What is keenwah. Quinoa: A Nutritional Powerhouse – Exploring the Benefits of this Ancient Superfood
What is quinoa and why is it considered a superfood. How does quinoa compare to other grains in terms of nutritional value. What are the health benefits of incorporating quinoa into your diet. How can you prepare and cook quinoa for optimal taste and nutrition.
The Origins and History of Quinoa
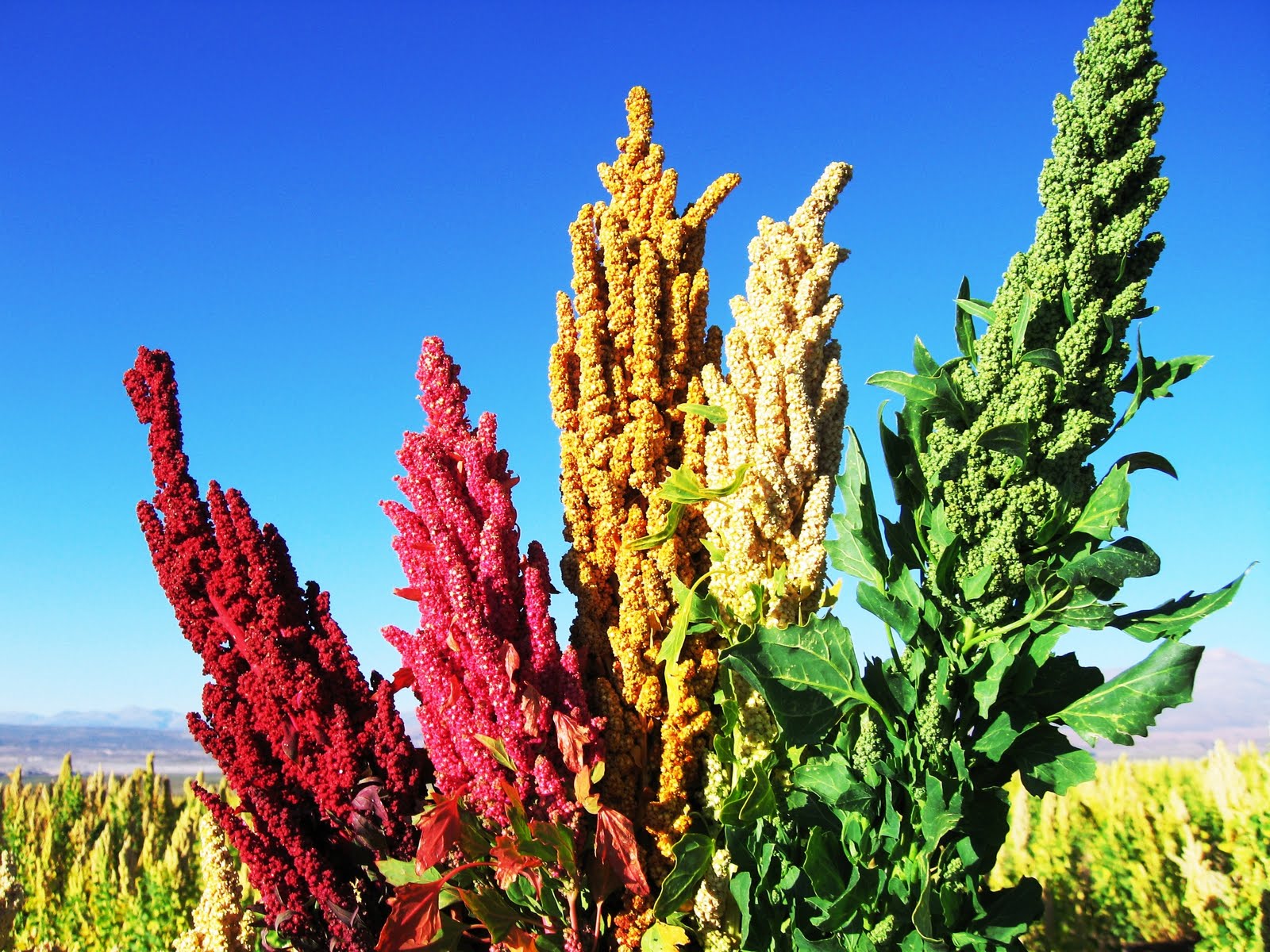
Quinoa, pronounced “KEEN-wah,” is an ancient grain with a rich history dating back thousands of years. Originally cultivated in the Andean region of South America, this remarkable seed has been a staple food for indigenous populations for millennia. The Incas, recognizing its immense nutritional value, referred to quinoa as the “mother grain” and held it in high regard, considering it sacred.
Despite its long history, quinoa remained relatively unknown to the rest of the world until recent decades. In 2013, the United Nations declared it the “International Year of Quinoa,” highlighting its potential to combat world hunger due to its exceptional nutritional profile and adaptability to various growing conditions.
