How much blood is spotting when pregnant. Understanding Spotting and Bleeding During Pregnancy: Causes, Risks, and When to Seek Help
How much blood is considered spotting during pregnancy. What are the common causes of vaginal bleeding in early and late pregnancy. When should you contact your healthcare provider about bleeding while pregnant. What are the potential complications associated with pregnancy bleeding.
Distinguishing Between Spotting and Bleeding in Pregnancy
During pregnancy, it’s crucial to understand the difference between spotting and bleeding. Spotting refers to light bleeding where only a few drops of blood appear on your underwear, not enough to cover a panty liner. Bleeding, on the other hand, is heavier and requires the use of a panty liner or pad to prevent soaking through clothes.
Up to 25% of pregnant women experience some form of vaginal bleeding or spotting during their pregnancy. While it doesn’t always indicate a problem, it’s essential to monitor any blood loss and report it to your healthcare provider.

When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider
- Any amount of bleeding or spotting, even if it stops
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding accompanied by pain or cramping
- Dizziness with bleeding
- Pain in the abdomen or pelvis
If you experience heavy bleeding or any of the symptoms listed above, seek immediate medical attention or go to the emergency room.
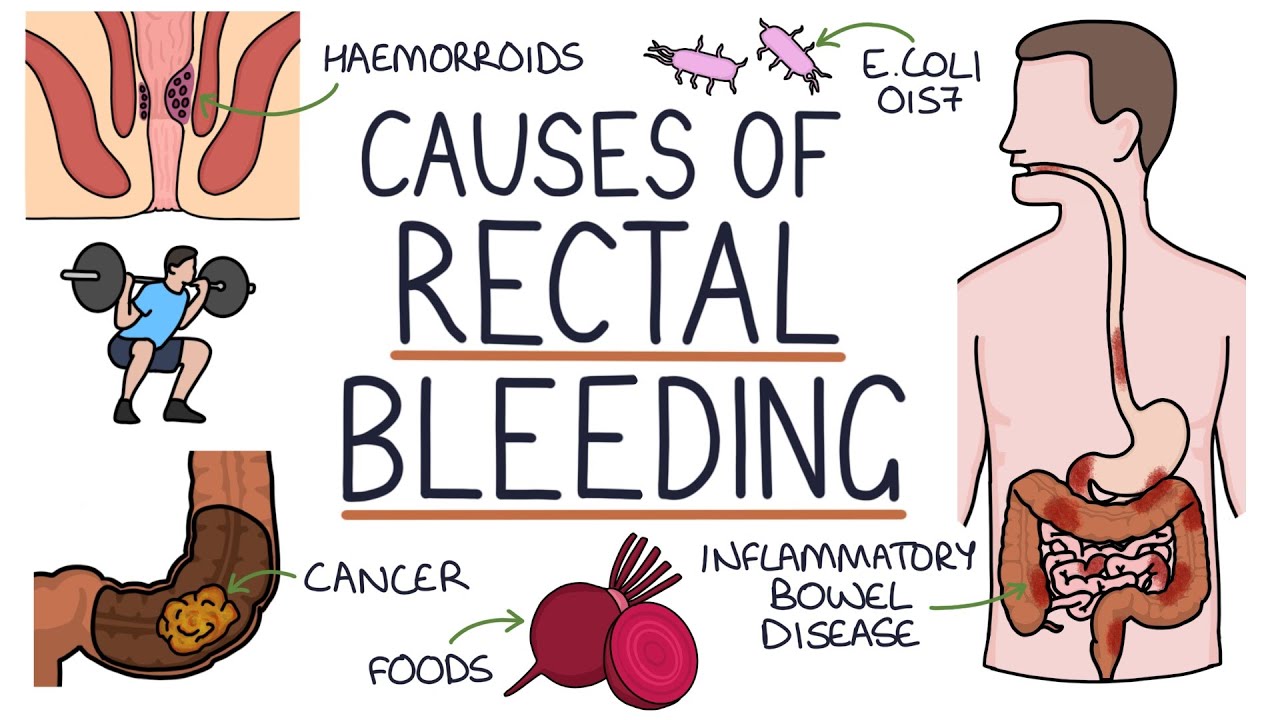
Common Causes of Early Pregnancy Bleeding
Bleeding or spotting in the first trimester can occur due to various reasons, many of which are not cause for concern. However, it’s always best to consult with your healthcare provider to rule out any serious issues.
Normal Causes of Early Pregnancy Bleeding
- Sexual intercourse
- Implantation bleeding
- Hormonal changes
- Cervical changes
- Infections
- Certain prenatal tests (e.g., amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling)
Implantation bleeding occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining, typically around 10-14 days after conception. This type of bleeding is usually light and short-lived.
Potential Serious Causes of Early Pregnancy Bleeding
- Miscarriage
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Molar pregnancy
While these conditions are less common, they require immediate medical attention. Miscarriage, the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks, is often accompanied by bleeding or spotting. An ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, can be life-threatening if left untreated. Molar pregnancy, a rare condition where abnormal tissue grows in the uterus instead of a fetus, also requires prompt medical intervention.

Causes of Bleeding in Later Stages of Pregnancy
As pregnancy progresses, the reasons for bleeding may change. Some causes of bleeding in later pregnancy include:
- Onset of labor
- Sexual intercourse
- Internal examinations by healthcare providers
- Cervical issues (infections, growths, inflammation, or cervical insufficiency)
Cervical insufficiency, also known as incompetent cervix, is a condition where the cervix begins to open prematurely. This can lead to preterm birth if not addressed promptly.
