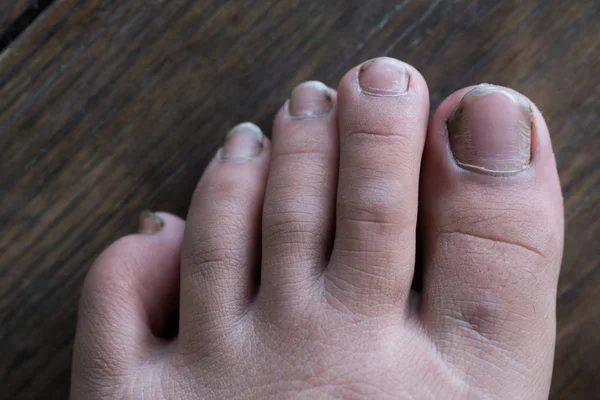
Images of infected fingernails. Understanding Nail Fungus: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Options
What are the common causes of nail fungus. How can you identify the symptoms of nail fungus. What are the most effective treatment options for nail fungus. How long does it take to cure nail fungus. Can nail fungus spread to other parts of the body. Are there any home remedies for treating nail fungus. When should you see a doctor for nail fungus.
The Nature and Prevalence of Nail Fungus
Nail fungus, medically known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when fungi invade one or more nails, leading to various symptoms and potential complications if left untreated.
The prevalence of nail fungus increases with age, with estimates suggesting that up to 50% of people over 70 may be affected. Several factors contribute to its widespread occurrence:
- Increased exposure to fungi in public spaces like gyms and swimming pools
- Compromised immune systems due to various health conditions
- Poor circulation, especially in the extremities
- Genetic predisposition to fungal infections
Are certain individuals more susceptible to nail fungus? People with diabetes, those who smoke, and individuals with a history of athlete’s foot are at higher risk of developing nail fungus. Additionally, those who frequently have wet hands or feet, such as swimmers or dishwashers, may be more prone to fungal infections.

Identifying the Signs and Symptoms of Nail Fungus
Recognizing the early signs of nail fungus is crucial for prompt treatment and prevention of further spread. Common symptoms include:
- Thickened nails
- Discoloration (white, yellow, or brown)
- Brittle, crumbly, or ragged nails
- Distorted nail shape
- Foul odor emanating from the affected nail
How can you distinguish nail fungus from other nail conditions? While some symptoms may overlap with other nail disorders, nail fungus typically progresses slowly and affects one or a few nails at a time. If you notice persistent changes in your nails, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
The Progression of Nail Fungus
Nail fungus often begins as a small white or yellow spot under the tip of the nail. As the infection deepens, it can cause:
- Nail thickening and discoloration
- Crumbling of the nail edges
- Separation of the nail from the nail bed (onycholysis)
- Pain or discomfort, especially when pressure is applied
Does nail fungus always cause pain? In its early stages, nail fungus may not cause any discomfort. However, as the infection progresses, it can lead to pain and difficulty walking or wearing shoes, particularly if it affects the toenails.

The Root Causes of Nail Fungus Infections
Understanding the underlying causes of nail fungus is essential for effective prevention and treatment. The primary culprits behind these infections are:
- Dermatophytes: A group of fungi that thrive on keratin, the protein found in nails and skin
- Yeasts: Particularly Candida species, which can infect nails, especially in people with compromised immune systems
- Molds: Less common but still capable of causing nail infections, especially in toenails
How do these fungi enter the nail? They typically invade through small cuts or separations between the nail and nail bed. Warm, moist environments provide ideal conditions for these fungi to thrive and spread.
Environmental Factors Contributing to Nail Fungus
Several environmental factors can increase the risk of developing nail fungus:
- Walking barefoot in public areas like locker rooms and swimming pools
- Wearing tight, non-breathable shoes that trap moisture
- Living in hot, humid climates
- Frequent hand washing or prolonged exposure to water
Can nail fungus be contracted from nail salons? Yes, if proper sterilization techniques are not employed, nail fungus can potentially spread through shared tools or foot baths in nail salons.
Effective Treatment Options for Nail Fungus
Treating nail fungus can be challenging, often requiring a combination of approaches for optimal results. The most common treatment options include:
- Oral antifungal medications
- Topical antifungal treatments
- Laser therapy
- Surgical or chemical nail removal
Which treatment is most effective for nail fungus? The efficacy of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of the infection, the type of fungus involved, and individual patient characteristics. Oral antifungal medications are often considered the most effective for severe cases, but they may have side effects and require close monitoring.
Prescription Medications for Nail Fungus
Several prescription medications have shown efficacy in treating nail fungus:
- Terbinafine (Lamisil): An oral medication taken for 6-12 weeks
- Itraconazole (Sporanox): Another oral option, often prescribed in pulse doses
- Ciclopirox (Penlac): A topical solution applied directly to the affected nail
How long does it take for prescription medications to work? While improvement may be visible within a few weeks, it can take several months to a year for the nail to grow out completely clear of fungus.
Over-the-Counter and Home Remedies
For mild cases or as complementary treatments, several over-the-counter options and home remedies may be beneficial:
- Tea tree oil: Known for its antifungal properties
- Vinegar soaks: May help create an inhospitable environment for fungi
- Vicks VapoRub: Some studies suggest it may have antifungal effects
- Snakeroot extract: A natural antifungal remedy
Are home remedies as effective as prescription treatments? While some home remedies show promise, they generally aren’t as effective as prescription medications for treating established nail fungus infections. They may be more useful for prevention or as adjunct therapies.
Preventing the Spread and Recurrence of Nail Fungus
Prevention is key in managing nail fungus, as recurrence is common even after successful treatment. Here are some strategies to prevent nail fungus:
- Keep nails short, dry, and clean
- Wear breathable footwear and moisture-wicking socks
- Use antifungal sprays or powders in shoes
- Avoid walking barefoot in public areas
- Don’t share nail clippers or other personal care items
How can you prevent nail fungus from spreading to other nails? Treat the affected nail promptly, keep it covered when possible, and avoid using the same nail tools on infected and healthy nails.

Lifestyle Changes to Support Nail Health
Certain lifestyle modifications can help prevent nail fungus and support overall nail health:
- Maintain good hygiene practices
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Manage underlying health conditions like diabetes
- Quit smoking to improve circulation
- Reduce alcohol consumption
Can diet influence the development of nail fungus? While diet alone may not prevent nail fungus, a balanced diet that supports immune function can help the body fight off fungal infections more effectively.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
While mild cases of nail fungus may respond to home treatments, it’s important to know when to consult a healthcare professional. Seek medical advice if:
- Home treatments haven’t improved the condition after several weeks
- The infection is causing pain or interfering with daily activities
- You have diabetes or a weakened immune system
- The infection appears to be spreading to other nails or areas of the body
What type of doctor should you see for nail fungus? A dermatologist or podiatrist specializes in treating nail conditions and can provide the most appropriate care for nail fungus.

