What does thickening of the bladder wall mean. Interstitial Cystitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options for Bladder Wall Thickening
What are the signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis. How is interstitial cystitis diagnosed and treated. What causes thickening of the bladder wall in interstitial cystitis. What are the risk factors for developing interstitial cystitis. How does interstitial cystitis affect quality of life.
Understanding Interstitial Cystitis: A Complex Bladder Condition
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also known as painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic condition characterized by pain and pressure in the bladder and pelvic area. This complex disorder can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing a range of symptoms that vary in intensity and duration. While the exact cause remains unknown, researchers have made significant strides in understanding the underlying mechanisms and developing effective treatment strategies.
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Interstitial Cystitis
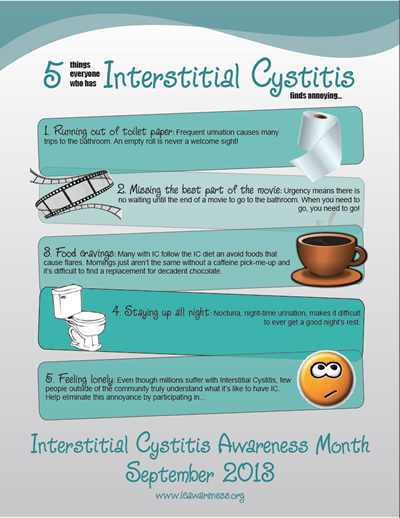
Interstitial cystitis manifests through a variety of symptoms, which can differ from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort, while others suffer from severe pain and disruption to their daily lives. The following are the primary symptoms associated with IC:

- Bladder pain and pressure
- Frequent urination
- Urgent need to urinate
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Nocturia (nighttime urination)
What sets interstitial cystitis apart from other bladder conditions? Unlike common urinary tract infections, IC typically does not cause urine leakage. In fact, the absence of leakage can be a distinguishing factor when diagnosing this condition.
The Impact of Pain in Interstitial Cystitis
Pain is a hallmark symptom of interstitial cystitis. How does this pain manifest? Patients often describe sensations of pressure, discomfort, or outright pain in and around the bladder area. This discomfort may extend to the vaginal, urethral, or scrotal regions. Interestingly, the pain associated with IC tends to worsen as the bladder fills and may be temporarily relieved upon urination.
Frequency and Urgency: Hallmarks of IC
Why do people with interstitial cystitis urinate so frequently? The condition causes the bladder to become stiff and lose its elasticity, leading to frequent urges to urinate both day and night. In severe cases, individuals may need to urinate up to 60 times per day, a stark contrast to the normal frequency of fewer than eight times during the day and once at night.

The urgency associated with IC can be particularly distressing. How intense can this urge become? For many patients, the need to urinate can be overwhelming and difficult to control. Some individuals report that this sensation persists even immediately after voiding their bladder.
Unraveling the Causes and Risk Factors of Interstitial Cystitis
While the exact cause of interstitial cystitis remains elusive, researchers have identified several potential factors that may contribute to its development. What are the leading theories about the origins of IC?
- Damage to the bladder lining
- Production of antiproliferative factor (APF)
- Bladder trauma or surgery
- Prolonged bladder distention
- Nerve damage or inflammation
- Bacterial infection
- Pelvic floor muscle dysfunction
- Autoimmune response
A significant breakthrough in understanding IC came from a 2017 study, which found that many people with the condition produce a protein called antiproliferative factor (APF). How does APF affect the bladder? This protein appears to increase bladder sensitivity to urine and inhibit the growth of bladder cells, potentially interfering with the organ’s ability to heal itself when damage occurs.

The Potential Link Between Interstitial Cystitis and Abuse
In recent years, researchers have explored the possibility of a connection between interstitial cystitis and various forms of abuse, including physical and sexual abuse. However, studies on this topic have yielded inconsistent results. What is the current consensus on this relationship? At present, there is no definitive conclusion, and more research is needed to fully understand any potential link between abuse and the development of IC.
Diagnosing Interstitial Cystitis: A Multifaceted Approach
Diagnosing interstitial cystitis can be challenging, as there is no single definitive test for the condition. How do healthcare providers approach the diagnosis of IC? The process typically involves a combination of methods:
- Comprehensive medical history
- Physical and neurological examination
- Symptom questionnaires
- Urine tests
- Bladder ultrasound
- Urodynamic evaluation
- Cystoscopy
Why is a multifaceted approach necessary for diagnosing IC? This comprehensive strategy allows healthcare providers to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms and gather a complete picture of the patient’s bladder health and function.

The Role of Imaging in IC Diagnosis
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis. How does ultrasound contribute to the diagnostic process? A bladder ultrasound provides a non-invasive way to visualize the shape and structure of the bladder, as well as assess how effectively it empties after urination. This information can help healthcare providers identify any abnormalities or functional issues that may be contributing to the patient’s symptoms.
Cystoscopy: A Window into the Bladder
Cystoscopy is a valuable diagnostic tool for interstitial cystitis. What can this procedure reveal? During a cystoscopy, a specialized viewing instrument is inserted into the bladder, allowing healthcare providers to directly observe the bladder lining. This examination can detect ulcers, lesions, or other abnormalities associated with IC, as well as rule out other potential causes of symptoms, such as bladder tumors.
Treatment Strategies for Interstitial Cystitis: A Personalized Approach
Managing interstitial cystitis often requires a multifaceted treatment plan tailored to the individual patient’s needs. What are the primary goals of IC treatment? The main objectives are to alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent further damage to the bladder. Treatment strategies may include:

- Lifestyle modifications
- Dietary changes
- Stress management techniques
- Physical therapy
- Medications
- Bladder instillations
- Nerve stimulation
- Surgical interventions (in severe cases)
How effective are these treatments for interstitial cystitis? The efficacy of treatment can vary significantly from person to person. Some individuals may experience rapid relief, while others may require a combination of therapies or longer treatment periods to achieve meaningful improvement.
Lifestyle Modifications and Dietary Changes
Simple lifestyle changes can often make a significant difference in managing IC symptoms. What dietary modifications can help alleviate IC symptoms? Many patients find relief by avoiding certain trigger foods and beverages, such as:
- Caffeine
- Alcohol
- Citrus fruits
- Spicy foods
- Artificial sweeteners
- Carbonated beverages
In addition to dietary changes, stress management techniques and gentle exercise can help reduce symptom flare-ups and improve overall well-being.
Medications and Advanced Therapies
For many patients, medications play a crucial role in managing interstitial cystitis. What types of medications are commonly used to treat IC? Treatment options may include:
- Pain relievers
- Antidepressants
- Antihistamines
- Pentosan polysulfate sodium (Elmiron)
- Bladder instillations (such as DMSO or heparin)
In cases where conservative treatments prove ineffective, more advanced therapies may be considered. How can nerve stimulation help in managing IC? Techniques such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) or sacral nerve stimulation can help modulate pain signals and improve bladder function in some patients.
Living with Interstitial Cystitis: Coping Strategies and Support
Interstitial cystitis can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, affecting relationships, work, and daily activities. How can individuals with IC cope with the challenges of this chronic condition?
- Educate yourself about the condition
- Join support groups or online communities
- Practice stress-reduction techniques
- Communicate openly with friends, family, and healthcare providers
- Explore complementary therapies (e.g., acupuncture, mindfulness meditation)
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle
What role does emotional support play in managing IC? Having a strong support system can be invaluable for individuals living with interstitial cystitis. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of the condition can provide comfort, practical advice, and a sense of community.

