Do gallstones go away by themselves. Gallstones: Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Self-Resolution Possibilities
How are gallstones diagnosed. What treatment options are available for gallstones. Can gallstones go away on their own. What are the risks and benefits of gallbladder removal surgery. How effective are nonsurgical therapies for gallstones. What lifestyle changes can help manage gallstone symptoms.
Understanding Gallstones: Formation and Symptoms
Gallstones are solid, pebble-like deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. These stones can vary in size and composition, typically consisting of cholesterol or bile pigments. While many people with gallstones remain asymptomatic, others may experience severe pain and complications.
Common symptoms of gallstones include:
- Sudden, intense pain in the upper right abdomen
- Pain that radiates to the back or right shoulder
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills (if infection is present)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Do gallstones always cause symptoms? Not necessarily. Many people have gallstones without ever experiencing discomfort, a condition known as “silent gallstones.” However, when symptoms do occur, they can be quite severe and may require medical attention.

Diagnosing Gallstones: Tests and Procedures
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective gallstone management. Healthcare providers employ various methods to confirm the presence of gallstones and assess their impact on the patient’s health.
Physical Examination and Blood Tests
The diagnostic process often begins with a thorough physical examination. A healthcare provider may check for signs of jaundice and abdominal tenderness. Blood tests can reveal elevated liver enzymes or bilirubin levels, indicating potential gallstone-related complications.
Imaging Techniques
Several imaging methods are used to visualize gallstones and evaluate the gallbladder’s condition:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive, painless procedure uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures. It is often the first-line imaging test for suspected gallstones.
- CT Scan: Computed tomography provides detailed cross-sectional images of the abdominal organs, helping to identify gallstones and any associated complications.
- ERCP: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography combines endoscopy with X-ray imaging to examine the bile ducts and pancreatic duct. This procedure can both diagnose and treat certain gallstone-related issues.
How accurate are these diagnostic methods? Ultrasound has a high sensitivity and specificity for detecting gallstones, with accuracy rates often exceeding 95%. CT scans and ERCP provide additional information about the biliary system and can help identify complications such as bile duct obstruction.

Treatment Options for Gallstones: From Watchful Waiting to Surgery
The management of gallstones depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. Treatment approaches range from conservative monitoring to surgical intervention.
Watchful Waiting: When Observation is Appropriate
For asymptomatic gallstones or those causing minimal discomfort, healthcare providers may recommend a “watchful waiting” approach. This involves monitoring the condition without immediate intervention, as many gallstone episodes resolve on their own.
Is watchful waiting always safe? While it can be appropriate for some patients, it’s crucial to remain under medical supervision and report any changes in symptoms promptly. Watchful waiting is not recommended for patients with severe or frequent symptoms, as this may increase the risk of complications.
Nonsurgical Therapies: Dissolving and Breaking Down Gallstones
Several nonsurgical options aim to eliminate gallstones without removing the gallbladder:
- Oral Dissolution Therapy: Medications like ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursodiol) can help dissolve small cholesterol gallstones over time.
- Shock Wave Lithotripsy: High-frequency sound waves are used to break gallstones into smaller fragments, which can then pass through the bile ducts more easily.
- Endoscopic Stone Removal: During an ERCP procedure, small gallstones can sometimes be removed from the bile duct using specialized instruments.
How effective are these nonsurgical treatments? While they can be successful in some cases, their long-term efficacy is limited. Recurrence rates are high, and these methods are generally not recommended as first-line treatments for most patients with symptomatic gallstones.
Surgical Intervention: Gallbladder Removal
Cholecystectomy, or surgical removal of the gallbladder, is the most definitive treatment for gallstones. This procedure eliminates the risk of future gallstone formation and provides long-term relief for most patients.
Two main surgical approaches are used:
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A minimally invasive procedure using small incisions and a camera-guided technique. This is the most common method, offering faster recovery times and less postoperative pain.
- Open Cholecystectomy: A traditional surgical approach involving a larger incision. This method may be necessary in complex cases or when laparoscopic surgery is not feasible.
What are the risks and benefits of gallbladder removal? While cholecystectomy is generally safe and effective, it does carry some risks, including infection, bleeding, and bile duct injury. However, the benefits of permanent gallstone relief often outweigh these potential complications for most patients with recurrent or severe symptoms.
Can Gallstones Go Away on Their Own?
One of the most common questions patients ask is whether gallstones can resolve without medical intervention. The answer is not straightforward and depends on various factors.
Do gallstones ever dissolve naturally? In some cases, small gallstones may indeed pass through the bile ducts on their own or dissolve over time. This is more likely to occur with cholesterol stones, which can sometimes respond to changes in diet and body chemistry.
However, it’s important to note that spontaneous resolution of gallstones is not guaranteed and may not be a reliable solution for everyone. Factors influencing the likelihood of self-resolution include:
- Stone size and composition
- Number of stones present
- Overall gallbladder health
- Patient’s diet and lifestyle
While waiting for gallstones to resolve on their own may be tempting, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on individual circumstances.
Lifestyle Modifications and Dietary Approaches for Gallstone Management
While lifestyle changes alone may not cure existing gallstones, they can play a significant role in managing symptoms and potentially reducing the risk of future stone formation.
Dietary Considerations
A gallstone-friendly diet typically focuses on:
- Reducing intake of saturated and trans fats
- Increasing consumption of fiber-rich foods
- Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition
- Avoiding rapid weight loss, which can increase the risk of gallstone formation
Can specific foods help prevent or manage gallstones? While no single food can guarantee prevention, some studies suggest that certain dietary components may be beneficial:

- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish, flaxseed, and walnuts, these may help reduce inflammation and improve gallbladder function.
- Vitamin C: Some research indicates that vitamin C supplementation may lower the risk of gallstone formation.
- Coffee: Regular coffee consumption has been associated with a reduced risk of gallstones in some studies.
Exercise and Weight Management
Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy body weight are crucial aspects of gallstone prevention and management. Exercise can help improve overall metabolic health and reduce the risk factors associated with gallstone formation.
How much exercise is recommended for gallstone prevention? While individual needs may vary, general guidelines suggest aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Complementary and Alternative Approaches to Gallstone Management
Some patients explore complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) approaches to manage gallstone symptoms or support conventional treatments. While scientific evidence for many of these methods is limited, some people report finding relief through:

- Herbal remedies: Certain herbs like milk thistle, dandelion root, and artichoke leaf are believed to support liver and gallbladder health.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique may help alleviate pain and improve gallbladder function in some individuals.
