended dosage. If you have liver disease, always check with your doctor about which medications you can take.
If you have liver disease, always check with your doctor about which medications you can take.
5. Quitting bad habits
Smoking and drug use directly damage the liver, increasing the risk of developing jaundice, cirrhosis of the liver and other diseases. It is better to give up these bad habits to keep your liver healthy.
Where can I get a liver test?
If you suspect that you have a liver problem, it is important to see a doctor and get appropriate tests done. Examinations to detect liver diseases can be taken in both public and private medical institutions.
Public clinics and hospitals provide free or subsidized services to patients. Private medical centers often have newer, better equipment and faster test results. However, prices for consultations and analyzes in private medical institutions are higher than in public institutions.
To choose a medical institution, it is recommended to consult with the doctor who ordered the examination. You can also refer to other people’s reviews and assessments of medical institutions on sites on the Internet.
You can also refer to other people’s reviews and assessments of medical institutions on sites on the Internet.
Regardless of the chosen medical institution, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, take tests on time and, if necessary, undergo treatment. This will help keep the liver healthy and prevent the development of dangerous diseases.
Liver Test List
When examining the liver for function and disease, comprehensive blood tests are required. The list of samples required for liver examination includes:
- AST and ALT are indicators of the activity of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, respectively. The release of these enzymes into the blood indicates the presence of inflammatory processes in the liver;
- Total bilirubin is a bile pigment that is produced in the liver and then excreted in the bile into the intestines. Elevated levels of bilirubin may indicate hepatitis, yellow fever and other liver diseases;
- Prothrombin time is an indicator of the rate of blood clotting.
 It is an early sign of liver disease such as cirrhosis or hepatitis.
It is an early sign of liver disease such as cirrhosis or hepatitis. - Albumins are proteins that are formed by the liver and are needed to maintain the body’s vital functions. A normal level of albumin in the blood indicates the proper functioning of the liver.
Why check liver function tests?
The liver is one of the most important organs in the human body and performs many functions, including participation in metabolism, production of hormones and bile, cleaning the blood of toxins and other harmful substances. In addition, the liver is involved in maintaining the acid-base balance and regulating blood sugar levels.
But despite the fact that the liver is the “filter” of the body, it is also exposed to various external factors such as alcohol consumption, poor diet, diseases and other negative influences. In this regard, there is a risk of developing liver diseases, which can lead to serious health consequences.
Checking the level of liver tests in the blood allows early detection of the presence of liver diseases, as well as assessing their severity.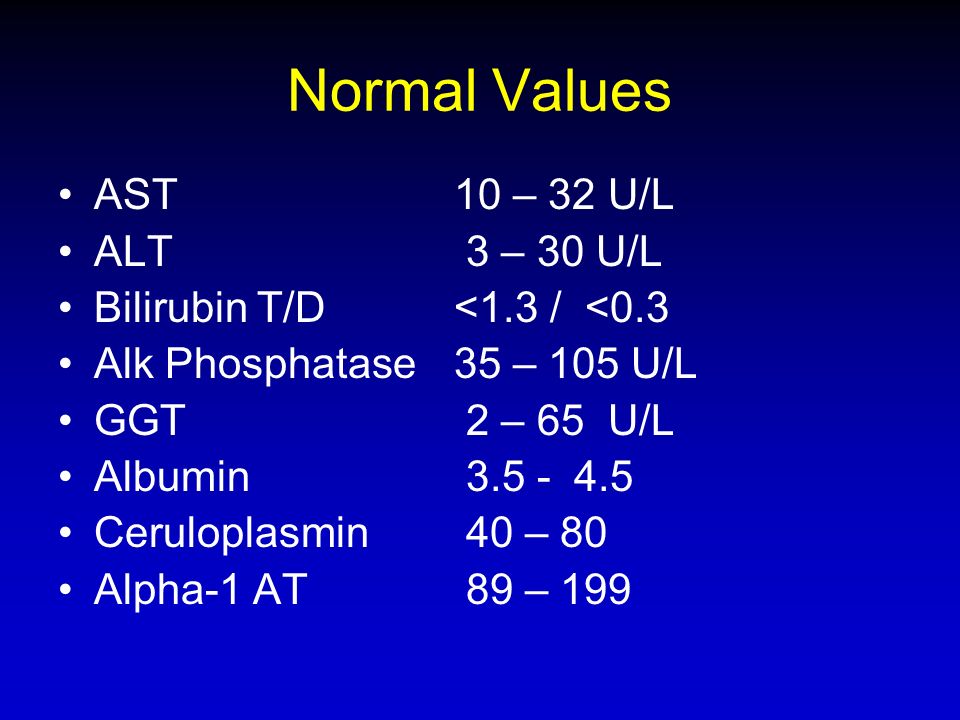 This is important for the timely initiation of treatment and the prevention of complications.
