Medicine for stomach pain for kids. Effective Remedies for Children’s Stomach Pain: First Aid Guide for Parents
What are the common causes of stomach pain in children. How can parents provide first aid for abdominal discomfort in kids. Which over-the-counter medicines are safe for treating children’s stomach aches. When should you seek medical attention for a child’s stomach pain.
Common Causes of Stomach Pain in Children
Stomach pain is a frequent complaint among children and teenagers. While most cases are not serious, understanding the potential causes can help parents provide appropriate care and know when to seek medical attention. Here are some of the most common reasons children experience abdominal discomfort:
- Gas pain and indigestion
- Constipation
- Overeating
- Lactose intolerance
- Milk allergy
- Stress and anxiety
Gas pain and indigestion are often diet-related. Carbonated beverages, spicy foods, beans, citrus fruits, and caffeine-containing products like chocolate can contribute to stomach upset. Constipation is another frequent cause, especially in younger children who may not recognize the symptoms. Overeating, particularly of rich or fatty foods, can lead to abdominal discomfort.

Identifying Lactose Intolerance and Milk Allergies in Children
Lactose intolerance and milk allergies can both cause stomach pain in children, but they are distinct conditions. Lactose intolerance occurs when the body lacks sufficient lactase, an enzyme needed to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. Symptoms may include abdominal cramps, gas, diarrhea, or constipation after consuming dairy.
A milk allergy, on the other hand, is an immune system reaction to milk proteins. It can cause more severe symptoms, including stomach cramps, and may be accompanied by other allergic reactions. If you suspect your child has either condition, consult with a pediatrician for proper diagnosis and management strategies.
Over-the-Counter Medicines for Children’s Stomach Pain
When it comes to treating stomach pain in children, several over-the-counter options are available. However, it’s crucial to use these medications appropriately and consult with a healthcare provider when necessary. Here are some common remedies:

- Infant gas relief drops (e.g., Mylicon)
- Electrolyte solutions (e.g., Pedialyte)
- Antacids (for older children, as recommended by a doctor)
- Probiotics (consult with a pediatrician first)
Infant gas relief drops containing simethicone can help alleviate discomfort caused by excess gas. Electrolyte solutions are beneficial for maintaining hydration, especially if the stomach pain is accompanied by diarrhea or vomiting. For older children, antacids may be appropriate for occasional indigestion, but should only be used under medical guidance. Probiotics can support digestive health, but it’s essential to choose a product suitable for children and consult with a healthcare provider before use.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes for Stomach Pain Relief
In addition to over-the-counter medications, several home remedies and lifestyle adjustments can help alleviate stomach pain in children:
- Encourage small, frequent meals instead of large portions
- Offer clear fluids to prevent dehydration
- Apply a warm compress to the abdomen
- Encourage relaxation techniques for stress-related stomach pain
- Promote good posture during meals
- Ensure regular physical activity
Encouraging children to eat slowly and chew their food thoroughly can also help prevent indigestion and overeating. For constipation-related discomfort, increasing fiber intake and ensuring adequate hydration can be beneficial. Always monitor your child’s response to these remedies and consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen.

When to Seek Medical Attention for a Child’s Stomach Pain
While most cases of stomach pain in children are not serious, there are instances when medical attention is necessary. Parents should be aware of the following red flags:
- Severe or persistent pain lasting more than a few hours
- Pain accompanied by high fever (over 102°F or 39°C)
- Bloody stools or vomit
- Signs of dehydration (dry mouth, sunken eyes, decreased urination)
- Abdominal swelling or tenderness
- Pain that wakes the child from sleep
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhea
If your child experiences any of these symptoms or if you’re unsure about the severity of their condition, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider promptly. Certain conditions, such as appendicitis, require immediate medical intervention.
