What happens when you get strep throat. Strep Throat: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment – A Comprehensive Guide
How does strep throat spread. What are the main symptoms of strep throat. How is strep throat diagnosed. What treatments are available for strep throat. Can strep throat be prevented. What complications can arise from untreated strep throat.
Understanding Strep Throat: A Common Bacterial Infection
Strep throat is a bacterial infection that affects the throat and tonsils. It’s caused by group A streptococcus, also known as Streptococcus pyogenes. This bacteria resides in the nose and throat, making it easily transmissible from person to person. While anyone can contract strep throat, it’s particularly prevalent among children and teenagers.
The bacteria responsible for strep throat can spread through various means:
- Respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing
- Close contact with an infected individual
- Touching contaminated surfaces and then touching your face
- Sharing personal items like utensils or toothbrushes
- Kissing someone who has the infection
Once exposed to the bacteria, symptoms typically appear within 2 to 5 days. Without treatment, an infected person can remain contagious for up to a month. However, with appropriate antibiotic treatment, the contagious period can be reduced to about 24 hours.
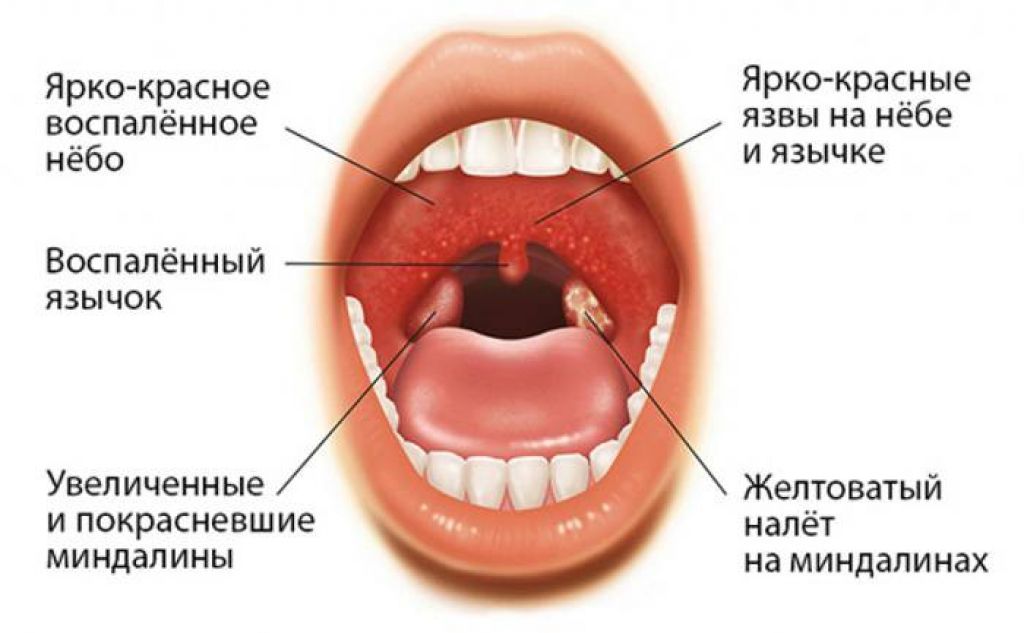
Recognizing the Symptoms of Strep Throat
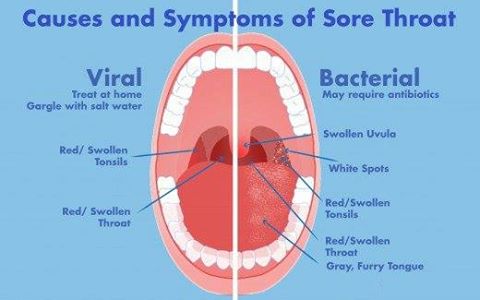
The primary symptom of strep throat is a sore throat that develops rapidly. However, it’s important to note that not all sore throats are caused by strep bacteria. Other symptoms that may indicate strep throat include:
- Fever of 101°F (38.3°C) or higher
- Red and swollen tonsils
- Pain when swallowing
- Swollen and tender lymph nodes in the neck
- White patches in the throat
- Tiny red spots on the roof of the mouth (petechiae)
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach pain
- Headache and body aches
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rash
Do these symptoms always indicate strep throat? Not necessarily. Some signs may suggest a viral infection rather than strep, such as a runny nose or cough. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosing Strep Throat: The Importance of Testing
Accurately diagnosing strep throat is essential for proper treatment. Healthcare professionals use two primary methods to test for strep throat:
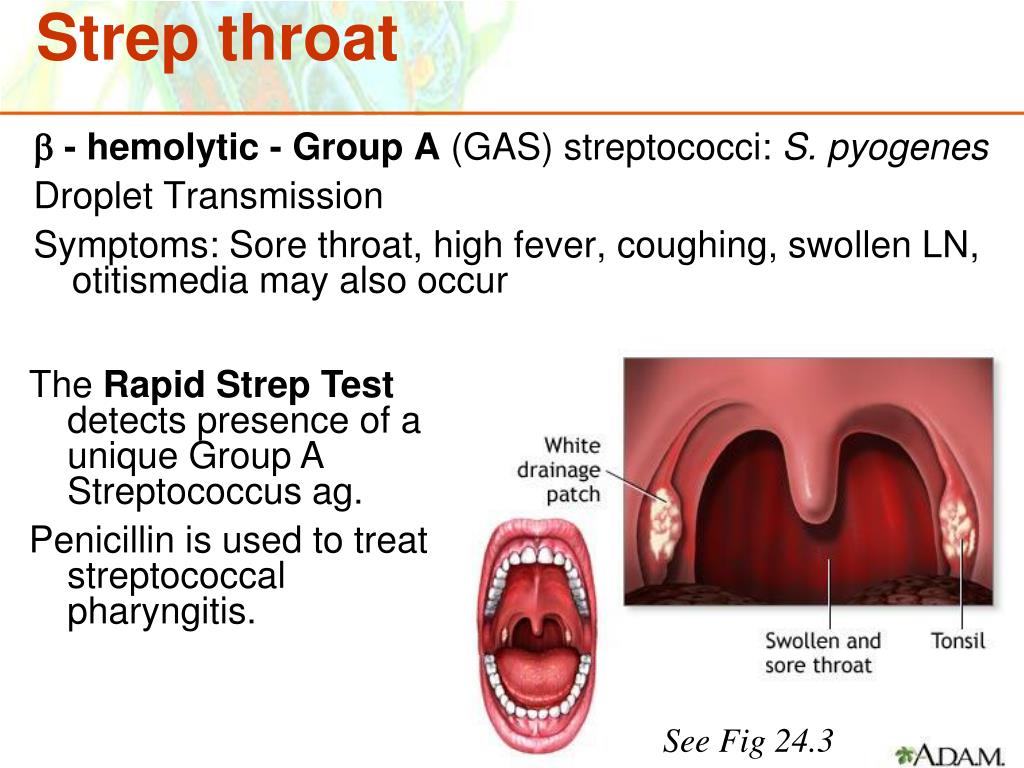
1. Rapid Strep Test
This quick test can provide results in about 20 minutes. The process involves swabbing the back of the throat and tonsils. If the test is positive, antibiotics may be prescribed. However, a negative result doesn’t necessarily rule out strep throat, as the test can sometimes miss infections.