Diagnostic Procedures for Nail Fungus
To confirm a diagnosis of nail fungus, a healthcare provider may perform the following tests:
- Visual examination of the affected nail
- Nail clippings or scraping for microscopic examination
- Fungal culture to identify the specific type of fungus
- In some cases, nail biopsy to rule out other conditions
Is a fungal culture always necessary for diagnosing nail fungus? While visual examination is often sufficient for diagnosis, a fungal culture may be recommended to identify the specific pathogen and guide treatment, especially in cases that don’t respond to initial therapy.
The Impact of Nail Fungus on Quality of Life
Nail fungus can have significant effects on an individual’s quality of life, extending beyond mere cosmetic concerns. Some of the ways nail fungus can impact daily life include:
- Embarrassment and self-consciousness about nail appearance
- Discomfort or pain when wearing shoes or walking
- Difficulty with certain activities, such as sports or dancing
- Potential spread of the infection to other parts of the body or to other people
Can nail fungus affect your social life? For some individuals, the visible symptoms of nail fungus can lead to social anxiety and a reluctance to engage in activities where their nails might be exposed, such as swimming or getting pedicures.

Psychological Effects of Chronic Nail Fungus
The persistent nature of nail fungus can take a toll on mental health. Some psychological effects may include:
- Decreased self-esteem
- Anxiety about the appearance of nails
- Frustration with lengthy treatment processes
- Depression, especially if the condition interferes with daily activities
How can individuals cope with the psychological impact of nail fungus? Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional can be beneficial. Additionally, focusing on treatment adherence and adopting a positive outlook can help manage the emotional aspects of dealing with nail fungus.
Emerging Research and Future Treatments for Nail Fungus
The field of nail fungus treatment is continually evolving, with researchers exploring new approaches to combat this persistent condition. Some promising areas of research include:
- Novel antifungal compounds with improved efficacy and fewer side effects
- Nanotechnology-based treatments for enhanced drug delivery
- Combination therapies that target multiple aspects of fungal growth
- Photodynamic therapy using light-activated compounds
Will there be a cure for nail fungus in the near future? While a definitive cure remains elusive, ongoing research suggests that more effective treatments with shorter durations and fewer side effects may become available in the coming years.

Advancements in Diagnostic Technologies
Improved diagnostic tools are also being developed to enhance the accuracy and speed of nail fungus detection. These include:
- Molecular diagnostic techniques for rapid pathogen identification
- Advanced imaging technologies for early detection of fungal infections
- Artificial intelligence-assisted diagnosis using visual recognition
How will these advancements impact nail fungus treatment? More accurate and timely diagnoses could lead to earlier interventions and potentially better outcomes for patients with nail fungus.
2.100+ Fotos, Bilder und lizenzfreie Bilder zu Nail Fungus
Bilder
- Bilder
- Fotos
- Grafiken
- Vektoren
- Videos
Videos zu nail fungus ansehen
Durchstöbern Sie 2.171
nail fungus Stock-Fotografie und Bilder. Oder suchen Sie nach pilz, um noch mehr faszinierende Stock-Bilder zu entdecken.
Sortieren nach:
Am beliebtesten
schwerer nagelpilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Schwerer Nagelpilz
zehennagelpilz. menschliche viruserkrankungen. hintergrund für das design. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
menschliche viruserkrankungen. hintergrund für das design. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagelpilz. menschliche Viruserkrankungen. Hintergrund für…
zehennagel pilz (isolated on white – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagel Pilz (Isolated on White
“Makro-Nahaufnahme eines männlichen Fußes, der mit Zehennagelpilz infiziert ist. Flaches DOF, bitte zoomen Sie hinein, um die Details zu sehen. (Canon 5D Mark II, Adobe RGB) Verwandte Fotos:”
mikroskopische nahaufnahme des wachsenden mehltaus – 3d-illustration – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Mikroskopische Nahaufnahme des wachsenden Mehltaus – 3D-Illustrati
Mikroskopische Nahaufnahme des wachsenden Mehltaus – 3D-Darstellung
pilz pilz zwischen zehennagel. smelly feet – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Pilz Pilz zwischen Zehennagel. Smelly Feet
dermatophytische onychomykose – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Dermatophytische Onychomykose
onychomykose – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Onychomykose
pilzinfektion des bereichs zwischen den zehen. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
– nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Pilzinfektion des Bereichs zwischen den Zehen.
onychomykose-nägel vor grauem hintergrund – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Onychomykose-Nägel vor grauem Hintergrund
infizierter zehennagel – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Infizierter Zehennagel
Pilzinfektion des Zehennagels.
ärztliche untersuchung auf pilz am zehennagel. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Ärztliche Untersuchung auf Pilz am Zehennagel.
Fuß eines Mannes mit Pilzkrankheit.
daumen der menschlichen hand mit von zähnen gebissenem nagel unter schwarzem hintergrund – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Daumen der menschlichen Hand mit von Zähnen gebissenem Nagel…
nahaufnahme der hand einer frau. handflächenrückseite – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Nahaufnahme der Hand einer Frau. Handflächenrückseite
mikroskopische bilder zeigen pilztest im mikrobiologischen labor, nagelkratzen, hautkratzen. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
– nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Mikroskopische Bilder zeigen Pilztest im mikrobiologischen Labor,
zehennagel mit pilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagel mit Pilz
vor und nach erfolgreicher behandlung einer pilzinfektion an den zehen – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Vor und nach erfolgreicher Behandlung einer Pilzinfektion an den…
Vor und nach der topischen antimykotischen Behandlung wird im großen Zeh einer Person gesehen, die an Onychomykose leidet, einer Pilzinfektion, die eine Gelbfärbung des Zehennagels verursacht
laserbehandlung auf zehennagel, pilzinfektion auf den zehennagel – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Laserbehandlung auf Zehennagel, Pilzinfektion auf den Zehennagel
pilze zwischen frau zehen – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Pilze zwischen Frau Zehen
nagelpilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Nagelpilz
Betroffene Fuß- und Pilzkrankheit
dermatologe untersucht patient mit zehennagelpilz. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
– nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Dermatologe untersucht Patient mit Zehennagelpilz.
großer zeh eines mannes mit zehennagelpilz. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Großer Zeh eines Mannes mit Zehennagelpilz.
