Spicy food and heartburn. Heartburn Triggers: Spicy Foods, High-Fat Meals, and Prevention Strategies
What foods commonly trigger heartburn. How can you prevent heartburn symptoms. Why do spicy and fatty foods often cause acid reflux. What lifestyle changes help reduce heartburn frequency.
Common Foods That Trigger Heartburn Symptoms
Heartburn is an uncomfortable condition characterized by a burning sensation in the chest, often accompanied by acid reflux. While many factors can contribute to heartburn, certain foods are known to be common triggers. Understanding which foods may exacerbate your symptoms is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Spicy Foods: A Major Culprit in Heartburn
Spicy foods are notorious for causing heartburn in many individuals. But why do spicy foods lead to this uncomfortable sensation? There are two primary reasons:
- Capsaicin, a compound found in many spicy foods, slows down digestion. This causes food to remain in the stomach for a longer period, increasing the risk of acid reflux.
- Spicy foods can irritate the esophagus directly, worsening heartburn symptoms for those already prone to acid reflux or esophageal issues.
For individuals with pre-existing conditions such as esophageal problems or ulcers, the impact of spicy foods on heartburn can be even more pronounced and immediate.

High-Fat Foods: Another Common Heartburn Trigger
High-fat foods are another category of cuisine that frequently leads to heartburn. The mechanism behind this is twofold:
- Slower digestion: Fat-rich foods take longer for the stomach to process compared to proteins and carbohydrates. This extended presence in the stomach prompts increased acid production, potentially irritating the digestive system.
- Lower esophageal sphincter relaxation: Regular consumption of high-fat foods can cause the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to relax. The LES is a group of muscles at the bottom of the esophagus that prevents stomach contents and acid from traveling upwards. When these muscles relax inappropriately, acid can enter the esophagus, causing irritation and potentially long-term damage if it occurs frequently.
Examples of high-fat foods that may trigger heartburn include fried items like breaded chicken and fish, deep-fried French fries, chicken wings, doughnuts, processed baked goods, and chips.

Specific Foods Known to Trigger Heartburn
While spicy and high-fat foods are common culprits, several specific food items are known to trigger heartburn in many individuals. It’s important to note that triggers can vary from person to person, so it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional about your specific dietary needs.
Tomatoes and Tomato-Based Products
Tomatoes and foods made from tomatoes, such as spaghetti sauce, are highly acidic. They contain both malic and citric acids, which can increase gastric acid production in the stomach. As this excess acid rises, it can back up into the esophagus, causing the characteristic burning sensation associated with heartburn.
Onions: A Hidden Heartburn Trigger
Onions, whether sautéed or caramelized, are a staple in many cuisines. However, they can be problematic for individuals prone to heartburn. Onions have the potential to relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing acid to travel from the stomach into the esophagus.
High-Fat Cheese and Its Impact on Digestion
High-fat cheese is another food that can contribute to heartburn. The high fat content slows down stomach emptying, which can increase pressure in the stomach. This pressure may force acid from the stomach into the esophagus, leading to heartburn symptoms.
Coffee: The Morning Cup That Can Cause Discomfort
For many, the day begins with a cup of coffee. However, frequent or high-quantity consumption of coffee can impact the lower esophageal muscles. The caffeine in coffee may cause these muscles to relax, allowing stomach acid to enter the esophagus and potentially trigger heartburn.
Chocolate: A Sweet Treat with Potential Side Effects
Most chocolates contain cocoa, which is rich in serotonin. While serotonin is often associated with mood improvement, it can also relax the esophageal muscles. This relaxation may lead to heartburn in susceptible individuals.
Peppermint: A Double-Edged Sword for Digestive Health
Peppermint is often touted for its ability to ease nausea and indigestion by relaxing the digestive tract. However, this same property can be problematic for people with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or those prone to heartburn. The relaxation of the lower esophageal muscles caused by peppermint can exacerbate reflux symptoms, especially in individuals with a hiatal hernia.

Understanding the Mechanics of Heartburn
To better manage heartburn, it’s crucial to understand the underlying mechanisms that cause this uncomfortable condition. Heartburn occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, a process known as acid reflux. This backflow of acid can irritate the lining of the esophagus, leading to a burning sensation in the chest or throat.
The Role of the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES)
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) plays a vital role in preventing heartburn. This ring of muscle acts as a valve between the esophagus and stomach, opening to allow food and drink to enter the stomach and closing to prevent stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus. When the LES weakens or relaxes inappropriately, it can lead to acid reflux and heartburn.
Factors That Influence LES Function
Several factors can affect the function of the LES, including:
- Certain foods and beverages
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Some medications
Understanding these factors can help individuals make lifestyle changes to reduce the frequency and severity of heartburn episodes.

Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Heartburn
While avoiding trigger foods is an essential step in managing heartburn, several lifestyle modifications can also help prevent or reduce the frequency of heartburn episodes.
Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals
Large meals can put pressure on the LES, increasing the likelihood of acid reflux. How can eating smaller, more frequent meals help prevent heartburn? By reducing the amount of food in the stomach at any given time, you decrease the pressure on the LES, making it less likely for stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
Timing Your Meals
Eating close to bedtime can increase the risk of nighttime heartburn. Why is it beneficial to eat earlier in the evening? When you lie down shortly after eating, gravity is no longer helping to keep stomach contents in place, making it easier for acid to flow back into the esophagus. Aim to eat your last meal of the day at least three hours before bedtime.