2. Throat Culture
A more definitive but slower method, a throat culture involves sending a throat swab to a laboratory. Results typically take about two days. This test can confirm whether strep bacteria are present, even if the rapid test was negative.
Why is proper diagnosis crucial? It helps distinguish between bacterial and viral infections, ensuring appropriate treatment and preventing unnecessary antibiotic use.
Treating Strep Throat: Antibiotics and Symptom Management
The primary treatment for strep throat is antibiotics. These medications serve several purposes:
- Killing the strep bacteria
- Reducing symptom duration and severity
- Preventing the spread of infection to others
- Lowering the risk of complications
Antibiotic courses typically last about 10 days. It’s crucial to complete the entire course as prescribed, even if symptoms improve earlier. Stopping antibiotics prematurely can leave some bacteria alive, potentially leading to a recurrence of the infection.
Are there any risks associated with antibiotic treatment? While generally safe, some individuals may be allergic to certain antibiotics. It’s important to inform your healthcare provider of any known allergies before starting treatment.
Symptom Relief
In addition to antibiotics, over-the-counter medications can help manage symptoms:
- Ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain relief and fever reduction
- Throat lozenges or sprays for temporary throat pain relief
- Warm salt water gargles to soothe the throat
Remember, these treatments address symptoms but do not cure the underlying bacterial infection.
Home Remedies for Strep Throat: Complementing Medical Treatment
While medical treatment is essential for strep throat, several home remedies can provide additional comfort and support recovery:
- Rest: Adequate sleep helps the body fight infection more effectively.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids prevents dehydration and soothes the throat.
- Soft foods: Consuming easy-to-swallow foods reduces throat irritation.
- Honey: Its natural antibacterial properties may help soothe the throat.
- Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can relieve throat dryness and irritation.
How effective are these home remedies? While they can provide symptomatic relief, they should not replace prescribed medical treatment. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice.
Preventing Strep Throat: Hygiene and Lifestyle Practices
Preventing strep throat involves a combination of good hygiene practices and lifestyle habits:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals
- Not sharing personal items like utensils or towels
- Covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support your immune system
Can these measures completely prevent strep throat? While they significantly reduce the risk, it’s not always possible to avoid exposure entirely, especially in school or work environments.
Complications of Untreated Strep Throat: Why Prompt Treatment Matters
Left untreated, strep throat can lead to several serious complications:
- Rheumatic fever: An inflammatory condition affecting the heart, joints, and nervous system
- Kidney inflammation (post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis)
- Scarlet fever: A strep-related illness characterized by a distinctive rash
- Peritonsillar abscess: A collection of pus near the tonsils
- Sinus and ear infections
- Toxic shock syndrome (rare but severe)
How common are these complications? While relatively rare in developed countries with access to antibiotics, they underscore the importance of prompt and appropriate treatment for strep throat.
Strep Throat in Special Populations: Children, Elderly, and Immunocompromised
While strep throat can affect anyone, certain groups may experience it differently or face higher risks:
Children
Children, especially those between 5 and 15 years old, are most susceptible to strep throat. They may experience more severe symptoms and are at higher risk for complications if left untreated.
Elderly
Older adults may have milder symptoms, making diagnosis challenging. However, they face increased risks of complications due to potentially weaker immune systems.
Immunocompromised Individuals
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, may experience more severe infections and are at higher risk for complications.
How does the approach to treatment differ for these groups? While the basic treatment remains the same, healthcare providers may monitor these patients more closely and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Recurrent Strep Throat: Causes and Management
Some individuals experience recurrent strep throat infections. Possible reasons include:
- Incomplete antibiotic treatment
- Reinfection from family members or close contacts
- Being a strep carrier (harboring the bacteria without symptoms)
- Weakened immune system
Management of recurrent strep throat may involve:
- Extended antibiotic courses
- Testing and treating family members
- Tonsillectomy in severe cases
- Investigating underlying immune system issues
Is tonsillectomy always necessary for recurrent strep throat? Not always. The decision to remove tonsils depends on various factors, including the frequency of infections and their impact on quality of life.
The Future of Strep Throat Management: Research and Innovations
Ongoing research in strep throat management focuses on several areas:
- Development of a strep throat vaccine
- Improved rapid diagnostic tests
- Novel antibiotic treatments
- Understanding the long-term effects of recurrent infections
- Exploring the role of the microbiome in susceptibility to strep infections
How might these advancements change strep throat management? Future innovations could lead to more accurate diagnoses, more effective treatments, and potentially even prevention through vaccination.

