Sick from a tick bite. Tick Bites: Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment of Tickborne Illnesses
What are the common symptoms of tick bites. How can you prevent tick bites and associated illnesses. What should you do if you find a tick on your body. How are tickborne diseases diagnosed and treated.
Understanding Ticks: Nature’s Tiny Blood-Sucking Arachnids
Ticks are small arachnids closely related to spiders, but with a crucial difference: they feed on blood. Unlike their web-spinning cousins, ticks have evolved to become efficient parasites, capable of transmitting a variety of diseases to humans and animals.
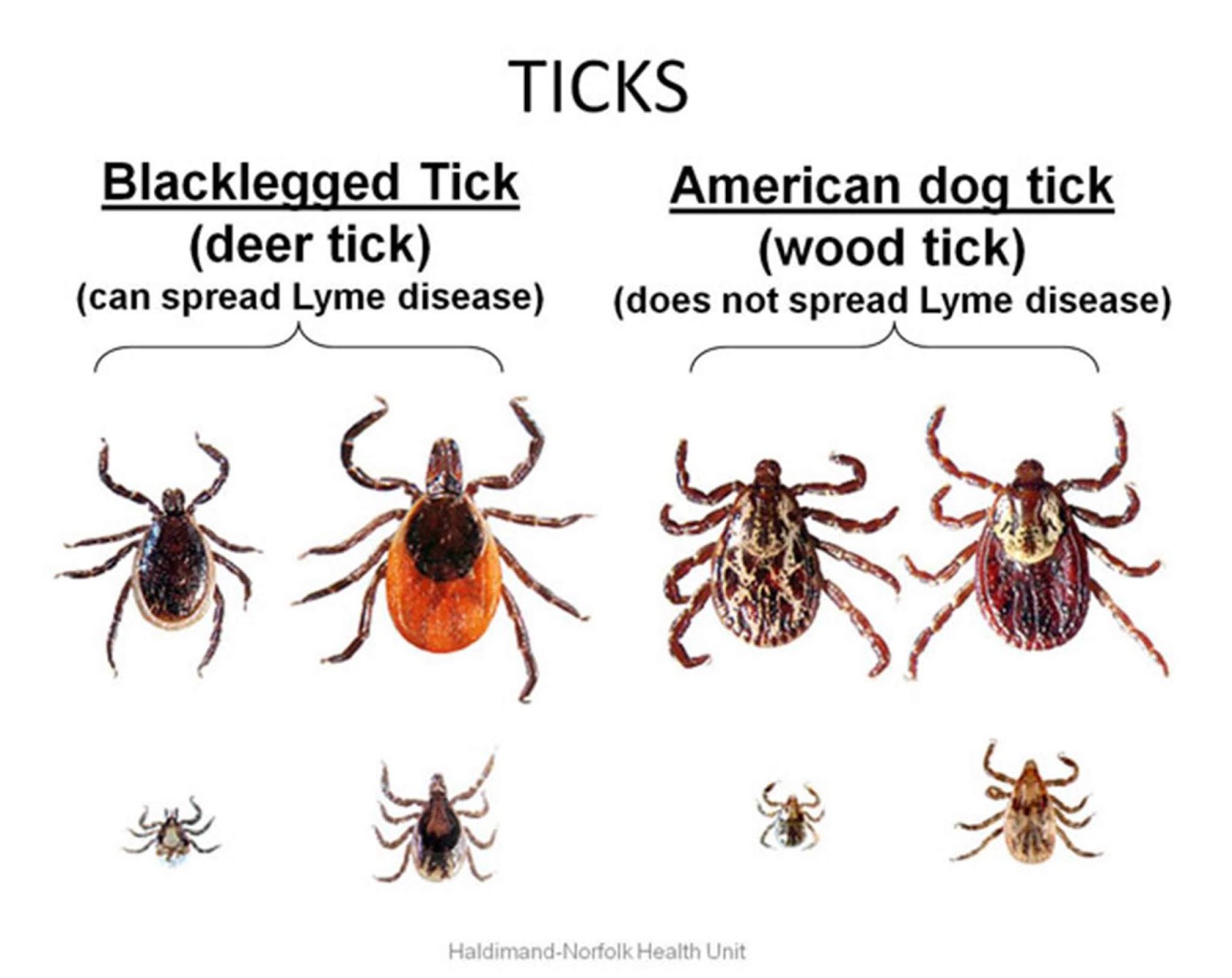
These tiny creatures possess eight legs and range in size from a minuscule poppy seed to a more noticeable pencil eraser. The most common disease-carrying tick in Illinois is the blacklegged tick, also known as the deer tick. Its diminutive size often leads to it being mistaken for a freckle or speck of dirt on the skin.
Tick Habitats and Feeding Habits
Ticks thrive in environments close to the ground, particularly in areas with tall grass, shrubs, and fallen leaves. They employ a clever hunting technique called “questing,” where they perch on the tips of vegetation, waiting to latch onto passing animals or humans.

Their diet consists solely of blood, which they obtain by burrowing their feeding parts into the skin of their host. Interestingly, tick bites are often painless, making them difficult to detect immediately.
The Hidden Dangers of Tick Bites
While not all tick bites lead to illness, these tiny arachnids can transmit a variety of pathogens that cause serious diseases. The risk of infection increases the longer a tick remains attached to its host.
Common Tickborne Diseases
- Lyme disease
- Anaplasmosis
- Babesiosis
- Human monocytic ehrlichiosis
- Tularemia
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Colorado tick fever
- Relapsing fever
These diseases can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild flu-like illness to severe, life-threatening conditions. Early detection and treatment are crucial for managing tickborne illnesses effectively.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Tick Bites and Tickborne Illnesses
Identifying the signs of a tick bite or a resulting infection is essential for prompt treatment. While many tick bites may not cause any noticeable symptoms, it’s important to be vigilant for potential reactions or signs of illness.