Preventing Stomach Pain in Children: Diet and Lifestyle Tips
Prevention is often the best approach when it comes to managing stomach pain in children. Here are some strategies to help reduce the likelihood of abdominal discomfort:

- Encourage a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Limit intake of known trigger foods (e.g., spicy or fatty foods)
- Promote regular meal times and avoid skipping meals
- Ensure adequate hydration throughout the day
- Encourage regular physical activity
- Teach stress management techniques
- Maintain good hygiene practices to prevent infections
Establishing healthy eating habits early in life can significantly reduce the incidence of stomach pain. Encourage your child to listen to their body’s hunger and fullness cues to prevent overeating. If your child has known food sensitivities or allergies, work with a healthcare provider to develop an appropriate diet plan.
Understanding the Link Between Stress and Stomach Pain in Children
Stress and anxiety can manifest as physical symptoms in children, including stomach pain. This phenomenon, often referred to as the gut-brain connection, highlights the importance of addressing both physical and emotional well-being. Here’s how stress can affect a child’s digestive system:

- Increased muscle tension in the abdomen
- Changes in gut motility and digestion
- Altered appetite
- Exacerbation of existing digestive issues
To help children manage stress-related stomach pain, consider the following approaches:
- Teach relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness
- Encourage open communication about worries and concerns
- Ensure adequate sleep and a consistent routine
- Promote regular physical activity
- Consider professional support if stress seems overwhelming
By addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of stomach pain, parents can provide comprehensive support for their children’s well-being.
The Role of Hydration in Preventing and Managing Stomach Pain
Proper hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health and preventing stomach pain in children. Adequate fluid intake helps in several ways:
- Supports proper digestion and nutrient absorption
- Helps prevent constipation
- Maintains electrolyte balance, especially during illness
- Supports overall body function and well-being
To ensure your child stays well-hydrated:

- Offer water throughout the day, not just during meals
- Provide hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables
- Use electrolyte solutions during illness or intense physical activity
- Limit sugary drinks and caffeine, which can contribute to dehydration
If your child is experiencing stomach pain, clear fluids can help soothe the digestive system while preventing dehydration. Always consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns about your child’s hydration status, especially during illness.
Recognizing Different Types of Abdominal Pain in Children
Understanding the nature and location of abdominal pain can provide valuable insights into its cause. Here are some common types of stomach pain children may experience:
- Generalized pain: Discomfort throughout the abdomen, often associated with stomach viruses or indigestion
- Localized pain: Pain in a specific area, which may indicate a more serious condition like appendicitis
- Cramping pain: Often related to gas, bloating, or digestive issues
- Sharp or stabbing pain: May indicate more severe conditions and requires prompt medical attention
When assessing your child’s stomach pain, consider the following factors:
- Location of the pain
- Intensity and duration
- Any accompanying symptoms (e.g., fever, nausea, changes in bowel movements)
- Factors that worsen or alleviate the pain
This information can be helpful when communicating with healthcare providers and determining the appropriate course of action.
The Importance of Food Safety in Preventing Stomach Pain
Foodborne illnesses can cause significant stomach pain and discomfort in children. Practicing good food safety habits can help prevent these issues. Here are some key food safety tips:
- Wash hands thoroughly before handling food and after using the bathroom
- Clean fruits and vegetables properly before consumption
- Cook meats to appropriate temperatures
- Avoid cross-contamination between raw and cooked foods
- Store foods at proper temperatures
- Check expiration dates and discard spoiled foods
Teaching children about food safety can empower them to make healthier choices and reduce their risk of foodborne illnesses. Encourage good hygiene practices and involve children in age-appropriate food preparation tasks to reinforce these important habits.

The Impact of Sleep on Digestive Health in Children
Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health, including digestive function. Poor sleep patterns can contribute to stomach discomfort in children. Here’s how sleep affects digestive health:
- Regulates hormone production that influences digestion
- Supports the body’s natural healing and repair processes
- Helps manage stress, which can impact digestive function
- Influences appetite and food choices
To promote better sleep and digestive health:
- Establish a consistent bedtime routine
- Create a comfortable sleep environment
- Limit screen time before bed
- Avoid large meals close to bedtime
- Encourage regular physical activity during the day
By prioritizing good sleep habits, parents can support their child’s overall health and potentially reduce the incidence of stomach pain and other digestive issues.
