Diarrhea and loss of appetite in dogs. Gastroenteritis in Dogs: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
What are the common causes of gastroenteritis in dogs. How is canine gastroenteritis diagnosed. What treatment options are available for dogs with gastroenteritis. What are the clinical signs of gastroenteritis in dogs. How can dehydration be prevented in dogs with gastroenteritis. What diagnostic tests are used to identify gastroenteritis in dogs. How long does it typically take for a dog to recover from gastroenteritis.
Understanding Gastroenteritis in Dogs: An Overview
Gastroenteritis is a common condition in dogs that affects the gastrointestinal tract, specifically the stomach and intestines. This inflammatory condition can be caused by various factors, including bacterial or viral infections, parasites, medications, or even the introduction of new foods to a dog’s diet. The condition often manifests through symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and other clinical signs that can significantly impact a dog’s overall health and well-being.
Dogs suffering from gastroenteritis may experience intermittent episodes of vomiting and diarrhea. The vomit might contain foamy, yellowish bile, especially after the stomach has been emptied. Some dog owners may observe their pets dry heaving or gagging after eating or drinking. A characteristic sign of gastroenteritis is the production of large volumes of diarrhea several times a day, often with a consistency similar to soft-serve ice cream.
Recognizing the Clinical Signs of Canine Gastroenteritis
Identifying the symptoms of gastroenteritis in dogs is crucial for prompt treatment. What are the most common clinical signs of gastroenteritis in dogs? The primary indicators include:
- Intermittent vomiting and diarrhea
- Abdominal tenderness or resistance to handling
- Lethargy and decreased activity
- Reduced appetite
- Low-grade fever
Dogs affected by gastroenteritis may appear less active and show a decreased interest in food. Many will be tender when picked up around the abdomen or resist handling of the stomach and hindquarters. It’s important to note that dehydration can occur rapidly if vomiting and diarrhea persist for more than 24 hours, making it essential to monitor your dog’s condition closely.

Diagnosing Gastroenteritis: A Process of Elimination
Gastroenteritis is typically diagnosed through a process of elimination. Veterinarians work to rule out other more serious causes of the clinical signs before arriving at a diagnosis of gastroenteritis. How do veterinarians diagnose gastroenteritis in dogs? The diagnostic process usually involves several steps:
- Gathering a comprehensive medical history
- Performing a thorough physical examination
- Conducting diagnostic tests
A detailed medical history is crucial in determining the cause of your dog’s symptoms. Your veterinarian will inquire about your dog’s current diet, recent food intake, exposure to potential toxins or new environments, and any previous episodes of vomiting and diarrhea. This information helps in narrowing down potential causes and guiding the diagnostic process.
Key Diagnostic Tests for Canine Gastroenteritis
What diagnostic tests are commonly used to identify gastroenteritis in dogs? Veterinarians may recommend several tests to rule out other conditions and confirm a diagnosis of gastroenteritis:

- Complete blood cell count (CBC)
- Serum chemistries and electrolytes
- Urinalysis
- Abdominal radiographs (X-rays)
- Abdominal ultrasound
These tests help detect dehydration, infection, organ system abnormalities, electrolyte imbalances, and potential obstructions or abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract. The specific diagnostic workup will depend on the severity and duration of clinical signs, medical history, and physical examination findings.
Common Causes of Gastroenteritis in Dogs
Gastroenteritis in dogs can be triggered by various factors. What are the most frequent causes of canine gastroenteritis? Some common culprits include:
- Infections (bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic)
- Ingestion of foreign bodies (e.g., string, thread, or other objects)
- Intussusception (telescoping of the intestine into itself)
- Tumors or cancer
- Exposure to toxins or poisons (plants, cleaning agents)
- Endocrine diseases (e.g., diabetes, hyperthyroidism)
- Pancreatic, liver, or kidney diseases
It’s important to note that this list is not exhaustive, and your veterinarian may consider other possibilities based on your dog’s specific condition and symptoms.

Treatment Approaches for Canine Gastroenteritis
The primary focus of gastroenteritis treatment is rehydration and restoring blood electrolyte balance. How is gastroenteritis in dogs typically treated? The treatment approach may include:
- Fluid replacement therapy
- Antibiotic administration
- Use of antidiarrheal medications
- Dietary management
Depending on the severity of dehydration, fluid replacement may be administered orally, subcutaneously (beneath the skin), or intravenously (IV). In cases of severe clinical signs or suspected bacterial infection, antibiotics such as metronidazole or ampicillin may be prescribed. Antidiarrheal drugs might be used to alter intestinal motility, but only after ruling out intestinal obstructions or other mechanical issues.