Elevate Your Upper Body While Sleeping
For individuals who experience nighttime heartburn, elevating the head of the bed can be helpful. How does this simple change make a difference? By keeping your upper body slightly elevated, you can use gravity to your advantage, making it more difficult for stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus during sleep.

Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight, especially around the abdomen, can put pressure on the stomach and LES, increasing the risk of acid reflux. How can weight loss help reduce heartburn symptoms? Losing excess weight can alleviate pressure on the stomach and LES, potentially reducing the frequency and severity of heartburn episodes.
Quit Smoking
Smoking can weaken the LES, making it easier for stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. How does quitting smoking benefit those with heartburn? Cessation of smoking can help strengthen the LES, reducing the likelihood of acid reflux and improving overall digestive health.
Natural Remedies for Heartburn Relief
While lifestyle changes and avoiding trigger foods are crucial for managing heartburn, some natural remedies may provide relief from occasional symptoms.
Chewing Gum
Chewing gum after meals can help reduce acid reflux. How does this simple act provide relief? Chewing gum stimulates saliva production, which can help neutralize stomach acid and wash it back down into the stomach.

Aloe Vera Juice
Aloe vera is known for its soothing properties, and some people find relief from heartburn by drinking aloe vera juice. How might aloe vera help with heartburn? The anti-inflammatory properties of aloe vera may help reduce irritation in the digestive tract, potentially easing heartburn symptoms.
Baking Soda
A teaspoon of baking soda mixed with water can provide quick relief from heartburn. Why is baking soda effective against heartburn? Baking soda is a natural antacid that can help neutralize stomach acid, potentially alleviating the burning sensation associated with heartburn.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Heartburn
While occasional heartburn is common and can often be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter remedies, frequent or severe heartburn may indicate a more serious condition.
Signs That Warrant Medical Attention
When should you consult a healthcare professional about your heartburn symptoms? Consider seeking medical attention if you experience:

- Heartburn more than twice a week
- Persistent heartburn that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter medications
- Difficulty swallowing
- Unintended weight loss
- Chest pain, especially if it’s accompanied by shortness of breath or jaw or arm pain
These symptoms may indicate gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or other serious conditions that require medical evaluation and treatment.
The Role of Medications in Managing Heartburn
For some individuals, lifestyle changes and natural remedies may not be sufficient to control heartburn symptoms. In these cases, medications may be necessary to manage acid reflux effectively.
Over-the-Counter Options
Several types of over-the-counter medications are available for heartburn relief:
- Antacids: These provide quick relief by neutralizing stomach acid.
- H2 blockers: These reduce acid production in the stomach.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): These block acid production and allow time for damaged esophageal tissue to heal.
It’s important to use these medications as directed and consult with a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen.
Prescription Medications
For more severe cases of heartburn or GERD, prescription medications may be necessary. These can include stronger versions of H2 blockers and PPIs, as well as medications to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter.
When considering medication options, it’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs.
Understanding the foods that trigger heartburn, making appropriate lifestyle changes, and knowing when to seek medical attention are all crucial aspects of managing this common but uncomfortable condition. By being proactive and informed, individuals can take control of their digestive health and minimize the impact of heartburn on their daily lives.
Foods that Cause Heartburn | Austin Gastroenterology
Heartburn is an unpleasant issue that may cause you to experience chest pain, ingestion, acidity, or a bitter taste in your mouth. The pain may worsen when you bend over or lie down.
Heartburn typically develops after you eat certain foods or if you eat too much. While there are many treatments for heartburn, the best way to reduce symptoms and keep the condition under control is by avoiding foods that cause it.
Here are some foods your doctor may recommend limiting if you have heartburn.
Spicy Foods
Spicy foods are notorious for causing heartburn. The reason is twofold. First, many spicy foods contain capsaicin, which slows down digestion and causes food to sit in the stomach longer. The longer food is in the stomach, the more risk of you having heartburn. Second, spicy food can irritate the esophagus, which can worsen heartburn symptoms. People who have heartburn, esophageal issues, or an ulcer often experience heartburn quicker and with more intensity when eating spicy foods than others do.
High-Fat Foods
High-fat foods are known to cause heartburn, as well. These foods take longer for your stomach to process then compared to proteins and carbohydrates. Since they’re in your stomach longer, your stomach produces more acid, which leads to digestive system irritation.
Not to mention, if you consume high-fat foods regularly, they can cause your lower esophageal sphincter to relax. The lower esophageal sphincter is a group of muscles located toward the bottom of your esophagus. The muscles close to prevent your stomach contents and acid from entering your esophagus. When they relax, acid can travel up your esophagus and irritate it. This can cause permanent damage when it happens frequently.
Examples of unhealthy, high-fat foods include fried foods like breaded chicken and fish, deep-fried French fries and chicken wings, and doughnuts. Processed baked goods and chips are also foods with a high concentration of fat.