The Role of Probiotics in Children’s Digestive Health
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can support digestive health and potentially alleviate certain types of stomach pain in children. Here’s what parents should know about probiotics:

- May help balance gut microbiome
- Can reduce symptoms of certain digestive disorders
- May strengthen the immune system
- Can be found in fermented foods or supplements
When considering probiotics for children:
- Consult with a pediatrician before starting any probiotic regimen
- Choose age-appropriate probiotic strains
- Consider incorporating probiotic-rich foods into the diet (e.g., yogurt, kefir)
- Monitor for any adverse reactions
While probiotics can be beneficial, they’re not a cure-all for digestive issues. Always work with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your child’s specific needs.
Addressing Chronic Stomach Pain in Children
Some children may experience recurrent or chronic stomach pain, which can significantly impact their quality of life. In these cases, a comprehensive approach is necessary:
- Keep a detailed symptom diary to identify patterns or triggers
- Work with a pediatric gastroenterologist for thorough evaluation
- Consider potential underlying conditions (e.g., irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease)
- Explore both medical and lifestyle interventions
- Address any psychological factors contributing to the pain
Management strategies for chronic stomach pain may include:

- Dietary modifications
- Stress reduction techniques
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Regular follow-ups to monitor progress and adjust treatment
Chronic stomach pain can be challenging for both children and parents. A multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare providers, mental health professionals, and nutritionists can provide the most comprehensive care.
Children Stomach Pain | Walgreens
62 items filtered*
Price and inventory may vary from online to in store.
Sort by:RelevanceTop SellersPrice Low To HighPrice High To LowUnit Price Low To HighBrand Name A – ZBrand Name Z – AMost ReviewedHighest RatedMost ViewedNewest Arrival
62 items*
Price and inventory may vary from online to in store.
- FREE gift offerMylicon Infant Gas Relief Drops Original (1 fl oz )
Mylicon
Infant Gas Relief Drops Original –
1 fl oz
49
$11.99 $11.99 / oz
FREE gift offerOpens a simulated dialog
Pickup Pickup available
Same Day DeliverySame Day Delivery available
Shipping Available
123456789101112
- FREE gift offerWalgreens Infants’ Gas Relief (1 oz )Walgreens
Infants’ Gas Relief –
1 oz
20
$7.19$7.19 $7.19 / ozold price$8.
 99strike through
99strike throughExtra 15% off $35+ Beauty…
FREE gift offerOpens a simulated dialog
Pickup Pickup available
Same Day DeliverySame Day Delivery available
Shipping Available
123456789101112
- Pedialyte Electrolyte Solution Pops Variety Pack (2.1 fl oz )
Pedialyte
Electrolyte Solution Pops Variety Pack –
2.1 fl oz
x
16 pack
129
$6.49
Pickup Pickup available
Same Day DeliverySame Day Delivery available
Shipping unavailable
123456789101112
- FREE gift offerPedialyte Electrolyte Solution Grape (33.8 fl oz )
Pedialyte
Electrolyte Solution Grape –
33.8 fl oz
76
$6.99 $0.21 / oz
Buy 1, Get 1 50% OFFBuy 1, Get 1 50% OFF
FREE gift offerOpens a simulated dialog
Pickup Pickup available
Same Day DeliverySame Day Delivery available
Shipping Available
123456789101112
- FREE gift offerPedialyte Electrolyte Solution Mixed Fruit (33.