Research and Future Directions in Interstitial Cystitis
The field of interstitial cystitis research is continuously evolving, with scientists working to uncover new insights into the condition’s underlying mechanisms and develop more effective treatments. What are some promising areas of research in IC?
- Genetic factors contributing to IC susceptibility
- Novel biomarkers for improved diagnosis
- Targeted therapies based on individual patient profiles
- Regenerative medicine approaches for bladder repair
- Advanced imaging techniques for early detection
How might future research impact the lives of those with interstitial cystitis? As our understanding of IC grows, there is hope for more precise diagnostic tools, personalized treatment strategies, and potentially even preventive measures for those at risk of developing the condition.
The Promise of Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine holds great promise for improving the management of interstitial cystitis. How might this approach benefit IC patients? By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup, biomarkers, and other factors, healthcare providers may be able to tailor treatments more effectively, maximizing benefits while minimizing side effects.

Preventing Interstitial Cystitis: Is It Possible?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent interstitial cystitis, certain strategies may help reduce the risk of developing the condition or experiencing symptom flare-ups. What preventive measures can individuals take?
- Maintain good bladder health habits
- Stay hydrated
- Practice proper hygiene
- Manage stress levels
- Avoid potential bladder irritants
- Seek prompt treatment for urinary tract infections
How important is early intervention in managing IC? Recognizing the signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis early and seeking prompt medical attention can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life for those affected by this challenging condition.
In conclusion, interstitial cystitis remains a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While there is still much to learn about its causes and optimal treatment strategies, ongoing research and advances in medical understanding offer hope for improved management and quality of life for those living with IC. By raising awareness, promoting early diagnosis, and supporting continued research efforts, we can work towards a future where interstitial cystitis is better understood, more effectively treated, and perhaps even prevented.