Nahaufnahme des großen Zehs eines Mannes mit Zehennagelpilz. Gesundheitskonzept.
roter und brauner zehennagel auf weißer haut – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
roter und brauner Zehennagel auf weißer Haut
zehennagel pilz (isolated on white – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagel Pilz (Isolated on White
Makro-Nahaufnahme eines männlichen Fußes, der mit Zehennagelpilz infiziert ist. Flaches DOF, bitte zoomen Sie hinein, um die Details zu sehen. (Canon 5D Mark II, Adobe RGB)
nahaufnahme im großzehennagelpilz zerlumpt – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Nahaufnahme im Großzehennagelpilz zerlumpt
gesunde und ungesunde nägel – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
gesunde und ungesunde Nägel
zehennagel pilz (isolated on white – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagel Pilz (Isolated on White
podologe frau hält in ihren händen ein gerät zur pediküre und behandlung von onychomykose – eine nagelpilzkrankheit – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Podologe Frau hält in ihren Händen ein Gerät zur Pediküre und.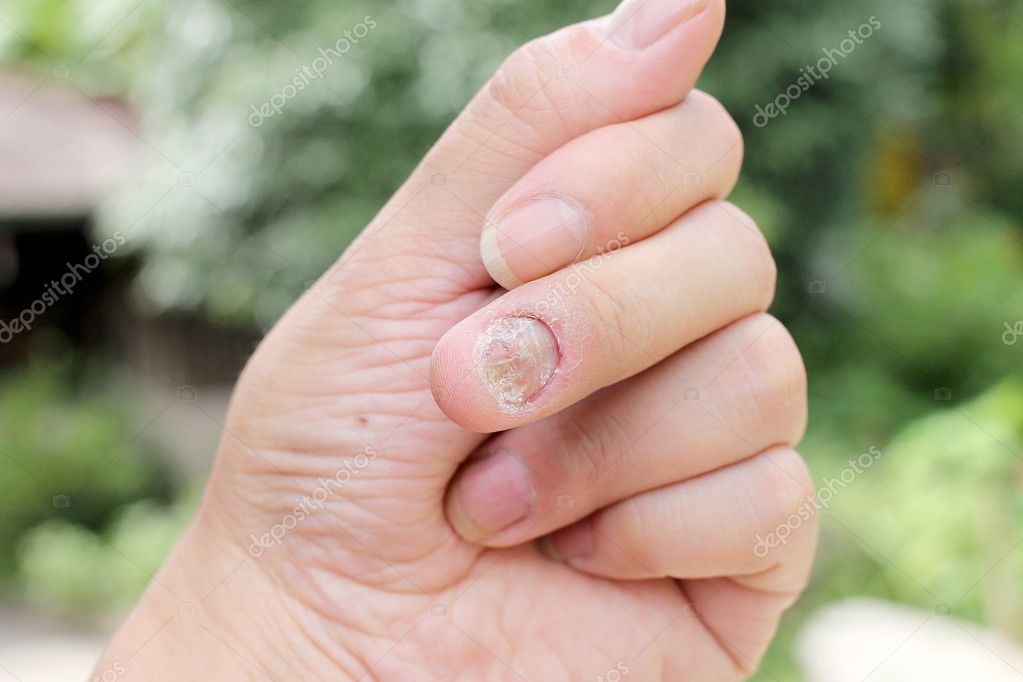 ..
..
ein gebrochener zehennagel. nagelpilzkrankheit – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Ein gebrochener Zehennagel. Nagelpilzkrankheit
großzeh einer person, die an onychomykose, einer pilzinfektion leidet – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Großzeh einer Person, die an Onychomykose, einer Pilzinfektion…
big toe hallux, blauer fleck hematoma – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Big Toe Hallux, Blauer Fleck Hematoma
nagel eines afrikanischen subjekts, das von onychomykose betroffen ist – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Nagel eines afrikanischen Subjekts, das von Onychomykose…
füße alter männer. trockener fuß und hautalterung. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Füße alter Männer. Trockener Fuß und Hautalterung.
männliche geschnittene nägel mit nagelpilz. pilzinfektion an nägelbeinen, finger mit onychomykose. pflege und behandlung. nahaufnahme eines fußes mit beschädigten nägeln wegen pilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Männliche geschnittene Nägel mit Nagelpilz. Pilzinfektion an Nägel
Pilzinfektion an Nägel
onychomykose, eine nagelkrankheit, die durch pathogene pilze verursacht wird. speicherplatz für text kopieren – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Onychomykose, eine Nagelkrankheit, die durch pathogene Pilze…
Onychomykose, eine Nagelerkrankung, die durch pathogene Pilze verursacht wird. Kopieren Sie Speicherplatz für Text. Hochwertiges Foto
nagel-pilz, trockenen rough fuß große makro – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Nagel-Pilz, trockenen rough Fuß große Makro
“Nagelpilz, trockener rauer Zehenfuß Makro. Nikon D800e Konvertiert von RAW.”
professionelle kosmetikerin, während onychomykose-behandlung und nagelrekonstruktion zu einem kunden, gesundheitstherapie – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Professionelle Kosmetikerin, während Onychomykose-Behandlung und…
laser-nagelpilzbehandlung in der klinik – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Laser-Nagelpilzbehandlung in der Klinik
onycholyse-nagel. die inschrift pilz in holzbuchstaben auf grauem grund – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
die inschrift pilz in holzbuchstaben auf grauem grund – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Onycholyse-Nagel. Die Inschrift Pilz in Holzbuchstaben auf…
Onycholyse-Nagel. Die Inschrift Pilz in Holzbuchstaben auf grauem Hintergrund.
nagelpilz pilz-infektion auf nägel – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Nagelpilz Pilz-Infektion auf Nägel
Onychomykose, dermatophytische Onychomykose, Ringelflechte des Nagels, Tinea unguium oder Pilzinfektion des Nagels, häufige Erkrankung der Nägel.
onychomykose mit pilzartige nagel infektion zwei füße – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Onychomykose mit pilzartige Nagel Infektion zwei Füße
Onychomykose mit Nagelpilzinfektion zwei Fuß
mit einem lack gegen nagelpilz. behandlung von nagelpilzinfektionen. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Mit einem Lack gegen Nagelpilz. Behandlung von…
Mit einem Lack gegen Nagelpilz.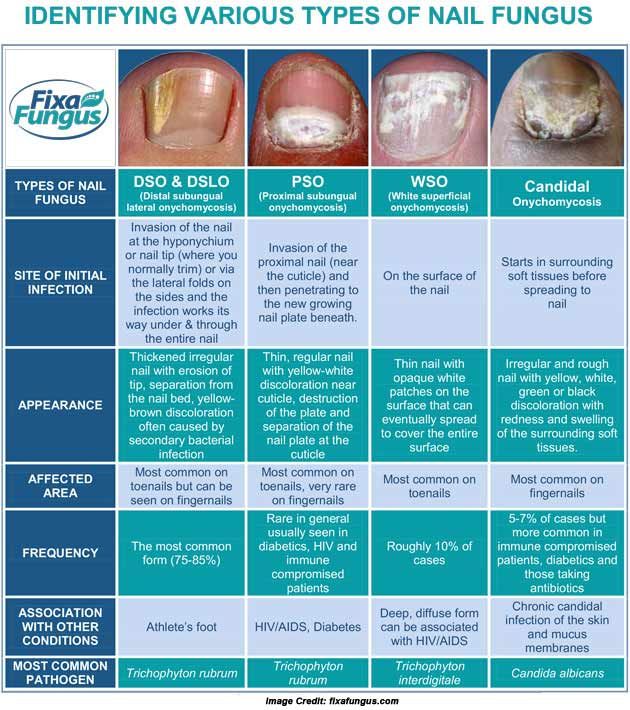 Nagelpilzinfektionsbehandlung.