Dietary Management in Gastroenteritis Treatment
What dietary changes are recommended for dogs with gastroenteritis? Initially, a brief period of fasting (12-24 hours) may be advised to rest the gastrointestinal tract. Following this, a bland, easily digestible diet is typically introduced gradually. This may include:

- Boiled white meat chicken (without skin or bones) and white rice
- Lean ground beef and white rice
- Specialized veterinary diets designed for gastrointestinal support
It’s crucial to reintroduce food slowly and in small, frequent meals to avoid overwhelming the digestive system. As your dog’s condition improves, you can gradually transition back to their regular diet over several days.
Preventing Dehydration in Dogs with Gastroenteritis
Dehydration is a serious concern in dogs with gastroenteritis due to fluid loss through vomiting and diarrhea. How can you prevent dehydration in dogs suffering from gastroenteritis? Here are some strategies:
- Encourage frequent water intake in small amounts
- Offer ice cubes for licking if drinking water is difficult
- Use oral rehydration solutions designed for dogs
- Monitor urine output and gum moisture
If your dog shows signs of severe dehydration, such as sunken eyes, dry gums, or loss of skin elasticity, immediate veterinary attention is necessary. In such cases, subcutaneous or intravenous fluid therapy may be required to restore hydration quickly and effectively.
Recovery and Prognosis for Dogs with Gastroenteritis
The recovery time for dogs with gastroenteritis can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. How long does it typically take for a dog to recover from gastroenteritis? In most cases of uncomplicated gastroenteritis, dogs begin to show improvement within 24 to 48 hours of starting treatment. However, full recovery may take several days to a week.
Factors that can influence recovery time include:
- The dog’s age and overall health
- The underlying cause of gastroenteritis
- The promptness of treatment initiation
- Compliance with prescribed treatment and dietary recommendations
It’s essential to follow your veterinarian’s instructions carefully and complete the full course of any prescribed medications. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor your dog’s progress and make any needed adjustments to the treatment plan.
Long-term Management and Prevention
While some cases of gastroenteritis are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of recurrence or prevent future episodes. What preventive measures can dog owners implement? Consider the following strategies:

- Maintain a consistent, balanced diet
- Avoid sudden changes in food or treats
- Keep your dog away from garbage and potentially toxic substances
- Practice good hygiene, especially when handling your dog’s food and water
- Stay up-to-date with vaccinations and parasite prevention
- Schedule regular veterinary check-ups
By implementing these preventive measures and being vigilant about your dog’s health, you can help minimize the risk of gastroenteritis and ensure prompt treatment if symptoms do occur.
When to Seek Immediate Veterinary Care
While many cases of gastroenteritis can be managed at home with proper guidance, there are situations where immediate veterinary attention is crucial. When should you seek emergency care for a dog with gastroenteritis? Be alert for the following signs:
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhea lasting more than 24 hours
- Blood in vomit or stool
- Severe lethargy or collapse
- Signs of severe dehydration (sunken eyes, dry gums, loss of skin elasticity)
- Abdominal bloating or severe pain
- Fever above 103°F (39.4°C)
These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition or severe complications from gastroenteritis. Prompt veterinary intervention in these cases can be life-saving and prevent further complications.
The Importance of Follow-up Care
Even after your dog shows signs of improvement, follow-up care is essential to ensure complete recovery and prevent recurrence. What should you expect during follow-up care for canine gastroenteritis? Your veterinarian may recommend:
- Repeat physical examinations
- Follow-up blood tests to monitor organ function and electrolyte balance
- Gradual dietary transitions
- Discussion of long-term preventive strategies
These follow-up measures help ensure that your dog has fully recovered and allow for early detection of any potential complications or underlying issues that may have been masked by the initial symptoms of gastroenteritis.
Understanding the Impact of Gastroenteritis on Your Dog’s Quality of Life
Gastroenteritis can significantly affect your dog’s overall well-being and quality of life. How does gastroenteritis impact a dog’s daily life and behavior? The condition can lead to:
- Decreased energy and enthusiasm for activities
- Changes in appetite and eating habits
- Disruptions in sleep patterns
- Increased neediness or desire for comfort
- Temporary changes in bathroom habits and routines
As a pet owner, it’s important to be patient and supportive during your dog’s recovery period. Providing a calm, comfortable environment and following your veterinarian’s recommendations can help ease your dog’s discomfort and promote faster healing.

Emotional Support for Dogs with Gastroenteritis
While the physical symptoms of gastroenteritis are the primary concern, it’s also important to consider your dog’s emotional well-being during illness. How can you provide emotional support to a dog recovering from gastroenteritis? Consider these approaches:
- Offer gentle companionship and reassurance
- Create a quiet, stress-free environment for rest
- Provide comfortable bedding and easy access to water
- Use positive reinforcement for good behavior and compliance with treatment
- Gradually reintroduce normal activities as your dog recovers
By addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of your dog’s recovery, you can help ensure a smoother healing process and strengthen your bond with your pet.
Gastroenteritis in Dogs | VCA Animal Hospital
Gastroenteritis is inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach and the intestines). It can be caused by infection with bacteria, viruses, parasites, medications, or even new foods. The condition often causes abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and other clinical signs.