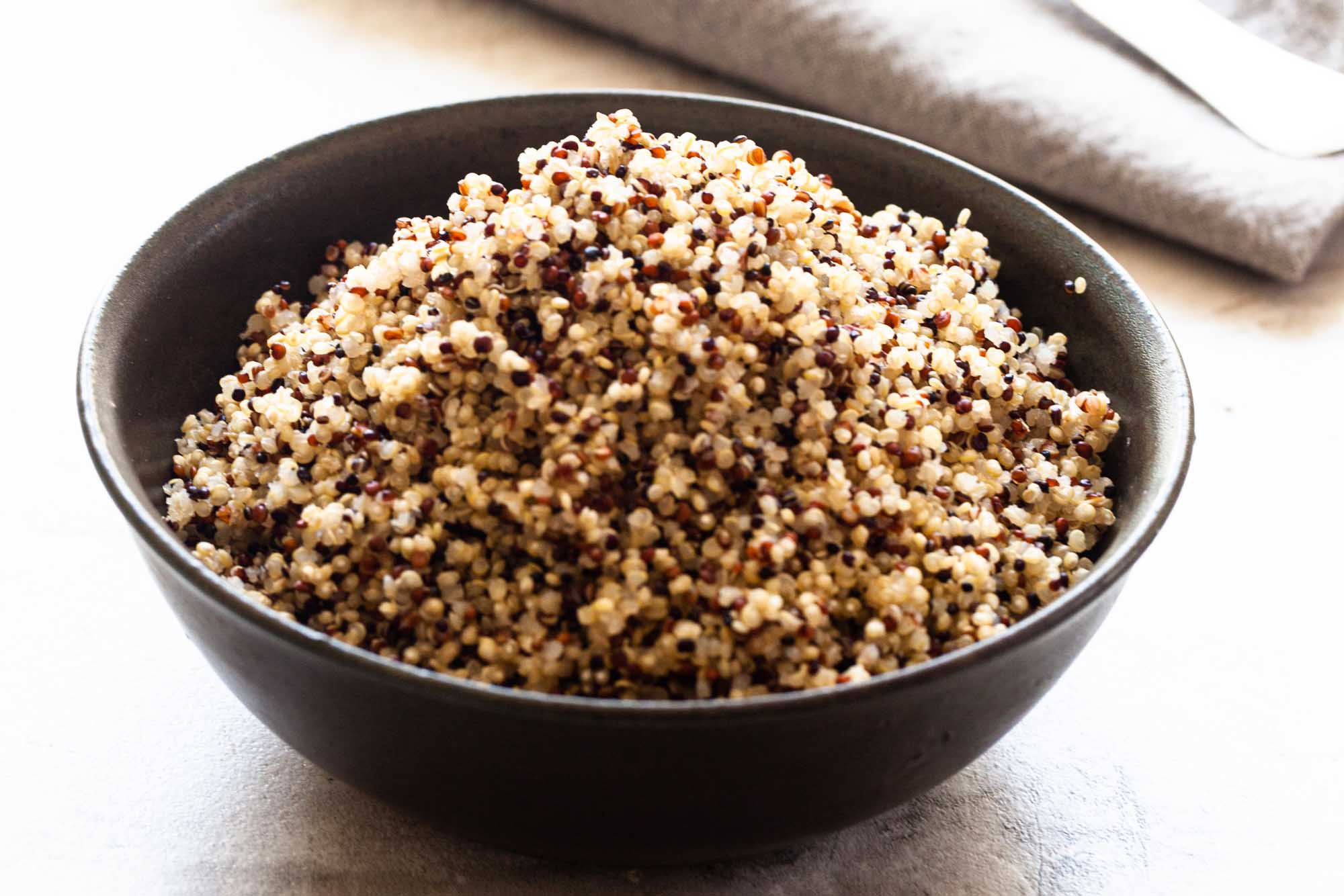

Is quinoa a true grain?
Technically, quinoa is not a true grain but rather a seed from the Chenopodium quinoa plant. However, it is often classified as a “pseudograin” due to its similar nutritional composition and culinary uses to cereal grains. This distinction is important for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivities, as quinoa is naturally gluten-free and can be a valuable addition to their diets.
Nutritional Profile of Quinoa
Quinoa has gained popularity as a “superfood” due to its impressive nutritional profile. A single cup (185 grams) of cooked quinoa provides a wealth of essential nutrients:
- Protein: 8 grams
- Fiber: At least 5 grams
- Fat: 4 grams
- Calories: 220
Additionally, quinoa is an excellent source of various vitamins and minerals:
- Manganese: 58% of the Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
- Magnesium: 30% of the RDI
- Phosphorous: 28% of the RDI
- Folate: 19% of the RDI
- Copper: 18% of the RDI
- Iron: 15% of the RDI
- Zinc: 13% of the RDI
- Thiamin: 13% of the RDI
- Riboflavin: 12% of the RDI
- Vitamin B6: 11% of the RDI
How does quinoa’s protein content compare to other plant-based foods?
Quinoa stands out among plant-based foods due to its complete protein profile. It contains all nine essential amino acids that the human body cannot produce on its own, making it a valuable protein source for vegetarians and vegans. Quinoa is particularly high in lysine, methionine, and cysteine, amino acids often lacking in other plant proteins.