In conclusion, while strep throat is a common and generally treatable condition, it requires prompt attention and appropriate care. Understanding its symptoms, seeking timely medical intervention, and following prescribed treatments are key to managing this bacterial infection effectively and preventing potential complications. As research progresses, we can look forward to even better ways of dealing with strep throat in the future.
Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Medically Reviewed by Poonam Sachdev on February 15, 2023
- What Is Strep Throat?
- Is Strep Throat Contagious?
- Strep Throat Symptoms
- Strep Throat Diagnosis
- Strep Throat Treatment
- Strep Throat Home Remedies
- Strep Throat Prevention
- Strep Throat Complications
- More
Strep throat is an infection of the throat and tonsils caused by a bacteria called group A streptococcus, which is also known as Streptococcus pyogenes. This bacteria lives in the nose and throat. You can get the infection from someone who is carrying strep A bacteria or is sick from it.
Anyone can get strep throat, but it’s most common in children and teens.
The bacteria that cause strep throat pass easily from person to person through close contact.
Strep throat spreads when someone who has the infection coughs or sneezes. Droplets filled with bacteria spray into the air.
Droplets filled with bacteria spray into the air.
You can give yourself strep throat (or catch it from someone else) if you:
- Breathe it in
- Touch something these droplets land on, such as a doorknob or table, and then rub your eyes, nose, or mouth
- Share personal items such as a fork or spoon, glass, or toothbrush with someone who is sick
- Kiss a person who has it
When you get infected, you typically start to show symptoms about 2 to 5 days after you were exposed to the bacteria.
You can stay contagious for up to a month if you don’t get treated. Antibiotics can prevent the infection from spreading. People who take antibiotics stop being contagious after about 24 hours.
A sore throat is the main sign you or your child has strep. Colds and other viruses can also cause a sore throat. One way to tell the difference between strep throat and another virus is that a virus will often cause a runny nose, too.
With strep, the sore throat comes on quickly and is more likely to cause these other symptoms. Call your doctor if you or a child in your care has these symptoms:
A fever of 101 F or higher
Red, swollen tonsils
Pain when you swallow
Swollen and/or tender lymph nodes at the front of your neck
White patches in the throat
Tiny red spots on the roof of the mouth (called petechiae)
Appetite loss
Stomachache
Headache
Body aches
Nausea or vomiting
Loss of appetite
Rash
Signs that the infection might be viral rather than caused by strep bacteria include:
To see whether you have strep throat, contact your health care professional.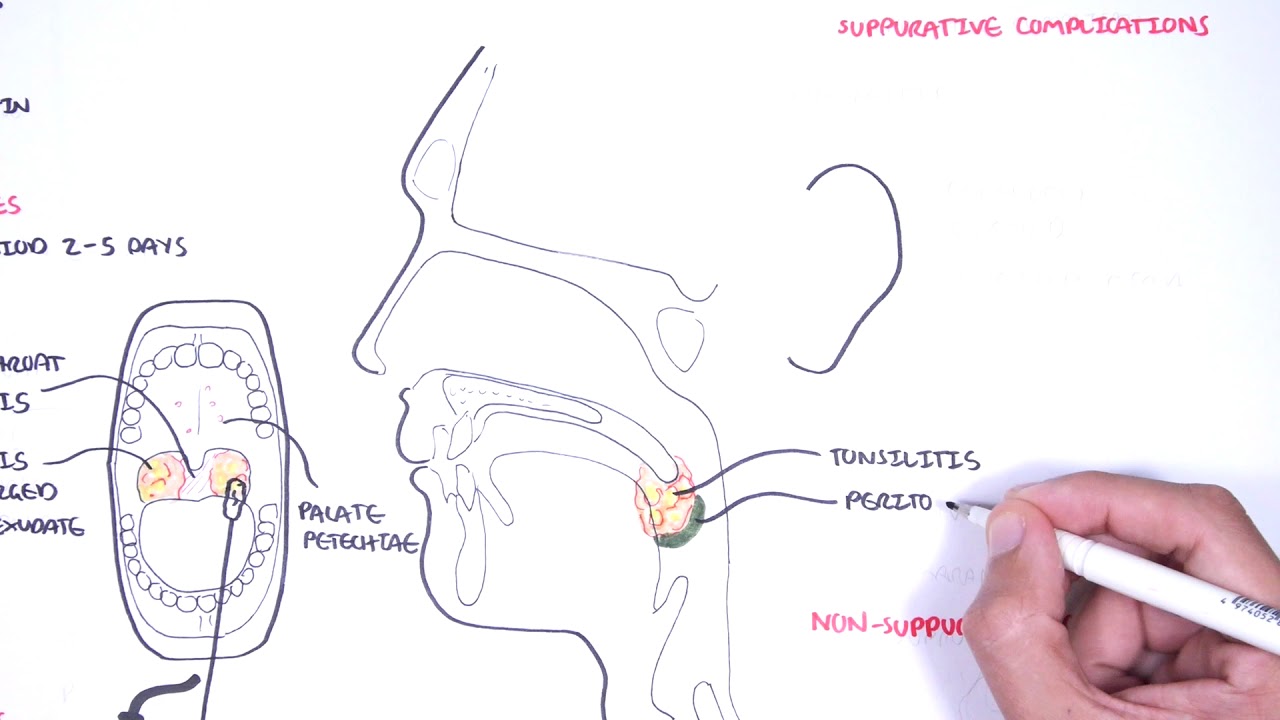 They’ll will ask about your or your child’s symptoms. The only sure way to tell strep from viruses that cause a sore throat is to do a test. There are two kinds of strep throat tests:
They’ll will ask about your or your child’s symptoms. The only sure way to tell strep from viruses that cause a sore throat is to do a test. There are two kinds of strep throat tests:
Rapid strep test: It can identify a case in just a few minutes. The doctor will gently hold down your or your child’s tongue with a depressor. Then, they will swipe a cotton swab around the back of the throat.
You’ll get the results in 20 minutes or less. If the test is positive, which means strep is there, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat it.
If the test is negative, that means they didn’t find strep bacteria. Your doctor might send the sample to a lab for a follow-up test that takes longer.