What are the clinical signs of gastroenteritis?
Most dogs with gastroenteritis will have intermittent episodes of vomiting and diarrhea. The vomit may contain foamy, yellowish bile, especially after emptying the stomach. Many owners observe dry heaving or gagging after their dog eats or drinks. Characteristically, large volumes of diarrhea will be produced several times a day. The diarrhea may have the consistency of soft-serve ice cream.
Many dogs will be tender when picked up around the abdomen or resist handling the stomach and hindquarters. Most dogs affected with gastroenteritis will appear less active (lethargic) and have a decreased appetite. A low-grade fever is also common. Dehydration can occur quickly if the vomiting and diarrhea persist for more than 24 hours.
A low-grade fever is also common. Dehydration can occur quickly if the vomiting and diarrhea persist for more than 24 hours.
How is gastroenteritis diagnosed?
Gastroenteritis is a diagnosis of exclusion. This means that your veterinarian will eliminate or rule out other more serious causes of the clinical signs before making a general diagnosis, such as gastroenteritis. A good medical history is the first step toward determining what is causing your dog’s vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, and other associated clinical signs. Some critical information in your dog’s medical history includes:
- Your dog’s current diet, how much you feed, and how often you feed your dog
- Everything your dog ate or drank within the past 48 hours
- Any new foods, treats, or rewards
- Any recent exposure to pesticides, medications, cleaning agents, or any other new materials
- Any recent exposure to a new animal or person
- Any previous episodes of vomiting and diarrhea (including their cause and treatment)
- Any illness within the past month
- Any medications, vitamins, or supplements given within the past month
Your veterinary health team may have you complete a questionnaire before your visit. See the “Diarrhea Questionnaire and Checklist for Dogs” handout for an example.
See the “Diarrhea Questionnaire and Checklist for Dogs” handout for an example.
After obtaining the medical history, your veterinarian will perform a thorough physical examination. Your veterinarian will look for evidence of dehydration, abdominal pain, tenderness, bloating or gas, swellings, or any other physical abnormality. Your dog’s temperature and other vital signs (heart and respiratory rates) will be recorded.
At this stage, diagnostic testing will be recommended and may include:
- Complete blood cell count (CBC) – indicates the presence of dehydration and infection
- Serum chemistries and electrolytes – detect organ system abnormalities and electrolyte imbalances due to vomiting and diarrhea
- Urinalysis – detects urinary tract infections, kidney disease, dehydration, urine glucose for diabetes, etc.
- Abdominal radiographs (X-rays) – to search for stomach or intestinal obstruction or other abnormal findings
- Abdominal ultrasound – to look for intestinal obstructions or other abnormalities
Your dog’s specific diagnostic workup will be determined by the severity and duration of clinical signs, medical history, and physical examination. Once the diagnostic tests are complete and other causes of the clinical signs have been eliminated, treatment will be prescribed.
Once the diagnostic tests are complete and other causes of the clinical signs have been eliminated, treatment will be prescribed.
What are some of the causes of gastroenteritis?
There are many causes of the symptoms of vomiting and diarrhea in dogs. Some of the more common conditions that your veterinarian will attempt to eliminate during the diagnostic workup include:
- Infections (e.g., bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic)
- Foreign bodies (especially string or thread) or other objects
- Intussusception (the telescoping of the intestine into itself, causing an intestinal blockage) • Tumors/cancer • Poisoning/toxins (e.g., plants, cleaning agents)
- Endocrine disease (e.g., diabetes, hyperthyroidism)
- Pancreatic, liver, or kidney disease
This is only a partial list of more serious conditions that can cause vomiting and diarrhea in dogs. Your veterinarian may discuss other possibilities based on your dog’s specific condition.
How is gastroenteritis treated?
The principal treatment of gastroenteritis is rehydration and restoring blood electrolyte balance (sodium, potassium, and chloride). Depending on the degree of dehydration, this fluid replacement will be given orally, subcutaneously (beneath the skin), or by intravenous (IV) treatment. Medical treatment may also include:
- Antibiotics (e.g., metronidazole, ampicillin) if the clinical signs are severe or if diagnostic tests suggest a bacterial infection.
- Antidiarrheal drugs may be used to alter intestinal motility (activity) after intestinal obstruction or other mechanical and anatomical issues have been ruled out. Motility-modifying agents are generally not recommended if your dog is experiencing severe colitis.
- Anti-emetic (anti-vomiting) medications, such as maropitant (Cerenia®) or metoclopramide (Reglan®)
- Gastrointestinal protectants used to prevent stomach ulcers, such as famotidine (Pepcid®) or ranitidine (Zantac®)
Food is often withheld during the initial stages of treatment for 12-24 hours and then slowly reintroduced.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/side-effects-of-flagyl-metronidazole-1941759-FINAL-7b1b3d3abd1c4b7789af8de7e97386ab.png) Small, frequent feedings of a highly digestible, low-fat, low-fiber diet are generally prescribed. Your veterinarian will advise you on the best diet to feed your dog for a speedy recovery.