Specific Foods to Avoid
Many specific foods can trigger heartburn symptoms. Talk to your doctor about whether limiting consumption of such foods could help reduce your symptoms. Examples include:
Talk to your doctor about whether limiting consumption of such foods could help reduce your symptoms. Examples include:
· Tomatoes and Tomato-Based Products Tomatoes and foods made from tomatoes, like spaghetti sauce, have a lot of acidity. They have both malic and citric acids, which can cause heartburn in many. The extra acid can cause too much gastric acid in the stomach. As the acid rises, it backs up into the esophagus, which causes a burning sensation in the chest.
· Onions Onions work well in a variety of dishes, whether they’re sauteed or caramelized. However, some people may experience heartburn when they consume it. Onion has the potential to relax your lower esophageal sphincter, which allows acid to travel from your stomach into your esophagus.
- High-Fat Cheese High-fat cheese is another food that can contribute to heartburn because the fat content decreases the speed at which your stomach empties. Therefore, the pressure from your stomach will force acid from your stomach into your esophagus.

· Coffee Your morning cup o’ joe may lead to heartburn. When you consume coffee in a high quantity or frequently, the caffeine may impact your lower esophageal muscles. It causes them to relax and allow stomach acid to enter the esophagus.
· Chocolate Most chocolates contain cocoa. Cocoa has serotonin, which may also relax your esophageal muscles and lead to heartburn.
· Peppermint Foods and drinks containing peppermint are known to help ease nausea and indigestion because it relaxes your digestive tract. This is not good for people who have gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD) or those who experience heartburn, because it relaxes the lower esophageal muscles. Peppermint may also worsen reflux symptoms if you have a hiatal hernia.
At Austin Gastroenterology, our practitioners are dedicated to getting to the root of your heartburn and other unpleasant digestive issues. When you work with us, you can expect expert care, a quick and accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment solutions.
Book an appointment with Austin Gastroenterology, serving Austin and the nearby Texas region, if you have frequent bouts of heartburn. Call one of our locations today, or request an appointment online. We look forward to serving you soon!
Heartburn Prevention
You don’t have to stop eating spicy foods just because you have heartburn.
Written by Peter Jaret
- Preventing Heartburn: Recognize Your Own Heartburn Triggers
- Dispelling Myths About Heartburn Triggers
- Heartburn Prevention: Eat Smaller Servings
- Heartburn Prevention: Eat Early and Often
- Heartburn Prevention: Rely on Gravity
- Heartburn Prevention: Chew Gum
- Heartburn Prevention: Get Healthy
- More
“How hot would you like that?” the server at my favorite Thai restaurant asks. My taste buds whisper: fiery. My belly moans, What about me?
I love a hot, spicy meal. But an hour later, like many people, I can end up wishing I’d never lifted my fork. The culprit? Heartburn and acid reflux. Officially known as gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, acid reflux occurs when food and stomach acids escape up into the esophagus through the valve at the top of the stomach. That causes the burning sensation that can sometimes rise up into the throat, known as heartburn.
The culprit? Heartburn and acid reflux. Officially known as gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, acid reflux occurs when food and stomach acids escape up into the esophagus through the valve at the top of the stomach. That causes the burning sensation that can sometimes rise up into the throat, known as heartburn.
Surveys of heartburn sufferers suggest spicy foods are among of the worst offenders. Whether spicy foods deserve their reputation is controversial, I’ve discovered. Many different foods can trigger heartburn.But luckily, you don’t have to say no to Chinese kung pao chicken, Mexican salsa, or fiery Thai noodle dishes. A few practical tips can help you put out the fire of heartburn before it starts.
Researchers have compiled a long list of foods that seem to trigger heartburn. These include alcohol, citrus fruits and juices, carbonated beverages, coffee and caffeine, chocolate, tomato sauce, fatty foods, mint, and, of course, spicy foods.
“But no single food stands out,” says Anish Sheth, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Yale University and co-author of What’s Your Poo Telling You? “For some people, the same food can cause problems after one meal but not after others. ”
”
In theory, foods most likely to cause acid reflux and symptoms of heartburn are those that cause the valve at the top of the stomach to relax. Mint, alcohol, and caffeinated coffee, among other foods, are believed to have that effect.
Yet when gastroenterologist Lauren B. Gerson, MD, an associate professor of medicine at Stanford University, and colleagues looked at trials designed to test the effects of these and other particular foods on heartburn symptoms, they found very little evidence to support the associations.
Even spicy foods may not deserve their reputation as being the worst culprits. Sure they taste hot, but that doesn’t mean they cause acid reflux. They may simply irritate the stomach.
“Still,” Gerson says, “it’s commonsense that if a particular food happens to cause you problems, the best advice is to avoid it.”
Since even heartburn sufferers can be misled by popular misconceptions, experts recommend keeping a food diary for several weeks.
“As soon as heartburn strikes, jot down what and how much you ate,” suggests dietitian Elaine Magee, author of Tell Me What to Eat If I Have Acid Reflux. “Also keep track of foods you thought might cause trouble but don’t. That way you won’t have to eliminate foods unnecessarily.”
“Also keep track of foods you thought might cause trouble but don’t. That way you won’t have to eliminate foods unnecessarily.”
Not ready to let heartburn force you to say no to salsa caliente? The next best strategy, then, is to limit the amount you eat.