A rapid strep test can be positive if you have a sore throat that’s caused by a virus. It can be difficult to tell what’s causing the sore throat in that situation because you’re carrying the bacteria and a virus. If you keep getting a sore throat after taking antibiotics, you (or your child) could have a viral throat infection and be a strep throat carrier.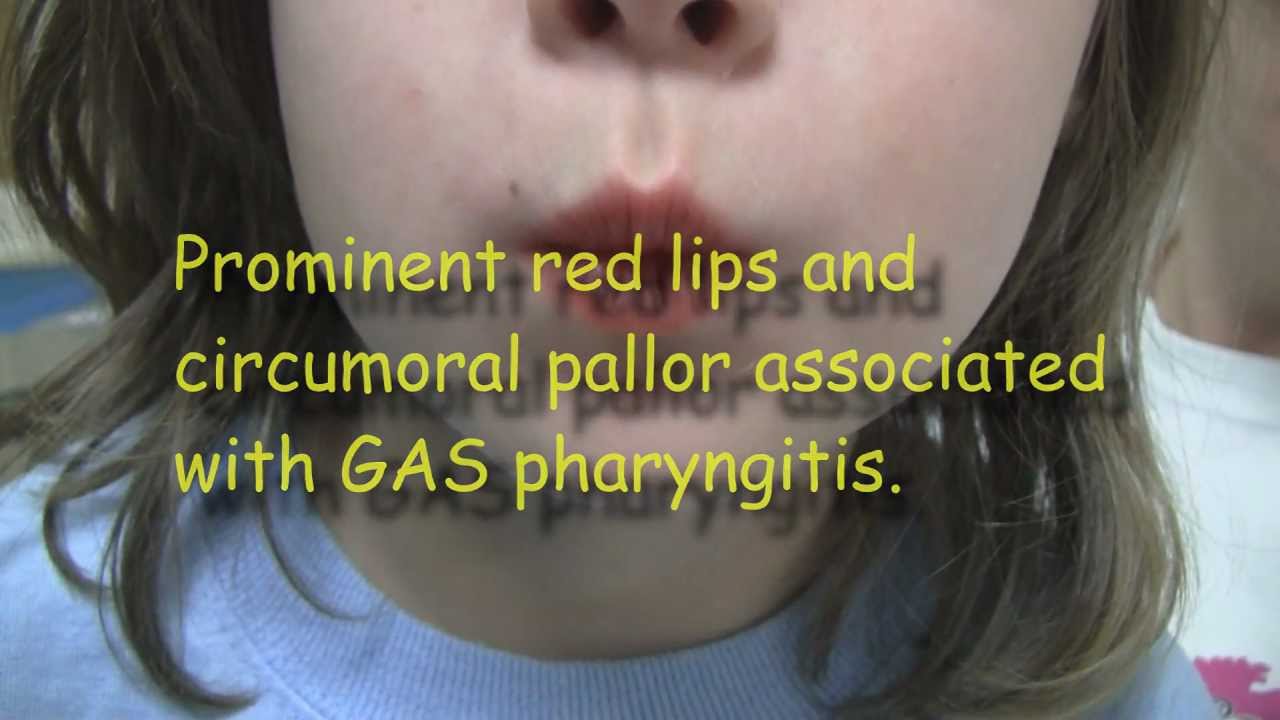 You might be less likely to spread it to other people, though.
You might be less likely to spread it to other people, though.
Throat culture: The doctor will rub a swab over the throat and tonsils to be sent to the lab. If you or your child has strep throat, the streptococci bacteria will grow in it.
It usually takes about 2 days to get results from a throat culture. It can confirm whether it’s strep throat or not.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria that cause the infection. Most treatments last about 10 days. The medicine can make symptoms go away faster and help prevent complications.
If you or your child has a positive test but no symptoms, you’re probably just a carrier. In that case, you’re less likely to spread the bacteria to others, and unlikely to have complications. So you probably won’t need antibiotics. Your doctor can let you know if you need them or not.
Make sure you or your child takes all of the doses. Stopping the medicine too early can leave some bacteria alive. These can make you or your child sick again. Be sure to tell the doctor if you or your child is allergic to any types of antibiotics.
These can make you or your child sick again. Be sure to tell the doctor if you or your child is allergic to any types of antibiotics.
If the strep test is negative, a virus likely caused the sore throat. Antibiotics won’t be needed because these medications don’t kill viruses.
You can take medications to ease the pain of strep throat and lower fever, including over-the-counter medicines such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Don’t give aspirin to children or teens. It can cause a rare but dangerous condition called Reye’s syndrome.
There are a number of things you can do at home to lessen pain and make you feel more comfortable:
- Gargle with a mixture of a quarter-teaspoon of salt and 8 ounces of warm water.
- Suck on a throat lozenge or piece of hard candy. But don’t give small pieces of candy to children younger than 4.
- Throw out your toothbrush and use a new one.
- Drink warm liquids such as tea and broth, and drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration .

- Suck on something cold such as an ice pop or ice chips.
- Choose soft foods that are easy to swallow such as soups, applesauce, or oatmeal. Pass on orange juice and other drinks that have a lot of acid. They’ll sting.
- Honey can help ease pain and inflammation.
- Use a humidifier and/or saline nasal sprays to keep your airways moist, which can help you feel more comfortable.
- Get lots of rest so your body can recover from the infection.
The best way to avoid strep is to stay away from anyone who looks or sounds sick. Signs of strep throat can include:
- A sore throat
- Swollen glands
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rash
Try not to share any personal items with someone who is sick. This includes:
- Cups and plates
- Knives, forks, and spoons
- Toothbrushes
- Food and drinks
If you have strep, here are some things you or your child can do to avoid getting sick again:
- Take all the medicine your doctor prescribed, even if you start to feel better.
 Some bacteria may live and rebound if you stop the medication too soon.
Some bacteria may live and rebound if you stop the medication too soon. - Once you’ve been on antibiotics for 2 to 3 days, throw out your old toothbrush and get a new one.