Nagelpilzinfektionsbehandlung.
pilz trichophyton rubrum, 3d-illustration – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Pilz Trichophyton rubrum, 3D-Illustration
Pilz Trichophyton rubrum, 3D-Illustration mit Makrokonidien, Mikrokonidien und septierten Hyphen. Infiziert Haut und Nägel und verursacht Dermatophytose, insbesondere an Füßen (Tinea pedis) und Onychomykose
zehennagel pilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagel Pilz
pilze wachsen aus den nagelplatten an den füßen. konzept von nagelpilz, haut- und nagelinfektionen. zwei beine mit einem pilz aus nächster nähe im hintergrundlicht. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Pilze wachsen aus den Nagelplatten an den Füßen. Konzept von…
podiatrist behandlung von füßen während des eingriffs – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Podiatrist Behandlung von Füßen während des Eingriffs
zehennagel pilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagel Pilz
Zehennagelpilz
mikroskopisch kleine pilze malassezia furfur mit hefezellen und hyphen. dermatophyten, nagelkratzen oder hautschaben für pilztest. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
dermatophyten, nagelkratzen oder hautschaben für pilztest. – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Mikroskopisch kleine Pilze Malassezia furfur mit Hefezellen und…
gesunde und problematische fußfiguren. haut- oder nagelpilz. paar lustige menschliche bein. medizinische behandlung von derma beinerkrankungen, pilzinfektion. vektor im cartoon-stil. – nail fungus stock-grafiken, -clipart, -cartoons und -symbole
Gesunde und problematische Fußfiguren. Haut- oder Nagelpilz….
nagel pilz-infektion. vor und nach der erneuerung behandlung. – nail fungus stock-grafiken, -clipart, -cartoons und -symbole
Nagel Pilz-Infektion. Vor und nach der Erneuerung Behandlung.
fußhygiene – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Fußhygiene
Hautdesinfektion, Kosmetikerin desinfiziert die Füße von Frauen mit dem Präparat
zehennagel pilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagel Pilz
“Makro-Nahaufnahme eines männlichen Fußes, der mit Zehennagelpilz infiziert ist. Flaches DOF, bitte zoomen Sie hinein, um die Details zu sehen. (Canon 5D Mark II, Adobe RGB) Verwandte Fotos:”
Flaches DOF, bitte zoomen Sie hinein, um die Details zu sehen. (Canon 5D Mark II, Adobe RGB) Verwandte Fotos:”
fuß mit beschädigten nägeln dorsal, kallus, mais, wegen pilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Fuß mit beschädigten Nägeln dorsal, Kallus, Mais, wegen Pilz
Nahaufnahme eines Fußes mit beschädigten Nägeln wegen Pilz. Dorsal-, Hornhaut- und Maisfüße sind mit Keimen infiziert, die Nagelluxationen verursachen.
fuß mit beschädigten nägeln dorsal, kallus, mais, wegen pilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Fuß mit beschädigten Nägeln dorsal, Kallus, Mais, wegen Pilz
Nahaufnahme eines Fußes mit beschädigten Nägeln wegen Pilz. Dorsal-, Hornhaut- und Maisfüße sind mit Keimen infiziert, die Nagelluxationen verursachen.
nahaufnahme der zehennägel mit einem mit pilz infizierten nagel, häufige erkrankungen und infektionen – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Nahaufnahme der Zehennägel mit einem mit Pilz infizierten Nagel,. ..
..
Nahaufnahme von Zehennägeln mit einem pilzinfizierten Nagel, Volkskrankheiten und Infektionen
menschliche zeigefinger mit onychomykose – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Menschliche Zeigefinger mit Onychomykose
ungesunder fuß mit nagelinfektion oder virus – nail fungus stock-grafiken, -clipart, -cartoons und -symbole
Ungesunder Fuß mit Nagelinfektion oder Virus
Person Füße mit Nagelkrankheit oder Infektion. Fuß mit Onychomykose oder Pilz an den Fingern. Medizinische Behandlung und Verfahren. Gesundheits- und Medizinkonzept. Flache Vektordarstellung.
nagelpilz an den händen krankheit. pilzinfektion an nagelhänden, finger mit onychomykose, schäden an menschlichen händen – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Nagelpilz an den Händen Krankheit. Pilzinfektion an Nagelhänden,…
Nagelpilz auf Händen Krankheit. Pilzinfektion an Nägeln, Händen, Finger mit Onychomykose, Schäden an menschlichen Händen
zehennagelpilz auf weiß. wunde zehennagel, nagelpilz aus der nähe – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
wunde zehennagel, nagelpilz aus der nähe – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagelpilz auf weiß. Wunde Zehennagel, Nagelpilz aus der Nähe
Zehennagelpilz auf weiß. Wunder Zehennagel, Nagelpilz aus nächster Nähe
zehennagel pilz – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Zehennagel Pilz
pilze zwischen frau zehen – nail fungus stock-fotos und bilder
Pilze zwischen Frau Zehen
Nahaufnahme der Füße einer Frau mit essbaren Pilzen zwischen den Zehen
von 37
Nail diseases chart: Pictures, symptoms, and treatments
The following are diseases that commonly affect the nails:
Nail psoriasis
Nail psoriasis can cause nail denting or crumbling.
Causes
People living with psoriasis may develop symptoms. It occurs when psoriasis affects the skin of the nail bed or near the nail beds.
Symptoms
Potential symptoms include:
- crumbling nails
- pitting
- changes in color to yellow or brown
- a build-up of skin under the nails
- blood under the nails
- the nail separates from the bed
Treatments
People should talk to their doctor if they live with psoriasis and notice symptoms on their fingernails. Treatments may include:
Treatments may include:
- strong corticosteroid cream
- tazarotene, to treat pitting and discoloration
- calcipotriol, to treat build-up under the nail
- injections of corticosteroids
- laser treatment
Learn more about nail psoriasis here.
Brittle splitting nails
Brittle splitting nails, or onychoschizia, is a common issue that dermatologists see. The condition can cause brittle, soft, splitting, or thin nails.
Causes
Common causes of brittle nails are repeatedly wetting and drying the nails. Though less common, other causes may include iron deficiency or underlying illness.
Symptoms
The most common symptom is that the nails break easily. The American Osteopathic College of Dermatology state people can often tell if the cause is internal, as the condition affects both fingernails and toenails. If there is an external cause, symptoms will typically only affect the fingernails.
Treatments
The most common remedy is for people to use moisturizer, and keep the nails protected from chemicals and repeated exposure to water.
Onychogryphosis
Onychogryphosis is a condition where the nail becomes overgrown and thick, often affecting the big toe. It can cause one portion of the nail to grow longer than the other part.