Serious Causes of Late Pregnancy Bleeding
- Preterm labor
- Placenta previa
- Placenta accreta
- Placental abruption
- Uterine rupture
These conditions can pose significant risks to both mother and baby. Placenta previa occurs when the placenta covers part or all of the cervix, while placenta accreta involves the placenta growing too deeply into the uterine wall. Placental abruption is the separation of the placenta from the uterine wall before birth. Uterine rupture, though rare, can occur during labor, especially in women with previous cesarean sections.
How to Monitor and Report Pregnancy Bleeding
If you experience bleeding during pregnancy, it’s important to document the following information for your healthcare provider:
- The amount of blood (light spotting or heavier flow)
- Whether the bleeding is getting heavier or lighter
- The number of pads used
- The color of the blood (brown, dark red, or bright red)
Avoid using tampons, douching, or having sexual intercourse while experiencing bleeding. These activities can introduce bacteria and potentially worsen the situation.
Diagnostic Procedures for Pregnancy Bleeding
When you report bleeding to your healthcare provider, they may perform several tests to determine the cause:
- Physical examination
- Ultrasound
- Blood tests
- Fetal heart rate monitoring
These tests help assess the health of both mother and baby, as well as identify any potential complications that may be causing the bleeding.
Treatment Options for Pregnancy Bleeding
The treatment for pregnancy bleeding depends on the underlying cause and the stage of pregnancy. Some possible interventions include:

- Bed rest
- Medication to prevent preterm labor
- Progesterone supplementation
- Cerclage (for cervical insufficiency)
- Close monitoring
- In severe cases, early delivery may be necessary
Your healthcare provider will recommend the most appropriate treatment based on your individual situation and the well-being of your baby.
Preventing Pregnancy Bleeding: Risk Factors and Lifestyle Changes
While not all causes of pregnancy bleeding are preventable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Quit smoking before or as soon as you become pregnant
- Maintain a healthy weight before and during pregnancy
- Attend all prenatal appointments
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for activity levels and sexual intercourse
- Manage chronic health conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension
- Avoid known risk factors for placental problems, such as cocaine use
By taking these precautions, you can help minimize the risk of complications that may lead to pregnancy bleeding.
Emotional Support and Coping Strategies for Women Experiencing Pregnancy Bleeding
Dealing with bleeding during pregnancy can be emotionally challenging. Here are some strategies to help cope with the stress and anxiety:

- Communicate openly with your partner and healthcare provider
- Join support groups for women experiencing high-risk pregnancies
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation
- Seek professional counseling if needed
- Focus on self-care and stress reduction
Remember that experiencing bleeding doesn’t necessarily mean your pregnancy is at risk. Many women who have bleeding go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies.
Understanding the causes and implications of pregnancy bleeding can help you navigate this potentially stressful situation. Always err on the side of caution and contact your healthcare provider if you experience any bleeding or spotting during pregnancy. Prompt medical attention can make a significant difference in ensuring the health and safety of both you and your baby.
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common
If you bleed or spot during pregnancy, it doesn’t always mean there’s a problem but in some cases they may be signs of a problem for you or your baby’s health
If you have heavy bleeding, call your health care provider right away
Tell your provider about any bleeding or spotting you have during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common. Up to 1 out of 4 (up to 25%) of all pregnant women have some bleeding or spotting during their pregnancy.
Bleeding and spotting in pregnancy don’t always mean there’s a problem, but they can be a sign of miscarriage or other serious complications. Miscarriage is when a baby dies in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Call your health care provider if you have any bleeding or spotting, even if it stops. It may not be caused by anything serious, but your provider needs to find out what’s causing it.
What’s the difference between bleeding and spotting?
Bleeding or spotting can happen anytime, from the time you get pregnant to right before you give birth. Spotting is light bleeding. It happens when you have a few drops of blood on your underwear. Spotting is so light that the blood wouldn’t cover a panty liner. Bleeding is when the blood flow is heavier, enough that you need a panty liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your underwear and clothes.
What should you do if you have bleeding or spotting during pregnancy?
Call your health care provider if you have any kind of bleeding during pregnancy and do these things:
- Keep track of how heavy your bleeding is, if it gets heavier or lighter, and how many pads you are using.
- Check the color of the blood. Your provider may want to know. It can be different colors, like brown, dark or bright red.
- Don’t use a tampon, douche or have sex when you’re bleeding.

Call your health care provider right away at any time during pregnancy or go to the emergency room if you have:
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding with pain or cramping
- Dizziness and bleeding
- Pain in your belly or pelvis
What causes bleeding or spotting early in pregnancy?
It’s normal to have some spotting or bleeding early in pregnancy. Bleeding or spotting in the first trimester may not be a problem. It can be caused by:
- Having sex
- An infection
- Implantation. When a fertilized egg (embryo) attaches to the lining of the uterus (womb) and begins to grow.
- Hormone changes. Hormones are chemicals made by the body.
- Changes in your cervix. The cervix is opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina.
- Certain types of testing during pregnancy like an amniocentesis or Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These are tests that are done to check for genetic abnormalities in your baby.
 Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby.
Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby. - Problems related to smoking. If you smoke, it’s best to stop before pregnancy or as soon as you know you’re pregnant.