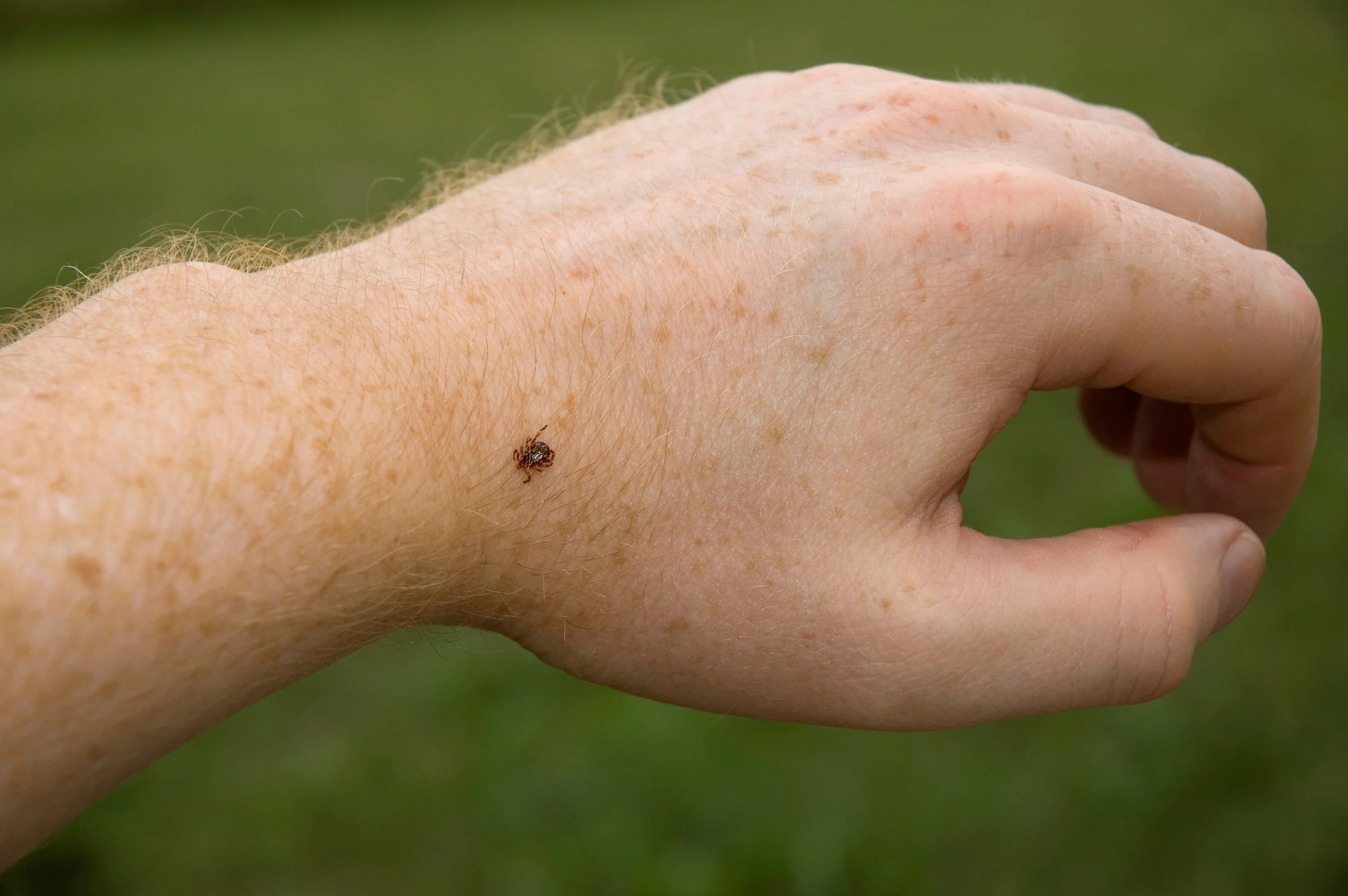

Immediate Reactions to Tick Bites
Some people may experience localized skin reactions at the site of a tick bite, including:
- Raised areas
- Lumps
- Granulomas (small areas of inflammation)
Symptoms of Tickborne Illnesses
If you develop any of the following symptoms within 30 days of a tick bite or potential exposure to ticks, seek medical attention:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Skin rash (particularly the bullseye rash associated with Lyme disease)
In rare cases, tick bites can cause paralysis due to a toxin in the tick’s secretions. This condition is separate from infections and typically resolves once the tick is removed.
Preventing Tick Bites: Strategies for Outdoor Enthusiasts
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce your risk of encountering ticks and contracting tickborne illnesses. By implementing these strategies, you can enjoy outdoor activities with greater peace of mind.
Personal Protection
- Use insect repellents containing DEET on exposed skin
- Treat clothing and gear with products containing 0.5% permethrin
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants
- Tuck pants into socks to create a barrier
- Wear light-colored clothing to make ticks more visible
Environmental Awareness
- Stick to the center of trails when hiking
- Avoid areas with tall grass and dense vegetation
- Conduct thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors
- Shower within two hours of coming indoors
Proper Tick Removal Techniques
If you discover a tick attached to your skin, it’s crucial to remove it promptly and correctly to minimize the risk of disease transmission. Follow these steps for safe tick removal:

- Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible
- Pull upward with steady, even pressure
- Avoid twisting or jerking the tick, which can cause the mouth-parts to break off and remain in the skin
- After removing the tick, thoroughly clean the bite area and your hands with rubbing alcohol, an iodine scrub, or soap and water
- Dispose of the live tick by submersing it in alcohol, placing it in a sealed bag/container, wrapping it tightly in tape, or flushing it down the toilet
Never crush a tick with your fingers, as this can release potentially infectious fluids.
Diagnosing and Treating Tickborne Illnesses
If you suspect you may have contracted a tickborne illness, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly. Diagnosing these diseases can be challenging, as symptoms often mimic other common illnesses.
Diagnostic Process
Healthcare providers typically use a combination of the following to diagnose tickborne illnesses:
- Detailed medical history, including recent outdoor activities and potential tick exposures
- Physical examination
- Blood tests to detect antibodies or genetic material from infectious agents
- In some cases, analysis of cerebrospinal fluid or tissue samples
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for tickborne illnesses varies depending on the specific pathogen involved. However, most bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics. Early treatment is crucial for preventing complications and improving outcomes.

Common antibiotics used for tickborne diseases include:
- Doxycycline
- Amoxicillin
- Cefuroxime axetil
The duration of treatment can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the disease and its severity.
Protecting Your Pets from Ticks
Our furry companions are also susceptible to tick bites and tickborne diseases. As responsible pet owners, it’s essential to take steps to protect them from these parasites.