What Is Interstitial Cystitis? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Signs and Symptoms of Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis causes mild symptoms in some people and terrible pain and disruption in others. For some, symptoms come and go, while in others they’re present all the time.
Symptoms of IC may go away for a while, only to return months or even years later.
Changes in the bladder caused by interstitial cystitis may have the following symptoms:
Pain Interstitial cystitis can cause sensations of pressure, discomfort, or pain in or around the bladder. The pain may be mild or severe and may also affect the vaginal, urethral, or scrotal areas.
Pain in IC often gets worse as the bladder fills up and is relieved with urination.
Frequent Urination Because the bladder becomes stiff and loses elasticity, people with interstitial cystitis often have the urge to urinate frequently both day and night.
Urinating fewer than eight times during the day and no more than once at night is considered normal. In severe cases of IC, a person may need to urinate up to 60 times per day.
Urgency In people with interstitial cystitis, the need to urinate can be intense and hard to control. In some people, this sensation never goes away, even right after urination.
While certain other disorders that affect the bladder can cause urine leakage, IC typically does not. In fact, leakage can be a clue that you have a different condition.
Sexual Dysfunction Many people with interstitial cystitis experience pain during sexual intercourse. In men, this may include pain after ejaculation.
Nocturia This term denotes the need to urinate multiple times during the night. If it causes nocturia, IC can lead to significant sleep disruption. (1,2)
Causes and Risk Factors of Interstitial Cystitis
Doctors don’t know the exact cause of interstitial cystitis, but many researchers believe that it is initially triggered by damage to the bladder lining. (2)
(2)
In a 2017 study, researchers found that many people with IC produce a protein, called antiproliferative factor, that makes the bladder sensitive to urine. (3)
This protein prevents the growth of bladder cells, so it may prevent the bladder from healing itself when damage occurs. (2)
Many researchers believe that IC may develop for a number of different reasons, such as the following:
Damage to the Bladder Surgery or other types of trauma may damage the bladder, contributing to this condition.
Bladder Distention The inability to empty your bladder for long periods of time has been associated with interstitial cystitis.
Nerve Damage Spinal cord trauma and inflammation of the pelvic nerves have been suspected as causes.
Bacterial Infection A bladder infection, or cystitis, may contribute to the onset of IC in some people.
Muscle Dysfunction When the pelvic floor muscles aren’t working right, they may contribute to bladder problems.
Autoimmune Disorder Some researchers suspect that the body’s own immune system may attack certain bladder cells in some people with IC. (1,2)
In recent years, the relationship between interstitial cystitis and forms of abuse — including physical and sexual abuse — has been widely discussed. Different studies have come to vastly different conclusions about whether any relationship exists between IC and abuse. (2)
How Is Interstitial Cystitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing interstitial cystitis typically isn’t a simple process. There isn’t any single medical test that can definitively diagnose IC, or rule it out.
To diagnose IC, your doctor will consider your symptoms and medical history, and perform a physical and neurological exam. Your doctor may also give you a questionnaire about bladder or pelvic pain.
Your doctor may also order or administer other tests to help diagnose IC, or to rule out other health conditions. These tests may include:
Urine Tests Simple tests of a urine sample can rule out other conditions by detecting signs of an active infection or blood in your urine.
Ultrasound of Bladder This noninvasive test allows doctors to see the shape and structure of your bladder, as well as how well you empty it after urination.
Urodynamic Evaluation This test involves filling your bladder with water through a catheter (narrow tube) to measure pressure as it fills and empties.
Cystoscopy This procedure involves inserting a specialized viewing instrument into your bladder to look for ulcers or lesions caused by IC, or other problems, such as a tumor. (1)
Prognosis of Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis may come and go on its own, even for extended periods of time. But in some people, meaningful relief from symptoms will occur only with treatment.
Symptom relief may not occur right away with treatment, and it may take several attempts to find a treatment strategy that works for you. But most people with IC eventually achieve significant relief and can live a normal life.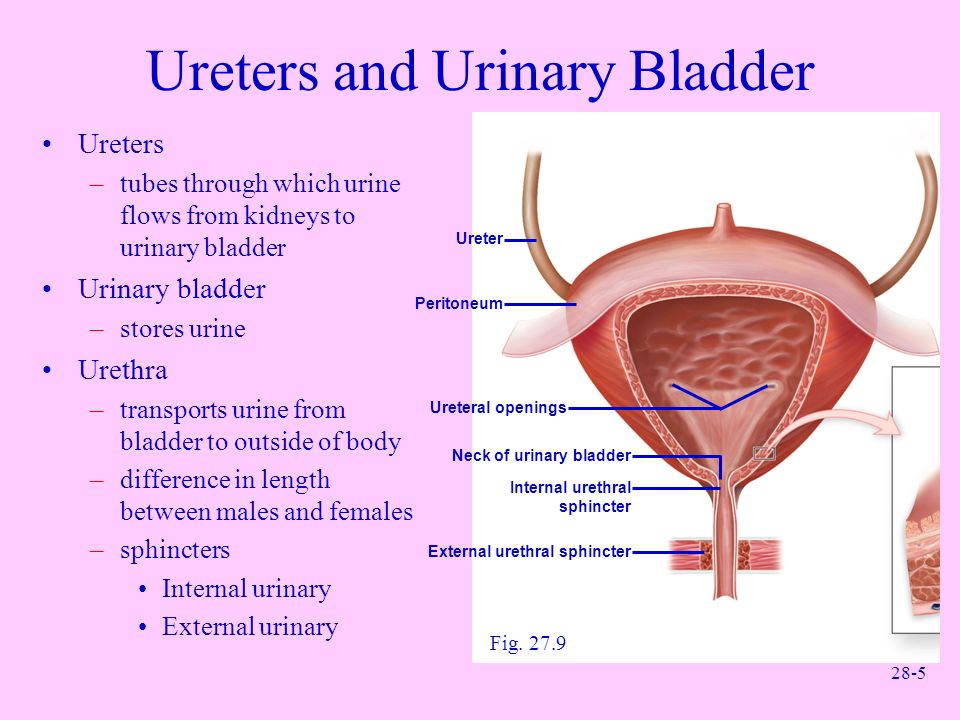 (1,2)
(1,2)
Treatment and Medication Options for Interstitial Cystitis
There isn’t any single treatment that works for everyone with interstitial cystitis. Your doctor will recommend treatments on the basis of your symptoms and whether previous treatments have failed to control them. (1)
The American Urological Association recommends starting with more conservative therapies in most cases (e.g. when ulcers or lesions are not present), before gradually moving to more invasive treatments when “other treatments have not provided adequate symptom control and quality of life improvement.” (4)
Treatment strategies for IC typically follow this series of phases.
Phase 1: Lifestyle measures and physical therapy. The first step in treating IC is to identify things that trigger your symptoms, such as stress or certain foods and beverages. Your doctor may also recommend that you see a pelvic floor physical therapist, who can manipulate muscles in the area or prescribe exercises to help with symptoms.
Phase 2: Medications. Your doctor may prescribe a number of drugs to treat IC symptoms. Some of these medications are taken by mouth, while others are applied directly to the bladder through a catheter (narrow tube).
Phase 3: Neuromodulation, ulcer cauterization, and Botox. Neuromodulation involves delivering electrical impulses to nerves to change how they work. Cauterizing bladder ulcers (known as Hunner’s ulcers or Hunner’s lesions) can offer long-term pain relief, and botulinum toxin (Botox) injections into the bladder muscle may help reduce IC pain when other treatments don’t.
Phase 4: Cyclosporine. The immunosuppressant drug cyclosporine (Neoral) carries many risks, but it may help when other treatments for IC are ineffective.
Phase 5: Surgery. As a last resort, surgery to divert the flow of urine or remove the bladder may be considered. (1,2)
Medication Options
At first, your doctor may recommend that you take over-the-counter pain relief medications for interstitial cystitis. If additional drug treatments are needed, your doctor may recommend the following oral drugs (taken by mouth):
If additional drug treatments are needed, your doctor may recommend the following oral drugs (taken by mouth):
- amitriptyline (Elavil)
- cimetidine (Tagamet)
- hydroxyzine (Vistaril)
- pentosan polysulfate (Elmiron)
Your doctor may also consider administering the following drugs by injection to your bladder:
- dimethyl sulfoxide (Rimso-50)
- heparin
- lidocaine
As an alternative to cauterization, your doctor may decide to inject the steroid drug triamcinolone at the site of a bladder ulcer.
Botox is a drug that paralyzes muscles when injected into them, and may be considered as a bladder treatment for IC when prior treatments are no longer adequate.
Cyclosporine, the last drug that is typically considered for IC, is an oral drug that suppresses the immune system. While it may provide symptom relief, it carries significant risks, including a generally higher risk of infection. (1,4)
Prevention of Interstitial Cystitis
Since the causes of interstitial cystitis are unclear, and the condition may have multiple causes, there aren’t any specific steps you can take to avoid IC in the first place.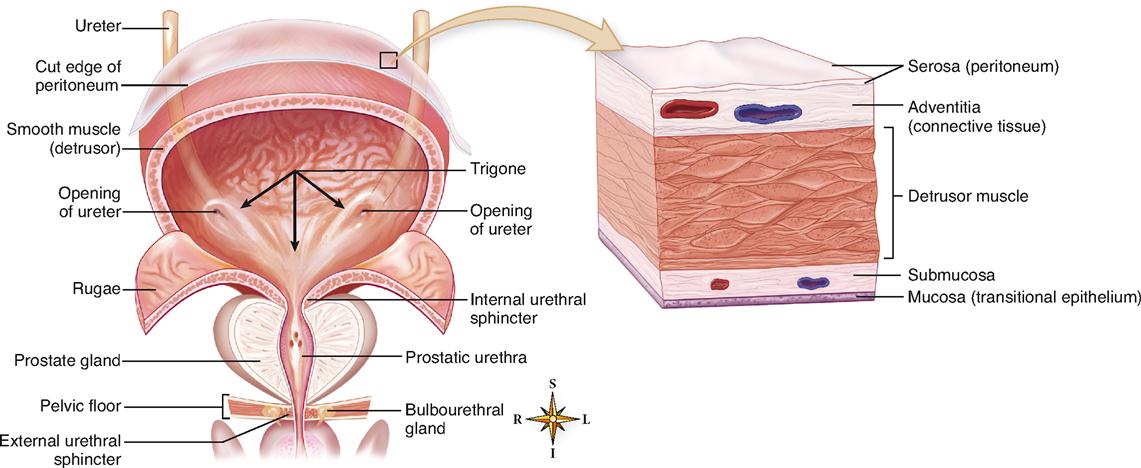
But once you have IC, there are a number of lifestyle measures that may help reduce your symptoms.
Avoiding foods that cause bladder irritation may help relieve symptoms of interstitial cystitis.
Common bladder-irritating foods include:
- Tomatoes
- Citrus fruits
- Spicy foods
- Chocolate
- Coffee and caffeinated beverages
- Alcoholic beverages
- Carbonated beverages
Since so many foods can contribute to symptoms of interstitial cystitis, you may benefit from an elimination diet, in which you stop eating all potential irritant foods for one to two weeks. If your symptoms improve, you can then gradually reintroduce eliminated foods to see if they trigger any symptoms.
Emotional or mental stress can contribute to IC symptoms, so it’s important to identify potential sources of stress in your life and avoid or cope with them to the best of your ability. (1)
Resources We Love
The following organizations and websites offer information and support on interstitial cystitis and related health conditions.
Interstitial Cystitis Association
This nonprofit group is the only charitable organization dedicated to improving the lives of people with interstitial cystitis. Its website provides information on countless aspects of IC, online support groups and forums, virtual education resources, and tips for how to get involved in research or advocacy.
Urology Care Foundation
This website from the American Urological Association provides information on various health conditions, including IC, as well as an overview of the organization’s research efforts and tips for general urological health.
American Chronic Pain Association
This organization’s website provides an overview of different health conditions that can cause chronic pain, as well as online support groups for people with chronic pain and resources for dealing with pain.
International Pelvic Pain Society
This group aims to support people living with conditions that cause pelvic pain, and advocates for greater awareness and “interdisciplinary approaches” to evaluating and treating these conditions. Its website has information on meetings and membership, the group’s annual convention, and fundraising events (all of which follow a virtual format this year).
Its website has information on meetings and membership, the group’s annual convention, and fundraising events (all of which follow a virtual format this year).
Bladder and Bowel Community
This website has articles on a wide range of topics related to bladder and bowel dysfunction, including helpful forms of exercise, mental health concerns, and problems that could be causing bladder symptoms.
Additional reporting by Chris Iliades, MD.
7 Home Remedies for Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Symptoms
Home remedies for urinary tract infection, or UTI, like drinking more water, may help bring relief to symptoms. Learn about more UTI remedies and how …
By Lindsey Konkel
9 Smart Ways to Manage a Leaky Bladder
These 9 healthy habits can make a difference for people with urinary incontinence — and even help them overcome fears of bladder leakage.
By Katherine Lee
10 Ways to Keep Your Bladder Healthy and Happy
Improve your bladder health and avoid urologic conditions like incontinence and UTIs with these helpful tips.
By Eric Metcalf, MPH
The Best and Worst Foods and Drinks for ADPKD
Diet tips to manage the progression of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and to help keep symptoms in check.
By Becky Upham
7 Tips to Reduce Your Risk for UTIs With ADPKD
People with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease are at greater risk for UTIs. Lower your chances of getting a UTI with these expert tips.
By Erica Patino
Urinary Tract Infections Linked to Bacteria in Meat