- Castor oil packs: Applied externally over the gallbladder area, these are thought to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Are alternative therapies effective for gallstone treatment? While some patients report positive experiences with CAM approaches, it’s important to note that these methods are not scientifically proven to cure or prevent gallstones. Always consult with a healthcare provider before trying any alternative treatments, especially if you have diagnosed gallstones or ongoing symptoms.
Living Without a Gallbladder: What to Expect After Cholecystectomy
For many patients, gallbladder removal surgery is the most effective long-term solution for gallstone-related problems. However, adapting to life without a gallbladder can require some adjustments.

Digestive Changes
After gallbladder removal, bile flows directly from the liver into the small intestine. This can lead to some digestive changes, including:
- Diarrhea or loose stools, especially after fatty meals
- Difficulty digesting certain fats
- Occasional bloating or gas
Do these digestive issues persist long-term? For most people, these symptoms are temporary and resolve within a few weeks to months after surgery. However, a small percentage of patients may experience ongoing digestive changes that require dietary modifications or medical management.
Dietary Adaptations
To minimize post-cholecystectomy symptoms, patients may benefit from:
- Gradually reintroducing fats into the diet
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals
- Avoiding trigger foods that cause discomfort
- Increasing fiber intake to help regulate bowel movements
Is a special diet necessary after gallbladder removal? While there’s no one-size-fits-all diet for post-cholecystectomy patients, many find that making mindful food choices and paying attention to their body’s responses helps them adjust to life without a gallbladder.

Preventing Future Gallstone Formation: Long-term Strategies
Even after successful treatment of gallstones, it’s important to adopt habits that can reduce the risk of future stone formation, especially for those who have not undergone gallbladder removal.
Risk Factor Management
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing gallstones. Addressing these can help minimize future risks:
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Avoiding rapid weight loss or extreme dieting
- Managing conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol
- Staying physically active
- Limiting alcohol consumption
Can gallstones be prevented entirely? While it’s not always possible to prevent gallstones completely, especially if there’s a genetic predisposition, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of stone formation.
Regular Health Monitoring
For individuals with a history of gallstones or those at high risk, regular check-ups and monitoring can be beneficial. This may include:
- Periodic ultrasound examinations
- Blood tests to assess liver function and cholesterol levels
- Discussions with healthcare providers about any new or changing symptoms
How often should follow-up appointments be scheduled? The frequency of monitoring will depend on individual risk factors and medical history. Healthcare providers can offer personalized recommendations based on each patient’s specific situation.
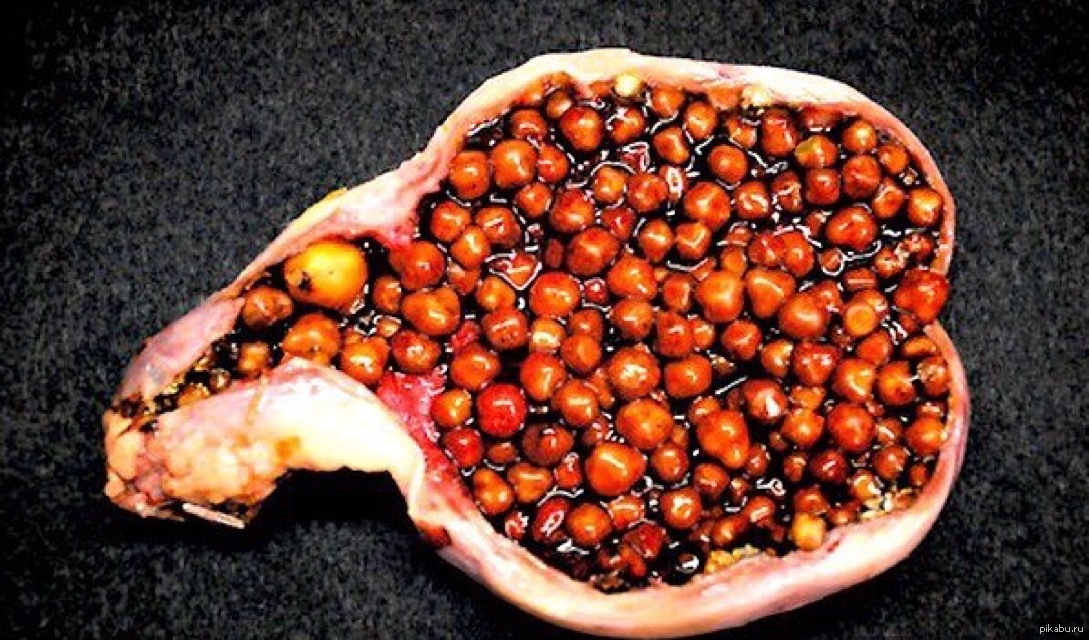

In conclusion, while gallstones can be a painful and disruptive condition, numerous treatment options and management strategies are available. From watchful waiting to surgical intervention, the approach to gallstone management should be tailored to each individual’s needs and circumstances. By understanding the nature of gallstones, exploring available treatments, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, patients can work towards effective management and prevention of this common digestive issue.
Gallstones Diagnosis, Tests, & Treatments
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
- How Do I Know if I Have Gallstones?
- What Are the Treatments for Gallstones?
- Conventional Medicine for Gallstones
- Gallstones and Watchful Waiting
- Nonsurgical Therapy for Gallstones
- Surgery to Remove the Gallbladder
- More
If your symptoms suggest a gallstone problem, your doctor might first examine your skin for jaundice, and then feel your abdomen to check for tenderness. A blood test may reveal evidence of an obstruction.
Because other digestive problems, such as an infection of the duct, can produce symptoms similar to those of a gallstone attack, the doctor may also run other tests to determine if gallstones are in fact the culprit.
The most common technique is an ultrasound exam. This quick, painless procedure uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures of the gallbladder, bile duct, and their contents. CT scans are also sometimes done to look at the anatomy of your internal organs.
CT scans are also sometimes done to look at the anatomy of your internal organs.
A more complicated test may be used if the doctor suspects that a gallstone is lodged in a bile duct. Commonly known by the acronym ERCP, this test allows the doctor to look at the bile duct through a small flexible tube called an endoscope. The doctor sprays the back of the patient’s throat with an anesthetic drug to prevent gagging, sedates the patient, and passes the endoscope into the mouth, through the stomach, and into the area of the small intestine where the bile duct enters. Dye is injected through the tube and into the bile duct, and then the doctor takes X-rays. Stone removal can be done during this procedure as well. The procedure takes about an hour.
In most cases, treatment of gallstones is considered necessary only if you are having symptoms. Of the various conventional treatments that are available, surgical removal of the gallbladder is the most widely used. Some alternative treatments have also been found to be effective in alleviating the symptoms of troublesome gallstones.