This is important for the timely initiation of treatment and the prevention of complications.
In addition, liver test levels are also carried out as a preventive measure to monitor the condition of the liver, especially if there are risk factors, such as alcohol or medication.
Related videos:
Q&A:
What values are normal in liver tests?
Normal values of liver tests depend on the method of analysis and the laboratory in which the study was performed. However, on average, the following values are considered normal: ALT – no more than 40 U / l for men and no more than 32 U / l for women, AST – no more than 40 U / l for men and no more than 35 U / l for women, alkaline phosphatase – 30-130 U / l, GGT – 0-70 U / l, bilirubin – 3.4-17.1 μmol / l. But still, for an accurate assessment, you need to consult a doctor.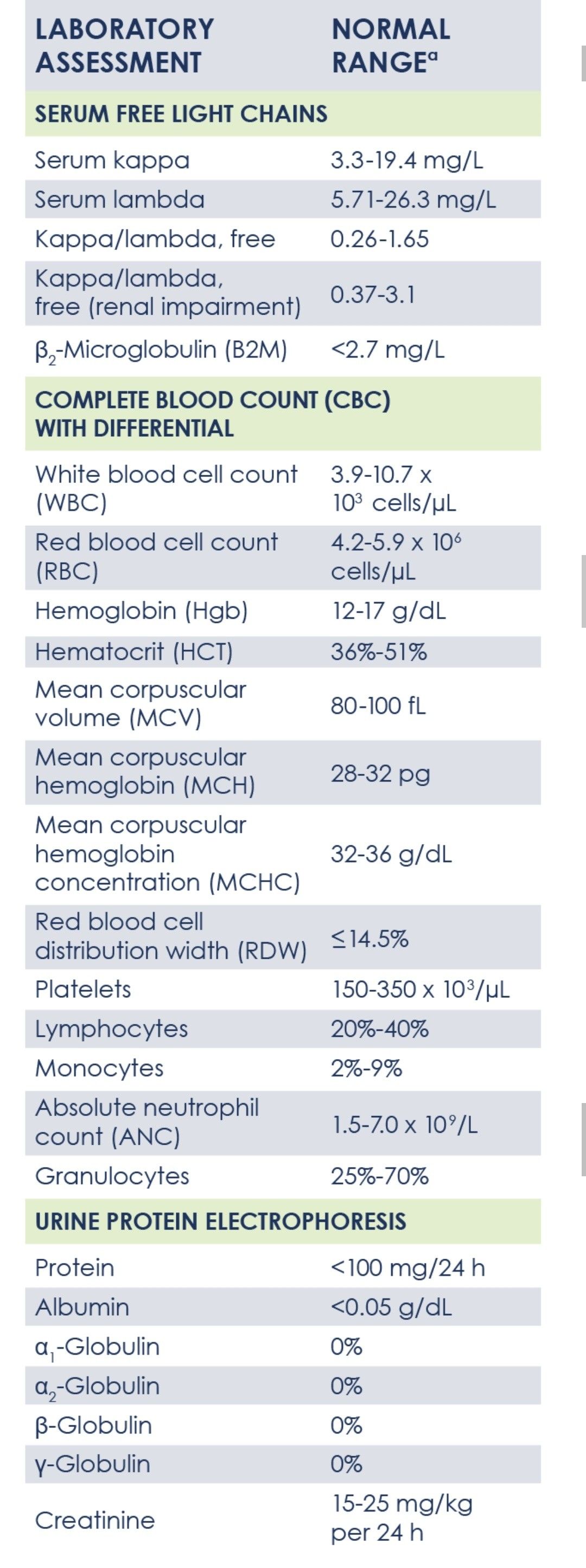
How to prepare for liver tests?