E. coli is the leading cause of UTI infections, but a new study reveals that over half a millions cases each year could come from E. coli originating …
By Lisa Rapaport
Chronic Kidney Disease: Are You at Risk?
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is called a “silent killer” because it often causes no symptoms until an advanced stage. Knowing your risk factors for CKD…
Knowing your risk factors for CKD…
By Colleen de Bellefonds
Bladder Wall Thickening: Causes and Treatment
Introduction
Your urinary bladder is a balloon-shaped organ that stores urine from the kidneys until it’s released through the urethra. The bladder is located in the pelvic cavity between the pelvic bones. It can hold around 2 cups of urine.
When the bladder is filling with urine, the muscles in the bladder wall relax. When it’s time to urinate, the bladder wall muscles tighten to help push urine out through the urethra.
A thickening of the bladder wall can be a sign of several medical conditions. It’s usually accompanied by other symptoms, too. Many of these conditions are easily treatable with an early diagnosis.
It’s important to report any changes in your urinary habits to your doctor. Bladder infections, for example, can lead to kidney infections. These can be quite serious if not treated early.
The muscular wall of your bladder tends to grow thicker if it has to work harder to urinate. It can also thicken if it becomes irritated and inflamed. Scarring of the bladder wall may also cause it to thicken.
Common causes of bladder wall thickening include:
Inflammation due to urinary tract infection (UTI)
A UTI is often the result of bacteria entering the urethra and then the bladder. These infections are more common among females than males.
UTIs are often associated with sexual intercourse, but a woman who isn’t sexually active can also develop a bladder infection. This is simply because of the amount of bacteria in and around the vagina.
One of the major responses to a UTI is inflammation of the bladder wall, a condition known as cystitis. Prolonged inflammation can lead to thickening of the wall. Some other causes of cystitis include inflammation triggered by cancer treatments, like radiation and chemotherapy, or prolonged use of a catheter./cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/10732403/WumKAm3.jpg)
Noncancerous tissue growths
Abnormal tissue growth in the bladder wall causes tumors to grow and the wall to thicken. Noncancerous (benign) tumors include papillomas. For some cases, viruses may be the cause of these growths.
Other benign bladder tumors include leiomyomas, but these are rare. They result from an overgrowth of smooth muscle cells in the bladder wall.
Fibromas are another benign bladder tumor. Abnormal growth of fibrous connective tissue in the bladder wall causes these.
Cancer
Cancerous (malignant) tumors tend to form first in the innermost lining of the bladder wall. This lining is known as the transitional epithelium.
The abnormal growth of cells in the bladder wall may be related to smoking tobacco or exposure to chemicals. Chronic irritation of the bladder wall or previous radiation exposure can also be the culprit.
Hemorrhagic cystitis
Sometimes irritation and inflammation of the bladder wall causes bleeding from the bladder lining. This is considered hemorrhagic cystitis. Causes may include:
This is considered hemorrhagic cystitis. Causes may include:
- radiation therapy
- chemotherapy
- an infection
- exposure to certain chemicals, such as insecticides or dyes
Amyloidosis
Amyloid is a type of abnormal protein that’s made in your bone marrow. Amyloidosis is the buildup of amyloid in an organ. The bladder is one of several organs that can be vulnerable to this disease, but it’s not common.
End stage renal disease can trigger the abnormal growth of amyloid when dialysis doesn’t filter out amyloid that may be present. Autoimmune inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can also trigger amyloidosis, as well as other conditions. There’s also an inherited version called familial amyloidosis.
Bladder outlet obstruction
Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) is a blockage at the base of the bladder where it empties into the urethra. For men, an enlarged prostate or prostate cancer can result in BOO. Other causes of BOO for men and women include:
- bladder stones
- tumors
- scar tissue in the urethra
Symptoms of bladder wall thickening usually relate to changes in your urinary habits. You may urinate more frequently, or you may notice that it feels different when you relieve yourself. You may also notice changes in the urine itself.
You may urinate more frequently, or you may notice that it feels different when you relieve yourself. You may also notice changes in the urine itself.
Underlying causes, such as infections or tumors, can lead to some of the following symptoms:
Fever
Cystitis may cause a low-grade fever. A fever is a symptom of many conditions. But if a fever develops at the same time as bladder-related symptoms, see your doctor right away.
Pain when urinating
Painful urination is a symptom of many conditions as well, ranging from sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) to bladder cancer. A bladder or kidney infection can also cause a burning sensation when you’re urinating. This is one of the surest signs that you should seek medical treatment soon.
Urgency or difficulty urinating
A bladder disorder can make it difficult to fully empty your bladder. This can cause frequent urination, feeling like you always have to urinate, or both.
When the bladder wall thickens, the bladder may not be able to hold as much urine as it normally does. This can create those urgent feelings of having to urinate more frequently. BOO can also make it harder to urinate.
This can create those urgent feelings of having to urinate more frequently. BOO can also make it harder to urinate.
Cloudy urine or blood in urine
You may also see a small amount of blood in your urine. Sometimes this occurs from something as harmless as a strenuous workout. It could also be a sign of cystitis, bladder cancer, or another urinary tract problem.
Often, blood in urine can only be seen under a microscope. If you can see blood in your urine yourself or notice your urine turning cloudy, see your doctor, even if you have no other symptoms yet. It can be a sign of several potentially serious conditions. It’s best to get an early diagnosis sooner rather than later.
Foul-smelling urine
Foul-smelling urine or urine with a very strong smell could simply be related to food or beverages you recently consumed. However, it may be a sign of infection. Once a bladder infection is effectively treated, the related foul smell should disappear.
The underlying causes of a thickened bladder wall can differ between men and women.
BOO is more common among men, because it’s often linked to prostate problems. An enlarged prostate forces the bladder to work harder to empty itself of urine. This in turn causes the bladder wall to thicken. Prostate treatment can help reduce the burden on the bladder.
UTIs are more common among women. Thorough treatment can ease the strain on the bladder and allow thickened bladder walls to return to normal.
If you notice symptoms of bladder wall thickening or any symptoms related to your urinary tract system, see your doctor.
They’ll likely have you undergo several tests, such as a urinalysis. For this test, a sample of your urine is checked for signs of infection, blood cells, or abnormal protein levels. If your doctor suspects bladder cancer, they’ll check for cancer cells, too.
If cancer is a possibility, a cystoscopy may also be performed. During this procedure, a thin, flexible scope is guided up the urethra to check the lining of your urethra and bladder. A cystoscopy can also evaluate recurrent infections in the urinary tract.
A cystoscopy can also evaluate recurrent infections in the urinary tract.
In addition, a woman may undergo a pelvic exam to help diagnose an infection or other disorder.
Treating a thickened bladder wall means treating the underlying condition that caused the change in the wall.
For example, UTI treatment usually involves a course of antibiotic therapy. To prevent UTIs, practice good hygiene. Wipe front to back to reduce the risk of germs from the rectum reaching the urethra.
Surgery can remove noncancerous tumors that are causing you symptoms. The tumors usually won’t recur.
Cancerous growths can sometimes be removed with surgery, too. Additional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation, may also be necessary.
Prostate treatment is a somewhat controversial subject. Prostate surgery can sometimes lead to incontinence or erectile dysfunction. If prostate symptoms are minor, your doctor may recommend a watch-and-wait approach to monitor your prostate regularly. Prostate cancer is often a slow-growing cancer. This means aggressive treatment isn’t always best.
Prostate cancer is often a slow-growing cancer. This means aggressive treatment isn’t always best.
If excess bladder emptying due to urge incontinence is a problem, your doctor may recommend anticholinergic drugs. These medications relax the detrusor muscle of the bladder.
If urinary retention is occurring due to BOO, your doctor may prescribe medication, such as tamsulosin, to help your urine flow be stronger.
A range of conditions can trigger bladder wall thickening. If you suspect that you have a condition causing you bladder problems, see your doctor, even if it just seems like a minor annoyance at first. Doing so will prevent your symptoms from worsening. Some bladder conditions can lead to life-threatening kidney problems.
Early treatment can prevent long-term harm and provide fast relief for uncomfortable symptoms.
Bladder ultrasound – price in Moscow, done at Medcenterservice
Bladder ultrasound prices for men and women
*The administration of the Medcenterservice clinic takes all necessary measures to update prices on the website in a timely manner. But we
But we
we recommend that you clarify the cost of services with the administrators of clinics or with the operators of our Call-center by phone
+7 (495) 324-88-99.
Ultrasound of the bladder is a diagnostic examination using ultrasound. The procedure helps to evaluate the size and contours of the organ, identify neoplasms, inflammation, sand and stones.
Where to get an ultrasound of the bladder?
You can undergo an ultrasound examination of the bladder in the MedCenterService network of clinics. The patients of the medical center receive many benefits:
- High information content. Thanks to the latest generation equipment, it is possible to obtain accurate diagnostic results.
- Examination in comfortable conditions and without queues.
- Individual and competent approach. Reception is conducted by highly qualified doctors with extensive experience.
The result of an ultrasound of the bladder will be ready immediately after the procedure, which allows you to immediately contact a doctor for interpretation and treatment.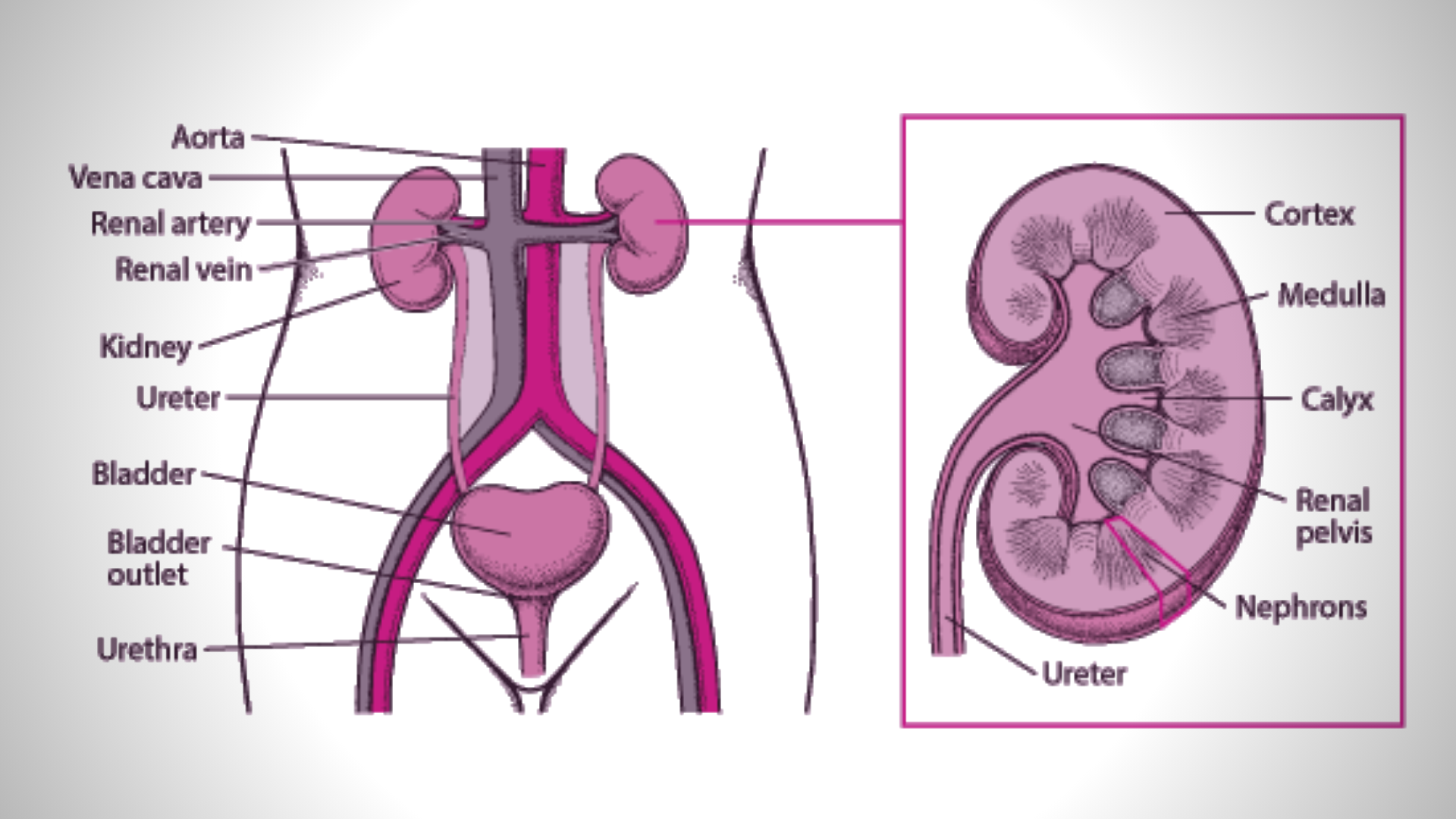
What does an ultrasound of the bladder show?
- Cystitis or inflammation, in acute and chronic stages.
- Stones and sand in the bladder.
- Polyps, cysts, papillomas.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
- Neurogenic bladder.
- Omission of an organ. Usually found in women.
- Protrusion of the wall of the bladder – diverticulum. More common in men.
- Congestion of urine. This pathology is often found in men with prostatitis.
During an ultrasound, the doctor evaluates the contours of the bladder, its location and size, wall thickness, as well as the condition of the blood vessels and nerve endings around the organ. These indicators help to suspect a pathological process.
Indications for bladder ultrasound
- After mechanical trauma or surgery.
- If a tumor is suspected.
- Men are prescribed for prostate adenoma and prostatitis.
- For women, the procedure is indicated in a comprehensive examination of the pelvic organs.

