How to reduce gas from stomach. 10 Effective Tips to Reduce Stomach Gas, Relieve Pain, and Alleviate Bloating
How can you effectively reduce stomach gas. What are the best methods to relieve gas pain. Which natural remedies help alleviate bloating. What dietary changes can reduce excessive gas. How do over-the-counter medications help with gas symptoms. When should you see a doctor about gas issues. What lifestyle modifications can prevent gas buildup.
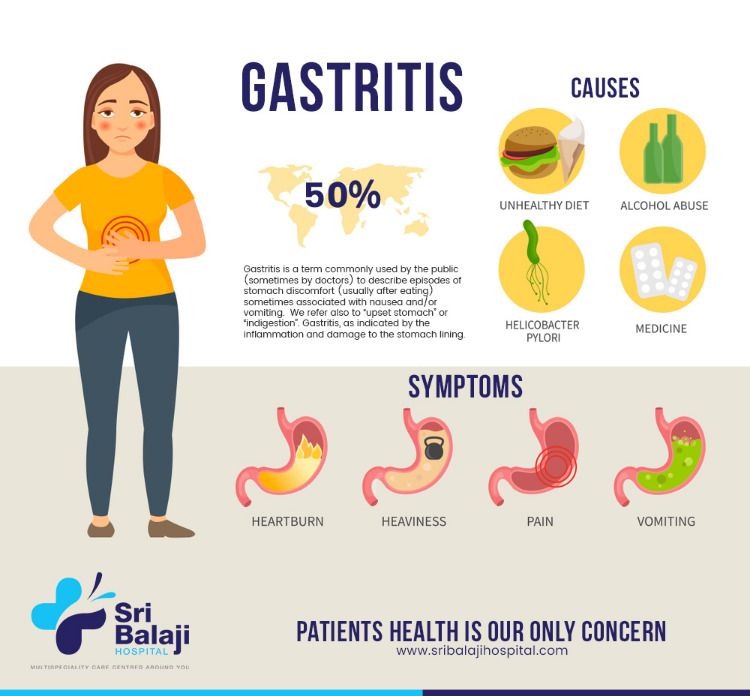
Understanding Stomach Gas: Causes and Prevalence
Abdominal gas is a common digestive issue that affects many individuals. The average adult passes gas between 13 and 21 times daily, which is considered a normal part of the digestive process. However, when gas accumulates in the intestines and cannot be expelled, it can lead to discomfort and pain.
Several factors can contribute to increased gas production and exacerbate symptoms:
- Overeating
- Swallowing air while eating or drinking
- Chewing gum
- Smoking cigarettes
- Consuming certain foods
Additionally, conditions that cause diarrhea or constipation can worsen gas-related symptoms. It’s important to note that while gas is typically harmless, persistent or severe symptoms may warrant medical attention.

Natural Remedies for Gas Relief
Many individuals find relief from gas symptoms through natural remedies. These options are often easily accessible and can be incorporated into daily routines.
Peppermint: A Soothing Solution
Peppermint has shown promising results in reducing symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome, including gas. How can you incorporate peppermint into your routine? Consider drinking a cup of peppermint tea before each meal or taking peppermint supplements. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen, as peppermint can interfere with iron absorption and certain medications.
Chamomile Tea: A Calming Brew
Chamomile tea is another natural remedy that may help alleviate indigestion, trapped gas, and bloating. For optimal results, try consuming a cup of chamomile tea before meals and at bedtime. This soothing beverage may provide relief for some individuals experiencing gas-related discomfort.
Apple Cider Vinegar: A Potential Bacterial Fighter
Apple cider vinegar has gained popularity as a natural remedy for various digestive issues. How can it help with gas? It may combat bacteria that contribute to gas accumulation and discomfort. To use apple cider vinegar, dilute a tablespoon in water or tea and consume it before meals or up to three times daily as needed.

Cloves: Nature’s Digestive Aid
Cloves, commonly used in cooking, may help reduce bloating and gas by stimulating the production of digestive enzymes. To harness the potential benefits of cloves, add two to five drops of clove oil to an 8-ounce glass of water and drink after meals.
Physical Activity: A Simple Yet Effective Approach
Exercise can play a significant role in relieving trapped gas and associated pain. How does physical activity help with gas? Movement stimulates the digestive system, potentially aiding in the expulsion of excess gas. Consider incorporating these activities into your routine:
- Walking after meals
- Jumping rope
- Running
- Brisk walking
These exercises may help you expel trapped gas and alleviate discomfort. Remember to start slowly and gradually increase intensity, especially if you’re new to regular physical activity.
Dietary Modifications for Gas Prevention
For many individuals, dietary changes can significantly impact gas production and associated symptoms. Understanding how food is digested and fermented in the body can help explain why certain foods may lead to increased gas.

The Digestion Process and Gas Production
Food is primarily digested in the small intestine. Any undigested matter then moves to the colon, where it undergoes fermentation by bacteria, fungi, and yeast as part of the digestive process. This fermentation produces methane and hydrogen, which are eventually expelled as flatus.
Identifying Trigger Foods
Common foods that may contribute to increased gas production include:
- Beans and lentils
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage)
- Dairy products (for those with lactose intolerance)
- Carbonated beverages
- High-fiber foods
- Artificial sweeteners
Keeping a food diary can help identify specific trigger foods that may be causing excessive gas in your individual case. Once identified, you can experiment with reducing or eliminating these foods to see if symptoms improve.