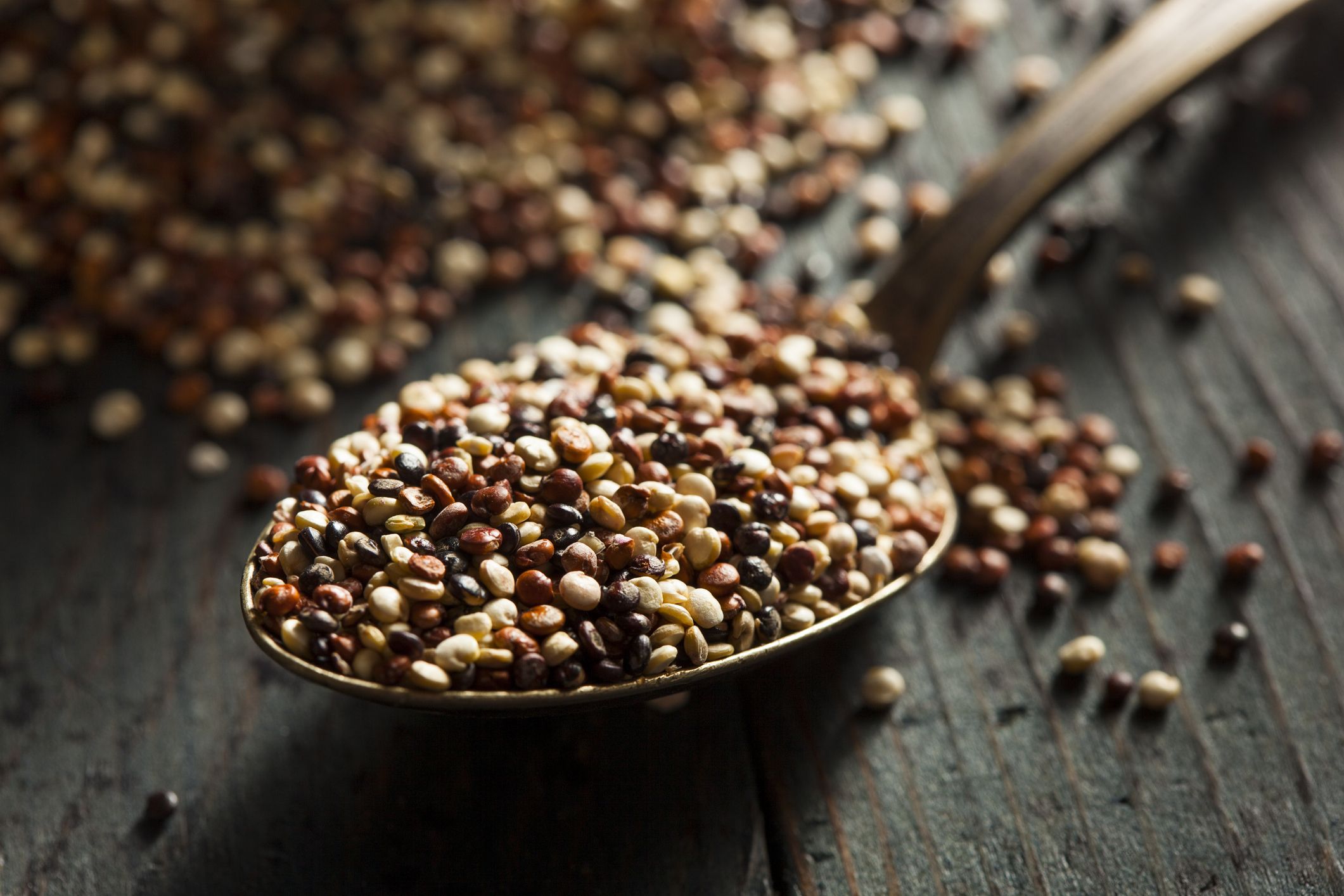
Varieties of Quinoa and Their Unique Properties
While there are over 3,000 varieties of quinoa, the most commonly consumed types are white, red, and black. Each variety offers slightly different nutritional profiles and culinary applications:
- White Quinoa: The most widely available and mildest in flavor.
- Red Quinoa: Maintains its shape better after cooking and has a nuttier taste.
- Black Quinoa: Has the lowest fat content but the highest omega-3 fatty acid and carotenoid levels.
Research has shown that darker quinoa varieties generally have higher antioxidant capacities. Red and black quinoa contain nearly twice the vitamin E content of white quinoa, making them excellent choices for those seeking to maximize their nutrient intake.
Health Benefits of Quinoa Consumption
Incorporating quinoa into your diet can offer numerous health benefits due to its rich nutrient profile and unique plant compounds. Some potential advantages include:
Can quinoa help with weight management?
Quinoa’s high fiber and protein content can contribute to increased feelings of fullness, potentially aiding in weight management. The complex carbohydrates in quinoa also provide sustained energy, helping to stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings.

Does quinoa have anti-inflammatory properties?
Quinoa contains various antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, and betacyanins. These substances may help protect against chronic diseases and support overall health by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the body.
Can quinoa benefit heart health?
The high fiber content in quinoa may help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, its magnesium content supports healthy blood pressure regulation, further contributing to cardiovascular health.
Cooking and Preparing Quinoa
Quinoa is versatile and easy to prepare, making it an excellent addition to various dishes. Here are some tips for cooking and incorporating quinoa into your meals:
How do you cook quinoa?
To cook quinoa, rinse it thoroughly to remove any residual saponins, which can impart a bitter taste. Use a 2:1 ratio of liquid to quinoa (e.g., 2 cups of water for 1 cup of quinoa). Bring to a boil, then reduce heat and simmer for about 15-20 minutes until the liquid is absorbed and the quinoa is fluffy.

What are some creative ways to use quinoa in meals?
Quinoa can be used in a variety of dishes, including:
- As a base for salads or grain bowls
- As a substitute for rice or couscous in side dishes
- In breakfast porridge or as an addition to smoothies
- As a gluten-free flour alternative in baking
- In veggie burgers or meatless meatballs
Potential Considerations and Precautions
While quinoa is generally safe and beneficial for most people, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
Can quinoa cause digestive issues?
Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort when consuming quinoa, particularly if they are not used to high-fiber foods. It’s advisable to introduce quinoa gradually into your diet and ensure proper hydration to minimize any potential digestive issues.
Are there any concerns for people with food sensitivities?
Although quinoa is naturally gluten-free, cross-contamination can occur during processing. Those with celiac disease or severe gluten sensitivities should opt for certified gluten-free quinoa to ensure safety.

Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Quinoa Production
As quinoa’s popularity has surged worldwide, concerns have been raised about its environmental impact and effects on local communities in traditional growing regions. It’s important to consider these factors when choosing quinoa:
How has increased global demand affected quinoa production?