- If urine and blood tests, urethral swabs are negative.
- If urolithiasis is suspected.
- In the presence of malformations.
- If pelvic organ prolapse has occurred.
- With exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory process.
- If you are concerned about urinary incontinence.
- If varicose veins of the bladder are suspected.
It is recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan on your own if the following symptoms appear:
- Pain during urination, burning sensation.
- Any problems with urination, such as a very thin stream and the need to push, too little urine.
- Feeling of a full bladder even after going to the toilet.
- Frequent urge to urinate, especially against the background of pain in the lower abdomen.
- Blood and pus in the urine.
Regular ultrasound of the bladder is recommended for patients with chronic cystitis and in the presence of a diagnosis of urolithiasis. The risk group includes people with a history of kidney disease, women immediately after childbirth, and patients with a hereditary predisposition.
The risk group includes people with a history of kidney disease, women immediately after childbirth, and patients with a hereditary predisposition.
There are no contraindications to the study, the procedure is safe and can be performed during pregnancy and even newborns. The exception is situations where it is not possible to use the external sensor, for example, severe skin lesions with ulcers or an open wound in the affected area. In this case, the skin is treated first, and then an ultrasound diagnosis is performed.
Bladder ultrasound preparation
The training for men and women is the same. 2-3 days before the procedure, the following recommendations must be observed:
- Avoid foods that cause excessive gas. These include peas, corn, whole milk, raw vegetables and fruits, carbonated drinks, and yeast.
- Cleanse the bowels the day before. If defecation occurred naturally in the evening or in the morning before the ultrasound, then nothing needs to be done.
 In other cases, a microclyster or laxative is used.
In other cases, a microclyster or laxative is used. - In the presence of bloating, it is recommended to take a carminative, such as Espumizan.
- The day before the consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited.
Dieting is very important, as the intestines are located nearby, in which gases can accumulate. Excess air interferes and makes the ultrasound scan uninformative.
Ultrasound diagnostics is carried out with a full bladder, the only way to straighten the organ in order to clearly see the condition of the walls and mucous membranes. To fill the bladder, you need to drink a liter of clean water without gas an hour before the diagnosis and do not urinate. When there is a strong urge to go to the toilet, you can go for a diagnosis. If you cannot tolerate the urge at all, you can release some fluids to relieve the pressure, but at the same time the bladder should remain full.
Specific training for men
A male bladder exam can be done through the rectum.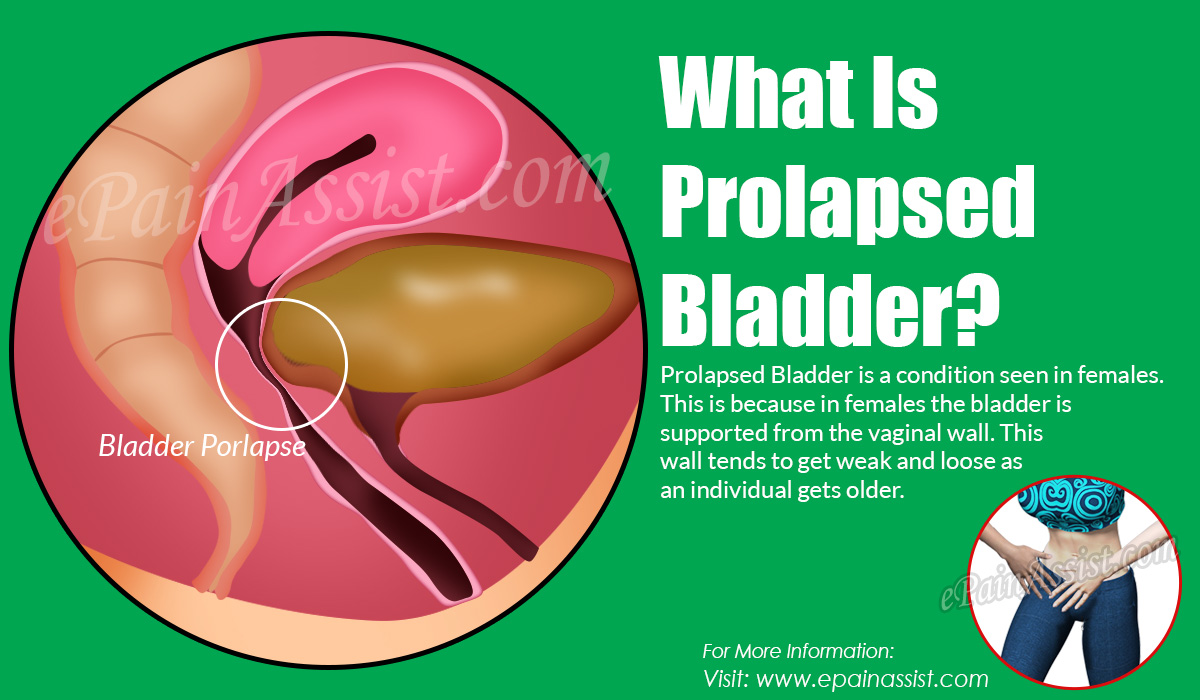 In this case, it is necessary to conduct a cleansing enema before the procedure. Otherwise, the feces will not allow visualization of the bladder and surrounding tissues.
In this case, it is necessary to conduct a cleansing enema before the procedure. Otherwise, the feces will not allow visualization of the bladder and surrounding tissues.
How is a bladder ultrasound done for women?
The method of the procedure is chosen by the doctor, depending on the gender of the patient, his individual characteristics and the need to visualize certain structures, for women:
- transabdominally – through the anterior wall of the abdomen;
- transvaginally – through the vagina.
Adult women are more often prescribed transvaginal ultrasound, as it helps to more accurately examine the pelvic organs. But if the patient is a virgin or the insertion of the sensor into the vagina is not possible, the transabdominal method is used.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the bladder is performed in the following order:
- You need to undress below the waist, take off your underwear and lie down on the couch.