Sometimes bleeding or spotting in the first trimester is a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Miscarriage. Almost all women who miscarry have bleeding or spotting before the miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy. This is when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus and begins to grow. An ectopic pregnancy cannot result in the birth of a baby. It can cause serious, dangerous problems for the pregnant woman.
- Molar pregnancy. This is when a mass of tissue forms inside the womb, instead of a baby. Molar pregnancy is rare.
What causes bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy?
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be caused by:
- Labor
- Having sex
- An internal exam by your health care provider
- Problems with the cervix, like an infection, growths, inflammation or cervical insufficiency.
 This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Preterm labor. This is labor that happens too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Placenta previa. This is when the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix.
- Placenta accreta. This is when the placenta grows into the wall of the uterus too deeply.
- Placental abruption. This is when the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus before birth.
- Uterine rupture. This is when the uterus tears during labor. This happens very rarely. It can happen if you have a scar in the uterus from a prior cesarean birth (also called c-section) or another kind of surgery on the uterus.
 A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
How are bleeding and spotting treated?
Your treatment depends on what caused your bleeding. You may need a medical exam and tests.
Most of the time, treatment for bleeding or spotting is rest. Your provider may also suggest treatments like:
- Take time off from work and stay off your feet for a little while
- You may need medicine to help protect your baby from Rh disease. Rh disease is when your blood and baby’s blood are incompatible (can’t be together). This disease can cause serious problems — even death — for your baby.
- Don’t have sex, douche or use tampons
- If you have heavy bleeding, you may need a hospital stay or surgery
Last reviewed April 2020
How Much Bleeding During Pregnancy Is Normal?
Contrary to how it may seem, bleeding during pregnancy is actually common. About 25% of pregnant women experience some form of bleeding or spotting during pregnancy. This doesn’t always indicate there is an issue, but it should be monitored. This could be a sign of complications or a miscarriage before 20 weeks of pregnancy. Keeping in contact with your healthcare provider during this time will help you navigate bleeding during pregnancy.
About 25% of pregnant women experience some form of bleeding or spotting during pregnancy. This doesn’t always indicate there is an issue, but it should be monitored. This could be a sign of complications or a miscarriage before 20 weeks of pregnancy. Keeping in contact with your healthcare provider during this time will help you navigate bleeding during pregnancy.
Bleeding Vs Spotting: What’s the Difference?
Spotting is considered light bleeding. This might mean a few drops of blood at a time. Spotting during early pregnancy is normally not a concern. However, if the blood is heavy enough to cover a panty liner, that is considered ‘bleeding’. This type of flow is usually heavy enough to soak your clothes. Talk to your healthcare provider about heavier bleeding. They may want to set up an exam or perform an ultrasound to determine if the cause is something underlying.
Why Do You Bleed During Pregnancy?
Bleeding during pregnancy can be an indicator of a lot of things./can-cervical-mucus-tell-you-if-youre-pregnant-1960286_color1-5b4e3085c9e77c0037c50cc7.png) At some point during your pregnancy, you may experience bleeding or spotting. This happens for many reasons – commonly in the first trimester. Although, bleeding can also be a sign of an underlying issue or complication. If you are experiencing any symptoms of the sort, it’s a good idea to share them with your healthcare provider so they can help you determine if this is something to look into. But! No reason to panic, many women experience bleeding during pregnancy and go on to have a seamless birth and healthy baby.
At some point during your pregnancy, you may experience bleeding or spotting. This happens for many reasons – commonly in the first trimester. Although, bleeding can also be a sign of an underlying issue or complication. If you are experiencing any symptoms of the sort, it’s a good idea to share them with your healthcare provider so they can help you determine if this is something to look into. But! No reason to panic, many women experience bleeding during pregnancy and go on to have a seamless birth and healthy baby.
If you start to experience any kind of bleeding during pregnancy, call your healthcare provider. In the meantime here are a few to help your healthcare provider have the most information about the situation:
- Check the color of the blood. Blood can vary in color. Take note if you are experiencing bright red, dark or brown blood.
- Keep track of how heavy the flow is. Does it fluctuate between heavy and light? How many pads or panty liners have you used?
- Make sure to avoid tampons, douches and intercourse when you are bleeding during pregnancy.

If you start to experience any of the following, call your healthcare provider immediately or go to the emergency room:
- Bleeding with pain or cramping
- Very heavy bleeding
- Pain in your abdomen or pelvis
- Bleeding and dizziness
Bleeding and Spotting In The First Trimester
Spotting or bleeding in the first trimester is fairly common and normally doesn’t indicate a major issue. There are many reasons you might experience this in the first trimester. Some of those reasons could be:
- Implantation – this means the fertilized egg is starting to attach itself to the lining of the uterus to begin growing
- Hormone fluctuations
- Intercourse
- Changes in the cervix
- An Infection – infections such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, UTIs, and other STIs can cause light bleeding and need to be treated by your healthcare provider
- Problems in relation to smoking.
 Smoking should be avoided during pregnancy
Smoking should be avoided during pregnancy - Certain tests during pregnancy. CVS and amniocentesis for example. These tests are done to check for genetic abnormalities in your baby that affect the baby’s genetics. Some genetic abnormalities passed down to the baby from mom or dad can cause health problems.