The growing global demand for quinoa has led to increased pressure on traditional growing regions in Bolivia and Peru. This has raised concerns about soil degradation, water usage, and the economic impact on local farmers. However, efforts are being made to implement sustainable farming practices and expand quinoa cultivation to other regions to meet demand responsibly.
What can consumers do to support sustainable quinoa production?
Consumers can support sustainable quinoa production by:
- Choosing fair trade certified quinoa
- Opting for quinoa grown in diverse regions to reduce pressure on traditional growing areas
- Supporting brands that prioritize sustainable and ethical farming practices
- Considering locally grown alternative grains when possible
By making informed choices, consumers can enjoy the nutritional benefits of quinoa while supporting sustainable agriculture and fair trade practices.

What Is Quinoa? One of The World’s Healthiest Foods
Quinoa is a whole grain packed with nutrients, fiber, protein, and plant compounds. It has many health benefits and is an easy way to add variety to your diet.
Quinoa is an ancient South American grain that was largely ignored for centuries.
Interestingly, it was only recently noticed by the rest of the world and hailed as a “superfood” due to its high nutritional content.
It is now considered a specialty food by foodies and the health conscious.
This article takes a look at what quinoa is, where it comes from and why it’s so good for you.
What Is Quinoa?
Quinoa (pronounced KEEN-wah) is the seed of the Chenopodium quinoa plant.
Botanically speaking, it’s not a grain. However, it’s often called a “pseudograin” because it’s similar in nutrients and eaten the same way as cereal grains (1).
Quinoa was first grown for food 7,000 years ago in the Andes. The Incas called it “the mother grain” and believed it was sacred (2).
The Incas called it “the mother grain” and believed it was sacred (2).
Although it’s now grown around the world, the majority is still produced in Bolivia and Peru. It was largely unknown to the rest of the world until very recently (1).
Since then, it has experienced a huge surge in popularity because of its high nutrient content and health benefits. It is also easy to grow in a range of conditions.
In fact, the year 2013 was named “The International Year of Quinoa” by the UN because of its valuable qualities and potential to fight world hunger.
Quinoa is also popular because it’s a gluten-free grain. This means people with celiac disease, wheat allergies or those who avoid gluten can consume it.
Bottom Line:
Quinoa is a seed classified as a pseudograin. Nutritionally, it is considered to be a whole grain and is also gluten-free.
Types of Quinoa
There are over 3,000 varieties of quinoa (2).
However, the most widely grown types are red, black and white. There is also a tricolor variety, which is a mixture of all three.
Quinoa can also be rolled into flakes or ground into flour, which can then be used for cooking and baking.
White quinoa is the most commonly consumed variety, and is what you’ll usually find at the store. Interestingly, the different types also have varying nutrient contents.
A study examining red, black and white quinoa found that while black quinoa has the lowest fat content, it has the highest omega-3 fatty acid and carotenoid contents (3).
Red and black quinoa also have nearly twice the vitamin E content of white quinoa.
The same study analyzed the antioxidant content of each type and found that the darker the color, the higher the antioxidant capacity.
Bottom Line:
There are many types of quinoa, but red, black and white are the most popular. They vary in both color and nutrient composition.
Quinoa Is Loaded With Nutrients
This grain is also popular because it’s very nutritious.
It’s packed with vitamins and minerals and contains more protein, fiber and healthy fats than other grains.
Just one cup (185 grams) of cooked quinoa is a great source of the following nutrients (4):
- Manganese: 58% of the RDI.
- Magnesium: 30% of the RDI.
- Phosphorous: 28% of the RDI.
- Folate: 19% of the RDI.
- Copper: 18% of the RDI.
- Iron: 15% of the RDI.
- Zinc: 13% of the RDI.
- Thiamin: 13% of the RDI.
- Riboflavin: 12% of the RDI.
- Vitamin B6: 11% of the RDI.
The same cup provides only 220 calories, in addition to 8 grams of protein, 4 grams of fat and at least 5 grams of fiber.
Adding quinoa to your diet is a great way to increase your daily intake of important vitamins, minerals and fiber.
Bottom Line:
Quinoa is loaded with vitamins and minerals and contains more fiber and protein than most other grains.
Quinoa Contains Complete Proteins
Proteins are made of amino acids, which can either be made by your body or found in certain foods.
Nine of the amino acids are essential amino acids, meaning your body cannot produce them and you must get them from your diet.
Complete proteins contain all nine amino acids in significant amounts. While all animal sources of protein are complete, the majority of plant proteins are not. As a complete plant protein, quinoa is one of the exceptions.
This is one of its most unique qualities and makes it a very valuable source of protein, especially for someone whose diet is mostly plant-based.
While it’s possible to get all of the essential amino acids from a plant-based diet, it does require eating a variety of plant-based proteins.
Quinoa is especially high in lysine, methionine and cysteine, which are some of the amino acids that plant foods are frequently low in (5).
Bottom Line:
Quinoa is one of the few plant proteins that is a complete protein. This means it contains all of the essential amino acids you need.
It Contains Beneficial Plant Compounds
Quinoa is very high in beneficial plant compounds. Some examples are saponins, phenolic acids, flavonoids and betacyanins (6).
Many of these compounds may act as antioxidants, which means they can neutralize the free radicals that damage your body on the molecular level.
One study examined 10 types of grain from Peru. It found that quinoa had an antioxidant capacity of 86%, which was higher than all the other grains analyzed (7).
While all varieties of quinoa are high in antioxidants, the darkest seeds contain the highest amounts. This means black quinoa contains more antioxidants than white (3).
Also, sprouting the seeds can increase the antioxidant content even further (8).
