What is anoxic encephalopathy. Anoxic Encephalopathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
What are the main causes of anoxic encephalopathy. How is anoxic encephalopathy diagnosed. What are the treatment options for anoxic encephalopathy. Can patients recover from anoxic encephalopathy. What are the long-term effects of anoxic brain injury.
Understanding Anoxic Encephalopathy: A Comprehensive Overview
Anoxic encephalopathy, also known as cerebral hypoxia or hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, is a serious medical condition that occurs when the brain is deprived of oxygen. This oxygen deprivation can lead to widespread damage to brain cells, potentially resulting in severe neurological impairment or death. The severity of the condition depends on various factors, including the duration and extent of oxygen deprivation, as well as the specific areas of the brain affected.
Oxygen is crucial for the proper functioning of brain cells. When the brain is deprived of oxygen, even for a short period, it can have devastating consequences. The brain consumes about 20% of the body’s oxygen supply, despite only accounting for about 2% of body weight. This high oxygen demand makes the brain particularly vulnerable to oxygen deprivation.

Causes and Risk Factors of Anoxic Encephalopathy
Anoxic encephalopathy can result from various situations that disrupt the brain’s oxygen supply. Some common causes include:
- Cardiac arrest
- Severe asthma attacks
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Drowning or near-drowning incidents
- Choking or strangulation
- Severe blood loss
- Drug overdose
- Complications during surgery or anesthesia
- Severe electric shock
- Extreme altitude sickness
Certain medical conditions can also increase the risk of developing anoxic encephalopathy. These include heart disease, respiratory disorders, and conditions that affect blood clotting or circulation. Additionally, individuals with a history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks may be at higher risk.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Anoxic Encephalopathy
The symptoms of anoxic encephalopathy can vary depending on the severity and duration of oxygen deprivation. Initial symptoms may include:
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion or disorientation
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heartbeat
- Seizures
- Blue-tinged skin (cyanosis)
In cases of prolonged oxygen deprivation, more severe symptoms may develop, such as:

- Coma
- Persistent vegetative state
- Memory loss
- Cognitive impairment
- Motor function deficits
- Sensory disturbances
- Personality changes
Are there any early warning signs of anoxic encephalopathy? While the onset of anoxic encephalopathy is often sudden and severe, some individuals may experience subtle warning signs before a major event. These can include dizziness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath, or chest pain. However, it’s important to note that these symptoms are not specific to anoxic encephalopathy and can be associated with various other conditions.
Diagnostic Approaches for Anoxic Encephalopathy
Diagnosing anoxic encephalopathy typically involves a combination of clinical assessment and diagnostic tests. The initial evaluation often includes:
- Physical examination
- Neurological assessment
- Review of medical history
- Blood tests to check oxygen levels and other vital parameters
Further diagnostic procedures may include:
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Evoked potential tests
- Cerebral angiography
How accurate are these diagnostic methods in detecting anoxic encephalopathy? While these tests can provide valuable information about brain structure and function, the diagnosis of anoxic encephalopathy is often based on a combination of clinical presentation, medical history, and test results. Some imaging techniques, particularly MRI, can be highly sensitive in detecting brain damage associated with oxygen deprivation. However, the interpretation of these results requires expertise and consideration of the individual patient’s circumstances.
Treatment Strategies for Anoxic Encephalopathy
The treatment of anoxic encephalopathy focuses on two main goals: addressing the underlying cause of oxygen deprivation and minimizing further brain damage. Immediate interventions may include:
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
- Mechanical ventilation
- Administration of oxygen
- Medications to support blood pressure and heart function
Once the patient is stabilized, additional treatments may be employed:
- Therapeutic hypothermia: Lowering the body temperature to reduce brain swelling and metabolic demands
- Neuroprotective medications: Drugs that may help protect brain cells from further damage
- Management of cerebral edema: Medications or procedures to reduce brain swelling
- Seizure control: Antiepileptic drugs to prevent or manage seizures
- Nutritional support: Ensuring adequate nutrition through feeding tubes if necessary
Is there a specific timeframe for initiating treatment to maximize the chances of recovery? The timing of treatment is crucial in cases of anoxic encephalopathy. Immediate intervention is essential to restore oxygen supply to the brain and prevent further damage. The concept of the “golden hour” emphasizes the importance of rapid treatment within the first 60 minutes after the onset of symptoms. However, even beyond this window, prompt medical attention can still make a significant difference in patient outcomes.

Rehabilitation and Long-Term Care for Anoxic Encephalopathy Patients
Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process for patients with anoxic encephalopathy. The rehabilitation program is typically tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may include:
- Physical therapy to improve motor function and mobility
- Occupational therapy to enhance daily living skills
- Speech and language therapy to address communication difficulties
- Cognitive rehabilitation to improve memory and thinking skills
- Psychological support to manage emotional and behavioral changes
Long-term care may be necessary for patients with severe brain damage. This can involve:
- Specialized nursing care
- Ongoing medical management
- Assistive devices and technologies
- Home modifications to accommodate physical limitations
- Support services for families and caregivers
How long does the rehabilitation process typically last for anoxic encephalopathy patients? The duration of rehabilitation can vary greatly depending on the severity of the brain injury and the individual’s response to treatment. Some patients may show significant improvement within weeks or months, while others may require ongoing rehabilitation for years. It’s important to note that recovery can continue for an extended period, and patients may continue to make progress even years after the initial injury.
Prognosis and Recovery Outlook for Anoxic Encephalopathy
The prognosis for anoxic encephalopathy varies widely depending on several factors:
- Duration and severity of oxygen deprivation
- Areas of the brain affected
- Age and overall health of the patient
- Timeliness and effectiveness of initial treatment
- Access to comprehensive rehabilitation services
Recovery outcomes can range from near-complete recovery to persistent vegetative state or death. Some patients may experience significant improvement in function, while others may be left with long-term disabilities.
Are there any reliable predictors of recovery in anoxic encephalopathy cases? While it’s challenging to predict individual outcomes with certainty, some factors may indicate a better prognosis:
- Shorter duration of oxygen deprivation
- Rapid initiation of treatment
- Younger age
- Absence of pre-existing brain damage
- Early signs of neurological improvement
However, it’s important to note that even patients with initially poor prognostic indicators may sometimes show unexpected improvement. Each case is unique, and ongoing assessment and support are crucial throughout the recovery process.
Prevention and Risk Reduction Strategies for Anoxic Encephalopathy
While not all cases of anoxic encephalopathy can be prevented, there are several strategies that can help reduce the risk:
- Proper management of underlying health conditions, particularly heart and lung diseases
- Regular health check-ups and screenings
- Avoiding high-risk activities without proper safety measures
- Learning and practicing CPR
- Installing carbon monoxide detectors in homes
- Wearing appropriate safety gear during sports and recreational activities
- Avoiding substance abuse and practicing safe medication use
Can lifestyle modifications significantly reduce the risk of anoxic encephalopathy? While lifestyle changes alone cannot eliminate the risk of anoxic encephalopathy, they can play a crucial role in reducing vulnerability to certain causes. For example:
- Regular exercise can improve cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of cardiac events
- A balanced diet and weight management can help control risk factors like hypertension and diabetes
- Smoking cessation can improve lung function and reduce the risk of respiratory emergencies
- Stress management techniques can contribute to overall heart health
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and being aware of potential risks, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their brain health and reduce the likelihood of experiencing oxygen deprivation events.

Emerging Research and Future Directions in Anoxic Encephalopathy Treatment
The field of anoxic encephalopathy research is rapidly evolving, with scientists exploring new avenues for treatment and recovery. Some promising areas of investigation include:
- Neuroprotective agents: Development of new drugs that can protect brain cells from damage during oxygen deprivation
- Stem cell therapy: Exploring the potential of stem cells to regenerate damaged brain tissue
- Brain-computer interfaces: Utilizing technology to bypass damaged areas and restore communication and function
- Targeted temperature management: Refining protocols for therapeutic hypothermia to maximize benefits and minimize risks
- Biomarkers for prognosis: Identifying specific biological markers that can help predict recovery outcomes
- Neuroplasticity enhancement: Developing techniques to stimulate the brain’s ability to form new neural connections
What are the most promising breakthroughs in anoxic encephalopathy research? While many areas show potential, some of the most exciting developments include:

- Optogenetics: This technique uses light to control genetically modified neurons, potentially offering new ways to stimulate brain activity in affected areas.
- Exosomes: These tiny vesicles released by cells show promise in delivering therapeutic agents directly to damaged brain tissue.
- Mitochondrial transplantation: Early studies suggest that transplanting healthy mitochondria into damaged cells may help restore energy production and cell function.
- Advanced imaging techniques: New methods for visualizing brain activity and connectivity could lead to more accurate prognosis and tailored treatment plans.
While these areas of research offer hope for improved treatments in the future, it’s important to note that many are still in early stages and require further study before they can be applied clinically. Ongoing research continues to deepen our understanding of anoxic encephalopathy and pave the way for more effective interventions.
Anoxic Encephalopathy – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
Bateman RM, Sharpe MD, Jagger JE, Ellis CG, Solé-Violán J, López-Rodríguez M, Herrera-Ramos E, Ruíz-Hernández J, Borderías L, Horcajada J, González-Quevedo N, Rajas O, Briones M, Rodríguez de Castro F, Rodríguez Gallego C, Esen F, Orhun G, Ergin Ozcan P, Senturk E, Ugur Yilmaz C, Orhan N, Arican N, Kaya M, Kucukerden M, Giris M, Akcan U, Bilgic Gazioglu S, Tuzun E, Riff R, Naamani O, Douvdevani A, Takegawa R, Yoshida H, Hirose T, Yamamoto N, Hagiya H, Ojima M, Akeda Y, Tasaki O, Tomono K, Shimazu T, Ono S, Kubo T, Suda S, Ueno T, Ikeda T, Hirose T, Ogura H, Takahashi H, Ojima M, Kang J, Nakamura Y, Kojima T, Shimazu T, Ikeda T, Suda S, Izutani Y, Ueno T, Ono S, Taniguchi T, O M, Dinter C, Lotz J, Eilers B, Wissmann C, Lott R, Meili MM, Schuetz PS, Hawa H, Sharshir M, Aburageila M, Salahuddin N, Chantziara V, Georgiou S, Tsimogianni A, Alexandropoulos P, Vassi A, Lagiou F, Valta M, Micha G, Chinou E, Michaloudis G, Kodaira A, Ikeda T, Ono S, Ueno T, Suda S, Izutani Y, Imaizumi H, De la Torre-Prados MV, Garcia-De la Torre A, Enguix-Armada A, Puerto-Morlan A, Perez-Valero V, Garcia-Alcantara A, Bolton N, Dudziak J, Bonney S, Tridente A, Nee P, Nicolaes G, Wiewel M, Schultz M, Wildhagen K, Horn J, Schrijver R, Van der Poll T, Reutelingsperger C, Pillai S, Davies G, Mills G, Aubrey R, Morris K, Williams P, Evans P, Gayat EG, Struck J, Cariou A, Deye N, Guidet B, Jabert S, Launay J, Legrand M, Léone M, Resche-Rigon M, Vicaut E, Vieillard-Baron A, Mebazaa A, Arnold R, Capan M, Linder A, Akesson P, Popescu M, Tomescu D, Sprung CL, Calderon Morales R, Munteanu G, Orenbuch-Harroch E, Levin P, Kasdan H, Reiter A, Volker T, Himmel Y, Cohen Y, Meissonnier J, Girard L, Rebeaud F, Herrmann I, Delwarde B, Peronnet E, Cerrato E, Venet F, Lepape A, Rimmelé T, Monneret G, Textoris J, Beloborodova N, Moroz V, Osipov A, Bedova A, Sarshor Y, Pautova A, Sergeev A, Chernevskaya E, Odermatt J, Bolliger R, Hersberger L, Ottiger M, Christ-Crain M, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Sharma NK, Tashima AK, Brunialti MK, Machado FR, Assuncao M, Rigato O, Salomao R, Cajander SC, Rasmussen G, Tina E, Söderquist B, Källman J, Strålin K, Lange AL, Sundén-Cullberg JS, Magnuson AM, Hultgren OH, Davies G, Pillai S, Mills G, Aubrey R, Morris K, Williams P, Evans P, Pillai S, Davies G, Mills G, Aubrey R, Morris K, Williams P, Evans P, Pillai S, Davies G, Mills G, Aubrey R, Morris K, Williams P, Evans P, Van der Geest P, Mohseni M, Linssen J, De Jonge R, Duran S, Groeneveld J, Miller R, Lopansri BK, McHugh LC, Seldon A, Burke JP, Johnston J, Reece-Anthony R, Bond A, Molokhia A, Mcgrath C, Nsutebu E, Bank Pedersen P, Pilsgaard Henriksen D, Mikkelsen S, Touborg Lassen A, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Wiewel MA, Harmon MB, Van Vught LA, Scicluna BP, Hoogendijk AJ, Horn J, Zwinderman AH, Cremer OL, Bonten MJ, Schultz MJ, Van der Poll T, Juffermans NP, Wiersinga WJ, Eren G, Tekdos Y, Dogan M, Acicbe O, Kaya E, Hergunsel O, Alsolamy S, Ghamdi G, Alswaidan L, Alharbi S, Alenezi F, Arabi Y, Heaton J, Boyce A, Nolan L, Johnston J, Dukoff-Gordon A, Dean A, Molokhia A, Mann Ben Yehudah T, Fleischmann C, Thomas-Rueddel D, Haas C, Dennler U, Reinhart K, Suntornlohanakul O, Khwannimit B, Breckenridge F, Puxty A, Szturz P, Folwarzcny P, Svancara J, Kula R, Sevcik P, Caneva L, Casazza A, Bellazzi E, Marra S, Pagani L, Vetere M, Vanzino R, Ciprandi D, Preda R, Boschi R, Carnevale L, Lopez V, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Escalante A, Gongora J, Cetina M, Adamik B, Jakubczyk D, Kübler A, Radford A, Lee T, Singer J, Boyd J, Fineberg D, Williams M, Russell J, Scarlatescu E, Tomescu D, Droc G, Arama S, Müller M, Straat M, Zeerleder SS, Juffermans NP, Fuchs CF, Scheer CS, Wauschkuhn SW, Vollmer MV, Meissner KM, Kuhn SK, Hahnenkamp KH, Rehberg SR, Gründling MG, Yamamoto N, Ojima M, Hamaguchi S, Hirose T, Akeda Y, Takegawa R, Tasaki O, Shimazu T, Tomono K, Gómez-Sánchez E, Heredia-Rodríguez M, Álvarez-Fuente E, Lorenzo-López M, Gómez-Pesquera E, Aragón-Camino M, Liu-Zhu P, Sánchez-López A, Hernández-Lozano A, Peláez-Jareño MT, Tamayo E, Thomas-Rüddel DO, Fleischmann C, Haas C, Dennler U, Reinhart K, Adora V, Kar A, Chakraborty A, Roy S, Bandyopadhyay A, Das M, Mann Ben Yehudah T, BenYehudah G, Salim M, Kumar N, Arabi L, Burger T, Lephart P, Toth-martin E, Valencia C, Hammami N, Blot S, Vincent JL, Lambert ML, Brunke J, Riemann T, Roschke I, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Nimitvilai S, Jintanapramote K, Jarupongprapa S, Adukauskiene D, Valanciene D, Bose G, Lostarakos V, Carr B, Khedher S, Maaoui A, Ezzamouri A, Salem M, Chen J, Cranendonk DR, Van Vught LA, Wiewel MA, Cremer OL, Horn J, Bonten MJ, Schultz MJ, Van der Poll T, Wiersinga WJ, Day M, Penrice G, Roy K, Robertson P, Godbole G, Jones B, Booth M, Donaldson L, Kawano Y, Ishikura H, Al-Dorzi H, Almutairi M, Alhamadi B, Crizaldo Toledo A, Khan R, Al Raiy B, Arabi Y, Talaie H, Van Oers JA, Harts A, Nieuwkoop E, Vos P, Boussarsar Y, Boutouta F, Kamoun S, Mezghani I, Koubaji S, Ben Souissi A, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Giamarellos-Bourboulis E, Tziolos N, Routsi C, Katsenos C, Tsangaris I, Pneumatikos I, Vlachogiannis G, Theodorou V, Prekates A, Antypa E, Koulouras V, Kapravelos N, Gogos C, Antoniadou E, Mandragos K, Armaganidis A, Robles Caballero AR, Civantos B, Figueira JC, López J, Silva-Pinto A, Ceia F, Sarmento A, Santos L, Almekhlafi G, Sakr Y, Al-Dorzi H, Khan R, Baharoon S, Aldawood A, Matroud A, Alchin J, Al Johani S, Balkhy H, Arabi Y, Alsolamy S, Yousif SY, Alotabi BO, Alsaawi AS, Ang J, Curran MD, Enoch D, Navapurkar V, Morris A, Sharvill R, Astin J, Heredia-Rodríguez M, Gómez-Sánchez E, Peláez-Jareño MT, Gómez-Pesquera E, Lorenzo-López M, Liu-Zhu P, Aragón-Camino M, Hernández-Lozano A, Sánchez-López A, Álvarez-Fuente E, Tamayo E, Patel J, Kruger C, O’Neal J, Rhodes H, Jancik J, François B, Laterre PF, Eggimann P, Torres A, Sánchez M, Dequin PF, Bassi GL, Chastre J, Jafri HS, Ben Romdhane M, Douira Z, Kamoun S, Bousselmi M, Ben Souissi A, Boussarsar Y, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Craven TH, Wojcik G, Kefala K, McCoubrey J, Reilly J, Paterson R, Inverarity D, Laurenson I, Walsh TS, Mongodi S, Bouhemad B, Orlando A, Stella A, Via G, Iotti G, Braschi A, Mojoli F, Haliloglu M, Bilgili B, Kasapoglu U, Sayan I, Süzer Aslan M, Yalcın A, Cinel I, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Ellis HE, Bauchmuller K, Miller D, Temple A, Chastre J, François B, Torres A, Luyt CE, Sánchez M, Singer M, Jafri HS, Nassar Y, Ayad MS, Trifi A, Abdellatif S, Daly F, Nasri R, Ben Lakhal S, Bilgili B, Haliloglu M, Gul F, Cinel I, Kuzovlev A, Shabanov A, Polovnikov S, Moroz V, Kadrichu N, Dang T, Corkery K, Challoner P, Bassi GL, Aguilera E, Chiurazzi C, Travierso C, Motos A, Fernandez L, Amaro R, Senussi T, Idone F, Bobi J, Rigol M, Torres A, Hodiamont CJ, Juffermans NP, Janssen JM, Bouman CS, Mathôt RA, De Jong MD, Van Hest RM, Payne L, Fraser GL, Tudor B, Lahner M, Roth G, Krenn C, Talaie H, Jault P, Gabard J, Leclerc T, Jennes S, Que Y, Rousseau A, Ravat F, Al-Dorzi H, Eissa A, Al-Harbi S, Aldabbagh T, Khan R, Arabi Y, Trifi A, Abdellatif. S, Daly F, Nasri R, Ben Lakhal S, Paramba F, Purayil N, Naushad V, Mohammad O, Negi V, Chandra P, Kleinsasser A, Witrz MR, Buchner-Doeven JF, Tuip-de Boer AM, Goslings JC, Juffermans NP, Van Hezel M, Straat M, Boing A, Van Bruggen R, Juffermans N, Markopoulou D, Venetsanou K, Kaldis V, Koutete D, Chroni D, Alamanos I, Koch L, Jancik J, Rhodes H, Walter E, Maekawa K, Hayakawa M, Kushimoto S, Shiraishi A, Kato H, Sasaki J, Ogura H, Matauoka T, Uejima T, Morimura N, Ishikura H, Hagiwara A, Takeda M, Tarabrin O, Shcherbakow