- Cervical polyps – a benign growth on the cervix that can bleed during pregnancy. Normally due to increased estrogen levels
Other times, bleeding can be a symptom of a much larger problem. Some of those issues can be:
- Ectopic pregnancy: this is when a pregnancy starts to form outside of the uterus, for instance, the fallopian tubes. This can not only be serious, but life-threatening. An ectopic pregnancy cannot result in the birth of the baby
- Molar pregnancy: this condition is rare but possible. This is when a fertilized egg implants in your uterus, but instead of a baby forming – it becomes a tumor/mass tissue
- Subchorionic hematoma: this is when one of the membranes that surround the embryo inside your uterus.
 This can also resolve on their own
This can also resolve on their own - Miscarriage: this is the loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks. Miscarriages can start with light bleeding and then gets heavier over time accompanied by severe cramping.
Bleeding and Spotting in the Second or Third Trimester
Bleeding after the first trimester is often caused by a more serious condition. If you start to bleed in the second or third trimester, speak to your healthcare provider so they’re aware of your symptoms and can help you plan what to do next.
Here are a few reasons that you might be bleeding during your second and third trimester:
Placental Abruption: this is a rare condition but can be very dangerous for both the mother and the fetus. This is when the placenta detaches from the wall of the uterus.
Placenta Previa: this is another rare condition that is even more rare after 20 weeks of pregnancy. This is when the placenta covers all or part of your cervix.
Placenta Accreta: this happens when the placenta grows deep into the wall of the uterus
Uterine Rupture: this is a rare occurrence when the uterus tears during labor. This can happen if you have previous scarring from a poor c-section birth for instance.
Incompetent Cervix: this is when the cervix opens too early and causes premature labor.
Preterm Labor: this can be defined by other symptoms other than bleeding like, cramping, contraction or rupturing membranes. In addition, bleeding can be a sign of premature labor which is defined as labor occuring earlier than 37 weeks.
Bloody Show: this means the bleeding is mixed with mucus. This normally happens at the end of the pregnancy and is a sign that the body is preparing for labor.
Miscarriage: however, a miscarriage after the 20th week of pregnancy is normally labeled a stillbirth.
How Much Bleeding Is Normal In Pregnancy?
Early on in pregnancy, spotting is often a normal symptom and nothing to be overly concerned with. Regardless of how common it is, it’s important to let your healthcare provider know and ensure there isn’t more to take into consideration.
Regardless of how common it is, it’s important to let your healthcare provider know and ensure there isn’t more to take into consideration.
Although spotting or bleeding can look different for everyone, if, at any time during your pregnancy you start to experience bleeding that resembles menstruation contact your healthcare provider right away. Menstruation type bleeding meaning: a steady flow of blood that lasts several days. At no point should that bleeding also be accompanied by pain.
When talking to your healthcare provider, take note of what the blood looks like so they can help you evaluate your symptoms. Some details could include:
- The consistency of your blood. Is it thick or more watery? Is the flow accompanied by clots?
- The color of your blood. Is the blood more pink or red? Maybe it’s more of a brown color?
- The amount of blood. Is it a few more drops than normal? Are you filling a panty liner or pad?
Details like these will help your healthcare provider figure out the level of care you might need at the time and how urgent your situation could be.
Is Bleeding and Spotting Treated?
Treatment is entirely based on the situation. Depending on what caused the bleeding, and the symptoms surrounding the bleeding will all determine if treatment is necessary. At times, healthcare providers might use medical exams and tests to help determine their next recommendation.
There are many times that the treatment recommended is just rest. Aside from rest, common treatments could also be:
- Medication to help protect the baby from Rh disease. A disease that means the baby and the mother’s blood are incompatible.
- Time off work and bedrest
- Heavy bleeding may mean a hospital stay or surgery
- Avoiding douches, tampons and sex
When it comes to bleeding during pregnancy, it is best to follow the recommendations from your doctor. Try to avoid activities like rigorous movement and exercise and use a pad or panty liner to help contain the bleeding.
Bleeding During Pregnancy? Call Rosh Maternal and Fetal Medicine for Complete Access Obstetric Care
Here at Rosh Maternal & Fetal Medicine, we’re committed to making sure all our expectant moms can reach us any time of day and any day of the week to report potential problems, discuss pressing concerns, or ask a simple question.
As such, you can always get in touch with one of our experienced obstetricians for prompt advice if you happen to experience spotting or bleeding during any trimester.
To learn more, call our Manhattan, New York City office today, or use the easy online tool to schedule a visit with one of our board-certified obstetricians.
articles of the Oxford Medical clinic Kyiv
Contents:
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal?
When should you see a doctor for discharge?
Discharge during early pregnancy
Discharge during late pregnancy
Discharge during pregnancy by color
- 9000 8 Spotting during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes a number of physiological changes – her body changes, adapts to carrying a baby and future childbirth. Changes can also occur with vaginal discharge. After conception, their number or color may become different, which often makes a woman worry. In order not to worry for no reason, but also not to miss a possible reason to see a doctor, you need to know which discharges are normal and which are not.
Changes can also occur with vaginal discharge. After conception, their number or color may become different, which often makes a woman worry. In order not to worry for no reason, but also not to miss a possible reason to see a doctor, you need to know which discharges are normal and which are not.
What discharge during pregnancy is considered normal?
The nature of the discharge at different stages of pregnancy may vary slightly. Standard variant are:
transparent or white discharge;
odor free;
not exceeding the usual volume;
not accompanied by itching, burning or other painful symptoms.