However, a high antioxidant capacity in the lab does not necessarily translate to a higher antioxidant capacity in your body.
Nonetheless, one study found that consuming 25 grams (just under 1 oz) of quinoa daily increased levels of the important antioxidant glutathione by 7% (9).
This shows that it really can help your body fight oxidative damage from free radicals.
Bottom Line:
Quinoa contains beneficial plant compounds. Many of them act as antioxidants and protect your body from free radicals.
It May Improve Blood Sugar Control
Quinoa is considered to be a whole grain.
Several studies have linked whole grain intake to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes and improved blood sugar control (10).
One large review found that consuming just 16 grams of fiber from whole grains per day was linked to a 33% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes (10).
However, there aren’t many studies on the specific health effects of quinoa.
Nonetheless, one rat study found that it could reverse some negative effects of a high-fructose diet, including high blood sugar (11).
This could be because it contains phytoecdysteroids, which have been shown to lower blood sugar in mice (12).
It also appears to contain compounds that inhibit alpha-glucosidase, one of the enzymes involved in digesting carbs. This could delay the breakdown of carbs, causing a slower release of glucose into the blood stream (13).
Quinoa’s high fiber and protein content may also contribute to its positive effects on blood sugar. However, it is a grain and is still relatively high in carbs (7).
Bottom Line:
Whole grains like quinoa appear to lower the risk of type 2 diabetes. Quinoa may also help with blood sugar control.
Other Health Benefits
Quinoa may also have benefits for metabolic health, inflammation and more.
May Improve Metabolic Health
Quinoa is a good choice for people who have high blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides).
One study found that eating 50 grams (1. 7 oz) daily for 6 weeks lowered total cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL cholesterol (14).
7 oz) daily for 6 weeks lowered total cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL cholesterol (14).
However, the effects were small, and it lowered the levels of the “good” HDL cholesterol too.
Another study compared quinoa and corn flakes. It found that only quinoa significantly reduced triglycerides, total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol (9).
This is preliminary, but suggests quinoa could help improve metabolic health.
May Help Fight Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is involved in a wide range of diseases, from type 2 diabetes to cancer and heart disease (15).
Although studies have not shown consistent results, a diet high in antioxidants is thought to help fight inflammation in the body (15).
Quinoa appears to be very high in antioxidants, yet may help fight inflammation in other ways as well.
Saponins are one of the plant compounds found in quinoa. They give it a bitter taste, and some people rinse or soak quinoa to try and remove this taste (16).
However, saponins also seem to have some positive effects. In addition to acting as antioxidants, they appear to have anti-inflammatory effects.
One study found that saponins could inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory compounds by 25–90% in isolated cells (16).
Read this article for even more information about the health benefits of quinoa.
Bottom Line:
Quinoa appears to help lower blood cholesterol and triglycerides. It may also reduce inflammation.
It Does Contain Some Antinutrients
Certain foods, such as grains and legumes, contain antinutrients. Saponins, phytic acid and oxalates are the most common antinutrients found in quinoa (5).
However, quinoa is very well tolerated and antinutrients are not a big concern for healthy people with a well-balanced diet.
Saponins
Saponins can have both positive and negative qualities.
On one hand, they have beneficial antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Some saponins have even been shown to help reduce blood cholesterol levels (5).
Some saponins have even been shown to help reduce blood cholesterol levels (5).
However, saponins also have a bitter taste and can prevent the absorption of certain minerals, such as zinc and iron.
Some varieties are lower in saponins than others. Rinsing, scrubbing with water or soaking can also help reduce their levels if desired.
Oxalate
Oxalate is a compound found in several foods, including spinach, rhubarb and buckwheat. It can decrease the absorption of some minerals and can bind with calcium to form kidney stones (5).
While oxalate does not cause problems for most people, those who are prone to developing these types of kidney stones may want to avoid foods that are high in it.
Phytic acid
Phytic acid is found in a range of foods, including nuts, seeds and grains (17).
It can also be both positive and negative. On one hand, phytic acid has antioxidant effects and can block kidney stone formation.
On the other hand, it can also block mineral absorption. This might raise the risk of deficiencies in an unbalanced diet.
This might raise the risk of deficiencies in an unbalanced diet.
Bottom Line:
Like other grains and legumes, quinoa contains some antinutrients. However, they do not cause problems for most people.
How to Eat Quinoa
Quinoa is very versatile and easy to prepare. It has a nutty flavor and a chewy, fluffy texture. You can cook it just like rice, with two parts liquid to one part quinoa.
Simply bring the water to a boil, then reduce the heat and let it simmer for about 15 minutes. Fluff and serve.
Try using broth instead of water or adding different seasonings for even more flavor.
Watch the video below for a demonstration of how to cook quinoa:
Quinoa can be used like any other grain. It can be served plain, as a side dish or incorporated into other recipes. Quinoa flour can also be used in baking.
Here’s a list of some ways to enjoy quinoa:
- Mix with chopped vegetables, served warm or cold.
- Season and serve as a side dish.
- Cook into breakfast cereal with bananas or blueberries.
- Mix with veggies and stuff into bell peppers.
- Add to chili.
- Toss into a spinach or kale salad.
Take Home Message
Quinoa is a delicious whole grain packed with nutrients, fiber, protein and plant compounds. It has a unique flavor and is an easy way to add variety to your diet.
It’s particularly great for vegans, vegetarians and people on a gluten-free diet.
However, its impressive nutrient profile and health benefits make quinoa an excellent addition to any diet.
More about quinoa:
- 11 Proven Health Benefits of Quinoa
- Quinoa 101: Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits
Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits
Quinoa is gluten-free and packed with nutrients like protein, zinc, fiber, and folate, as well as antioxidants. Quinoa doesn’t take long to prepare, and you can add it to your diet in both sweet and savory dishes.