Causes
Potential causes of onychogryphosis include:
- genetics
- injury
- circulation issues
- psoriasis
- ichthyosis
Symptoms
When a person has onychogryphosis, the nail grows very thick. In other cases, a portion of the nail may grow larger than the other part. The growth can resemble a ram’s horn, so people often refer to it as Ram’s horn nails.
Treatments
A person will likely need to see a podiatrist or dermatologist, to help cut the nail. They may be able to show the person how to do this at home. People may need several trips to the doctor to cut it back and let it regrow. The only permanent treatment is the removal of the nail bed.
Ingrown toenails
An ingrown toenail can cause pain and swelling, and in some cases, they can become infected.
Causes
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, genetics may play a role in the development of ingrown toenails. Also, there are other potential causes, including:
- not keeping nails trimmed
- wearing tight socks or shoes
- physical injury
Symptoms
Symptoms can include:
- swelling and tenderness
- redness
- soreness
- pus
Treatments
Treatments may include:
- surgery
- soaking the nail in warm water 3 to 4 times each day
- wearing comfortable shoes
- keeping the foot dry
- taking acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain
Learn more about ingrown toenails here.
Nail fungal infections
Nail fungal infections are a common condition that causes the nails to become thick, discolored, and easier to break. Nail fungus is more common in the toes than fingers.
Causes
Several different types of molds and fungus can affect nails. They grow when a crack or break traps fungi between the nail and the nail bed.
They grow when a crack or break traps fungi between the nail and the nail bed.
Sweat, athlete’s foot, and salon manicures and pedicures can put people at higher risk of nail fungal infections.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- thick nails
- discolored nails that are brown, yellow or white
- fragile or cracked nails
Fungus under the nails often is not painful.
Treatments
Remedies typically involve the use of antifungal medication. People may need a prescription, or a doctor can fully remove the nail.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), it can take more than a year for successful treatment.
Learn more about nail fungal infections.
Onycholysis
Onycholysis is when the toe or fingernail painlessly separates from the nail bed. It typically occurs slowly over time and could result from an underlying health condition or injury.
Causes
The most common cause is from local injury to the nail.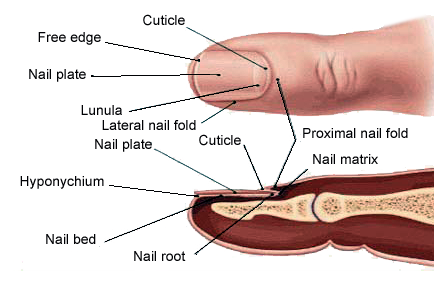 Other triggers include:
Other triggers include:
- excessive filing
- exposure to chemicals
- allergic contact dermatitis
- submersion in water
Psoriasis, fungal infections, and reactions to certain medications are also common causes.
Symptoms
The main symptom of onycholysis is the separation of the nail from the nail bed. This can result in discoloration of the nail, turning it green, yellow, or opaque. It can also cause additional skin tissue under the nail, nail pitting, nail thickening, or bending of the nail edges.
Treatments
Management varies based on the exact cause of the onycholysis. Some potential treatments could include:
- treating psoriasis with oral or other medications
- treating iron deficiency
- oral antifungal treatments
Prevention is also important. Harvard Health Publishing recommend people take the following steps:
- keeping their nails trimmed
- using rubber gloves when submerging hands in water for long periods
- avoiding harsh chemicals
- treating underlying conditions
Learn more about onycholysis here.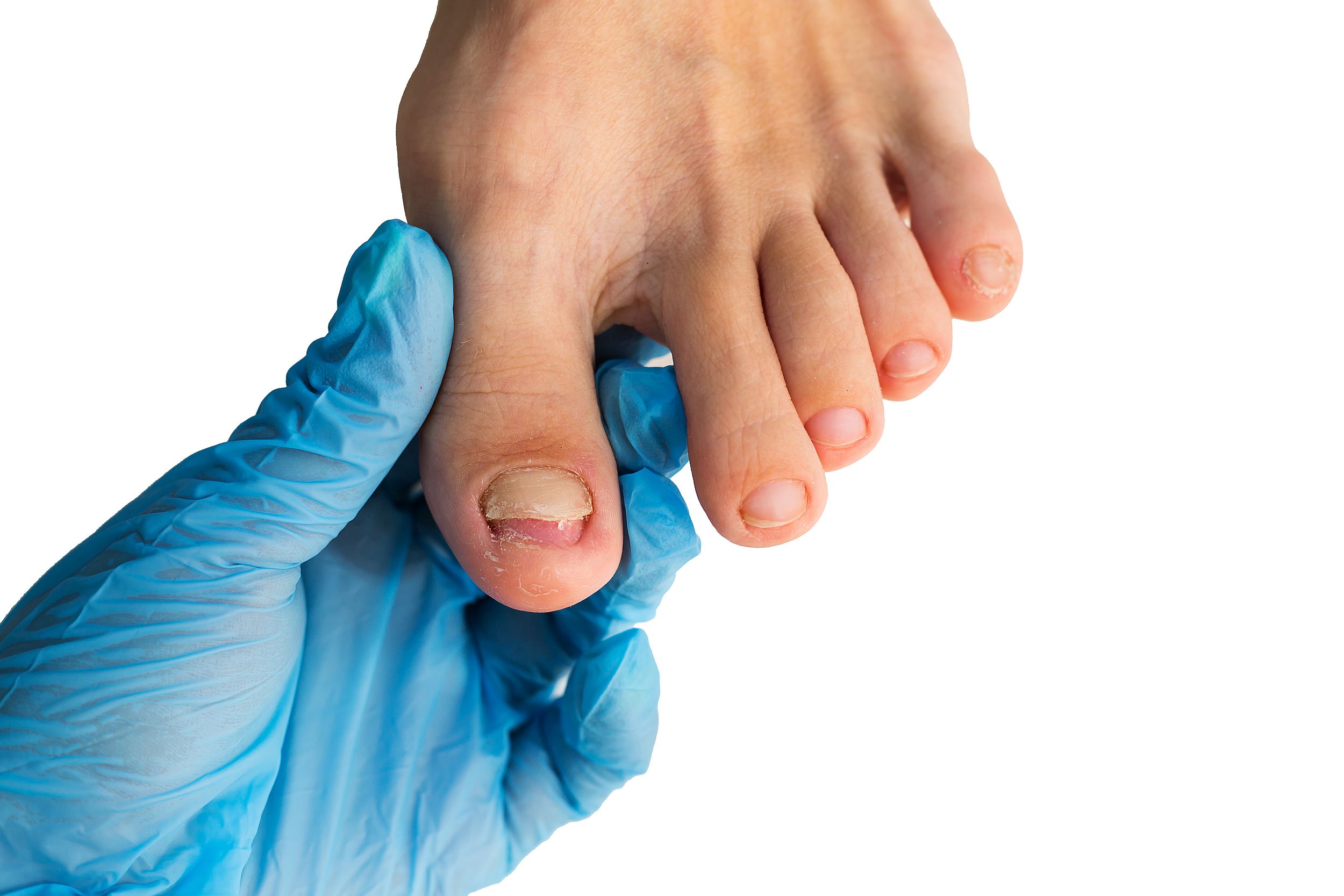
Paronychia
Paronychia is an infection that causes redness and swelling around the edges of a nail bed.