Implementing Dietary Changes
When making dietary modifications to reduce gas, consider the following strategies:
- Gradually increase fiber intake to allow your digestive system to adjust
- Chew food thoroughly to aid digestion
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to prevent overloading the digestive system
- Stay hydrated to support healthy digestion
- Consider probiotics to promote a healthy gut microbiome
Remember that dietary changes may take time to show effects, so patience and consistency are key when implementing these modifications.

Over-the-Counter Solutions for Gas Relief
When natural remedies and dietary changes aren’t providing sufficient relief, over-the-counter (OTC) medications can offer additional support in managing gas symptoms.
Activated Charcoal: An Absorption Aid
Activated charcoal is an OTC medication that can help eliminate gas trapped in the colon. How should you use activated charcoal for gas relief? Typically, tablets are taken right before and one hour after meals. However, it’s important to follow the dosage instructions on the product label and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Simethicone: Consolidating Gas Bubbles
Simethicone, found in products like Gas-X, Mylanta Gas, and Phazyme, works by consolidating gas bubbles in the stomach, making them easier to expel. This medication can provide relief from gas-related discomfort. As with any medication, follow dosing instructions carefully and discuss use with your doctor, especially if you’re pregnant or taking other medications.

Beano: Enzyme Support for Digestion
Beano is an OTC digestive aid containing an enzyme that breaks down sugars in beans and certain vegetables. How does Beano help with gas? By aiding in the digestion of these potentially gas-producing foods, Beano can help reduce abdominal gas. It’s available in liquid or pill form. Individuals with galactosemia should consult their doctor before using this product.
Lactase Supplements: Aid for Lactose Intolerance
For those with lactose intolerance, lactase supplements can be a game-changer. Lactase is the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose, the sugar found in milk. By taking lactase supplements, individuals who struggle to digest dairy products may be able to consume them with reduced gas and discomfort.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Gas Issues
While occasional gas is normal, certain symptoms may indicate a need for medical evaluation. It’s important to recognize when gas-related issues might be a sign of an underlying condition.

Red Flags to Watch For
Consider making an appointment with your doctor if your gas symptoms:
- Cause significant distress or interfere with daily activities
- Change suddenly or drastically
- Are accompanied by constipation, diarrhea, or unexplained weight loss
- Persist despite lifestyle and dietary changes
- Are associated with severe abdominal pain or bloating
These symptoms may indicate an underlying digestive disorder or other medical condition that requires professional evaluation and treatment.
Potential Underlying Conditions
Persistent or severe gas symptoms can sometimes be related to conditions such as:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Celiac disease
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
- Gastroparesis
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
A healthcare professional can perform the necessary tests and examinations to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Prescription Medications for Chronic Gas Issues
In some cases, over-the-counter remedies and lifestyle changes may not be sufficient to manage gas-related symptoms. When this occurs, your doctor may consider prescription medications to address the underlying cause of your gas issues.

Medications for Specific Conditions
Depending on the diagnosed condition, your doctor may prescribe medications such as:
- Proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers for GERD
- Antispasmodics or antidepressants for IBS
- Immunosuppressants or biologics for IBD
- Prokinetics for gastroparesis
- Antibiotics for SIBO
These medications are tailored to address specific digestive issues and should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Importance of Professional Guidance
Why is it crucial to work closely with your doctor when using prescription medications for gas issues? Prescription medications can have potential side effects and interactions with other drugs or supplements. Your doctor can monitor your progress, adjust dosages as needed, and ensure that the chosen treatment plan is effective and safe for your individual situation.
Lifestyle Modifications to Prevent Gas Buildup
In addition to dietary changes and medical interventions, certain lifestyle modifications can help prevent excessive gas buildup and associated discomfort.

Mindful Eating Habits
Adopting mindful eating practices can significantly impact gas production. Consider implementing these habits:
- Eat slowly and chew food thoroughly
- Avoid talking while eating to reduce air swallowing
- Sit upright while eating to aid digestion
- Avoid using straws, which can introduce extra air into the digestive system
- Limit carbonated beverages
Stress Management
Stress can impact digestive function and potentially exacerbate gas-related symptoms. How can you manage stress to improve digestive health? Consider incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as:
- Regular meditation or mindfulness practices
- Deep breathing exercises
- Yoga or tai chi
- Regular exercise
- Adequate sleep
By managing stress levels, you may notice improvements in overall digestive function and a reduction in gas-related discomfort.
Quitting Smoking
Smoking can contribute to increased gas production and digestive discomfort. If you smoke, consider quitting or seeking support to reduce your tobacco use. Not only can this improve your digestive health, but it also offers numerous other health benefits.

Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight, particularly around the abdominal area, can put pressure on the digestive system and potentially exacerbate gas-related symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise may help alleviate these issues.
By implementing these lifestyle modifications alongside other strategies discussed in this article, you can take a comprehensive approach to managing and preventing excessive gas. Remember that everyone’s digestive system is unique, so it may take some time and experimentation to find the combination of strategies that works best for you. If you continue to experience persistent or severe gas-related symptoms despite these interventions, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
10 Tips to Get Rid of Gas, Pains, and Bloating
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission Here’s our process.
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.
Was this helpful?
Abdominal gas is quite typical. Often, certain home remedies and supplements can help you release it from your stomach. But if you’re still experiencing discomfort, you may want to see a doctor.
But if you’re still experiencing discomfort, you may want to see a doctor.
The average adult passes gas between 13 and 21 times a day. Gas is a healthy part of the digestion process. But if gas builds up in your intestines and you’re unable to expel it, you may start to feel pain and discomfort.