 8 fl oz )
8 fl oz )Pedialyte
Electrolyte Solution Mixed Fruit –
33.8 fl oz
48
$6.99 $0.21 / oz
Buy 1, Get 1 50% OFFBuy 1, Get 1 50% OFF
FREE gift offerOpens a simulated dialog
Pickup Pickup available
Same Day DeliverySame Day Delivery available
Shipping Available
123456789101112
- FREE gift offerPedialyte AdvancedCare Electrolyte Solution Strawberry Lemonade (33.8 fl oz )
Pedialyte
AdvancedCare Electrolyte Solution Strawberry Lemonade –
33.8 fl oz
24
$7.49 $0.22 / oz
Buy 1, Get 1 50% OFFBuy 1, Get 1 50% OFF
FREE gift offerOpens a simulated dialog
Pickup Pickup available
Same Day DeliverySame Day Delivery available
Shipping Available
123456789101112
- FREE gift offerPedialyte AdvancedCare Electrolyte Solution Blue Raspberry (33.8 fl oz )
Pedialyte
AdvancedCare Electrolyte Solution Blue Raspberry –
33.
 8 fl oz
8 fl oz23
$7.49 $0.22 / oz
Buy 1, Get 1 50% OFFBuy 1, Get 1 50% OFF
FREE gift offerOpens a simulated dialog
Pickup Pickup available
Same Day DeliverySame Day Delivery available
Shipping Available
123456789101112
- FREE gift offerPedialyte Electrolyte Solution Iced Grape (33.8 fl oz )
Pedialyte
Electrolyte Solution Iced Grape –
33.8 fl oz
20
$8.99 $0.27 / oz
Buy 1, Get 1 50% OFFBuy 1, Get 1 50% OFF
FREE gift offerOpens a simulated dialog
Pickup Pickup available
Same Day DeliverySame Day Delivery available
Shipping Available
123456789101112
Online and store prices may vary
Find what you’re looking for?YesNo
Browse your previously purchased items
Stomach Ache in Kids and Teens and What You Can Do
“My stomach hurts.” If you have children, chances are you’ve heard this before.
Stomach pain is one of the most common complaints among children and teens. It can range from mild discomfort to severe cramping, burning or nausea. While most cases aren’t serious, it’s helpful to know what can cause stomach pain and when to call a doctor.
It can range from mild discomfort to severe cramping, burning or nausea. While most cases aren’t serious, it’s helpful to know what can cause stomach pain and when to call a doctor.
Here are some of the most frequent causes of stomach problems in small children and teens:
Gas pain or indigestion is common in kids of all ages. Diet often plays a role. Carbonated drinks, such as soda may upset the stomach, especially if the child drinks through a straw. Spicy foods, beans, citrus and caffeine (including chocolate) may cause gas.
Younger kids may not know what constipation is or that it can lead to stomach pain. If your child complains of stomach pain around the belly button or the left lower side of the abdomen, ask them when they last pooped, or if they’re having problems doing it.
Too much of anything, from pizza and popcorn to Halloween candy, can cause abdominal pain. Kids often eat quickly and don’t realize they’re full until they’ve overdone it. Plus, eating too quickly can contribute to discomfort.
Lactose is a type of sugar found in milk and milk products. “In order to digest lactose properly, the body produces an enzyme called lactase,” explains Sangita Bhasin, MD, a pediatrician at Scripps Coastal Medical Center Encinitas. “People who do not have this enzyme have a condition called lactose intolerance. When they consume milk products, they may have symptoms such as abdominal cramps, gas, diarrhea or constipation.”
Milk allergy is a reaction to a protein in milk that may cause cramps. It is not the same as lactose intolerance.
When kids feel stressed or worried, they may feel abdominal pain. “Stomach aches that appear to have no apparent cause may be due to stress, especially if the pain is recurrent. But all the child knows is that their stomach hurts,” says Dr. Bhasin. “When this happens, gently ask the child if they’re worried about something and want to talk about it. There could be problems at school or with friends.”
Bacterial or viral infections can affect the stomach and may be spread between students at school or in common areas. Stomach pain is often the first symptom, usually followed within 24 hours by vomiting and diarrhea.
Stomach pain is often the first symptom, usually followed within 24 hours by vomiting and diarrhea.
If your child complains of severe, constant pain in the low right side of the abdomen and even slight movement is painful, appendicitis may be to blame. Appendicitis is more common in older children and teens; it is unusual in children under age 5.