Causes
There are two types of paronychia: acute and chronic. Acute paronychia occurs when there is an infection due to direct or indirect trauma to the cuticle or nail fold. Chronic paronychia is often the result of allergens or irritants.
Symptoms
Acute paronychia symptoms can include:
- swelling
- pain
- redness
- fever and gland pain in severe cases
- yellow pus
Chronic paronychia often starts on one nail and spreads to others. The nail folds may have the following symptoms:
- redness
- pain
- swelling
- yellow or green pus
- lifting of the nail from the bed
- tenderness
Treatments
Treatments vary based on the cause of the paronychia. For acute cases, the options may consist of:
- warm compresses
- topical antibiotics
- corticosteroids
- oral antibiotics
- surgical incision and drainage, in severe cases
To manage chronic paronychia, a doctor will typically treat the underlying cause of the inflammation.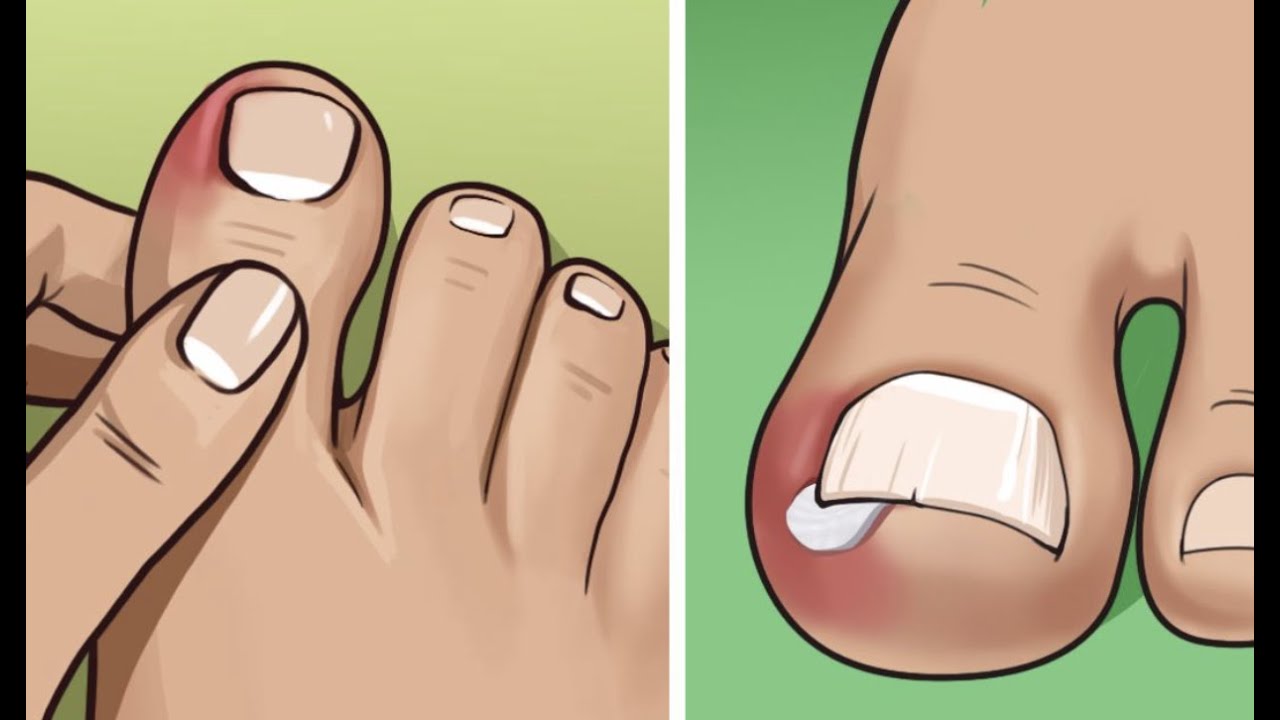 This can include avoiding allergens and irritants. Treatment can take several weeks to months.
This can include avoiding allergens and irritants. Treatment can take several weeks to months.
Learn more about paronychia here.
People should talk to their doctor if they notice changes to their nails. A medical professional can diagnose the condition and recommend suitable treatment.
If someone undergoes treatment for a nail disease and there is no improvement, or new symptoms develop, they should seek medical advice.
Many diseases can affect the nails. Treatments typically involve preventing further nail damage and treating the underlying condition.
Green nail syndrome – causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
August 06, 2021
Almost every one of us faced different problems with nails. Ribbing, delamination, discoloration are the most common of them. Often the nail turns green – this means that one of the infections has got into the nail plate: a virus, bacterium or fungus. The treatment in each case is different, so you need to “know the enemy by sight” and be able to fight him.
The treatment in each case is different, so you need to “know the enemy by sight” and be able to fight him.
Causes of green nail syndrome
The most common causes of green nails are:
Traumatic injuries
As a result of microtrauma or bruising, blood accumulates under the nail, soaking the soft tissues. At first, the skin becomes purple-cyanotic, with time it becomes green, and then yellowish. This is a natural process that should not be interfered with. If the cause of the problem is an injury, over time, the nail plate will again acquire a uniform healthy shade.
Fungi of the subspecies Candida
They do not damage the nail plate itself, but parasitize under it, causing a whole range of unpleasant symptoms, including greening of the nail. The cause of infection is a weakened immune system, because this fungus in a small amount always lives on the mucous membranes of the body. When natural defenses fail, pathogens become active.
Fungi of the genus Aspergillus
They multiply on the surface of the nail, causing visible damage, discoloration and an unpleasant smell.
Bacterial infections
One of the most common pathogens is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This is the most dangerous pathogen that can even lead to death, spreading throughout the body.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Pseudomonas – the most common “culprit” of green nails
Pseudomonas live in the external environment, the human body is in constant contact with them. In the case of a weakened immune system, pathogen cells are activated, which leads to the development of green nail syndrome and a number of other problems. When Pseudomonas enters the nail cavity, it begins to multiply, forming a greenish-blue pigment, as a result of which the nail plate turns marsh-green. Spots can occupy both the entire nail and part of it, localized on one or more fingers.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa develops in the nail plate in two ways:
- Only in the upper part. This is visible to the naked eye: green spots are located in the outer layers of the nail, without affecting the soft tissues and without being accompanied by other symptoms.
 A person has no pain, onycholysis. To fix the problem in this case, it is enough to cut off the top layer of the nail.