Gas pain, bloating, and flatus frequency can be exacerbated by anything that causes diarrhea or constipation. Gas can also be caused by:
- overeating
- swallowing air while you eat or drink
- gum chewing
- smoking cigarettes
- eating certain foods
Make an appointment with your doctor if your gas symptoms:
- cause you distress
- change suddenly
- are accompanied by constipation, diarrhea, or weight loss
Your doctor can determine the underlying cause.
If changing your diet doesn’t completely do the trick, you have several options to try.
1. Peppermint
Research has shown that peppermint tea or peppermint supplements can help reduce symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome, including gas.
Talk with your doctor before you start using supplements. Peppermint can interfere with iron absorption and certain medications. It may also cause heartburn in some people.
Supplements will have directions about how much you should take on the bottle. For peppermint tea, drink one cup before each meal for the best results.
2. Chamomile tea
Chamomile tea can also help reduce indigestion, trapped gas, and bloating. Drinking chamomile tea before meals and at bedtime may reduce symptoms for some people.
3. Activated charcoal
Activated charcoal is another type of over-the-counter medication that helps eliminate gas trapped in your colon. You take tablets right before and one hour after meals.
4. Apple cider vinegar
Drinking apple cider vinegar may help fight against bacteria that can cause abdominal gas accumulation and discomfort. Dilute a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar in a beverage, like water or tea. Drink right before meals or up to three times daily as long as needed to reduce symptoms.
5. Physical activity
Exercise can help release trapped gas and gas pain. Try walking after meals as a way to avoid gas. If you have gas pain, jumping rope, running, or walking may help you expel it.
6. Lactase supplements
Lactose is a sugar in milk. People with lactose intolerance can’t digest this sugar. Lactase is the enzyme the body uses to break down lactose. Lactase supplements are available over the counter and can help your body digest lactose.
7. Cloves
Cloves are an herb used in cooking. Clove oil may help reduce bloating and gas by producing digestive enzymes. Add two to five drops to an 8-ounce glass of water and drink after meals.
8. Over-the-counter medications
Simethicone (Gas-X. Mylanta Gas, Phazyme) is an over-the-counter medication that works by consolidating gas bubbles in your stomach, allowing you to expel them more easily.
Follow dosing instructions, and make sure to discuss this medication with your doctor if you’re taking other medications or pregnant.
Another option is Beano, which is an OTC digestive aid containing an enzyme that breaks down sugars in beans and certain vegetables, which can help reduce abdominal gas. It comes as a liquid or a pill. People with galactosemia should ask their doctor before using it.
9. Prescription medications
Depending on the cause of your abdominal gas, there are many medications that your doctor may prescribe.
This includes medications for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
10. Diet
If your gas isn’t caused by an underlying medical condition, it may be caused by what you eat. Food is digested primarily in your small intestine. What is left undigested is fermented in your colon with bacteria, fungi, and yeast as part of digestion. This process produces methane and hydrogen, which are expelled as flatus.
For many people, changing dietary habits is enough to alleviate gas and its accompanying symptoms. One way to determine which foods are giving you gas is by keeping a food diary. Common culprits include high fat or high fiber food, carbonated beverages, and beans and lentils.
One way to determine which foods are giving you gas is by keeping a food diary. Common culprits include high fat or high fiber food, carbonated beverages, and beans and lentils.
Here are 10 foods that can cause gas. Once you figure out what food is causing the gas, you can modify your diet to avoid the culprit.
Some conditions can cause excess gas. They include:
- gastroenteritis
- lactose intolerance
- celiac disease
- Crohn’s disease
- diabetes
- peptic ulcer
- irritable bowel syndrome
If no medical condition is causing the problem, preventing gas may best be accomplished by altering lifestyle habits and diet:
- Sit down during each meal and eat slowly.
- Try not to take in too much air while you eat and talk.
- Stop chewing gum.
- Avoid soda and other carbonated beverages.
- Avoid smoking.
- Find ways to work exercise into your routine, such as taking a walk after a meal.
- Eliminate foods known to cause gas.

- Avoid drinking through straws.
How do you get rid of gas quickly?
One thing that may help abdominal relieve gas a bit faster is to change your body position. Positions to reduce gas can include , for example, which can help push the gas out of the body. Other than that, medications and remedies may take some time to work, depending on the cause of your gas.
How long can trapped gas last?
Usually, trapped gas is released within a few hours. If it’s not, you should seek medical treatment in case you have another more serious medical condition.
What does trapped gas feel like?
Typically you would feel some discomfort and even pain in your stomach. It can affect the left, the right, the upper, or the lower part of your abdomen.
Gas can be painful, but it typically isn’t dangerous. If gas pain or bloating are issues for you, look to your diet and lifestyle to see what changes you can make. In many cases, lifestyle and diet modification may be able to eliminate the issue completely.
Make an appointment with your doctor if you don’t notice a difference after several weeks of lifestyle and diet changes. They can run tests to see if your symptoms are caused by a medical condition.
Trapped Gas: 9 remedies for relief
If you have trapped gas, trying home remedies and moving around may help you pass it. If it lasts a long time or occurs frequently, or you have other symptoms, you may have a health condition that needs treatment.
Trapped gas can feel like a stabbing pain in your chest or abdomen. The pain can be sharp enough to send you to the emergency room, thinking it’s a heart attack, appendicitis, or gallbladder.
Producing and passing gas is a typical part of your digestion. But when a bubble of gas gets stuck inside you, you want to relieve the pain as fast as possible. And if you have other symptoms, it’s a good idea to find out what’s causing the pain.