Small, frequent feedings of a highly digestible, low-fat, low-fiber diet are generally prescribed. Your veterinarian will advise you on the best diet to feed your dog for a speedy recovery.
What is the prognosis for gastroenteritis?
Most cases of acute gastroenteritis improve rapidly after rehydration. Call your veterinarian if the vomiting and diarrhea do not improve significantly within 48 hours of treatment. Gastroenteritis is a common condition seen in veterinary practice. Early recognition and treatment are the cornerstones to returning your dog to a normal healthy state as quickly as possible.
7 Reasons Your Dog May Be Experiencing a Loss of Appetite
Dogs are usually known to have a ravenous appetite and devour any food you give them. That’s why you might have heard someone tell you that “you eat like a dog” when you gobble up a big fat juicy burger in a matter of seconds, leaving nothing but trickles of burger sauce on your face. But what happens when your actual dog stops eating like one? There are times when dogs lose their appetite, and it worries their dog owners. There are various reasons why your canine might experience a loss in appetite, and we’ll tell you what they could be.
There are various reasons why your canine might experience a loss in appetite, and we’ll tell you what they could be.
A temporary loss of appetite in your dog is not something to become immediately concerned about. Just like us, dogs are sometimes not hungry, or else some stress in their day has caused them to lose interest in food. However, a more prolonged loss of appetite in your dog is a serious sign that something is wrong. What things contribute to a poor appetite? The desire to eat is regulated by an interaction between the digestive tract, adipose tissue, and the brain.
- Lifestyle and lack of exercise
Two chief hormones affected by exercise also control appetite, but in different directions. Ghrelin stimulates appetite, causing hunger, while peptide YY suppresses appetite./stomach-flu-symptoms-770657-86-310db9fd0f1543e289250a64c8384d58.png)
The sedentary lifestyle of most urban populations and the pets that share their homes have undoubtedly contributed to the reduced utilization of metabolic calorie intake. When coupled with a lack of regular exercise, caloric utilization is further stagnated.
- Dietary issues and indiscretion
A transient “sugar high” results from foods with a high glycemic index, such as sugars, flour, rice, white potatoes, and bread. This is followed by feelings of hunger, which promote a craving for more food. Furthermore, well-intentioned people may share unsuitable foods with their “hungry” pets to stop them begging, such as bacon, burgers, or fries, which just aggravates the situation.
- The gut microbiome
Gut bacteria can affect how different foods are digested and produce chemicals that produce a feeling of satiety. People and pets that eat food high in fiber generally have lower weight, likely due to the role of gut bacteria in digesting fiber. These bacteria also digest certain antioxidants, known as flavonoids, found in plants; this helps prevent weight gain. Lastly, gut bacteria can influence how dietary fats are absorbed in the intestines, affecting how body fat is stored.
Lastly, gut bacteria can influence how dietary fats are absorbed in the intestines, affecting how body fat is stored.
Gut microbiota regulate the brain-gut axis. While the hypothalamus and brain stem are the primary central sites of appetite regulation, the gut microbiome can stimulate peripheral sensory neurons (cells that transmit nerve impulses). The vagus nerve is the major nervous system pathway involved and conveys information from the gastrointestinal contents to the brain: it also modulates gastrointestinal motility and feeding behavior.
1. Your Dog Is Experiencing Stress or Hormonal Changes
Dogs are sensitive creatures, and they like their environment a certain way. When there’s a disruption to that sense of order they have, it can be a very stressful situation for your pup, and that might cause him to stop eating. Tons of stressors can cause a hormonal imbalance in your dog. For example, moving to a new home, being away from their pet parents, introducing a new household member, leaving their litter, losing a fur friend, or being left in a kennel or someone else’s care./hemorrhagic-gastroenteritis-hge-in-dogs-338428_round1-990c45142e65445a9cfa7541bd284d4f.png)
There are cases when a dog might have severe separation anxiety inasmuch as he wouldn’t eat his meal while his owners are away. If your dog is depressed from losing someone dear to him, he might not eat for days. It could also be that your dog is pregnant, and all the hormonal changes going on in her body is causing her to lose her appetite. However, loss of appetite in pregnant dogs is normal, and you shouldn’t be too worried about it as it will only last for the first few days of her pregnancy.
2. Your Dog Doesn’t Like Gross Food or Prescription Diets
Sometimes people say that dogs like to eat anything, but that’s not necessarily true. Since dogs have a more sensitive nose than humans, they can smell if the food in their bowl has gone bad. Make sure to read the label of any dog food you’re giving your pet to make sure it hasn’t expired. If you’re feeding your dog fresh food, make sure nothing is rotten or growing molds or has been left out in the open for too long.![]()
If your dog is on a prescription diet, there’s a big chance that he won’t like the new food being presented to him and refuse it. Choosing a hydrated, natural diet like Volhard gives your dog whole food ingredients, no synthetics, and makes your dog feel good when they eat.