“When you eat a large meal, pressure on the valve increases. So there’s a predisposition to reflux after a big meal,” Sheth says. The problem is worse if the meal causes you to belch, since that requires the valve at the top of the stomach to open. When it does, it allows trapped air to escape, sometimes bringing up acidic stomach contents along with it. For some people, drinking carbonated beverages along with a meal can exacerbate the problem.
Fatty meals can also increase the risk of reflux. “Eating fatty foods delays stomach emptying, since fat takes longer to digest,” explains Gerson. “The longer food remains in the stomach, the more chance there is of reflux.” To help prevent heartburn and GERD, choose roasted, grilled, or baked foods over fried foods, and go easy on butter.
Some heartburn sufferers find relief by eating smaller meals distributed more frequently throughout the day — a light breakfast, a midmorning snack, a light lunch followed by a midafternoon snack, for example. Scheduling dinner early can also help.
About 50% of heartburn sufferers have nighttime reflux, according to Gerson. This form can be especially unpleasant because when you’re lying down, more stomach contents can flow up into the esophagus. Nighttime reflux can also disturb sleep. Gerson’s tip? Eat dinner at least three hours before bedtime. That’s enough time to allow the stomach to empty before you hit the pillow.
Another way to relieve nighttime reflux requires nothing more than two wood blocks. Elevating the head of your bed a few inches enlists gravity to help keep stomach contents from rising, Sheth says. You can also use a wedge-shaped pillow to elevate your upper body at night. For daytime heartburn, the best way to employ gravity is to remain upright after a meal.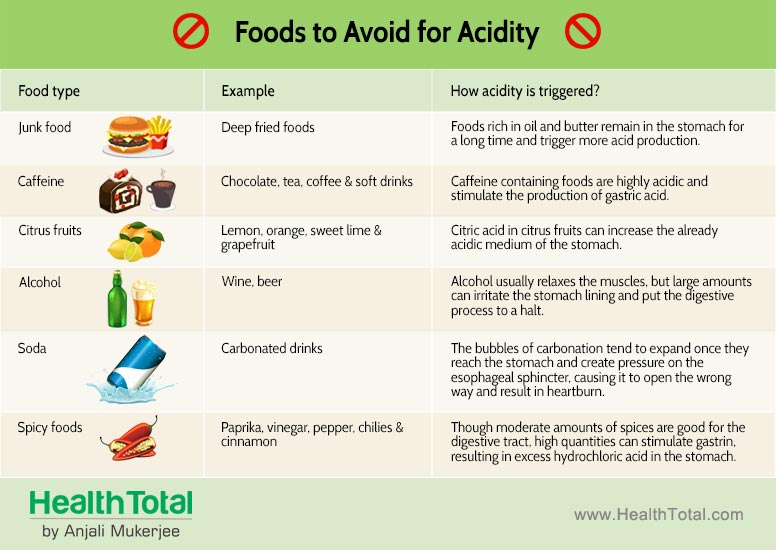 Walking after a big meal can also help. But don’t overdo it. Some research links vigorous exercise to an increase in reflux risk.
Walking after a big meal can also help. But don’t overdo it. Some research links vigorous exercise to an increase in reflux risk.
Saliva helps move food down through the esophagus and can ease the symptoms of heartburn. To increase salivation, try chewing gum after a meal or an attack of heartburn. Avoid mint-flavored gums, however, since these may relax the valve at the top of the stomach.