Read on to learn how to relieve trapped gas, what the causes might be, and tips for prevention.
Certain home remedies for relieving trapped gas work better for some people than others. You may have to experiment to see what works best and fastest for you. Most of the evidence behind these home remedies is anecdotal.
Here are some quick ways to expel trapped gas, either by burping or passing gas.
1. Move around
Walk around or exercise. Movement may help you expel the gas.
2. Get a massage
Try gently massaging the painful spot, which can stimulate gas to move downward and out of the body. In particular, using the “I LOV U” technique may be helpful.
This involves making circular massage movements on your abdominal area in the shape of the letters I, L, U, and O in the direction your bowel movements pass through the colon and small intestine.
3. Do yoga poses
Yoga may help your body relax to aid the passing of gas.
Here’s a pose to start with:
- Lie on your back and extend your legs straight up with your feet together.

- Bend your knees and put your arms around them.
- Pull your knees down to your chest.
- At the same time, pull your head up to your knees. You can also keep your head flat if it’s more comfortable.
- Hold the pose for 20 seconds or more.
Certain yoga poses may work better than others.
4. Drink more liquids
Drink noncarbonated liquids. Warm water or herbal tea helps some people. Try peppermint, ginger, or chamomile tea.
Use prepared teabags, or make your own herbal tea by steeping ginger root, peppermint leaves, or dried chamomile.
A traditional Persian remedy advises mixing 10 grams (g) each of ground cumin and fennel with 5 g of ground anise and steeping them in a cup of boiling water for 20 minutes.
5. Try herbs
Natural kitchen remedies for gas include:
- anise
- caraway
- coriander
- fennel
- turmeric
Mix one of these ground herbs or seeds into a glass of warm water and drink.
6. Try baking soda
Dissolve 1/2 teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) in a glass of water and drink it.
Be careful not to use more than 1/2 teaspoon of baking soda. Too much baking soda taken when you have a full stomach could lead to a stomach rupture.
7. Drink apple cider vinegar
Dissolving 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water and drinking it is a traditional remedy for gas release.
Anecdotal evidence suggests this may be effective, but there’s no scientific evidence to support this claim. However, there aren’t any negative side effects to this method.
Many over-the-counter (OTC) remedies exist for gas relief. Again, the evidence for effectiveness may be anecdotal only. You’ll have to experiment to see what works for you.
Here are some products to try.
8. Enzyme preparations
Certain products may help if you are lactose intolerant. But these are usually taken as a preventive measure. These enzyme products include:
- Lactaid
- Digest Dairy Plus
- Dairy Relief
Alpha-galactosidase is a natural enzyme that helps prevent gas from legumes. There’s older evidence that it works to prevent gas and bloating. But again, it’s usually taken as a preventive measure.
There’s older evidence that it works to prevent gas and bloating. But again, it’s usually taken as a preventive measure.
Beano is a well-known version of this enzyme, available in tablet form.
9. Adsorbents
Simethicone products have possible benefits in relieving gas, according to some studies. They work by breaking up bubbles in gas.
These products include:
- Gas-X
- Alka-Seltzer Anti-Gas
- Mylanta Gas
Activated charcoal tablets, capsules, or powder may also help reduce gas. The charcoal is activated by heating it to make it more porous, which traps gas molecules in the spaces created. However, these products may have unwanted side effects, such as turning your tongue black.
These products include:
- Activated Charcoal
- CharcoCaps
Trapped gas symptoms usually come on suddenly. The pain can be sharp and stabbing. It can also be a general feeling of acute discomfort.
Your stomach may be bloated, and you may have stomach cramps.
Pain from gas that collects on the left side of your colon can radiate up to your chest. You may think this is a heart attack.
Gas that collects on the right side of the colon can feel like it might be appendicitis or gallstones.
There are many causes of trapped gas bubbles. Most are related to the process of digestion. But some may result from physical conditions that need treatment.
The following chart summarizes the variety of causes of trapped gas:
| Common causes of excess gas | Other factors that may cause excess gas | Health conditions |
| digestion | persistent post-nasal drip | irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) |
| food intolerance | certain medications, such as OTC cold medications | Crohn’s disease |
| bacterial overgrowth | fiber supplements that contain psyllium | ulcerative colitis |
| constipation | artificial sugar substitutes, such as sorbitol, mannitol, and xylitol | peptic ulcers |
| lifestyle behaviors, such as chewing gum, overeating, and smoking | stress | |
| a previous surgery or pregnancy that altered your pelvic muscles |
You can lower your risk of getting a painful trapped gas bubble by watching what and how you eat.
It may be useful to keep a food diary. This can help you keep track of the foods and circumstances that lead to a gas bubble. Then you can avoid those foods or behaviors that seem to give you a problem.
Try eliminating foods one by one so that you can pinpoint possible problems.
Here are some basic tips to start with:
- Stay hydrated.
- Avoid carbonated beverages.
- Drink liquids at room temperature, not too hot or too cold.
- Avoid foods known to cause excess gas.
- Avoid artificial sweeteners.
- Eat slowly and chew your food well.
- Don’t chew gum.
- Don’t smoke or chew tobacco.
- If you wear dentures, have your dentist check on whether they let in too much air when you eat.
- Increase your physical activity.
Try some of the home remedies or OTC remedies for gas, and see what might work for you.
It’s a good idea to see your doctor if you frequently have trapped gas bubbles, if they last a long time, or if you have any worrisome symptoms.