When deciding what course of action to take for symptomatic gallstones, doctors usually choose from among three main treatment options: Watchful waiting, nonsurgical therapy, and surgical removal of the gallbladder.
Though a gallstone episode can be extremely painful or frightening, almost a third to half of all people who experience an attack never have a recurrence. In some cases, the stone dissolves or becomes dislodged and thereby resumes its “silence.” Because the problem may solve itself without intervention, many doctors take a wait-and-see approach following the initial episode.
Even when the patient has had repeated gallstone episodes, the doctor may postpone treatment or surgery because of other health concerns. If your surgery has been delayed, you should remain under a doctor’s care and report any recurrences of gallstone symptoms immediately.
If you are unable or unwilling to go through surgery for a gallstone problem that requires treatment, your doctor may recommend one of several noninvasive techniques.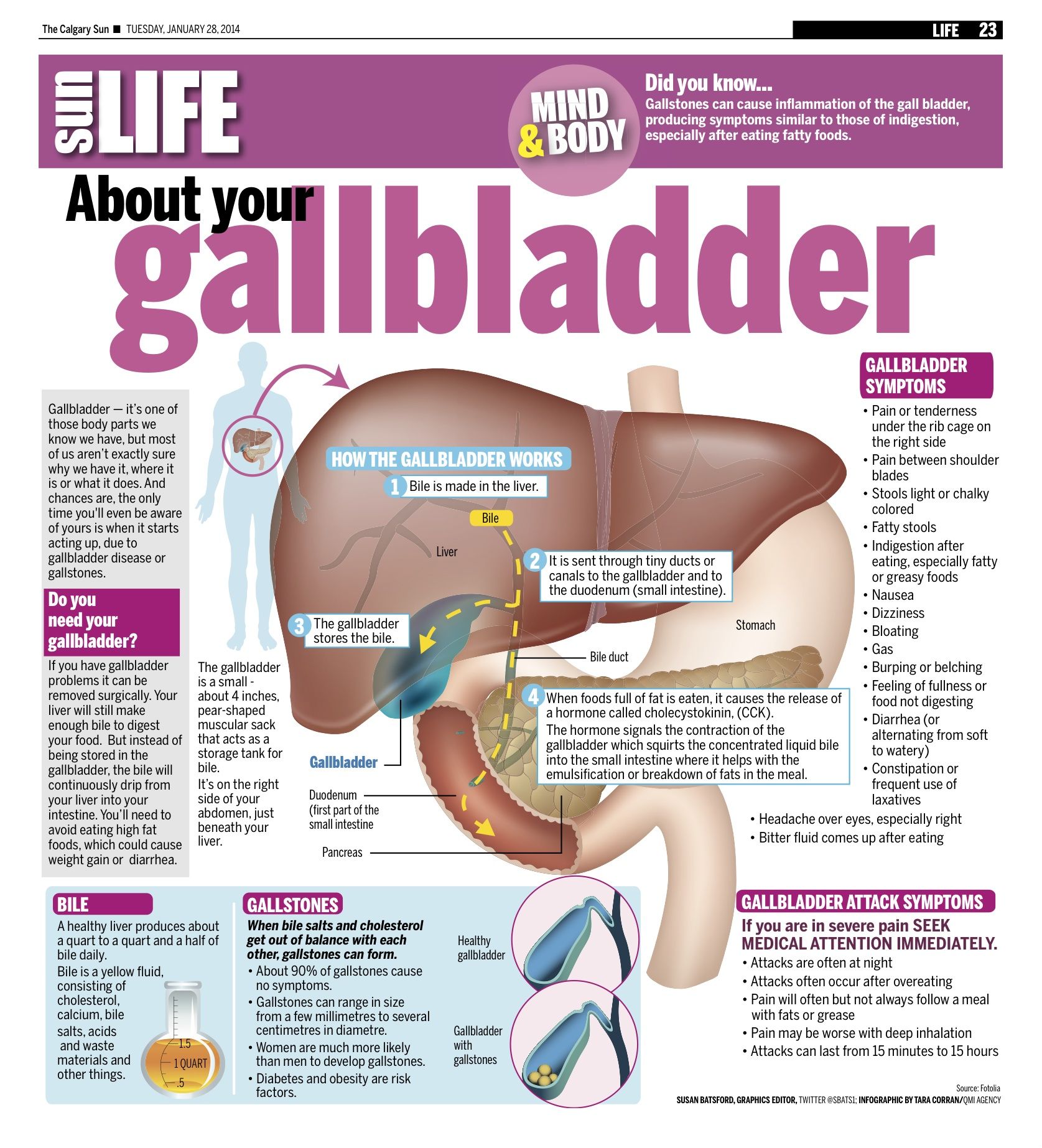 Note that though these methods may destroy symptom-causing gallstones, they can do nothing to prevent others from forming, and recurrence is common.
Note that though these methods may destroy symptom-causing gallstones, they can do nothing to prevent others from forming, and recurrence is common.
Some gallstones can be dissolved through the use of a bile salt, although the procedure can be used only with stones formed from cholesterol and not from bile pigments. The drug Actigall (ursodiol) is taken as a tablet; depending on its size, the gallstone may take months or even years to go away. Because some stones are calcified, this treatment often doesn’t work.
Another nonsurgical technique, shock wave therapy, uses high-frequency sound waves to fragment the stones. Bile salt is administered afterward to dissolve small pieces. This therapy is rarely used.
Doctors can also attempt to remove gallstones during an ERCP. During the procedure an instrument is inserted through the endoscope to attempt removal of the stone.
While these therapies may work for some, all of the above nonsurgical therapies are usually unsuccessful long term (since recurrence is common) and are rarely advised in clinical practice.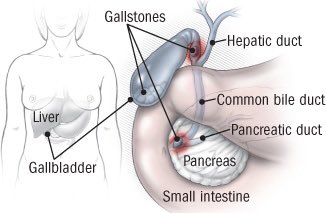
While the gallbladder serves an important function, it is not essential for a normal, healthy life. When gallstones are persistently troublesome, doctors often recommend removing the organ entirely. This operation is considered among the safest of all surgical procedures. Each year approximately 750,000 Americans have their gallbladder removed. It is also the only treatment method that eliminates the possibility that other gallstones will develop in the future.
When the gallbladder has been removed, bile flows directly from the liver into the small intestine, and this sometimes leads to diarrhea. Because bile no longer accumulates in the gallbladder, quantities of the digestive fluid cannot be stored up and used to break down an especially fatty meal. This condition is not considered serious, however, and can be corrected by simply limiting fat in the diet.
In the past, removal of the gallbladder was done through traditional “open” surgery, which requires surgeons to make a large incision in the abdomen. Patients faced a two- or three-day hospital stay plus several weeks of recovery at home.