The most reliable ways to avoid GERD may be the hardest to accomplish: quit smoking if you smoke and lose weight if you’re overweight. Studies show that smokers are more prone to heartburn than nonsmokers. And the longer people smoke, the more likely they are to suffer acid reflux.
Being overweight can add to the pressure on the valve between the stomach and the esophagus. One study showed that every increase of 5 on the body mass index increases the risk of GERD by 1.2%. Eating smaller portions and walking after a meal can help you shed pounds at the same time they help prevent heartburn.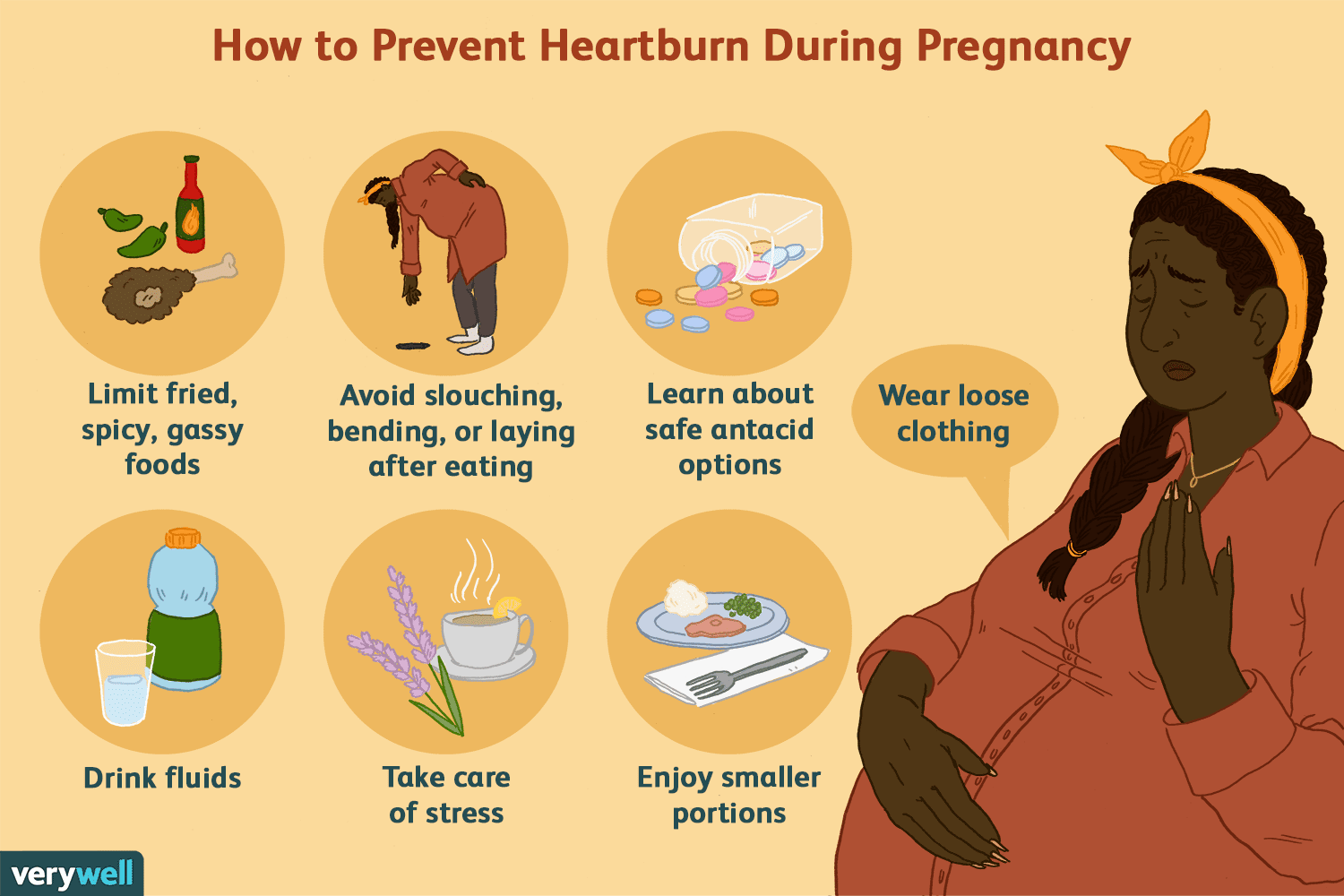
Top Picks
The benefits and harms of spicy food for the human body: myths and truth about spicy food – October 31, 2021
Some add hot peppers to food to lose weight. But does it make any sense?
Photo: Daria Selenskaya / Network of city portals
Share
Doctors often quote Paracelsus and say that “everything is poison, everything is medicine; both are determined by the dose. But what if some foods are a definite poison? Here is an example of a sharp one. Some people can’t stand it, while others can’t have a meal without it. But is it worth it to constantly wind up peppers, spices and seasonings? Why does acute heartburn appear? And is it true that such food can damage the receptors? We asked these and other questions to our experts – gastroenterologists and nutritionists.
But what if some foods are a definite poison? Here is an example of a sharp one. Some people can’t stand it, while others can’t have a meal without it. But is it worth it to constantly wind up peppers, spices and seasonings? Why does acute heartburn appear? And is it true that such food can damage the receptors? We asked these and other questions to our experts – gastroenterologists and nutritionists.
This is partly true. For example, hot spices such as habanero, jalapeno, and cayenne pepper have been proven to help with weight loss. The effect is easily explained by the influence of spices on metabolism. They speed up the metabolism and make the body burn energy faster and more efficiently. And this, in turn, leads to weight loss.
And it’s all about capsaicin – the very substance that is responsible for burning in the mouth. It can also speed up metabolism and reduce appetite.