- Stay out of work or school for at least 24 hours after you start taking an antibiotic.
- Wash your hands and your children’s hands often. Or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer several times a day. Always clean your hands before you eat and after you use the bathroom.
- Ask your children to cover their mouths with a tissue or sleeve whenever they cough or sneeze.
Strep complications are rare today, thanks to better diagnosis and treatment. But untreated strep throat can cause serious diseases, such as:
The infection spreading to the tonsils, sinuses, middle ear, the mastoid bone behind the ear (mastoiditis), skin, or blood
A peritonsillar abscess – it’s a collection of pus around the tonsils or behind the throat that can be extremely painful
Other strep complications involve an inflammatory response in different parts of your body, including:
Scarlet fever, a red rash that can be tiny pin pricks that are hard to see or intense redness on the body that gives it its name
Rheumatic fever, which can damage the heart, brain, and joints
A kidney disease called glomerulonephritis
Poststreptococcal reactive arthritis, which is inflammation in your joints
Another rare complication that is not well-understood is a condition called PANDAS, which stands for pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections. It usually involves developing the tics and habits of obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) after a strep infection. Symptoms of OCD can worsen after a strep infection, too.
It usually involves developing the tics and habits of obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) after a strep infection. Symptoms of OCD can worsen after a strep infection, too.
Guttate psoriasis, a skin condition in which tear drop scales appear on the surface of the skin. They may be red or silver in color and can be itchy.
Top Picks
Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Medically Reviewed by Poonam Sachdev on February 15, 2023
- What Is Strep Throat?
- Is Strep Throat Contagious?
- Strep Throat Symptoms
- Strep Throat Diagnosis
- Strep Throat Treatment
- Strep Throat Home Remedies
- Strep Throat Prevention
- Strep Throat Complications
- More
Strep throat is an infection of the throat and tonsils caused by a bacteria called group A streptococcus, which is also known as Streptococcus pyogenes. This bacteria lives in the nose and throat. You can get the infection from someone who is carrying strep A bacteria or is sick from it.
This bacteria lives in the nose and throat. You can get the infection from someone who is carrying strep A bacteria or is sick from it.
Anyone can get strep throat, but it’s most common in children and teens.
The bacteria that cause strep throat pass easily from person to person through close contact.
Strep throat spreads when someone who has the infection coughs or sneezes. Droplets filled with bacteria spray into the air.
You can give yourself strep throat (or catch it from someone else) if you:
- Breathe it in
- Touch something these droplets land on, such as a doorknob or table, and then rub your eyes, nose, or mouth
- Share personal items such as a fork or spoon, glass, or toothbrush with someone who is sick
- Kiss a person who has it
When you get infected, you typically start to show symptoms about 2 to 5 days after you were exposed to the bacteria.
You can stay contagious for up to a month if you don’t get treated. Antibiotics can prevent the infection from spreading. People who take antibiotics stop being contagious after about 24 hours.
Antibiotics can prevent the infection from spreading. People who take antibiotics stop being contagious after about 24 hours.
A sore throat is the main sign you or your child has strep. Colds and other viruses can also cause a sore throat. One way to tell the difference between strep throat and another virus is that a virus will often cause a runny nose, too.
With strep, the sore throat comes on quickly and is more likely to cause these other symptoms. Call your doctor if you or a child in your care has these symptoms:
A fever of 101 F or higher
Red, swollen tonsils
Pain when you swallow
Swollen and/or tender lymph nodes at the front of your neck
White patches in the throat
Tiny red spots on the roof of the mouth (called petechiae)
Appetite loss
Stomachache
Headache
Body aches
Nausea or vomiting
Loss of appetite
Rash
Signs that the infection might be viral rather than caused by strep bacteria include:
To see whether you have strep throat, contact your health care professional. They’ll will ask about your or your child’s symptoms. The only sure way to tell strep from viruses that cause a sore throat is to do a test. There are two kinds of strep throat tests:
They’ll will ask about your or your child’s symptoms. The only sure way to tell strep from viruses that cause a sore throat is to do a test. There are two kinds of strep throat tests:
Rapid strep test: It can identify a case in just a few minutes. The doctor will gently hold down your or your child’s tongue with a depressor. Then, they will swipe a cotton swab around the back of the throat.
You’ll get the results in 20 minutes or less. If the test is positive, which means strep is there, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat it.
If the test is negative, that means they didn’t find strep bacteria. Your doctor might send the sample to a lab for a follow-up test that takes longer.
A rapid strep test can be positive if you have a sore throat that’s caused by a virus. It can be difficult to tell what’s causing the sore throat in that situation because you’re carrying the bacteria and a virus. If you keep getting a sore throat after taking antibiotics, you (or your child) could have a viral throat infection and be a strep throat carrier. You might be less likely to spread it to other people, though.
You might be less likely to spread it to other people, though.
Throat culture: The doctor will rub a swab over the throat and tonsils to be sent to the lab. If you or your child has strep throat, the streptococci bacteria will grow in it.
It usually takes about 2 days to get results from a throat culture. It can confirm whether it’s strep throat or not.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria that cause the infection. Most treatments last about 10 days. The medicine can make symptoms go away faster and help prevent complications.
If you or your child has a positive test but no symptoms, you’re probably just a carrier. In that case, you’re less likely to spread the bacteria to others, and unlikely to have complications. So you probably won’t need antibiotics. Your doctor can let you know if you need them or not.
Make sure you or your child takes all of the doses. Stopping the medicine too early can leave some bacteria alive. These can make you or your child sick again. Be sure to tell the doctor if you or your child is allergic to any types of antibiotics.
These can make you or your child sick again. Be sure to tell the doctor if you or your child is allergic to any types of antibiotics.
If the strep test is negative, a virus likely caused the sore throat. Antibiotics won’t be needed because these medications don’t kill viruses.
You can take medications to ease the pain of strep throat and lower fever, including over-the-counter medicines such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Don’t give aspirin to children or teens. It can cause a rare but dangerous condition called Reye’s syndrome.
