Sulfamethoxazole tmp side effects. Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim: Uses, Side Effects, and Interactions
What are the main uses of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. How does this antibiotic combination work. What are the most common side effects and drug interactions to be aware of. When should this medication be avoided.
Overview of Sulfamethoxazole-Trimethoprim
Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, also known as co-trimoxazole, is a combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. This powerful drug combines two antibiotics – sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim – which work together to stop the growth of bacteria.
The medication is available in oral tablet form, with the most common being the double strength (DS) version containing 800 mg sulfamethoxazole and 160 mg trimethoprim. It’s typically prescribed for infections of the urinary tract, respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, and other areas.
How Does Sulfamethoxazole-Trimethoprim Work?
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim work synergistically to interfere with bacteria’s ability to produce folate, an essential nutrient for bacterial growth and reproduction. Specifically:

- Sulfamethoxazole inhibits an enzyme involved in bacterial folate synthesis
- Trimethoprim blocks a different enzyme in the folate production pathway
- Together, they create a “one-two punch” that’s more effective than either antibiotic alone
By disrupting folate production, the antibiotic combination prevents bacteria from synthesizing DNA and proteins needed for survival and replication. This bacteriostatic effect stops the infection from spreading while allowing the immune system to clear the existing bacteria.
Common Uses and Indications
Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim is prescribed for a wide range of bacterial infections affecting different parts of the body. Some of the most common uses include:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
This antibiotic combination is a first-line treatment for uncomplicated UTIs caused by susceptible organisms. It’s effective against common urinary pathogens like E. coli.
Respiratory Infections
Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim can treat certain respiratory tract infections, including:
- Acute bronchitis
- Pneumonia (including Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in immunocompromised patients)
- Sinusitis
- Otitis media (middle ear infection)
Gastrointestinal Infections
The medication is used to treat some intestinal infections, particularly traveler’s diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic E. coli.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Certain skin infections, including impetigo and cellulitis, may be treated with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim when caused by susceptible bacteria.
Prophylaxis
In some cases, the drug is used preventively, such as to prevent Pneumocystis pneumonia in immunocompromised individuals.
Proper Administration and Dosage
Correct administration of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim is crucial for its effectiveness and safety. Here are some key points about dosing:
- Tablets should be taken orally with a full glass of water
- Can be taken with or without food, but taking with food may reduce stomach upset
- Typical adult dose for most infections is one double-strength tablet every 12 hours
- Duration of treatment varies depending on the infection, usually ranging from 3 to 14 days
- Dosage may be adjusted for certain conditions or in patients with kidney impairment
Can sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim be crushed or split. Yes, most formulations can be crushed or split if needed, but it’s best to consult a pharmacist or healthcare provider first, as some extended-release versions should not be altered.

Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
While sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Understanding these potential reactions is important for patients and healthcare providers.
Common Side Effects
The most frequently reported side effects include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Skin rash or itching
- Headache
- Dizziness
These effects are usually mild and often resolve on their own as the body adjusts to the medication. However, persistent or severe symptoms should be reported to a healthcare provider.
Serious Adverse Reactions
While less common, some individuals may experience more serious side effects that require immediate medical attention:
- Severe skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis)
- Blood disorders (e.g., agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia)
- Liver damage
- Kidney problems
- Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis
Is there a higher risk of side effects in certain populations. Yes, elderly patients, those with kidney or liver disease, and individuals with a history of allergies to sulfa drugs may be at increased risk for adverse reactions.
Drug Interactions and Precautions
Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim can interact with numerous other medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Understanding these interactions is crucial for safe use of the antibiotic.
Major Drug Interactions
Some of the most significant interactions include:
- Warfarin: May increase anticoagulant effect, raising bleeding risk
- Methotrexate: Can increase methotrexate levels, potentially leading to toxicity
- ACE inhibitors and ARBs: May increase risk of hyperkalemia (high potassium levels)
- Certain diabetes medications: Can enhance hypoglycemic effects
- Phenytoin: May increase phenytoin levels, risking toxicity
Moderate Interactions
Moderate interactions, which may require closer monitoring or dosage adjustments, include:
- Certain antidepressants (e.g., SSRIs)
- Some statins
- Digoxin
- Cyclosporine
- Potassium-sparing diuretics
How many total drug interactions are known for sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim. According to drug interaction databases, there are over 400 known drug interactions with this antibiotic combination, including 68 major interactions, 133 moderate interactions, and 201 minor interactions.