— The substances contained in hot spices reduce the level of triglycerides in the blood, increase the number of enzymes in the liver that are involved in fat metabolism, speed up metabolism, activate the process of fat oxidation, says nutritionist Polina Topilina.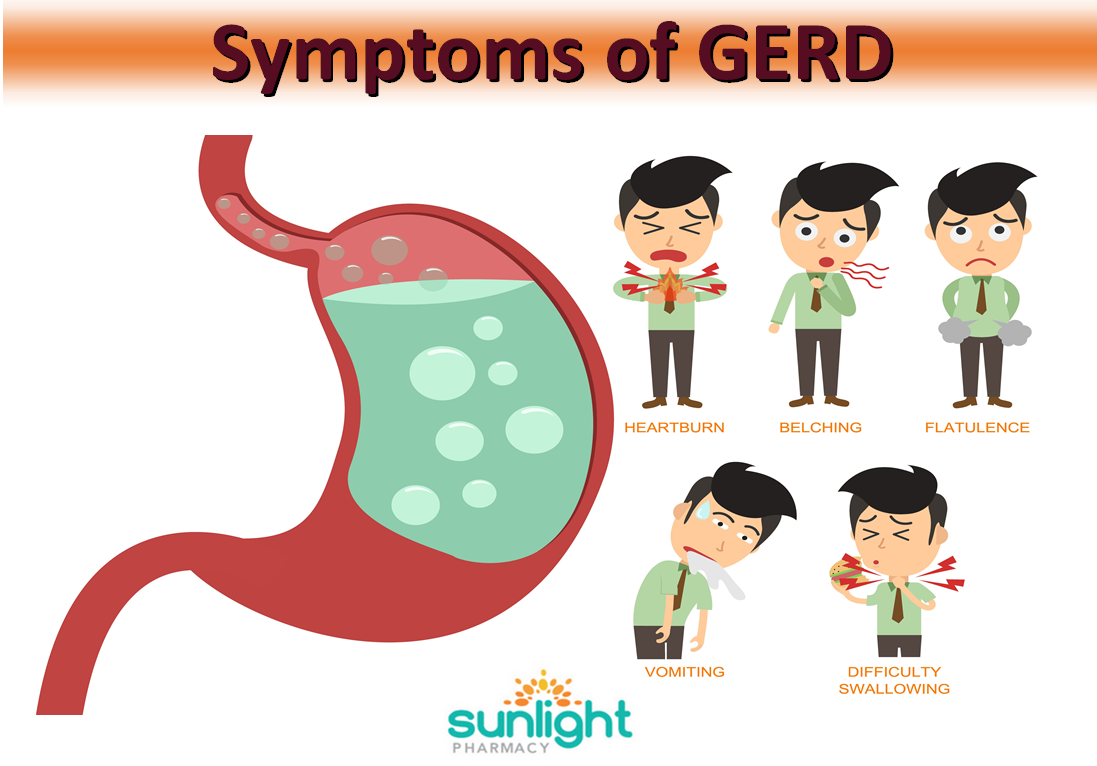 – Capsaicin neutralizes chronic inflammation caused by fat cells and reduces the production of the hormone ghrelin, which is responsible for the feeling of hunger.
– Capsaicin neutralizes chronic inflammation caused by fat cells and reduces the production of the hormone ghrelin, which is responsible for the feeling of hunger.
Polina Topilina — nutritionist, doctor of the 1st category.
But don’t think you can lose weight just by adding pepper to your diet. A calorie deficit will always be responsible for weight loss, not pepper. In addition, scientists have found that spicy lovers develop a kind of immunity to the product, so its fat-burning properties are minimized.
“Any spicy spices stimulate the secretion of gastric juice,” says Polina Topilina. – This, in turn, improves blood flow to the walls of the stomach and helps to restore its mucous membrane. At the same time, the substance capsaicin contained in hot peppers fights bacteria that can enter the digestive tract with food.
Foods and spices such as chili, cumin, ginger and garlic kill most of the causative agents of gastrointestinal infections, E. coli and bacteria. But do not try spicy food to be treated. Except for prevention. And even then, if you have no contraindications.
coli and bacteria. But do not try spicy food to be treated. Except for prevention. And even then, if you have no contraindications.
– The human body, especially gastroprofile patients, will react very violently to a garlic libation – an irritating effect may form, it will be difficult with the pancreas, an exacerbation of gastritis may appear, – says gastroenterologist Galina Bartashevich. – I do not recommend trying on yourself whether you will have gastritis with garlic belching or not. For those who cannot imagine food without garlic, and the stomach is already suffering, there is a standard culinary technique when a salad plate is simply wiped from the inside with a clove of garlic. Or grate a toast with a clove of garlic. The gastrointestinal tract takes this quite calmly.
Galina Bartashevich — gastroenterologist of the highest category, pediatric gastroenterologist, nutritionist, candidate of sciences.
If nature has rewarded you with these diseases, stay away from spicy things.
Infographics: Vitaly Kalistratov / Network of city portals But only if you seriously overdo it with spices. It happens like this: excess gastric juice (and spices increase its secretion) can enter the esophagus and cause an unpleasant burning sensation. If there is acute in small quantities, this will not happen. So don’t blame spicy food for everything. There can be many reasons for your heartburn.
Our body has many causes for heartburn, even without acute
Infographics: Vitaly Kalistratov / Network of city portals
Share
If heartburn has tormented you, don’t diagnose yourself and don’t experiment with food. Better go to the doctor. As planned. The doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination and establish the causes of the development of symptoms.
“First of all, the diagnosis-exclusion is functional non-ulcer dyspepsia, that is, an episode of heartburn occurred, but does not recur and is explained by eating disorders,” says gastroenterologist Galina Bartashevich. – More serious is the manifestation of the so-called acid-dependent diseases – this is gastroesophageal reflux disease, chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, chronic pancreatitis. All these diseases require treatment, and not just relief of the symptom.
– More serious is the manifestation of the so-called acid-dependent diseases – this is gastroesophageal reflux disease, chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, chronic pancreatitis. All these diseases require treatment, and not just relief of the symptom.
If you have had heartburn once a week or more frequently for the past 12 months, it could be reflux disease.
— For the treatment of acid-dependent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, a course of various groups of drugs is used, among which the main place is occupied by proton pump inhibitors, — adds gastroenterologist Dmitry Karpenko. – Of course, it is necessary to correct risk factors, change lifestyle and eating habits.
Dmitry Karpenko — Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor, Department of Polyclinic Therapy, Faculty of Medicine, Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education Russian National Research Medical University. N. I. Pirogova, general practitioner, gastroenterologist.
