What medicine to reduce fever. Best Fever Reducers: Comprehensive Guide to Treating Fevers Effectively
What are the most effective fever-reducing medications. How do acetaminophen and NSAIDs compare for fever treatment. When should you seek medical attention for a fever. What are the potential side effects and risks of common fever reducers.
Understanding Fever and Its Treatment Options
Fever is a common symptom of many illnesses, typically indicating that the body is fighting off an infection. While uncomfortable, fever itself is not usually dangerous for healthy adults. However, reducing fever can help alleviate discomfort and other associated symptoms. This article explores the most effective over-the-counter (OTC) options for treating fever.
What defines a fever?
A fever is generally considered to be a body temperature above 100.4°F (38°C). Low-grade fevers between 100.4°F and 102.2°F (39°C) are usually not cause for major concern in otherwise healthy adults. However, fevers above 103°F (39.4°C) or lasting more than 3 days may require medical attention.
Acetaminophen: A Popular Fever Reducer
Acetaminophen, also known as paracetamol, is one of the most widely used fever reducers and pain relievers. It works by affecting the brain’s temperature regulation center and pain perception.
How does acetaminophen reduce fever?
Acetaminophen helps lower body temperature by acting on the hypothalamus, the part of the brain responsible for regulating temperature. It also modulates pain signals, providing relief from fever-associated discomfort.
Available forms of acetaminophen
Acetaminophen comes in various forms to suit different needs:
- Tablets
- Extended-release tablets
- Chewable tablets
- Disintegrating tablets
- Capsules
- Liquid solutions or suspensions
- Syrups
- Rectal suppositories
Common brand names include Tylenol, Feverall, and Mapap. The variety of forms makes acetaminophen suitable for different age groups and preferences.
Side effects and precautions
When used as directed, acetaminophen is generally safe. However, potential side effects may include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Trouble sleeping
- Allergic reactions
- Serious skin reactions (rare)
The most significant risk associated with acetaminophen is liver damage from overdose. It’s crucial to follow dosage instructions carefully and be aware of other medications that may contain acetaminophen to avoid accidental overdose.
NSAIDs: Alternative Fever Reducers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are another class of medications effective in reducing fever. Common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen.
How do NSAIDs work to reduce fever?
NSAIDs work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are involved in the body’s inflammatory response and temperature regulation. This action helps lower body temperature and reduce inflammation.
Comparing different NSAIDs
While all NSAIDs work similarly, they have some differences:
- Ibuprofen (e.g., Advil, Motrin): Fast-acting, suitable for children and adults
- Aspirin: Effective for adults but not recommended for children due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome
- Naproxen (e.g., Aleve): Longer-lasting effect, typically used for adults
Side effects and precautions for NSAIDs
Common side effects of NSAIDs may include:

- Stomach upset or pain
- Heartburn
- Headache
- Dizziness
Long-term or high-dose use of NSAIDs can increase the risk of stomach ulcers, bleeding, and kidney problems. People with certain medical conditions or taking specific medications should consult a healthcare provider before using NSAIDs.
Choosing the Right Fever Reducer
Selecting the most appropriate fever reducer depends on various factors, including age, existing health conditions, and other medications being taken.
Factors to consider when selecting a fever reducer
- Age: Some medications are not suitable for young children or older adults
- Medical history: Certain health conditions may contraindicate specific fever reducers
- Other medications: Check for potential drug interactions
- Duration of use: Some fever reducers are better suited for short-term use
- Personal preference: Consider the form of medication (tablet, liquid, etc.) that’s easiest to take
Can you alternate acetaminophen and NSAIDs?
In some cases, alternating between acetaminophen and an NSAID like ibuprofen can be more effective in managing fever than using either medication alone. However, this approach should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure proper dosing and avoid potential complications.
Natural Remedies for Fever Reduction
While OTC medications are effective, some people prefer to try natural remedies first or in conjunction with pharmaceutical options.
What are some natural ways to reduce fever?
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration
- Rest: Allow your body time to recover and fight off infection
- Cool compress: Apply a damp, cool cloth to the forehead or wrists
- Lukewarm bath: A tepid bath can help lower body temperature
- Light clothing: Wear lightweight, breathable clothing to allow heat to dissipate
- Herbal teas: Some herbs like peppermint or chamomile may have mild fever-reducing properties
While these methods can provide comfort, they may not be as effective as medication for significantly reducing fever. Always consult a healthcare provider if you have concerns about fever management.
When to Seek Medical Attention for a Fever
While most fevers can be managed at home, certain situations warrant medical attention.
Signs that indicate a fever requires medical evaluation
- Temperature above 103°F (39.4°C) in adults
- Fever lasting more than 3 days
- Severe headache or neck stiffness
- Confusion or altered mental state
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe abdominal pain
- Seizures
- Rash accompanying the fever
For infants and young children, lower temperature thresholds and additional symptoms may necessitate medical attention. When in doubt, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider.
Special Considerations for Fever Treatment in Children
Treating fever in children requires extra caution and attention to dosage and medication choice.
How does fever treatment differ for children?
- Dosage: Always based on the child’s weight, not age
- Medication choice: Acetaminophen is generally safe for all ages, while ibuprofen is approved for infants over 6 months
- Aspirin avoidance: Not recommended for children due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome
- Liquid formulations: Often preferred for ease of administration and accurate dosing
- Closer monitoring: Children’s fevers should be watched more carefully than adults’
Parents should always consult a pediatrician before administering fever reducers to infants or if they have any concerns about their child’s fever.
Fever Myths and Misconceptions
There are many common myths surrounding fever and its treatment that can lead to unnecessary worry or inappropriate management.
What are some common misconceptions about fever?