To obtain reliable liver test results, certain rules must be followed. You should not eat food 8-10 hours before the analysis, as this may distort the results. It is also advisable to refrain from drinking alcohol 72 hours before the test, as well as from physical activity for 24 hours. Before the procedure, you should not take medication, if necessary, the doctor must be informed about this.
How to interpret abnormal liver tests?
Abnormal liver tests may indicate various diseases such as hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, cholelithiasis and others. Deviations can manifest themselves in different ways, both in an increase and in a decrease in indicators. To accurately determine the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Can drugs affect liver tests?
Yes, drugs can affect liver function tests. Some medications increase ALT and AST levels, such as hepatitis medications, antibiotics, and heart failure medications.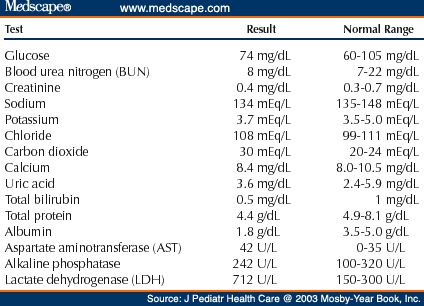 Other medicines can lower the levels, such as hormonal drugs, some anti-inflammatory drugs. Therefore, before conducting tests, it is necessary to inform the doctor about all the medications taken so that he can take this into account when deciphering the results.
Other medicines can lower the levels, such as hormonal drugs, some anti-inflammatory drugs. Therefore, before conducting tests, it is necessary to inform the doctor about all the medications taken so that he can take this into account when deciphering the results.
What symptoms can signal problems in the liver?
Symptoms indicative of problems with the liver may vary and include icteric coloration of the skin and sclera of the eyes, pain or discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, stool disturbances, fatigue, general malaise, decreased appetite, nausea and vomiting. If there is a suspicion of liver problems, you should consult a doctor for examination and prescribing the correct treatment.
ALT up to 50% discount
Analysis description
Index
ALT is a test that is used to evaluate liver function. An increase in ALT in the blood in a certain proportion with another enzyme, AST, may also indicate a previous heart attack.
Appointments
As a rule, it is necessary after a long-term use of medications, interaction with toxic substances (including alcohol), in the diagnosis of hepatitis, suspected pancreatitis.
Specialist
It is prescribed both in a complex of biochemical analyzes, and separately, by a therapist or hepatologist.
Important
The results of the analysis are very significantly affected by food intake, so it is important to strictly abstain for 12 hours before blood sampling.
Test method – UV kinetic test
Test material
– Serum
Due date
The analysis will be ready in
within 1 day, excluding the day of collection.
The term can be extended by 1 day if necessary.
You will receive results by email. email as soon as it’s ready.
Deadline: within 1 day, excluding the day of sampling, excluding Saturday and Sunday (except for the day of taking the biomaterial)
How to prepare
In advance
Do not take a blood test immediately after X-ray, fluorography, ultrasound, physiotherapy.
The day before
24 hours before blood sampling:
- Limit fatty and fried foods, do not take alcohol.
- Avoid strenuous exercise.
From 8 to 14 hours before donating blood, do not eat, drink only clean still water.
On the day of donation
Before blood sampling
- Do not smoke for 60 minutes,
- 15-30 minutes to be in a calm state.
Result
Analysis result example. pdf
pdf
Explanation of
Interpretation of test results is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a diagnosis or
replaces medical advice. Reference values may differ from those indicated in
depending on the equipment used, the actual values will be indicated on the form
results.
Unit: U/l
Reference values:
Age, gender | ALT, U/l |
0 – 1 month | < 56 |
1 – 12 months | < 54 |
1 – 14 years old: | < 45 |
women (>14 years old) | < 35 |
men (>14 years old) | < 50 |
Increase:
- Necrosis of liver cells of any etiology (viral hepatitis, toxic liver damage).

- Cirrhosis of the liver.
- Cholestatic and obstructive jaundice.
- Myocarditis.
- Heart failure.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Myositis.
- Major trauma and necrosis of skeletal muscle.
- Pancreatitis.
- Burn disease.
- Alcoholism.