S, Gavrychenko D, Mazurenko G, Ivanova V, Chystikov O, Plourde C, Lessard J, Chauny J, Daoust R, Shcherbakow S, Tarabrin O, Gavrychenko D, Mazurenko G, Chystikov O, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Kropman L, In het Panhuis L, Konings J, Huskens D, Schurgers E, Roest M, De Laat B, Lance M, Durila M, Lukas P, Astraverkhava M, Jonas J, Budnik I, Shenkman B, Hayami H, Koide Y, Goto T, Iqbal R, Alhamdi Y, Venugopal N, Abrams S, Downey C, Toh CH, Welters ID, Bombay VB, Chauny JM, Daoust RD, Lessard JL, Marquis MM, Paquet JP, Siemens K, Sangaran D, Hunt BJ, Durward A, Nyman A, Murdoch IA, Tibby SM, Ampatzidou F, Moisidou D, Dalampini E, Nastou M, Vasilarou E, Kalaizi V, Chatzikostenoglou H, Drossos G, Spadaro S, Fogagnolo A, Fiore T, Schiavi A, Fontana V, Taccone F, Volta C, Chochliourou E, Volakli E, Violaki A, Samkinidou E, Evlavis G, Panagiotidou V, Sdougka M, Mothukuri R, Battle C, Guy K, Mills G, Evans P, Wijesuriya J, Keogh S, Docherty A, O’Donnell R, Brunskill S, Trivella M, Doree C, Holst L, Parker M, Gregersen M, Almeida J, Walsh T, Stanworth S, Moravcova S, Mansell J, Rogers A, Smith RA, Hamilton-Davies C, Omar A, Allam M, Bilala O, Kindawi A, Ewila H, Ampatzidou F, Moisidou D, Nastou M, Dalampini E, Malamas A, Vasilarou E, Drossos G, Ferreira G, Caldas J, Fukushima J, Osawa EA, Arita E, Camara L, Zeferino S, Jardim J, Gaioto F, Dallan L, Jatene FB, Kalil Filho R, Galas F, Hajjar LA, Mitaka C, Ohnuma T, Murayama T, Kunimoto F, Nagashima M, Takei T, Tomita M, Omar A, Mahmoud K, Hanoura S, Sudarsanan S, Sivadasan P, Othamn H, Shouman Y, Singh R, Al Khulaifi A, Mandel I, Mikheev S, Suhodolo I, Kiselev V, Svirko Y, Podoksenov Y, Jenkins SA, Griffin R, Tovar Doncel MS, Lima A, Aldecoa C, Ince C, Taha A, Shafie A, Mostafa M, Syed N, Hon H, Righetti F, Colombaroli E, Castellano G, Righetti F, Colombaroli E, Hravnak M, Chen LC, Dubrawski AD, Clermont GC, Pinsky MR, Gonzalez S, Macias D, Acosta J, Jimenez P, Loza A, Lesmes A, Lucena F, Leon C, Tovar Doncel MS, Ince C, Aldecoa C, Lima A, Bastide M, Richecoeur J, Frenoy E, Lemaire C, Sauneuf B, Tamion F, Nseir S, Du Cheyron D, Dupont H, Maizel J, Shaban M, Kolko R, Salahuddin N, Sharshir M, AbuRageila M, AlHussain A, Mercado P, Maizel J, Kontar L, Titeca D, Brazier F, Riviere A, Joris M, Soupison T, De Cagny B, Slama M, Wagner J, Körner A, Kubik M, Kluge S, Reuter D, Saugel B, Colombaroli E, Righetti F, Castellano G, Tran T, De Bels D, Cudia A, Strachinaru M, Ghottignies P, Devriendt J, Pierrakos C, Martínez González Ó, Blancas R, Luján J, Ballesteros D, Martínez Díaz C, Núñez A, Martín Parra C, López Matamala B, Alonso Fernández M, Chana M, Huber W, Eckmann M, Elkmann F, Gruber A, Klein I, Schmid RM, Lahmer T, Moller PW, Sondergaard S, Jakob SM, Takala J, Berger D, Bastoni D, Aya H, Toscani L, Pigozzi L, Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Ostrowska C, Aya H, Abbas A, Mellinghoff J, Ryan C, Dawson D, Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Cronhjort M, Wall O, Nyberg E, Zeng R, Svensen C, Mårtensson J, Joelsson-Alm E, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Lopez V, Cetina M, Parenti N, Palazzi C, Amidei LA, Borrelli FB, Campanale SC, Tagliazucchi FT, Sedoni GS, Lucchesi DL, Carella EC, Luciani AL, Mackovic M, Maric N, Bakula M, Aya H, Rhodes A, Grounds RM, Fletcher N, Cecconi M, Avard B, Zhang P, Mezidi M, Charbit J, Ould-Chikh M, Deras P, Maury C, Martinez O, Capdevila X, Hou P, Linde-Zwirble WZ, Douglas ID, Shapiro NS, Ben Souissi A, Mezghani I, Ben Aicha Y, Kamoun S, Laribi B, Jeribi B, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Pereira C, Marinho R, Antunes R, Marinho A, Crivits M, Raes M, Decruyenaere J, Hoste E, Bagin V, Rudnov V, Savitsky A, Astafyeva M, Korobko I, Vein V, Kampmeier T, Arnemann P, Hessler M, Wald A, Bockbreder K, Morelli A, Van Aken H, Rehberg S, Ertmer C, Arnemann P, Hessler M, Kampmeier T, Rehberg S, Van Aken H, Ince C, Ertmer C, Reddy S, Bailey M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Mackle D, Psirides A, Young P, Reddy S, Bailey M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Mackle D, Young P, Venkatesh H, Ramachandran S, Basu A, Nair H, Egan S, Bates J, Oliveira S, Rangel Neto NR, Reis FQ, Lee CP, Lin XL, Choong C, Eu KM, Sim WY, Tee KS, Pau J, Abisheganaden J, Maas K, De Geus H, Lafuente E, Marinho R, Moura J, Antunes R, Marinho A, Doris TE, Monkhouse D, Shipley T, Kardasz S, Gonzalez I, Stads S, Groeneveld AJ, Elsayed I, Ward N, Tridente A, Raithatha A, Steuber A, Pelletier C, Schroeder S, Michael E, Slowinski T, Kindgen-Milles D, Ghabina S, Turani F, Belli A, Busatti S, Barettin G, Candidi F, Gargano F, Barchetta R, Falco M, Demirkiran O, Kosuk M, Bozbay S, Weber V, Hartmann J, Harm S, Linsberger I, Eichhorn T, Valicek G, Miestinger G, Hoermann C, Faenza S, Ricci D, Mancini E, Gemelli C, Cuoghi A, Magnani S, Atti M, Laddomada T, Doronzio A, Balicco B, Gruda MC, O’Sullivan P, Dan VP, Guliashvili T, Scheirer A, Golobish TD, Capponi VJ, Chan PP, Kogelmann K, Drüner M, Jarczak D, Turani F, Belli AB, Martni SM, Cotticelli VC, Mounajergi F, Barchetta R, Morimoto S, Ishikura H, Hussain I, Salahuddin N, Nadeem A, Ghorab K, Maghrabi K, Kloesel SK, Goldfuss C, Stieglitz A, Stieglitz AS, Krstevska L, Albuszies G, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Lopez V, Escalante A, Jimmy G, Cetina M, Izawa J, Iwami T, Uchino S, Takinami M, Kitamura T, Kawamura T, Powell-Tuck JG, Crichton S, Raimundo M, Camporota L, Wyncoll D, Ostermann M, Hana A, De Geus HR, De Geus HR, Hana A, Aydogdu M, Boyaci N, Yuksel S, Gursel G, Cayci Sivri AB, Meza-Márquez J, Nava-López J, Carrillo-Esper R, Dardashti A, Grubb A, Maizel J, Wetzstein M, Titeca D, Kontar L, Brazier F, De Cagny B, Riviere A, Soupison T, Joris M, Slama M, Peters E, Njimi H, Pickkers P, Vincent JL, Waraich M, Doyle J, Samuels T, Forni L, Desai N, Baumber R, Gunning P, Sell A, Lin S, Torrence H, O’Dwyer M, Kirwan C, Prowle J, Kim T, O’Connor ME, Hewson RW, Kirwan CJ, Pearse RM, Prowle J, Hanoura S, Omar A, Othamn H, Sudarsanan S, Allam M, Maksoud M, Singh R, Al Khulaifi A, O’Connor ME, Hewson RW, Kirwan CJ, Pearse RM, Prowle J, Uzundere O, Memis D, Ýnal M, Gultekin A, Turan N, Aydin MA, Basar H, Sencan I, Kapuagasi A, Ozturk M, Uzundurukan Z, Gokmen D, Ozcan A, Kaymak C, Artemenko VA, Budnyuk A, Pugh R, Bhandari S, Mauri T, Turrini C, Langer T, Taccone P, Volta CA, Marenghi C, Gattinoni L, Pesenti A, Sweeney L, O’Sullivan A, Kelly P, Mukeria E, MacLoughlin R, Pfeffer M, Thomas JT, Bregman GB, Karp GK, Kishinevsky EK, Stavi DS, Adi NA, Poropat T, Knafelj R, Llopart E, Batlle M, De Haro C, Mesquida J, Artigas A, Pavlovic D, Lewerentz L, Spassov A, Schneider R, De Smet S, De Raedt S, Derom E, Depuydt P, Oeyen S, Benoit D, Decruyenaere J, Gobatto A, Besen B, Tierno P, Melro L, Mendes P, Cadamuro F, Park M, Malbouisson LM, Civantos BC, Lopez JL, Robles A, Figueira J, Yus S, Garcia A, Oglinda A, Ciobanu G, Oglinda C, Schirca L, Sertinean T, Lupu V, Kelly P, O’Sullivan A, Sweeney L, MacLoughlin R, O’Sullivan A, Kelly P, Sweeney L, Mukeria E, Wolny M, MacLoughlin R, Pagano A, Numis F, Visone G, Saldamarco L, Russo T, Porta G, Paladino F, Bell C, Liu J, Debacker J, Lee C, Tamberg E, Campbell V, Mehta S, Silva-Pinto A, Sarmento A, Santos L, Kara Ý, Yýldýrým F, Zerman A, Güllü Z, Boyacý N, Basarýk Aydogan B, Gaygýsýz Ü, Gönderen K, Arýk G, Turkoglu M, Aydogdu M, Aygencel G, Ülger Z, Gursel G, Boyacý N, Isýkdogan Z, Özdedeoglu Ö, Güllü Z, Badoglu M, Gaygýsýz U, Aydogdu M, Gursel G, Kongpolprom N, Sittipunt C, Eden A, Kokhanovsky Y, Bursztein – De Myttenaere S, Pizov R, Neilans L, MacIntyre N, Radosevich M, Wanta B, Weber V, Meyer T, Smischney N, Brown D, Diedrich D, Fuller A, McLindon P, Sim K, Shoaeir M, Noeam K, Mahrous A, Matsa R, Ali A, Dridi C, Koubaji S, Kamoun S, Haddad F, Ben Souissi A, Laribi B, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Pérez-Calatayud A, Carrillo-Esper R, Zepeda-Mendoza A, Diaz-Carrillo M, Arch-Tirado E, Carbognin S, Pelacani L, Zannoni F, Agnoli A, Gagliardi G, Cho R, Adams A, Lunos S, Ambur S, Shapiro R, Prekker M, Thijssen M, Janssen L, Foudraine N, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, George E, Voscopoulos CJ, Eversole D, Freeman J, George E, Muttini S, Bigi R, Villani G, Patroniti N, Williams G, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, George E, Waldmann A, Böhm S, Windisch W, Strassmann S, Karagiannidis C, Waldmann A, Böhm S, Windisch W, Strassmann S, Karagiannidis C, Karagiannidis CK, Waldmann AW, Böhm SB, Strassmann S, Windisch WW, Persson P, Lundin S, Stenqvist O, Porta G, Numis F, Serra CS, Pagano AP, Masarone MM, Rinaldi LR, Amelia AA, Fascione MF, Adinolfi LA, Ruggiero ER, Asota F, O’Rourke K, Ranjan S, Morgan P, DeBacker JW, Tamberg E, O’Neill L, Munshi L, Burry L, Fan E, Mehta S, Poo S, Mahendran K, Fowles J, Gerrard C, Vuylsteke A, Loveridge R, Chaddock C, Patel S, Kakar V, Willars C, Hurst T, Park C, Best T, Vercueil A, Auzinger G, Borgman A, Proudfoot AG, Grins E, Emiley KE, Schuitema J, Fitch SJ, Marco G, Sturgill J, Dickinson MG, Strueber M, Khaghani A, Wilton P, Jovinge SM, Sampson C, Harris-Fox S, Cove ME, Vu LH, Sen A, Federspiel WJ, Kellum JA, Mazo Torre C, Riera J, Ramirez S, Borgatta B, Lagunes L, Rello J, Kuzovlev AK, Moroz V, Goloubev A, Polovnikov S, Nenchuk S, Karavana V, Glynos C, Asimakos A, Pappas K, Vrettou C, Magkou M, Ischaki E, Stathopoulos G, Zakynthinos S, Spadaro S, Kozhevnikova I, Dalla Corte F, Grasso S, Casolari P, Caramori G, Volta C, Andrianjafiarinoa T, Randriamandrato T, Rajaonera T, El-Dash S, Costa ELV, Tucci MR, Leleu F, Kontar L, De Cagny B, Brazier F, Titeca D, Bacari-Risal G, Maizel J, Amato M, Slama M, Mercado P, Maizel J, Kontar L, Titeca D, Brazier F, Riviere A, Joris M, Soupison T, De Cagny B, El Dash S, Slama M, Remmington, Fischer A, Squire S, Boichat M, Honzawa H, Yasuda H, Adati T, Suzaki S, Horibe M, Sasaki M, Sanui M, Marinho R, Daniel J, Miranda H, Marinho A, Milinis K, Cooper M, Williams GR, McCarron E, Simants S, Patanwala I, Welters I, Su Y, Fernández Villanueva J, Fernández Garda R, López Lago A, Rodríguez Ruíz E, Hernández Vaquero R, Tomé Martínez de Rituerto S, Varo Pérez E, Lefel N, Schaap F, Bergmans D, Olde Damink S, Van de Poll M, Tizard K, Lister C, Poole L, Ringaitiene D, Gineityte D, Vicka V, Norkiene I, Sipylaite J, O’Loughlin A, Maraj V, Dowling J, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Dias EB, Fernandes SL, Oshima T, Graf S, Heidegger C, Genton L, Karsegard V, Dupertuis Y, Pichard C, Friedli N, Stanga Z, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Vandersteen L, Stessel B, Evers S, Van Assche A, Jamaer L, Dubois J, Marinho R, Castro H, Moura J, Valente J, Martins P, Casteloes P, Magalhaes C, Cabral S, Santos M, Oliveira B, Salgueiro A, Marinho A, Marinho R, Santos M, Lafuente E, Castro H, Cabral S, Moura J, Martins P, Oliveira B, Salgueiro A, Duarte S, Castro S, Melo M, Casteloes P, Marinho A, Gray S, Maipang K, Bhurayanontachai R, Grädel LG, Schütz P, Langlois P, Manzanares W, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Manzanares W, Langlois P, Lemieux M, Elke G, Bloos F, Reinhart K, Heyland D, Langlois P, Lemieux M, Aramendi I, Heyland D, Manzanares W, Su Y, Marinho R, Babo N, Marinho A, Hoshino M, Haraguchi Y, Kajiwara S, Mitsuhashi T, Tsubata T, Aida M, Rattanapraphat T, Bhurayanontachai R, Kongkamol C, Khwannimit B, Marinho R, Santos M, Castro H, Lafuente E, Salgueiro A, Cabral S, Martins P, Moura J, Oliveira B, Melo M, Xavier B, Valente J, Magalhaes C, Casteloes P, Marinho A, Moisidou D, Ampatzidou F, Koutsogiannidis C, Moschopoulou M, Drossos G, Taskin G, Çakir M, Güler AK, Taskin A, Öcal N, Özer S, Yamanel L, Wong JM, Fitton C, Anwar S, Stacey S, Aggou M, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Oloktsidou E, Lolakos K, Papapostolou E, Grosomanidis V, Suda S, Ikeda T, Ono S, Ueno T, Izutani Y, Gaudry S, Desailly V, Pasquier P, Brun PB, Tesnieres AT, Ricard JD, Dreyfuss D, Mignon A, White JC, Molokhia A, Dean A, Stilwell A, Friedlaender G, Peters M, Stipulante S, Delfosse A, Donneau AF, Ghuysen A, Feldmann C, Freitag D, Dersch W, Irqsusi M, Eschbach D, Steinfeldt T, Wulf H, Wiesmann T, Kongpolprom N, Cholkraisuwat J, Beitland S, Nakstad E, Stær-Jensen H, Drægni T, Andersen G, Jacobsen D, Brunborg C, Waldum-Grevbo B, Sunde K, Hoyland K, Pandit D, Hayakawa K, Oloktsidou E, Kotzampassi K, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Loukipoudi L, Doumaki E, Grosomanidis V, Yasuda H, Admiraal MM, Van Assen M, Van Putten MJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans M, Van Rootselaar AF, Horn J, Ragusa F, Marudi A, Baroni S, Gaspari A, Bertellini E, Taha A, Abdullah T, Abdel Monem S, Alcorn S, McNeill S, Russell S, Eertmans W, Genbrugge C, Meex I, Dens J, Jans F, De Deyne C, Cholkraisuwat J, Kongpolprom N, Avard B, Burns R, Patarchi A, Spina T, Tanaka H, Otani N, Ode S, Ishimatsu S, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Won MH, Dakova S, Ramsheva Z, Ramshev K, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Marudi A, Baroni S, Gaspari A, Bertellini E, Orhun G, Senturk E, Ozcan PE, Sencer S, Ulusoy C, Tuzun E, Esen F, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Van Assen M, Admiraal MM, Van Putten MJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans M, Van Rootselaar AF, Horn J, Fallenius M, Skrifvars MB, Reinikainen M, Bendel S, Raj R, Abu-Habsa M, Hymers C, Borowska A, Sivadhas H, Sahiba S, Perkins S, Rubio J, Rubio JA, Sierra R, English S, Chasse M, Turgeon A, Lauzier F, Griesdale D, Garland A, Fergusson D, Zarychanski R, Tinmouth A, Van Walraven C, Montroy K, Ziegler J, Dupont Chouinard R, Carignan R, Dhaliwal A, Lum C, Sinclair J, Pagliarello G, McIntyre L, English S, Chasse M, Turgeon A, Lauzier F, Griesdale D, Garland A, Fergusson D, Zarychanski R, Tinmouth A, Van Walraven C, Montroy K, Ziegler J, Dupont Chouinard R, Carignan R, Dhaliwal A, Lum C, Sinclair J, Pagliarello G, McIntyre L, Groza T, Moreau N, Castanares-Zapatero D, Hantson P, Carbonara M, Ortolano F, Zoerle T, Magnoni S, Pifferi S, Conte V, Stocchetti N, Carteron L, Suys T, Patet C, Quintard H, Oddo M, Rubio JA, Rubio J, Sierra R, Spatenkova V, Pokorna E, Suchomel P, Ebert N, Jancik J, Rhodes H, Bylinski T, Hawthorne C, Shaw M, Piper I, Kinsella J, Kink AK, Rätsep IR, Boutin A, Moore L, Chasse M, Zarychanski R, Lauzier F, English S, McIntyre L, Lacroix J, Griesdale D, Lessard-Bonaventure P, Turgeon AF, Boutin A, Moore L, Green R, Lessard-Bonaventure P, Erdogan M, Butler M, Lauzier F, Chasse M, English S, McIntyre L, Zarychanski R, Lacroix J, Griesdale D, Desjardins P, Fergusson DA, Turgeon AF, Goncalves B, Vidal B, Valdez C, Rodrigues AC, Miguez L, Moralez G, Hong T, Kutz A, Hausfater P, Amin D, Struja T, Haubitz S, Huber A, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Brown T, Collinson J, Pritchett C, Slade T, Le Guen M, Hellings S, Ramsaran R, Alsheikhly A, Abe T, Kanapeckaite L, Abu-Habsa M, Bahl R, Russell MQ, Real KJ, Abu-Habsa M, Lyon RM, Oveland NP, Penketh J, Mcdonald M, Kelly F, Alfafi M, Alsolamy S, Almutairi W, Alotaibi B, Van den Berg AE, Schriel Y, Dawson L, Meynaar IA, Talaie H, Silva D, Fernandes S, Gouveia J, Santos Silva J, Foley J, Kaskovagheorgescu A, Evoy D, Cronin J, Ryan J, Huck M, Hoffmann C, Renner J, Laitselart P, Donat N, Cirodde A, Schaal JV, Masson Y, Nau A, Leclerc T, Howarth O, Davenport K, Jeanrenaud P, Raftery S, MacTavish P, Devine H, McPeake J, Daniel M, Kinsella J, Quasim T, Alrabiee S, Alrashid A, Alsolamy S, Gundogan O, Bor C, Akýn Korhan E, Demirag K, Uyar M, Frame F, Ashton C, Bergstrom Niska L, Dilokpattanamongkol P, Suansanae T, Suthisisang C, Morakul S, Karnjanarachata C, Tangsujaritvijit V, Mahmood S, Al Thani H, Almenyar A, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Sharvill R, Penketh J, Morton SE, Chiew YS, Pretty C, Chase JG, Shaw GM, Knafelj R, Kordis P, Patel S, Grover V, Kuchyn I, Bielka K, Aidoni Z, Grosomanidis V, Kotzampassi K, Stavrou G, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Skourtis C, Lee SD, Williams K, Weltes ID, Berhane S, Arrowsmith C, Peters C, Robert S, Caldas J, Panerai RB, Robinson TG, Camara L, Ferreira G, Borg-Seng-Shu E, De Lima Oliveira M, Mian NC, Santos L, Nogueira R, Zeferino SP, Jacobsen Teixeira M, Galas F, Hajjar LA, Killeen P, McPhail M, Bernal W, Maggs J, Wendon J, Hughes T, Taniguchi LU, Siqueira EM, Vieira Jr JM, Azevedo LC, Ahmad AN, Abu-Habsa M, Bahl R, Helme E, Hadfield S, Loveridge R, Shak J, Senver C, Howard-Griffin R, Wacharasint P, Fuengfoo P, Sukcharoen N, Rangsin R, Sbiti-Rohr D, Schuetz P, Na H, Song S, Lee S, Jeong E, Lee K, Cooper M, Milinis K, Williams G, McCarron E, Simants S, Patanwala I, Welters ID, Zoumpelouli E, Volakli EA, Chrysohoidou V, Georgiou S, Charisopoulou K, Kotzapanagiotou E, Panagiotidou V, Manavidou K, Stathi Z, Sdougka M, Salahuddin N, AlGhamdi B, Marashly Q, Zaza K, Sharshir M, Khurshid M, Ali Z, Malgapo M, Jamil M, Shafquat A, Shoukri M, Hijazi M, Abe T, Uchino S, Takinami M, Rangel Neto NR, Oliveira S, Reis FQ, Rocha FA, Moralez G, Ebecken K, Rabello LS, Lima MF, Hatum R, De Marco FV, Alves A, Pinto JE, Godoy M, Brasil PE, Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Soares M, Krinsley J, Kang G, Perry J, Hines H, Wilkinson KM, Tordoff C, Sloan B, Bellamy MC, Moreira E, Verga F, Barbato M, Burghi G, Soares M, Silva UV, Azevedo LC, Torelly AP, Kahn JM, Angus DC, Knibel MF, Brasil PE, Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Marshall R, Gilpin T, Tridente A, Raithatha A, Mota D, Loureiro B, Dias J, Afonso O, Coelho F, Martins A, Faria F, Al-Dorzi H, Al Orainni H, AlEid F, Tlaygeh H, Itani A, Hejazi A, Arabi Y, Gaudry S, Messika J, Ricard JD, Guillo S, Pasquet B, Dubief E, Dreyfuss D, Tubach F, Battle C, James K, Temblett P, Davies L, Battle C, Lynch C, Pereira S, Cavaco S, Fernandes J, Moreira I, Almeida E, Seabra Pereira F, Malheiro M, Cardoso F, Aragão I, Cardoso T, Fister M, Knafelj R, Muraray Govind P, Brahmananda Reddy N, Pratheema R, Arul ED, Devachandran J, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Knafelj R, Fister M, Chin-Yee N, D’Egidio G, Thavorn K, Heyland D, Kyeremanteng K, Murchison AG, Swalwell K, Mandeville J, Stott D, Guerreiro I, Devine H, MacTavish P, McPeake J, Quasim T, Kinsella J, Daniel M, Goossens C, Marques MB, Derde S, Vander Perre S, Dufour T, Thiessen SE, Güiza F, Janssens T, Hermans G, Vanhorebeek I, De Bock K, Van den Berghe G, Langouche L, Devine H, MacTavish P, Quasim T, Kinsella J, Daniel M, McPeake J, Miles B, Madden S, Devine H, Weiler M, Marques P, Rodrigues C, Boeira M, Brenner K, Leães C, Machado A, Townsend R, Andrade J, MacTavish P, McPeake J, Devine H, Kinsella J, Daniel M, Kishore R, Fenlon C, Quasim T, Fiks T, Ruijter A, Te Raa M, Spronk P, Chiew YS, Docherty P, Dickson J, Moltchanova E, Scarrot C, Pretty C, Shaw GM, Chase JG, Hall T, Ngu WC, Jack JM, Morgan P, Avard B, Pavli A, Gee X, Bor C, Akin Korhan E, Demirag K, Uyar M, Shirazy M, Fayed A, Gupta S, Kaushal A, Dewan S, Varma A, Ghosh E, Yang L, Eshelman L, Lord B, Carlson E, Helme E, Broderick R, Hadfield S, Loveridge R, Ramos J, Forte D, Yang F, Hou P, Dudziak J, Feeney J, Wilkinson K, Bauchmuller K, Shuker K, Faulds M, Raithatha A, Bryden D, England L, Bolton N, Tridente A, Bauchmuller K, Shuker K, Tridente A, Faulds M, Matheson A, Gaynor J, Bryden D, S South Yorkshire Hospitals Research Collaboration.