There are a number of things you can do at home to lessen pain and make you feel more comfortable:
- Gargle with a mixture of a quarter-teaspoon of salt and 8 ounces of warm water.
- Suck on a throat lozenge or piece of hard candy. But don’t give small pieces of candy to children younger than 4.
- Throw out your toothbrush and use a new one.
- Drink warm liquids such as tea and broth, and drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration .

- Suck on something cold such as an ice pop or ice chips.
- Choose soft foods that are easy to swallow such as soups, applesauce, or oatmeal. Pass on orange juice and other drinks that have a lot of acid. They’ll sting.
- Honey can help ease pain and inflammation.
- Use a humidifier and/or saline nasal sprays to keep your airways moist, which can help you feel more comfortable.
- Get lots of rest so your body can recover from the infection.
The best way to avoid strep is to stay away from anyone who looks or sounds sick. Signs of strep throat can include:
- A sore throat
- Swollen glands
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rash
Try not to share any personal items with someone who is sick. This includes:
- Cups and plates
- Knives, forks, and spoons
- Toothbrushes
- Food and drinks
If you have strep, here are some things you or your child can do to avoid getting sick again:
- Take all the medicine your doctor prescribed, even if you start to feel better.
 Some bacteria may live and rebound if you stop the medication too soon.
Some bacteria may live and rebound if you stop the medication too soon. - Once you’ve been on antibiotics for 2 to 3 days, throw out your old toothbrush and get a new one.
- Stay out of work or school for at least 24 hours after you start taking an antibiotic.
- Wash your hands and your children’s hands often. Or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer several times a day. Always clean your hands before you eat and after you use the bathroom.
- Ask your children to cover their mouths with a tissue or sleeve whenever they cough or sneeze.
Strep complications are rare today, thanks to better diagnosis and treatment. But untreated strep throat can cause serious diseases, such as:
The infection spreading to the tonsils, sinuses, middle ear, the mastoid bone behind the ear (mastoiditis), skin, or blood
A peritonsillar abscess – it’s a collection of pus around the tonsils or behind the throat that can be extremely painful
Other strep complications involve an inflammatory response in different parts of your body, including:
Scarlet fever, a red rash that can be tiny pin pricks that are hard to see or intense redness on the body that gives it its name
Rheumatic fever, which can damage the heart, brain, and joints
A kidney disease called glomerulonephritis
Poststreptococcal reactive arthritis, which is inflammation in your joints
Another rare complication that is not well-understood is a condition called PANDAS, which stands for pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infections. It usually involves developing the tics and habits of obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) after a strep infection. Symptoms of OCD can worsen after a strep infection, too.
It usually involves developing the tics and habits of obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) after a strep infection. Symptoms of OCD can worsen after a strep infection, too.
Guttate psoriasis, a skin condition in which tear drop scales appear on the surface of the skin. They may be red or silver in color and can be itchy.
Top Picks
Angina: causes, symptoms, treatment In other cases, when diagnosing a disease, the following pathogens are detected:
- staphylococci;
- adenovirus;
- fungi of the genus Candida;
- Coxsackie virus group A.

The main mode of entry of microbes is airborne, however, it is also possible to become infected from a person infected with sore throat when using common household products. Getting an infection and settling it on the tonsils does not always lead to the development of a sore throat. The action of microbes is activated under the influence of provoking factors: hypothermia, sudden changes in ambient temperature, reduced immunity.
Stimulate the development of the disease and some irritants that regularly enter the throat: dust, smoke, pollen, wool. With frequent cases of development of pathologies of the nasopharynx, which can be caused by the growth of adenoids or other diseases, the likelihood of getting a sore throat increases.
When purulent inflammation spreads to the surrounding tissues, which was initially localized in the paranasal sinuses, the infection will affect the entire nasopharynx, which will also lead to tonsillitis.
Symptoms of the disease
Depending on the form of the disease, the type of pathogen and the degree of angina, the general clinical symptoms will differ:
- Catarrhal.
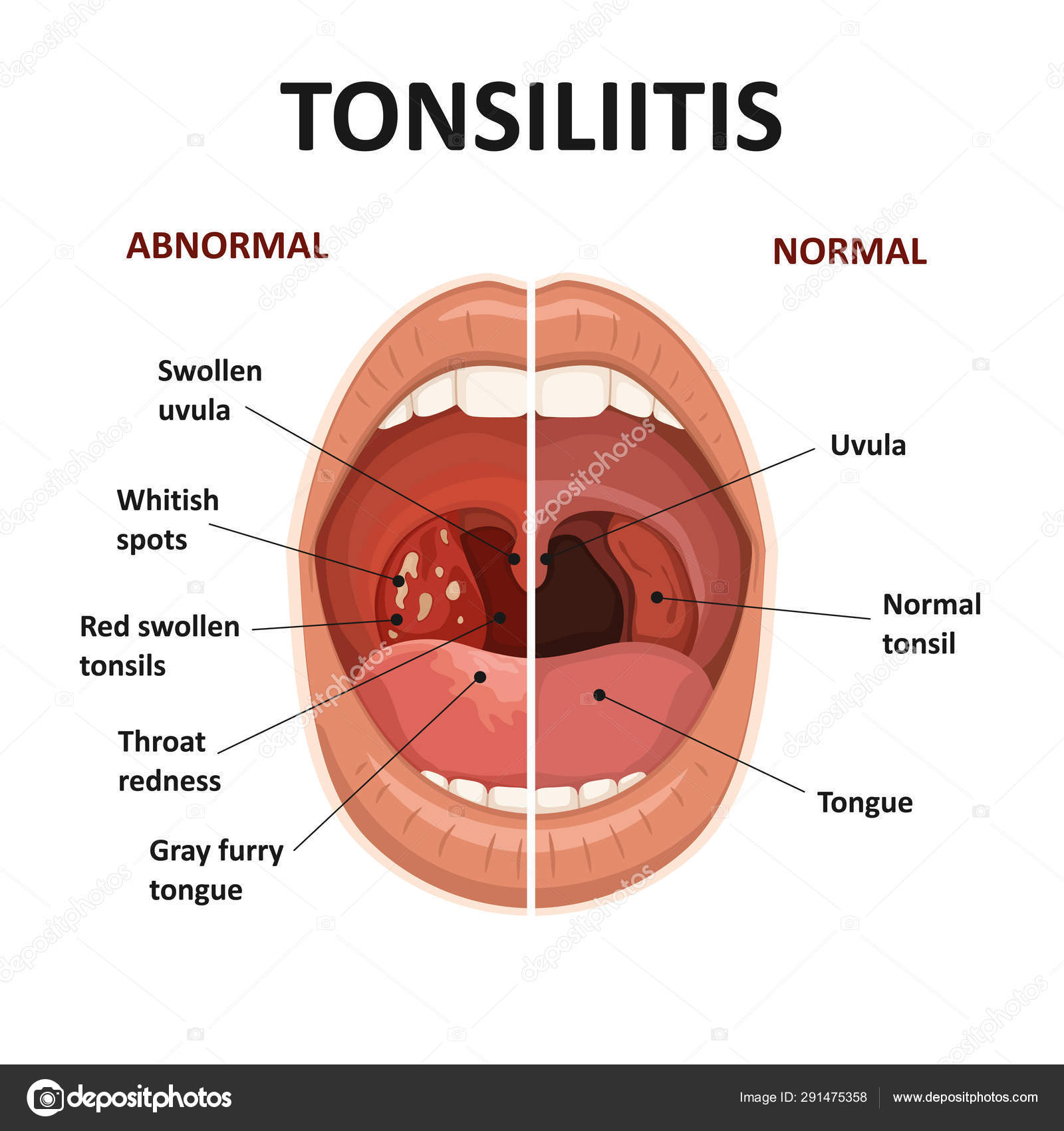
 With this form of angina, the infection spreads to the mucous membrane of the tonsils. The main symptoms are: sore throat, which reaches its maximum strength during swallowing, redness and swelling of the tonsils. Against the background of the inflammatory process, an increase in temperature is observed.