Patients faced a two- or three-day hospital stay plus several weeks of recovery at home.
Today, however, the most commonly used surgical technique is a much simpler approach known as laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The doctor makes several small incisions in the abdomen, then uses special pencil-thin instruments to remove the gallbladder. A tiny microscope and video camera, snaked through the incision to the site, allow the surgeon to view the operation.
Laparoscopic surgery is highly effective and very safe. It has reduced the hospital stay to a day or two. Patients report less pain and are generally able to resume a normal lifestyle in a short period of time. However, people who are obese or who have a severe infection or inflammation in the gallbladder may still be considered candidates for traditional open surgery.
Top Picks
Gallstones Picture, Causes, Age, & Symptoms
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
- What Causes Gallstones?
Gallstones are crystal-like deposits that develop in the gallbladder — a small, pear-shaped organ that stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver.
These deposits may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball; they may be hard or soft, smooth or jagged. You may have several gallstones or just one.
Some 30 million American adults suffer from gallstones. Yet most of those who have the condition do not realize it. In this case, what you don’t know probably won’t hurt you; gallstones that are simply floating around inside the gallbladder generally cause no symptoms and no harm.
These “silent” stones usually go unnoticed unless they show up in an ultrasound exam conducted for some other reason. However, the longer a stone exists in the gallbladder, the more likely it is to become problematic. People who have gallstones without symptoms have 20% chance of having an episode of pain during their lifetime.
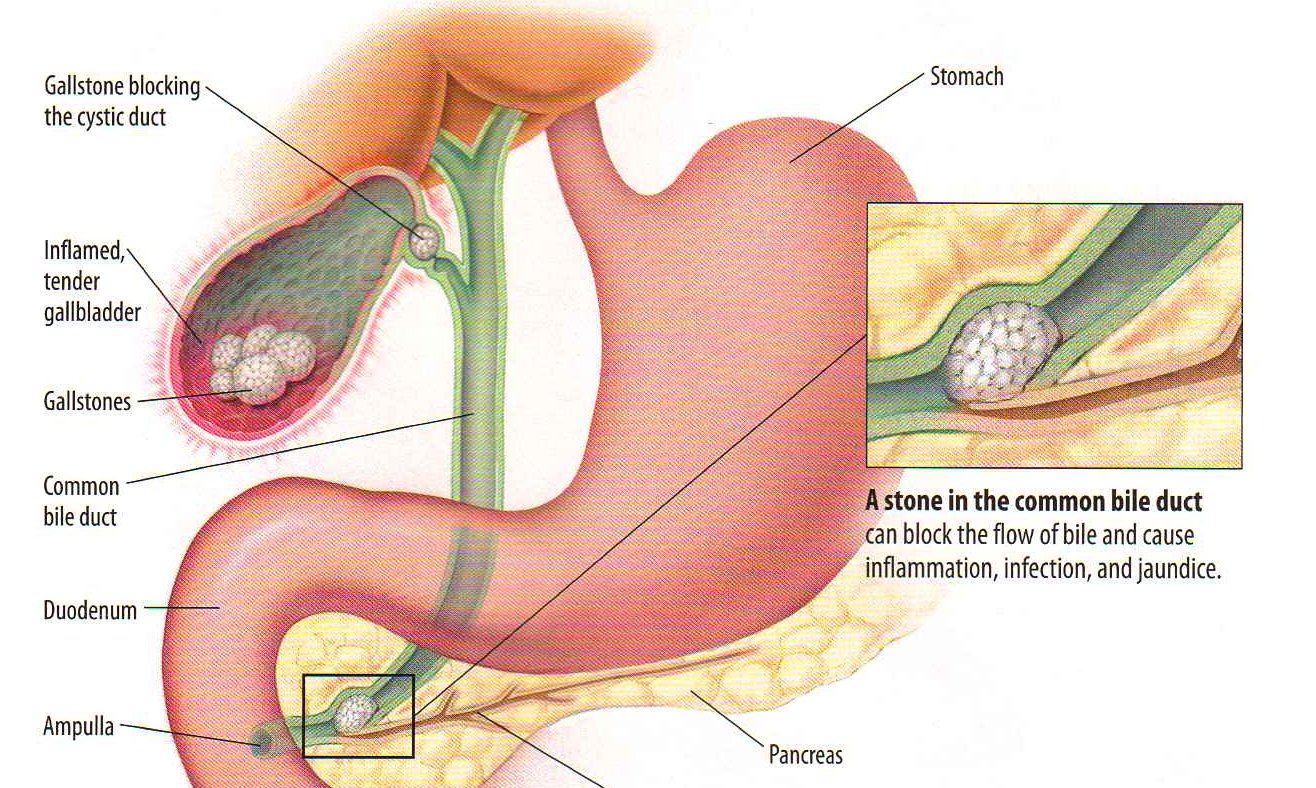
When symptoms do occur, it’s usually because the gallstone has moved and become lodged within a duct that carries bile, such as the cystic duct, a small conduit that connects the gallbladder to another tube called the common bile duct. The typical symptom is abdominal pain, perhaps accompanied by nausea, indigestion, or fever. The pain, caused by the gallbladder’s contraction against the lodged stone, generally occurs within an hour of eating a large meal or in the middle of the night. Stones can also clog the common bile duct, which carries bile into the small intestine, and the hepatic ducts, which take bile out of the liver.
The typical symptom is abdominal pain, perhaps accompanied by nausea, indigestion, or fever. The pain, caused by the gallbladder’s contraction against the lodged stone, generally occurs within an hour of eating a large meal or in the middle of the night. Stones can also clog the common bile duct, which carries bile into the small intestine, and the hepatic ducts, which take bile out of the liver.
Obstructions in the bile pathway may cause a duct to become inflamed and possibly infected. Blockage of the common bile duct, which merges with the pancreatic duct at the small intestine, can also lead to inflammation of the pancreas (gallstone pancreatitis).
In a rare but dangerous condition that occurs most often in older women, gallstones migrate into the small intestine and block the passageway into the large intestine; symptoms include severe and frequent vomiting. Although gallstones are present in about 80% of people with gallbladder cancer, it is uncertain whether gallstones play a role, except when really large stones (greater than 3 centimeters in diameter) are present.
About a million new cases of gallstones are diagnosed in the U.S. each year. For reasons that are still unclear, women are two times more likely than men to be afflicted. Native Americans have the highest rates of gallstones in the U.S. because they have a genetic disposition to secrete high levels of cholesterol in bile (a contributing factor to gallstones.) Mexican-Americans also have high rates of gallstones.