3. Your Dog is Overfed
Many dogs today are overfed and overweight. A lot of that is due to the feeding guidelines written on the back of commercial dog food. Some guidelines would tell you to serve 4-5 cups of food to your pup, but not all dogs can finish that recommended amount. Forcing your dogs to eat more than they need can cause digestive problems and lethargy, which will lead to more appetite loss. It is about understanding calories- just like you do with your food. If the dog is taking in more calories than expending them- then you will get a dog that is obese or not eating when food is presented.
Additionally, giving them too many doggy treats to reward them for good behavior or just to show them some extra love can lead to overfeeding. Remember that treats should be no more than 10 percent of their daily calorie intake. As tempting as it is to give your dog all the doggy treats he wants, don’t. Your dog will only end up relying on those treats as their sustenance instead of the real food they should be eating.
Remember that treats should be no more than 10 percent of their daily calorie intake. As tempting as it is to give your dog all the doggy treats he wants, don’t. Your dog will only end up relying on those treats as their sustenance instead of the real food they should be eating.
4. Your dog simply does not like to eat a lot
Some canines just don’t have a big appetite, and you shouldn’t worry about that. There is nothing wrong with them. They were just born that way, and it’s in their genetics. For example, thousands of years ago, Huskies were bred to run and carry sleds all day. Their bodies have adapted to working all day and not stopping for any lunch breaks, so their metabolism is highly efficient, and they can go on happily about their day even with just a tiny amount of food in their system.
Moreover, your hound has descended from long ancestors that hunt in the wild and can only eat when they find food. That means that dogs’ bodies are fully adapted to living a life of fasting and gorging. Their bodies are masters of storing energy, and once it’s depleted, your dog will eat on its own.
Their bodies are masters of storing energy, and once it’s depleted, your dog will eat on its own.
5. Your dog is spoiled
We know that it’s easy to get carried away with spoiling our beloved fur children. We want them to have all the finer things in life and live like kings and queens of the household. However, spoiling your dog with too many grub options can create a tiny fur monster. This is especially true for the smaller, furry dog breeds like Shih Tzus. They are as picky as they are cute. One day you might switch out their regular dog food for something else and notice that they’re not eating it, so you give them a nice juicy steak instead. If you keep dressing up your puppy’s food with something more mouthwatering, your dog will develop an attention-seeking mindset of, “If I don’t eat this, my owner will give me something better.”
Giving them treats before their meal times will also cause them to lose their appetite. That’s why you never give dessert before dinner. Try not to be swayed by their puppy-dog eyes when they ask for a better dish. Dogs will never starve themselves to death, and they will eat when they are hungry.
Try not to be swayed by their puppy-dog eyes when they ask for a better dish. Dogs will never starve themselves to death, and they will eat when they are hungry.
6. Your dog is ill
The most probable reason why your dog has lost his appetite is that he is sick. When you look up different symptoms for dog illnesses, you will see that loss of appetite is the most common. Whether it be bacterial or viral infections, dental issues, or more severe illnesses, dogs will not even want to think about eating when they can feel something wrong going on inside their body. As soon as you see that your dog’s loss of appetite is accompanied by other symptoms like vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, bloody stools, and other concerning signs, take them straight to the vet so you can diagnose and treat them as quickly as possible.
7. Your dog has kidney problems
As your dog ages, it starts to develop more chronic diseases. If you see a drastic change in your dog’s eating, drinking, and urinating patterns, then your dog might be exhibiting symptoms of kidney disease. Kidney failure in dogs can present with several gastrointestinal symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, increased thirst, and a loss of appetite. This is because the kidneys are not filtering the toxins out of the system, causing damage to the digestive tract. This means that your dog may feel pain or nausea when eating and blame the food, therefore refusing to eat any more as it causes such discomfort.
Kidney failure in dogs can present with several gastrointestinal symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, increased thirst, and a loss of appetite. This is because the kidneys are not filtering the toxins out of the system, causing damage to the digestive tract. This means that your dog may feel pain or nausea when eating and blame the food, therefore refusing to eat any more as it causes such discomfort.
Changes in diet are often used to treat kidney disease, and changes are made depending on the stage and severity of the disease, so check with your vet before altering the food you give your dog.
Dogs will experience a loss of their healthy appetite at some point in their lives, and as dog parents, you will always be concerned whenever they do. However, being aware of the different reasons for their decreased eating habits can help you solve the problem faster and get them back to eating well. You know your dog best, so trust your instincts and pay attention when your dog expresses any change in his eating patterns.
However, being aware of the different reasons for their decreased eating habits can help you solve the problem faster and get them back to eating well. You know your dog best, so trust your instincts and pay attention when your dog expresses any change in his eating patterns.
What to do if a puppy or dog does not eat and why it happens
Why a dog does not eat. What could it be and what to do?