With this form of angina, the infection spreads to the mucous membrane of the tonsils. The main symptoms are: sore throat, which reaches its maximum strength during swallowing, redness and swelling of the tonsils. Against the background of the inflammatory process, an increase in temperature is observed. - Follicular. With angina, not only the mucous membrane is affected, but also the lymphoid follicles. The primary symptom is sore throat, which begins acutely and is accompanied by a sharp rise in temperature to high levels. A person feels weakness, aching muscles and joints, headaches. Festering follicles 1-3 mm in size appear on the tonsils, which open on the second or fourth day.
- Lacunar tonsillitis, which is characterized by a deep degree of damage to the tonsils, accompanied by an accumulation of pus in the lacunae. The tonsils become bright red in color, a yellow-white coating is clearly visible on them. Soreness in the throat is accompanied by general intoxication of the body.

- Necrotic angina is quite rare and is characterized by the presence of necrotic areas.
The onset of symptoms begins after the end of the incubation period. Against the background of elevated temperature, febrile convulsions can occur – severe muscle tension, followed by shudders and twitches.
Diagnosis of angina
The success of treatment will depend on timely and competent diagnosis. The first stage of the examination is an examination of the condition of the patient’s pharynx, in which the attending physician will assess the main signs of the disease: the degree of enlargement of the tonsils and the presence or absence of purulent plaque. It is also necessary to assess the degree of enlargement of the lymph nodes in the ears, neck and neck.
Blood tests will allow you to determine the degree of increase in leukocytes and ESR, characteristic of bacterial tonsillitis. With viral sore throat, the level of leukocytes remains within the normal range or slightly decreases, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases slightly.
To determine the causative agent of the disease in the laboratory, an examination of mucus cultures from the oropharynx is carried out. This is important for determining the class of the disease and the competent prescription of drugs for the treatment of angina. For complicated or especially acute symptoms, the attending physician may prescribe an ultrasound of the neck.
Treatment for angina
The patient is admitted to the infectious disease department only in complicated cases. Most often, angina can be treated on an outpatient basis. The method of treatment consists not only in the elimination of common signs of angina, but also in the impact on the causative agent of the disease. The patient is prescribed:
- Regular gargling with saline solution or special antibacterial agents. During treatment, it is necessary to act on the deep parts of the pharynx, therefore, when rinsing, it is recommended to tilt your head back.
- Antibacterial and analgesic local preparations: tablets, sprays, lozenges.

- Treat with antipyretics if needed.
- Antibiotics given only after evaluating the results of laboratory tests of blood and smears. Antibacterial drugs may have varying degrees of sensitivity to a particular group of pathogenic microorganisms. When treating a bacterial infection, antibiotics of the penicillin group, macrolides, or cephalosporins may be prescribed.
During the treatment of angina, the patient should be given bed rest. It is recommended to use sparing, non-irritating food for the throat, mainly vegetable and dairy. Due to the high degree of spread of angina, a sick person should use separate personal hygiene products and utensils, limit contact with others.
Remember to consult a doctor at the first sign of illness. Ignoring the symptoms of a sore throat or a poorly treated disease can provoke complications, as well as contribute to the development of a chronic latent form, which will turn into an acute phase when the immune system is weakened.
Preventive measures include increasing the body’s defenses by taking vitamin complexes and a balanced diet, daily walks in the fresh air, eliminating irritants, responding quickly to characteristic symptoms, and limiting contact with infected people.
Angina (acute tonsillitis): features, classification, symptoms
For corporate clients
- st. Khersonskaya, 4
- st. Khersonskaya, 2
- Ligovsky Ave., 108 A
Services
Doctors
Prices
Stock
dms
Reviews
about the medical center
Contacts
online consultation
Angina (acute tonsillitis) is an infectious and inflammatory process affecting one or more tonsils of the peripharyngeal ring. In most cases, the palatine tonsils become inflamed. The disease can have severe symptoms with fever, severe fever and chills, severe hyperemia of the palatine tonsils, pain when swallowing, the appearance of purulent plaque and an increase in regional lymph nodes. Or proceed without pronounced characteristic symptoms.