Tick Prevention for Pets
- Use veterinarian-approved tick preventives (collars, topical treatments, or oral medications)
- Regularly check your pets for ticks, especially after outdoor activities
- Keep lawns mowed and remove leaf litter to reduce tick habitats around your home
- Consider creating a buffer zone between wooded areas and your yard using wood chips or gravel
Where to Check Your Pet for Ticks
Pay close attention to these areas when examining your pet for ticks:
- In and around the ears
- Around the eyelids
- Under the collar
- Under the front legs
- Between the back legs
- Between the toes
- Around the tail
If you find a tick on your pet, remove it carefully using the same techniques described for human tick removal. Consider consulting your veterinarian if you have concerns about tickborne illnesses in your pet.

The Ecological Role of Ticks and Future Challenges
While ticks pose significant health risks to humans and animals, they play an important role in many ecosystems. Understanding their ecological function and the challenges posed by changing environments can help us develop more effective strategies for tick management and disease prevention.
Ticks in the Ecosystem
Ticks serve as a food source for various animals, including birds, reptiles, and small mammals. They also play a role in regulating wildlife populations by transmitting diseases that can control animal numbers naturally.
Climate Change and Tick Populations
Climate change is altering tick habitats and behaviors, potentially leading to:
- Expanded geographical ranges for certain tick species
- Longer active seasons in temperate regions
- Changes in host-parasite relationships
- Increased prevalence of tickborne diseases in new areas
These changes underscore the importance of ongoing research and surveillance to monitor tick populations and associated disease risks.
Emerging Tickborne Diseases
Scientists continue to discover new pathogens transmitted by ticks. Recent examples include:
- Bourbon virus
- Heartland virus
- Powassan virus
These emerging diseases highlight the need for continued vigilance and research in the field of tick-borne illnesses.
Advancements in Tick Control and Disease Prevention
As our understanding of ticks and tickborne diseases grows, researchers are developing innovative approaches to prevent tick bites and reduce disease transmission.
Novel Tick Control Methods
- Biological control using tick-parasitic fungi
- Gene drive technologies to reduce tick populations
- Development of anti-tick vaccines for humans and animals
- Landscape management techniques to create tick-unfriendly environments
Improved Diagnostic Tools
Advances in molecular biology and immunology are leading to more accurate and rapid diagnostic tests for tickborne diseases. These include:
- Multiplex PCR assays capable of detecting multiple pathogens simultaneously
- Next-generation sequencing for identifying novel tick-borne pathogens
- Point-of-care tests for rapid diagnosis in clinical settings
These developments promise to improve our ability to diagnose and treat tickborne illnesses more effectively in the future.

Public Health Initiatives
Many public health organizations are implementing comprehensive tick management programs that include:
- Enhanced surveillance of tick populations and associated diseases
- Community education and outreach programs
- Collaborative research efforts between academic institutions, government agencies, and private sector partners
- Development of predictive models to forecast tick activity and disease risk
By combining these various approaches, we can work towards reducing the impact of ticks and tickborne diseases on human and animal health.
Don’t Let a Tick Make You Sick
Download Flyer
Download Flyer (en Español)
What is a tick?
Ticks are small bugs that are related to spiders. Like spiders, they have 8 legs, but they don’t spin webs like spiders do. There are many kinds of ticks that can make you sick, but the most common tick in Illinois that can make you sick is the blacklegged tick (also called a deer tick). Blacklegged ticks are so tiny they can be mistaken for a freckle or a speck of dirt on your skin.
Where do ticks live?
Ticks live close to the ground where there is tall grass, shrubs, and leaves. They wait on tips of tall grass and shrubs and grab on to an animal or human when they walk by. You may come in close contact with ticks when doing outdoor activities in areas ticks live, such as camping, hiking, fishing, mushroom hunting, or walking your dog.
What do ticks eat?
Unlike spiders that get their food from eating bugs, ticks get their food from drinking blood from the animals and humans they bite. Tick bites don’t usually hurt, so most people don’t notice when they have been bitten.
Tick bites don’t usually hurt, so most people don’t notice when they have been bitten.
Can a tick bite make me sick?
Tick bites can make people sick, but there are some things you can do to decrease your chances of getting sick after a tick bite.
What do I do if I see a tick on me?
Tell your parents or another adult right away. They can use tweezers to pull the tick off. Once the tick is removed, be sure to wash the area of the bite with soap and water or disinfectant.
What if I get sick after a tick bite?
If you get a fever, skin rash, headache, sore muscles or feel really tired up to 30 days after a tick bite or being in an area where ticks live, tell your parents. They should call your doctor to see if you need to be tested for a tick illness and if you need medicine.
How can I keep ticks away from me?
When you go outside, wear insect repellant that has DEET and stay out of wooded areas and places with tall grass and weeds where ticks live.
If you go where ticks live, wear long sleeves and long pants and tuck your pants in your socks and walk in the center of trails. When you come back inside, take a bath or shower and let your parents check you for ticks.
Your pets can also get ticks, so always check them when they come in from outside.
Where to Check for Ticks
- In and around the hair
- In and around the ears
- Under the arms
- Inside the belly button
- Around the waist
- Between the legs
- Back of the knees
Where to Check Your Pet for Ticks
- In and around the ears
- Around the eyelids
- Under the collar
- Under the front legs
- Between the back legs
- Between the toes
- Around the tail
Tick Bites – Harvard Health
What is it?
Ticks are tiny, biting arachnids that feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals, including humans. They burrow painlessly into the skin with their feeding parts, bite, draw blood and eventually drop off when they become engorged with blood. Only the feeding parts are inserted into the skin. The body, which is dark in color and ranges from the size of a poppy seed to a pencil eraser, remains visible on the skin surface or scalp. Ticks swell and turn bluish-gray when filled with blood. Most tick bites in the United States involve hard ticks (Ixodidae), which have been increasing in number since the middle 1900s.
Only the feeding parts are inserted into the skin. The body, which is dark in color and ranges from the size of a poppy seed to a pencil eraser, remains visible on the skin surface or scalp. Ticks swell and turn bluish-gray when filled with blood. Most tick bites in the United States involve hard ticks (Ixodidae), which have been increasing in number since the middle 1900s.