Most causes of stomach pain don’t require medical care, but do call your child’s doctor right away if any of the following occur:
- Pain on the lower right side is severe and constant, which may indicate appendicitis
- Pain is severe and lasts more than an hour
- Pain is constant and lasts more than two hours
- Your child has a fever and/or is vomiting
- You see blood in your child’s stool
- Your baby is younger than 12 months
“It’s always better to err on the side of caution,” says Dr. Bhasin. “If you’re concerned about your child’s stomach pain, call the doctor.”
Most stomach aches won’t last more than an hour or two, and often you can help your child feel better by trying these tips:
- Have your child lie down and rest.

- Place a warm compress or heating pad on their stomach.
- Gently massage your child’s belly, which can help with gas and indigestion.
- Give small sips of water.
- Check with your doctor before giving any over-the-counter medication. Ibuprofen, for example, can further upset the stomach.
- If indigestion occurs often, keep a food diary and look for links between certain foods and stomach pain.
Finally, if stomach aches are a frequent problem, talk with your pediatrician. You may be able to work together to identify the cause and make changes to help your child feel better.
Interesting facts
For the most comfortable viewing of the site, please turn on
JavaScript in browser settings
What to give a child if his stomach hurts
Complaints about discomfort in the tummy is something that almost every mother encounters and what new parents are very afraid of. This is quite understandable, because the baby is suffering a lot, crying, and with babies it is not always clear right away what the reason is.
This is quite understandable, because the baby is suffering a lot, crying, and with babies it is not always clear right away what the reason is.
Therefore, it is very important theoretically to prepare well, to know as much as possible about the problems that may arise with digestion at different stages of growing up, in order to understand how to act correctly in a given situation.
In our article, we will talk about what can be given to a child from the stomach if it hurts, in what situations it is absolutely impossible to give anything, we will understand the possible causes of this condition and consider the correct actions of parents depending on the specific situation.
Why pain can occur
A similar problem can be encountered at any age. But in children, especially in the first year of life, such a nuisance happens much more often due to the fact that their enzyme system and gastrointestinal tract are not yet fully formed.
Various conditions can lead to the appearance of unpleasant and painful sensations – from an improper diet to functional disorders of the internal organs. Consider the most common reasons.
Neonatal colic
Young parents are often lost and cannot understand why the baby is crying all the time. Colic occurs at the age of 2 months and may continue throughout the first year of life. At the same time, the baby is very worried, tightens his legs, his abdominal wall is tense.
Such states should not be allowed to last long, as prolonged crying can provoke the appearance of a hernia. In this case, you can help the newborn by giving carminatives. Among folk recipes, dill water is the most famous. You can buy it at a pharmacy, but it’s also easy to cook it yourself using dill seed. Of the medications, pediatricians recommend Plantex, Espumizan and others.
However, it is worth remembering that these are medicines and it is not worth giving them to a child as a drink or for prevention.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pepto-bismol-and-kids-2634641-FINAL1-77efdb7f4e1240f5afc851cb48f6cc55.jpg) In addition, you can save the baby from torment without resorting to pills at all.
In addition, you can save the baby from torment without resorting to pills at all.
To do this, you should perform a light massage in a clockwise direction, put the crumbs on your stomach and calmly pat on the back. Mom is advised to reconsider her diet and exclude all foods that can lead to increased gas formation in the baby’s intestines.
Signs of poisoning
Children are more susceptible to the quality of foods, as their digestive system is more sensitive. Therefore, what an adult eats without consequences can lead to indigestion in children.
Signs of poisoning are:
- diarrhea;
- vomiting;
- temperature increase;
- lethargy, weakness, apathy;
- loss of appetite.
In the event of all these symptoms, we recommend calling an ambulance, especially when a child under three years of age falls ill. Before the arrival of the doctor, it is often necessary to give the baby water. This is very important, because children develop dehydration very quickly, which only aggravates the situation. To do this, you can bring electrolyte-salt solutions, which are sold in pharmacies, such as Regidron. Giving such remedies to children for abdominal pain, if their cause is poisoning, costs a tablespoon, which will avoid repeated vomiting in the child.