- The doctor will ask you to bend your knees and spread them apart.
- The vaginal transducer is covered with a condom and lubricated with hydrogel for better ultrasound conduction.
- The device is inserted into the vagina while viewing the result on the monitor.
- The physician records all data in the study protocol.
The procedure is painless, but may cause some discomfort associated with the need to insert the probe into the vagina.
To conduct transabdominal ultrasound, the doctor lubricates the skin of the abdomen with a hydrogel and applies an external sensor that moves smoothly from side to side for better visualization of all structures.
How an ultrasound of the bladder is done for men
Male patients are diagnosed in the following ways:
- transrectal – through the rectum.
- transabdominally – through the anterior wall of the abdomen.
Men are more likely to have a transrectal examination, because it allows a good view of the prostate gland and an assessment of the level of residual urine.
Transrectal ultrasound is performed in the following order:
- The patient undresses below the waist, removes underwear.
- The doctor invites you to the couch, you need to lie on your side with your legs tucked up to your stomach and open access to the anus for the doctor.
- The doctor takes a transrectal tube-shaped transducer, puts a condom on it for ultrasound examination and lubricates it with a hydrogel for better conduction of ultrasound waves.
- The doctor slowly inserts the sensor into the rectum and observes the results of the examination on the computer monitor, and records the data obtained in the examination protocol.
Many men are interested in the question of whether it hurts to do a transrectal examination of the bladder. The procedure causes discomfort and can be painful if the patient is tense. There will be no pain if you can completely relax the anus.
Transabdominal ultrasound is no different from any other external study. The doctor lubricates the skin in the lower abdomen with gel and applies a sensor that moves from side to side.
The doctor lubricates the skin in the lower abdomen with gel and applies a sensor that moves from side to side.
Norms and interpretation of bladder ultrasound
When deciphering the result of an ultrasound of the bladder, the doctor pays attention not only to the data obtained, but also to the patient’s complaints, the results of other studies and the presence of chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system. Ultrasound indicators are compared with the norms, which are based on statistical data.
Normal indicators:
- The filled bladder is pear-shaped.
- The empty organ is saucer-shaped.
- The structure of the organ is echo-negative.
- The contours are even, clear.
- In men, the normal volume is 450-750 ml.
- Volume for women – 250-550 ml.
- Wall thickness up to 4 mm.
- The filling rate of the organ is 50 ml per hour.
- The volume of residual urine must not exceed 50 ml.