S, Daly F, Nasri R, Ben Lakhal S, Paramba F, Purayil N, Naushad V, Mohammad O, Negi V, Chandra P, Kleinsasser A, Witrz MR, Buchner-Doeven JF, Tuip-de Boer AM, Goslings JC, Juffermans NP, Van Hezel M, Straat M, Boing A, Van Bruggen R, Juffermans N, Markopoulou D, Venetsanou K, Kaldis V, Koutete D, Chroni D, Alamanos I, Koch L, Jancik J, Rhodes H, Walter E, Maekawa K, Hayakawa M, Kushimoto S, Shiraishi A, Kato H, Sasaki J, Ogura H, Matauoka T, Uejima T, Morimura N, Ishikura H, Hagiwara A, Takeda M, Tarabrin O, Shcherbakow S, Gavrychenko D, Mazurenko G, Ivanova V, Chystikov O, Plourde C, Lessard J, Chauny J, Daoust R, Shcherbakow S, Tarabrin O, Gavrychenko D, Mazurenko G, Chystikov O, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Kropman L, In het Panhuis L, Konings J, Huskens D, Schurgers E, Roest M, De Laat B, Lance M, Durila M, Lukas P, Astraverkhava M, Jonas J, Budnik I, Shenkman B, Hayami H, Koide Y, Goto T, Iqbal R, Alhamdi Y, Venugopal N, Abrams S, Downey C, Toh CH, Welters ID, Bombay VB, Chauny JM, Daoust RD, Lessard JL, Marquis MM, Paquet JP, Siemens K, Sangaran D, Hunt BJ, Durward A, Nyman A, Murdoch IA, Tibby SM, Ampatzidou F, Moisidou D, Dalampini E, Nastou M, Vasilarou E, Kalaizi V, Chatzikostenoglou H, Drossos G, Spadaro S, Fogagnolo A, Fiore T, Schiavi A, Fontana V, Taccone F, Volta C, Chochliourou E, Volakli E, Violaki A, Samkinidou E, Evlavis G, Panagiotidou V, Sdougka M, Mothukuri R, Battle C, Guy K, Mills G, Evans P, Wijesuriya J, Keogh S, Docherty A, O’Donnell R, Brunskill S, Trivella M, Doree C, Holst L, Parker M, Gregersen M, Almeida J, Walsh T, Stanworth S, Moravcova S, Mansell J, Rogers A, Smith RA, Hamilton-Davies C, Omar A, Allam M, Bilala O, Kindawi A, Ewila H, Ampatzidou F, Moisidou D, Nastou M, Dalampini E, Malamas A, Vasilarou E, Drossos G, Ferreira G, Caldas J, Fukushima J, Osawa EA, Arita E, Camara L, Zeferino S, Jardim J, Gaioto F, Dallan L, Jatene FB, Kalil Filho R, Galas F, Hajjar LA, Mitaka C, Ohnuma T, Murayama T, Kunimoto F, Nagashima M, Takei T, Tomita M, Omar A, Mahmoud K, Hanoura S, Sudarsanan S, Sivadasan P, Othamn H, Shouman Y, Singh R, Al Khulaifi A, Mandel I, Mikheev S, Suhodolo I, Kiselev V, Svirko Y, Podoksenov Y, Jenkins SA, Griffin R, Tovar Doncel MS, Lima A, Aldecoa C, Ince C, Taha A, Shafie A, Mostafa M, Syed N, Hon H, Righetti F, Colombaroli E, Castellano G, Righetti F, Colombaroli E, Hravnak M, Chen LC, Dubrawski AD, Clermont GC, Pinsky MR, Gonzalez S, Macias D, Acosta J, Jimenez P, Loza A, Lesmes A, Lucena F, Leon C, Tovar Doncel MS, Ince C, Aldecoa C, Lima A, Bastide M, Richecoeur J, Frenoy E, Lemaire C, Sauneuf B, Tamion F, Nseir S, Du Cheyron D, Dupont H, Maizel J, Shaban M, Kolko R, Salahuddin N, Sharshir M, AbuRageila M, AlHussain A, Mercado P, Maizel J, Kontar L, Titeca D, Brazier F, Riviere A, Joris M, Soupison T, De Cagny B, Slama M, Wagner J, Körner A, Kubik M, Kluge S, Reuter D, Saugel B, Colombaroli E, Righetti F, Castellano G, Tran T, De Bels D, Cudia A, Strachinaru M, Ghottignies P, Devriendt J, Pierrakos C, Martínez González Ó, Blancas R, Luján J, Ballesteros D, Martínez Díaz C, Núñez A, Martín Parra C, López Matamala B, Alonso Fernández M, Chana M, Huber W, Eckmann M, Elkmann F, Gruber A, Klein I, Schmid RM, Lahmer T, Moller PW, Sondergaard S, Jakob SM, Takala J, Berger D, Bastoni D, Aya H, Toscani L, Pigozzi L, Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Ostrowska C, Aya H, Abbas A, Mellinghoff J, Ryan C, Dawson D, Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Cronhjort M, Wall O, Nyberg E, Zeng R, Svensen C, Mårtensson J, Joelsson-Alm E, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Lopez V, Cetina M, Parenti N, Palazzi C, Amidei LA, Borrelli FB, Campanale SC, Tagliazucchi FT, Sedoni GS, Lucchesi DL, Carella EC, Luciani AL, Mackovic M, Maric N, Bakula M, Aya H, Rhodes A, Grounds RM, Fletcher N, Cecconi M, Avard B, Zhang P, Mezidi M, Charbit J, Ould-Chikh M, Deras P, Maury C, Martinez O, Capdevila X, Hou P, Linde-Zwirble WZ, Douglas ID, Shapiro NS, Ben Souissi A, Mezghani I, Ben Aicha Y, Kamoun S, Laribi B, Jeribi B, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Pereira C, Marinho R, Antunes R, Marinho A, Crivits M, Raes M, Decruyenaere J, Hoste E, Bagin V, Rudnov V, Savitsky A, Astafyeva M, Korobko I, Vein V, Kampmeier T, Arnemann P, Hessler M, Wald A, Bockbreder K, Morelli A, Van Aken H, Rehberg S, Ertmer C, Arnemann P, Hessler M, Kampmeier T, Rehberg S, Van Aken H, Ince C, Ertmer C, Reddy S, Bailey M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Mackle D, Psirides A, Young P, Reddy S, Bailey M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Mackle D, Young P, Venkatesh H, Ramachandran S, Basu A, Nair H, Egan S, Bates J, Oliveira S, Rangel Neto NR, Reis FQ, Lee CP, Lin XL, Choong C, Eu KM, Sim WY, Tee KS, Pau J, Abisheganaden J, Maas K, De Geus H, Lafuente E, Marinho R, Moura J, Antunes R, Marinho A, Doris TE, Monkhouse D, Shipley T, Kardasz S, Gonzalez I, Stads S, Groeneveld AJ, Elsayed I, Ward N, Tridente A, Raithatha A, Steuber A, Pelletier C, Schroeder S, Michael E, Slowinski T, Kindgen-Milles D, Ghabina S, Turani F, Belli A, Busatti S, Barettin G, Candidi F, Gargano F, Barchetta R, Falco M, Demirkiran O, Kosuk M, Bozbay S, Weber V, Hartmann J, Harm S, Linsberger I, Eichhorn T, Valicek G, Miestinger G, Hoermann C, Faenza S, Ricci D, Mancini E, Gemelli C, Cuoghi A, Magnani S, Atti M, Laddomada T, Doronzio A, Balicco B, Gruda MC, O’Sullivan P, Dan VP, Guliashvili T, Scheirer A, Golobish TD, Capponi VJ, Chan PP, Kogelmann K, Drüner M, Jarczak D, Turani F, Belli AB, Martni SM, Cotticelli VC, Mounajergi F, Barchetta R, Morimoto S, Ishikura H, Hussain I, Salahuddin N, Nadeem A, Ghorab K, Maghrabi K, Kloesel SK, Goldfuss C, Stieglitz A, Stieglitz AS, Krstevska L, Albuszies G, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Lopez V, Escalante A, Jimmy G, Cetina M, Izawa J, Iwami T, Uchino S, Takinami M, Kitamura T, Kawamura T, Powell-Tuck JG, Crichton S, Raimundo M, Camporota L, Wyncoll D, Ostermann M, Hana A, De Geus HR, De Geus HR, Hana A, Aydogdu M, Boyaci N, Yuksel S, Gursel G, Cayci Sivri AB, Meza-Márquez J, Nava-López J, Carrillo-Esper R, Dardashti A, Grubb A, Maizel J, Wetzstein M, Titeca D, Kontar L, Brazier F, De Cagny B, Riviere A, Soupison T, Joris M, Slama M, Peters E, Njimi H, Pickkers P, Vincent JL, Waraich M, Doyle J, Samuels T, Forni L, Desai N, Baumber R, Gunning P, Sell A, Lin S, Torrence H, O’Dwyer M, Kirwan C, Prowle J, Kim T, O’Connor ME, Hewson RW, Kirwan CJ, Pearse RM, Prowle J, Hanoura S, Omar A, Othamn H, Sudarsanan S, Allam M, Maksoud M, Singh R, Al Khulaifi A, O’Connor ME, Hewson RW, Kirwan CJ, Pearse RM, Prowle J, Uzundere O, Memis D, Ýnal M, Gultekin A, Turan N, Aydin MA, Basar H, Sencan I, Kapuagasi A, Ozturk M, Uzundurukan Z, Gokmen D, Ozcan A, Kaymak C, Artemenko VA, Budnyuk A, Pugh R, Bhandari S, Mauri T, Turrini C, Langer T, Taccone P, Volta CA, Marenghi C, Gattinoni L, Pesenti A, Sweeney L, O’Sullivan A, Kelly P, Mukeria E, MacLoughlin R, Pfeffer M, Thomas JT, Bregman GB, Karp GK, Kishinevsky EK, Stavi DS, Adi NA, Poropat T, Knafelj R, Llopart E, Batlle M, De Haro C, Mesquida J, Artigas A, Pavlovic D, Lewerentz L, Spassov A, Schneider R, De Smet S, De Raedt S, Derom E, Depuydt P, Oeyen S, Benoit D, Decruyenaere J, Gobatto A, Besen B, Tierno P, Melro L, Mendes P, Cadamuro F, Park M, Malbouisson LM, Civantos BC, Lopez JL, Robles A, Figueira J, Yus S, Garcia A, Oglinda A, Ciobanu G, Oglinda C, Schirca L, Sertinean T, Lupu V, Kelly P, O’Sullivan A, Sweeney L, MacLoughlin R, O’Sullivan A, Kelly P, Sweeney L, Mukeria E, Wolny M, MacLoughlin R, Pagano A, Numis F, Visone G, Saldamarco L, Russo T, Porta G, Paladino F, Bell C, Liu J, Debacker J, Lee C, Tamberg E, Campbell V, Mehta S, Silva-Pinto A, Sarmento A, Santos L, Kara Ý, Yýldýrým F, Zerman A, Güllü Z, Boyacý N, Basarýk Aydogan B, Gaygýsýz Ü, Gönderen K, Arýk G, Turkoglu M, Aydogdu M, Aygencel G, Ülger Z, Gursel G, Boyacý N, Isýkdogan Z, Özdedeoglu Ö, Güllü Z, Badoglu M, Gaygýsýz U, Aydogdu M, Gursel G, Kongpolprom N, Sittipunt C, Eden A, Kokhanovsky Y, Bursztein – De Myttenaere S, Pizov R, Neilans L, MacIntyre N, Radosevich M, Wanta B, Weber V, Meyer T, Smischney N, Brown D, Diedrich D, Fuller A, McLindon P, Sim K, Shoaeir M, Noeam K, Mahrous A, Matsa R, Ali A, Dridi C, Koubaji S, Kamoun S, Haddad F, Ben Souissi A, Laribi B, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Pérez-Calatayud A, Carrillo-Esper R, Zepeda-Mendoza A, Diaz-Carrillo M, Arch-Tirado E, Carbognin S, Pelacani L, Zannoni F, Agnoli A, Gagliardi G, Cho R, Adams A, Lunos S, Ambur S, Shapiro R, Prekker M, Thijssen M, Janssen L, Foudraine N, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, George E, Voscopoulos CJ, Eversole D, Freeman J, George E, Muttini S, Bigi R, Villani G, Patroniti N, Williams G, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, George E, Waldmann A, Böhm S, Windisch W, Strassmann S, Karagiannidis C, Waldmann A, Böhm S, Windisch W, Strassmann S, Karagiannidis C, Karagiannidis CK, Waldmann AW, Böhm SB, Strassmann S, Windisch WW, Persson P, Lundin S, Stenqvist O, Porta G, Numis F, Serra CS, Pagano AP, Masarone MM, Rinaldi LR, Amelia AA, Fascione MF, Adinolfi LA, Ruggiero ER, Asota F, O’Rourke K, Ranjan S, Morgan P, DeBacker JW, Tamberg E, O’Neill L, Munshi L, Burry L, Fan E, Mehta S, Poo S, Mahendran K, Fowles J, Gerrard C, Vuylsteke A, Loveridge R, Chaddock C, Patel S, Kakar V, Willars C, Hurst T, Park C, Best T, Vercueil A, Auzinger G, Borgman A, Proudfoot AG, Grins E, Emiley KE, Schuitema J, Fitch SJ, Marco G, Sturgill J, Dickinson MG, Strueber M, Khaghani A, Wilton P, Jovinge SM, Sampson C, Harris-Fox S, Cove ME, Vu LH, Sen A, Federspiel WJ, Kellum JA, Mazo Torre C, Riera J, Ramirez S, Borgatta B, Lagunes L, Rello J, Kuzovlev AK, Moroz V, Goloubev A, Polovnikov S, Nenchuk S, Karavana V, Glynos C, Asimakos A, Pappas K, Vrettou C, Magkou M, Ischaki E, Stathopoulos G, Zakynthinos S, Spadaro S, Kozhevnikova I, Dalla Corte F, Grasso S, Casolari P, Caramori G, Volta C, Andrianjafiarinoa T, Randriamandrato T, Rajaonera T, El-Dash S, Costa ELV, Tucci MR, Leleu F, Kontar L, De Cagny B, Brazier F, Titeca D, Bacari-Risal G, Maizel J, Amato M, Slama M, Mercado P, Maizel J, Kontar L, Titeca D, Brazier F, Riviere A, Joris M, Soupison T, De Cagny B, El Dash S, Slama M, Remmington, Fischer A, Squire S, Boichat M, Honzawa H, Yasuda H, Adati T, Suzaki S, Horibe M, Sasaki M, Sanui M, Marinho R, Daniel J, Miranda H, Marinho A, Milinis K, Cooper M, Williams GR, McCarron E, Simants S, Patanwala I, Welters I, Su Y, Fernández Villanueva J, Fernández Garda R, López Lago A, Rodríguez Ruíz E, Hernández Vaquero R, Tomé Martínez de Rituerto S, Varo Pérez E, Lefel N, Schaap F, Bergmans D, Olde Damink S, Van de Poll M, Tizard K, Lister C, Poole L, Ringaitiene D, Gineityte D, Vicka V, Norkiene I, Sipylaite J, O’Loughlin A, Maraj V, Dowling J, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Dias EB, Fernandes SL, Oshima T, Graf S, Heidegger C, Genton L, Karsegard V, Dupertuis Y, Pichard C, Friedli N, Stanga Z, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Vandersteen L, Stessel B, Evers S, Van Assche A, Jamaer L, Dubois J, Marinho R, Castro H, Moura J, Valente J, Martins P, Casteloes P, Magalhaes C, Cabral S, Santos M, Oliveira B, Salgueiro A, Marinho A, Marinho R, Santos M, Lafuente E, Castro H, Cabral S, Moura J, Martins P, Oliveira B, Salgueiro A, Duarte S, Castro S, Melo M, Casteloes P, Marinho A, Gray S, Maipang K, Bhurayanontachai R, Grädel LG, Schütz P, Langlois P, Manzanares W, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Manzanares W, Langlois P, Lemieux M, Elke G, Bloos F, Reinhart K, Heyland D, Langlois P, Lemieux M, Aramendi I, Heyland D, Manzanares W, Su Y, Marinho R, Babo N, Marinho A, Hoshino M, Haraguchi Y, Kajiwara S, Mitsuhashi T, Tsubata T, Aida M, Rattanapraphat T, Bhurayanontachai R, Kongkamol C, Khwannimit B, Marinho R, Santos M, Castro H, Lafuente E, Salgueiro A, Cabral S, Martins P, Moura J, Oliveira B, Melo M, Xavier B, Valente J, Magalhaes C, Casteloes P, Marinho A, Moisidou D, Ampatzidou F, Koutsogiannidis C, Moschopoulou M, Drossos G, Taskin G, Çakir M, Güler AK, Taskin A, Öcal N, Özer S, Yamanel L, Wong JM, Fitton C, Anwar S, Stacey S, Aggou M, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Oloktsidou E, Lolakos K, Papapostolou E, Grosomanidis V, Suda S, Ikeda T, Ono S, Ueno T, Izutani Y, Gaudry S, Desailly V, Pasquier P, Brun PB, Tesnieres AT, Ricard JD, Dreyfuss D, Mignon A, White JC, Molokhia A, Dean A, Stilwell A, Friedlaender G, Peters M, Stipulante S, Delfosse A, Donneau AF, Ghuysen A, Feldmann C, Freitag D, Dersch W, Irqsusi M, Eschbach D, Steinfeldt T, Wulf H, Wiesmann T, Kongpolprom N, Cholkraisuwat J, Beitland S, Nakstad E, Stær-Jensen H, Drægni T, Andersen G, Jacobsen D, Brunborg C, Waldum-Grevbo B, Sunde K, Hoyland K, Pandit D, Hayakawa K, Oloktsidou E, Kotzampassi K, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Loukipoudi L, Doumaki E, Grosomanidis V, Yasuda H, Admiraal MM, Van Assen M, Van Putten MJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans M, Van Rootselaar AF, Horn J, Ragusa F, Marudi A, Baroni S, Gaspari A, Bertellini E, Taha A, Abdullah T, Abdel Monem S, Alcorn S, McNeill S, Russell S, Eertmans W, Genbrugge C, Meex I, Dens J, Jans F, De Deyne C, Cholkraisuwat J, Kongpolprom N, Avard B, Burns R, Patarchi A, Spina T, Tanaka H, Otani N, Ode S, Ishimatsu S, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Won MH, Dakova S, Ramsheva Z, Ramshev K, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Marudi A, Baroni S, Gaspari A, Bertellini E, Orhun G, Senturk E, Ozcan PE, Sencer S, Ulusoy C, Tuzun E, Esen F, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Van Assen M, Admiraal MM, Van Putten MJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans M, Van Rootselaar AF, Horn J, Fallenius M, Skrifvars MB, Reinikainen M, Bendel S, Raj R, Abu-Habsa M, Hymers C, Borowska A, Sivadhas H, Sahiba S, Perkins S, Rubio J, Rubio JA, Sierra R, English S, Chasse M, Turgeon A, Lauzier F, Griesdale D, Garland A, Fergusson D, Zarychanski R, Tinmouth A, Van Walraven C, Montroy K, Ziegler J, Dupont Chouinard R, Carignan R, Dhaliwal A, Lum C, Sinclair J, Pagliarello G, McIntyre L, English S, Chasse M, Turgeon A, Lauzier F, Griesdale D, Garland A, Fergusson D, Zarychanski R, Tinmouth A, Van Walraven C, Montroy K, Ziegler J, Dupont Chouinard R, Carignan R, Dhaliwal A, Lum C, Sinclair J, Pagliarello G, McIntyre L, Groza T, Moreau N, Castanares-Zapatero D, Hantson P, Carbonara M, Ortolano F, Zoerle T, Magnoni S, Pifferi S, Conte V, Stocchetti N, Carteron L, Suys T, Patet C, Quintard H, Oddo M, Rubio JA, Rubio J, Sierra R, Spatenkova V, Pokorna E, Suchomel P, Ebert N, Jancik J, Rhodes H, Bylinski T, Hawthorne C, Shaw M, Piper I, Kinsella J, Kink AK, Rätsep IR, Boutin A, Moore L, Chasse M, Zarychanski R, Lauzier F, English S, McIntyre L, Lacroix J, Griesdale D, Lessard-Bonaventure P, Turgeon AF, Boutin A, Moore L, Green R, Lessard-Bonaventure P, Erdogan M, Butler M, Lauzier F, Chasse M, English S, McIntyre L, Zarychanski R, Lacroix J, Griesdale D, Desjardins P, Fergusson DA, Turgeon AF, Goncalves B, Vidal B, Valdez C, Rodrigues AC, Miguez L, Moralez G, Hong T, Kutz A, Hausfater P, Amin D, Struja T, Haubitz S, Huber A, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Brown T, Collinson J, Pritchett C, Slade T, Le Guen M, Hellings S, Ramsaran R, Alsheikhly A, Abe T, Kanapeckaite L, Abu-Habsa M, Bahl R, Russell MQ, Real KJ, Abu-Habsa M, Lyon RM, Oveland NP, Penketh J, Mcdonald M, Kelly F, Alfafi M, Alsolamy S, Almutairi W, Alotaibi B, Van den Berg AE, Schriel Y, Dawson L, Meynaar IA, Talaie H, Silva D, Fernandes S, Gouveia J, Santos Silva J, Foley J, Kaskovagheorgescu A, Evoy D, Cronin J, Ryan J, Huck M, Hoffmann C, Renner J, Laitselart P, Donat N, Cirodde A, Schaal JV, Masson Y, Nau A, Leclerc T, Howarth O, Davenport K, Jeanrenaud P, Raftery S, MacTavish P, Devine H, McPeake J, Daniel M, Kinsella J, Quasim T, Alrabiee S, Alrashid A, Alsolamy S, Gundogan O, Bor C, Akýn Korhan E, Demirag K, Uyar M, Frame F, Ashton C, Bergstrom Niska L, Dilokpattanamongkol P, Suansanae T, Suthisisang C, Morakul S, Karnjanarachata C, Tangsujaritvijit V, Mahmood S, Al Thani H, Almenyar A, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Sharvill R, Penketh J, Morton SE, Chiew YS, Pretty C, Chase JG, Shaw GM, Knafelj R, Kordis P, Patel S, Grover V, Kuchyn I, Bielka K, Aidoni Z, Grosomanidis V, Kotzampassi K, Stavrou G, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Skourtis C, Lee SD, Williams K, Weltes ID, Berhane S, Arrowsmith C, Peters C, Robert S, Caldas J, Panerai RB, Robinson TG, Camara L, Ferreira G, Borg-Seng-Shu E, De Lima Oliveira M, Mian NC, Santos L, Nogueira R, Zeferino SP, Jacobsen Teixeira M, Galas F, Hajjar LA, Killeen P, McPhail M, Bernal W, Maggs J, Wendon J, Hughes T, Taniguchi LU, Siqueira EM, Vieira Jr JM, Azevedo LC, Ahmad AN, Abu-Habsa M, Bahl R, Helme E, Hadfield S, Loveridge R, Shak J, Senver C, Howard-Griffin R, Wacharasint P, Fuengfoo P, Sukcharoen N, Rangsin R, Sbiti-Rohr D, Schuetz P, Na H, Song S, Lee S, Jeong E, Lee K, Cooper M, Milinis K, Williams G, McCarron E, Simants S, Patanwala I, Welters ID, Zoumpelouli E, Volakli EA, Chrysohoidou V, Georgiou S, Charisopoulou K, Kotzapanagiotou E, Panagiotidou V, Manavidou K, Stathi Z, Sdougka M, Salahuddin N, AlGhamdi B, Marashly Q, Zaza K, Sharshir M, Khurshid M, Ali Z, Malgapo M, Jamil M, Shafquat A, Shoukri M, Hijazi M, Abe T, Uchino S, Takinami M, Rangel Neto NR, Oliveira S, Reis FQ, Rocha FA, Moralez G, Ebecken K, Rabello LS, Lima MF, Hatum R, De Marco FV, Alves A, Pinto JE, Godoy M, Brasil PE, Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Soares M, Krinsley J, Kang G, Perry J, Hines H, Wilkinson KM, Tordoff C, Sloan B, Bellamy MC, Moreira E, Verga F, Barbato M, Burghi G, Soares M, Silva UV, Azevedo LC, Torelly AP, Kahn JM, Angus DC, Knibel MF, Brasil PE, Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Marshall R, Gilpin T, Tridente A, Raithatha A, Mota D, Loureiro B, Dias J, Afonso O, Coelho F, Martins A, Faria F, Al-Dorzi H, Al Orainni H, AlEid F, Tlaygeh H, Itani A, Hejazi A, Arabi Y, Gaudry S, Messika J, Ricard JD, Guillo S, Pasquet B, Dubief E, Dreyfuss D, Tubach F, Battle C, James K, Temblett P, Davies L, Battle C, Lynch C, Pereira S, Cavaco S, Fernandes J, Moreira I, Almeida E, Seabra Pereira F, Malheiro M, Cardoso F, Aragão I, Cardoso T, Fister M, Knafelj R, Muraray Govind P, Brahmananda Reddy N, Pratheema R, Arul ED, Devachandran J, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Knafelj R, Fister M, Chin-Yee N, D’Egidio G, Thavorn K, Heyland D, Kyeremanteng K, Murchison AG, Swalwell K, Mandeville J, Stott D, Guerreiro I, Devine H, MacTavish P, McPeake J, Quasim T, Kinsella J, Daniel M, Goossens C, Marques MB, Derde S, Vander Perre S, Dufour T, Thiessen SE, Güiza F, Janssens T, Hermans G, Vanhorebeek I, De Bock K, Van den Berghe G, Langouche L, Devine H, MacTavish P, Quasim T, Kinsella J, Daniel M, McPeake J, Miles B, Madden S, Devine H, Weiler M, Marques P, Rodrigues C, Boeira M, Brenner K, Leães C, Machado A, Townsend R, Andrade J, MacTavish P, McPeake J, Devine H, Kinsella J, Daniel M, Kishore R, Fenlon C, Quasim T, Fiks T, Ruijter A, Te Raa M, Spronk P, Chiew YS, Docherty P, Dickson J, Moltchanova E, Scarrot C, Pretty C, Shaw GM, Chase JG, Hall T, Ngu WC, Jack JM, Morgan P, Avard B, Pavli A, Gee X, Bor C, Akin Korhan E, Demirag K, Uyar M, Shirazy M, Fayed A, Gupta S, Kaushal A, Dewan S, Varma A, Ghosh E, Yang L, Eshelman L, Lord B, Carlson E, Helme E, Broderick R, Hadfield S, Loveridge R, Ramos J, Forte D, Yang F, Hou P, Dudziak J, Feeney J, Wilkinson K, Bauchmuller K, Shuker K, Faulds M, Raithatha A, Bryden D, England L, Bolton N, Tridente A, Bauchmuller K, Shuker K, Tridente A, Faulds M, Matheson A, Gaynor J, Bryden D, S South Yorkshire Hospitals Research Collaboration. Ramos J, Peroni B, Daglius-Dias R, Miranda L, Cohen C, Carvalho C, Velasco I, Forte D, Kelly JM, Neill A, Rubenfeld G, Masson N, Min A, Boezeman E, Hofhuis J, Hovingh A, De Vries R, Spronk P, Cabral-Campello G, Aragão I, Cardoso T, Van Mol M, Nijkamp M, Kompanje E, Ostrowski P, Omar A, Kiss K, Köves B, Csernus V, Molnár Z, Hoydonckx Y, Vanwing S, Stessel B, Van Assche A, Jamaer L, Dubois J, Medo V, Galvez R, Miranda JP, Stone C, Wigmore T, Arunan Y, Wheeler A, Bauchmuller K, Bryden D, Wong Y, Poi C, Gu C, Molmy P, Van Grunderbeeck N, Nigeon O, Lemyze M, Thevenin D, Mallat J, Ramos J, Correa M, Carvalho RT, Forte D, Fernandez A, McBride C, Koonthalloor E, Walsh C, Webber A, Ashe M, Smith K, Jeanrenaud P, Marudi A, Baroni S, Ragusa F, Bertellini E, Volakli EA, Chochliourou E, Dimitriadou M, Violaki A, Mantzafleri P, Samkinidou E, Vrani O, Arbouti A, Varsami T, Sdougka M, Bollen JA, Van Smaalen TC, De Jongh WC, Ten Hoopen MM, Ysebaert D, Van Heurn LW, Van Mook WN, Sim K, Fuller A, Roze des Ordons A, Couillard P, Doig C, Van Keer RV, Deschepper RD, Francke AF, Huyghens LH, Bilsen JB, Nyamaizi B, Dalrymple C, Molokhia A, Dobru A, Marrinan E, Ankuli A, Molokhia A, McPeake J, Struthers R, Crawford R, Devine H, Mactavish P, Quasim T, Morelli P, Degiovanangelo M, Lemos F, MArtinez V, Verga F, Cabrera J, Burghi G, Rutten A, Van Ieperen S, De Geer S, Van Vugt M, Der Kinderen E, Giannini A, Miccinesi G, Marchesi T, Prandi E.