- Myth: Fever is always harmful and must be treated aggressively
- Fact: Mild to moderate fevers are often beneficial in fighting infections
- Myth: The height of a fever correlates directly with the severity of illness
- Fact: How a person feels and other symptoms are often more important indicators than temperature alone
- Myth: Fevers can cause brain damage
- Fact: Typical fevers (under 107°F/41.7°C) do not cause brain damage
- Myth: Bundling up helps “sweat out” a fever
- Fact: This can actually increase body temperature and discomfort
- Myth: Cold baths are effective for reducing fever
- Fact: Cold baths can cause shivering, which raises body temperature; lukewarm baths are more effective
Understanding these myths can help individuals make more informed decisions about fever management and reduce unnecessary anxiety.
The Role of Fever in the Immune Response
While fever can be uncomfortable, it plays a crucial role in the body’s defense against infections.
How does fever help fight infections?
Fever serves several important functions in the immune response:
- Enhances immune cell function: Higher temperatures can improve the efficiency of white blood cells
- Inhibits pathogen growth: Many bacteria and viruses struggle to replicate at higher temperatures
- Increases metabolic rate: A faster metabolism can help the body process and eliminate toxins more quickly
- Signals the immune system: Fever activates various components of the immune system to combat infection
Understanding the beneficial aspects of fever can help individuals make informed decisions about when to treat it and when to let it run its course under medical supervision.
Should all fevers be treated with medication?
Not necessarily. Low-grade fevers (up to 102°F/38.9°C) in otherwise healthy adults often don’t require treatment with medication unless they cause significant discomfort. The decision to treat should be based on individual circumstances, overall health, and advice from a healthcare provider.

Potential Complications of Fever-Reducing Medications
While generally safe when used as directed, fever reducers can have potential complications, especially with long-term or improper use.
What are the risks associated with long-term use of fever reducers?
- Acetaminophen:
- Liver damage (especially with high doses or in combination with alcohol)
- Rare but serious skin reactions
- NSAIDs:
- Increased risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding
- Kidney problems, especially in older adults or those with existing kidney issues
- Increased risk of heart attack and stroke with long-term use
It’s important to use these medications only as needed and to follow dosage instructions carefully. Consult a healthcare provider if you need to use fever reducers frequently or for extended periods.
Fever Management in Special Populations
Certain groups may require special consideration when it comes to fever management.
How does fever treatment differ for pregnant women?
Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking any medication for fever. Generally, acetaminophen is considered safer during pregnancy than NSAIDs. However, all medications should be used cautiously and only when necessary.

What about fever management in older adults?
Older adults may be more susceptible to the side effects of fever-reducing medications. They may also have a diminished fever response, meaning their temperature might not rise as high even with significant infections. Close monitoring and consultation with a healthcare provider are important for fever management in this population.
Fever treatment for individuals with chronic health conditions
People with chronic health conditions such as liver disease, kidney problems, or cardiovascular issues may need to approach fever management differently. These individuals should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a safe and effective fever management plan that takes into account their specific health needs and medication regimens.
The Future of Fever Management
As medical research advances, new approaches to fever management are being explored.
What are some emerging trends in fever treatment?
- Targeted therapies: Medications that address specific causes of fever rather than general symptom relief
- Smart thermometers: Devices that can track temperature trends and provide personalized recommendations
- AI-assisted diagnosis: Using artificial intelligence to help interpret fever patterns and associated symptoms
- Immunomodulatory approaches: Treatments that work with the body’s immune system to manage fever more effectively
While these advancements are promising, it’s important to remember that traditional fever management techniques remain effective and should not be discounted.

Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Fever Treatment
Managing fever effectively requires a balance between providing relief and allowing the body’s natural defenses to work. By understanding the role of fever, the options for treatment, and when to seek medical attention, individuals can make informed decisions about fever management for themselves and their families.
Remember that while fever reducers can provide comfort, they are not always necessary for mild fevers in otherwise healthy individuals. Always follow medication instructions carefully, be aware of potential side effects and interactions, and consult a healthcare provider when in doubt or when dealing with high or persistent fevers.
By taking a thoughtful and informed approach to fever management, you can help ensure the best possible outcome while supporting your body’s natural healing processes.
Best Fever Reducers: Options and Helpful Information
Best Fever Reducers: Options and Helpful Information
- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer’s & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn’s Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women’s Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Mohamed Jalloh — By University of Illinois — Updated on March 8, 2019
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission Here’s our process.
If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.
Was this helpful?
Introduction
When you or your child has a fever, you want something that works quickly and works well. But with so many over-the-counter (OTC) medications available, it can be tough to know which one is best for you.
You can choose between two main types of OTC fever reducers: acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs include ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen. In general, no particular one of these fever-reducing drugs is better than the others. Instead, you should compare the drug forms, side effects, and other factors to choose a fever reducer that will work well for you or your child. Here’s what you need to know to make an informed decision.
Acetaminophen is a fever reducer and a pain reliever. It’s not fully understood how this drug works. Acetaminophen doesn’t decrease swelling or inflammation. Instead, it likely changes the way your body senses pain. It also helps cool your body to bring your fever down.
Forms and brand-name versions
Acetaminophen comes in several forms. These include:
- tablets
- extended-release tablets
- chewable tablets
- disintegrating tablets
- capsules
- liquid solution or suspension
- syrup
You take any of these forms by mouth. Acetaminophen is also available as a rectal suppository.
Acetaminophen is also available as a rectal suppository.
Common brand-name drugs that contain acetaminophen include Tylenol, Feverall, and Mapap.
Find acetaminophen online.