Only if you cannot live without spicy food and eat it every time for breakfast, lunch and dinner in industrial quantities.
— An excess of spicy food can lead to the development of gastritis — inflammation of the stomach lining — says Polina Topilina. – It is usually caused by an infection, but regular irritation of the stomach walls with spicy foods can lead to a decrease in their protective barrier.
Doctors agree that spicy food does not provoke gastritis by itself, but causes pain in people with existing problems. Acute increases the secretion of acid in the stomach, and with gastritis, its mucosa is already poorly protected.
If you abuse spices, there is a chance that you will lose your taste for a while. However, this does not mean at all that you will never feel anything again. To protect the body from pain, capsaicin causes numbness in the mouth and loss of sensation. Taste buds send a signal to the brain about a burning sensation in the mouth, and it begins to produce endorphins to block the unpleasant sensations. This is what causes numbness.
This is what causes numbness.
This is not the first time we have had to deal with myths and truths about popular products. During the existence of our column “Interesting about food”, so many of them have accumulated that it seems time to refresh our memory of what we did before.
For example, we analyzed the composition of hematogen and the pineapple diet, tried to find a connection between the seeds of appendicitis – that’s the whole truth about popular products that you don’t want to know.
Asked obvious and strange questions about chickens and eggs to a former poultry farm manager, breaking 9egg myths.
Learned why it is better not to drink juice for breakfast and not to give it to children.
We also researched various products together with experts. And they found 7 myths about healthy food that will ruin your appetite. Then 6 products turned out to be pseudo-useful, and breakfast generally let everyone down.
Increased acidity of the stomach: spicy food is to blame
Nutrition
What will you eat this week? Mustard? Spicy chicken? Korean salads? Many of us love to eat something spicy, but does everyone like heartburn? Stomach acidity is not an inevitable consequence of eating spicy food, but it can ruin your evening.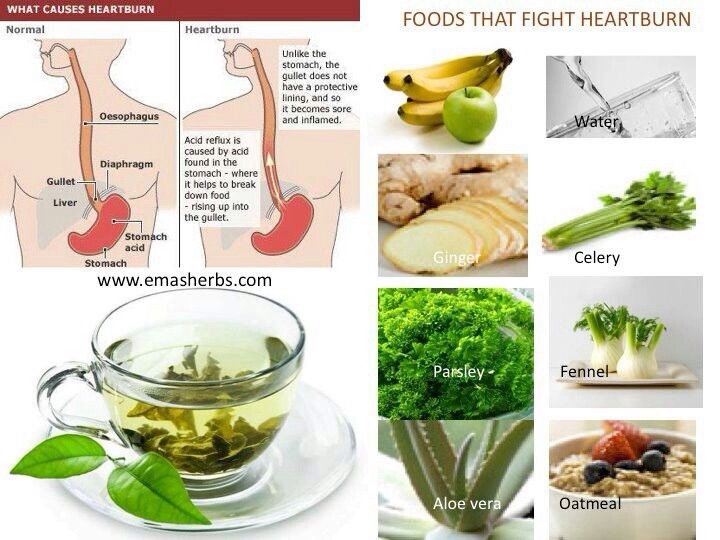 Why?
Why?
Why spicy foods can cause heartburn
Heartburn is known to be associated with spicy foods. There are many explanations for this:
- Mild sauces like satsebeli and curry contain peppers and tomatoes that can cause heartburn.
- Spicy foods can exacerbate heartburn symptoms if the lining of the lower esophagus is already irritated by stomach acid. 1
- The muscles of the upper part of the stomach help keep its contents inside. If we consume food that relaxes these muscles, stomach acid can enter the esophagus and cause heartburn. Certain foods – fatty, spicy, high in oil and acid – can have this relaxing effect. 2.3
- Spicy and fatty foods (particularly dishes with curry sauce or spicy sausage) are difficult to digest, which can increase the amount of gastric juice and cause heartburn.
What food should I avoid with heartburn?
If you experience stomach discomfort every time you eat spicy food, then you probably already know what foods to avoid. However, it is worth revisiting this list again.
However, it is worth revisiting this list again.
- Onions and garlic – these are found in most spicy dishes, but those where onions are present raw are especially dangerous.
- Tomatoes and peppers – found in curry sauce, chili sauce and many others.
- Black pepper – found in many dishes (and not only hot ones). It rarely causes severe flare-ups of heartburn.
- Citrus – found in many Mediterranean dishes, such as tagine.
- Meat – the fatter the meat, the faster it will cause heartburn – for example, lamb in curry sauce.
- Cooking oil, such as ghee or fat, is used in curry sauces and in many other dishes.
Avoid foods that cause heartburn
To protect yourself from heartburn, it is best to carefully study the composition of the dish that you are going to eat. If you prefer to eat out, ask a chef, a waiter, or a friend who invited you to dinner at an unfamiliar place for advice. If heartburn caught you right during a meal, it is better to refuse the dish that caused this.