Ramos J, Peroni B, Daglius-Dias R, Miranda L, Cohen C, Carvalho C, Velasco I, Forte D, Kelly JM, Neill A, Rubenfeld G, Masson N, Min A, Boezeman E, Hofhuis J, Hovingh A, De Vries R, Spronk P, Cabral-Campello G, Aragão I, Cardoso T, Van Mol M, Nijkamp M, Kompanje E, Ostrowski P, Omar A, Kiss K, Köves B, Csernus V, Molnár Z, Hoydonckx Y, Vanwing S, Stessel B, Van Assche A, Jamaer L, Dubois J, Medo V, Galvez R, Miranda JP, Stone C, Wigmore T, Arunan Y, Wheeler A, Bauchmuller K, Bryden D, Wong Y, Poi C, Gu C, Molmy P, Van Grunderbeeck N, Nigeon O, Lemyze M, Thevenin D, Mallat J, Ramos J, Correa M, Carvalho RT, Forte D, Fernandez A, McBride C, Koonthalloor E, Walsh C, Webber A, Ashe M, Smith K, Jeanrenaud P, Marudi A, Baroni S, Ragusa F, Bertellini E, Volakli EA, Chochliourou E, Dimitriadou M, Violaki A, Mantzafleri P, Samkinidou E, Vrani O, Arbouti A, Varsami T, Sdougka M, Bollen JA, Van Smaalen TC, De Jongh WC, Ten Hoopen MM, Ysebaert D, Van Heurn LW, Van Mook WN, Sim K, Fuller A, Roze des Ordons A, Couillard P, Doig C, Van Keer RV, Deschepper RD, Francke AF, Huyghens LH, Bilsen JB, Nyamaizi B, Dalrymple C, Molokhia A, Dobru A, Marrinan E, Ankuli A, Molokhia A, McPeake J, Struthers R, Crawford R, Devine H, Mactavish P, Quasim T, Morelli P, Degiovanangelo M, Lemos F, MArtinez V, Verga F, Cabrera J, Burghi G, Rutten A, Van Ieperen S, De Geer S, Van Vugt M, Der Kinderen E, Giannini A, Miccinesi G, Marchesi T, Prandi E. 36th International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine : Brussels, Belgium. 15-18 March 2016. Crit Care. 2016 Apr 20;20(Suppl 2):94. [PMC free article: PMC5493079] [PubMed: 27885969]
36th International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine : Brussels, Belgium. 15-18 March 2016. Crit Care. 2016 Apr 20;20(Suppl 2):94. [PMC free article: PMC5493079] [PubMed: 27885969]
Anoxic Encephalopathy – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf
Bateman RM, Sharpe MD, Jagger JE, Ellis CG, Solé-Violán J, López-Rodríguez M, Herrera-Ramos E, Ruíz-Hernández J, Borderías L, Horcajada J, González-Quevedo N, Rajas O, Briones M, Rodríguez de Castro F, Rodríguez Gallego C, Esen F, Orhun G, Ergin Ozcan P, Senturk E, Ugur Yilmaz C, Orhan N, Arican N, Kaya M, Kucukerden M, Giris M, Akcan U, Bilgic Gazioglu S, Tuzun E, Riff R, Naamani O, Douvdevani A, Takegawa R, Yoshida H, Hirose T, Yamamoto N, Hagiya H, Ojima M, Akeda Y, Tasaki O, Tomono K, Shimazu T, Ono S, Kubo T, Suda S, Ueno T, Ikeda T, Hirose T, Ogura H, Takahashi H, Ojima M, Kang J, Nakamura Y, Kojima T, Shimazu T, Ikeda T, Suda S, Izutani Y, Ueno T, Ono S, Taniguchi T, O M, Dinter C, Lotz J, Eilers B, Wissmann C, Lott R, Meili MM, Schuetz PS, Hawa H, Sharshir M, Aburageila M, Salahuddin N, Chantziara V, Georgiou S, Tsimogianni A, Alexandropoulos P, Vassi A, Lagiou F, Valta M, Micha G, Chinou E, Michaloudis G, Kodaira A, Ikeda T, Ono S, Ueno T, Suda S, Izutani Y, Imaizumi H, De la Torre-Prados MV, Garcia-De la Torre A, Enguix-Armada A, Puerto-Morlan A, Perez-Valero V, Garcia-Alcantara A, Bolton N, Dudziak J, Bonney S, Tridente A, Nee P, Nicolaes G, Wiewel M, Schultz M, Wildhagen K, Horn J, Schrijver R, Van der Poll T, Reutelingsperger C, Pillai S, Davies G, Mills G, Aubrey R, Morris K, Williams P, Evans P, Gayat EG, Struck J, Cariou A, Deye N, Guidet B, Jabert S, Launay J, Legrand M, Léone M, Resche-Rigon M, Vicaut E, Vieillard-Baron A, Mebazaa A, Arnold R, Capan M, Linder A, Akesson P, Popescu M, Tomescu D, Sprung CL, Calderon Morales R, Munteanu G, Orenbuch-Harroch E, Levin P, Kasdan H, Reiter A, Volker T, Himmel Y, Cohen Y, Meissonnier J, Girard L, Rebeaud F, Herrmann I, Delwarde B, Peronnet E, Cerrato E, Venet F, Lepape A, Rimmelé T, Monneret G, Textoris J, Beloborodova N, Moroz V, Osipov A, Bedova A, Sarshor Y, Pautova A, Sergeev A, Chernevskaya E, Odermatt J, Bolliger R, Hersberger L, Ottiger M, Christ-Crain M, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Sharma NK, Tashima AK, Brunialti MK, Machado FR, Assuncao M, Rigato O, Salomao R, Cajander SC, Rasmussen G, Tina E, Söderquist B, Källman J, Strålin K, Lange AL, Sundén-Cullberg JS, Magnuson AM, Hultgren OH, Davies G, Pillai S, Mills G, Aubrey R, Morris K, Williams P, Evans P, Pillai S, Davies G, Mills G, Aubrey R, Morris K, Williams P, Evans P, Pillai S, Davies G, Mills G, Aubrey R, Morris K, Williams P, Evans P, Van der Geest P, Mohseni M, Linssen J, De Jonge R, Duran S, Groeneveld J, Miller R, Lopansri BK, McHugh LC, Seldon A, Burke JP, Johnston J, Reece-Anthony R, Bond A, Molokhia A, Mcgrath C, Nsutebu E, Bank Pedersen P, Pilsgaard Henriksen D, Mikkelsen S, Touborg Lassen A, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Wiewel MA, Harmon MB, Van Vught LA, Scicluna BP, Hoogendijk AJ, Horn J, Zwinderman AH, Cremer OL, Bonten MJ, Schultz MJ, Van der Poll T, Juffermans NP, Wiersinga WJ, Eren G, Tekdos Y, Dogan M, Acicbe O, Kaya E, Hergunsel O, Alsolamy S, Ghamdi G, Alswaidan L, Alharbi S, Alenezi F, Arabi Y, Heaton J, Boyce A, Nolan L, Johnston J, Dukoff-Gordon A, Dean A, Molokhia A, Mann Ben Yehudah T, Fleischmann C, Thomas-Rueddel D, Haas C, Dennler U, Reinhart K, Suntornlohanakul O, Khwannimit B, Breckenridge F, Puxty A, Szturz P, Folwarzcny P, Svancara J, Kula R, Sevcik P, Caneva L, Casazza A, Bellazzi E, Marra S, Pagani L, Vetere M, Vanzino R, Ciprandi D, Preda R, Boschi R, Carnevale L, Lopez V, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Escalante A, Gongora J, Cetina M, Adamik B, Jakubczyk D, Kübler A, Radford A, Lee T, Singer J, Boyd J, Fineberg D, Williams M, Russell J, Scarlatescu E, Tomescu D, Droc G, Arama S, Müller M, Straat M, Zeerleder SS, Juffermans NP, Fuchs CF, Scheer CS, Wauschkuhn SW, Vollmer MV, Meissner KM, Kuhn SK, Hahnenkamp KH, Rehberg SR, Gründling MG, Yamamoto N, Ojima M, Hamaguchi S, Hirose T, Akeda Y, Takegawa R, Tasaki O, Shimazu T, Tomono K, Gómez-Sánchez E, Heredia-Rodríguez M, Álvarez-Fuente E, Lorenzo-López M, Gómez-Pesquera E, Aragón-Camino M, Liu-Zhu P, Sánchez-López A, Hernández-Lozano A, Peláez-Jareño MT, Tamayo E, Thomas-Rüddel DO, Fleischmann C, Haas C, Dennler U, Reinhart K, Adora V, Kar A, Chakraborty A, Roy S, Bandyopadhyay A, Das M, Mann Ben Yehudah T, BenYehudah G, Salim M, Kumar N, Arabi L, Burger T, Lephart P, Toth-martin E, Valencia C, Hammami N, Blot S, Vincent JL, Lambert ML, Brunke J, Riemann T, Roschke I, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Nimitvilai S, Jintanapramote K, Jarupongprapa S, Adukauskiene D, Valanciene D, Bose G, Lostarakos V, Carr B, Khedher S, Maaoui A, Ezzamouri A, Salem M, Chen J, Cranendonk DR, Van Vught LA, Wiewel MA, Cremer OL, Horn J, Bonten MJ, Schultz MJ, Van der Poll T, Wiersinga WJ, Day M, Penrice G, Roy K, Robertson P, Godbole G, Jones B, Booth M, Donaldson L, Kawano Y, Ishikura H, Al-Dorzi H, Almutairi M, Alhamadi B, Crizaldo Toledo A, Khan R, Al Raiy B, Arabi Y, Talaie H, Van Oers JA, Harts A, Nieuwkoop E, Vos P, Boussarsar Y, Boutouta F, Kamoun S, Mezghani I, Koubaji S, Ben Souissi A, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Giamarellos-Bourboulis E, Tziolos N, Routsi C, Katsenos C, Tsangaris I, Pneumatikos I, Vlachogiannis G, Theodorou V, Prekates A, Antypa E, Koulouras V, Kapravelos N, Gogos C, Antoniadou E, Mandragos K, Armaganidis A, Robles Caballero AR, Civantos B, Figueira JC, López J, Silva-Pinto A, Ceia F, Sarmento A, Santos L, Almekhlafi G, Sakr Y, Al-Dorzi H, Khan R, Baharoon S, Aldawood A, Matroud A, Alchin J, Al Johani S, Balkhy H, Arabi Y, Alsolamy S, Yousif SY, Alotabi BO, Alsaawi AS, Ang J, Curran MD, Enoch D, Navapurkar V, Morris A, Sharvill R, Astin J, Heredia-Rodríguez M, Gómez-Sánchez E, Peláez-Jareño MT, Gómez-Pesquera E, Lorenzo-López M, Liu-Zhu P, Aragón-Camino M, Hernández-Lozano A, Sánchez-López A, Álvarez-Fuente E, Tamayo E, Patel J, Kruger C, O’Neal J, Rhodes H, Jancik J, François B, Laterre PF, Eggimann P, Torres A, Sánchez M, Dequin PF, Bassi GL, Chastre J, Jafri HS, Ben Romdhane M, Douira Z, Kamoun S, Bousselmi M, Ben Souissi A, Boussarsar Y, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Craven TH, Wojcik G, Kefala K, McCoubrey J, Reilly J, Paterson R, Inverarity D, Laurenson I, Walsh TS, Mongodi S, Bouhemad B, Orlando A, Stella A, Via G, Iotti G, Braschi A, Mojoli F, Haliloglu M, Bilgili B, Kasapoglu U, Sayan I, Süzer Aslan M, Yalcın A, Cinel I, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Ellis HE, Bauchmuller K, Miller D, Temple A, Chastre J, François B, Torres A, Luyt CE, Sánchez M, Singer M, Jafri HS, Nassar Y, Ayad MS, Trifi A, Abdellatif S, Daly F, Nasri R, Ben Lakhal S, Bilgili B, Haliloglu M, Gul F, Cinel I, Kuzovlev A, Shabanov A, Polovnikov S, Moroz V, Kadrichu N, Dang T, Corkery K, Challoner P, Bassi GL, Aguilera E, Chiurazzi C, Travierso C, Motos A, Fernandez L, Amaro R, Senussi T, Idone F, Bobi J, Rigol M, Torres A, Hodiamont CJ, Juffermans NP, Janssen JM, Bouman CS, Mathôt RA, De Jong MD, Van Hest RM, Payne L, Fraser GL, Tudor B, Lahner M, Roth G, Krenn C, Talaie H, Jault P, Gabard J, Leclerc T, Jennes S, Que Y, Rousseau A, Ravat F, Al-Dorzi H, Eissa A, Al-Harbi S, Aldabbagh T, Khan R, Arabi Y, Trifi A, Abdellatif. S, Daly F, Nasri R, Ben Lakhal S, Paramba F, Purayil N, Naushad V, Mohammad O, Negi V, Chandra P, Kleinsasser A, Witrz MR, Buchner-Doeven JF, Tuip-de Boer AM, Goslings JC, Juffermans NP, Van Hezel M, Straat M, Boing A, Van Bruggen R, Juffermans N, Markopoulou D, Venetsanou K, Kaldis V, Koutete D, Chroni D, Alamanos I, Koch L, Jancik J, Rhodes H, Walter E, Maekawa K, Hayakawa M, Kushimoto S, Shiraishi A, Kato H, Sasaki J, Ogura H, Matauoka T, Uejima T, Morimura N, Ishikura H, Hagiwara A, Takeda M, Tarabrin O, Shcherbakow S, Gavrychenko D, Mazurenko G, Ivanova V, Chystikov O, Plourde C, Lessard J, Chauny J, Daoust R, Shcherbakow S, Tarabrin O, Gavrychenko D, Mazurenko G, Chystikov O, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Kropman L, In het Panhuis L, Konings J, Huskens D, Schurgers E, Roest M, De Laat B, Lance M, Durila M, Lukas P, Astraverkhava M, Jonas J, Budnik I, Shenkman B, Hayami H, Koide Y, Goto T, Iqbal R, Alhamdi Y, Venugopal N, Abrams S, Downey C, Toh CH, Welters ID, Bombay VB, Chauny JM, Daoust RD, Lessard JL, Marquis MM, Paquet JP, Siemens K, Sangaran D, Hunt BJ, Durward A, Nyman A, Murdoch IA, Tibby SM, Ampatzidou F, Moisidou D, Dalampini E, Nastou M, Vasilarou E, Kalaizi V, Chatzikostenoglou H, Drossos G, Spadaro S, Fogagnolo A, Fiore T, Schiavi A, Fontana V, Taccone F, Volta C, Chochliourou E, Volakli E, Violaki A, Samkinidou E, Evlavis G, Panagiotidou V, Sdougka M, Mothukuri R, Battle C, Guy K, Mills G, Evans P, Wijesuriya J, Keogh S, Docherty A, O’Donnell R, Brunskill S, Trivella M, Doree C, Holst L, Parker M, Gregersen M, Almeida J, Walsh T, Stanworth S, Moravcova S, Mansell J, Rogers A, Smith RA, Hamilton-Davies C, Omar A, Allam M, Bilala O, Kindawi A, Ewila H, Ampatzidou F, Moisidou D, Nastou M, Dalampini E, Malamas A, Vasilarou E, Drossos G, Ferreira G, Caldas J, Fukushima J, Osawa EA, Arita E, Camara L, Zeferino S, Jardim J, Gaioto F, Dallan L, Jatene FB, Kalil Filho R, Galas F, Hajjar LA, Mitaka C, Ohnuma T, Murayama T, Kunimoto F, Nagashima M, Takei T, Tomita M, Omar A, Mahmoud K, Hanoura S, Sudarsanan S, Sivadasan P, Othamn H, Shouman Y, Singh R, Al Khulaifi A, Mandel I, Mikheev S, Suhodolo I, Kiselev V, Svirko Y, Podoksenov Y, Jenkins SA, Griffin R, Tovar Doncel MS, Lima A, Aldecoa C, Ince C, Taha A, Shafie A, Mostafa M, Syed N, Hon H, Righetti F, Colombaroli E, Castellano G, Righetti F, Colombaroli E, Hravnak M, Chen LC, Dubrawski AD, Clermont GC, Pinsky MR, Gonzalez S, Macias D, Acosta J, Jimenez P, Loza A, Lesmes A, Lucena F, Leon C, Tovar Doncel MS, Ince C, Aldecoa C, Lima A, Bastide M, Richecoeur J, Frenoy E, Lemaire C, Sauneuf B, Tamion F, Nseir S, Du Cheyron D, Dupont H, Maizel J, Shaban M, Kolko R, Salahuddin N, Sharshir M, AbuRageila M, AlHussain A, Mercado P, Maizel J, Kontar L, Titeca D, Brazier F, Riviere A, Joris M, Soupison T, De Cagny B, Slama M, Wagner J, Körner A, Kubik M, Kluge S, Reuter D, Saugel B, Colombaroli E, Righetti F, Castellano G, Tran T, De Bels D, Cudia A, Strachinaru M, Ghottignies P, Devriendt J, Pierrakos C, Martínez González Ó, Blancas R, Luján J, Ballesteros D, Martínez Díaz C, Núñez A, Martín Parra C, López Matamala B, Alonso Fernández M, Chana M, Huber W, Eckmann M, Elkmann F, Gruber A, Klein I, Schmid RM, Lahmer T, Moller PW, Sondergaard S, Jakob SM, Takala J, Berger D, Bastoni D, Aya H, Toscani L, Pigozzi L, Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Ostrowska C, Aya H, Abbas A, Mellinghoff J, Ryan C, Dawson D, Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Cronhjort M, Wall O, Nyberg E, Zeng R, Svensen C, Mårtensson J, Joelsson-Alm E, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Lopez V, Cetina M, Parenti N, Palazzi C, Amidei LA, Borrelli FB, Campanale SC, Tagliazucchi FT, Sedoni GS, Lucchesi DL, Carella EC, Luciani AL, Mackovic M, Maric N, Bakula M, Aya H, Rhodes A, Grounds RM, Fletcher N, Cecconi M, Avard B, Zhang P, Mezidi M, Charbit J, Ould-Chikh M, Deras P, Maury C, Martinez O, Capdevila X, Hou P, Linde-Zwirble WZ, Douglas ID, Shapiro NS, Ben Souissi A, Mezghani I, Ben Aicha Y, Kamoun S, Laribi B, Jeribi B, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Pereira C, Marinho R, Antunes R, Marinho A, Crivits M, Raes M, Decruyenaere J, Hoste E, Bagin V, Rudnov V, Savitsky A, Astafyeva M, Korobko I, Vein V, Kampmeier T, Arnemann P, Hessler M, Wald A, Bockbreder K, Morelli A, Van Aken H, Rehberg S, Ertmer C, Arnemann P, Hessler M, Kampmeier T, Rehberg S, Van Aken H, Ince C, Ertmer C, Reddy S, Bailey M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Mackle D, Psirides A, Young P, Reddy S, Bailey M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Mackle D, Young P, Venkatesh H, Ramachandran S, Basu A, Nair H, Egan S, Bates J, Oliveira S, Rangel Neto NR, Reis FQ, Lee CP, Lin XL, Choong C, Eu KM, Sim WY, Tee KS, Pau J, Abisheganaden J, Maas K, De Geus H, Lafuente E, Marinho R, Moura J, Antunes R, Marinho A, Doris TE, Monkhouse D, Shipley T, Kardasz S, Gonzalez I, Stads S, Groeneveld AJ, Elsayed I, Ward N, Tridente A, Raithatha A, Steuber A, Pelletier C, Schroeder S, Michael E, Slowinski T, Kindgen-Milles D, Ghabina S, Turani F, Belli A, Busatti S, Barettin G, Candidi F, Gargano F, Barchetta R, Falco M, Demirkiran O, Kosuk M, Bozbay S, Weber V, Hartmann J, Harm S, Linsberger I, Eichhorn T, Valicek G, Miestinger G, Hoermann C, Faenza S, Ricci D, Mancini E, Gemelli C, Cuoghi A, Magnani S, Atti M, Laddomada T, Doronzio A, Balicco