Precautions and Contraindications
Certain conditions or factors may necessitate avoiding or using sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim with caution:
- Allergy to sulfa drugs or trimethoprim
- Pregnancy, especially in the third trimester
- Severe liver or kidney disease
- G6PD deficiency
- Folate deficiency
- Porphyria
Special Considerations for Specific Populations
The use of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim requires special attention in certain groups of patients due to increased risks or altered drug metabolism.
Pediatric Use
While the medication is approved for use in children, there are important considerations:
- Not recommended for infants under 2 months due to risk of kernicterus
- Dosage is based on weight in children
- Increased risk of severe skin reactions in children
Geriatric Use
Older adults may be more sensitive to the effects of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim:
- Higher risk of side effects, especially with concurrent medications
- May require dose adjustment due to decreased kidney function
- Increased risk of hyperkalemia and blood disorders
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The use of this antibiotic during pregnancy and lactation requires careful consideration:
- Generally avoided in late pregnancy due to risk of kernicterus in the newborn
- May be used with caution in early pregnancy if benefits outweigh risks
- Excreted in breast milk, so caution is advised when breastfeeding
Are there alternative antibiotics for pregnant women. Yes, depending on the infection, alternatives like penicillins or cephalosporins may be preferred during pregnancy.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Proper monitoring during treatment with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim is essential to ensure safety and efficacy. This includes:
Laboratory Tests
Depending on the duration of treatment and individual risk factors, the following tests may be recommended:
- Complete blood count (CBC) to monitor for blood disorders
- Liver function tests
- Kidney function tests
- Electrolyte levels, particularly potassium
Clinical Monitoring
Patients should be monitored for:
- Resolution of infection symptoms
- Development of new symptoms or side effects
- Signs of allergic reactions
How often should follow-up occur during treatment. The frequency of follow-up depends on the severity of the infection and individual patient factors, but typically ranges from every few days for severe infections to weekly for less serious cases.

Patient Education
Educating patients about the following is crucial:
- Importance of completing the full course of antibiotics
- Potential side effects and when to seek medical attention
- Drug interactions, including with over-the-counter medications
- Proper storage and handling of the medication
Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim is a potent antibiotic combination with a wide range of applications in treating bacterial infections. While it’s highly effective when used appropriately, the potential for side effects and drug interactions necessitates careful consideration and monitoring. By understanding its proper use, potential risks, and important precautions, healthcare providers can optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing adverse effects. Patients, too, play a crucial role in ensuring safe and effective use of this medication by adhering to prescribed regimens and promptly reporting any concerns or unusual symptoms.
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim Interactions – Drugs.com
Save
There are 402 drugs known to interact with
sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, along with
12 disease interactions, and 1 alcohol/food interaction.
Of the total drug interactions,
68 are major, 133 are moderate, and 201 are minor.
Does sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim interact with my other drugs?
Enter other medications to view a detailed report.
- View all 402 medications that may interact with sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim
- View sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim alcohol/food interactions (1)
- View sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim disease interactions (12)
Most frequently checked interactions
View interaction reports for sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim and the medicines listed below.
- Major
- Moderate
- Minor
- Unknown
- Aspirin Low Strength (aspirin)
- Azithromycin Dose Pack (azithromycin)
- Benadryl (diphenhydramine)
- Celebrex (celecoxib)
- Claritin (loratadine)
- CoQ10 (ubiquinone)
- Cymbalta (duloxetine)
- Eliquis (apixaban)
- Fish Oil (omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids)
- Flonase (fluticasone nasal)
- Lexapro (escitalopram)
- Lyrica (pregabalin)
- Metoprolol Succinate ER (metoprolol)
- Metoprolol Tartrate (metoprolol)
- MiraLAX (polyethylene glycol 3350)
- Norco (acetaminophen / hydrocodone)
- ProAir HFA (albuterol)
- Probiotic Formula (bifidobacterium infantis / lactobacillus acidophilus)
- Symbicort (budesonide / formoterol)
- Synthroid (levothyroxine)
- Tylenol (acetaminophen)
- Tylenol Extra Strength (acetaminophen)
- Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin)
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol)
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol)
- Xanax (alprazolam)
- Zofran (ondansetron)
- Zoloft (sertraline)
- Zyrtec (cetirizine)
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim alcohol/food interactions
There is 1 alcohol/food interaction with sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim.