At the same time, in the first 2-4 weeks, the daily discharge may increase slightly and become thicker. It is also possible the appearance of light spotting within a few hours or a day, which occurs as a result of the implantation of the embryo to the uterine wall.
It is also possible the appearance of light spotting within a few hours or a day, which occurs as a result of the implantation of the embryo to the uterine wall.
When should you see a doctor for discharge?
During pregnancy, a woman is advised to visit a gynecologist regularly for examinations and tests. First, consultations are prescribed once a month, and then once every 2 weeks. This allows you to carefully monitor the health of the pregnant woman and the development of the fetus. But, if discomfort appears, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
One of the alarming symptoms is the appearance of atypical discharge:
yellow, green, brown;
bloody;
thick;
too abundant;
slimy;
malodorous;
accompanied by itching, burning and other symptoms.

Such a change in the nature of the discharge may be associated with the development of an inflammatory or infectious disease, as well as complications of pregnancy. To find out the exact cause, you need to do tests, conduct an ultrasound and, if necessary, other studies.
Discharge during early pregnancy
When conception occurs, changes begin in the body. First of all, the synthesis of the hormone progesterone increases and blood flow to the pelvic organs increases. These processes are often accompanied by profuse vaginal discharge. They can be translucent, white or with a slight yellowish tint. There should be no unpleasant odor or skin irritation.
Shortly thereafter, progesterone levels decrease and estrogen levels rise. At this time, a mucous plug is formed that covers the cervix. Its formation can also cause increased secretion, but gradually it should decrease and become more liquid and transparent.
In addition, in the first weeks, the ovum attaches to the wall of the uterus, which can cause light brown discharge. As a rule, they are scarce and quickly stop – within a few hours or a day. If heavy bleeding has begun, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Approximately from 5 to 20 weeks, the discharge should be the same – transparent or whitish, in small volume, odorless.
Discharge in late pregnancy
From 20 to 40 weeks of pregnancy, the discharge is normally white, free of impurities and unpleasant odor.
In the last week before childbirth, the discharge may become thinner. If they are very abundant, leakage or discharge of amniotic fluid is possible, which requires a visit to a doctor.
Characterization of pregnancy discharge by color
Normal discharge should be colorless or white. A change in color and consistency may indicate the development of a disease or complications of pregnancy.
Bright or dark yellow discharge most often occurs when inflammation develops. Grey-green and green may result from infection. Thick white discharge speaks about it – as a rule, candidiasis manifests itself. Brown discharge may be due to slight bleeding.
Oxford Medical says it is important to consider not only the color of the discharge, but also its smell, volume and consistency. A sharp and unpleasant odor appears only with bacterial or fungal diseases, so it should by no means be ignored. Also, an alarming signal is a strong increase in the volume of secretions, a change in structure, foaminess and other deviations from the norm.
There can be many reasons for abnormal discharge. To find them out, you need to conduct examinations, and then, if necessary, treatment.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy
The appearance of bloody discharge at any stage of pregnancy is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.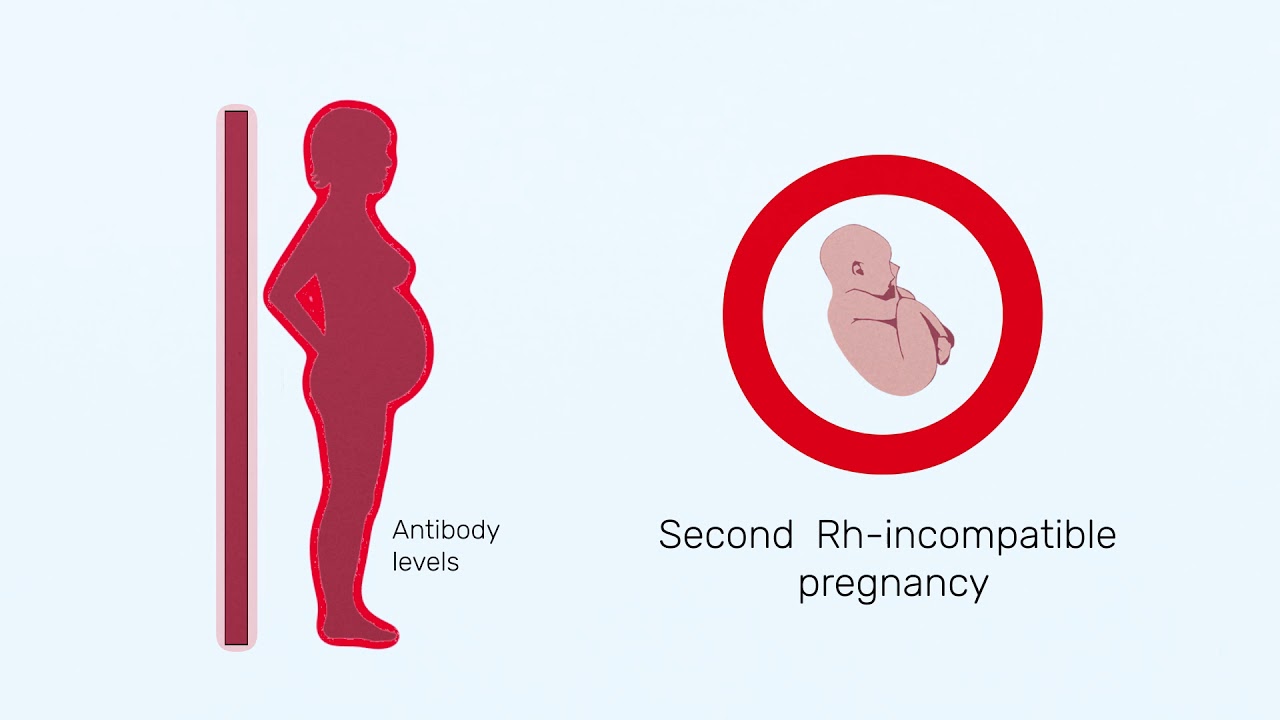
The exception is small spotting in the first weeks (usually the date of the expected menstruation), which indicates the implantation of the embryo. At this point, capillaries and small vessels can be injured, which causes light bleeding. Normally, it is very weak, not accompanied by pain or other unpleasant symptoms.