A person has no pain, onycholysis. To fix the problem in this case, it is enough to cut off the top layer of the nail. - Getting into deep soft layers under the plate. In this situation, in addition to greening, burning, itching, suppuration, exfoliation of the nail, and the spread of infection to the cuticle zone join the symptoms of the pathology. Bacteria multiply rapidly – it takes 2-3 days for Pseudomonas to get into the blood.
Causes of Pseudomonas getting into the nail plate
The fact that the bacterium is on the surface of a healthy nail will not turn green. In the vast majority of cases, Pseudomonas infection occurs when extended nails are detached and air pockets form under them. Once there, pathogen cells begin to multiply actively. The problem arises due to non-compliance with the technological conditions of extension:
- insufficient degreasing of the nail plate before the procedure;
- ignoring the application of a primer that provides a sufficient level of adhesion of natural and artificial nails;
- insufficient treatment of the nail with a buff, as a result of which areas with a natural shine remain on the plate;
- non-compliance with the technology of correction of extended nails and incomplete removal of the old layer of the nail, as a result of which air pockets remain in place, and a new layer of gel is simply “poured” from above.

Also, risk factors that can cause Pseudomonas aeruginosa to enter the nail plate are:
- Detachment of the nail, inflammation of the periungual fold, damage to the cuticle, destruction of the nail plate under the influence of external or internal factors.
- Prolonged exposure to moisture on the nail plate.
- Prolonged wearing of extended nails.
- Regular contact with aggressive chemicals, the ground without protective gloves.
- Permanent trauma to the nail plate.
- Contact with Pseudomonas aeruginosa carriers.
Pathology treatment methods
Elimination of the problem of green nails is carried out in two ways and depends on the stage of development of the pathology.
Superficial stage
If there are small superficial green spots on one or more nails of the client, proceed as follows:
- Treat hands with antiseptic.
- Remove the artificial material with a cutter or file to the natural nail plate.
 Here, the MAX manicure vacuum cleaner will be an excellent assistant – it does its job perfectly, protecting the master and the client from microparticles of harmful substances and materials getting into the lungs and eyes. The company manufactures professional accessories used by thousands of professionals around the world.
Here, the MAX manicure vacuum cleaner will be an excellent assistant – it does its job perfectly, protecting the master and the client from microparticles of harmful substances and materials getting into the lungs and eyes. The company manufactures professional accessories used by thousands of professionals around the world. - Spread a paper towel or napkin on the table, file down the affected area with a disposable file to a healthy layer. If the client experiences pain, the manipulation must be stopped. The pain indicates that the pseudomonad has penetrated into the deep layers of the nail, and one cannot do without consulting a dermatologist.
- Throw away the file, napkin, treat the client’s hands and your own with an antiseptic.
- Take a cotton pad, moisten it with plenty of antiseptic, apply to the affected area.
- Additionally, you can treat the problem area with a slice of fresh lemon. Acid neutralizes Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and also neutralizes the remnants of green in the nail plate.

- After all disinfecting measures, it is necessary to apply an acid primer to the nail and wait for it to dry completely.
- Upon completion of the procedure, a new decorative coating can be applied in compliance with all antiseptic treatment measures and relevant technologies.
Some manufacturers produce preparations intended for salon treatment of nail plates affected by Pseudomonas. They have proven effectiveness, so experts recommend that all manicure masters acquire such tools.
Deep stage
Antibacterial treatment is indispensable in this case. It should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor – a person may have an individual intolerance to the drug. If the case is complex, both topical antibiotics and oral medications will be prescribed. The doctor will make the correct treatment and give recommendations that will make the therapy as effective as possible.
On average, drug treatment lasts 2-3 weeks. In advanced cases, therapy lasts up to 4 months. During this period, it is necessary to regularly visit a doctor who will monitor the dynamics of treatment, if necessary, adjust the prescribed drugs.
During this period, it is necessary to regularly visit a doctor who will monitor the dynamics of treatment, if necessary, adjust the prescribed drugs.
It is important to understand that green nail syndrome can be caused not only by bacteria, but also by fungi. That is why it is so important to contact a dermatologist – he will conduct an examination, take a nail sample for analysis, identify the cause of the development of the pathology, and then prescribe treatment. It is not recommended to purchase antifungal and antibacterial drugs on your own: they can not only be ineffective, but even harm the body.
Folk remedies
There are a number of folk remedies that will help you deal with Pseudomonas aeruginosa faster. It is recommended to use them in combination with medical treatment and only after prior consultation with a doctor:
Rubbing tea tree oil into the affected nail. The substance has a proven bactericidal effect.
Alcohol compresses. They quickly and effectively kill bacteria in the upper layers of the nail plate.
Vinegar bath, 1 tablespoon of acid in 250 ml of warm water. The procedure should be performed 4 times a day for 5 minutes.
Preventing nail problems
Treating green nail syndrome is not an easy task. Therefore, it is easier to follow the basic principle of preventive medicine and prevent the problem, rather than deal with it.
There are a number of general recommendations to help avoid fungal or bacterial infection of the skin and nail plate:
- Use only your own shoes and do not wear someone else’s, even at a party.
- Do not walk barefoot in public places – beaches, swimming pools, changing rooms, etc.
- A person struggling with Pseudomonas aeruginosa or fungal infection of the nail should not go home without shoes. He should also have his own hygiene products – towels, nail files, scissors.
- Wear comfortable footwear that will keep your feet from sweating.
- Regularly visit the manicurist and monitor the condition of the nails.

You should take a responsible approach to choosing a nail master. By themselves, healthy nails are a sufficient protective barrier to prevent bacteria and fungi from entering them. It is also recommended to regularly inspect the nail plates for visible changes – especially if a person constantly wears a decorative coating. In case of the slightest suspicion of the presence of Pseudomonas or other problems, you should contact a specialized medical specialist – a podiatrist or dermatologist.
Collection of material for sowing parasitic fungi in Khabarovsk
Taking material for sowing mushrooms with onychomycosis is an opportunity not only
to establish the fact of infection, but also to determine the type of pathogen. Analysis
helps to distinguish nail fungus from other diseases with similar
symptoms, but also to determine the type of onychomycosis, the correct treatment regimen.
The fact is that drugs that treat yeast often
ineffective against dermatomycetes and vice versa. About the features of the procedure
About the features of the procedure
a Podiatry Lab specialist will tell you.
What is onychomycosis
Spores are introduced into the nail plates, gradually along it
spread, go into the deep layers of the skin, can get into
blood flow. The fungus has the following effect on the nails:
- destroys collagen – a protein that holds cells together, makes nails
durable; - damages keratin, the protein that makes up nails;
- inhibits immune reactions, which allows the fungus to resist
immunity; - produces substances that contribute to the appearance of corns and
hyperkeratosis; - reduces local immunity, which often leads to reproduction
papillomaviruses, the formation of warts on the soles.