Gallstones are also more common in people over age 60, in those who are obese or have lost a lot of weight in a short amount of time, in those who have diabetes or sickle cell disease, and in women who have had multiple pregnancies and who take hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills.
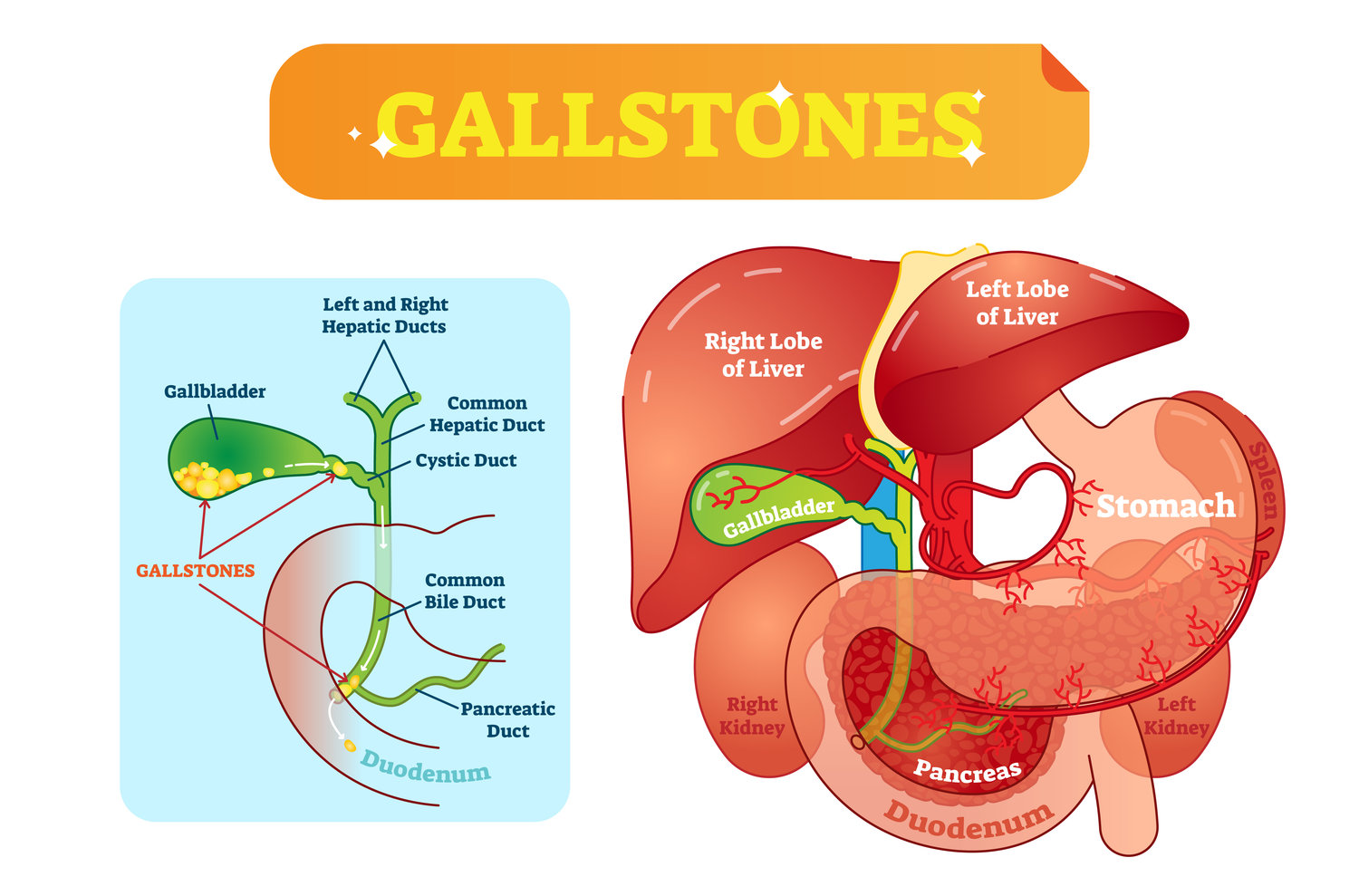
The primary function of the gallbladder is to store bile, a brown or yellowish fluid that helps the body break down fatty food. When you eat a meal, the gallbladder releases its stored bile into the cystic duct. From there the fluid passes through the common bile duct and into the small intestine to mix with food.
Chief among the ingredients of bile are cholesterol and bile acids. Normally, the concentration of bile acids is high enough to break down the cholesterol in the mixture and keep it in liquid form. However, a diet high in fat can tip this delicate balance, causing the liver to produce more cholesterol than the bile acids are able to handle. As a result, some of this excess cholesterol begins to solidify into crystals, which we call gallstones. About 80% of all gallstones are called cholesterol stones and are created this way. The remaining 20% consist of calcium mixed with the bile pigment bilirubin and are called pigment stones. Sickle cell and other blood disorders where red blood cells are destroyed can often lead to pigment gallstones
Gallstones can form even in people who eat properly. And as researchers have found, a diet extremely low in fat can also contribute to gallstone formation: With little fatty food to digest, the gallbladder is called into play less frequently than usual, so the cholesterol has more time to solidify. Other factors that can reduce activity in the gallbladder, possibly leading to gallstone formation, include cirrhosis, the use of birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, and pregnancy.
Other factors that can reduce activity in the gallbladder, possibly leading to gallstone formation, include cirrhosis, the use of birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, and pregnancy.
Family history, diabetes, sudden weight loss, and cholesterol drugs, and older age can also increase risk for gallstones.
Top Picks
symptoms and when to see a doctor
Gallstone disease (GSD) is the formation of stones (calculi) in the gallbladder and bile ducts. Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that most commonly form in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just below your liver. The gallbladder contains a digestive fluid called bile, which is secreted into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of food.
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that most commonly form in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just below your liver. The gallbladder contains a digestive fluid called bile, which is secreted into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of food.
Gallbladder stones range in size from a grain of sand to a golf ball. Some people develop only one gallstone, while others develop many small stones at the same time.
The presence of stones carries the risk of developing dangerous conditions and severe complications.
Symptoms
Gallstones often cause no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone gets stuck in the duct and causes a blockage, the following symptoms develop:
- Sudden and rapidly increasing pain in the center of the abdomen, just below the sternum, on the right
- Pain in the back between the shoulder blades
- Right shoulder pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pain associated with gallstone disease can last from several minutes to several hours
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you.
Read about the diagnosis and treatment of cholelithiasis at the link.