Side effects
When taken as directed, acetaminophen is generally safe and well-tolerated. However, in some cases, it can cause side effects such as:
- nausea
- vomiting
- trouble sleeping
- allergic reaction
- serious skin reactions, including severe rash
Warnings
Overdose
Because acetaminophen is found in many over-the-counter medications, it’s easy to take too much of it. That makes overdose a concern. You should not take more than 4,000 mg of acetaminophen in a 24-hour period.
This limit includes acetaminophen from all sources, including over-the-counter and prescription forms. Other common OTC drugs that contain acetaminophen include Alka-Seltzer Plus, Dayquil, Nyquil, Excedrin, Robitussin, and Sudafed. To be safe, avoid taking more than one product that contains acetaminophen at a time.
In case of overdose, call your local poison control center or 911 right away.
Liver damage
If you take too much acetaminophen, it can also cause liver damage. In severe cases, this can lead to liver failure, the need for a liver transplant, or death. Again, only take one medication that contains acetaminophen at a time, and always carefully follow the dosage instructions on the medication package.
Alcohol
Taking acetaminophen and drinking alcohol can also cause liver damage. In general, you should not take acetaminophen if you have three or more drinks that contain alcohol every day.
Extended fever or drug reaction
Stop taking acetaminophen if your fever gets worse or lasts more than three days. Also stop using it if you develop new symptoms such as skin redness or swelling. In these cases, call your doctor right away. They could be a signs of a more serious condition.
Drug interactions
Acetaminophen can interact with other drugs. An interaction is when a substance changes the way a drug works. This can be harmful or prevent the drug from working well. Examples of drugs that can cause dangerous interactions when used with acetaminophen include:
An interaction is when a substance changes the way a drug works. This can be harmful or prevent the drug from working well. Examples of drugs that can cause dangerous interactions when used with acetaminophen include:
- warfarin, a blood thinner
- isoniazid, a tuberculosis drug
- certain seizure medications such as carbamazepine and phenytoin
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) include drugs such as:
- ibuprofen
- aspirin
- naproxen
NSAIDs help decrease inflammation, pain, and fever. They do this by blocking the body’s production of a substance called prostaglandin. This substance promotes inflammation and fever by causing the release of various chemical signals in your body.
Forms and brand-name versions
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen comes in several forms. These include:
- tablets
- chewable tablets
- capsules
- liquid suspension
You take ibuprofen by mouth. Common brand-name products that contain ibuprofen include Advil and Motrin.
Common brand-name products that contain ibuprofen include Advil and Motrin.
Shop for ibuprofen on Amazon.
Aspirin
Aspirin comes in these forms:
- tablets
- delayed-release tablets
- chewable tablets
- gum
You take any of these forms by mouth. Aspirin also comes as a rectal suppository. Common brand-name products that contain aspirin include Bayer Aspirin and Ecotrin.
Purchase aspirin here.
Naproxen
Naproxen comes in these forms:
- tablets
- delayed-release tablets
- capsules
- liquid suspension
You take naproxen by mouth. A common brand-name product that contains naproxen is Aleve.
Find naproxen online.
Side effects
The most common side effect of NSAIDs is an upset stomach. To help prevent stomach upset, take ibuprofen or naproxen with food or milk. You can take aspirin with food or a full glass of water.
NSAIDs can also have more serious side effects. The more serious side effects of ibuprofen or naproxen can include:
The more serious side effects of ibuprofen or naproxen can include:
- stomach problems such as bleeding and ulcers
- heart problems such as heart attack and stroke
- kidney problems
The more serious side effects of aspirin can include:
- stomach problems such as bleeding and ulcers
- allergic reactions, with symptoms such as:
- breathing trouble
- wheezing
- swelling of face
- hives
- shock
Warnings
Talk with your doctor before taking an NSAID if any of these warnings pertain to you.
History of heart disease
If you have a history of heart disease, you have increased risk of heart attack or stroke when taking ibuprofen or naproxen. The risk is still higher if you take more of these medications than directed or if you take them for a long time.
History of stomach ulcers or bleeding problems
If this applies to you, you have an increased risk of ulcers or bleeding when taking ibuprofen or naproxen. The risk is still higher if you:
The risk is still higher if you:
- take these medications for a long time
- take other medications that contain NSAIDs
- take any blood thinner drugs or steroids
- are 60 years or older
Extended fever or drug reaction
There are several instances that indicate you should not continue to treat your fever with an NSAID. Stop taking NSAIDs if:
- your fever gets worse or lasts more than three days
- you develop any new symptoms
- you have skin redness or swelling
- you have ringing in your ears or hearing loss
- you have signs of a stomach bleed
Signs of stomach bleeding include:
- faintness
- blood in your vomit or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- bloody or black stools
- stomach pain that does not improve
Stop taking the drug and call your doctor if you have any of these symptoms. These effects could be signs of a more serious condition.
Alcohol
If you have three or more drinks that contain alcohol per day, you’re at higher risk of ulcers or bleeding when taking ibuprofen, aspirin, or naproxen. Taking NSAIDs and drinking alcohol can cause severe stomach problems.
Taking NSAIDs and drinking alcohol can cause severe stomach problems.
Problems in children
Avoid using aspirin in children and adolescents who are younger than 12 years and are recovering from chickenpox or flu symptoms.
Call your child’s doctor right away if your child has nausea and vomiting along with certain behavior changes. These include aggressive behavior, confusion, or loss of energy. These behavior changes may be early signs of a rare condition called Reye’s syndrome. If left untreated, Reye’s syndrome can be life-threatening.
Learn more about why aspirin and children don’t mix: Reye’s syndrome »
Drug interactions
NSAIDs can interact with other medications you may be taking. For example, NSAIDs can interact with:
- warfarin, a blood thinner
- celecoxib, another NSAID
- cyclosporine, a drug that weakens your immune system
- diuretics and other medications to treat high blood pressure
Fever reducers can affect people of different ages differently. Follow these age guidelines to help determine which fever reducer is best for you or your child.