A dog may refuse food for a variety of reasons. Many diseases can begin with this symptom.
If your dog has one of the following signs, then it is better for you to go to the veterinarian without delay:
- depression, lethargy
- elevated body temperature
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- constipation
- change in quantity and color of urine
- discharge from nose and/or eyes
- shortness of breath, labored breathing
- bitch leaks
The reasons why a dog does not eat are not necessarily related to illness.
 Various factors can affect the lack of appetite in a dog:
Various factors can affect the lack of appetite in a dog:
- The dog has already managed to satisfy his hunger))). Check to see if the dog has eaten something that you didn’t know about, such as from a trash bin, from a table, or by opening a bag of food yourself. It happens that way too. Interview relatives – perhaps someone has already fed a pet.
- Change in feed type and quality. Dogs are less sensitive to dietary changes than cats. However, they, too, may “overshoot” if the food has a change in taste or smell. Therefore, think about what could have changed in the last 1-2 days in the pet’s diet. The transition from one type of food to another should be carried out gradually, over 7-10 days, mixing the new food with the old one.
- Features of sexual behavior. During the period of active sexual hunting, both in males and in females, appetite may decrease. The reproductive instinct overcomes the basic physiological needs 😉 .
- Severe stress. A long trip, great physical activity, the departure of a beloved owner can reduce the dog’s appetite.

What diseases are most often accompanied by a dog’s refusal to eat?
1. Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
In such a situation, very often the dog may want to eat, be interested in food, but when approaching the bowl or trying to eat something, he will refuse the offered food. Can take a piece in his mouth and spit it out, try to eat on one side. Most common dental problems in dogs:
- traumatized teeth
- Tartar
- gum disease
- papillomatosis (more often in young dogs)
- abscesses
- foreign objects lodged between teeth or soft tissue
- tumors of the oral cavity.
You can read about the prevention of dental diseases on the website page.
2. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
A dog may not eat or eat poorly if it develops any of the following problems of the gastrointestinal tract: gastroenteritis, duodenitis, colitis As a rule, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract will be accompanied by other symptoms – vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, weight loss with a long course. In this case, you should not self-medicate or treat on the Internet, but consult a doctor with your pet as soon as possible. Dogs, especially puppies and toy breeds, can become dehydrated and dehydrated very quickly. To establish a diagnosis after examination by a doctor, additional research methods are most likely required – clinical and biochemical blood tests, ultrasound, and in some cases x-rays. Acute viral infections in dogs, in addition to a decrease in appetite, will be accompanied by fever, deterioration in general condition, digestive disorders, cough, nasal discharge. Chronic infections can occur without pronounced symptoms. Only a doctor can determine the disease by conducting a complete clinical examination and the necessary diagnostics. Especially relevant for dogs are diseases that are carried by ticks (vector diseases) – babesiosis (formerly called piroplasmosis), ehrlichiosis, Lyme disease. This applies more to females. Since quite often, especially with age, in the period after estrus, they develop inflammation of the uterus (endometritis, pyometra). With an open form of pyometra, you can see bloody or purulent discharge from the loop. With a closed form, there may be no discharge. In the later stages of pyometra, you can notice an increase in the volume of the abdomen. Sometimes, after estrus, females have a false pregnancy, which may be accompanied by a change in behavior (the dog is actively carrying toys), the appearance of milk, and thickening of the mammary glands (mastitis). The area of the mammary glands can become inflamed, cause pain, deterioration in general well-being. All of them will be accompanied by additional characteristic symptoms. Based on this information, let’s summarize – what to do if your dog does not eat. Do not give your dog any medication before he sees a doctor. When refusing food, there can be no generally accepted recommendations, since the causes of lack of appetite in dogs are very diverse. If the cause is physiological or not very serious, the appetite will recover on its own. And if more than a day has passed and you do not understand the reasons for the condition of the pet, only a veterinary specialist should understand the reasons and give recommendations. The sooner the cause is identified, the more targeted the treatment will be and the better the result! If the puppy does not eat, this is always a reason to take a closer look at his condition. The younger the puppy, the higher the risk of a poor outcome, since the immune system is not yet ready to fully fight viruses. But let’s go in order. The first thing to exclude is not diseases, but the influence of third-party factors: If you just adopted a puppy, find out exactly what the previous owners or breeders fed him. And the first time feed exactly the same. And when the baby gets used to the new home, then you can gradually switch to the food you want. The most common diseases that cause a puppy to refuse food: 1. First of all, these are parasitic diseases. 90% of puppies have worms and/or protozoa, even if they come from a “good” family and his mother has been dewormed. There is no doubt about puppies picked up on the street. If the puppy is very malnourished, has external parasites, deworming is best done under medical supervision. 2. Viral infections. As mentioned above, this is a very dangerous situation for the puppy’s health and life. Most often in small puppies, parvovirus enteritis occurs (causes very severe inflammation of the intestines, destroys the immune system, in the smallest it affects the heart muscle). The disease is life threatening. And it requires prompt intervention of a specialist. 3. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. At a young age, in addition to inflammation of the stomach and intestines of a parasitic and infectious nature, foreign bodies and poisoning are more common when the puppy has eaten something inedible and harmful (leaves of poisonous plants, chocolate and other “goodies”) With regard to puppies, the recommendation is doubly relevant do not self-medicate. And if the condition of the four-legged baby causes concern, seek professional help as soon as possible. This could save his life.