This is very important, because children develop dehydration very quickly, which only aggravates the situation. To do this, you can bring electrolyte-salt solutions, which are sold in pharmacies, such as Regidron. Giving such remedies to children for abdominal pain, if their cause is poisoning, costs a tablespoon, which will avoid repeated vomiting in the child.
If you are sure that the state of the child will allow you to cure it on your own, then the general scheme will be as follows:
- Rinse the stomach with a large drink of 1.5 liters, then induce vomiting.
- Give enterosorbents inside (the simplest and most famous is activated carbon at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight, also Polysorb, Smecta, Enterosgel).
- Provide plenty of fluids.
- Give a cleansing enema if necessary.
It is worth remembering that the same symptoms can be with an intestinal infection and with other pathologies, so it would still be more correct to invite a specialist for an accurate diagnosis.
Diarrhea and constipation: what to give a child when he has a stomachache
Diarrhea can develop due to many diseases – gastroenteritis, poisoning, intestinal infections. In each case, you need to carry out your own treatment.
Constipation is considered a condition when there was no stool for more than two days. In this case, not only the period between bowel movements often increases, but the nature of the discharge also changes: the feces become denser, the emptying process causes discomfort. You can help the child with this by using microclysters. Young children are not recommended to give laxatives by mouth.
Irregular stools, alternating diarrhea with constipation indicates the development of diseases in the baby’s intestines.
Association of pain localization with the pathological process
With different diseases, discomfort manifests itself in different ways. Depending on where exactly they are localized and its nature, one can make an assumption about a particular pathology.
Right upper abdomen . Dull pain in this area, combined with fever up to 39 C, mucous diarrhea, nausea, almost certainly indicates appendicitis. In this case, you should immediately contact the ambulance, because surgery may be required. In addition, pain on the right side may indicate liver pathology.
Left hypochondrium . Unpleasant sensations here indicate problems with the pancreas. If soreness occurs after physical exertion, the work of the diaphragm may be impaired.
Center . Usually, pains near the navel indicate problems in the small and large intestines. This is often found in teenagers who do not watch their diet and eat a lot of junk food and fast food. If such symptoms are accompanied by fever, acute poisoning is possible.
Boca. When discomfort in the flanks is accompanied by fever and when pressure is applied to problem areas, the pain radiates to the back, inflammation of the kidneys most likely developed. This is an occasion for immediate medical attention.
This is an occasion for immediate medical attention.
“Acute abdomen”. A condition common in preschoolers. At the same time, the abdominal wall is strongly strained, nausea may appear and the temperature rises. The cause of this disease are chronic diseases of the digestive tract, for example, biliary dyskinesia.
Penetrating pain indicates that the nerve endings of the peritoneum are irritated, i.e. developed peritonitis. This happens with a perforating ulcer, rupture of the appendix, intestinal obstruction. In this case, the baby takes a forced position, turns pale, cold sweat may come out. Emergency ambulance in this case is the only right decision.
Attention! Keep in mind that you should not give a child with acute pain in the abdomen with a rise in temperature, tension in the abdominal muscles and the appearance of nausea, no drugs! This can blur the clinical picture, make it difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis and force him to spend precious time, which takes minutes in acute processes.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/severe-stomach-pain-when-to-go-to-the-er-19452821-5c869d9446e0fb00011366d7.png)
How to relieve pain in the gastrointestinal tract in a child: first aid and drugs for the stomach for children
In conditions that do not cause severe anxiety, you can and should provide first aid to the baby yourself.
In this regard, in the home first aid kit of each parent, there should be special medicines for children from abdominal pain in a child, which, if necessary, can be used to relieve symptoms of discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract in children. They can be divided into groups:
- carminative;
- absorbents;
- prebiotics;
- laxative;
- antipyretic;
- antispasmodics.
Neobutin is a new, but already proven clinically effective remedy.
Neobutin eliminates various manifestations of abdominal pain: spasm, colic, bloating in 20 minutes, and with systematic use it normalizes the motility of the gastrointestinal tract.