Secretions from the tick’s feeding parts can cause skin reactions, such as raised areas, lumps, and growths called granulomas. Fever and paralysis also may develop after tick bites, although paralysis is rare. Paralysis is due to a toxin transmitted from the tick’s secretions, not due to an infection. However, ticks can be infected with bacteria, viruses, or protozoa, and these organisms can be transmitted from the tick to the host (the animal or person) as the tick feeds, causing disease.
Tick-borne infectious diseases include:
- Lyme disease
- Anaplasmosis (formerly known as human granulocytic ehrlichiosis)
- Babesiosis
- Human monocytic ehrlichiosis
- Tularemia
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Colorado tick fever
- Relapsing fever
Ticks live in tall grass and in wooded areas, particularly cool, moist, mature woods with thick undergrowth. They also can be found at the edges of woods near lawns or fields, but rarely in lawns, which are too dry and hot. Ticks wait in the underbrush for an animal or human to brush by, and then grasp the fur or skin and crawl up the leg. They don’t fly, jump or drop from trees. They wander the body for 30 minutes to an hour before inserting their feeding parts into the skin.
Symptoms
Most tick bites do not cause any symptoms. However, the following symptoms can develop as a reaction to tick secretions:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
Skin reactions include:
- Pus-filled bumps
- Hardened skin elevations
- Nodules (granulomas) that, in rare cases, can grow large enough to require surgical removal
Tick paralysis is relatively rare. Paralysis begins in the feet and legs and gradually works its way to the upper body, arms and head over a period of hours or days. Once the tick is removed, a person with tick paralysis will recover completely. If the tick is not removed, the person can die if the muscles that control breathing are paralyzed.
Paralysis begins in the feet and legs and gradually works its way to the upper body, arms and head over a period of hours or days. Once the tick is removed, a person with tick paralysis will recover completely. If the tick is not removed, the person can die if the muscles that control breathing are paralyzed.
Symptoms associated with tick-borne infections differ depending on the type of infection. Common symptoms are as follows:
- Lyme disease – A variety of symptoms can occur, including a flulike illness, an expanding red rash that may include a central clear area (a bull’s-eye rash), arthritis, heart rhythm problems, difficulties in thinking or perception, and neuropathies (pain or changes in sensation as a result of nerve damage).
Human monocytic ehrlichiosis – Symptoms ranging from mild to severe can involve many organ systems.
 Common symptoms include high fever, headache, fatigue, nausea, weight loss and a spotted rash. Patients with weak immune systems can develop a fatal, overwhelming infection. Breathing difficulties and mental changes may also occur.
Common symptoms include high fever, headache, fatigue, nausea, weight loss and a spotted rash. Patients with weak immune systems can develop a fatal, overwhelming infection. Breathing difficulties and mental changes may also occur.Anaplasmosis – Symptoms ranging from mild to severe include high fever, headache, a general sick feeling (malaise), achy muscles (myalgia), nausea, vomiting, cough, stiff neck and confusion. Less than 10% of people with this disease will develop a rash.
Colorado tick fever – Flulike symptoms include fever and chills, severe headache, achy muscles (myalgia), stiff neck, light intolerance and, in some cases, a spotted rash.
Babesiosis – Many people will not have any symptoms. Others develop fatigue, fever, drenching sweats, nausea, vomiting, headache, muscle aches, joint aches and jaundice.
 Patients with suppressed immune systems may develop severe disease.
Patients with suppressed immune systems may develop severe disease.Tularemia – The symptoms of this disease vary widely. Some people do not have any symptoms, but this disease also can be severe, causing septic shock and death. Common symptoms include fever, chills, headache and a general sick feeling (malaise). Many people also develop a single, red ulcerated lump with a central scab and tender, swollen lymph nodes in the area. A small number of patients develop pneumonia.
Rocky Mountain spotted fever – Symptoms include fever, headache, a spotted rash on wrists and ankles, and a patchy rash on arms and legs. Muscle aches (myalgia), nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain are also common.
Diagnosis
If you see your doctor for a tick bite, you will be asked about the size of the tick, whether it was attached to your skin and how long you think it had been attached. Your doctor will examine your skin for rashes and ask you about any symptoms that could suggest that you have developed a tick-borne infection. No further diagnostic tests are necessary unless you develop symptoms. If you develop symptoms that suggest a tick-borne illness, your physician will order a variety of blood tests to determine the cause.
Your doctor will examine your skin for rashes and ask you about any symptoms that could suggest that you have developed a tick-borne infection. No further diagnostic tests are necessary unless you develop symptoms. If you develop symptoms that suggest a tick-borne illness, your physician will order a variety of blood tests to determine the cause.
Expected duration
A tick bite can cause many different tick-borne infections. How long each illness lasts depends on the infecting organism. In general, the tick bite itself does not cause any symptoms, although some people may develop fever, headache, nausea and a general sick feeling caused by tick secretions. These symptoms usually go away within 24 to 36 hours after the tick is removed.
Tick-induced paralysis begins in the legs five to six days after the tick has attached to the skin, and it progresses to complete paralysis over several days. Paralysis begins to improve within a few hours of removing the tick, and complete recovery takes several days.
The organisms that cause Lyme disease and babesiosis rarely are transmitted to the person or animal if ticks are removed within the first 24 hours after they attach and before they become engorged.
Prevention
To prevent tick bites in tick-infested areas, take the following precautions:
- When in the woods, walk on cleared trails. Avoid walking through tall grass and low brush in wooded areas.
- Wear light-colored clothing covering both the arms and legs.
- Tuck pant legs into socks.
- Treat clothing and skin with tick repellents containing diethyltoluamide (DEET), or use the pesticide permethrin on clothing (but not skin).
- Thoroughly check yourself, children and pets for ticks after spending time in tick-infested areas. Remember to check the scalp. If one tick is found, check for more.