Blood-streaked discharge may also occur on the eve of childbirth as a result of cervical dilatation. This is normal, but a doctor’s consultation is required.
In other cases, both in the first and last trimester, any discharge from pale pink and brown to red is a dangerous symptom. The violation may be minor, but it is necessary to conduct an examination.
Bleeding can be caused by:
hormonal disorders;
cervical erosion;
cysts;
fibroids;
inflammatory and infectious diseases;
ectopic pregnancy;
miscarriage;
placental abruption;
threatened miscarriage or premature birth.

Regular follow-up with an experienced obstetrician-gynecologist and the implementation of all recommendations will help to avoid possible complications and concentrate on the most important thing – the joyful expectation of the baby and preparation for meeting him.
Sources:
US National Library of Medicine
International Journal of Medicine
IntechOpen
Related Services:
Pregnancy Management
Published: 09/09/2021
Updated: 09/09/2021
( Rating: 4.53, votes: 19 )
ᐉ Discharges during pregnancy ➡ What are the discharges at different periods
Pregnancy is a time of serious physiological restructuring of a woman’s body. Under the influence of hormones, the body of the expectant mother changes, adaptive-protective mechanisms are activated, the work of all organs and systems is directed to bearing a child and successful delivery. Changes in the nature of vaginal discharge is one of the reasons for concern during early and late pregnancy. Discharge during pregnancy can be dark, light, brown, bloody, spotting, not typically liquid and plentiful, with or without odor – which of them are considered normal, and which ones need to urgently run to the gynecology? Read our article.
Discharge during pregnancy can be dark, light, brown, bloody, spotting, not typically liquid and plentiful, with or without odor – which of them are considered normal, and which ones need to urgently run to the gynecology? Read our article.
What is normal discharge during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the level of activity of hormones increases, the metabolism accelerates, in connection with this, the volume of vaginal discharge may increase.
What should be the normal discharge during pregnancy:
- Transparent, homogeneous mucous, not viscous consistency.
- Color whitish or slightly yellowish.
- No off-flavour. Normally, the aroma is slightly sour.
- May be more abundant than usual in quantity, especially in the first weeks (as during ovulation, before conception).
- Without other symptoms – itching, burning, redness, hyperemia and swelling of the vulva, pain and discomfort.
During late pregnancy, the discharge is mixed with urine – the result of incontinence due to the pressure of the growing uterus on the bladder. This is also a variant of the norm, just try to visit the toilet more often.
This is also a variant of the norm, just try to visit the toilet more often.
When should you see a doctor for discharge
During pregnancy, it is important to periodically see an obstetrician-gynecologist, and the first question that the doctor asks at the consultation is is there any unusual discharge? It is by the nature of the vaginal secret that one can judge the course of pregnancy, the presence of hormonal imbalance, inflammation and other health problems. Signs of pathological discharge:
- Curdled consistency, the presence of white clots with an unpleasant sour smell – with vaginal candidiasis. This is a fungal infection that is activated against the background of hormonal changes, occurs in 30% of women during pregnancy. In addition to the characteristic discharge, thrush is accompanied by itching, redness and rashes in the vulva.
- Unpleasant aroma, atypical color and consistency are signs of dysbacteriosis or infection with bacteria, parasites.
 The most common sexually transmitted infections are chlamydia, Trichomonas, and gonococci. Atypical discharge is accompanied by pain, itching, skin rashes, ulcers, swollen lymph nodes in the groin. During pregnancy, STIs are especially dangerous: they can cause miscarriage, premature birth, placental insufficiency and abnormal development of the unborn child. If infections are detected in a pregnant woman, treatment is necessary.
The most common sexually transmitted infections are chlamydia, Trichomonas, and gonococci. Atypical discharge is accompanied by pain, itching, skin rashes, ulcers, swollen lymph nodes in the groin. During pregnancy, STIs are especially dangerous: they can cause miscarriage, premature birth, placental insufficiency and abnormal development of the unborn child. If infections are detected in a pregnant woman, treatment is necessary. - Bloody, brown discharge, sometimes with clots – may occur with the threat of fetal loss, ectopic pregnancy or the presence of pathologies of the cervix. Blood discharge during pregnancy is usually accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen – with such symptoms, urgent medical attention is needed.
To find out the exact cause of changes in the vaginal secretion, a doctor’s consultation and examination (ultrasound, tests) is necessary.
What can be discharge during early pregnancy?