- Liver cancer (primary and metastatic).
Decrease:
- Has no diagnostic value.
Quality Assurance
Examination performed by Biochemistry Analyzer AU 5800 from Beckman Coulter, USA
Modular technology that provides simultaneous work with a large number of samples, high speed of their processing, dosing accuracy for each study, which minimizes the total testing time
ALT
Learn more about biochemical blood tests:
Do’s and don’ts before a blood test?
How to decipher the general and biochemical blood tests?
Biochemical blood tests – meaning and importance
ALT is an enzyme from the group of aminotransferases, which is responsible for amino acid metabolism and is produced intracellularly.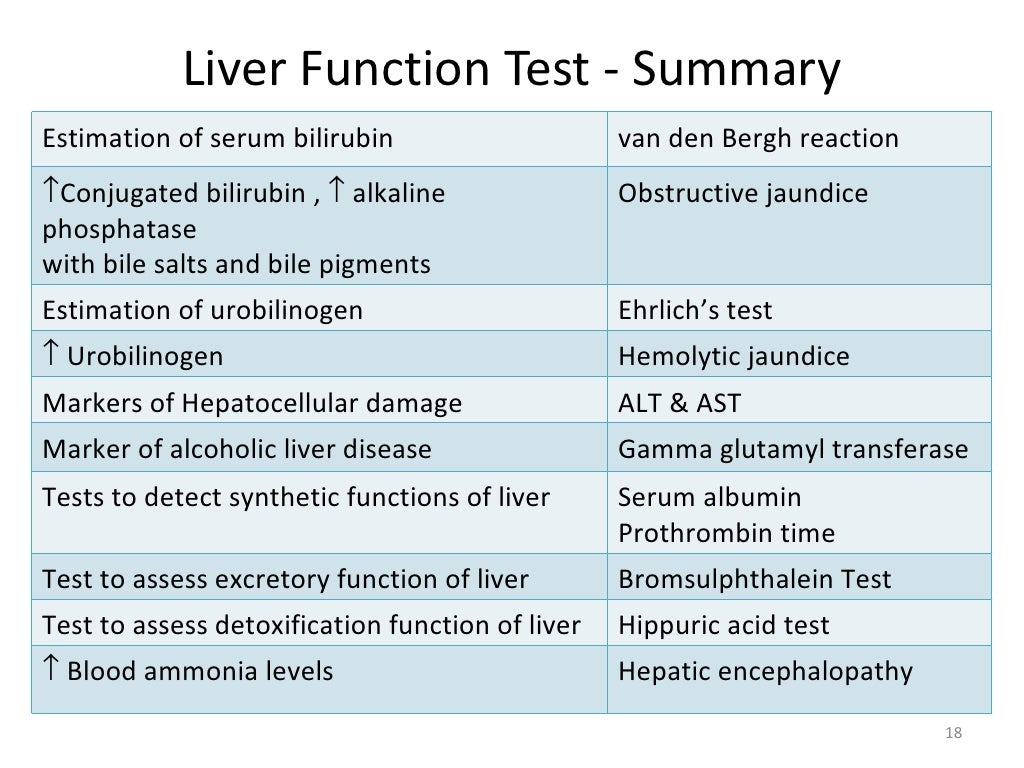 Normally, the content of ALT in the blood is negligible, and the highest level of the enzyme is observed in the liver cells. Therefore, with an increase in the concentration of ALT in the blood, the first suspicion falls on asymptomatic lesions of this particular organ. As a rule, this analysis is necessary after a long-term use of medications, interaction with toxic substances (including alcohol), in the diagnosis of hepatitis, and suspicion of pancreatitis.
Normally, the content of ALT in the blood is negligible, and the highest level of the enzyme is observed in the liver cells. Therefore, with an increase in the concentration of ALT in the blood, the first suspicion falls on asymptomatic lesions of this particular organ. As a rule, this analysis is necessary after a long-term use of medications, interaction with toxic substances (including alcohol), in the diagnosis of hepatitis, and suspicion of pancreatitis.
An increase in ALT in the blood in a certain proportion with another enzyme, AST (aspartate aminotransferase), may also indicate a previous heart attack. The results of the analysis are very significantly affected by food intake, so it is important to strictly abstain for 12 hours before blood sampling.