Treatment
When a tick is discovered on the skin or scalp, it should be removed immediately to avoid a skin reaction and to reduce the likelihood of developing a tick-borne infectious disease.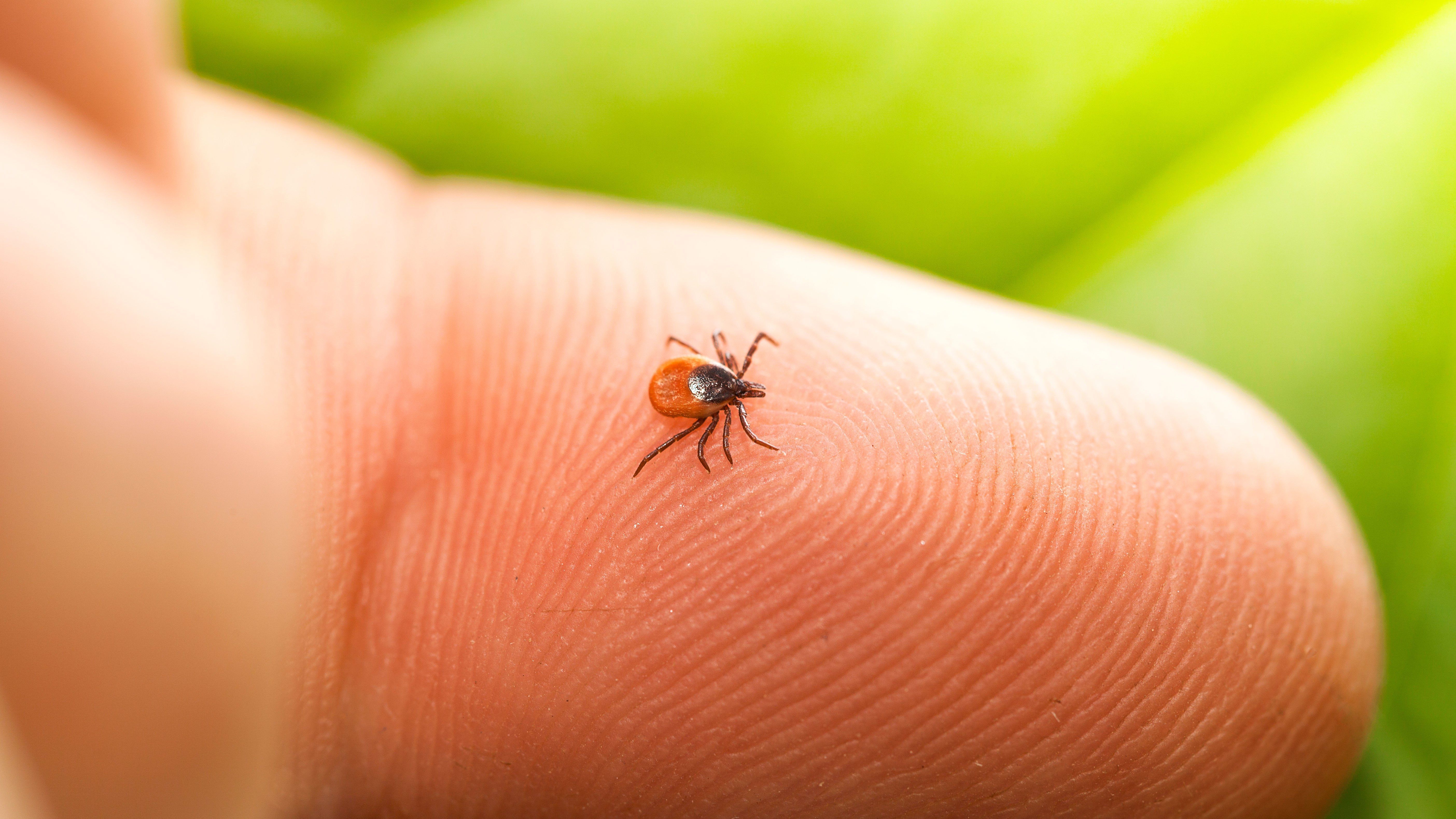 Grasp the head of the tick with a pair of flat or curved forceps or tweezers held as close to the skin as possible. Avoid squeezing the tick. Gently pull the head of the tick away from the skin without twisting. The bite should be cleaned with soap and water. Save the tick in a container with a tight-fitting lid.
Grasp the head of the tick with a pair of flat or curved forceps or tweezers held as close to the skin as possible. Avoid squeezing the tick. Gently pull the head of the tick away from the skin without twisting. The bite should be cleaned with soap and water. Save the tick in a container with a tight-fitting lid.
For people in areas where Lyme disease rates are high, one dose of doxycycline can prevent disease if taken within three days of a tick bite. So for those at highest risk, early treatment may be appropriate. This is especially important if the tick was engorged, as this suggests it was attached for long enough to transmit the bacterium that causes Lyme disease.
When to call a professional
Seek medical attention if a tick has buried itself deep in the skin and you cannot remove it or if you find an engorged tick on your skin and are living in or visiting an area where Lyme disease is a risk. Fever and flulike symptoms require medical attention if you know you’ve recently been bitten by a tick or if the symptoms are accompanied by a skin rash, particularly the bull’s-eye rash characteristic of Lyme disease. Muscle weakness or paralysis requires immediate medical attention.
Fever and flulike symptoms require medical attention if you know you’ve recently been bitten by a tick or if the symptoms are accompanied by a skin rash, particularly the bull’s-eye rash characteristic of Lyme disease. Muscle weakness or paralysis requires immediate medical attention.
Prognosis
If no infectious organisms have been transmitted by the tick, you should recover from symptoms within a day or two. The outlook for specific tick-borne illnesses varies.
Additional info
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov/ncezid/dvbd/index.html
Tick bite. Tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. Symptoms, prevention and treatment
A carefree holiday in nature can be overshadowed by a tick bite.
In the hot weather of the spring-summer season, ticks wait for their prey, sitting in the grass or bushes. When a person appears, insects move from foliage to clothes, move along it in search of an open area of \u200b\u200bthe body to which they can attach. To bite, ticks choose warm, moist areas of the skin where the blood vessels are not deep (neck, head, armpits, buttocks, the area between the shoulder blades, earlobes, calf muscles).
To bite, ticks choose warm, moist areas of the skin where the blood vessels are not deep (neck, head, armpits, buttocks, the area between the shoulder blades, earlobes, calf muscles).
When bitten, ticks inject an anesthetic into the skin of the victim, so this goes unnoticed.
After saturation, the males quickly fall off the person, and the females can stay on their prey for several more days, having managed to lay up to 2 thousand eggs and increase to 10 mm in diameter.
Attention! Very often, ticks are carriers of such dangerous diseases as systemic borreliosis and tick-borne viral encephalitis!