Other symptoms to watch for include:
- unexplained weight loss
- bowel movement frequency changes
- blood in your stool
- constipation
- diarrhea
- nausea or vomiting
- heartburn
- loss of appetite
Your doctor can diagnose other possible conditions. They may also advise you to take a probiotic or a prescription antibiotic.
It’s a good idea to discuss the remedies that you’re already trying, especially any herbal supplements.
What is the best position to relieve gas?
Several poses can help relieve gas, particularly yoga poses. Examples include the child’s pose and knee-to-chest pose.
How long can trapped gas last?
Gas can stay trapped, causing pain, for a couple of hours. If you do not experience relief within that time frame, you may wish to see your doctor in case you have a more serious issue like appendicitis.
Does drinking hot water relieve gas?
Drinking more water, regardless of its temperature, can help you relieve trapped gas.
Trapped gas can be acutely painful. It’s usually not serious but may be a sign of a food intolerance or an underlying digestive problem.
Watching what you eat and taking some preventive measures can help.
Getting rapid relief may take some experimenting with different remedies to see what works for you.
Increased gas formation in the intestines and stomach – causes, treatment
home
Articles
Suffering from increased gas production? What to do.
November 12, 2019
Increased flatulence or flatulence is a common and rather unpleasant pathology.
Increased gas formation or flatulence is a common and rather unpleasant pathology. Flatulence can be an independent disorder or a symptom of another disease. The causes of increased gas formation are often diet errors and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If you are tormented by increased gas formation, you should find out its nature together with the doctor and carry out a timely correction.
Increased gas formation in the intestines
Increased gas formation in the intestines is one of several causes of flatulence in adults. The content of gases in the gastrointestinal tract can increase due to three factors:
- Aerophagia or swallowing of air. Excess gas comes from the mouth when chewing or drinking liquids through a straw.
- Increased gas formation in the stomach. Occurs due to the contact of gastric acid and food alkalis.
- Actually increased gas formation in the intestines. It is a consequence of the processes of fermentation and dysbacteriosis.
In most patients with increased gas formation, the cause of the problem is nutritional factors – eating certain foods.
Causes of increased gas formation in the intestines
With increased gas formation in the intestines, the cause is often the excessive intake of such foods:
- legumes (peas, beans, etc.
 ),
), - apples,
- cabbage,
- bread (especially black),
- beer,
- carbonated (especially sweet) drinks, etc.
Alimentary or food flatulence is its most harmless form. This condition is easily eliminated by the exclusion from the diet of the above products or by reducing their number.
Less often, in patients with increased gas formation in the intestine, gastrointestinal diseases are the cause. Gastritis, esophagitis, colitis, enzymatic deficiency, adhesive disease, tumors of the abdominal cavity – this is not a complete list of pathologies that may be accompanied by metorism. Sometimes in patients with persistent flatulence, a parasitic invasion is found – various types of worms that change the normal processes of digestion.
Increased gas formation in the stomach
Increased gas formation in the stomach is manifested by belching and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen. Pathology can occur for two reasons. Aerophagia, leading to the accumulation of air in the stomach, is a consequence of hasty eating, smoking, drinking drinks through a straw.
Pathology can occur for two reasons. Aerophagia, leading to the accumulation of air in the stomach, is a consequence of hasty eating, smoking, drinking drinks through a straw.
Often the condition is observed in patients with defects in the dentition, diseases of the nasopharynx. Increased gas formation in the stomach is sometimes the result of a chemical reaction between the hydrochloric acid of gastric juice and the alkalis of food. In this case, carbon dioxide is released, which inflates the walls of the stomach.
What causes increased gas formation in the stomach
As already mentioned, the use of gas-producing foods is why increased gas formation in the stomach occurs most often. Correction of the diet in such cases quickly eliminates the symptoms. However, it happens that even the complete exclusion of unwanted products does not solve the problem.
Such a development of events may indicate the presence of anatomical or functional changes in the gastrointestinal tract. The causes of increased gas formation in the stomach can also be diseases such as:
The causes of increased gas formation in the stomach can also be diseases such as:
- peptic ulcer,
- gastritis,
- reflux esophagitis,
- duodenitis,
- secretory insufficiency,
- abdominal adhesions,
- Tumors of the stomach and duodenum.
Any of the above diseases may be complicated or manifested by flatulence. However, in addition to bloating, other symptoms are usually noted: pain, changes in body weight, and a shift in laboratory parameters.
How to treat gas
Any violation of the activity of the intestines or stomach should be analyzed by a doctor gastroenterologist. With alimentary increased gas formation, treatment consists in taking drugs that precipitate gases and correcting the diet.
Among the drugs, the most effective are three groups: sorbents, defoamers and herbal remedies. All of them have a certain effect in symptomatic increased gas formation in the intestine. In this case, treatment often begins with defoamers, which are considered the most effective.
In this case, treatment often begins with defoamers, which are considered the most effective.
The disadvantages of sorbents are their low selectivity and the possibility of only a short-term intake. Such drugs absorb both harmful and beneficial substances, and with prolonged use they lead to vitamin deficiency and a lack of minerals. Herbal carminatives (often these are preparations based on dill) do not always have a sufficient effect.
With painful increased gas formation, treatment should be carried out after a detailed clarification of the nature of the process. Our center has all the possibilities for a full examination and treatment of patients with any disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Friendly staff, the best equipment and doctors contribute to a quick and lasting recovery.
How to get rid of flatulence and bloating: causes and treatments
Contents
- 1 Flatulence and bloating: causes, symptoms and effective treatments
- 1.