Seek care right away if you develop signs and symptoms of a serious complication associated with gallstones, for example:
- Abdominal pain so severe that you cannot sit still or find a comfortable position
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- High fever with chills
Number for calling an ambulance in Moscow – 103
Causes of cholelithiasis
It is unclear what causes gallstones. Doctors believe that gallstones can occur in the following cases:
Your bile contains too much cholesterol . Normally, your bile contains enough chemicals to dissolve the cholesterol secreted by your liver. But if your liver secretes more cholesterol than bile can dissolve, the excess cholesterol can turn into crystals and eventually stones.
Your bile contains too much bilirubin . Bilirubin is a chemical produced when red blood cells are broken down in the body. Under certain conditions, the liver produces too much bilirubin, including cirrhosis of the liver, biliary tract infections, and certain blood disorders. Excess bilirubin contributes to the formation of gallstones.
Bilirubin is a chemical produced when red blood cells are broken down in the body. Under certain conditions, the liver produces too much bilirubin, including cirrhosis of the liver, biliary tract infections, and certain blood disorders. Excess bilirubin contributes to the formation of gallstones.
Your gallbladder is not emptying properly. If the gallbladder does not empty completely or often enough, the bile can become very concentrated, which promotes the formation of gallstones.
Types of gallstones
Types of gallstones that can form in the gallbladder include:
Cholesterol stones in the gallbladder. The most common type of gallstones, called cholesterol gallstones, are often yellow in color. These gallstones are made up primarily of undissolved cholesterol, but may contain other components.
Pigment stones in the gallbladder. These dark brown or black stones form when your bile contains too much bilirubin.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase the risk of gallstones include:
- Female gender
- Age 40 and over
- Overweight or obese
- Sedentary
- Pregnancy
- High fat diet
- High cholesterol diet
- Low fiber diet
- Family history of gallstones
- Diabetes
- Presence of certain blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia or leukemia
- Very fast weight loss
- Taking medications containing estrogen, such as oral contraceptives or hormone therapy drugs.
- Liver disease
Complications
Complications of gallstones may include:
Inflammation of the gallbladder . A gallstone lodged in the neck of the gallbladder can cause inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis). Cholecystitis can cause severe pain, peritonitis.
Blockage of the common bile duct . Gallstones can block the channels (ducts) that carry bile from the gallbladder or liver to the small intestine. This can lead to severe pain, jaundice, and bile duct infection.
This can lead to severe pain, jaundice, and bile duct infection.
Obstruction of the pancreatic duct . The pancreatic duct is a tube from the pancreas and joins the common bile duct just before entering the duodenum. The pancreatic juices that aid digestion pass through the pancreatic duct.
A gallstone can cause blockage of the pancreatic duct, which can lead to inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Pancreatitis causes severe, persistent abdominal pain and usually requires hospitalization. Severe forms of pancreatitis often end in the death of the patient.
Gall bladder cancer . People with gallstones have an increased risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Prevention of gallstones
You can reduce the risk of gallstones:
Do not skip meals . Try to stick to your regular meal times every day. Skipping meals or fasting can increase your risk of gallstones.
Lose weight slowly . If you need to lose weight, take your time. Rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallstones.
Eat more high fiber foods . Include more fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Maintain a healthy weight . Obesity and overweight increase the risk of gallstones. Work towards a healthy weight by cutting calories and increasing physical activity. Once you reach a healthy weight, work on maintaining it by continuing to eat a healthy diet and keep exercising.
Gallstone disease: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
General practitioner
Belyaeva
Iraida Viktorovna
Experience 25 years
District physician of the highest category, member of the Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists
Make an appointment
Gallstone disease is also known as cholelithiasis in specialist circles. In general, this is a disease that is directly related to a violation of human metabolism. The classic sign of gallstone disease is stones that form in a person’s gallbladder or in the ducts that remove bile from the body. If a malfunction is detected in the human body and the metabolism is significantly disturbed, then this can lead to the fact that the composition of bile will also change. If a failure occurs, then over time the bile begins to thicken, and the acid precipitates. After such a transformation, the liquid hardens and stones form. Stones not only do not allow the body to function calmly, but also contain cholesterol, harmful salts.
In general, this is a disease that is directly related to a violation of human metabolism. The classic sign of gallstone disease is stones that form in a person’s gallbladder or in the ducts that remove bile from the body. If a malfunction is detected in the human body and the metabolism is significantly disturbed, then this can lead to the fact that the composition of bile will also change. If a failure occurs, then over time the bile begins to thicken, and the acid precipitates. After such a transformation, the liquid hardens and stones form. Stones not only do not allow the body to function calmly, but also contain cholesterol, harmful salts.
People who suffer from cholelithiasis and know what it is, note that the number of stones can be different, just like their sizes. Some doctors find hundreds of very small stones like sand, while others have only a few, but the size of a large walnut. Quite often, stones are located in the gallbladder, causing a number of other chronic diseases. There are cases when specialists in the clinic find stones in the bile ducts of the liver.
There are cases when specialists in the clinic find stones in the bile ducts of the liver.
Classic gallstone disease is a disease that can and should be treated under the supervision of a physician. If you immediately pay attention to some signs and react in time, you can soon forget about the problem forever. Often, in a person suffering from this disease, the gallbladder becomes inflamed and the flow of bile into the stomach is disrupted. There are also severe cases when the patient ignored all the signs or was engaged in home self-medication. In such cases, the stone can block the outflow of bile completely and cause the development of obstructive jaundice.
It is important to note that both gallstone disease and obstructive jaundice are not to be trifled with, because the latter is a disease that can lead to death. In general, ignoring the disease can lead to a number of other serious complications, such as, for example, peritonitis, toxic shock, body imbalance and death. Women are often more affected by this disease. It can even be caused by pregnancy. But there are a number of other factors, such as diet, lifestyle, environment, genetics, chronic diseases, that can cause gallstone disease to develop. In general, everyone can get sick with this disease, regardless of age or gender, so it is important to pay attention to the symptoms that appear.
Women are often more affected by this disease. It can even be caused by pregnancy. But there are a number of other factors, such as diet, lifestyle, environment, genetics, chronic diseases, that can cause gallstone disease to develop. In general, everyone can get sick with this disease, regardless of age or gender, so it is important to pay attention to the symptoms that appear.
Most often, the onset of the disease occurs in people who are overweight or, on the contrary, have lost a lot of weight, as well as in women whose age has exceeded 60 years. Diabetes mellitus can also cause a complication in the form of gallstone disease, so one disease can cause another to develop. If the disease is not cured and the gallstone disease continues to progress, then gallbladder cancer may well develop.