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim disease interactions
There are 12 disease interactions with sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim which include:
- colitis
- hematologic toxicity
- hypersensitivity reactions
- liver disease
- porphyria
- renal dysfunction
- folate deficiency
- crystalluria
- hemodialysis
- urinary obstruction
- dialysis
- renal dysfunction
Report options
Loading…
QR code containing a link to this page
More about sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim
- sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim consumer information
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (1,708)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- Patient tips
- During pregnancy
- Support group
- Drug class: sulfonamides
- En español
Related treatment guides
- Bacterial Infection
- Acne
- Bacterial Skin Infection
- Bronchitis
Drug Interaction Classification
| Major | Highly clinically significant. Avoid combinations; the risk of the interaction outweighs the benefit. |
|---|---|
| Moderate | Moderately clinically significant. Usually avoid combinations; use it only under special circumstances. |
| Minor | Minimally clinically significant. Minimize risk; assess risk and consider an alternative drug, take steps to circumvent the interaction risk and/or institute a monitoring plan. |
| Unknown | No interaction information available. |
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
Medical Disclaimer
Sulfamethoxazole-TMP DS Oral: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing
Uses
This medication is a combination of two antibiotics: sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. It is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections (such as middle ear, urine, respiratory, and intestinal infections). It is also used to prevent and treat a certain type of pneumonia (pneumocystis-type).This medication should not be used by children less than 2 months of age due to the risk of serious side effects.This medication treats only certain types of infections. It will not work for viral infections (such as flu). Unnecessary use or misuse of any antibiotic can lead to its decreased effectiveness.
How to use Sulfamethoxazole-TMP DS Tablet
Take this medication by mouth, as directed by your doctor, with a full glass of water (8 ounces / 240 milliliters). If stomach upset occurs, take with food or milk. Drink plenty of fluids while taking this medication to lower the unlikely risk of kidney stones forming, unless your doctor advises you otherwise.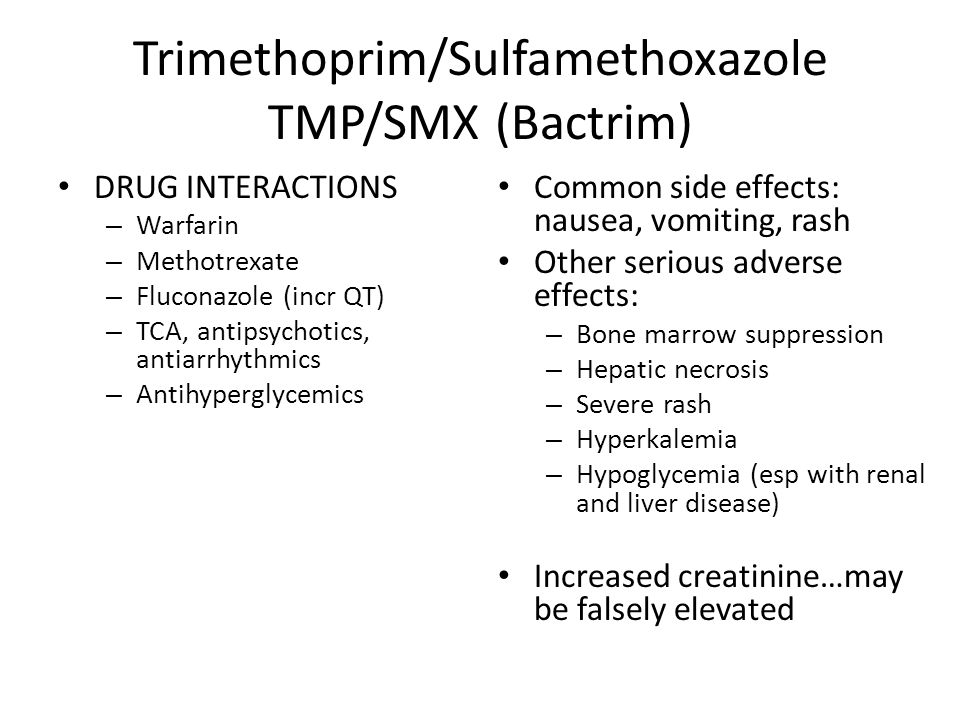 Dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment.
Dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment.
For the best effect, take this antibiotic at evenly spaced times. To help you remember, take this medication at the same time(s) every day.
Continue to take this medication until the full prescribed amount is finished, even if symptoms disappear after a few days. Stopping it too early may allow bacteria to continue to grow, which may result in a relapse of the infection.