3. Infectious and parasitic diseases
 They can also occur in acute and chronic forms. May be accompanied by depression, fever, discoloration of urine (dark yellow, red, burgundy), swollen lymph nodes, stiffness of gait and lameness. They can occur alone or in combination with each other.
They can also occur in acute and chronic forms. May be accompanied by depression, fever, discoloration of urine (dark yellow, red, burgundy), swollen lymph nodes, stiffness of gait and lameness. They can occur alone or in combination with each other. 4. Diseases of the reproductive system
 Any of these conditions require professional medical attention.
Any of these conditions require professional medical attention. 5. Other systemic diseases
 And many drugs for dogs are not only not useful, but, on the contrary, are very dangerous. Therefore, you should not independently give activated charcoal, levomycetin, nifuroxazide, linex and other medicines beloved by the masses. It is strictly forbidden to drink mixtures containing alcohol to dogs (vodka with an egg is a terrible legacy of Soviet self-treatment methods) – it causes severe poisoning and burns of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach.
And many drugs for dogs are not only not useful, but, on the contrary, are very dangerous. Therefore, you should not independently give activated charcoal, levomycetin, nifuroxazide, linex and other medicines beloved by the masses. It is strictly forbidden to drink mixtures containing alcohol to dogs (vodka with an egg is a terrible legacy of Soviet self-treatment methods) – it causes severe poisoning and burns of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach. What to do if the puppy does not eat
 If the lack of appetite in a puppy is the first sign of an acute viral infection, then the bill goes not for days, but for hours. And the sooner you seek help from a veterinarian, the more chances your baby has. Unfortunately, puppies are more prone to infections and they can occur at lightning speed, with high mortality, even with the right treatment.
If the lack of appetite in a puppy is the first sign of an acute viral infection, then the bill goes not for days, but for hours. And the sooner you seek help from a veterinarian, the more chances your baby has. Unfortunately, puppies are more prone to infections and they can occur at lightning speed, with high mortality, even with the right treatment. Especially if the puppy is weakened by other factors:
1. Type of feed
 Avoid abrupt feed changes, do not introduce several new foods at once.
Avoid abrupt feed changes, do not introduce several new foods at once. 2. The puppy has already eaten something without your knowledge
3. Stress after moving to a new home, traveling in a car or transport – any factor can cause a puppy to have a poor appetite.
The following signs will also indicate the presence of helminths:
 Since the mass death of parasites can worsen the condition of the baby.
Since the mass death of parasites can worsen the condition of the baby.
CALL, take care of your pet’s health!
VET CLINIC DOG AND CAT
Call-center:
☏ (057) 751-32-42
☏ (063) 722-88-48
☏ (066) 875-31-13
☏ (096) 880-89-11 viber
Why did the dog lose his appetite?
THE DOG IS NOT EATING – WHY THE PET HAS A POOR APPETITE
Appetite is an important indicator of a pet’s health. Refusal of food may be the first sign of illness in a dog and is a reason to show the animal to a veterinarian.
WHAT TO DO IF THE DOG WON’T EAT
Short-term refusal of food, when the dog does not eat during the day, may be associated with mild malaise. It is also necessary to remember that a pet may refuse food for reasons not related to health problems.
If, in the absence of appetite, the general condition of the dog is good, it is active, meets you, wants to play and communicate, drinks water and no other symptoms are observed, analyze the animal’s feeding regimen and diet. Your dog may be getting too many treats between meals, or the daily amount of food has been exceeded. It is not uncommon for dogs to eat up the cat food that is always in the cat’s bowl and refuse their usual dog food.
Your dog may be getting too many treats between meals, or the daily amount of food has been exceeded. It is not uncommon for dogs to eat up the cat food that is always in the cat’s bowl and refuse their usual dog food.
To maintain a good appetite in a healthy dog:
-
select the type of feeding – industrial feed or natural feeding;
stick to the feed of one manufacturer, observe the daily feed rate;
try not to keep wet food in the bowl for a long time, if the dog has not eaten everything, remove the food leftovers;
do not treat your dog between feedings;
exclude the dog’s access to the food of other pets;
do not let the dog eat grass and pick up something on the street;
walk with your pet more often.