Follow these age guidelines to help determine which fever reducer is best for you or your child.
Adults (ages 18 years and older)
Acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin are generally safe for reducing fever in adults.
Children (ages 4-17 years)
Acetaminophen and ibuprofen are generally safe for reducing fever in children who are 4-17 years old.
Do not give aspirin to children unless your doctor says it’s okay.
Naproxen is safe in children ages 12 years and older. If your child is younger than 12 years of age, talk to your doctor before giving your child naproxen.
Children (ages 3 years and younger)
Acetaminophen and ibuprofen are generally safe for reducing fever in young children. However, be sure to talk to your child’s doctor first if your child is younger than 2 years.
Do not give aspirin to young children unless your doctor says it’s okay.
For infants younger than 3 months, call your doctor first before giving any medication.
When choosing a fever reducer, you have a few options. Acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin can each help treat a fever. They each come with their own unique considerations, including what drugs they interact with, who they’re safe to treat, and their possible side effects. While there is no one best fever reducer, there may be a fever reducer that is the best option for you. Consider the information in this article carefully to make a healthy choice.
A:
Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice.
Was this helpful?
Last medically reviewed on July 29, 2016
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Acetaminophen – acetaminophen tablet, coated. (2012, December)
dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e4cfbe12-d712-4ca6-8400-14eec2eca019 - Advil – ibuprofen sodium tablet, coated. (2015, September)
dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5be198b8-396e-4b44-8819-e2e3b5d2ad0e - Advil – ibuprofen capsule, liquid filled. (2016, June)
dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=1f01c10a-9434-91a4-2ee4-352315a6b610 - Aspirin 325 MG – aspirin tablet. (2016, February)
dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=28c48336-c238-0141-e054-00144ff8d46c - Motrin IB – ibuprofen tablet, film coated. (2015, September)
dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5bca517f-94a5-428c-b716-80c6b0b86980 - U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2014, August). Acetaminophen
nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a681004.html - U.
 S. National Library of Medicine. (2016, June). Aspirin
S. National Library of Medicine. (2016, June). Aspirin
nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a682878.html - U.S. National Library of Medicine. (2015, September). Ibuprofen
nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a682159.html
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Mar 8, 2019
Written By
University of Illinois-Chicago
Edited By
Juan Armstrong
Jul 29, 2016
Medically Reviewed By
Mohamed Jalloh
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Mohamed Jalloh — By University of Illinois — Updated on March 8, 2019
Read this next
- What You Need to Know About Breaking a Fever
Medically reviewed by Angelica Balingit, MD
When should you break a fever, and when should you let it run its course? Here’s everything you need to know about when and how to break a fever.

READ MORE
- Do You Have a Fever? How to Tell and What You Should Do Next
Medically reviewed by Sirisha Yellayi, DO
A fever is the body’s way of battling an illness. Here’s how to tell if you have a fever, plus what you should do and when you should seek help.
READ MORE
- What Causes Shivering with Fever?
Medically reviewed by Stacy Sampson, D.O.
People often associate shivers with being cold, but they are also a symptom with fever. Learn how to manage shivering, treat a fever, and when to seek…
READ MORE
- Symptoms of Fever in Adults, Children, and Babies, and When to Seek Help
Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD
Fever symptoms may include more than just an increase in body temperature. In adults and children, a temperature of 100.4F (38C) or higher marks a…
READ MORE
- Why Are My Hands Always Warm?
Medically reviewed by Stacy Sampson, D.O.
Have warm hands that aren’t cooling down? We’ll explain what could be causing it and how you can find relief.

READ MORE
- Everything You Should Know About Heatstroke
Heatstroke is a serious medical emergency. Learn how to identify the symptoms, what to do if you suspect heatstroke, and tips for prevention.
READ MORE
- What Is a Periodic Fever Syndrome?
Medically reviewed by Carissa Stephens, R.N., CCRN, CPN
Periodic fever syndrome is a group of conditions that cause fevers and other symptoms. These syndromes are more common in kids but can also affect…
READ MORE
- Understanding Familial Mediterranean Fever
Medically reviewed by Stella Bard, MD
Familial Mediterranean fever is an inherited condition that causes episodes of high fever and other symptoms like stomach, chest, and joint pain…
READ MORE
- Understanding Abortion Restrictions in Your State
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Abortion restrictions are constantly changing as new legislation is passed in individual states. Here’s what to expect in all 50 states and Washington,
READ MORE
Medication for fever: Options to consider
Two over-the-counter (OTC) options can help reduce a fever. They are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil), and acetaminophen (Tylenol).
They are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil), and acetaminophen (Tylenol).
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines a fever as any temperature at 100.4ºF (38ºC) or above.
A fever is the immune system’s response to illness. It is an attempt to kill viruses and bacteria by raising the body’s temperature a few degrees.
While it is a natural process, it can be uncomfortable and become dangerous if a person’s temperature becomes too high.
Medications for fever do not treat the underlying condition causing the fever, but they can help reduce it and other symptoms of the illness.
People who are pregnant should consult a doctor before taking OTC medication for a fever. Parents and caregivers should also consult a doctor before administering any medications to a child.
This article outlines the medications available to treat a fever at home. It also discusses when to seek medical attention.
The following table provides a general overview of the medications a person can take to treat a fever. People should always check the medication label.