Normal discharge in early pregnancy – translucent, whitish or yellowish, without foreign smell, itching and skin irritation. During the first month, the secret is released more abundantly than always, and from 5 to 20 weeks, its volume decreases to the usual, the consistency becomes more liquid and transparent.
During the first month, the secret is released more abundantly than always, and from 5 to 20 weeks, its volume decreases to the usual, the consistency becomes more liquid and transparent.
In the first days of pregnancy, due to slight damage to the blood vessels of the myometrium during the implantation of a fertilized egg, there may be a smearing brown discharge. Usually they are scarce and short-term, pass in a couple of days.
Can there be spotting during early pregnancy – a frequent topic of discussion in women’s forums. If the bleeding is severe and even more so accompanied by pain, urgently call an ambulance. The cause may be a threatened miscarriage or a miscarriage that has already begun, a tubal pregnancy, or a hydatidiform mole.
Brown discharge during early pregnancy (at 5, 6, 7 weeks), even without pain and foreign smell, is another reason not to postpone a visit to the gynecologist. Such symptoms often indicate a threatened miscarriage or missed pregnancy./implantation-bleeding-or-early-miscarriage-2371266_V22-9ee423cc0f334d29b0f2639baedbb480.png)
Discharge in late pregnancy
From the 20th week of pregnancy, a whitish discharge without blood, clots or foreign smell is normal. In the last three months, from 7 to 9, you need to pay special attention to the quality and volume of vaginal secretions:
- Too abundant, watery discharge may be the result of leakage of amniotic fluid. The risk of such a problem increases from 18-20 weeks and later. Amniotic fluid is released when the fetal membrane is ruptured, it leaks especially strongly when moving or changing position. If you find this – do not delay a visit to the doctor.
- Spots of gray or yellowish color on linen in combination with liquid, non-viscous secretions may indicate the onset of labor – the release of the mucous plug and the outflow of amniotic fluid. Need medical help.
- The presence of brown or bloody discharge during late pregnancy is one of the likely signs of a dangerous pathology, premature placental abruption.
Discharge during pregnancy: differences in color
The color of vaginal discharge, as well as other characteristics (smell, volume, density) is an important indicator of health and the absence of complications during pregnancy. Normally, the secret is colorless, slightly whitish or yellowish. Color changes should be a concern:
Normally, the secret is colorless, slightly whitish or yellowish. Color changes should be a concern:
- Greenish-yellow, frothy discharge is a sign of trichomoniasis.
- Greyish-white secret of a sticky, frothy consistency with a fishy smell – a manifestation of gardnerellosis.
- Yellow-green, mucoid or purulent, sometimes bloody, symptoms of gonorrhea.
- White or yellow, thick discharge with lumps – a sign of candidiasis.
- Brown, spotting, pink or red mucus (not during the first weeks of pregnancy, but later) – indicate the threat of interruption, uterine polyps and other disorders.
If there are changes in the shade and other characteristics of the discharge during pregnancy, an examination is necessary. Upon confirmation of the diagnosis, a course of therapy will be required.
Spotting during pregnancy
Even slight spotting during pregnancy, regardless of the duration, requires a doctor’s consultation.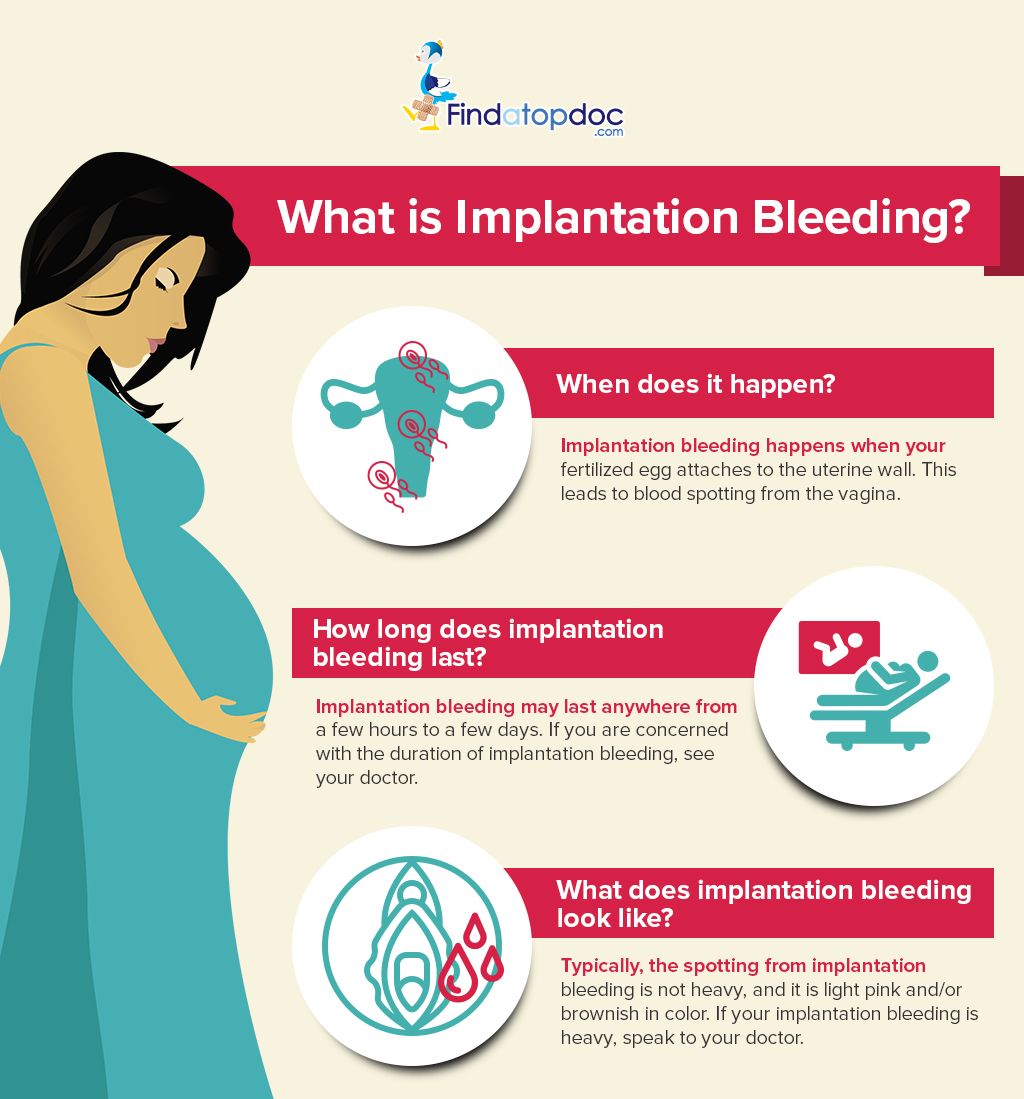


 Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby.
Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby. This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.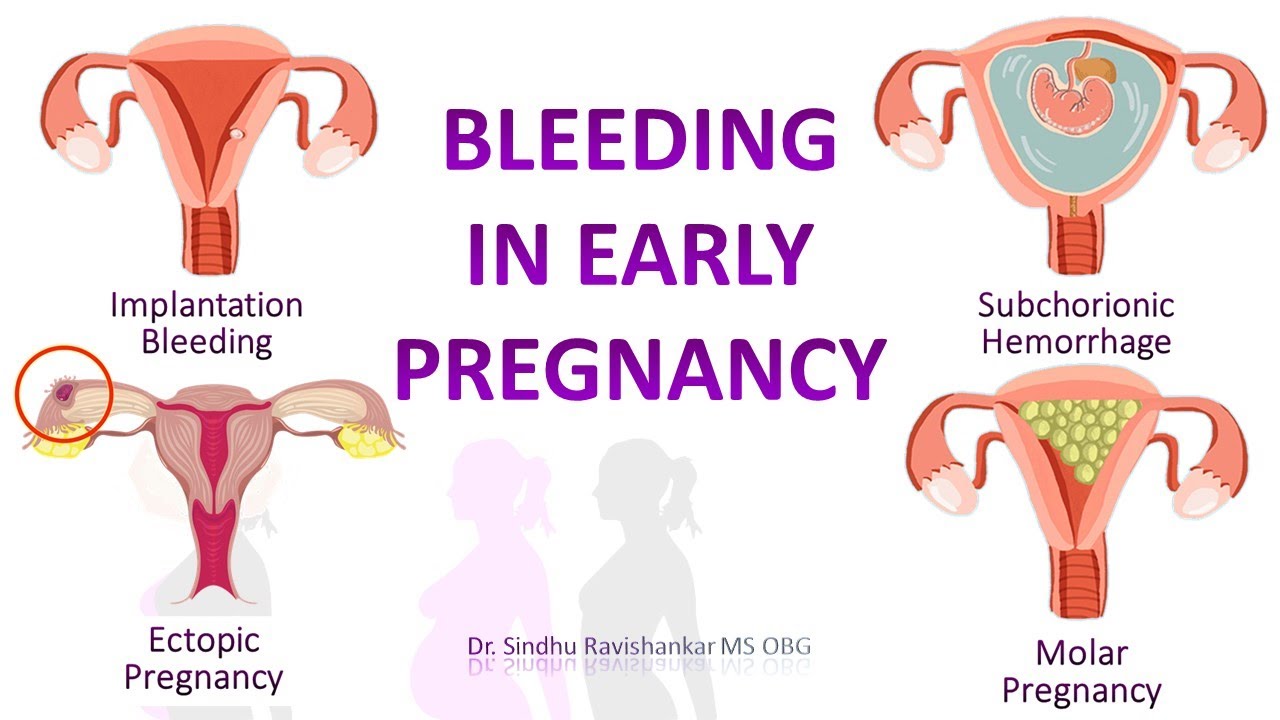 A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
 Smoking should be avoided during pregnancy
Smoking should be avoided during pregnancy This can also resolve on their own
This can also resolve on their own

 The most common sexually transmitted infections are chlamydia, Trichomonas, and gonococci. Atypical discharge is accompanied by pain, itching, skin rashes, ulcers, swollen lymph nodes in the groin. During pregnancy, STIs are especially dangerous: they can cause miscarriage, premature birth, placental insufficiency and abnormal development of the unborn child. If infections are detected in a pregnant woman, treatment is necessary.
The most common sexually transmitted infections are chlamydia, Trichomonas, and gonococci. Atypical discharge is accompanied by pain, itching, skin rashes, ulcers, swollen lymph nodes in the groin. During pregnancy, STIs are especially dangerous: they can cause miscarriage, premature birth, placental insufficiency and abnormal development of the unborn child. If infections are detected in a pregnant woman, treatment is necessary.