If the general condition of the animal worsens, refusal to feed is a sign of the disease. If the dog is lethargic and has no appetite, you need to pay attention to the activity and coordination of the animal, whether the dog drinks water, whether there is vomiting. Is there a desire to walk or does the pet reluctantly go outside. It is necessary to assess the behavior of the dog on a walk: weakness, lack of coordination, cough, discoloration of urine, stool disorder.
If the dog is lethargic and has no appetite, you need to pay attention to the activity and coordination of the animal, whether the dog drinks water, whether there is vomiting. Is there a desire to walk or does the pet reluctantly go outside. It is necessary to assess the behavior of the dog on a walk: weakness, lack of coordination, cough, discoloration of urine, stool disorder.
At home, a dog with reduced appetite and lethargy needs:
measure body temperature in the rectum. The normal temperature will be 37.5-39°C;
count the respiratory rate per minute at rest or in sleep. Normal number of breaths per minute: 27-30;
examine the eyes and nose for discharge;
inspect the external auditory meatus, is there any discharge;
assess the condition of the teeth, with the deposition of tartar and inflammation, it is possible that bad teeth prevent the dog from eating;
evaluate the color of the tongue, it should be pink;
in the summer, after each walk, it is necessary to examine the dog for the presence of ticks, which are carriers of certain diseases;
in case of refusal of food and lethargy, one should pay attention to the coat and skin of the animal, swelling and wounds can be a sign of bites or inflammation, redness and papules appear with allergic reactions;
it is necessary to assess the volume of the abdomen, the reaction to stimuli and the posture of the animal.

WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR
If puppy lies down and refuses to eat, this may be a sign of an incipient infection. Thus, unvaccinated puppies are prone to intestinal or respiratory infections due to underdeveloped immunity and sensitive digestion. Even a short refusal of food and water in puppies against the background of indigestion leads to bad consequences for a small organism: dehydration, intoxication, hypoglycemia. In such cases, the puppy must be immediately shown to the veterinarian.
Refusal of food in adult dog , accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, during the day, requires contacting a veterinary clinic. First aid for such symptoms is a starvation diet for 12-24 hours, giving adsorbents and preparations – sources of bifidus and lactobacilli.
Decreased appetite, wheezing and coughing in young dog for several days may be signs of inflammation of the respiratory system as a result of an infection or foreign body. Diagnosis in this case should be carried out by a veterinarian.
Diagnosis in this case should be carried out by a veterinarian.
When should you see a doctor if the dog does not eat or has a reduced appetite:
the animal has increased thirst;
the dog lies down, cannot get up, muscle trembling, weakness of the hind limbs;
pallor of the mucous membranes, impaired coordination;
a sharp increase in the volume of the abdomen;
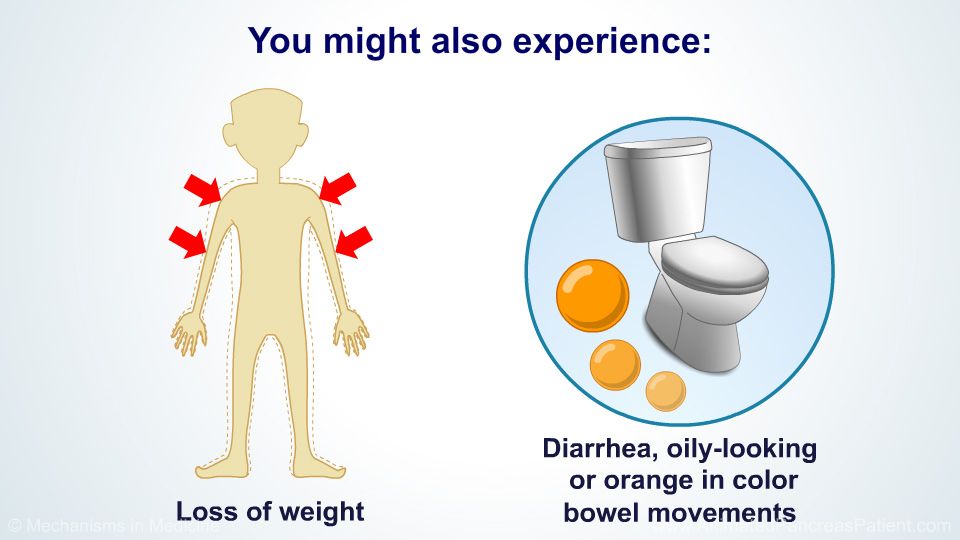
weight loss;
jaundice;
severe cough, wheezing, heavy breathing;
indomitable vomiting and profuse diarrhea;
salivation or foam from the mouth;
the dog cannot chew solid food;
bleeding from the nose or mouth;
sudden appearance of swelling in the muzzle;
violation or absence of urination for more than 12 hours;
purulent discharge from the genital loop in the female;
sharp swelling of the scrotum in a male;
lack of stool for several days;
paresis of the hind limbs;
forced hunched posture.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hemorrhagic-gastroenteritis-hge-in-dogs-3384289_FINAL-5be98e32c9e77c0051f435fb.png)