B, Gruda MC, O’Sullivan P, Dan VP, Guliashvili T, Scheirer A, Golobish TD, Capponi VJ, Chan PP, Kogelmann K, Drüner M, Jarczak D, Turani F, Belli AB, Martni SM, Cotticelli VC, Mounajergi F, Barchetta R, Morimoto S, Ishikura H, Hussain I, Salahuddin N, Nadeem A, Ghorab K, Maghrabi K, Kloesel SK, Goldfuss C, Stieglitz A, Stieglitz AS, Krstevska L, Albuszies G, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Lopez V, Escalante A, Jimmy G, Cetina M, Izawa J, Iwami T, Uchino S, Takinami M, Kitamura T, Kawamura T, Powell-Tuck JG, Crichton S, Raimundo M, Camporota L, Wyncoll D, Ostermann M, Hana A, De Geus HR, De Geus HR, Hana A, Aydogdu M, Boyaci N, Yuksel S, Gursel G, Cayci Sivri AB, Meza-Márquez J, Nava-López J, Carrillo-Esper R, Dardashti A, Grubb A, Maizel J, Wetzstein M, Titeca D, Kontar L, Brazier F, De Cagny B, Riviere A, Soupison T, Joris M, Slama M, Peters E, Njimi H, Pickkers P, Vincent JL, Waraich M, Doyle J, Samuels T, Forni L, Desai N, Baumber R, Gunning P, Sell A, Lin S, Torrence H, O’Dwyer M, Kirwan C, Prowle J, Kim T, O’Connor ME, Hewson RW, Kirwan CJ, Pearse RM, Prowle J, Hanoura S, Omar A, Othamn H, Sudarsanan S, Allam M, Maksoud M, Singh R, Al Khulaifi A, O’Connor ME, Hewson RW, Kirwan CJ, Pearse RM, Prowle J, Uzundere O, Memis D, Ýnal M, Gultekin A, Turan N, Aydin MA, Basar H, Sencan I, Kapuagasi A, Ozturk M, Uzundurukan Z, Gokmen D, Ozcan A, Kaymak C, Artemenko VA, Budnyuk A, Pugh R, Bhandari S, Mauri T, Turrini C, Langer T, Taccone P, Volta CA, Marenghi C, Gattinoni L, Pesenti A, Sweeney L, O’Sullivan A, Kelly P, Mukeria E, MacLoughlin R, Pfeffer M, Thomas JT, Bregman GB, Karp GK, Kishinevsky EK, Stavi DS, Adi NA, Poropat T, Knafelj R, Llopart E, Batlle M, De Haro C, Mesquida J, Artigas A, Pavlovic D, Lewerentz L, Spassov A, Schneider R, De Smet S, De Raedt S, Derom E, Depuydt P, Oeyen S, Benoit D, Decruyenaere J, Gobatto A, Besen B, Tierno P, Melro L, Mendes P, Cadamuro F, Park M, Malbouisson LM, Civantos BC, Lopez JL, Robles A, Figueira J, Yus S, Garcia A, Oglinda A, Ciobanu G, Oglinda C, Schirca L, Sertinean T, Lupu V, Kelly P, O’Sullivan A, Sweeney L, MacLoughlin R, O’Sullivan A, Kelly P, Sweeney L, Mukeria E, Wolny M, MacLoughlin R, Pagano A, Numis F, Visone G, Saldamarco L, Russo T, Porta G, Paladino F, Bell C, Liu J, Debacker J, Lee C, Tamberg E, Campbell V, Mehta S, Silva-Pinto A, Sarmento A, Santos L, Kara Ý, Yýldýrým F, Zerman A, Güllü Z, Boyacý N, Basarýk Aydogan B, Gaygýsýz Ü, Gönderen K, Arýk G, Turkoglu M, Aydogdu M, Aygencel G, Ülger Z, Gursel G, Boyacý N, Isýkdogan Z, Özdedeoglu Ö, Güllü Z, Badoglu M, Gaygýsýz U, Aydogdu M, Gursel G, Kongpolprom N, Sittipunt C, Eden A, Kokhanovsky Y, Bursztein – De Myttenaere S, Pizov R, Neilans L, MacIntyre N, Radosevich M, Wanta B, Weber V, Meyer T, Smischney N, Brown D, Diedrich D, Fuller A, McLindon P, Sim K, Shoaeir M, Noeam K, Mahrous A, Matsa R, Ali A, Dridi C, Koubaji S, Kamoun S, Haddad F, Ben Souissi A, Laribi B, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Pérez-Calatayud A, Carrillo-Esper R, Zepeda-Mendoza A, Diaz-Carrillo M, Arch-Tirado E, Carbognin S, Pelacani L, Zannoni F, Agnoli A, Gagliardi G, Cho R, Adams A, Lunos S, Ambur S, Shapiro R, Prekker M, Thijssen M, Janssen L, Foudraine N, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, George E, Voscopoulos CJ, Eversole D, Freeman J, George E, Muttini S, Bigi R, Villani G, Patroniti N, Williams G, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, George E, Waldmann A, Böhm S, Windisch W, Strassmann S, Karagiannidis C, Waldmann A, Böhm S, Windisch W, Strassmann S, Karagiannidis C, Karagiannidis CK, Waldmann AW, Böhm SB, Strassmann S, Windisch WW, Persson P, Lundin S, Stenqvist O, Porta G, Numis F, Serra CS, Pagano AP, Masarone MM, Rinaldi LR, Amelia AA, Fascione MF, Adinolfi LA, Ruggiero ER, Asota F, O’Rourke K, Ranjan S, Morgan P, DeBacker JW, Tamberg E, O’Neill L, Munshi L, Burry L, Fan E, Mehta S, Poo S, Mahendran K, Fowles J, Gerrard C, Vuylsteke A, Loveridge R, Chaddock C, Patel S, Kakar V, Willars C, Hurst T, Park C, Best T, Vercueil A, Auzinger G, Borgman A, Proudfoot AG, Grins E, Emiley KE, Schuitema J, Fitch SJ, Marco G, Sturgill J, Dickinson MG, Strueber M, Khaghani A, Wilton P, Jovinge SM, Sampson C, Harris-Fox S, Cove ME, Vu LH, Sen A, Federspiel WJ, Kellum JA, Mazo Torre C, Riera J, Ramirez S, Borgatta B, Lagunes L, Rello J, Kuzovlev AK, Moroz V, Goloubev A, Polovnikov S, Nenchuk S, Karavana V, Glynos C, Asimakos A, Pappas K, Vrettou C, Magkou M, Ischaki E, Stathopoulos G, Zakynthinos S, Spadaro S, Kozhevnikova I, Dalla Corte F, Grasso S, Casolari P, Caramori G, Volta C, Andrianjafiarinoa T, Randriamandrato T, Rajaonera T, El-Dash S, Costa ELV, Tucci MR, Leleu F, Kontar L, De Cagny B, Brazier F, Titeca D, Bacari-Risal G, Maizel J, Amato M, Slama M, Mercado P, Maizel J, Kontar L, Titeca D, Brazier F, Riviere A, Joris M, Soupison T, De Cagny B, El Dash S, Slama M, Remmington, Fischer A, Squire S, Boichat M, Honzawa H, Yasuda H, Adati T, Suzaki S, Horibe M, Sasaki M, Sanui M, Marinho R, Daniel J, Miranda H, Marinho A, Milinis K, Cooper M, Williams GR, McCarron E, Simants S, Patanwala I, Welters I, Su Y, Fernández Villanueva J, Fernández Garda R, López Lago A, Rodríguez Ruíz E, Hernández Vaquero R, Tomé Martínez de Rituerto S, Varo Pérez E, Lefel N, Schaap F, Bergmans D, Olde Damink S, Van de Poll M, Tizard K, Lister C, Poole L, Ringaitiene D, Gineityte D, Vicka V, Norkiene I, Sipylaite J, O’Loughlin A, Maraj V, Dowling J, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Dias EB, Fernandes SL, Oshima T, Graf S, Heidegger C, Genton L, Karsegard V, Dupertuis Y, Pichard C, Friedli N, Stanga Z, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Vandersteen L, Stessel B, Evers S, Van Assche A, Jamaer L, Dubois J, Marinho R, Castro H, Moura J, Valente J, Martins P, Casteloes P, Magalhaes C, Cabral S, Santos M, Oliveira B, Salgueiro A, Marinho A, Marinho R, Santos M, Lafuente E, Castro H, Cabral S, Moura J, Martins P, Oliveira B, Salgueiro A, Duarte S, Castro S, Melo M, Casteloes P, Marinho A, Gray S, Maipang K, Bhurayanontachai R, Grädel LG, Schütz P, Langlois P, Manzanares W, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Manzanares W, Langlois P, Lemieux M, Elke G, Bloos F, Reinhart K, Heyland D, Langlois P, Lemieux M, Aramendi I, Heyland D, Manzanares W, Su Y, Marinho R, Babo N, Marinho A, Hoshino M, Haraguchi Y, Kajiwara S, Mitsuhashi T, Tsubata T, Aida M, Rattanapraphat T, Bhurayanontachai R, Kongkamol C, Khwannimit B, Marinho R, Santos M, Castro H, Lafuente E, Salgueiro A, Cabral S, Martins P, Moura J, Oliveira B, Melo M, Xavier B, Valente J, Magalhaes C, Casteloes P, Marinho A, Moisidou D, Ampatzidou F, Koutsogiannidis C, Moschopoulou M, Drossos G, Taskin G, Çakir M, Güler AK, Taskin A, Öcal N, Özer S, Yamanel L, Wong JM, Fitton C, Anwar S, Stacey S, Aggou M, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Oloktsidou E, Lolakos K, Papapostolou E, Grosomanidis V, Suda S, Ikeda T, Ono S, Ueno T, Izutani Y, Gaudry S, Desailly V, Pasquier P, Brun PB, Tesnieres AT, Ricard JD, Dreyfuss D, Mignon A, White JC, Molokhia A, Dean A, Stilwell A, Friedlaender G, Peters M, Stipulante S, Delfosse A, Donneau AF, Ghuysen A, Feldmann C, Freitag D, Dersch W, Irqsusi M, Eschbach D, Steinfeldt T, Wulf H, Wiesmann T, Kongpolprom N, Cholkraisuwat J, Beitland S, Nakstad E, Stær-Jensen H, Drægni T, Andersen G, Jacobsen D, Brunborg C, Waldum-Grevbo B, Sunde K, Hoyland K, Pandit D, Hayakawa K, Oloktsidou E, Kotzampassi K, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Loukipoudi L, Doumaki E, Grosomanidis V, Yasuda H, Admiraal MM, Van Assen M, Van Putten MJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans M, Van Rootselaar AF, Horn J, Ragusa F, Marudi A, Baroni S, Gaspari A, Bertellini E, Taha A, Abdullah T, Abdel Monem S, Alcorn S, McNeill S, Russell S, Eertmans W, Genbrugge C, Meex I, Dens J, Jans F, De Deyne C, Cholkraisuwat J, Kongpolprom N, Avard B, Burns R, Patarchi A, Spina T, Tanaka H, Otani N, Ode S, Ishimatsu S, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Won MH, Dakova S, Ramsheva Z, Ramshev K, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Marudi A, Baroni S, Gaspari A, Bertellini E, Orhun G, Senturk E, Ozcan PE, Sencer S, Ulusoy C, Tuzun E, Esen F, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Van Assen M, Admiraal MM, Van Putten MJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans M, Van Rootselaar AF, Horn J, Fallenius M, Skrifvars MB, Reinikainen M, Bendel S, Raj R, Abu-Habsa M, Hymers C, Borowska A, Sivadhas H, Sahiba S, Perkins S, Rubio J, Rubio JA, Sierra R, English S, Chasse M, Turgeon A, Lauzier F, Griesdale D, Garland A, Fergusson D, Zarychanski R, Tinmouth A, Van Walraven C, Montroy K, Ziegler J, Dupont Chouinard R, Carignan R, Dhaliwal A, Lum C, Sinclair J, Pagliarello G, McIntyre L, English S, Chasse M, Turgeon A, Lauzier F, Griesdale D, Garland A, Fergusson D, Zarychanski R, Tinmouth A, Van Walraven C, Montroy K, Ziegler J, Dupont Chouinard R, Carignan R, Dhaliwal A, Lum C, Sinclair J, Pagliarello G, McIntyre L, Groza T, Moreau N, Castanares-Zapatero D, Hantson P, Carbonara M, Ortolano F, Zoerle T, Magnoni S, Pifferi S, Conte V, Stocchetti N, Carteron L, Suys T, Patet C, Quintard H, Oddo M, Rubio JA, Rubio J, Sierra R, Spatenkova V, Pokorna E, Suchomel P, Ebert N, Jancik J, Rhodes H, Bylinski T, Hawthorne C, Shaw M, Piper I, Kinsella J, Kink AK, Rätsep IR, Boutin A, Moore L, Chasse M, Zarychanski R, Lauzier F, English S, McIntyre L, Lacroix J, Griesdale D, Lessard-Bonaventure P, Turgeon AF, Boutin A, Moore L, Green R, Lessard-Bonaventure P, Erdogan M, Butler M, Lauzier F, Chasse M, English S, McIntyre L, Zarychanski R, Lacroix J, Griesdale D, Desjardins P, Fergusson DA, Turgeon AF, Goncalves B, Vidal B, Valdez C, Rodrigues AC, Miguez L, Moralez G, Hong T, Kutz A, Hausfater P, Amin D, Struja T, Haubitz S, Huber A, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Brown T, Collinson J, Pritchett C, Slade T, Le Guen M, Hellings S, Ramsaran R, Alsheikhly A, Abe T, Kanapeckaite L, Abu-Habsa M, Bahl R, Russell MQ, Real KJ, Abu-Habsa M, Lyon RM, Oveland NP, Penketh J, Mcdonald M, Kelly F, Alfafi M, Alsolamy S, Almutairi W, Alotaibi B, Van den Berg AE, Schriel Y, Dawson L, Meynaar IA, Talaie H, Silva D, Fernandes S, Gouveia J, Santos Silva J, Foley J, Kaskovagheorgescu A, Evoy D, Cronin J, Ryan J, Huck M, Hoffmann C, Renner J, Laitselart P, Donat N, Cirodde A, Schaal JV, Masson Y, Nau A, Leclerc T, Howarth O, Davenport K, Jeanrenaud P, Raftery S, MacTavish P, Devine H, McPeake J, Daniel M, Kinsella J, Quasim T, Alrabiee S, Alrashid A, Alsolamy S, Gundogan O, Bor C, Akýn Korhan E, Demirag K, Uyar M, Frame F, Ashton C, Bergstrom Niska L, Dilokpattanamongkol P, Suansanae T, Suthisisang C, Morakul S, Karnjanarachata C, Tangsujaritvijit V, Mahmood S, Al Thani H, Almenyar A, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Sharvill R, Penketh J, Morton SE, Chiew YS, Pretty C, Chase JG, Shaw GM, Knafelj R, Kordis P, Patel S, Grover V, Kuchyn I, Bielka K, Aidoni Z, Grosomanidis V, Kotzampassi K, Stavrou G, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Skourtis C, Lee SD, Williams K, Weltes ID, Berhane S, Arrowsmith C, Peters C, Robert S, Caldas J, Panerai RB, Robinson TG, Camara L, Ferreira G, Borg-Seng-Shu E, De Lima Oliveira M, Mian NC, Santos L, Nogueira R, Zeferino SP, Jacobsen Teixeira M, Galas F, Hajjar LA, Killeen P, McPhail M, Bernal W, Maggs J, Wendon J, Hughes T, Taniguchi LU, Siqueira EM, Vieira Jr JM, Azevedo LC, Ahmad AN, Abu-Habsa M, Bahl R, Helme E, Hadfield S, Loveridge R, Shak J, Senver C, Howard-Griffin R, Wacharasint P, Fuengfoo P, Sukcharoen N, Rangsin R, Sbiti-Rohr D, Schuetz P, Na H, Song S, Lee S, Jeong E, Lee K, Cooper M, Milinis K, Williams G, McCarron E, Simants S, Patanwala I, Welters ID, Zoumpelouli E, Volakli EA, Chrysohoidou V, Georgiou S, Charisopoulou K, Kotzapanagiotou E, Panagiotidou V, Manavidou K, Stathi Z, Sdougka M, Salahuddin N, AlGhamdi B, Marashly Q, Zaza K, Sharshir M, Khurshid M, Ali Z, Malgapo M, Jamil M, Shafquat A, Shoukri M, Hijazi M, Abe T, Uchino S, Takinami M, Rangel Neto NR, Oliveira S, Reis FQ, Rocha FA, Moralez G, Ebecken K, Rabello LS, Lima MF, Hatum R, De Marco FV, Alves A, Pinto JE, Godoy M, Brasil PE, Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Soares M, Krinsley J, Kang G, Perry J, Hines H, Wilkinson KM, Tordoff C, Sloan B, Bellamy MC, Moreira E, Verga F, Barbato M, Burghi G, Soares M, Silva UV, Azevedo LC, Torelly AP, Kahn JM, Angus DC, Knibel MF, Brasil PE, Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Marshall R, Gilpin T, Tridente A, Raithatha A, Mota D, Loureiro B, Dias J, Afonso O, Coelho F, Martins A, Faria F, Al-Dorzi H, Al Orainni H, AlEid F, Tlaygeh H, Itani A, Hejazi A, Arabi Y, Gaudry S, Messika J, Ricard JD, Guillo S, Pasquet B, Dubief E, Dreyfuss D, Tubach F, Battle C, James K, Temblett P, Davies L, Battle C, Lynch C, Pereira S, Cavaco S, Fernandes J, Moreira I, Almeida E, Seabra Pereira F, Malheiro M, Cardoso F, Aragão I, Cardoso T, Fister M, Knafelj R, Muraray Govind P, Brahmananda Reddy N, Pratheema R, Arul ED, Devachandran J, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Knafelj R, Fister M, Chin-Yee N, D’Egidio G, Thavorn K, Heyland D, Kyeremanteng K, Murchison AG, Swalwell K, Mandeville J, Stott D, Guerreiro I, Devine H, MacTavish P, McPeake J, Quasim T, Kinsella J, Daniel M, Goossens C, Marques MB, Derde S, Vander Perre S, Dufour T, Thiessen SE, Güiza F, Janssens T, Hermans G, Vanhorebeek I, De Bock K, Van den Berghe G, Langouche L, Devine H, MacTavish P, Quasim T, Kinsella J, Daniel M, McPeake J, Miles B, Madden S, Devine H, Weiler M, Marques P, Rodrigues C, Boeira M, Brenner K, Leães C, Machado A, Townsend R, Andrade J, MacTavish P, McPeake J, Devine H, Kinsella J, Daniel M, Kishore R, Fenlon C, Quasim T, Fiks T, Ruijter A, Te Raa M, Spronk P, Chiew YS, Docherty P, Dickson J, Moltchanova E, Scarrot C, Pretty C, Shaw GM, Chase JG, Hall T, Ngu WC, Jack JM, Morgan P, Avard B, Pavli A, Gee X, Bor C, Akin Korhan E, Demirag K, Uyar M, Shirazy M, Fayed A, Gupta S, Kaushal A, Dewan S, Varma A, Ghosh E, Yang L, Eshelman L, Lord B, Carlson E, Helme E, Broderick R, Hadfield S, Loveridge R, Ramos J, Forte D, Yang F, Hou P, Dudziak J, Feeney J, Wilkinson K, Bauchmuller K, Shuker K, Faulds M, Raithatha A, Bryden D, England L, Bolton N, Tridente A, Bauchmuller K, Shuker K, Tridente A, Faulds M, Matheson A, Gaynor J, Bryden D, S South Yorkshire Hospitals Research Collaboration.