 99strike through
99strike through 8 fl oz )
8 fl oz )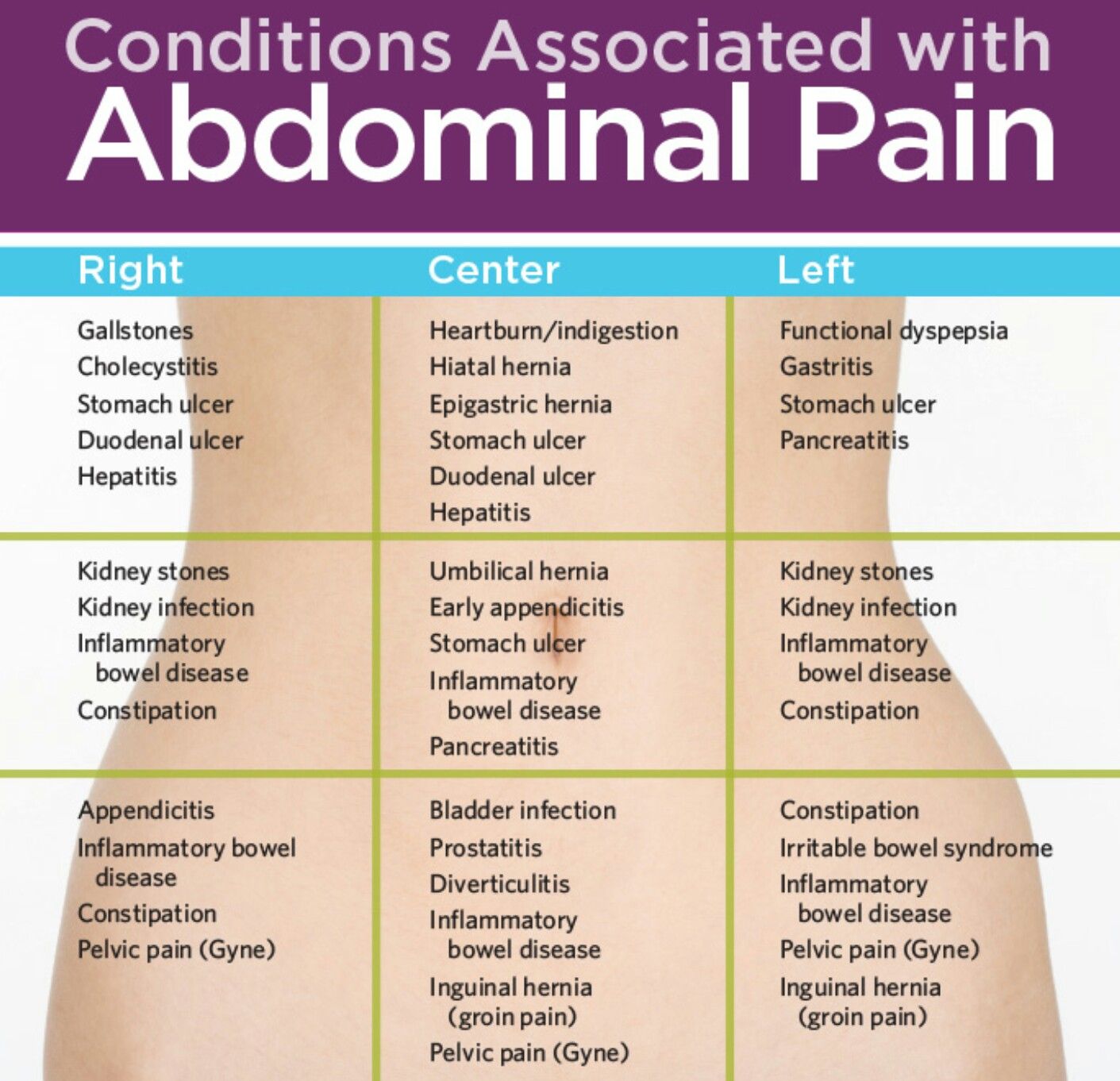 8 fl oz
8 fl oz