Quinoa doesn’t take long to prepare, and you can add it to your diet in both sweet and savory dishes.
Quinoa has gained popularity as a health food in the United States and other Westernized countries, though people have been cultivating it in South America since ancient times (1).
In fact, hundreds of years ago, the Inca people considered this ancient grain a sacred food.
In the past couple of decades, quinoa’s popularity has grown exponentially as the demand for easy-to-grow, nutritious, gluten-free grain alternatives has soared.
Not only is quinoa nutrient-dense, but it may offer health benefits, too.
This article covers 8 health benefits of quinoa and gives tips on how to incorporate it into your diet.
Quinoa is a grain crop grown for its edible seeds. These seeds are what we call quinoa — pronounced KEEN-wah.
Although it’s usually lumped in with cereal grains, like oats and barley, quinoa is actually a pseudocereal grain (2).
In other words, it is basically a seed that is prepared and eaten similarly to a grain. Other examples of pseudocereal grains include buckwheat and amaranth (2).
Other examples of pseudocereal grains include buckwheat and amaranth (2).
There are many types of quinoa, including red, black, and white (3).
Here is the nutrient breakdown for 1 cup (185 grams) of cooked quinoa (4):
- Calories: 222
- Protein: 8 grams
- Fat: 3.55 grams
- Carbohydrates: 39 grams
- Fiber: 5 grams
- Folate: 19% of the daily value (DV)
- Vitamin B6: 13% of the DV
- Vitamin E: 8% of the DV
- Copper: 39% of the DV
- Iron: 15% of the DV
- Zinc: 18% of the DV
- Manganese: 51% of the DV
- Magnesium: 28% of the DV
- Potassium: 7% of the DV
- Phosphorus: 22% of the DV
Quinoa is a good source of a number of important nutrients, including folate, magnesium, zinc, and iron.
It’s also rich in fiber and protein, nutrients that play an important role in helping you feel full (5).
Summary
Quinoa is an edible seed that has become increasingly popular. It’s loaded with many important nutrients, including fiber, protein, folate, and magnesium.
The health effects of real foods go beyond the vitamins and minerals they provide.
For example, quinoa contains several plant compounds that may benefit health in a number of ways.
Two flavonoid plant compounds that have been particularly well studied are quercetin and kaempferol. These are the main flavonoids found in quinoa (6).
Quercetin and kaempferol have anti-inflammatory qualities and act as antioxidants in the body, meaning they help protect cells from damage caused by unstable molecules called free radicals (6).
Consuming more flavonoid-rich foods like quinoa may help promote overall health and protect against certain diseases and overall mortality (7).
By including nutritious foods like quinoa in your diet, you will significantly increase your total intake of these and other antioxidant compounds.
Summary
Quinoa contains flavonoids, including quercetin and kaempferol, which have powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in the body.
Another important benefit of quinoa is its high fiber content.
A 1-cup (185-gram) serving of cooked quinoa contains 5.18 grams of fiber. That’s about 18% of the current 28-gram DV (4).
Quinoa contains more fiber than several other popular grains, like brown rice.
For example, a 1-cup (195-gram) serving of cooked brown rice contains 3.51 grams of fiber, which is 1.67 grams less than the same serving size of quinoa (8).
Adding fiber-rich foods like quinoa into your diet can help support your digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and fueling beneficial bacteria in your gut (9).
Plus, eating a high fiber diet can support a body weight that’s healthy for you. Fiber helps promote feelings of fullness. Pairing high fiber foods like quinoa with high protein foods can help you feel full and may help keep your portion sizes in check (9).
Fiber helps promote feelings of fullness. Pairing high fiber foods like quinoa with high protein foods can help you feel full and may help keep your portion sizes in check (9).
Summary
Quinoa is high in fiber, a nutrient that’s important for health. Adding more fiber-rich foods into your diet can help support gut health, body weight maintenance, and more.
Some people with gluten intolerance, including those with celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, need to avoid foods containing gluten (10).
People following a gluten-free diet need to choose gluten-free alternatives to gluten-containing grains like wheat, barley, and rye.
Quinoa is naturally gluten-free and makes a nutritious choice for people who want to or need to cut gluten from their diet.
Unlike gluten-free products made with refined ingredients, quinoa is a good source of nutrients that gluten-free diets often lack, like (11):
- fiber
- folate
- zinc
- magnesium
Summary
Quinoa is naturally gluten-free.
Using it in place of highly processed gluten-free foods can increase the nutrient value of your diet when you’re avoiding gluten.
Quinoa is a good source of protein, providing 8 grams per cooked cup (185 grams) (4).
Quinoa is often referred to as a complete protein. This is because it contains all nine of the essential amino acids that your body can’t make on its own.
However, experts argue that quinoa should not be considered a complete protein because it contains low amounts of certain amino acids, like lysine (12).
For this reason, experts have suggested that quinoa be considered a “nearly complete” protein, not a complete protein (12).
Either way, quinoa is a good source of protein — and incorporating quinoa into your diet can help you meet your daily protein needs.
This is especially true for those who follow plant-based diets, like vegans. You can make a plant-based, protein-rich meal in no time by combining quinoa with beans, tofu, and mixed vegetables.
Summary
Quinoa is a good source of protein and can help you meet your daily protein needs.
Many people don’t get enough of certain important nutrients.
For example, studies show that many children and adults don’t consume enough vitamins and minerals, including folate, potassium, iron, and magnesium (13, 14).
Plus, studies estimate that 95% of American adults and children don’t consume the recommended amount of fiber. Not getting enough fiber can affect your health in a number of ways (15).