ALT (alanine aminotransferase, ALAT) is an intracellular enzyme from the group of transferases, a subgroup of transaminases, which catalyzes the conversion of a-keto acids into amino acids by transferring amino groups.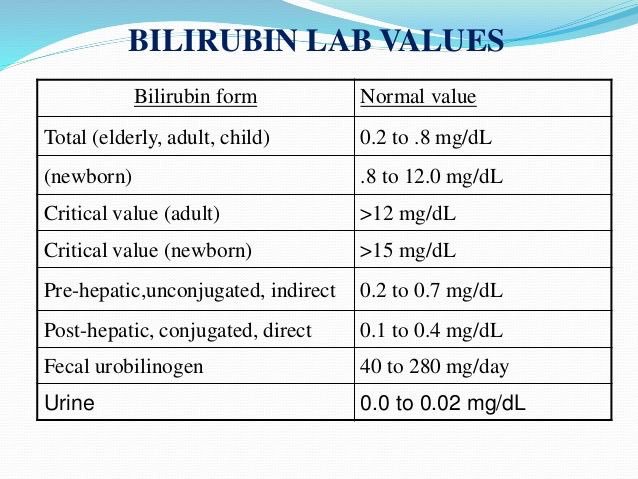 Normally, only a small part of this enzyme disappears into the blood. The enzyme is present mainly in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes, but it is also found in skeletal muscle and myocardial cells. The biochemical activity of ALT in the liver is almost 10 times higher than in the myocardium and skeletal muscles, therefore, an increase in the level of ALT in the blood is mainly considered as an indicator of damage to the liver parenchyma. When liver cells are damaged, the integrity of their membrane is violated and ALT enters the bloodstream. ALT has a greater diagnostic sensitivity in diseases of the hepatobiliary system than AST.
Normally, only a small part of this enzyme disappears into the blood. The enzyme is present mainly in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes, but it is also found in skeletal muscle and myocardial cells. The biochemical activity of ALT in the liver is almost 10 times higher than in the myocardium and skeletal muscles, therefore, an increase in the level of ALT in the blood is mainly considered as an indicator of damage to the liver parenchyma. When liver cells are damaged, the integrity of their membrane is violated and ALT enters the bloodstream. ALT has a greater diagnostic sensitivity in diseases of the hepatobiliary system than AST.
If a biochemical blood test ALT (ALAT) showed an increase in ALT activity by 50 times or more, then this can mainly be due to acute violation of hepatic perfusion, acute necrosis of liver cells caused by exotoxins, including paracetamol and carbon tetrachloride, viral hepatitis, infectious mononucleosis. An increase in the concentration of ALT in the blood is diagnostically significant, since its level increases even before the appearance of other clinical symptoms of liver diseases (jaundice, etc. ). With viral hepatitis, an increase in enzyme activity occurs at a very early time – in the prodromal period (it is noted in 50% of patients – in 5 days, in 90% – 2 days before the clinical manifestation of the disease).
). With viral hepatitis, an increase in enzyme activity occurs at a very early time – in the prodromal period (it is noted in 50% of patients – in 5 days, in 90% – 2 days before the clinical manifestation of the disease).