Symptoms and signs
According to experienced specialists and doctors, often at the stage of their manifestation, stones that are in the gallbladder do not cause any symptoms of gallstone disease at all. The main symptom appears only when the stone begins to gradually get out of the bubble. The stone comes out through the bile ducts, which are in the body of every person. The channels themselves are quite small and narrow. Due to a stone getting into one of the ducts, such a main symptom appears as a sharp pain due to the fact that the stone or all of them are stuck in the duct.
The main symptom appears only when the stone begins to gradually get out of the bubble. The stone comes out through the bile ducts, which are in the body of every person. The channels themselves are quite small and narrow. Due to a stone getting into one of the ducts, such a main symptom appears as a sharp pain due to the fact that the stone or all of them are stuck in the duct.
The main symptoms of gallstone disease:
- sharp pain in the abdomen. Basically, the pain is felt in the upper right side near the hypochondrium;
- a symptom such as pain in the back or right shoulder blade. The disease itself can also spread to a feeling of discomfort in the shoulders;
- Nausea and vomiting are frequent, but such symptoms are justified only if bile is noted along with the exiting mass.
There are several stages in which cholelithiasis can develop, each of the stages has its own cholelithiasis symptoms and cause. For example, if the patient is only at an early stage and thinks to fight the disease, then a doctor is needed. As mentioned earlier, at first, the disease does not manifest itself in any way and the course of gallstone disease can be without symptoms. Sometimes it also happens that the disease develops on its own and even at later stages does not make itself felt. Then it can lead to cancer and death.
As mentioned earlier, at first, the disease does not manifest itself in any way and the course of gallstone disease can be without symptoms. Sometimes it also happens that the disease develops on its own and even at later stages does not make itself felt. Then it can lead to cancer and death.
If pain in cholelithiasis has not been experienced, then the disease can be detected only by accidentally contacting a doctor. Then an X-ray examination will help to identify the stone carrier, which did not show any symptoms. But most often, after some time, the patient still feels some signs of gallstone disease. In addition to the above nausea, vomiting and pain in the ribs, there may be constant bitterness in the mouth or even a feeling that something is moving under the skin.
When the stones begin to actively move along the channels and a manifestation of cholelithiasis occurs, then one of the symptoms of cholelithiasis, which will help determine cholelithiasis, is colic. During colic, the patient goes to the doctor with a complaint of pain from the ribs to the shoulder blades. Basically, the pain manifests itself after eating, so it can appear at any time, the head may still hurt. Accompanied by a feeling of pain again with nausea or vomiting.
During colic, the patient goes to the doctor with a complaint of pain from the ribs to the shoulder blades. Basically, the pain manifests itself after eating, so it can appear at any time, the head may still hurt. Accompanied by a feeling of pain again with nausea or vomiting.
Diagnostics
In order to accurately identify the symptoms of the disease and determine the further treatment of the disease, the doctor sends the patient for testing and consultation with a specialist. The first thing that helps to make an accurate diagnosis is a physical examination. With its help, the doctor can accurately identify some of the signs that confirm the presence of the disease. Only technology can confirm the presence in the human body of Murphy, Zakharyin – clear signs of problems with the gallbladder. Professional diagnostics by a doctor in Moscow allows you to determine the level of skin soreness and the degree of muscle tension in a person, this is very important if the gallbladder area is being considered.
In the real presence of the disease, a specialist may notice xanthemas, yellowness on the skin, and this is a clear sign of cholelithiasis. A general blood test can identify problems and the presence of stones in the body. If the patient currently has a clinical exacerbation, then the blood will quickly indicate all problems and inflammations, but only a professional can deal with them. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis only on the basis of blood tests. But he will indicate the presence of leukocytosis in the blood, bile and other aspects that only a specialist understands.
The most maximum amount of information during the diagnosis is given by ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. With the help of ultrasound radiation, the gallbladder is examined, and the doctor can determine whether there are echo-tight formations in the patient’s body. This complex name refers to already known stones that are deformed on the walls of the bubble and change its motility. In addition, if the patient has already noticed heart problems during the check-up of other diseases, then ultrasound will help to find out the level of cholesterol.
In addition, if the patient has already noticed heart problems during the check-up of other diseases, then ultrasound will help to find out the level of cholesterol.
During gallstone disease, the patient must constantly take tests, as their results can affect all treatment. If you refuse procedures or come unprepared for testing, this can affect all diagnostic results. The fact is that, as mentioned earlier, cholelithiasis develops gradually and manifests itself at different stages or does not manifest itself at all, so a blood test and urine test can help.
Such a diagnosis of gallstone disease as MRI is also considered successful, but this is a kind of analysis that the doctor recommends doing only one or several times, since this can adversely affect the body. CT of the biliary tract is also actively used in a specialized clinic, but only by the decision of a specialist, which was transferred to the doctor. Such an analysis carries quite a lot of information, since it reveals whether there are any disturbances in the work and circulation of bile using special methods and approaches.
Without diagnostic studies and specialized analysis, the patient may have some complications of the disease, which at first, general tests do not reveal. Most often, due to gallstone disease, as a result, if specialized treatment is not used, inflammation of the gallbladder may begin. The lumen of the bile ducts in the body of a sick person can become blocked and this in turn causes pancreatitis.
It is best to undergo a diagnostic examination in a timely manner in one of the professional clinics, take tests, follow the doctor’s advice. One analysis of gallstone disease from all that a medical institution offers can help a specialist choose the right direction in treatment. Then it will be faster, easier and even cheaper to get rid of the disease, since the prices for treatment depend on the level of the neglected case.
Causes
If the diagnosis of gallstone disease reveals certain symptoms of the disease, then it is quite logical that there are also reasons due to which the disease begins to progress. If the quantitative ratio of bile components is violated, then the creation of flakes automatically begins in the human body. These peculiar hard flakes, as the results of the analysis show, turn into stones along with the development of the disease. Most often this happens due to the fact that a person suffers from impaired cholesterol metabolism. If there is too much cholesterol, then because of this reason, bile is modified and stones appear in it.
If the quantitative ratio of bile components is violated, then the creation of flakes automatically begins in the human body. These peculiar hard flakes, as the results of the analysis show, turn into stones along with the development of the disease. Most often this happens due to the fact that a person suffers from impaired cholesterol metabolism. If there is too much cholesterol, then because of this reason, bile is modified and stones appear in it.
A person suffers from an excess of cholesterol for the following reasons:
- the body suffers from obesity due to malnutrition, the reason for everything is the huge consumption of foods that just contain a large dose of cholesterol;
- the amount of bile acid has decreased, due to which the body has ceased to function normally, and the bile does not receive the elements it needs;
- in human blood, the volume of phospholipids has decreased, which has led to the fact that cholesterol cannot harden and settle in the body;
- bile began to stagnate and the whole reason is the improper circulation of fluid throughout the human body.