 1 Flatulence and bloating
1 Flatulence and bloating - 1.2 Causes of flatulence and bloating
- 1.3 Symptoms of flatulence and bloating
- 1.4 Diet for flatulence and bloating
- 1.5 Diet for flatulence and bloating
- 1.6 Herbs and preparations for flatulence and bloating
- 1.7 What to do about flatulence and bloating
- 1.8 What not to do about flatulence and bloating
- 1.8.1 Overeat
- 1.8.2 Eat foods that cause gas
- 1.8.3 Sitting in one position for a long time
- 1.8.4 Take drugs without consulting a doctor
- 1.9 Treatment of flatulence and bloating in children
- 1.10 How to restore the microflora in flatulence and bloating
- 1.11 When to see a doctor for flatulence and bloating
- 1.12 Preventing flatulence and bloating
- 1.13 Related videos:
- 1.14 Q&A:
- 9 0025 1.14.0.1 What are the causes of flatulence and bloating?
- 1.14.0.2 How can flatulence be reduced?
- 1.
 14.0.3 Which diet can get rid of flatulence?
14.0.3 Which diet can get rid of flatulence? - 1.14.0.4 What medications are available to treat flatulence and bloating?
- 1.14.0.5 Can probiotics help with flatulence and bloating?
- 1.14.0.6 When should I see a doctor if I have bloating and flatulence?
- 1.
Flatulence and bloating – causes and methods of control. Learn how to get rid of unpleasant symptoms and restore comfort in the stomach.
Flatulence and bloating are common problems that can affect quality of life. Bloating is due to the accumulation of a large amount of gas in the intestines, which can be caused by various factors, such as food intolerance, dysbacteriosis, sterile intestinal infection, etc.
Determining the cause of flatulence is the first step to successful treatment. In addition, there are many ways that can help manage this problem and get rid of discomfort, such as changing the diet, taking probiotics, exercising, and many others.
In this article we will consider the main causes of flatulence and bloating, as well as methods and means for their treatment and prevention of possible relapses.
Flatulence and bloating
Flatulence and bloating are common problems that can cause severe discomfort. These symptoms often occur due to poor diet, irregular meals, overeating, quick chewing of food, and consumption of carbonated drinks. They can also be the result of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as irritable bowel syndrome or peptic ulcer.
If problems with flatulence and bloating are persistent and do not disappear for several days, you should consult a doctor. They may recommend additional measures, such as taking probiotics, screening for infections, or changing medications.
Causes of flatulence and bloating
Flatulence and bloating are problems that occur when excess gas accumulates in the intestines. This process can be caused by several factors.
- Wrong diet: Food rich in fiber can cause flatulence, as our body cannot fully digest this type of food.
 Large amounts of sugar and fat can also cause gas.
Large amounts of sugar and fat can also cause gas. - Stress: Stress, nervous tension and anxiety can disrupt the gastrointestinal tract and cause intestinal dysfunction.
- Medicines: Some medicines can interfere with the gastrointestinal tract, causing flatulence and bloating.
- Bacteria: Improper balance of micro-organisms in the intestines can cause gas because bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract can also cause flatulence.
To get rid of flatulence and bloating, you need to understand the causes of these problems. If the cause lies in malnutrition, you need to change your diet by removing the excess of some foods and increasing the amount of others. It is also important to pay attention to your lifestyle, drink the right amount of fluid and control the level of stress in everyday life.
Symptoms of flatulence and bloating
Flatulence is a disorder of the digestive processes, in which free gas from the stomach and intestines is disturbed. One of the most striking symptoms of flatulence is increased gas formation in the stomach and intestines. This manifests itself in the form of belching, heartburn, constipation and diarrhea.
One of the most striking symptoms of flatulence is increased gas formation in the stomach and intestines. This manifests itself in the form of belching, heartburn, constipation and diarrhea.
Bloating manifests itself in the form of an increase in the volume of the abdomen, a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the abdomen, a feeling of fullness and tension. In this case, severe pain can be noted, not only in the abdomen, but also in the chest and neck. Pain increases after eating and may not stop for a long time.
- Gas can escape through the mouth, causing belching.
- Full stomach causes pain in the epigastric region.
- Sharp pain in the lower abdomen may indicate an intestinal obstruction.
- In case of persistent bloating, consult a doctor.
Nutrition for flatulence and bloating
Proper nutrition can significantly reduce flatulence and bloating. One way to reduce gas formation in the intestines is to eat foods rich in vegetable fibers. Vegetables, fruits, cereals, bread products, legumes, as well as nuts and seeds can reduce the likelihood of gas formation in the intestines and increase the efficiency of peristalsis.
Vegetables, fruits, cereals, bread products, legumes, as well as nuts and seeds can reduce the likelihood of gas formation in the intestines and increase the efficiency of peristalsis.
In addition, there are foods that should be excluded from the diet, such as carbonated drinks, dairy products, soy products, potatoes, cabbage, peppers, onions, corn, sweets and pastries. These foods can exacerbate flatulence and bloating and should not be consumed if patients feel bloated and uncomfortable during digestion.
- Pay attention to:
- – drinking water regularly to avoid dehydration, which can slow down digestion and produce gas;
- Avoid chewing gum, desserts, and sugary drinks that increase stomach gas.
- – taking probiotics, which improve the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and help fight bloating;
- – increased physical activity, as it improves intestinal motility and minimizes the likelihood of flatulence and bloating.
Diet for flatulence and bloating
Flatulence and bloating is a problem that can occur in every person. The severity of these symptoms can depend on many factors, including diet.
The severity of these symptoms can depend on many factors, including diet.