S, Daly F, Nasri R, Ben Lakhal S, Paramba F, Purayil N, Naushad V, Mohammad O, Negi V, Chandra P, Kleinsasser A, Witrz MR, Buchner-Doeven JF, Tuip-de Boer AM, Goslings JC, Juffermans NP, Van Hezel M, Straat M, Boing A, Van Bruggen R, Juffermans N, Markopoulou D, Venetsanou K, Kaldis V, Koutete D, Chroni D, Alamanos I, Koch L, Jancik J, Rhodes H, Walter E, Maekawa K, Hayakawa M, Kushimoto S, Shiraishi A, Kato H, Sasaki J, Ogura H, Matauoka T, Uejima T, Morimura N, Ishikura H, Hagiwara A, Takeda M, Tarabrin O, Shcherbakow S, Gavrychenko D, Mazurenko G, Ivanova V, Chystikov O, Plourde C, Lessard J, Chauny J, Daoust R, Shcherbakow S, Tarabrin O, Gavrychenko D, Mazurenko G, Chystikov O, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Kropman L, In het Panhuis L, Konings J, Huskens D, Schurgers E, Roest M, De Laat B, Lance M, Durila M, Lukas P, Astraverkhava M, Jonas J, Budnik I, Shenkman B, Hayami H, Koide Y, Goto T, Iqbal R, Alhamdi Y, Venugopal N, Abrams S, Downey C, Toh CH, Welters ID, Bombay VB, Chauny JM, Daoust RD, Lessard JL, Marquis MM, Paquet JP, Siemens K, Sangaran D, Hunt BJ, Durward A, Nyman A, Murdoch IA, Tibby SM, Ampatzidou F, Moisidou D, Dalampini E, Nastou M, Vasilarou E, Kalaizi V, Chatzikostenoglou H, Drossos G, Spadaro S, Fogagnolo A, Fiore T, Schiavi A, Fontana V, Taccone F, Volta C, Chochliourou E, Volakli E, Violaki A, Samkinidou E, Evlavis G, Panagiotidou V, Sdougka M, Mothukuri R, Battle C, Guy K, Mills G, Evans P, Wijesuriya J, Keogh S, Docherty A, O’Donnell R, Brunskill S, Trivella M, Doree C, Holst L, Parker M, Gregersen M, Almeida J, Walsh T, Stanworth S, Moravcova S, Mansell J, Rogers A, Smith RA, Hamilton-Davies C, Omar A, Allam M, Bilala O, Kindawi A, Ewila H, Ampatzidou F, Moisidou D, Nastou M, Dalampini E, Malamas A, Vasilarou E, Drossos G, Ferreira G, Caldas J, Fukushima J, Osawa EA, Arita E, Camara L, Zeferino S, Jardim J, Gaioto F, Dallan L, Jatene FB, Kalil Filho R, Galas F, Hajjar LA, Mitaka C, Ohnuma T, Murayama T, Kunimoto F, Nagashima M, Takei T, Tomita M, Omar A, Mahmoud K, Hanoura S, Sudarsanan S, Sivadasan P, Othamn H, Shouman Y, Singh R, Al Khulaifi A, Mandel I, Mikheev S, Suhodolo I, Kiselev V, Svirko Y, Podoksenov Y, Jenkins SA, Griffin R, Tovar Doncel MS, Lima A, Aldecoa C, Ince C, Taha A, Shafie A, Mostafa M, Syed N, Hon H, Righetti F, Colombaroli E, Castellano G, Righetti F, Colombaroli E, Hravnak M, Chen LC, Dubrawski AD, Clermont GC, Pinsky MR, Gonzalez S, Macias D, Acosta J, Jimenez P, Loza A, Lesmes A, Lucena F, Leon C, Tovar Doncel MS, Ince C, Aldecoa C, Lima A, Bastide M, Richecoeur J, Frenoy E, Lemaire C, Sauneuf B, Tamion F, Nseir S, Du Cheyron D, Dupont H, Maizel J, Shaban M, Kolko R, Salahuddin N, Sharshir M, AbuRageila M, AlHussain A, Mercado P, Maizel J, Kontar L, Titeca D, Brazier F, Riviere A, Joris M, Soupison T, De Cagny B, Slama M, Wagner J, Körner A, Kubik M, Kluge S, Reuter D, Saugel B, Colombaroli E, Righetti F, Castellano G, Tran T, De Bels D, Cudia A, Strachinaru M, Ghottignies P, Devriendt J, Pierrakos C, Martínez González Ó, Blancas R, Luján J, Ballesteros D, Martínez Díaz C, Núñez A, Martín Parra C, López Matamala B, Alonso Fernández M, Chana M, Huber W, Eckmann M, Elkmann F, Gruber A, Klein I, Schmid RM, Lahmer T, Moller PW, Sondergaard S, Jakob SM, Takala J, Berger D, Bastoni D, Aya H, Toscani L, Pigozzi L, Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Ostrowska C, Aya H, Abbas A, Mellinghoff J, Ryan C, Dawson D, Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Cronhjort M, Wall O, Nyberg E, Zeng R, Svensen C, Mårtensson J, Joelsson-Alm E, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Lopez V, Cetina M, Parenti N, Palazzi C, Amidei LA, Borrelli FB, Campanale SC, Tagliazucchi FT, Sedoni GS, Lucchesi DL, Carella EC, Luciani AL, Mackovic M, Maric N, Bakula M, Aya H, Rhodes A, Grounds RM, Fletcher N, Cecconi M, Avard B, Zhang P, Mezidi M, Charbit J, Ould-Chikh M, Deras P, Maury C, Martinez O, Capdevila X, Hou P, Linde-Zwirble WZ, Douglas ID, Shapiro NS, Ben Souissi A, Mezghani I, Ben Aicha Y, Kamoun S, Laribi B, Jeribi B, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Pereira C, Marinho R, Antunes R, Marinho A, Crivits M, Raes M, Decruyenaere J, Hoste E, Bagin V, Rudnov V, Savitsky A, Astafyeva M, Korobko I, Vein V, Kampmeier T, Arnemann P, Hessler M, Wald A, Bockbreder K, Morelli A, Van Aken H, Rehberg S, Ertmer C, Arnemann P, Hessler M, Kampmeier T, Rehberg S, Van Aken H, Ince C, Ertmer C, Reddy S, Bailey M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Mackle D, Psirides A, Young P, Reddy S, Bailey M, Beasley R, Bellomo R, Mackle D, Young P, Venkatesh H, Ramachandran S, Basu A, Nair H, Egan S, Bates J, Oliveira S, Rangel Neto NR, Reis FQ, Lee CP, Lin XL, Choong C, Eu KM, Sim WY, Tee KS, Pau J, Abisheganaden J, Maas K, De Geus H, Lafuente E, Marinho R, Moura J, Antunes R, Marinho A, Doris TE, Monkhouse D, Shipley T, Kardasz S, Gonzalez I, Stads S, Groeneveld AJ, Elsayed I, Ward N, Tridente A, Raithatha A, Steuber A, Pelletier C, Schroeder S, Michael E, Slowinski T, Kindgen-Milles D, Ghabina S, Turani F, Belli A, Busatti S, Barettin G, Candidi F, Gargano F, Barchetta R, Falco M, Demirkiran O, Kosuk M, Bozbay S, Weber V, Hartmann J, Harm S, Linsberger I, Eichhorn T, Valicek G, Miestinger G, Hoermann C, Faenza S, Ricci D, Mancini E, Gemelli C, Cuoghi A, Magnani S, Atti M, Laddomada T, Doronzio A, Balicco B, Gruda MC, O’Sullivan P, Dan VP, Guliashvili T, Scheirer A, Golobish TD, Capponi VJ, Chan PP, Kogelmann K, Drüner M, Jarczak D, Turani F, Belli AB, Martni SM, Cotticelli VC, Mounajergi F, Barchetta R, Morimoto S, Ishikura H, Hussain I, Salahuddin N, Nadeem A, Ghorab K, Maghrabi K, Kloesel SK, Goldfuss C, Stieglitz A, Stieglitz AS, Krstevska L, Albuszies G, Aguilar Arzapalo M, Barradas L, Lopez V, Escalante A, Jimmy G, Cetina M, Izawa J, Iwami T, Uchino S, Takinami M, Kitamura T, Kawamura T, Powell-Tuck JG, Crichton S, Raimundo M, Camporota L, Wyncoll D, Ostermann M, Hana A, De Geus HR, De Geus HR, Hana A, Aydogdu M, Boyaci N, Yuksel S, Gursel G, Cayci Sivri AB, Meza-Márquez J, Nava-López J, Carrillo-Esper R, Dardashti A, Grubb A, Maizel J, Wetzstein M, Titeca D, Kontar L, Brazier F, De Cagny B, Riviere A, Soupison T, Joris M, Slama M, Peters E, Njimi H, Pickkers P, Vincent JL, Waraich M, Doyle J, Samuels T, Forni L, Desai N, Baumber R, Gunning P, Sell A, Lin S, Torrence H, O’Dwyer M, Kirwan C, Prowle J, Kim T, O’Connor ME, Hewson RW, Kirwan CJ, Pearse RM, Prowle J, Hanoura S, Omar A, Othamn H, Sudarsanan S, Allam M, Maksoud M, Singh R, Al Khulaifi A, O’Connor ME, Hewson RW, Kirwan CJ, Pearse RM, Prowle J, Uzundere O, Memis D, Ýnal M, Gultekin A, Turan N, Aydin MA, Basar H, Sencan I, Kapuagasi A, Ozturk M, Uzundurukan Z, Gokmen D, Ozcan A, Kaymak C, Artemenko VA, Budnyuk A, Pugh R, Bhandari S, Mauri T, Turrini C, Langer T, Taccone P, Volta CA, Marenghi C, Gattinoni L, Pesenti A, Sweeney L, O’Sullivan A, Kelly P, Mukeria E, MacLoughlin R, Pfeffer M, Thomas JT, Bregman GB, Karp GK, Kishinevsky EK, Stavi DS, Adi NA, Poropat T, Knafelj R, Llopart E, Batlle M, De Haro C, Mesquida J, Artigas A, Pavlovic D, Lewerentz L, Spassov A, Schneider R, De Smet S, De Raedt S, Derom E, Depuydt P, Oeyen S, Benoit D, Decruyenaere J, Gobatto A, Besen B, Tierno P, Melro L, Mendes P, Cadamuro F, Park M, Malbouisson LM, Civantos BC, Lopez JL, Robles A, Figueira J, Yus S, Garcia A, Oglinda A, Ciobanu G, Oglinda C, Schirca L, Sertinean T, Lupu V, Kelly P, O’Sullivan A, Sweeney L, MacLoughlin R, O’Sullivan A, Kelly P, Sweeney L, Mukeria E, Wolny M, MacLoughlin R, Pagano A, Numis F, Visone G, Saldamarco L, Russo T, Porta G, Paladino F, Bell C, Liu J, Debacker J, Lee C, Tamberg E, Campbell V, Mehta S, Silva-Pinto A, Sarmento A, Santos L, Kara Ý, Yýldýrým F, Zerman A, Güllü Z, Boyacý N, Basarýk Aydogan B, Gaygýsýz Ü, Gönderen K, Arýk G, Turkoglu M, Aydogdu M, Aygencel G, Ülger Z, Gursel G, Boyacý N, Isýkdogan Z, Özdedeoglu Ö, Güllü Z, Badoglu M, Gaygýsýz U, Aydogdu M, Gursel G, Kongpolprom N, Sittipunt C, Eden A, Kokhanovsky Y, Bursztein – De Myttenaere S, Pizov R, Neilans L, MacIntyre N, Radosevich M, Wanta B, Weber V, Meyer T, Smischney N, Brown D, Diedrich D, Fuller A, McLindon P, Sim K, Shoaeir M, Noeam K, Mahrous A, Matsa R, Ali A, Dridi C, Koubaji S, Kamoun S, Haddad F, Ben Souissi A, Laribi B, Riahi A, Mebazaa MS, Pérez-Calatayud A, Carrillo-Esper R, Zepeda-Mendoza A, Diaz-Carrillo M, Arch-Tirado E, Carbognin S, Pelacani L, Zannoni F, Agnoli A, Gagliardi G, Cho R, Adams A, Lunos S, Ambur S, Shapiro R, Prekker M, Thijssen M, Janssen L, Foudraine N, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, George E, Voscopoulos CJ, Eversole D, Freeman J, George E, Muttini S, Bigi R, Villani G, Patroniti N, Williams G, Voscopoulos CJ, Freeman J, George E, Waldmann A, Böhm S, Windisch W, Strassmann S, Karagiannidis C, Waldmann A, Böhm S, Windisch W, Strassmann S, Karagiannidis C, Karagiannidis CK, Waldmann AW, Böhm SB, Strassmann S, Windisch WW, Persson P, Lundin S, Stenqvist O, Porta G, Numis F, Serra CS, Pagano AP, Masarone MM, Rinaldi LR, Amelia AA, Fascione MF, Adinolfi LA, Ruggiero ER, Asota F, O’Rourke K, Ranjan S, Morgan P, DeBacker JW, Tamberg E, O’Neill L, Munshi L, Burry L, Fan E, Mehta S, Poo S, Mahendran K, Fowles J, Gerrard C, Vuylsteke A, Loveridge R, Chaddock C, Patel S, Kakar V, Willars C, Hurst T, Park C, Best T, Vercueil A, Auzinger G, Borgman A, Proudfoot AG, Grins E, Emiley KE, Schuitema J, Fitch SJ, Marco G, Sturgill J, Dickinson MG, Strueber M, Khaghani A, Wilton P, Jovinge SM, Sampson C, Harris-Fox S, Cove ME, Vu LH, Sen A, Federspiel WJ, Kellum JA, Mazo Torre C, Riera J, Ramirez S, Borgatta B, Lagunes L, Rello J, Kuzovlev AK, Moroz V, Goloubev A, Polovnikov S, Nenchuk S, Karavana V, Glynos C, Asimakos A, Pappas K, Vrettou C, Magkou M, Ischaki E, Stathopoulos G, Zakynthinos S, Spadaro S, Kozhevnikova I, Dalla Corte F, Grasso S, Casolari P, Caramori G, Volta C, Andrianjafiarinoa T, Randriamandrato T, Rajaonera T, El-Dash S, Costa ELV, Tucci MR, Leleu F, Kontar L, De Cagny B, Brazier F, Titeca D, Bacari-Risal G, Maizel J, Amato M, Slama M, Mercado P, Maizel J, Kontar L, Titeca D, Brazier F, Riviere A, Joris M, Soupison T, De Cagny B, El Dash S, Slama M, Remmington, Fischer A, Squire S, Boichat M, Honzawa H, Yasuda H, Adati T, Suzaki S, Horibe M, Sasaki M, Sanui M, Marinho R, Daniel J, Miranda H, Marinho A, Milinis K, Cooper M, Williams GR, McCarron E, Simants S, Patanwala I, Welters I, Su Y, Fernández Villanueva J, Fernández Garda R, López Lago A, Rodríguez Ruíz E, Hernández Vaquero R, Tomé Martínez de Rituerto S, Varo Pérez E, Lefel N, Schaap F, Bergmans D, Olde Damink S, Van de Poll M, Tizard K, Lister C, Poole L, Ringaitiene D, Gineityte D, Vicka V, Norkiene I, Sipylaite J, O’Loughlin A, Maraj V, Dowling J, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Dias EB, Fernandes SL, Oshima T, Graf S, Heidegger C, Genton L, Karsegard V, Dupertuis Y, Pichard C, Friedli N, Stanga Z, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Vandersteen L, Stessel B, Evers S, Van Assche A, Jamaer L, Dubois J, Marinho R, Castro H, Moura J, Valente J, Martins P, Casteloes P, Magalhaes C, Cabral S, Santos M, Oliveira B, Salgueiro A, Marinho A, Marinho R, Santos M, Lafuente E, Castro H, Cabral S, Moura J, Martins P, Oliveira B, Salgueiro A, Duarte S, Castro S, Melo M, Casteloes P, Marinho A, Gray S, Maipang K, Bhurayanontachai R, Grädel LG, Schütz P, Langlois P, Manzanares W, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Manzanares W, Langlois P, Lemieux M, Elke G, Bloos F, Reinhart K, Heyland D, Langlois P, Lemieux M, Aramendi I, Heyland D, Manzanares W, Su Y, Marinho R, Babo N, Marinho A, Hoshino M, Haraguchi Y, Kajiwara S, Mitsuhashi T, Tsubata T, Aida M, Rattanapraphat T, Bhurayanontachai R, Kongkamol C, Khwannimit B, Marinho R, Santos M, Castro H, Lafuente E, Salgueiro A, Cabral S, Martins P, Moura J, Oliveira B, Melo M, Xavier B, Valente J, Magalhaes C, Casteloes P, Marinho A, Moisidou D, Ampatzidou F, Koutsogiannidis C, Moschopoulou M, Drossos G, Taskin G, Çakir M, Güler AK, Taskin A, Öcal N, Özer S, Yamanel L, Wong JM, Fitton C, Anwar S, Stacey S, Aggou M, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Oloktsidou E, Lolakos K, Papapostolou E, Grosomanidis V, Suda S, Ikeda T, Ono S, Ueno T, Izutani Y, Gaudry S, Desailly V, Pasquier P, Brun PB, Tesnieres AT, Ricard JD, Dreyfuss D, Mignon A, White JC, Molokhia A, Dean A, Stilwell A, Friedlaender G, Peters M, Stipulante S, Delfosse A, Donneau AF, Ghuysen A, Feldmann C, Freitag D, Dersch W, Irqsusi M, Eschbach D, Steinfeldt T, Wulf H, Wiesmann T, Kongpolprom N, Cholkraisuwat J, Beitland S, Nakstad E, Stær-Jensen H, Drægni T, Andersen G, Jacobsen D, Brunborg C, Waldum-Grevbo B, Sunde K, Hoyland K, Pandit D, Hayakawa K, Oloktsidou E, Kotzampassi K, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Loukipoudi L, Doumaki E, Grosomanidis V, Yasuda H, Admiraal MM, Van Assen M, Van Putten MJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans M, Van Rootselaar AF, Horn J, Ragusa F, Marudi A, Baroni S, Gaspari A, Bertellini E, Taha A, Abdullah T, Abdel Monem S, Alcorn S, McNeill S, Russell S, Eertmans W, Genbrugge C, Meex I, Dens J, Jans F, De Deyne C, Cholkraisuwat J, Kongpolprom N, Avard B, Burns R, Patarchi A, Spina T, Tanaka H, Otani N, Ode S, Ishimatsu S, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Won MH, Dakova S, Ramsheva Z, Ramshev K, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Cho J, Moon JB, Park CW, Ohk TG, Shin MC, Marudi A, Baroni S, Gaspari A, Bertellini E, Orhun G, Senturk E, Ozcan PE, Sencer S, Ulusoy C, Tuzun E, Esen F, Tincu R, Cobilinschi C, Tomescu D, Ghiorghiu Z, Macovei R, Van Assen M, Admiraal MM, Van Putten MJ, Tjepkema-Cloostermans M, Van Rootselaar AF, Horn J, Fallenius M, Skrifvars MB, Reinikainen M, Bendel S, Raj R, Abu-Habsa M, Hymers C, Borowska A, Sivadhas H, Sahiba S, Perkins S, Rubio J, Rubio JA, Sierra R, English S, Chasse M, Turgeon A, Lauzier F, Griesdale D, Garland A, Fergusson D, Zarychanski R, Tinmouth A, Van Walraven C, Montroy K, Ziegler J, Dupont Chouinard R, Carignan R, Dhaliwal A, Lum C, Sinclair J, Pagliarello G, McIntyre L, English S, Chasse M, Turgeon A, Lauzier F, Griesdale D, Garland A, Fergusson D, Zarychanski R, Tinmouth A, Van Walraven C, Montroy K, Ziegler J, Dupont Chouinard R, Carignan R, Dhaliwal A, Lum C, Sinclair J, Pagliarello G, McIntyre L, Groza T, Moreau N, Castanares-Zapatero D, Hantson P, Carbonara M, Ortolano F, Zoerle T, Magnoni S, Pifferi S, Conte V, Stocchetti N, Carteron L, Suys T, Patet C, Quintard H, Oddo M, Rubio JA, Rubio J, Sierra R, Spatenkova V, Pokorna E, Suchomel P, Ebert N, Jancik J, Rhodes H, Bylinski T, Hawthorne C, Shaw M, Piper I, Kinsella J, Kink AK, Rätsep IR, Boutin A, Moore L, Chasse M, Zarychanski R, Lauzier F, English S, McIntyre L, Lacroix J, Griesdale D, Lessard-Bonaventure P, Turgeon AF, Boutin A, Moore L, Green R, Lessard-Bonaventure P, Erdogan M, Butler M, Lauzier F, Chasse M, English S, McIntyre L, Zarychanski R, Lacroix J, Griesdale D, Desjardins P, Fergusson DA, Turgeon AF, Goncalves B, Vidal B, Valdez C, Rodrigues AC, Miguez L, Moralez G, Hong T, Kutz A, Hausfater P, Amin D, Struja T, Haubitz S, Huber A, Mueller B, Schuetz P, Brown T, Collinson J, Pritchett C, Slade T, Le Guen M, Hellings S, Ramsaran R, Alsheikhly A, Abe T, Kanapeckaite L, Abu-Habsa M, Bahl R, Russell MQ, Real KJ, Abu-Habsa M, Lyon RM, Oveland NP, Penketh J, Mcdonald M, Kelly F, Alfafi M, Alsolamy S, Almutairi W, Alotaibi B, Van den Berg AE, Schriel Y, Dawson L, Meynaar IA, Talaie H, Silva D, Fernandes S, Gouveia J, Santos Silva J, Foley J, Kaskovagheorgescu A, Evoy D, Cronin J, Ryan J, Huck M, Hoffmann C, Renner J, Laitselart P, Donat N, Cirodde A, Schaal JV, Masson Y, Nau A, Leclerc T, Howarth O, Davenport K, Jeanrenaud P, Raftery S, MacTavish P, Devine H, McPeake J, Daniel M, Kinsella J, Quasim T, Alrabiee S, Alrashid A, Alsolamy S, Gundogan O, Bor C, Akýn Korhan E, Demirag K, Uyar M, Frame F, Ashton C, Bergstrom Niska L, Dilokpattanamongkol P, Suansanae T, Suthisisang C, Morakul S, Karnjanarachata C, Tangsujaritvijit V, Mahmood S, Al Thani H, Almenyar A, Vakalos A, Avramidis V, Sharvill R, Penketh J, Morton SE, Chiew YS, Pretty C, Chase JG, Shaw GM, Knafelj R, Kordis P, Patel S, Grover V, Kuchyn I, Bielka K, Aidoni Z, Grosomanidis V, Kotzampassi K, Stavrou G, Fyntanidou B, Patsatzakis S, Skourtis C, Lee SD, Williams K, Weltes ID, Berhane S, Arrowsmith C, Peters C, Robert S, Caldas J, Panerai RB, Robinson TG, Camara L, Ferreira G, Borg-Seng-Shu E, De Lima Oliveira M, Mian NC, Santos L, Nogueira R, Zeferino SP, Jacobsen Teixeira M, Galas F, Hajjar LA, Killeen P, McPhail M, Bernal W, Maggs J, Wendon J, Hughes T, Taniguchi LU, Siqueira EM, Vieira Jr JM, Azevedo LC, Ahmad AN, Abu-Habsa M, Bahl R, Helme E, Hadfield S, Loveridge R, Shak J, Senver C, Howard-Griffin R, Wacharasint P, Fuengfoo P, Sukcharoen N, Rangsin R, Sbiti-Rohr D, Schuetz P, Na H, Song S, Lee