In most cases, the palatine tonsils become inflamed. The disease can have severe symptoms with fever, severe fever and chills, severe hyperemia of the palatine tonsils, pain when swallowing, the appearance of purulent plaque and an increase in regional lymph nodes. Or proceed without pronounced characteristic symptoms.
Sore throat symptoms
Species
Causes
Complications
Angina or acute tonsillitis have a pronounced clinical picture. The incubation period lasts from 12 to 48 hours, after which clinical signs appear.
- Rise in body temperature (above 39°C, rarely 37-38°C). With angina, high body temperature is difficult to lower with the help of antipyretics.
- Signs of intoxication – body aches and weakness, headache, chills, dizziness, pain in the chest and heart area.
- Pain and sensation of a lump in the throat. Pain when swallowing.
- Hoarseness of voice.
- Inflammation of regional lymph nodes.

Examination reveals edema and hyperemia of the palatine tonsils. Depending on the type of inflammation, a purulent plaque forms on the lacunae or all tonsils.
In some cases, the symptoms of the disease may not be pronounced. The temperature can be kept within subfebrile or slightly elevated, against the background of unpleasant and painful sensations in the throat.
Inflammatory pathology of the tonsils varies:
- according to the type of pathogen, it can be bacterial, viral or fungal in nature;
- according to the nature of the course – acute or chronic;
- according to the clinical picture – catarrhal, follicular or lacunar.
Angina can be primary (simple), arising from the penetration of a bacterial infection, secondary, occurring against the background of other diseases of the body, as well as specific, caused by the action of a specific agent.
The peripharyngeal ring is an accumulation of lymphoid tissue, which is an important peripheral organ of the body’s immune system. Pathogenic microorganisms that enter the body with food and water are retained in the oral or nasal cavity precisely by the tonsils of the peripharyngeal ring. As a result of the struggle between the body and the infectious agent, a local reaction of the tonsils occurs, which is expressed in increased production of lymphocytes and can lead to tissue inflammation.
Pathogenic microorganisms that enter the body with food and water are retained in the oral or nasal cavity precisely by the tonsils of the peripharyngeal ring. As a result of the struggle between the body and the infectious agent, a local reaction of the tonsils occurs, which is expressed in increased production of lymphocytes and can lead to tissue inflammation.
Inflammation of the tonsils can also be caused by an internal infection of the body, namely diseases of the oral cavity or ENT organs: caries, sinusitis, rhinitis, otitis media, etc. When the body’s immune defenses are weakened due to illness or hypothermia, the opportunistic microflora found in the growth or nasal cavity can provoke acute inflammation of the palatine tonsils. The factors provoking pathology are bad habits (smoking and alcohol abuse), diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, work in harmful working conditions, and malnutrition.
The risk group for the disease includes pregnant women, the elderly and children, as well as people with chronic immune system damage.
Angina is dangerous for its complications, which can be early, ie. arising immediately after inflammation of the tonsils or delayed, which appear 3-4 weeks after purulent inflammation. Complications can be single (affect one organ), or multiple and affect several organs.
Early complications of angina are otitis media, lymphadenitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, laryngeal edema, tonsil abscess, etc. Delayed inflammation provokes diseases of the heart muscle (rheumatism of the heart muscle, myocarditis, pericarditis), joint pathologies (rheumatism, arthritis), kidney disease (glomerumetritis, pyelonephritis, renal failure).
Diagnosis
The disease is detected during a clinical examination of the patient by an otorhinolaryngologist during pharyngoscopy. Additionally, clinical blood tests are carried out, as well as a bacteriological examination of a throat swab to identify the causative agent of the disease and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Treatment of angina at the Gaide Clinic
In most cases, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Patients are shown bed rest, warm plentiful drink, food should be light and liquid. Treatment, depending on the type of angina, includes antibiotic therapy, antiviral drugs, and local symptomatic treatment. Additionally, tonsils are irrigated with anti-inflammatory drugs, gargling with herbal decoctions and antiseptic solutions. To reduce swelling and symptoms of intoxication, antihistamines are indicated. The course of treatment is 5-10 days.
Patients are shown bed rest, warm plentiful drink, food should be light and liquid. Treatment, depending on the type of angina, includes antibiotic therapy, antiviral drugs, and local symptomatic treatment. Additionally, tonsils are irrigated with anti-inflammatory drugs, gargling with herbal decoctions and antiseptic solutions. To reduce swelling and symptoms of intoxication, antihistamines are indicated. The course of treatment is 5-10 days.
Medical centers “Gaide” provide qualified assistance for any diseases of the ENT organs in patients of all age categories. The clinics are equipped with modern diagnostic equipment for diagnosing ENT diseases, as well as a modern diagnostic laboratory at the service of patients.
Our otorhinolaryngologists are highly experienced in diagnosing and treating various diseases of the ear, nose and throat in adults and children, both conservatively and surgically. When the first symptoms of angina or other pathologies appear, do not delay a visit to the doctor and seek qualified help at the Gaide medical centers./strep-throat-symptoms-5ae1f28aeb97de003955dcd2.png)


 Some bacteria may live and rebound if you stop the medication too soon.
Some bacteria may live and rebound if you stop the medication too soon.
 Some bacteria may live and rebound if you stop the medication too soon.
Some bacteria may live and rebound if you stop the medication too soon.
 With this form of angina, the infection spreads to the mucous membrane of the tonsils. The main symptoms are: sore throat, which reaches its maximum strength during swallowing, redness and swelling of the tonsils. Against the background of the inflammatory process, an increase in temperature is observed.
With this form of angina, the infection spreads to the mucous membrane of the tonsils. The main symptoms are: sore throat, which reaches its maximum strength during swallowing, redness and swelling of the tonsils. Against the background of the inflammatory process, an increase in temperature is observed.