Tell your doctor if your condition lasts or gets worse.
Side Effects
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Remember that this medication has been prescribed because your doctor has judged that the benefit to you is greater than the risk of side effects. Many people using this medication do not have serious side effects.
Tell your doctor right away if you have any serious side effects, including: muscle weakness, mental/mood changes, signs of kidney problems (such as change in the amount of urine, blood in the urine), extreme drowsiness, signs of low blood sugar (such as sudden sweating, shaking, fast heartbeat, hunger, blurred vision, dizziness, or tingling hands/feet).
Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: headache that doesn’t go away, neck stiffness, seizures, slow/irregular heartbeat.
This medication may rarely cause serious (possibly fatal) allergic reactions and other side effects such as a severe peeling skin rash (such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome), blood disorders (such as agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia), liver damage, or lung injury. If you notice any of the following, get medical help right away: sore throat or fever that doesn’t go away, cough that doesn’t go away, nausea/vomiting that doesn’t stop, skin rash/blisters, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), new or worsening lymph node swelling, paleness, joint pain/aches, trouble breathing, easy bleeding/bruising, yellowing eyes or skin, unusual fatigue, dark urine.
This medication may rarely cause a severe intestinal condition due to a bacteria called C. difficile. This condition may occur during treatment or weeks to months after treatment has stopped. Tell your doctor right away if you develop: diarrhea that doesn’t stop, abdominal or stomach pain/cramping, blood/mucus in your stool.
Tell your doctor right away if you develop: diarrhea that doesn’t stop, abdominal or stomach pain/cramping, blood/mucus in your stool.
If you have these symptoms, do not use anti-diarrhea or opioid products because they may make symptoms worse.
Use of this medication for prolonged or repeated periods may result in oral thrush or a new yeast infection. Contact your doctor if you notice white patches in your mouth, a change in vaginal discharge, or other new symptoms.
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. If you notice other effects not listed above, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
In the US – Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or at www.fda.gov/medwatch.
In Canada – Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345.
Precautions
Before taking this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to sulfamethoxazole or trimethoprim; or to sulfa medications; or if you have any other allergies. This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
This product may contain inactive ingredients, which can cause allergic reactions or other problems. Talk to your pharmacist for more details.
Before using this medication, tell your doctor or pharmacist your medical history, especially of: kidney disease, liver disease, certain blood disorders (such as porphyria, anemia due to folate vitamin deficiency), history of blood disorders caused by trimethoprim or sulfa medications, vitamin deficiency (folate or folic acid), severe allergies, asthma, decreased bone marrow function (bone marrow suppression), a certain metabolic disorder (G6PD deficiency), underactive thyroid, mineral imbalances (such as high level of potassium or low level of sodium in the blood).
This medication may cause live bacterial vaccines (such as typhoid vaccine) to not work well. Tell your health care professional that you are using this medication before having any immunizations/vaccinations.
Before having surgery, tell your doctor or dentist about all the products you use (including prescription drugs, nonprescription drugs, and herbal products).
This medication may make you more sensitive to the sun. Limit your time in the sun. Avoid tanning booths and sunlamps. Use sunscreen and wear protective clothing when outdoors. Get medical help right away if you get sunburned or have skin blisters/redness.
If you have diabetes, this product may affect your blood sugar. Check your blood sugar regularly as directed and share the results with your doctor. Tell your doctor right away if you have symptoms of low blood sugar (see Side Effects section). Your doctor may need to adjust your diabetes medication, exercise program, or diet.
Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially skin reactions, blood disorders, easy bleeding/bruising, and a high potassium blood level.
Patients with AIDS may be more sensitive to the side effects of this drug, especially skin reactions, fever, and blood disorders.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. You should not become pregnant while using sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim. This medication may harm an unborn baby. If you become pregnant, talk to your doctor right away about the risks and benefits of this medication.
This medication may harm an unborn baby. If you become pregnant, talk to your doctor right away about the risks and benefits of this medication.
This drug passes into breast milk. While there have been no reports of harm to healthy infants, this drug may have undesirable effects on infants who are ill or premature or have certain disorders (jaundice, high blood levels of bilirubin, G6PD deficiency). Breast-feeding is not recommended for infants with these conditions. Consult your doctor before breast-feeding.
Interactions
Drug interactions may change how your medications work or increase your risk for serious side effects. This document does not contain all possible drug interactions. Keep a list of all the products you use (including prescription/nonprescription drugs and herbal products) and share it with your doctor and pharmacist. Do not start, stop, or change the dosage of any medicines without your doctor’s approval.