People should always check the medication label.
| Generic name | Brand names | Adult dose | Side effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| ibuprofen | Motrin or Advil | 1–2 200 mg tablets every 4–6 hours, with a maximum of 1,200 mg per day | • constipation • gas • bloating • diarrhea • dizziness • nervousness • ringing in the ears • nausea • vomiting |
| naproxen | Aleve | 1–2 220 mg tablets every 8–12 hours, with a maximum of 660 mg per day | • gas • constipation • dizziness • headaches • excessive thirst • drowsiness • dizziness • lightheadedness • symptoms of a cold • ringing in the ears • difficulty with sleeping • hearing problems • a burning or tingling sensation in the legs and arms |
| aspirin (regular strength) | Bayer | 1–2 325 mg tablets every 4 hours, or 3 tablets every 6 hours, with a maximum of 4,000 mg per day | • nausea • heartburn • vomiting • stomach pain |
| acetaminophen | Tylenol | 500 mg or 1,000 mg every 4–6 hours, with a maximum of 4,000 mg per day | side effects are rare, but some people may experience an allergic reaction |
Ibuprofen is a type of NSAID sold under several brand names, including Advil and Motrin. It is a form of propionic acid and can help reduce fever as well as other symptoms, such as pain.
It is a form of propionic acid and can help reduce fever as well as other symptoms, such as pain.
Depending on the dose, a person can get ibuprofen OTC at stores and pharmacies or via prescription. It comes in various forms, including tablets or capsules.
A 2022 article notes that people in their third trimester of pregnancy should not take ibuprofen.
Children can take ibuprofen, but parents and caregivers should speak with a pediatrician before giving them the medication.
Side effects
Side effects can include:
- constipation
- gas
- bloating
- diarrhea
- dizziness
- feeling nervous
- ringing in the ears
It can also cause nausea and vomiting.
Learn more about ibuprofen.
Naproxen is another type of NSAID, commonly sold under the brand name Aleve. Similar to ibuprofen, it is a form of propionic acid and can treat additional symptoms other than a fever.
A person can take naproxen sodium as a tablet or capsule. Liquid forms are available for younger children, although a parent or caregiver should talk with the child’s doctor first.
Liquid forms are available for younger children, although a parent or caregiver should talk with the child’s doctor first.
People who are in their third trimester of pregnancy should not take naproxen.
Side effects
Side effects can include:
- gas
- constipation
- dizziness
- headache
- excessive thirst
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- lightheadedness
- symptoms of a cold
- ringing in the ears
- sleeping difficulties
- hearing problems
- a burning or tingling sensation in the legs and arms
Learn more about naproxen.
Aspirin is another common form of NSAID that consists of acetylated salicylates. A common brand name is Bayer. This medication comes in several different formulas, including regular strength, and different forms such as tablets.
Caregivers should not give aspirin to children or teens without first consulting a doctor. A 2022 article notes an association between taking aspirin and the development of Reye’s syndrome, which can be fatal.
People who are pregnant should speak with a doctor before taking aspirin.
Side effects
Side effects include:
- nausea
- heartburn
- vomiting
- stomach pain
Learn more about aspirin.
Acetaminophen, commonly sold under the brand name Tylenol, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent to treat pain and fever. Companies often add acetaminophen to other medications that treat allergies, colds, flu, and other medical conditions.
Acetaminophen is available OTC or as a prescription.
For teenagers and adults, it commonly comes in the form of tablets and capsules. Younger children may be able to take it in a liquid form, but caregivers should speak with a paediatrician first.
Side effects
The United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS) states that side effects are rare in adults and children if a person takes the correct dose.
However, in rare cases, a person can experience an allergic reaction.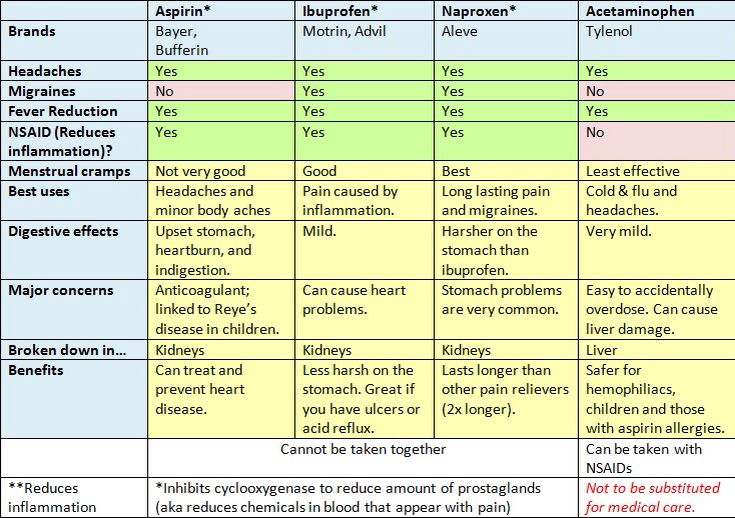
In some cases, NSAIDs can lead to serious adverse effects, including problems affecting the liver, heart, and blood circulation.
Compared to prescription-strength medications, OTC NSAIDs typically cause fewer side effects.
Acetaminophen can lead to liver failure or other issues with the liver.
People can also experience an allergic reaction to fever-reducing medications. People should seek medical help if they experience:
- rash
- inflamed, peeling, or blistering skin
- itching
- hives
- hoarse voice
- difficulty swallowing
- difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, tongue, throat, lips, hands, feet, eyes, lower legs, or ankles
A person should take fever-reducing medications only as a medical professional advises.
There are several formulas of NSAIDs and acetaminophen with differing doses. A person should follow the instructions on the packaging and pay attention to the maximum number of doses allowed in 24 hours.
When treating an underlying condition, a person should follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding how much to take and when to take it.
A person should also be mindful of other medications that may contain acetaminophen. Companies often mix it with other ingredients to create OTC medications for colds, flu, and other issues.
Can a person take acetaminophen and NSAIDs at the same time?
A person can take acetaminophen and ibuprofen at the same time.