1
Tick Bite Help
2
Tick Bite Help
3
Tick Bite Help
90 032 Symptoms of encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis is a seasonal viral disease. Encephalitis enters the human body after the bite of an infected tick or when drinking milk from infected cows or goats.
On average, clinical signs of the disease appear one month after the encephalitic tick bite.
Depending on the manifestation of symptoms, tick-borne encephalitis develops in 3 forms:
- focal form – observed in 20% of patients;
- febrile form – occurs in 50% of patients;
- meningeal form – in 30%.
With focal form of tick-borne encephalitis (the most severe form of the disease), the infection penetrates into the substance of the spinal cord and brain. The following signs of a tick bite are observed: chills, convulsions, a strong increase in temperature (above 40 degrees), the appearance of lethargy and drowsiness.
Depending on which part of the brain or spinal cord is affected, symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, cardiac and respiratory disorders, paralysis and paresis of the muscles of the shoulder and neck, impaired voluntary movements, etc. may be present.
may be present.
Febrile encephalitis lasts up to 10 days. The disease is undulating in nature, then subsiding, then reappearing in the form of a fever. But weakness, palpitations and sweating persist for a long time.
Menigeal shape . With this form of the disease, inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord and brain occurs. Within 2 weeks, the patient has a severe headache (in which pills do not help), neck muscle tension, vomiting, fever, fever.
Systemic tick-borne borreliosis (or Lyme disease)
Lyme disease was first identified in the US city of Lyme in 1975.
Borreliosis agent – the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which belongs to the spirochetes. The causative agent of the disease enters the cells of the body and remains dormant for 10 years. This explains the chronic nature of the disease. A patient with borreliosis is not contagious for others, since the infection is transmitted to a person only through a tick bite.
Symptoms of borreliosis
The disease begins 1-2 weeks after infection. In its development, the disease goes through 3 stages. Moreover, stages 1-2 are considered early, and stage 3 is chronic.
Stage 1 borreliosis lasts about a month. Signs of a tick bite resemble acute respiratory infections. A person has a fever, general malaise, body aches, muscle pain and weakness appear.
The main symptom of stage 1 is the appearance near the bite of a round red spot (erythema) with a diameter of 15-20 cm. Over time, the spot may increase in size.
Stage 2 disease lasts for 6 months. Skin lesions in the form of ring-shaped elements, urticaria are characteristic.
Infection spreads throughout the body through the blood and lymph circulation, resulting in damage to the nervous system, joints or heart.
With inflammation of the cardiovascular system, severe arrhythmias, pericarditis and myocarditis (dizziness, palpitations, chest pain and shortness of breath) are observed. There may also be a decrease in sensitivity.
There may also be a decrease in sensitivity.
Stage 3 borreliosis . The disease becomes chronic. The consequences of borreliosis are heart disease, severe inflammation of the joints, combined with extensive damage to the nervous system.
If a disease such as borreliosis is left untreated, it can lead to disability and even death.
With the correct diagnosis of borreliosis and adequate antibiotic therapy, there is a chance for recovery.
1
Tick Bite Help
2
Tick Bite Help
3
Tick Bite Help
First Aid in case of a tick bite
Immediately after a tick bite, try to go to the nearest emergency room. A qualified doctor will quickly and skillfully save you from an insect.
In specialized hospitals, if necessary, according to indications, emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis is carried out by administering immunoglobulin or another antiviral drug in the first three days after a tick bite. In order to prevent tick-borne borreliosis, a course of antibiotic treatment is carried out.
In order to prevent tick-borne borreliosis, a course of antibiotic treatment is carried out.
If the visit to the doctor is delayed for any reason, you can try to remove it yourself. However, it often happens that during self-extraction, the insect breaks in half, and the head remains in the wound.
It is necessary, by making counterclockwise movements, to “twist” the insect out of the skin. Keep the tick as close to the skin as possible to prevent tearing of the abdomen. In this case, the fingers must be wrapped with a bandage or gauze.
You can try to remove the tick with a thread: wrap the proboscis of the tick as close to the skin as possible and, performing swinging movements, slowly pull the insect out.
After the manipulations, the bite site must be treated with a solution of iodine or alcohol. The tick must be closed in a vessel with a tightly screwed lid and brought to the laboratory for examination for the presence of the borreliosis virus and tick-borne encephalitis.
What you need to know about a tick bite?
Even if you manage to get rid of a tick, pay attention to changes in your health. If you have a fever, a change in blood pressure or severe headaches, you must urgently make an appointment with an infectious disease specialist, take a blood test for tick-borne borreliosis and encephalitis.
In some cases, you may need to consult a cardiologist, neurologist, general practitioner, rheumatologist, infectious disease specialist.
The material was prepared with the participation of a specialist:
Kirichenko Alexey Viktorovich
Traumatologist, orthopedist
Second qualification category
Tick bite: what to do? (Sergiev Posad)
What should I do if bitten by a tick?
ATTENTION: Online consultations of doctors are available (more than 18 specialties).
A tick bite is an unpleasant situation that can lead to significant health consequences in the form of deadly complications.
The activity of parasites in nature increases in the warm season, and they can imperceptibly harm a person. Arthropods live mainly on trees, but they can also be on bushes and in the grass – they are able to adapt to different conditions.
Between the bite and the first symptoms of a lesion, a sufficiently long period of time usually passes, and the pathogens of neuroinfections have time to penetrate into the bloodstream, causing a number of irreversible changes.
The likelihood of interaction with these blood-sucking parasites makes people panic, but you should not worry without a reason – a tick bite does not mean an obligatory infection. It is important to know the precautions, as well as the diagnostic algorithm for recognizing a bite, and the immediate procedure for detecting a parasite. Early detection of the tick and timely initiation of treatment determine the success of therapeutic measures, while diagnosis in the later stages leads to difficulty in choosing a treatment, irreversible dysfunction of the central nervous system, or transition to a chronic form. It is also necessary to evaluate the benefits of vaccination and determine the feasibility of its implementation.
It is also necessary to evaluate the benefits of vaccination and determine the feasibility of its implementation.
Why are ticks dangerous?
Tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis (Lyme disease) are the main diseases that ticks can carry. This list also includes a number of other infections of the peripheral nervous system and brain. Tick-borne encephalitis is a serious disease with damage to various parts of the nervous structures, which can lead to irreversible changes in the form of paralysis or even death. Borreliosis is also characterized by a complex disorder of the nervous, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal systems. Parasites can become carriers of pathogens of hemorrhagic vasculitis – an acute viral disease in which the circulatory system is affected, causing serious complications in the form of internal bleeding.