Some products that may interact with this drug include: “blood thinners” (such as warfarin), dofetilide, methenamine, methotrexate.
This product may interfere with certain laboratory tests, possibly causing false test results. Make sure laboratory personnel and all your doctors know you use this product.
Does Sulfamethoxazole-TMP DS Tablet interact with other drugs you are taking?
Enter your medication into the WebMD interaction checker
Overdose
If someone has overdosed and has serious symptoms such as passing out or trouble breathing, call 911. Otherwise, call a poison control center right away. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center. Symptoms of overdose may include: severe nausea/vomiting/diarrhea, severe dizziness or drowsiness, mental/mood changes.
Do not share this medication with others.
This medication has been prescribed for your current condition only. Do not use it later for another infection unless your doctor tells you to.
If taking this medication for a long time, lab and/or medical tests (such as complete blood count, kidney function, potassium blood level, cultures) should be done while you are taking this medication. Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
Keep all medical and lab appointments. Consult your doctor for more details.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is near the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose. Take your next dose at the regular time. Do not double the dose to catch up.
Store at room temperature away from light and moisture. Do not store in the bathroom. Keep all medications away from children and pets.
Do not flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless instructed to do so. Properly discard this product when it is expired or no longer needed. Consult your pharmacist or local waste disposal company.
Selected from data included with permission and copyrighted by First Databank, Inc. This copyrighted material has been downloaded from a licensed data provider and is not for distribution, except as may be authorized by the applicable terms of use.
CONDITIONS OF USE: The information in this database is intended to supplement, not substitute for, the expertise and judgment of healthcare professionals. The information is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions or adverse effects, nor should it be construed to indicate that use of a particular drug is safe, appropriate or effective for you or anyone else. A healthcare professional should be consulted before taking any drug, changing any diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment.
The information is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions or adverse effects, nor should it be construed to indicate that use of a particular drug is safe, appropriate or effective for you or anyone else. A healthcare professional should be consulted before taking any drug, changing any diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment.
Use of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim in the treatment of children with cancer
Antibiotic
Brand names:
Bactrim®, Septra®, Sulfatrim®
Other names:
SMX-TMP, Co-trimoxazole
Often used for:
Infections
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is an antibiotic; its action is aimed at the destruction of bacteria that cause infections. Some patients are given this drug to prevent pneumonia during chemotherapy. This drug may also be used to treat infections. Follow dosage instructions carefully.
You may need to have blood tests while taking this drug.
Oral tablets
Oral liquid form
Administered intravenously (through a drip) in liquid form
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rash
- Sun sensitivity
- Loss of appetite
- Diarrhea
- Pain in the abdomen
- Low blood counts
These side effects may not occur in all patients treated with sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim. The most common side effects are highlighted in bold, but others are not excluded. Report all possible side effects to your doctor or pharmacist.
Be sure to discuss these and other recommendations with your doctor or pharmacist.
- It is important to drink plenty of fluids while taking this medicine. It is necessary to drink the amount of liquid recommended by the doctor.

- The drug may interfere with the results of some laboratory tests.
- Alcoholic beverages should be avoided while taking this drug.
- Patients should protect their skin from sunlight during treatment with this drug.
- Pregnant, planning pregnancy or breastfeeding patients should notify the attending physician.
- The course of taking the drug must be completed completely in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician or pharmacist.
Home use of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim:
- The drug should be taken at the same time every day.
- This drug can be taken with or without food. If the drug causes stomach upset, it must be taken with food.
- It is recommended to take the drug with a full glass of water.
- In liquid form: shake well before use, measure dosage using the measuring device included.
- Store at room temperature. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight.

- Take your dose as soon as possible if you miss it. Do not do this only if there is little time left until the next appointment. In no case do not double the dose at the next dose!
- Do not use an expired drug.
- Follow instructions for safe storage and disposal of the drug.
Learn more about sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim
ERIPRIM CONCENTRATE – instructions, description
ERIPRIM CONCENTRATE
Water-soluble powder for oral administration. Contains as active ingredients macrolide antibiotic tylosin – 5%, sulfanilamide sulfamethoxazole – 17.5%, trimethoprim – 3.5%, polypeptide antibiotic colistin – 1.5%, as well as auxiliary components. The drug is a white powder soluble in water.
Purpose
Used for therapeutic purposes in bacterial infections of poultry.