Learn more about acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
A person may find that certain home remedies may help reduce their fever. Other options include:
- resting
- taking lukewarm baths
- drinking plenty of fluids
- wearing loose clothing
A fever breaks when a person’s temperature drops below 100.4ºF (38°C), but they may still feel ill due to the underlying condition. Dropping the fever can help alleviate some symptoms and help people feel better overall.
Learn more
Find out more about treating a fever:
- How to reduce a fever
- Treatment tips for breaking a fever
- What are the best home remedies for fever?
- How to bring down a fever in babies
A person should seek medical help if they are unable to lower the fever on their own or if they suspect a more serious underlying condition. They should also contact a doctor if:
They should also contact a doctor if:
- a person experiences worsening symptoms
- they have a weakened immune system
- they reach a fever of 104°F (40ºC) or higher
- they are concerned about a fever in a child or older adult
A person can take NSAIDs and acetaminophen to help treat a fever at home. These medications can also help to treat additional symptoms, such as pain.
A person should consult a doctor if their fever lasts longer than a few days, causes additional symptoms, or does not go down with medication.
Effective antipyretic drugs for adults and children
CONTRAINDICATIONS. POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS. A SPECIALIST’S CONSULTATION IS REQUIRED. 010 Article content
- Effective at temperature
- Adults
- Children
- Summary
- References
- Ask an expert about the topic of the article
One of the most common symptoms of the disease is fever. Fever is especially common in respiratory viral infections. According to statistics, in Russia the number of ARVI and influenza patients annually reaches more than 30 million people. This means that on average an adult suffers from 2 to 4 colds during the year, a child gets sick from 6 to 9.once. In this case, it is logical to ask the question: what antipyretic drugs to use. The answer can be found in the article.
Fever is especially common in respiratory viral infections. According to statistics, in Russia the number of ARVI and influenza patients annually reaches more than 30 million people. This means that on average an adult suffers from 2 to 4 colds during the year, a child gets sick from 6 to 9.once. In this case, it is logical to ask the question: what antipyretic drugs to use. The answer can be found in the article.
Pharmacist Anna Sumenkova will talk about antipyretic drugs that are effective at fever, as well as introduce drugs for adults and children.
Effective at fever
Antipyretics are drugs that reduce elevated body temperature during feverish conditions. The normal temperature for adults is considered to be up to 37 degrees and up to 36.9for children.
The causes of fever are varied, ranging from physical and emotional fatigue to serious illness. Therefore, before taking antipyretic drugs, it is important to consult a doctor to determine the cause of the disease. It is worth bringing down the temperature when it rises more than 38.5 degrees.
It is worth bringing down the temperature when it rises more than 38.5 degrees.
At elevated temperatures it is important:
- Stay in bed to minimize stress on the body.
- Follow a diet: it is recommended to include easily digestible foods containing vitamins in your diet: lean meats and fish, dairy products, fruits and vegetables, juices and compotes.
- Drink plenty of fluids in your diet to avoid dehydration.
Effective antipyretic drugs for adults and children are similar, but there are differences. Therefore, we will consider children’s and adult medicines separately.
Adults
Clinically recommended non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs to reduce fever associated with muscle and joint pain in adults: Ibuprofen and Paracetamol . The drugs are available in different dosage forms, but tablets or capsules should be used to relieve fever in adults.
Ibuprofen is produced in forms of the same name, as well as under such trade names as: Nurofast , Nurofen and Mig 400 . A similar situation with Paracetamol . Both drugs can be part of complexes for a wide range of actions: anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic. These drugs include: Ibuklin, Nurofen Intensive and Nuralgon.
A similar situation with Paracetamol . Both drugs can be part of complexes for a wide range of actions: anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic. These drugs include: Ibuklin, Nurofen Intensive and Nuralgon.
A common dosage form of antipyretics for adults is powders for oral solution. Popular representatives: Theraflu, Antigrippin and Anvimax . Their use is justified in the presence of other symptoms of a cold. For example, a runny nose. Due to the presence of three or more drugs in the composition, they have a large number of contraindications and side effects. The list of clinical recommendations for the treatment of SARS is not included.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, only Paracetamol is approved for use, but it is also not recommended for use in the third trimester of pregnancy and in the first three months of lactation.
Aspirin and its derivatives should not be used at elevated temperatures due to the high risk of side effects in the form of hemostasis disorders and exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
All products Paracetamol
13 reviews
All products Nurofen
15 reviews
All products Aspirin
20 reviews
All products Theraflu
20 reviews
All products AnviMax
20 reviews
All products Ibuprofen
25 reviews
For children 9 0011 Due to proven safety, to reduce body temperature in only two drugs are recommended for children:
Paracetamol and Ibuprofen . The use of antipyretics for newborn healthy children up to 3 months is justified at temperatures above 39-39.5 degrees. Up to 1 month, the use of drugs is not recommended, and if fever occurs, emergency care should be called.
Paracetamol and Ibuprofen for children are available in the form of suspensions with different flavors and suppositories – rectal suppositories. Children’s dosage forms have names similar to active substances, and are also available under trade names: Nurofen and Panadol Children’s .
Children’s formulations are generally used for children from 3 months to 12 years of age. For adolescents from 12 years of age, adult products should be used, but in a modified dosage. You can get acquainted with the required dose in the instructions for the drug.
For adolescents from 12 years of age, adult products should be used, but in a modified dosage. You can get acquainted with the required dose in the instructions for the drug.
The pharmacist adds: “In my practice, most often, antipyretic drugs are purchased for children from 3 to 10 years old. Of course, at this age it is best to use Paracetamol and Ibuprofen in liquid forms or suppositories. Not recommended for children Aspirin and Nimesulide .
All products Panadol
20 reviews
Summary
- Antipyretics are medicines that reduce elevated body temperature during feverish conditions.