Signs of pathology after a bite
Careful examination reveals a suspicious area of redness on the skin of exposed parts of the body – the arthropod is not able to get through clothes.![]() Initially, you may not notice the parasite, especially if it is in the hair. Local immunity initiates the appearance of hyperreactivity – a rounded spot up to 10-20 cm in diameter, which can increase. Also, a characteristic sign of infection with borreliosis is the formation of a clearly defined contour of red color, which may eventually acquire a blue-white tint. A few weeks later, a crust with cicatricial changes forms at the site where the tick has bitten.
Initially, you may not notice the parasite, especially if it is in the hair. Local immunity initiates the appearance of hyperreactivity – a rounded spot up to 10-20 cm in diameter, which can increase. Also, a characteristic sign of infection with borreliosis is the formation of a clearly defined contour of red color, which may eventually acquire a blue-white tint. A few weeks later, a crust with cicatricial changes forms at the site where the tick has bitten.
Immediately after the discovery of an arthropod on the skin, it is necessary to establish the stage of its development – the adult form is distinguished by the presence of four pairs of legs, and the nymph larva has only three pairs. It has been studied that the female needs more time to saturate with blood, and an adult can feed for several days.
Timely detection of the parasite at the stage of suction avoids a bite, however, in case of biting through the skin, it is necessary to definitely consult a doctor for observation during the incubation period of possible diseases. This period can take up to two months – the characteristics of the human blood-brain barrier determine the rate of spread of pathogenic viruses or bacteria and the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
This period can take up to two months – the characteristics of the human blood-brain barrier determine the rate of spread of pathogenic viruses or bacteria and the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
The consequences of a tick bite and signs of infection vary depending on the form of the disease and the reaction of the body, but most often appear:
- characteristic swelling and bright redness at the site of contact with the tick;
- fever;
- chills;
- general deterioration of health;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- fatigue;
- attacks of nausea;
- photophobia – an unpleasant reaction to bright daylight or artificial light;
- various rashes in the form of spots, nodules, pustules;
- shortness of breath – shortness of breath with mild exertion;
- feeling of difficulty in moving and aching in the joints;
- mood changes, emotional instability;
- increased anxiety;
- possible changes in the perception of reality in the form of hallucinations.

Initially, the symptoms of a tick bite may be mild, the skin may look without visual changes, and the signs increase later. A vivid clinical picture is typical for children, elderly patients, as well as people with chronic diseases that adversely affect immune function.
Ordinary people may not feel the signs of a tick bite at first – neuroinfections that are carried by ticks develop rather slowly. Often the progression of the disease is accompanied by fever, increased heart rate, inflammation of the lymph nodes, skin rash, itching in the place where the tick bit.
Also, often an arthropod bite causes a relatively harmless allergic reaction that has nothing to do with a serious endemic disease. It is important to consult a doctor for differential diagnosis of conditions. An allergy to a tick bite is accompanied by a bright local reaction on the skin, nasal congestion, tearing, and redness of the eyes.
Tick-borne encephalitis has a number of characteristic symptoms that are dangerous to health and even life. The onset of the disease may resemble the flu – fever, chills, aching joints and muscles appear. Deterioration of the cardiovascular system leads to interruptions in the work of the heart, arrhythmia, shortness of breath. Often patients complain of changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract – nausea and vomiting, lack of appetite, loosening of the stool.
The onset of the disease may resemble the flu – fever, chills, aching joints and muscles appear. Deterioration of the cardiovascular system leads to interruptions in the work of the heart, arrhythmia, shortness of breath. Often patients complain of changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract – nausea and vomiting, lack of appetite, loosening of the stool.
Neurological complaints may begin – episodes of changes in consciousness up to epileptic seizures. Despite the fact that different microorganisms become the causative agents of diseases, the alarming symptoms in pathologies are similar.
Consequences of non-intervention
The lack of a timely response to a tick bite can lead to the progression of the disease – a neuroinfection develops, which often leads to paralysis, meningitis, deadly complications and disabling consequences. It is important to know how dangerous a tick bite is for a person in order to respond to the problem in time.
Do-it-yourself tick removal
It is necessary to follow all the principles of the removal technique – it is necessary to remove the arthropod completely in a living state in order to maintain the possibility of diagnosing for the presence of the virus.
The classic version involves the use of tweezers as the main tool for extracting the arthropod parasite. A full-fledged reliable girth of the body prevents the main complication of manipulation – the preservation of the head of the tick in the thickness of the human skin. You should rotate his body clockwise around the axis – this avoids sudden movements in order to safely remove the whole tick. There is also a method using sewing thread – the knot is attached to the tick, and twisting is done by rotating the thread.
Contrary to popular belief, the use of oily solutions only complicates the procedure, while making it impossible to analyze the parasite for pathogenic viruses or bacteria.
If, after an attempted removal, a trace remains on the skin in the form of a dark dot, this may indicate that the arthropod’s head was not removed. You should wipe the bite site with alcohol, and then remove the remnants of the parasite.
You can also use iodine or another effective antiseptic to treat the skin. After completing the manipulations, the removed tick must be stored in a glass container with a cotton pad moistened with water. The preservation of the parasite will determine the danger of ticks to humans in the area.
After completing the manipulations, the removed tick must be stored in a glass container with a cotton pad moistened with water. The preservation of the parasite will determine the danger of ticks to humans in the area.
However, it is better to entrust this task to specialists – experienced medical workers know how to quickly and correctly get rid of a tick, then they immediately deliver the material for research to the laboratory.
Non-specific prevention of tick bites
Preventive measures must be taken when traveling to endemic zones and disadvantaged forest-steppe regions with a high risk of infection from the parasite.
The main points to reduce the likelihood of tick bites:
- vaccination before traveling to forest-steppe zones;
- maximum coverage of all parts of the body with clothing, hats, closed shoes;
- avoiding passing under trees and thick bushes;
- thorough examination of all family members for bites, including the scalp;
- treatment with special external agents that repel insects.

Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis in the Paracelsus clinic
Doctors of the Paracelsus multidisciplinary medical clinic recommend that all people at risk be vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis – people who live in endemic areas or are going to come to such areas are vaccinated. The Ministry of Health of Russia has determined the list of vaccines that are allowed for vaccination, some of them are produced by domestic companies, and several items are supplied from other countries.
The scheme of application of the vaccine:
- consultation with a general practitioner and determination of the safety of vaccination;
- the first stage of the introduction of the vaccine on a certain day;
- revaccination – after 1-2 months according to the scheme;
- the third vaccination – 12 months after the second stage of the drug administration.
Vaccination can provide a reliable protective effect to prevent infection of the nervous system and the development of complications, so this method of prevention is necessary for everyone who is more susceptible to infection by ticks.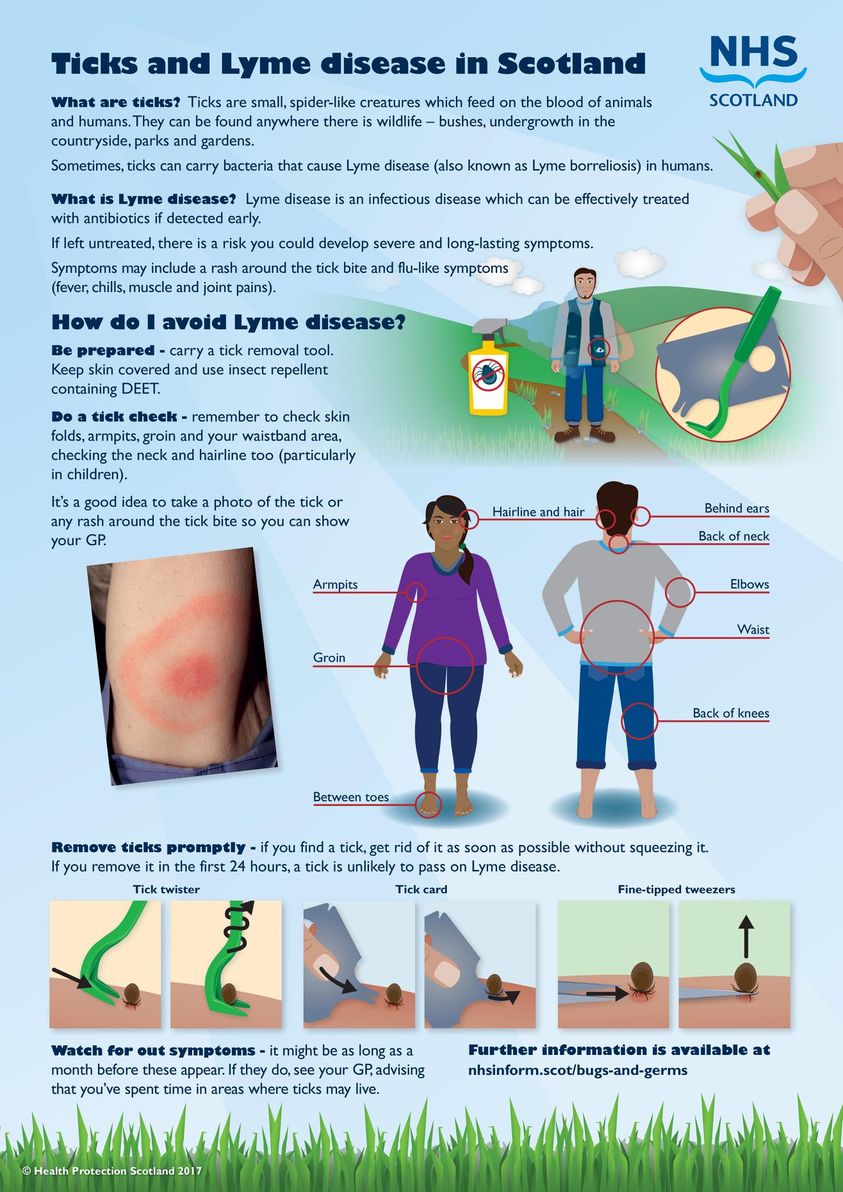
Paracelsus offers vaccination with the domestic vaccine EnceVir, which is effective against common strains of the virus that ticks carry. The Paracelsus team cares about the health of its clients, therefore, before the vaccination, everyone needs to undergo an examination by a therapist and some additional diagnostic methods to assess their general health, possible contraindications and the risk of developing complications of the vaccination.
Treatment at the Paracelsus Center
Timely access to a doctor is the key to preventing severe damage to the nervous system and internal organs, preventing serious complications and minimizing the risk of death.
Only in the conditions of a medical institution can all conditions be provided for the rapid and safe extraction of parasites with subsequent analysis of the tick, as well as a comprehensive diagnosis of the victim for the transmission of infections.
Paracelsus Medical Center is a complex clinic, which is attended by specialists from various fields of medicine. Infectionists and parasitologists of our institution know how to properly remove a tick, as well as treat the bite site. The study of a tick in order to determine the carriage of pathogens of neuroinfections is necessary to understand the further tactics of managing a victim of a bite, since changes that are noticeable during diagnosis may not yet develop in his body.
Infectionists and parasitologists of our institution know how to properly remove a tick, as well as treat the bite site. The study of a tick in order to determine the carriage of pathogens of neuroinfections is necessary to understand the further tactics of managing a victim of a bite, since changes that are noticeable during diagnosis may not yet develop in his body.
Further penetration of microorganisms into the human bloodstream causes the formation of specific antibodies that can be detected by laboratory blood tests.
Even if a long period has passed after the moment of the bite, and complaints have appeared recently, it is better to consult a doctor to exclude dangerous diagnoses and take the appropriate tests.
Also, a tick bite can cause allergic reactions, become inflamed and complicated by local infectious processes. In all such cases, a doctor’s examination is necessary with the further appointment of appropriate treatment. The use of antihistamines and local ointments quickly returns the quality of life.

 Common symptoms include high fever, headache, fatigue, nausea, weight loss and a spotted rash. Patients with weak immune systems can develop a fatal, overwhelming infection. Breathing difficulties and mental changes may also occur.
Common symptoms include high fever, headache, fatigue, nausea, weight loss and a spotted rash. Patients with weak immune systems can develop a fatal, overwhelming infection. Breathing difficulties and mental changes may also occur. Patients with suppressed immune systems may develop severe disease.
Patients with suppressed immune systems may develop severe disease.