Biological properties
Tylosin is a bacteriostatic macrolide antibiotic. Tylosin penetrates into the bacterial cell through passive diffusion, where it blocks protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit. The spectrum of action of tylosin covers gram-positive bacteria, as well as mycoplasmas. Sulfamethoxazole is a synthetic chemotherapeutic agent from the group of sulfonamides, the mechanism of action of which is to block the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which leads to a stop in the synthesis of bacterial nucleic acids. Trimethoprim is a synthetic chemotherapeutic agent derived from diaminopyrimidines. In combination, sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim has a synergistic effect and is effective against many gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Colistin belongs to polypeptide antibiotics and acts on gram-negative bacteria by replacing lipids and proteins of the bacterial cell wall. The components of the drug are distributed differently in the body. Tylosin is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and remains at therapeutic concentrations in the organs and tissues of the body for 15-20 hours. The highest concentrations are achieved in the lungs, liver and kidneys.
The spectrum of action of tylosin covers gram-positive bacteria, as well as mycoplasmas. Sulfamethoxazole is a synthetic chemotherapeutic agent from the group of sulfonamides, the mechanism of action of which is to block the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which leads to a stop in the synthesis of bacterial nucleic acids. Trimethoprim is a synthetic chemotherapeutic agent derived from diaminopyrimidines. In combination, sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim has a synergistic effect and is effective against many gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Colistin belongs to polypeptide antibiotics and acts on gram-negative bacteria by replacing lipids and proteins of the bacterial cell wall. The components of the drug are distributed differently in the body. Tylosin is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and remains at therapeutic concentrations in the organs and tissues of the body for 15-20 hours. The highest concentrations are achieved in the lungs, liver and kidneys. Excretion occurs mainly with bile. Sulfamethoxazole after oral administration is consistently absorbed and distributed in the tissues and body fluids of the bird. Transforms in the liver into acetylated and hydroxylated derivatives. Excreted from the body by the kidneys. When administered orally, trimethoprim is consistently absorbed, reaching peak plasma concentrations 2 to 4 hours after administration. The highest concentrations are achieved in the lungs, liver and kidneys. Plasma concentrations are usually lower than tissue concentrations. Excretion occurs by the kidneys and to a small extent – with bile. Colistin is absorbed very slowly from the gastrointestinal tract. Plasma concentrations are practically not determined. It stands out mainly with litter. Eriprim Concentrate belongs to drugs with low toxicity for poultry.
Excretion occurs mainly with bile. Sulfamethoxazole after oral administration is consistently absorbed and distributed in the tissues and body fluids of the bird. Transforms in the liver into acetylated and hydroxylated derivatives. Excreted from the body by the kidneys. When administered orally, trimethoprim is consistently absorbed, reaching peak plasma concentrations 2 to 4 hours after administration. The highest concentrations are achieved in the lungs, liver and kidneys. Plasma concentrations are usually lower than tissue concentrations. Excretion occurs by the kidneys and to a small extent – with bile. Colistin is absorbed very slowly from the gastrointestinal tract. Plasma concentrations are practically not determined. It stands out mainly with litter. Eriprim Concentrate belongs to drugs with low toxicity for poultry.
Dosage and route of administration
The drug is administered orally mixed with water at a daily dose of 1 g/l of water for 3-5 days. During treatment, the bird should receive only water containing Eriprim Concentrate.
Contraindications
Do not use in commercial laying hens.
Product form
Eriprim Concentrate is produced in sealed three-layer bags of 0.5 and 1 kg, packed in cardboard boxes of 10 pcs, as well as in 5 kg bags, packed in cardboard drums of 1 pc. List B. Store in a dry place out of direct sunlight at a temperature of 5 to 25 ° C. The shelf life of the drug is 2 years. Manufacturer s.p. veterinaria, s.a., RIUDOMS (Tarragona), Spain
Notes
Poultry may be slaughtered for meat 28 days after the last use of the preparation. Poultry meat, forced to be killed before the expiration of the specified period, can be used for feeding fur-bearing animals or for the production of meat and bone meal.
Side effects
Not observed at recommended doses. In some individuals, the use of the drug can cause dysbacteriosis. With prolonged use, dysbacteriosis may occur, leading to digestive disorders. In these cases, stop the administration of the drug and apply symptomatic treatment.

 The relevance of a particular drug interaction to a specific individual is difficult to determine. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medication.
The relevance of a particular drug interaction to a specific individual is difficult to determine. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medication.