It is important to note that bile can stagnate both mechanically and functionally, therefore, when prescribing treatment, the doctor pays attention to this. If we are talking about the fact that the bile in the human body has stagnated for mechanical reasons, then an additional tumor may occur, sometimes the lymph nodes increase. Patients often complain of scarring, persistent swelling and other discomfort, which becomes another cause for concern.
As for the functional stagnation of bile, here the problem lies in the fact that the motility of the gallbladder was upset, and the bile ducts clogged. Human genetics may also play a role here. If a woman or a man has a predisposition to gallstone disease. It is important to note that malnutrition, a sedentary lifestyle, sudden weight loss or weight gain can affect the development of the disease.
Treatment
Nowadays, effective treatment of gallstone disease is more than real if you use the services of a professional clinic that offers innovative treatment methods. Many books and scientific articles are written about how to treat the disease, but there are general rules that you should rely on. If the patient first needs to simply identify the presence of stones in the gallbladder and at the same time he does not have any complications, then specific treatment is not required. In this case, such a method of treating gallstone disease as waiting is used. This is a special tactic, during which the doctor monitors the change in the human body and tries to cure it with medication.
Many books and scientific articles are written about how to treat the disease, but there are general rules that you should rely on. If the patient first needs to simply identify the presence of stones in the gallbladder and at the same time he does not have any complications, then specific treatment is not required. In this case, such a method of treating gallstone disease as waiting is used. This is a special tactic, during which the doctor monitors the change in the human body and tries to cure it with medication.
If gallstone foreign bodies were noticed by a specialist during the examination or acute cholecystitis was diagnosed, then a method such as surgical removal of the gallbladder is used. This is a more complex approach in the treatment of gallstone disease, because it requires urgent surgical intervention. The fact is that it is the gallbladder that becomes the catalyst for the development and formation of stones. There are several types of surgical intervention, with one of which a specialist is determined after a thorough examination of the body. To do this, you need to get checked, because the wrong methods of treatment can lead to cancer.
To do this, you need to get checked, because the wrong methods of treatment can lead to cancer.
In the clinic, only the most effective and modern principles of treatment are used. The use of such a method of treatment as lithotripsy is considered progressive. Its main qualities are characterized by the fact that this method is used if there is one calculus. It is important to note that, in principle, there are a lot of treatment methods that can be used to treat gallstone disease.
It is impossible to check absolutely every approach, because the treatment and the gallstone process must follow the same plan. Through trial and possibly error, the attending physician will determine the best conditions for the treatment method that the clinic can offer. Of course, first of all, they try to eliminate the disease with medication and with the help of physical therapy, but sometimes this leads to the appearance of new stones. In this case, it is best to resort to surgery and further postoperative recovery.
Doctors involved in the treatment of this disease
If we consider the question of which doctor treats gallstone disease, then it is impossible to name only one specialist. The fact is that this disease is treated by both a gastroenterologist and a surgeon. In addition, the therapist must monitor the success of the treatment. In general, a gastroenterologist deals not only with the treatment of gallstone disease, he also specializes in other problems that may arise with the organs of the digestive system.
If we talk about the doctors of the treating clinics in general, then it is best to study the list of proposed specialists, since in the medical center each patient receives individual care. Initially, you can try to decide on the attending physician on your own, having studied the specifics of each activity. The modern clinic offers a wide range of specialists, which is constantly increasing.
So, already at the first appointment with the doctor, you can determine the symptoms, hear the testimony, choose the appropriate diagnostic methods and discuss the prices for treatment. Further, if the patient is satisfied with everything, the specialist begins to conduct an operative technique or prescribes an ultrasound scan, after which an active fight against the disease is carried out. If it is impossible to cure the disease with medication, then the surgeon intervenes in the treatment and promptly removes the gallbladder. This is a team work of doctors, during which each patient will receive due attention and an individual approach.
Further, if the patient is satisfied with everything, the specialist begins to conduct an operative technique or prescribes an ultrasound scan, after which an active fight against the disease is carried out. If it is impossible to cure the disease with medication, then the surgeon intervenes in the treatment and promptly removes the gallbladder. This is a team work of doctors, during which each patient will receive due attention and an individual approach.
Readings
In the presence of gallstone disease, experts recommend several indications that will help alleviate the disease or they can be used as a preventive measure.
Tips and preventive measures:
- it is recommended to eat less foods that contain a high dose of cholesterol, because it is because of it that stones begin to actively form;
- it is best to monitor the level of bilirubinemia, because this also plays an important role during the prevention or treatment of the disease;
- bile should never stagnate in the human body;
- in order to maintain health and not suffer from this disease, you need to monitor body weight and eat a balanced diet;
- with cholelithiasis there should not be a sharp weight loss or weight gain;
- it is recommended to lead a healthy and active lifestyle, to exercise, so that in the future there is no metabolic disorder;
- one of the main indications is that it is worth paying attention to all the symptoms and solving the problem in a timely manner;
- a person with a genetic predisposition to gallstone disease should visit a doctor periodically.

Contraindications
There are several contraindications that should never be forgotten by a person suffering from gallstone disease. The first thing every doctor focuses on is constant observation. The disease should not proceed on its own. If it has already been identified through suitable symptoms or professional diagnostics, it is imperative to contact a general practitioner or gastroenterologist in order not to allow the disease to go to another stage. Surgery is not always necessary for the treatment of gallstone disease, so it is experienced professional supervision that can help to avoid this.
It is impossible not to visit an ultrasound every six months, since it is precisely such an assessment of organs and possible stones that can help find out whether a person has a pressure sore or not. It is not recommended to constantly change doctors, so it is better to immediately choose a specialist with whom it will be comfortable to cooperate. If gallstone disease is detected in a patient, then he is strictly forbidden to engage in serious physical exertion. With such a disease, one cannot work in the garden, because because of this, everything can only worsen and this will interfere with treatment.
With such a disease, one cannot work in the garden, because because of this, everything can only worsen and this will interfere with treatment.
It is important to remember that cholesterol is strictly forbidden to the patient, because of this, one should not exchange a diet for malnutrition. It is best not to lead an active lifestyle during diagnosis and treatment. In addition, after the operation, the patient definitely needs a long recovery.
Cost of initial appointment, research, treatment
With regard to treatment in the clinic, it is not possible to give a certain and exact cost of treatment for each patient who wishes to apply for services. Everyone seeks individual help with their stage of the disease, so the price may vary. It is most correct to pay attention to the table, which shows the entire cost of treatment with any of the doctors. Already at the first appointment or having decided on the diagnosis, research, it will be possible to understand how much the treatment will cost.