To reduce flatulence and bloating, you need to watch what you eat and how much. Small portions of food, moderate fluid intake and avoiding overeating are the basic rules of a healthy diet.
When flatulence and bloating, it is important to avoid foods that cause fermentation in the intestines. To do this, it is worth reducing the consumption of dairy products, fruits, vegetables containing fiber, and any products associated with increased gas formation.
- Examples of foods that cause fermentation in the intestines:
- Carbonated drinks
- Brown bread
- Legumes
- Sweets with sugar substitutes
9000 2 Following a proper diet is an important step in the fight against flatulence and bloating. If you are unable to make your own diet, consult your doctor or nutritionist.
Herbs and preparations for flatulence and bloating
Among the herbs that can help with flatulence and bloating are yarrow, coriander, chamomile and mint. Yarrow relieves inflammation, improves digestion, and reduces gas formation. Coriander improves digestion, eliminates pain and bloating. Chamomile has a calming effect on the stomach, relieves inflammation, and improves digestion. Peppermint can relieve the symptoms of flatulence, reduce pain and intestinal spasms.
Yarrow relieves inflammation, improves digestion, and reduces gas formation. Coriander improves digestion, eliminates pain and bloating. Chamomile has a calming effect on the stomach, relieves inflammation, and improves digestion. Peppermint can relieve the symptoms of flatulence, reduce pain and intestinal spasms.
In addition to herbs, there are preparations designed to combat flatulence and bloating. One of the most popular is Espumizan – it destroys gas bubbles and reduces their number in the intestines. Another drug is Microsim – it increases the number of beneficial bacteria in the intestines and reduces gas formation. There are also preparations containing simethicone, a substance that destroys gases and helps to remove them from the intestines.
- Yarrow
- Coriander
- Chamomile
- Mint
- Espumizan
- Microsim
- Simethicone preparations
90 298
90 300
What to do with flatulence and bloating
Avoid foods that cause gas. Limit fruits that are high in sugar and fiber, such as apples and pears, and vegetables, such as cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and broccoli. You should also avoid carbohydrates that contain soluble fiber, such as some grated oatmeal and cereals.
Limit fruits that are high in sugar and fiber, such as apples and pears, and vegetables, such as cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and broccoli. You should also avoid carbohydrates that contain soluble fiber, such as some grated oatmeal and cereals.
Eat slowly and chew thoroughly. Rapid and incomplete chewing of food may increase the risk of flatulence.
Drink enough water. Water helps dissolve soluble fiber, which can cause flatulence, and aids in the rapid processing of food in the stomach and intestines.
Increase your intake of foods containing probiotics. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help reduce intestinal gas and improve digestion. Foods containing probiotics include yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
Avoid overeating. Overeating may increase the risk of flatulence and bloating. Try to eat smaller meals more often than 2-3 large meals a day.
Reduce fluid intake with meals. Drinking plenty of fluids with meals can increase the amount of fluid in the stomach and intestines, which can lead to bloating. Drink liquid some time after eating.
Drinking plenty of fluids with meals can increase the amount of fluid in the stomach and intestines, which can lead to bloating. Drink liquid some time after eating.
What not to do with flatulence and bloating
Overeating
Severe hunger and overwork can often cause flatulence and bloating. Therefore, it is necessary to follow a regular diet, diet and daily diet to reduce the risk of this problem.
Eat foods that promote gas
Foods containing sucrose, fructose, lactose, complex carbohydrates, carbonated drinks, alcohol, coffee, tea and dairy products can cause increased gas in the stomach and intestines. Therefore, it is recommended to limit the consumption of such foods to reduce bloating.
Sitting in one position for a long time
Insufficient movement can put pressure on the intestines, which can lead to poor digestion and flatulence. It is recommended to move every hour and do exercises while sitting at work or during long trips.
Take drugs without consulting a doctor.
Some drugs can have the side effect of a gas appliance and cause flatulence and bloating. Therefore, you should consult your doctor before taking any medication.
- Conclusion: If you suffer from flatulence and bloating, make sure you don’t do the above things to reduce the risk of the problem. If you are still experiencing this problem, you need to seek the help of a doctor to get diagnosed and treated.
Features of the treatment of flatulence and bloating in children
Flatulence and bloating are not rare problems in children. Usually the cause is malnutrition or disorders in the digestive tract. Treatment of flatulence and bloating in children has its own characteristics and should be carried out only under the supervision of a pediatrician.
One of the key ways to treat flatulence and bloating in children is to adjust their diet. It is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that can cause gas formation: carbonated drinks, burgers, fatty, fried and heavy foods.
It is also recommended to add fiber-rich foods such as fruits and vegetables to children’s diets. Attention should be paid to the fact that children should chew food properly and not eat it in large quantities at one meal.
If diet changes don’t work, your pediatrician may prescribe medications to help relieve flatulence and bloating. However, you need to take medicines only as prescribed by the pediatrician and in strict accordance with the dosage.
How to restore the microflora in flatulence and bloating
Restoring the intestinal microflora is one of the main ways to combat flatulence and bloating. To do this, you need to eat foods that promote the development of beneficial bacteria in the intestines.
It is important to include prebiotic foods such as chicory, turnips, onions, garlic, nuts, and oat or barley gruel in your diet. Prebiotics not only inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, but also stimulate the growth of beneficial ones.
It is also necessary to eat foods containing probiotics, which restore the intestinal microflora. It can be yogurt, kefir, cottage cheese, kvass, kimchi and other fermented foods. However, you should not abuse such products, especially if you experience allergic reactions.
It can be yogurt, kefir, cottage cheese, kvass, kimchi and other fermented foods. However, you should not abuse such products, especially if you experience allergic reactions.