- No neoplasms were found.
Thickening of the walls of the organ from 5 mm or more may indicate the presence of a tumor, stone, parasite damage, or the formation of a tuberculous granuloma. The general increase in the body is usually observed with its overstretching, which is associated with a constant increase in the level of residual urine. This is observed with prostatitis, prostate adenoma in men, with urolithiasis.
A decrease in the size of the bladder is observed with tuberculosis, parasitic pathologies, and also as a result of surgical intervention.
A precipitate in the form of flakes may indicate the presence of cystitis, there is also a thickening of the organ wall, a decrease in its volume. In chronic pathology, the contours of the organ are uneven.
Ultrasound of the Bladder – procedure
The bladder in the human body serves as a reservoir where the accumulation of urine, which is formed by the kidneys, takes place. For the timely detection of possible pathologies, various types of examinations are used, among them ultrasonic examination (ultrasound) is completely safe and effective.
For the timely detection of possible pathologies, various types of examinations are used, among them ultrasonic examination (ultrasound) is completely safe and effective.
Why ultrasound is done and what can be determined
The implementation of the ultrasound procedure helps to identify a wide range of abnormalities in the functioning of the organ and evaluate various parameters:
So, with a small size of the organ, the doctor can diagnose fibrosis of the walls, chronic cystitis. With an increased size, it is possible that there are stones in the bladder or prostate adenoma develops. After deciphering the data, they are transferred to a specialist with a narrow profile (urologists or nephrologist), who makes the diagnosis. It is worth noting that ultrasound is recommended even in the absence of obvious signs of diseases at least once every few years, since such prevention will avoid the development of complications, start treatment before the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
It is worth noting that ultrasound is recommended even in the absence of obvious signs of diseases at least once every few years, since such prevention will avoid the development of complications, start treatment before the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
Bladder normal values
The bladder is an organ capable of changing its size depending on how full it is. Ultrasound of the bladder helps to identify the following parameters:
- Shape. Description: The bladder can take on a variety of shapes, depending on how full it is and what condition the adjacent organs are in. For example, in female representatives, the form is directly related to the location of the uterus, childbirth (their number), and the state of pregnancy.
- Structural structure. The structure of the bladder in the normal state should be echo-negative. A parameter such as echogenicity is affected by the age criterion: with aging, it increases if chronic inflammatory processes are present.