Quinoa is high in fiber, plus several vitamins and minerals that are low in many people’s diets.
Regularly eating quinoa can help you meet your needs for magnesium, potassium, iron, fiber, and folate, a vitamin that’s especially important during pregnancy due to its role in fetal growth and development (14).
It’s important to note that quinoa contains antinutrients, including:
- saponins
- tannins
- phytic acid
These can bind with certain nutrients like iron and magnesium and reduce their absorption (16).
However, by rinsing, soaking, or sprouting the quinoa prior to cooking, you can reduce the antinutrient content and make these minerals more bioavailable (16).
Quinoa is also pretty high in oxalates. This could cause concerns if you have recurring kidney stones because oxalates can contribute to this condition (17, 18).
Summary
Quinoa is very high in minerals, but it also contains some antinutrients like saponins and phytic acid. Rinsing, soaking, and sprouting helps reduce these antinutrient compounds.
Some studies suggest that eating quinoa could benefit certain aspects of health.
A 2020 study in 40 older adults had participants eat 0.5 ounces (15 grams) of quinoa flour biscuits daily for 28 days.
By the end of the study, the participants who ate the quinoa biscuits had significantly greater reductions in LDL (bad) cholesterol, total cholesterol, and body weight than those who ate wheat-based biscuits (19).
Additionally, studies have found that eating quinoa and quinoa-based products may benefit (20, 21):
- blood sugar regulation
- fullness
- body weight
- triglyceride levels
A 2017 study that included 50 people with excess weight or obesity had participants consume 1. 8 ounces (50 grams) of quinoa daily for 12 weeks.
8 ounces (50 grams) of quinoa daily for 12 weeks.
Those who ate the quinoa had significant reductions in triglyceride levels compared with the control group and a group that consumed 0.88 ounces (25 grams) of quinoa per day (21).
Even though these results suggest that quinoa has a positive effect on metabolic health, it’s your diet and lifestyle as a whole that matter most when it comes to decreasing your risk of disease.
Following a dietary pattern rich in nutritious foods like quinoa, vegetables, fruits, fish, and beans is a smart way to protect your health and reduce disease risk factors, like high blood lipid levels and high blood sugar levels.
Summary
When you enjoy it as part of a well-rounded diet, quinoa can help support overall health and may improve certain disease risk factors, like high blood lipid levels.
While it’s not directly a health benefit, the fact that quinoa is very easy to incorporate into your diet is still important.
Quinoa is also tasty and goes well with many foods.
Depending on the type of quinoa, it can be important to rinse it with water before you cook it to get rid of saponins. These are found naturally on the outer layer and can have a bitter flavor.
However, some brands have already been rinsed, making this step unnecessary. Plus, you can purchase sprouted quinoa, which has a reduced antinutrient content and can help improve nutrient absorption (16, 22).
You can buy quinoa in most health food stores and many supermarkets.
How to cook quinoa
It can be ready to eat in as little as 15–20 minutes. To cook it:
- Rinse 1 cup (170 grams) quinoa thoroughly using a fine mesh strainer.
- Put 2 cups (240 mL) water in a pot and turn the heat to high.
- Add rinsed quinoa with a dash of salt.
- Boil 15–20 minutes.
- Enjoy.
It should now have absorbed most of the water and gotten a fluffy look. If done right, it should have a mild, nutty flavor and a satisfying crunch.
You can easily find many diverse recipes for quinoa online, including breakfast bowls, lunches, and dinners.
You can use quinoa in both sweet and savory recipes.
For example, you can try making a savory quinoa and vegetable salad topped with feta and grilled chicken. Or make a sweet breakfast porridge with cooked quinoa, coconut milk, fresh fruit, walnuts, cinnamon, and a drizzle of honey.
Summary
Quinoa is widely available, and you can use it in many different dishes, including sweet and savory options. Just make sure your quinoa has been rinsed before cooking to remove compounds called saponins — these can taste bitter.
Quinoa is becoming more popular in Western countries, but people in South America have eaten this ancient grain for thousands of years.
It’s technically a seed and is considered part of a small group of grains called pseudocereals, along with amaranth and buckwheat.
It’s a smart carbohydrate choice because it’s rich in fiber, minerals, antioxidants, and protein. It’s also gluten-free, delicious, versatile, and incredibly easy to prepare.
It’s also gluten-free, delicious, versatile, and incredibly easy to prepare.
Quinoa is a great carb option to include in your diet.
Just one thing
Try this today: You can enjoy quinoa any time of day. You can cook it in bulk and store it in the fridge for easy meal prep, too.
For a meal prep-friendly lunch idea, try layering quinoa, grilled vegetables, feta cheese, beans, and roasted chicken in mason jars and storing them in the fridge. Simply top your salad jar with a bit of olive oil and lemon juice and enjoy!
Was this helpful?
Kinva | it’s… What is Kinva?
InterpretationTranslation
- Kinva
?
Quinoa
Scientific classification Kingdom: Plants Department: Flowering plants Class: Dicots Order: Carnations Family: Gauze Subfamily: Chenopodioideae Gen.  :
:March Type: Quinoa Latin name Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Systematics
on WikispeciesPictures of
at Wikimedia CommonsQuinoa (rice quinoa, aka: quinoa, quinoa, kino quinoa), correct “quinoa”, from Quechua kinwa – a grain crop that grows on the slopes of the Andes in South America. Quinoa has a very ancient origin and was one of the most important food of the Indians. In the Inca civilization, quinoa was one of the three staple foods along with corn and potatoes.
Quinoa grains
Quinoa contains more protein than any other grain. Average 16.2 percent (compared to 7.5% in rice; 9.9% in millet, and 14% in wheat.