S, Jeong E, Lee K, Cooper M, Milinis K, Williams G, McCarron E, Simants S, Patanwala I, Welters ID, Zoumpelouli E, Volakli EA, Chrysohoidou V, Georgiou S, Charisopoulou K, Kotzapanagiotou E, Panagiotidou V, Manavidou K, Stathi Z, Sdougka M, Salahuddin N, AlGhamdi B, Marashly Q, Zaza K, Sharshir M, Khurshid M, Ali Z, Malgapo M, Jamil M, Shafquat A, Shoukri M, Hijazi M, Abe T, Uchino S, Takinami M, Rangel Neto NR, Oliveira S, Reis FQ, Rocha FA, Moralez G, Ebecken K, Rabello LS, Lima MF, Hatum R, De Marco FV, Alves A, Pinto JE, Godoy M, Brasil PE, Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Soares M, Krinsley J, Kang G, Perry J, Hines H, Wilkinson KM, Tordoff C, Sloan B, Bellamy MC, Moreira E, Verga F, Barbato M, Burghi G, Soares M, Silva UV, Azevedo LC, Torelly AP, Kahn JM, Angus DC, Knibel MF, Brasil PE, Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Marshall R, Gilpin T, Tridente A, Raithatha A, Mota D, Loureiro B, Dias J, Afonso O, Coelho F, Martins A, Faria F, Al-Dorzi H, Al Orainni H, AlEid F, Tlaygeh H, Itani A, Hejazi A, Arabi Y, Gaudry S, Messika J, Ricard JD, Guillo S, Pasquet B, Dubief E, Dreyfuss D, Tubach F, Battle C, James K, Temblett P, Davies L, Battle C, Lynch C, Pereira S, Cavaco S, Fernandes J, Moreira I, Almeida E, Seabra Pereira F, Malheiro M, Cardoso F, Aragão I, Cardoso T, Fister M, Knafelj R, Muraray Govind P, Brahmananda Reddy N, Pratheema R, Arul ED, Devachandran J, Velasco MB, Dalcomune DM, Knafelj R, Fister M, Chin-Yee N, D’Egidio G, Thavorn K, Heyland D, Kyeremanteng K, Murchison AG, Swalwell K, Mandeville J, Stott D, Guerreiro I, Devine H, MacTavish P, McPeake J, Quasim T, Kinsella J, Daniel M, Goossens C, Marques MB, Derde S, Vander Perre S, Dufour T, Thiessen SE, Güiza F, Janssens T, Hermans G, Vanhorebeek I, De Bock K, Van den Berghe G, Langouche L, Devine H, MacTavish P, Quasim T, Kinsella J, Daniel M, McPeake J, Miles B, Madden S, Devine H, Weiler M, Marques P, Rodrigues C, Boeira M, Brenner K, Leães C, Machado A, Townsend R, Andrade J, MacTavish P, McPeake J, Devine H, Kinsella J, Daniel M, Kishore R, Fenlon C, Quasim T, Fiks T, Ruijter A, Te Raa M, Spronk P, Chiew YS, Docherty P, Dickson J, Moltchanova E, Scarrot C, Pretty C, Shaw GM, Chase JG, Hall T, Ngu WC, Jack JM, Morgan P, Avard B, Pavli A, Gee X, Bor C, Akin Korhan E, Demirag K, Uyar M, Shirazy M, Fayed A, Gupta S, Kaushal A, Dewan S, Varma A, Ghosh E, Yang L, Eshelman L, Lord B, Carlson E, Helme E, Broderick R, Hadfield S, Loveridge R, Ramos J, Forte D, Yang F, Hou P, Dudziak J, Feeney J, Wilkinson K, Bauchmuller K, Shuker K, Faulds M, Raithatha A, Bryden D, England L, Bolton N, Tridente A, Bauchmuller K, Shuker K, Tridente A, Faulds M, Matheson A, Gaynor J, Bryden D, S South Yorkshire Hospitals Research Collaboration. Ramos J, Peroni B, Daglius-Dias R, Miranda L, Cohen C, Carvalho C, Velasco I, Forte D, Kelly JM, Neill A, Rubenfeld G, Masson N, Min A, Boezeman E, Hofhuis J, Hovingh A, De Vries R, Spronk P, Cabral-Campello G, Aragão I, Cardoso T, Van Mol M, Nijkamp M, Kompanje E, Ostrowski P, Omar A, Kiss K, Köves B, Csernus V, Molnár Z, Hoydonckx Y, Vanwing S, Stessel B, Van Assche A, Jamaer L, Dubois J, Medo V, Galvez R, Miranda JP, Stone C, Wigmore T, Arunan Y, Wheeler A, Bauchmuller K, Bryden D, Wong Y, Poi C, Gu C, Molmy P, Van Grunderbeeck N, Nigeon O, Lemyze M, Thevenin D, Mallat J, Ramos J, Correa M, Carvalho RT, Forte D, Fernandez A, McBride C, Koonthalloor E, Walsh C, Webber A, Ashe M, Smith K, Jeanrenaud P, Marudi A, Baroni S, Ragusa F, Bertellini E, Volakli EA, Chochliourou E, Dimitriadou M, Violaki A, Mantzafleri P, Samkinidou E, Vrani O, Arbouti A, Varsami T, Sdougka M, Bollen JA, Van Smaalen TC, De Jongh WC, Ten Hoopen MM, Ysebaert D, Van Heurn LW, Van Mook WN, Sim K, Fuller A, Roze des Ordons A, Couillard P, Doig C, Van Keer RV, Deschepper RD, Francke AF, Huyghens LH, Bilsen JB, Nyamaizi B, Dalrymple C, Molokhia A, Dobru A, Marrinan E, Ankuli A, Molokhia A, McPeake J, Struthers R, Crawford R, Devine H, Mactavish P, Quasim T, Morelli P, Degiovanangelo M, Lemos F, MArtinez V, Verga F, Cabrera J, Burghi G, Rutten A, Van Ieperen S, De Geer S, Van Vugt M, Der Kinderen E, Giannini A, Miccinesi G, Marchesi T, Prandi E.
Ramos J, Peroni B, Daglius-Dias R, Miranda L, Cohen C, Carvalho C, Velasco I, Forte D, Kelly JM, Neill A, Rubenfeld G, Masson N, Min A, Boezeman E, Hofhuis J, Hovingh A, De Vries R, Spronk P, Cabral-Campello G, Aragão I, Cardoso T, Van Mol M, Nijkamp M, Kompanje E, Ostrowski P, Omar A, Kiss K, Köves B, Csernus V, Molnár Z, Hoydonckx Y, Vanwing S, Stessel B, Van Assche A, Jamaer L, Dubois J, Medo V, Galvez R, Miranda JP, Stone C, Wigmore T, Arunan Y, Wheeler A, Bauchmuller K, Bryden D, Wong Y, Poi C, Gu C, Molmy P, Van Grunderbeeck N, Nigeon O, Lemyze M, Thevenin D, Mallat J, Ramos J, Correa M, Carvalho RT, Forte D, Fernandez A, McBride C, Koonthalloor E, Walsh C, Webber A, Ashe M, Smith K, Jeanrenaud P, Marudi A, Baroni S, Ragusa F, Bertellini E, Volakli EA, Chochliourou E, Dimitriadou M, Violaki A, Mantzafleri P, Samkinidou E, Vrani O, Arbouti A, Varsami T, Sdougka M, Bollen JA, Van Smaalen TC, De Jongh WC, Ten Hoopen MM, Ysebaert D, Van Heurn LW, Van Mook WN, Sim K, Fuller A, Roze des Ordons A, Couillard P, Doig C, Van Keer RV, Deschepper RD, Francke AF, Huyghens LH, Bilsen JB, Nyamaizi B, Dalrymple C, Molokhia A, Dobru A, Marrinan E, Ankuli A, Molokhia A, McPeake J, Struthers R, Crawford R, Devine H, Mactavish P, Quasim T, Morelli P, Degiovanangelo M, Lemos F, MArtinez V, Verga F, Cabrera J, Burghi G, Rutten A, Van Ieperen S, De Geer S, Van Vugt M, Der Kinderen E, Giannini A, Miccinesi G, Marchesi T, Prandi E. 36th International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine : Brussels, Belgium. 15-18 March 2016. Crit Care. 2016 Apr 20;20(Suppl 2):94. [PMC free article: PMC5493079] [PubMed: 27885969]
36th International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine : Brussels, Belgium. 15-18 March 2016. Crit Care. 2016 Apr 20;20(Suppl 2):94. [PMC free article: PMC5493079] [PubMed: 27885969]
Post-resuscitation encephalopathy. What is post-resuscitation encephalopathy?
IMPORTANT
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Post-resuscitation encephalopathy is a component of post-resuscitation illness, which manifests itself in a number of neurological and psychological disorders. It is characterized by damage to the tissues of the central nervous system. The clinical picture is varied, the main symptoms include hyperkinesis, visual disturbances, frontal ataxia, amental-delirious psychoses and convulsive seizures.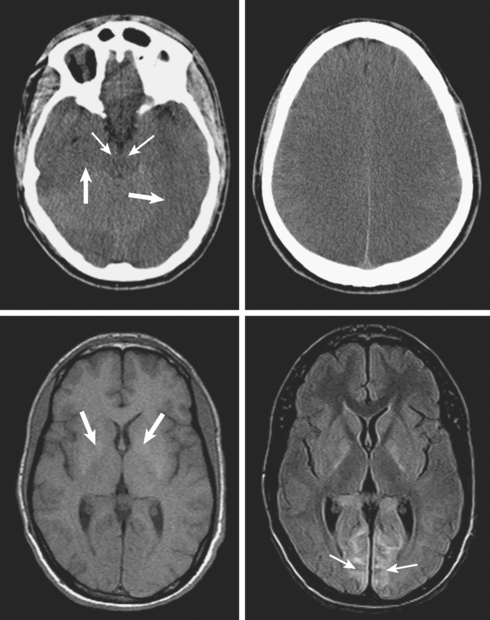 Pathology is diagnosed on the basis of clinical data and the results of an imaging examination (CT and MRI). Specific treatment: barbiturates, microcirculatory agents, calcium channel blockers, antioxidants, cell membrane stabilizers.
Pathology is diagnosed on the basis of clinical data and the results of an imaging examination (CT and MRI). Specific treatment: barbiturates, microcirculatory agents, calcium channel blockers, antioxidants, cell membrane stabilizers.
ICD-10
G93.1 Anoxic brain injury, not elsewhere classified
- Causes
- Pathogenesis
- Classification
- Symptoms of post-resuscitation encephalopathy
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of post-resuscitation encephalopathy
- Prognosis and prevention
- Prices for treatment
General
The concepts of “disease of a revived organism” and “postresuscitation encephalopathy” were introduced by the academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences V. A. Negovsky and the staff of the Clinical Hospital. S.P. Botkin at the end of the 60s, in the period of the birth and formation of resuscitation as an independent science. Today, PE is considered a common occurrence, occurring in every case of a temporary stop or a significant decrease in perfusion in the brain. The cause of the condition is the high sensitivity of neurons to hypoxia. The severity of clinical manifestations varies from their complete absence (the brain has great adaptive capabilities) to a detailed picture of damage to one or another part of the nervous tissue.
Today, PE is considered a common occurrence, occurring in every case of a temporary stop or a significant decrease in perfusion in the brain. The cause of the condition is the high sensitivity of neurons to hypoxia. The severity of clinical manifestations varies from their complete absence (the brain has great adaptive capabilities) to a detailed picture of damage to one or another part of the nervous tissue.
Post-resuscitation encephalopathy
Causes
Pathology is observed not only after clinical death, but also in people who have undergone a terminal state of a different origin: trauma, asphyxia, severe blood loss, and a prolonged episode of hypotension. It is based on oxygen starvation and violation of all metabolic processes. A metabolic storm plays a certain role in the formation of negative transformations, including the volumetric release of “shock” hormones. Changes occur at the molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, zonal and systemic levels of organization, can be reversible and irreversible. Causes of GM damage include:
Causes of GM damage include:
- Complete circulatory arrest. Occurs at the moment of cessation of the heart (asystole) or against the background of ventricular fibrillation, when the myocardial fibers are reduced separately, inefficiently. Similar conditions develop in acute coronary pathology, trauma, intoxication of endogenous or exogenous origin, senile degradation of the organs of the circulatory system, mechanical asphyxia, etc.
- Decreased perfusion. A sharp and prolonged weakening of blood flow in the control structures is the result of vascular pathology (collapse), shock conditions, loss of 50-60% of the BCC due to hemorrhage from large arteries. If the pulmonary trunk or vena cava is damaged, the volume of extravasate rarely exceeds 300-400 ml, but blood pressure decreases almost instantly, which leads to cerebral oxygen starvation.
- Ischemic stroke. It can occur both independently and against the background of resuscitation. In the latter case, obstruction of the feeding artery is a consequence of increased thrombus formation in the first stage of DIC.
 It is characterized by limited necrosis of brain tissue, focal symptoms, indicating a dysfunction of a certain area of the central nervous system.
It is characterized by limited necrosis of brain tissue, focal symptoms, indicating a dysfunction of a certain area of the central nervous system.
Pathogenesis
Hypoxia leads to the formation of regional ischemia. Tissues experience oxygen starvation, suffer from a lack of nutrients. Energy resources are quickly exhausted, lactate, lysosomal enzymes and acyl coenzymes accumulate. Electrolytes and water are redistributed between cells and intercellular space. Free radicals are strongly formed. At the organ level, this is manifested by swelling and edema of cerebral structures, an acute violation of their function.
In the postresuscitation period, the processes of reoxygenation and recirculation are observed. The work of nervous structures is restored unevenly. Nitrogen monoxide and new free radical compounds are formed in the interstitial fluid and cells. There is a repeated violation of the distribution of calcium ions. Nucleic and protein metabolism changes. In addition to the above, endogenous intoxication with cytotoxic products and metabolic acidosis negatively affect the work of the central nervous system. All this provokes malfunctions of the receptor apparatus, disruption of the synthesis and functionality of neurotransmitters, breakage of connections between neurons.
Nucleic and protein metabolism changes. In addition to the above, endogenous intoxication with cytotoxic products and metabolic acidosis negatively affect the work of the central nervous system. All this provokes malfunctions of the receptor apparatus, disruption of the synthesis and functionality of neurotransmitters, breakage of connections between neurons.
Classification
Postresuscitative encephalopathy can be divided using several principles. A classification is known according to the time elapsed since the development of an episode of hypoxia (early stage, period of acute manifestations, recovery period), the prevailing syndrome (cerebellar, stem, neurasthenic, intellectual-mnestic, apallic). The most common is the systematization based on the degree of recovery of the central nervous system:
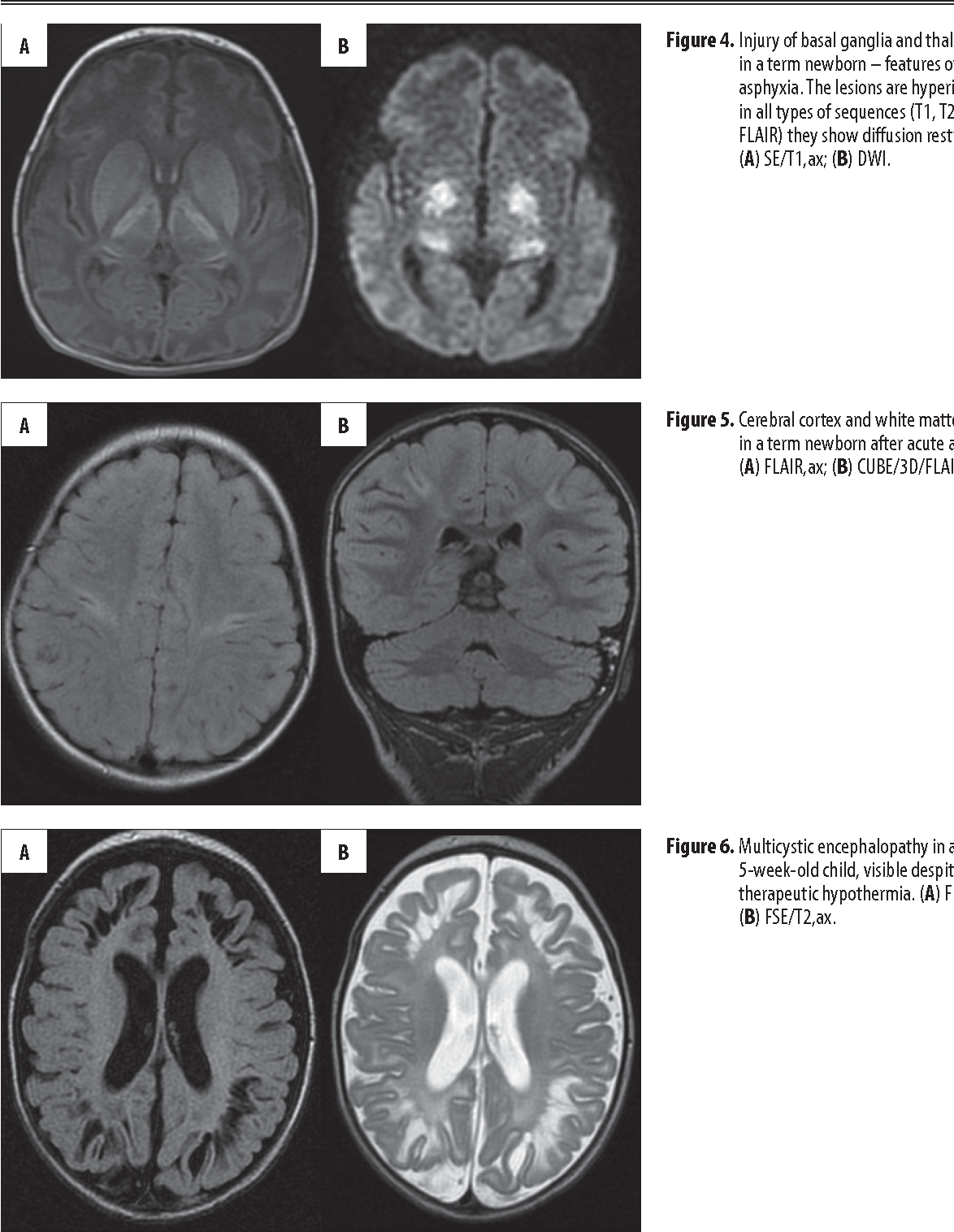 The final normalization of neurological parameters and psyche occurs within a few months. Further, postresuscitation encephalopathy disappears completely without residual effects.
The final normalization of neurological parameters and psyche occurs within a few months. Further, postresuscitation encephalopathy disappears completely without residual effects. Often ends with persistent disability of the patient or his death. Regression may occur after a few weeks or months have passed since discharge. The maximum registered term is 2 years. The nature of such phenomena remains unexplored. Experts suggest that increased psychological stress plays the role of a provoking factor.
Often ends with persistent disability of the patient or his death. Regression may occur after a few weeks or months have passed since discharge. The maximum registered term is 2 years. The nature of such phenomena remains unexplored. Experts suggest that increased psychological stress plays the role of a provoking factor.Symptoms of post-resuscitation encephalopathy
At the exit from the terminal state, the patient is in a deep coma. Later, there is a restoration of functions for which stem formations are responsible. The patient begins to breathe independently. Initially, shortness of breath, bradypnea, individual spastic breaths are noted. On average, after 5-6 hours, respiratory activity levels off. There is a reaction of the pupils to light, spinal reflexes, cough reflex. Consciousness is restored by gradually reducing the depth of the coma, first to moderate, later to a soporous state.
The patient begins to breathe independently. Initially, shortness of breath, bradypnea, individual spastic breaths are noted. On average, after 5-6 hours, respiratory activity levels off. There is a reaction of the pupils to light, spinal reflexes, cough reflex. Consciousness is restored by gradually reducing the depth of the coma, first to moderate, later to a soporous state.
After the restoration of consciousness, pronounced psychological defects are revealed: psychomotor and speech excitement, hallucinations, psychoses. Perhaps the development of large convulsive seizures, epileptiform syndrome. Violated visual, auditory and tactile perception, there is apraxia. Coordination of movements changed, weakened. Subsequently, most of these phenomena disappear. Some signs may persist for a long time or for life.
For the longest time, the patient shows evidence of emotional lability (mood swings), muscular asthenia (weakness), apathetic-abulic syndrome (emotional-volitional impoverishment). Often, patients complain of headaches, dizziness, jumps in blood pressure, periodic heaviness behind the sternum, shortness of breath. These phenomena are exacerbated by psychological and emotional overstrain. In varying degrees, permanent residual changes are present in 70% of patients. In 20-25%, violations of the musculoskeletal system (paralysis, paresis) remain.
Often, patients complain of headaches, dizziness, jumps in blood pressure, periodic heaviness behind the sternum, shortness of breath. These phenomena are exacerbated by psychological and emotional overstrain. In varying degrees, permanent residual changes are present in 70% of patients. In 20-25%, violations of the musculoskeletal system (paralysis, paresis) remain.
Complications
The main delayed complication is the regression of convalescence and the return of the disease clinic. Most often occurs on the 2nd-3rd or 10th day, however, it can develop on the 3rd-4th week and later. Presumably arises as a result of an increased load on an incompletely restored nervous tissue. Leads to persistent psychoneurological disability. In some cases, only motor functions are affected, mental abilities do not suffer. Regression during the first weeks is recorded in 4% of patients, after 4-24 months – in 0.3%.
In the early hours of restoring blood flow, severe pulmonary edema may occur, accompanied by a sharp increase in intracranial pressure. At the same time, a deep coma persists, swelling of the nipples of the optic nerves, anisocoria, nystagmus, hemodynamic instability, tachycardia, followed by bradycardia, are detected. When the thermoregulation center is involved in the process, hyperthermia up to 39-40 ° C is detected, which is not amenable to drug correction. In the absence of treatment, the outcome is the death of the patient.