High ALT and AST values in the results of a biochemical blood test are also observed in toxic hepatitis, especially in severe cases. A moderate increase in transaminases is observed with alcoholic liver damage. Depending on the stage of the cirrhotic process, the levels of ALT and AST can be either at the upper limit of normal, or at a 4-5-fold increase from the upper limit (the level of AST is higher than ALT). In patients with primary or metastatic liver carcinomas, an increase in transaminase activity by 5-10 times is observed, however, there are cases when their level remains within the normal range, mainly in the early stages of malignant infiltration of the organ. The level in the blood test ALT (ALAT), exceeding more than 15 times the upper limit of normal, is always an indicator of acute hepatocellular necrosis of toxic, viral or circulatory origin.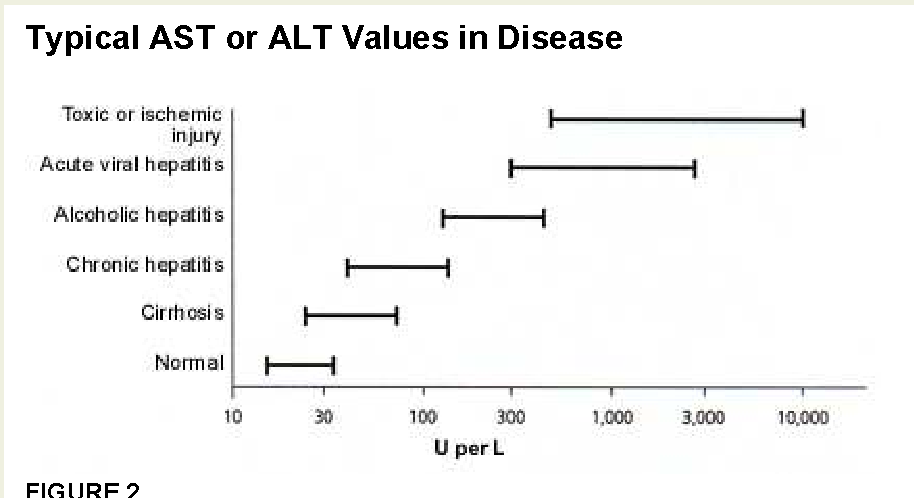


 Higher than normal concentrations of GGT in the blood may indicate alcohol-related liver damage. Elevated GGT levels can also increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Higher than normal concentrations of GGT in the blood may indicate alcohol-related liver damage. Elevated GGT levels can also increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. 10.1 Rules for preparing for tests
10.1 Rules for preparing for tests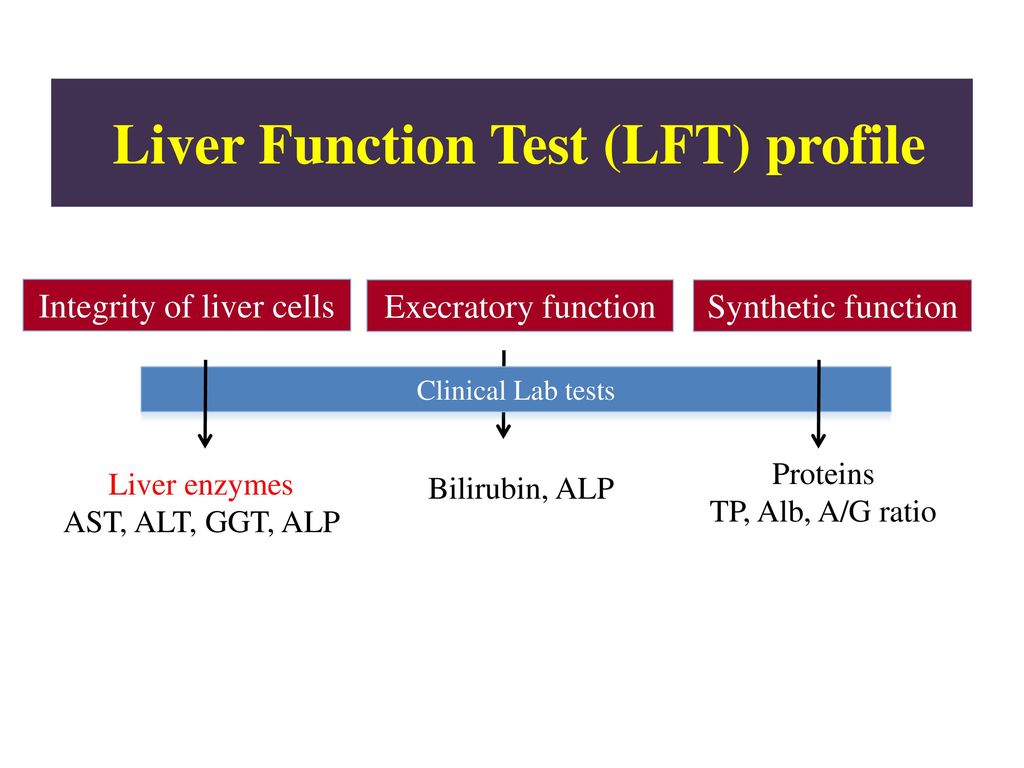
 It is an early sign of liver disease such as cirrhosis or hepatitis.
It is an early sign of liver disease such as cirrhosis or hepatitis.