 Some varieties of quinoa contain more than 20 percent protein.
Some varieties of quinoa contain more than 20 percent protein.In contrast to wheat and rice, which contain a small amount of lysine, the amino acid composition of quinoa proteins is very balanced and close to that of milk proteins. In addition to unique proteins, quinoa also contains carbohydrates, fats (high in lecithin), fibre, minerals and vitamins.
After soaking or rinsing the grain’s saponins, quinoa is relatively easy and quick to prepare. The grains are boiled at a ratio of two volumes of water to one volume of quinoa for 14-18 minutes or until the cotyledons separate from the sprout. You can also use a rice cooker for cooking.
Quinoa-derived flour is used to make pasta, bread and other foods.
- This grain gave its name to the 1992 album Quinoa by the German band Tangerine Dream.
Cereals Cereal crops: Corn | Oats | Wheat | Rye | Sorghum | Triticale | Barley | Quinoa | Cereals and legumes: Garden bean | Peas | Lupine | Mash | Chickpeas | Soya | Beans | China | Lentils
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Games ⚽
- Kinbur battle
- Kinval
Useful
Bangalore Kinvah Vineyards hotels booking from 10USD
Featured hotels in Bangalore
Show more
FAQ
- 9013 5
What popular hotels near Kinvah Vineyards have parking?
If you are planning to visit Kinvah Vineyards Bangalore, why not stop at
Go8485, The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru or Royal Orchid Resort & Convention Centre, Yelahanka Bangalore
? All of these hotels have parking facilities.What are some popular hotels near Kinvah Vineyards?
Go8485, The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru and Royal Orchid Resort & Convention Centre, Yelahanka Bangalore
one of the most popular hotels.
Which hotels near Kinvah Vineyards are good for business travelers?
When it comes to business travel, transportation is important to many when choosing a hotel.
Attide Hotel, Airport Gateway Hotel and Casa Oro
popular budget hotels.Which hotels near Kinvah Vineyards have non-smoking rooms?
For many guests, one of the important indicators of the quality of the rooms is clean and fresh air.
Fiestaa Resort n Events Venue, Sai Leela by Urban Gateway and Goldfinch Retreat Bangalore
Popular hotels with non-smoking rooms.What popular hotels near Kinvah Vineyards have restaurants?
If you enjoy tasting local cuisine while traveling, then this might be for you.
The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru, Royal Orchid Resort & Convention Centre, Yelahanka Bangalore and Dhruv Palace by JT Royal
. There are many restaurants serving local cuisine near these hotels.What are some popular cheap hotels near Kinvah Vineyards?
Whether you are traveling on business or on a long-awaited vacation,
Vaas Homestays, Zenith Hotels Hebbal Bangalore and Hotel Airo Nest
a popular choice at a great price.
What popular hotels near Kinvah Vineyards have pools?
Summer is a great time to take a family trip or a trip with children to Bangalore near Kinvah Vineyards.
The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru, Royal Orchid Resort & Convention Centre, Yelahanka Bangalore and Fiestaa Resort n Events Venue
are equipped with swimming pools and are popular with travelers.What luxury hotels are near Kinvah Vineyards?
Ramada by Wyndham Bengaluru Yelahanka and The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru
– popular and not very expensive luxury hotels.What hotels for disabled guests are close to Kinvah Vineyards?
The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru, Royal Orchid Resort & Convention Centre, Yelahanka Bangalore and Fiestaa Resort n Events Venue
are popular with guests with disabilities.What is the average price for hotels near Kinvah Vineyards this weekend?
According to Trip.
 com, average weekday rates for hotels in Bangalore near Kinvah Vineyards are USD 72. This information is for reference only as room rates fluctuate.
com, average weekday rates for hotels in Bangalore near Kinvah Vineyards are USD 72. This information is for reference only as room rates fluctuate.Which hotels near Kinvah Vineyards have a gym?
Many travelers like to keep fit, so it’s no surprise that many hotels are equipped with gyms.
The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru, Royal Orchid Resort & Convention Centre, Yelahanka Bangalore and Goldfinch Retreat Bangalore
– here are some popular hotels equipped with a gym.What is the average price per night for hotels near Kinvah Vineyards?
According to Trip.com, hotel rates in Bangalore near Kinvah Vineyards average USD 85. This information is for reference only as room rates change constantly.
What hotels near Kinvah Vineyards have free WiFi?
Wi-Fi is essential whether you are staying at a hotel for work or pleasure.
Go8485, The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru and Royal Orchid Resort & Convention Centre, Yelahanka Bangalore
– popular hotels with free Wi-Fi.
What hotels do they recommend near Kinvah Vineyards?
If you can’t decide which hotel to choose, you might like
Blvd Club, The Leela Bhartiya City Bengaluru or Hop Inn Bangalore Airport Hotel
. These hotels have great reviews. Don’t forget to order in advance!

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/commensalism-definition-and-examples-4114713-v2-706cadecce404b008d6620bb061841cc.png)
 Using it in place of highly processed gluten-free foods can increase the nutrient value of your diet when you’re avoiding gluten.
Using it in place of highly processed gluten-free foods can increase the nutrient value of your diet when you’re avoiding gluten. :
: Some varieties of quinoa contain more than 20 percent protein.
Some varieties of quinoa contain more than 20 percent protein.
 com, average weekday rates for hotels in Bangalore near Kinvah Vineyards are USD 72. This information is for reference only as room rates fluctuate.
com, average weekday rates for hotels in Bangalore near Kinvah Vineyards are USD 72. This information is for reference only as room rates fluctuate.