At the same time, a deep coma persists, swelling of the nipples of the optic nerves, anisocoria, nystagmus, hemodynamic instability, tachycardia, followed by bradycardia, are detected. When the thermoregulation center is involved in the process, hyperthermia up to 39-40 ° C is detected, which is not amenable to drug correction. In the absence of treatment, the outcome is the death of the patient.
Diagnostics
Postresuscitation encephalopathy is diagnosed by an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. A neurologist or neurosurgeon may be invited to clarify the depth and severity of the lesion. It is necessary to differentiate the state with hemorrhagic stroke, brain injury received before hospitalization or during resuscitation, cerebral edema. If the symptoms of PE occur after discharge from the hospital, a neurologist is involved in the examination, who, if necessary, refers the patient for re-hospitalization. The following methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- Physical.
 One or another characteristic clinical symptomatology, signs of a decrease in muscle tone or convulsive readiness are noted. Seizures resembling epilepsy are recorded. The picture varies over a very wide range, so the presence of external symptoms alone cannot serve as a basis for making a definitive diagnosis.
One or another characteristic clinical symptomatology, signs of a decrease in muscle tone or convulsive readiness are noted. Seizures resembling epilepsy are recorded. The picture varies over a very wide range, so the presence of external symptoms alone cannot serve as a basis for making a definitive diagnosis. - Hardware. The main methods are computed tomography, electroencephalography and transcranial dopplerography. Cerebral CT shows signs of hydration or edema, the presence of foci of organic damage. With the help of EEG, the dynamics of intracerebral impulse conduction is determined – usually postresuscitation encephalopathy leads to its weakening. TD allows you to assess the degree of blood supply to the brain and the work of the vascular apparatus. A more informative alternative to the study is isotope angiography.
- Laboratory. The results of laboratory blood tests revealed a decrease in the hydrogen number of less than 7.3, an imbalance of electrolytes. In most cases, there is an increase in the concentration of potassium, a decrease in the content of calcium.
 Dissolved gases may be normal if more than a day has passed since the stop of perfusion. Prior to this, there is an increased content of CO2, an insufficient percentage of oxygen.
Dissolved gases may be normal if more than a day has passed since the stop of perfusion. Prior to this, there is an increased content of CO2, an insufficient percentage of oxygen.
Treatment of post-resuscitation encephalopathy
Pathology requires a phased treatment. In the acute stage, external respiratory support using a ventilator, the introduction of agents to ensure adequate blood flow are shown: pressor amines to stabilize hemodynamics, vasodilators to eliminate the existing spasm of cerebral arteries. The patient’s head should be at the same level with the body, the foot end is raised. The introduction of drugs that reduce the energy needs of the brain is shown: sodium thiopental, diazepam. After the restoration of blood pressure, calcium channel blockers, antioxidants, glucocorticoids are used as stabilizers of cell membranes, and hepatoprotectors.
From the 3rd day, a course of nootropic drugs that improve metabolic processes in the nervous tissue begins.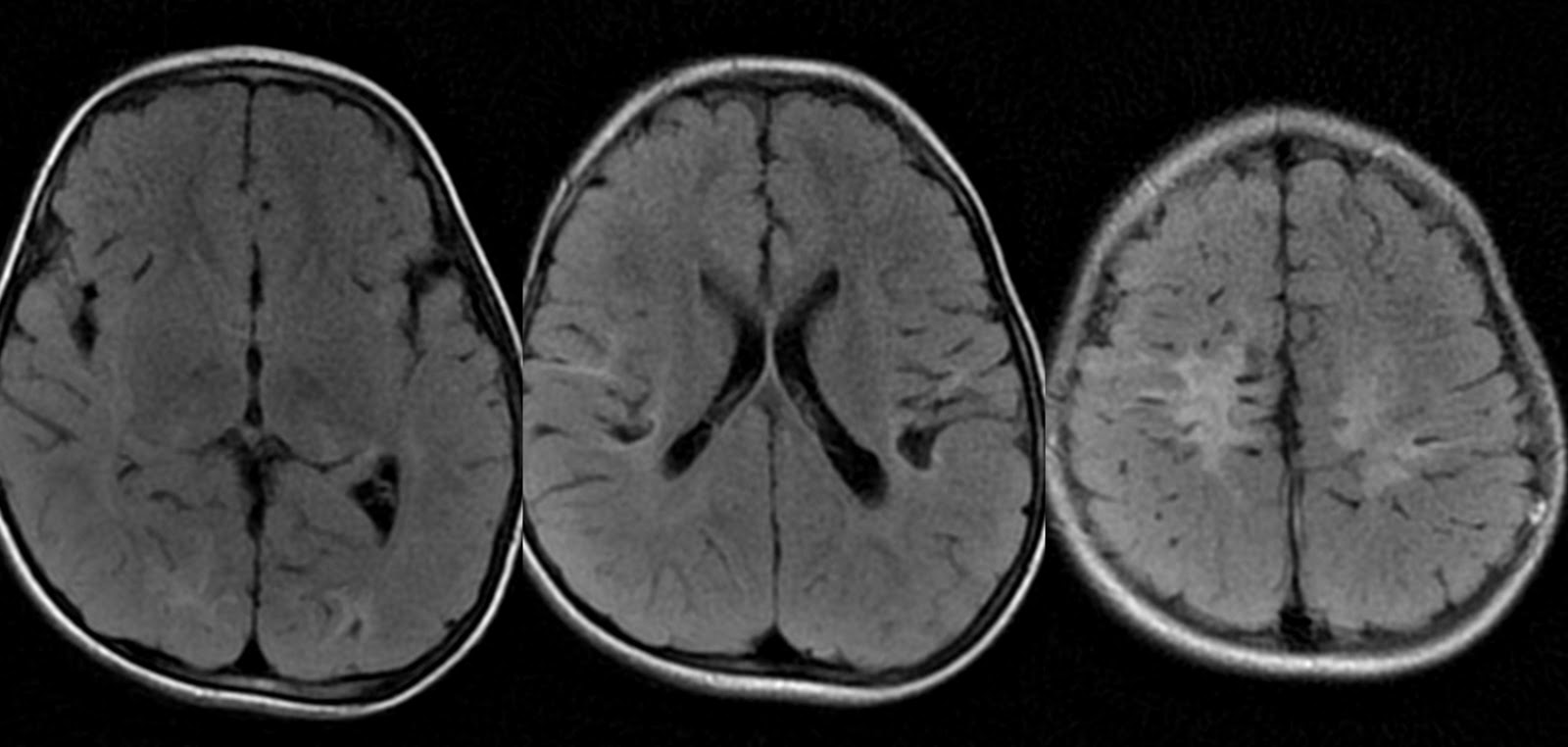 The therapeutic regimen includes piracetam and its analogues. Treatment is carried out for 1-1.5 years in courses of 1-2 months. If seizures persist, the patient should receive antiepileptic drugs. Symptomatic treatment is carried out, selected taking into account residual changes. For mental disorders, sedatives, anti-anxiety and sleeping pills are prescribed. A psychiatric consultation is required. Sanatorium-resort recovery is allowed no earlier than 2 months after leaving the critical condition.
The therapeutic regimen includes piracetam and its analogues. Treatment is carried out for 1-1.5 years in courses of 1-2 months. If seizures persist, the patient should receive antiepileptic drugs. Symptomatic treatment is carried out, selected taking into account residual changes. For mental disorders, sedatives, anti-anxiety and sleeping pills are prescribed. A psychiatric consultation is required. Sanatorium-resort recovery is allowed no earlier than 2 months after leaving the critical condition.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis depends on the severity and duration of the pathology. Long-term circulatory arrest causes neurological failure even in cases where resuscitation was started on time. A short-term decrease in perfusion without a complete cessation of blood flow has a favorable development for the patient. The overall mortality within 2 years is about 40%. The main proportion of the dead is exposed to severe long-term hypoxic damage.
Prevention consists in constant monitoring of the condition of unstable patients. If there are prerequisites for cardiac arrest, it is necessary to correct the condition in a short time. If resuscitation is nevertheless required, from the moment the CCC resumes its work, thrombosis prevention is carried out, measures are taken to ensure normal blood supply to the nervous system. Long-term mechanical ventilation in the mode of slight hypocapnia is recommended. In clinics equipped with hyperbaric chambers, patients undergo several procedures of hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
You can share your medical history, what helped you in the treatment of post-resuscitation encephalopathy.
Sources
- Cerebral insufficiency and structural targets of its protection in postresuscitation encephalopathy/ Tumansky V.A., Tumanskaya L.M., Tertyshny S.I., Timoshenko S.G., Evseev A.V. – 2010.
- Post-resuscitation encephalopathy / Alekseeva G.
 V., Gurvich A.M., Semchenko V.V. – 2002.
V., Gurvich A.M., Semchenko V.V. – 2002. - Neurology. Guidelines for doctors / Karlov V.A. – 2002.
- This article was prepared based on the materials of the site: https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/
IMPORTANT
Information from this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Encephalopathy and the army || Committee of Soldiers’ Mothers of Russia
Are people with encephalopathy recruited into the army?
Encephalopathy is a generic name for pathological processes of various origins, the basis of which is the degeneration of brain neurons due to a violation of their metabolism. Encephalopathy is manifested by polymorphic neurological disorders, disorders in the intellectual-mnestic and emotional-volitional spheres. Diagnostic search consists of a comprehensive neurological examination and the establishment of a causal pathology. Treatment of encephalopathy is reduced to the elimination of the pathological condition that caused it, the treatment of the causative disease and the maintenance of optimal metabolism of cerebral neurons.
Diagnostic search consists of a comprehensive neurological examination and the establishment of a causal pathology. Treatment of encephalopathy is reduced to the elimination of the pathological condition that caused it, the treatment of the causative disease and the maintenance of optimal metabolism of cerebral neurons.
Classification and types of encephalopathy
Doctors distinguish between congenital and acquired encephalopathy.
Congenital encephalopathy occurs against the background of an abnormal course of pregnancy or childbirth and often develops while the fetus is still in the womb. Its signs are detected immediately after childbirth or appear in the first weeks of life.
Acquired encephalopathy occurs already in adulthood. It is divided into several types depending on the cause of neuronal death:
- post-traumatic: occurs against the background of a traumatic brain injury; often develops within a few years after it and often leads to severe mental disorders
- toxic: associated with acute or chronic poisoning of the body with alcohol, poisons, drugs, drugs, salts of heavy metals, etc.
 ; often within this type, alcoholic encephalopathy is isolated separately
; often within this type, alcoholic encephalopathy is isolated separately - metabolic: associated with metabolic disorders in the body; distinguish the following subtypes of pathology:
- hepatic: occurs with damage to the liver or biliary tract;
- uremic: associated with impaired renal function;
- diabetic: is one of the frequent complications of diabetes mellitus, occurs against the background of persistent microcirculation disorders and increased blood viscosity;
- anoxic: develops after a clinical death and is associated with oxygen starvation of the brain with the subsequent development of a “metabolic storm”;
- Gaye-Wernicke syndrome: encephalopathy due to vitamin B1 deficiency;
- pancreatic: is a complication of inflammation of the pancreas;
- hypoglycemic: occurs against the background of a sharp decrease in blood glucose;
- dyscirculatory: associated with impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the brain; there are several forms of pathology:
- atherosclerotic: develops due to atherosclerosis and thickening of vessel walls;
- hypertensive: associated with a persistent increase in blood pressure;
- venous: occurs due to a violation of the venous outflow of blood.

Depending on the rate of development of the process, acute and chronic encephalopathy is distinguished. The first can develop within a few days or hours, more often occurs against the background of severe intoxication, trauma, and an infectious process. The chronic process can proceed for years and decades.
Encephalopathy stages:
The boundaries between the severity of encephalopathy are arbitrary, but for convenience, doctors use the following classification:
- Stage 1 – there are no clinical signs, a detailed examination reveals mild changes in brain structures
- stage 2 – symptoms of encephalopathy are mild or moderate, often temporary
- stage 3 – severe, irreversible changes, accompanied by severe symptoms, the patient becomes disabled.
Will you be called up for military service with encephalopathy?
Conscripts with encephalopathy are examined under Article 24 of the Schedule of Diseases. The eligibility category of a conscript with this diagnosis depends on his stage, symptoms and the presence of functional disorders.
The eligibility category of a conscript with this diagnosis depends on his stage, symptoms and the presence of functional disorders.
With dyscirculatory encephalopathy of the first stage, a conscript will be taken to serve in the army. In this case, the manifestations of the disease will not interfere with the call for military service, so the conscript will receive a fitness category B – fit for military service with minor restrictions, and with it a summons to send.
At the second stage, the doctors of the military commissariat will look at the manifestation of the disease. To receive a military ID with category B – limited fit for military service, neurological symptoms expressed in the recruit are required:
- vascular lesions of the brain that are detected on MRI
- pseudobulbar syndrome (impaired swallowing, speech, loudness of speech)
- pyramidal syndrome (dysmotility, decreased strength in arms and legs)
- cerebellar syndrome (disturbance of gait, coordination, sensory disturbances)
- asthenoneurotic syndrome (fatigue, irritability, constant feeling of fatigue and frequent mood swings)
Such a pronounced symptomatology of encephalopathy among young people of military age is extremely rare. Therefore, with stage 2 dyscirculatory encephalopathy, they are more often called up from military service than released from it. If the disease has moved to stage 3, then the conscript must be completely exempted from conscription with the fitness category D – not fit for military service.
Therefore, with stage 2 dyscirculatory encephalopathy, they are more often called up from military service than released from it. If the disease has moved to stage 3, then the conscript must be completely exempted from conscription with the fitness category D – not fit for military service.
Conscripts diagnosed with residual encephalopathy are also most likely to be drafted into the army. The call for service is explained by the fact that there is no article in the Schedule of Diseases that would provide for exemption from military service for this diagnosis.
Exemption from military service with encephalopathy in practice
Exemption from the army due to encephalopathy is very difficult. And the point is not only that a lot of functional disorders are required to write off a conscript to the reserve. The reason for the call may also be the absence of medical documents from the conscript; he needs to start preparing for the call in advance.
One of our clients, whom we treated for encephalopathy, from the conscript’s medical records indicated that he had encephalopathy of mixed origin.

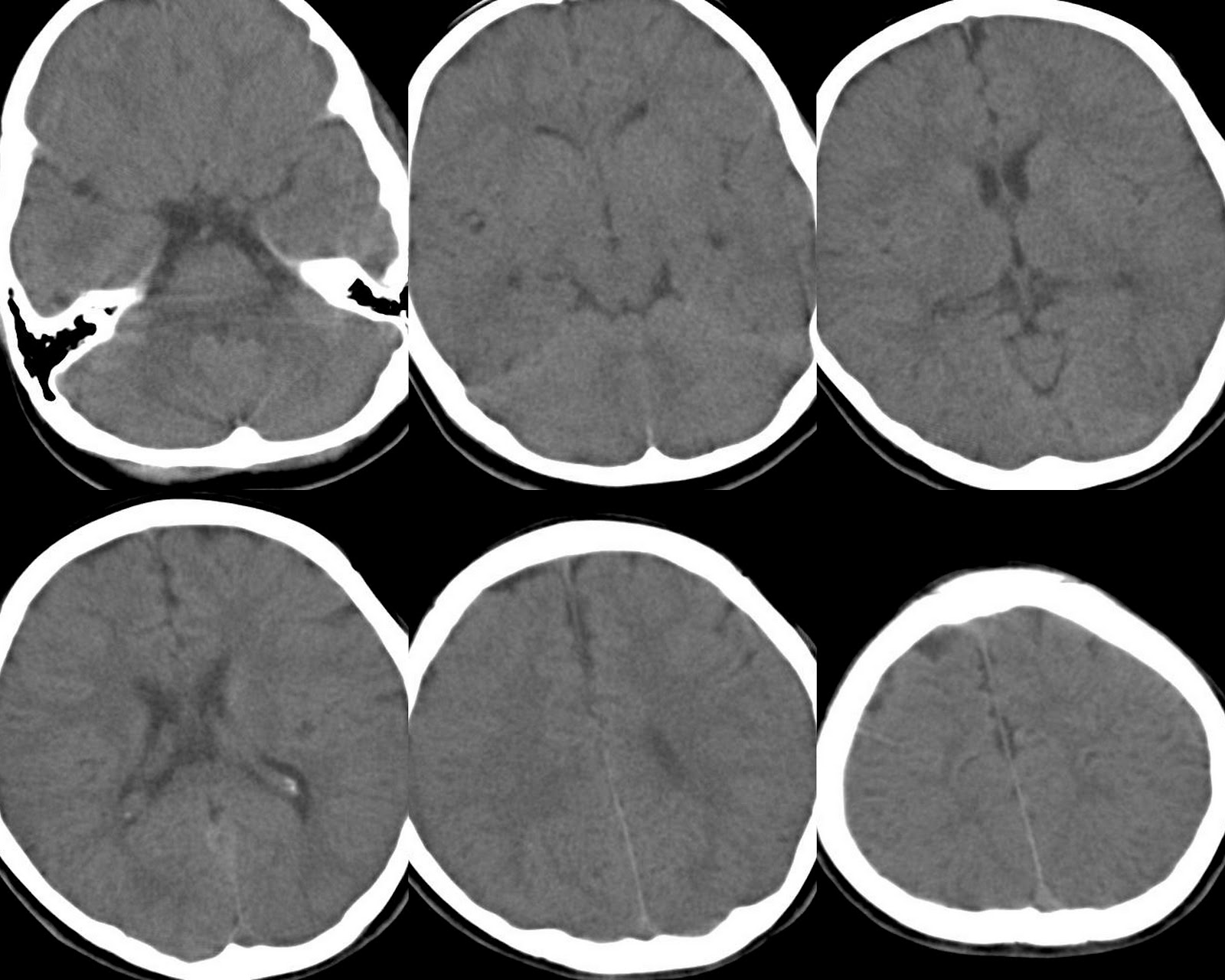 It is characterized by limited necrosis of brain tissue, focal symptoms, indicating a dysfunction of a certain area of the central nervous system.
It is characterized by limited necrosis of brain tissue, focal symptoms, indicating a dysfunction of a certain area of the central nervous system. One or another characteristic clinical symptomatology, signs of a decrease in muscle tone or convulsive readiness are noted. Seizures resembling epilepsy are recorded. The picture varies over a very wide range, so the presence of external symptoms alone cannot serve as a basis for making a definitive diagnosis.
One or another characteristic clinical symptomatology, signs of a decrease in muscle tone or convulsive readiness are noted. Seizures resembling epilepsy are recorded. The picture varies over a very wide range, so the presence of external symptoms alone cannot serve as a basis for making a definitive diagnosis.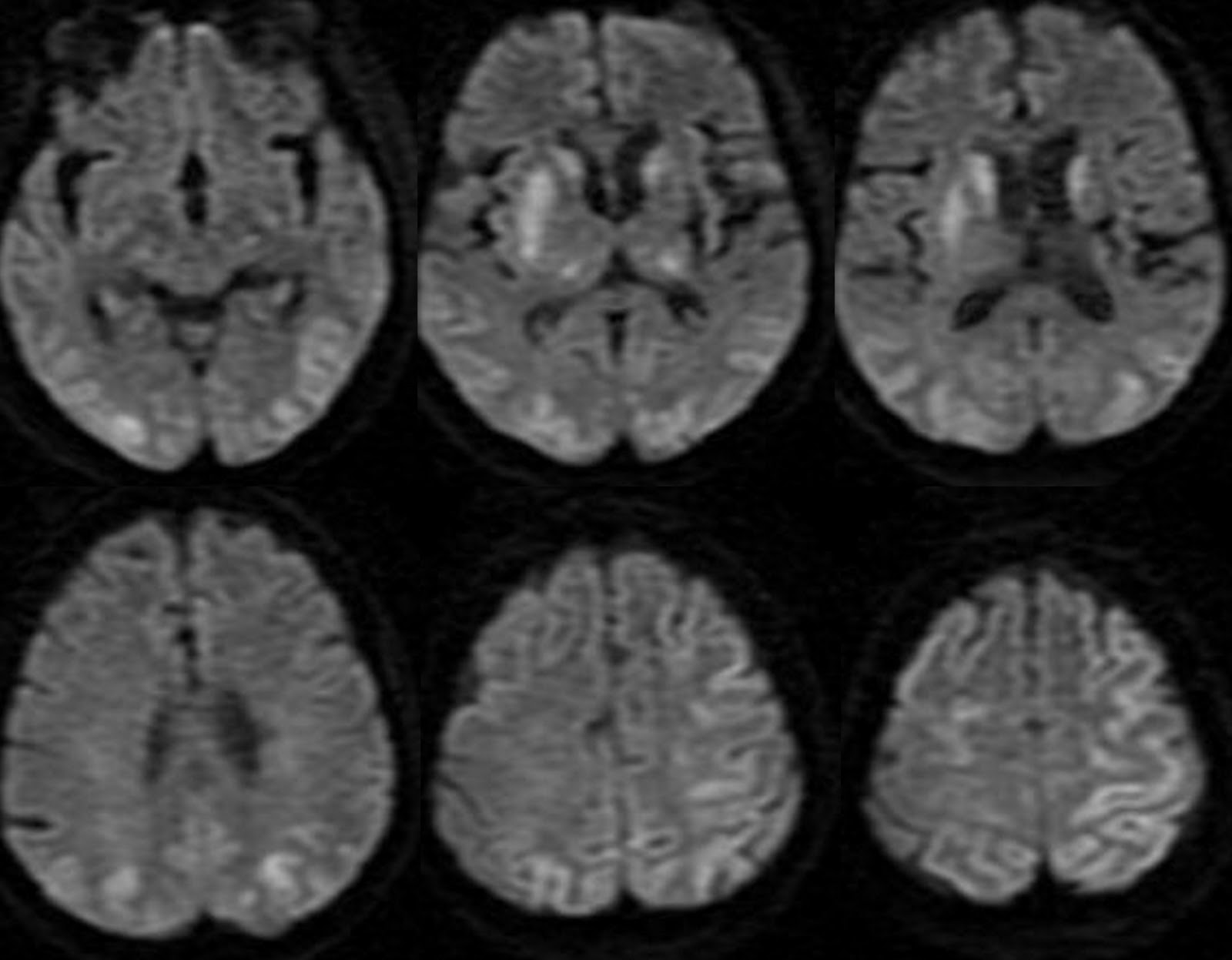 Dissolved gases may be normal if more than a day has passed since the stop of perfusion. Prior to this, there is an increased content of CO2, an insufficient percentage of oxygen.
Dissolved gases may be normal if more than a day has passed since the stop of perfusion. Prior to this, there is an increased content of CO2, an insufficient percentage of oxygen. V., Gurvich A.M., Semchenko V.V. – 2002.
V., Gurvich A.M., Semchenko V.V. – 2002. ; often within this type, alcoholic encephalopathy is isolated separately
; often within this type, alcoholic encephalopathy is isolated separately