- Volume. The volume of the organ in males is slightly larger than in women and, on average, is in the range of 350-750 milliliters. For female representatives, this value varies between 250-550 milliliters. Significant changes in this parameter due to pregnancy, the presence of tumor formations, pathologies in the change of organs in the immediate vicinity, surgeries and other factors are not excluded.
- Wall thickness. They are formed by the outer fibrous and inner mucosa. The degree of filling of the organ affects the wall thickness, due to which it can reach an average of 2-4 millimeters. With any violation of the local type of parameter, as a rule, the occurrence of pathology is judged.
- Filling and emptying. The filling rate is normally at least 50 milliliters per hour. With the accumulation of more than 100 milliliters of urine, a person feels the first urge to urinate. An adult should empty the bladder at least 4 times a day, while in one act 150-250 milliliters of urine is normally excreted.

- Amount of residual urine. This indicator should not exceed 50 milliliters according to established standards, the opposite situation indicates the possible presence of deviations in the functioning of the body.
Interpretation of ultrasound results
Ultrasound examination helps to identify the symptoms underlying the initial diagnosis. The information obtained as a result of the procedure can be interpreted in different ways depending on how it was carried out. The qualification of a specialist also has an impact. When deciphering an ultrasound of the bladder, attention is paid to the presence or absence of echographic signs indicating damage to the organ:
- Wall thickening. The wall can be considered thick if it exceeds the thickness of 4-5 millimeters. In this case, there is a selection of a uniform or local type of thickening. The detection of this symptom in most cases indicates the presence of chronic cystitis. Such a deviation can lead to bladder diverticulum, its parasitic lesion, tuberculous lesion and other diseases.

- Dimensional changes. It is expressed in an increase or vice versa, in a decrease in the bladder. A situation in which the bladder increases in size indicates its excessive distension with urine. This happens when an accumulation of stones or a tumor forms in the organ, clogging it and preventing the flow of urine, as a result of which its accumulation is observed.
- Reverse process. When the bladder is reduced in size, it occurs as a result of schistosomiasis in the last phase of development, frequent cystitis accompanied by tuberculosis, surgical procedures and chemotherapy. The process of size reduction can be observed if there are congenital anomalies or non-specific lesions of the organ at the last stage of development.
- Inflammatory infiltrate or presence of sediment. This symptom develops due to the acute phase of inflammation of the bladder, that is, cystitis. Sediment or flakes, as it is also called, refers to an accumulation of inflamed cells, which include epithelial cells and leukocytes.
 Less commonly, the precipitate is formed by salt crystals, oxalates. Acute cystitis is accompanied by the presence of a mobile sediment, the localization of which is the posterior wall of the organ. Ultrasound can detect this symptom.
Less commonly, the precipitate is formed by salt crystals, oxalates. Acute cystitis is accompanied by the presence of a mobile sediment, the localization of which is the posterior wall of the organ. Ultrasound can detect this symptom. - Echogenic lesions. Represents one of the most common symptoms observed as a result of ultrasound. Formations can have both tumor and non-tumor nature. They can have both a mobile character and adjoin the wall of the organ. The type of formation on ultrasound is determined by their echogenicity, for example, a stone has a maximum echogenicity, a cyst has a minimal one.
- Urinary reflux. Reflux refers to the flow of urine into the ureters. The most severe cases lead to its reflux into the renal pelvis. The occurrence of such a symptom is associated with various pathologies with simultaneous blockage of the mouths of the ureters. Urine reflux is formed due to congenital anomalies associated with the development of the urethra, the functioning of the bladder; the presence of foreign formations.
 Diagnosing this symptom on ultrasound suggests the need for a second Doppler study to determine the amount of urine reflux and the direction of its current. In addition, the study will reveal one of the 5 degrees of reflux itself.
Diagnosing this symptom on ultrasound suggests the need for a second Doppler study to determine the amount of urine reflux and the direction of its current. In addition, the study will reveal one of the 5 degrees of reflux itself.
How to properly prepare for an ultrasound scan
Correct execution of all preparatory procedures before the examination is of great importance in diagnostics. The basic requirements for preparing for ultrasound are the same for both men and women. It should be remembered that there should be fullness of the organ under study, for which it is necessary to try to refrain from emptying and drink the required amount of liquid – about 2 liters a few hours before the procedure. The method of conducting the study also affects the preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder. There are 4 main methods.
Transabdominal method
The transabdominal method of the procedure requires preliminary measures to prepare the intestines and fill the bladder. For this, a special diet is prescribed for 1-2 days before the study.
For this, a special diet is prescribed for 1-2 days before the study.
It is also recommended to avoid cooked vegetables and fruits from the diet. To reduce gases, the body should be prepared with microclysters, glycerin suppositories, activated charcoal or other drugs. It is also necessary to prepare the bladder. Approximately 4-5 hours before the procedure, you need to drink 2-3 glasses of water and try to refrain from going to the toilet. If you have delayed bladder filling, you can take diuretics prescribed by your doctor.
Transrectal
Transrectal ultrasound involves emptying the rectum. There are several methods of preparation, including the use of microclysters, glycerin suppositories, the use of a laxative that has a plant base.
To use a microclyster, the following items are required: Janet syringe, solution, agent to lubricate the tip. As a solution, you can prepare a chamomile decoction or saline solution, add oil and heat just before use. Then draw up the solution, lubricate the tip with petroleum jelly or some kind of greasy cream. The injection of the solution must be carried out slowly, while breathing deeply. After removing the can, it is recommended to lie on your side for at least 15 minutes. Emptying the intestines is facilitated by taking drugs that have a laxative effect, for example, phytolax, senadexin, mucofalk and others.
The injection of the solution must be carried out slowly, while breathing deeply. After removing the can, it is recommended to lie on your side for at least 15 minutes. Emptying the intestines is facilitated by taking drugs that have a laxative effect, for example, phytolax, senadexin, mucofalk and others.
Other methods of examination
Transvaginal ultrasound requires bowel cleansing as a prerequisite. The filling of the organ is not necessary. The transurethral method consists in observing preparatory measures to ensure good tolerability of the drug. So, before research based on this method, it is necessary to exclude the use of food in abundant quantities, alcoholic beverages, tobacco products.
How the procedure works
First, the patient lies down on the couch. After the release of the lower abdomen from clothing, a procedure for applying a special gel follows. Then the doctor applies a sensor to the area where the gel is applied, and with a slight pressure is applied to the stomach to examine the bladder and organs in the immediate vicinity.


 In other cases, a microclyster or laxative is used.
In other cases, a microclyster or laxative is used.



 Less commonly, the precipitate is formed by salt crystals, oxalates. Acute cystitis is accompanied by the presence of a mobile sediment, the localization of which is the posterior wall of the organ. Ultrasound can detect this symptom.
Less commonly, the precipitate is formed by salt crystals, oxalates. Acute cystitis is accompanied by the presence of a mobile sediment, the localization of which is the posterior wall of the organ. Ultrasound can detect this symptom. Diagnosing this symptom on ultrasound suggests the need for a second Doppler study to determine the amount of urine reflux and the direction of its current. In addition, the study will reveal one of the 5 degrees of reflux itself.
Diagnosing this symptom on ultrasound suggests the need for a second Doppler study to determine the amount of urine reflux and the direction of its current. In addition, the study will reveal one of the 5 degrees of reflux itself.