- The causes of fever are varied, ranging from physical and emotional fatigue to serious illness.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs such as Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are used to reduce fever accompanied by muscle and joint pain in adults.
- A common dosage form of antipyretics for adults is powders for oral solution.

- Due to proven safety, only two drugs are recommended for fever reduction in children: paracetamol and ibuprofen.
- Paracetamol and Ibuprofen for children are available in the form of suspensions with different flavors and suppositories – rectal suppositories.
Sources
1. Acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI). Union of Pediatricians of Russia. 2022.
2. Acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) in adults. Non-profit partnership “National Scientific Society of Infectionists”, All-Russian public organization “Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists”. 2022. https://cr.minzdrav.gov.ru/recomend/724_1
3. State Register of Medicinal Products
Ask an expert on the topic of the article
Still have questions? Ask them in the comments below and our experts will answer you. There you can also share your experience with other readers of Megasovets.
Share Mega Tip
Like this article? Tell mom, dad, grandma and aunt Galya from the third entrance
Copy link
How to lower the temperature at home: antipyretics
Let’s talk about the main groups of antipyretic drugs: what are the pitfalls, what should not be used with certain drugs, why are they needed at all and is it possible to do without them.
Tags:
Health
Medications
temperature
Shutterstock
High fever is a frequent companion of illnesses. When and how should it be brought down, and is it possible to do without drugs?
Content of article
Do not self-medicate! In our articles, we collect the latest scientific data and the opinions of authoritative health experts. But remember: only a doctor can diagnose and prescribe treatment.
An increase in temperature is a protective reaction of the body to serious external or internal stimuli, such as infections, poisoning with any toxins, inflammatory processes, and others. Normally, the temperature of the human body does not exceed 37.1 degrees Celsius, but during the period of illness it rises, and depending on how much, different types of temperature are distinguished:
- subfebrile – up to 37.9 degrees Celsius, does not require the use of antipyretics, usually accompanies sluggish inflammatory processes;
- febrile – from 38 to 38.
 9 degrees Celsius, the body actively fights irritants, many microorganisms cannot withstand such a temperature, so you need to bring it down only if the patient clearly feels unwell;
9 degrees Celsius, the body actively fights irritants, many microorganisms cannot withstand such a temperature, so you need to bring it down only if the patient clearly feels unwell; - pyretic – from 39 to 41 degrees Celsius, the protective reaction is out of control, doctors recommend lowering this temperature so as not to overload the body systems;
- hyperpyretic – over 41 degrees, in this case the patient needs medical help, it is unlikely to get off with conventional means. If the child has a temperature, an ambulance should be called already at 40 degrees.
ADVERTISING – CONTINUED BELOW
In general, raising the temperature is rather beneficial: firstly, as we have already said, many microbes do not like it, and secondly, it has been proven that in this way the body helps the immune system work – it hunts for irritants more efficiently. But, like everywhere else, there are nuances: in this mode, the load on the heart and nervous system may increase, and children may experience convulsions. The temperature still needs to be brought down, and not only when it is too high (38.5 degrees and above), but also earlier – if there is a possibility of convulsions or if the patient’s condition requires it. There are two main ways to reduce the temperature: take an antipyretic or use folk methods (however, the methods can be combined).
The temperature still needs to be brought down, and not only when it is too high (38.5 degrees and above), but also earlier – if there is a possibility of convulsions or if the patient’s condition requires it. There are two main ways to reduce the temperature: take an antipyretic or use folk methods (however, the methods can be combined).
The best fever reducers for high fever
Almost all fever reducers are nonsteroidal (meaning they are not hormonal) anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In addition to fighting fever, they also reduce inflammation and reduce pain. Such a complex action allows the patient to feel better faster, because pains of various types are frequent companions of temperature. The only active substance commonly used in medicines with a different mechanism of action is paracetamol.
However, all antipyretics act in the same way: they affect the processes taking place in the hypothalamus, as a result of which less heat begins to form in the body, and more is released, due to which it, of course, cools down, and usually quite quickly – already after half an hour after taking a tablet, syrup or suppository, the temperature drops. Antipyretics are symptomatic treatment, they are not taken in courses, unlike other drugs, such as antibiotics. The purpose of fever-lowering drugs is to give temporary relief to a sick patient. At the same time, each of them has certain side effects, so when taking them, you need to weigh the pros and cons. Let’s talk about the main means used in Russia: about their action and some features. We note in advance that it is impossible to list all contraindications, side effects, interactions within the framework of this article, before using this or that drug, you need to read the instructions, and even better, consult a doctor who can weigh the risks for you personally. In addition, a particular person may have hypersensitivity to absolutely any drug or even be allergic to it, so even “banal” antipyretics should be used with caution at least the first time.
Antipyretics are symptomatic treatment, they are not taken in courses, unlike other drugs, such as antibiotics. The purpose of fever-lowering drugs is to give temporary relief to a sick patient. At the same time, each of them has certain side effects, so when taking them, you need to weigh the pros and cons. Let’s talk about the main means used in Russia: about their action and some features. We note in advance that it is impossible to list all contraindications, side effects, interactions within the framework of this article, before using this or that drug, you need to read the instructions, and even better, consult a doctor who can weigh the risks for you personally. In addition, a particular person may have hypersensitivity to absolutely any drug or even be allergic to it, so even “banal” antipyretics should be used with caution at least the first time.
Paracetamol
There are many drugs with this active ingredient: panadol, calpol, tylenol, cefecon P, efferalgan – the list can be continued for a very long time. Paracetamol interacts with the hypothalamus, affecting the thermoregulatory center. This is one of the safest remedies, it can be used by both children and pregnant women, it helps to lower the temperature, thanks to it the pain subsides, but it does not fight inflammation very effectively. However, paracetamol is extremely common. The key recommendation of doctors when taking it is to follow the instructions in order to prevent an overdose.