What does onychomycosis look like
What do parasitic fungi cause
Nail fungus (onychomycosis) is a highly contagious disease.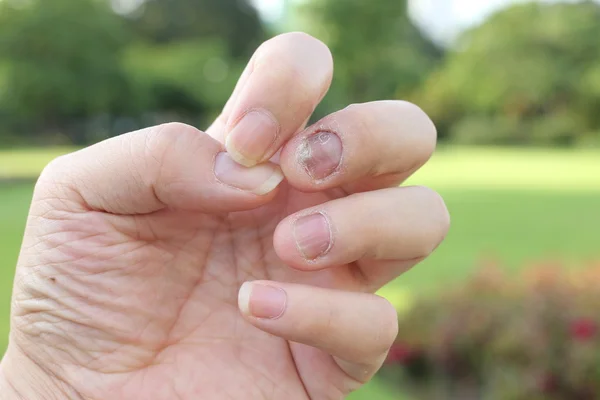
You can infect your feet if you walk barefoot on the floor in
public places (pool, sauna, etc.), use someone else’s
shoes, towel, nail scissors. His triggers are
yeast-like fungi Candida, dermatomycetes, filamentous
non-dermatomycetes.
Complications of onychomycosis
It is important to detect and treat the disease in time. On one’s own
onychomycosis will not disappear. Fungi penetrate the nail plate and begin
destroy her. Nails change color, deform, thicken. They
become brittle, irregularities, cracks, furrows appear.
Over time, the nail plates begin to crumble, peel off, poorly
regrow due to damaged matrix. Periungual ridges, area in
area of the matrix becomes inflamed. If the immune system is weak, as well as against the background
endocrine diseases mycosis is able to spread throughout the body.
Why choose PodiatryLab?
Cost of services
Qualification of doctors
Choice of services
Nail fungus visual
Laboratory diagnostics
Diagnosis of onychomycosis is based on:
- Clinic physical symptoms
- Microscopy – examination of a sample of infected tissue under
microscope. The procedure helps to determine the presence of fungus
The procedure helps to determine the presence of fungus - Cultural research – sampling of material for sowing with isolation
fungal culture to determine the type of pathogen
What material is used for inoculation
A piece of infected nail and skin is taken for analysis:
Distal subungual form. For research, they take not only a piece
infected nail, but also material from under it, from the nail bed.
They also capture the area of the unchanged nail plate, since on
border with the damaged area of the nail are the most active pathogens
matrix where it is formed) – a nail biopsy is performed when
taking a sample of the skin under the nail
How to prepare for the examination
To avoid false results, to the sampling of material for sowing mushrooms
you need to prepare properly:
- Antimycotics (tablets, creams) should not be taken before the procedure.
 If
If
this was done, the collection of material is transferred – for 4-7 days with
using an ointment, for 2-4 weeks when using systemic drugs
(tablets) - The day before the test, do not wash your fingers with antibacterial and
disinfectants - If there is varnish on the nails, remove it a few days before the procedure
How the procedure works
Before doing a cultural study, microscopy is prescribed,
which will determine the presence of the pathogen. If the diagnosis is confirmed or
doctor doubts as a result of microscopy, Podyatry Lab specialist
inoculates the material on a standard Sabouraud medium.
Collection of material for analysis
A Podyatry Lab specialist uses a scalpel to scrape off the top layer of the epithelium or nail plates. Nippers can be used to take a sample of the nail. The material is placed in a test tube filled with saline. The sample is delivered to the laboratory for testing.
The sample is delivered to the laboratory for testing.
Microscopy
- Tissue samples (pieces of the nail, subungual layers) are placed in
centrifuge tube - A 15-20% solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or hydroxide is poured into the container
sodium (NaOH) - The tube is left overnight at room temperature
- Sediment is captured with a special pipette and transferred to a subject
glass - The sample is covered with a coverslip and viewed under a microscope.
- If the tissue is infected with a fungus, the specialist detects mycelium in the form
threads – thick, thin, branched, even, etc. Under a microscope
budding spores or budding mycelium are also visible - To determine the type of fungus, sowing on a nutrient medium is prescribed.

Fungal inoculation
Direct microscopy can give both false positive and
false negative results. Moreover, it cannot be used
determine the type of fungus. Therefore, cultural
research – sowing the material on a standard Saburo medium.
The nutrient medium is rich in substances that are necessary for growth
bacteria and fungi – vitamins, carbohydrates, amino acids, minerals
salts. Antibiotics are often added (cycloheximide, penicillin,
streptomycin), which improve the isolation of pathogens, inhibit the growth
mushrooms that penetrate from the air. Some mushrooms do not grow with
cycloheximide, therefore, two options for sowing are done: with this antibiotic
and without it.
The procedure consists of 3 steps. Let’s consider each separately.
Preparation of culture medium
The culture medium is supplied in a special vial. Specialist:
- Loosen the lid and heat the container in a water bath for 45
minutes - Closes the lid and stirs the contents
- Flask for 15 sec.
 left at room temperature, then
left at room temperature, then
transferred to a thermostatically controlled water bath, which maintains
temperature 45-50°С - This is where the vial will remain until use
- Before sowing, its contents are mixed and poured into bowls.
Inoculation and incubation
Samples are placed in the bowl immediately after scraping. Fungal growth is
at a temperature of 30 ° C. Incubation time depends on the type of fungus.
Some types of molds, including dermatophytes, grow slowly
– 2-3 weeks.
Getting results
When the incubation ends, the specialist evaluates the results.
The determination of the microorganism is carried out using a microscopic
studies of the grown culture or reseeding on selective media.
The author of this article:
Pryanishnikov Roman Vyacheslavovich
Traumatologist-orthopedist, chief physician of the PodiatryLab clinic
Operative PodiatryLab
Indications
- Suspected onychomycosis
- Yellow, brown color of the nail plate
- Deformation of the nail (cracks, furrows, thinning)
- Thickening of the nail plate
- Chipping of the nail plate
- Stains, stripes on the nails
- Separation of the nail plate from the bed
- Increased fragility of nails
9028 5 Inflammation of tissues around the nail
Contraindications
- Internal or external use of antimycotics before the procedure
- Treatment of nails with antibacterial agents for several hours of sampling for culture
Possible test results
According to the cultural study, the dermatologist determines the type
pathogen and prescribe treatment.

 A person has no pain, onycholysis. To fix the problem in this case, it is enough to cut off the top layer of the nail.
A person has no pain, onycholysis. To fix the problem in this case, it is enough to cut off the top layer of the nail.
 Here, the MAX manicure vacuum cleaner will be an excellent assistant – it does its job perfectly, protecting the master and the client from microparticles of harmful substances and materials getting into the lungs and eyes. The company manufactures professional accessories used by thousands of professionals around the world.
Here, the MAX manicure vacuum cleaner will be an excellent assistant – it does its job perfectly, protecting the master and the client from microparticles of harmful substances and materials getting into the lungs and eyes. The company manufactures professional accessories used by thousands of professionals around the world.
 The procedure helps to determine the presence of fungus
The procedure helps to determine the presence of fungus If
If
 left at room temperature, then
left at room temperature, then