- To restore the microflora, you can use special medicines containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. However, before you start taking these drugs, you should consult your doctor.
- Drinking alcohol and smoking should be avoided, as this negatively affects the intestinal microflora.
- Antibiotics should not be abused, as they kill not only harmful but also beneficial bacteria in the intestines.
Gut microflora recovery may take some time, but if you follow the recommendations and change your diet, you can significantly improve your well-being and get rid of flatulence and bloating.
When to see a doctor for flatulence and bloating
Flatulence and bloating are fairly common problems that can be caused by a variety of reasons. However, in some cases, these symptoms may indicate a serious health problem that requires medical attention.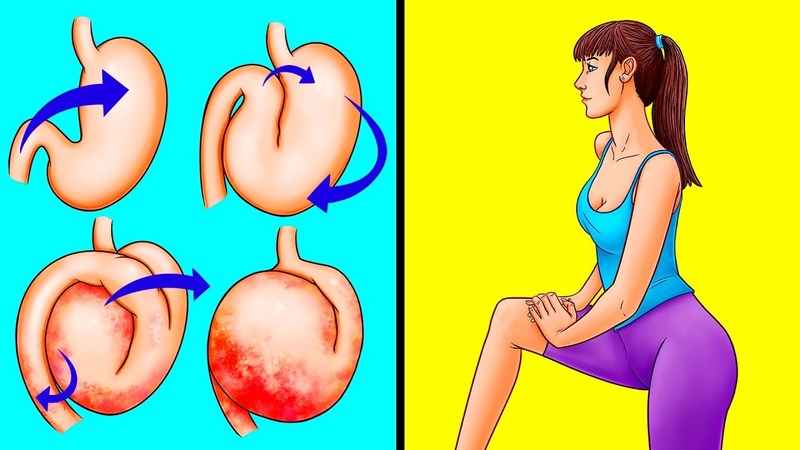
If you have persistent or frequent episodes of flatulence and bloating that do not go away or get worse over time, this could be a sign of a medical condition such as irritable bowel syndrome, colitis, stomach or intestinal ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, or other pathologies.
You should also see a doctor if symptoms of flatulence and bloating are accompanied by severe abdominal pain, problems with stool, appetite, fever, heaviness in the abdomen, excess weight or weight loss, and other unusual symptoms.
- Symptoms persist or worsen over time
- Severe abdominal pain
- Stool, appetite disorders
- Fever includes blood and urine tests , ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, gastroenterological and other procedures. Only after a specific diagnosis and identification of the causes of symptoms, the doctor can recommend appropriate treatment or prescribe other measures to improve health.
Prevention of flatulence and bloating
Flatulence and bloating often result from dietary errors and lack of physical activity.
 But there are ways to prevent these problems.
But there are ways to prevent these problems.- Get regular exercise such as running, walking, yoga or other sports activities. This will help improve the digestion of food and speed up the process of removing excess gas.
- Drink enough water to speed up digestion. It is recommended to consume 8-10 glasses of water a day.
- Avoid gas-forming foods such as carbonated drinks, beans, cabbage, peppers, mushrooms, and others. Instead, eat vegetables and fruits that are high in fiber.
- Reduce the amount of foods that are high in fat and sugar. They can slow down the digestion process and contribute to flatulence.
Remember that constant care of your health and proper lifestyle will help you avoid many diseases. If you experience severe discomfort and cannot solve this problem on your own, contact your doctor for advice.
Related videos:
youtube.com/embed/lLIFkKhqQNg” frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”>
Q&A:
What are the causes of flatulence and bloating?
The habit of eating fast, drinking large amounts of carbonated drinks, lactose intolerance, irritable bowel syndrome, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, peculiarities of the digestive system, antibiotics, stress and other factors can cause flatulence and bloating.
How can flatulence be reduced?
To reduce flatulence, it is recommended to reduce the amount of carbonated drinks consumed, chew food slowly and well, avoid chewing gum, eat fewer foods that can cause gas, increase fluid intake, exercise, and regularly perform good oral hygiene.
What kind of diet can get rid of flatulence?
It is advisable to avoid foods that accelerate fermentation in the intestines and can cause bloating. For example, dairy products, legumes, cabbage, onions, garlic, sweets, black bread. In the diet, you should increase the amount of vegetables, fruits, cereals, drink water and pay attention to the quality of the products.

What medications are available to treat flatulence and bloating?
There are enzyme preparations that facilitate the process of digestion and reduce flatulence. Drugs that reduce the amount of gas in the intestines, such as simethicone. Drugs that improve intestinal motility and accelerate the transit of food.
Can probiotics help with flatulence and bloating?
Yes, probiotics can help with flatulence and bloating. They improve the condition of the intestinal microbiota, which is responsible for the process of digestion of food. Probiotics containing streptococci, lactobacilli, and bifidobacteria are often used to treat flatulence and bloating.
When should I see a doctor if I have bloating and flatulence?
Seek medical attention if symptoms persist for several days, abdominal pain becomes worse, general well-being worsens, diarrhea or constipation develops, body temperature rises. This may be a sign of a serious gastrointestinal disorder that requires medical attention.



 ),
), 1 Flatulence and bloating
1 Flatulence and bloating 14.0.3 Which diet can get rid of flatulence?
14.0.3 Which diet can get rid of flatulence? Large amounts of sugar and fat can also cause gas.
Large amounts of sugar and fat can also cause gas. But there are ways to prevent these problems.
But there are ways to prevent these problems.