Perhaps the problem of heartburn is new to you, and you still do not know the list of foods that are potentially dangerous for your stomach. If heartburn has taken you by surprise, Gaviscon 9 may help0101 ® Double Action. It will help you get rid of your painful symptoms so that you can safely continue to enjoy a delicious lunch. Gaviscon ® Dual Action 4 acts quickly to form a protective barrier in the stomach. This barrier prevents stomach acid from entering the esophagus, protecting the lining of the esophagus from irritation. The drug thus reduces irritation of the mucous membrane. Gaviscon ® Dual Action also has a fairly long-lasting effect of over four hours 5 to help alleviate the discomfort of heartburn and indigestion.
In conclusion, let’s say – eat with pleasure. However, if your diet often includes spicy foods, do not forget about the possible consequences, be careful about the composition of the food.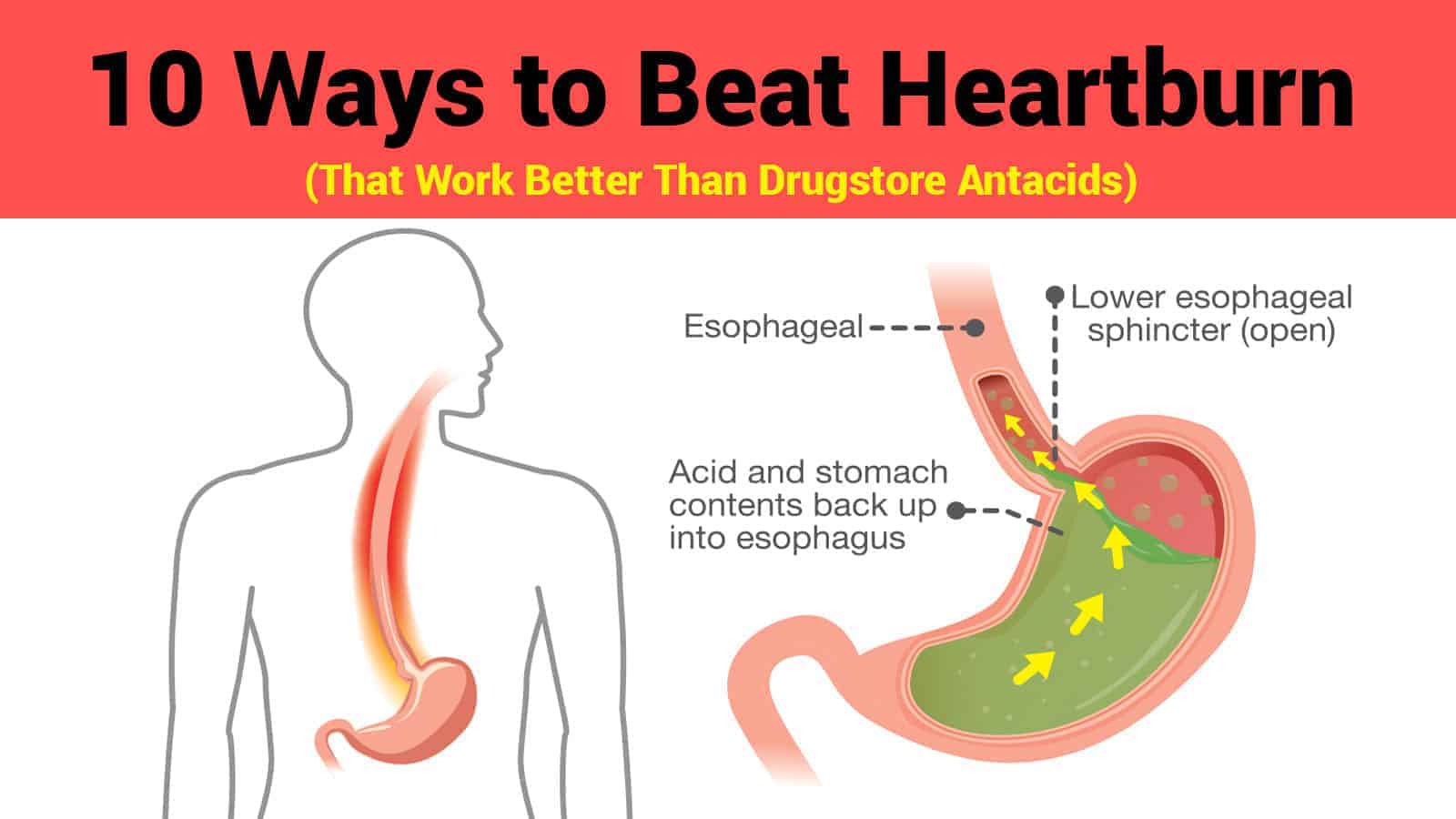
Method of administration and doses
Suspension: Adults and children over 12 years: 10-20 ml after meals and at bedtime up to 4 times a day
Maximum daily dose – 80 ml
Tablets: Adults and children over 12 years old: 2-4 tablets after meals and at bedtime up to 4 times a day
Maximum daily dose – 16 tablets 002 All information provided not intended for diagnosis or prescription of medications. For more information about Gaviscon ® , read the instructions for use. In case of complications or prolonged course of the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
1 Maev I.V., Samsonov A.A., Dicheva D.T., Andreev D.N., Andreev N.G., Buragina T.A. Current approaches to diet therapy for diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract // “Medical Bulletin of the Ministry of Internal Affairs” No. 4 (59). 2012. pp. 57–61.
2 Rohof W.