Paracetamol interacts with the hypothalamus, affecting the thermoregulatory center. This is one of the safest remedies, it can be used by both children and pregnant women, it helps to lower the temperature, thanks to it the pain subsides, but it does not fight inflammation very effectively. However, paracetamol is extremely common. The key recommendation of doctors when taking it is to follow the instructions in order to prevent an overdose.
Interaction: enhances the effect of coumarins, as well as drugs that harm the liver. Works worse with barbiturates. Some drugs may speed up or slow down absorption.
Contraindications: liver and kidney diseases, alcohol dependence.
Side effects: disruption of the circulatory system, kidneys, allergies.
Ibuprofen
Another drug that seems to be in all first aid kits. Demand for it is always stable (except perhaps during the coronavirus pandemic, for some time it was believed that ibuprofen should not be used for Covid-19 infection). Preparations with its content (a few examples) – nurofen, MIG, ibusan, bumidol. Ibuprofen, unlike paracetamol, also has an anti-inflammatory function – it weakens inflammatory processes, in addition, of course, it reduces the activity of thermoregulatory centers and drowns out pain. It works for a long time – up to 8 hours.
Preparations with its content (a few examples) – nurofen, MIG, ibusan, bumidol. Ibuprofen, unlike paracetamol, also has an anti-inflammatory function – it weakens inflammatory processes, in addition, of course, it reduces the activity of thermoregulatory centers and drowns out pain. It works for a long time – up to 8 hours.
Interaction: reduces the effectiveness of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), enhances the action of an anticoagulant, should not be taken together with thrombolytics, barbiturates and ethanol, works worse with antacids, anesthetizes better in combination with caffeine.
Contraindications: Do not use in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy or while breastfeeding, gastrointestinal ulcers during exacerbation, asthma, kidney or liver dysfunction, certain diseases of the cardiovascular, circulatory system, skin.
Side effects: dysfunctions of ECT, liver, kidneys, allergies, reactions from the nervous system, circulatory system.
Acetylsalicylic acid
It is also the good old aspirin, as well as bufferin, mikristin, acylpyrine and others. Acetylsalicylic acid is useful not only for high temperature, inflammation and pain, but also for cardiovascular diseases. Like other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it affects the centers of thermoregulation and pain sensitivity, reduces inflammation. This active substance primarily works as an antipyretic for adults.
Acetylsalicylic acid is useful not only for high temperature, inflammation and pain, but also for cardiovascular diseases. Like other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it affects the centers of thermoregulation and pain sensitivity, reduces inflammation. This active substance primarily works as an antipyretic for adults.
Interaction: should not be used together with paracetamol, caffeine, ethanol, glucocorticoids, diuretics, diabetes drugs, works worse with antacids.
Contraindications: certain diseases of the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal ulcers, acute liver or kidney failure. Do not take children, adolescents under 15 years of age, pregnant women with rare exceptions and breastfeeding.
Side effects: allergic reactions, disorders of the liver, gastrointestinal tract or kidneys, blood disorders.
Metamizole sodium
This name is not well known, but everyone knows the drug behind it – analgin (as well as baralgin M or optalgin). Basically, all these drugs are used as painkillers and sometimes anti-inflammatory, however, they also have antipyretic properties due to increased heat transfer. In many countries, the use of metamizole sodium has been questioned due to toxicity, but there is evidence that this toxicity occurs in people with a certain genetic defect.
Basically, all these drugs are used as painkillers and sometimes anti-inflammatory, however, they also have antipyretic properties due to increased heat transfer. In many countries, the use of metamizole sodium has been questioned due to toxicity, but there is evidence that this toxicity occurs in people with a certain genetic defect.
Interaction: becomes stronger in combination with caffeine, codeine, barbiturates, toxic with antidepressants, oral contraceptives, should not be used with radiopaque agents. When injected, it must not be mixed with other drugs.
Contraindications: pregnancy, breast-feeding, impaired hematopoiesis, impaired liver and kidney function.
Side effects: allergy, hypotension, nephritis, blood diseases.
There are also a variety of medicines that combine several active ingredients at once. In this case, relief may come earlier, but, firstly, the side effects may be cumulative, and secondly, if the temperature needs to be brought down repeatedly, it may turn out that you have to choose between exceeding the daily dose (that is, the probable overdose) and the actual high temperature.
Paracetamol and ibuprofen-based single drugs are considered the most reliable and safe antipyretics. If the regimen is followed, they have a minimum number of side effects, they can be used in the treatment of children, including infants, and these drugs have a lot of forms – syrups, suppositories, and tablets, so it is easy to choose a convenient method of use. Antipyretics are the easiest way to quickly reduce the temperature in an adult or child.
How to reduce the temperature at home without medication
If you suddenly find yourself somewhere where there is no pharmacy and you don’t have a supply of medicines with you, or you don’t want to use antipyretics for whatever reason, there are some folk methods of lowering the temperature. Perhaps they do this task more slowly than drugs specially designed for this purpose, but still they work.
- Rubbing with alcohol or vodka. Alcohol is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:1, vodka is used as is: moisten a cotton pad or a small towel with liquid and wipe the forehead, armpits, back of the hands.


 S. National Library of Medicine. (2016, June). Aspirin
S. National Library of Medicine. (2016, June). Aspirin


 9 degrees Celsius, the body actively fights irritants, many microorganisms cannot withstand such a temperature, so you need to bring it down only if the patient clearly feels unwell;
9 degrees Celsius, the body actively fights irritants, many microorganisms cannot withstand such a temperature, so you need to bring it down only if the patient clearly feels unwell;