Mosquito bite like bumps on body. Itchy Bumps on Skin: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments for Mosquito Bite-Like Rashes
What causes itchy bumps that look like mosquito bites. How to identify different skin conditions that cause raised, itchy rashes. What are the most effective treatments for various types of skin irritation.
Common Causes of Itchy Skin Bumps
Itchy bumps on the skin that resemble mosquito bites can be caused by various conditions, ranging from allergic reactions to infections. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some of the most common culprits:
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives, medically known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can appear suddenly. They affect about 20% of people at some point in their lives. Hives can be triggered by:
- Certain foods (e.g., peanuts, tree nuts, seafood)
- Latex
- Pollen
- Insect stings or bites
- Various plants
- Medications (e.g., sulfa drugs, aspirin)
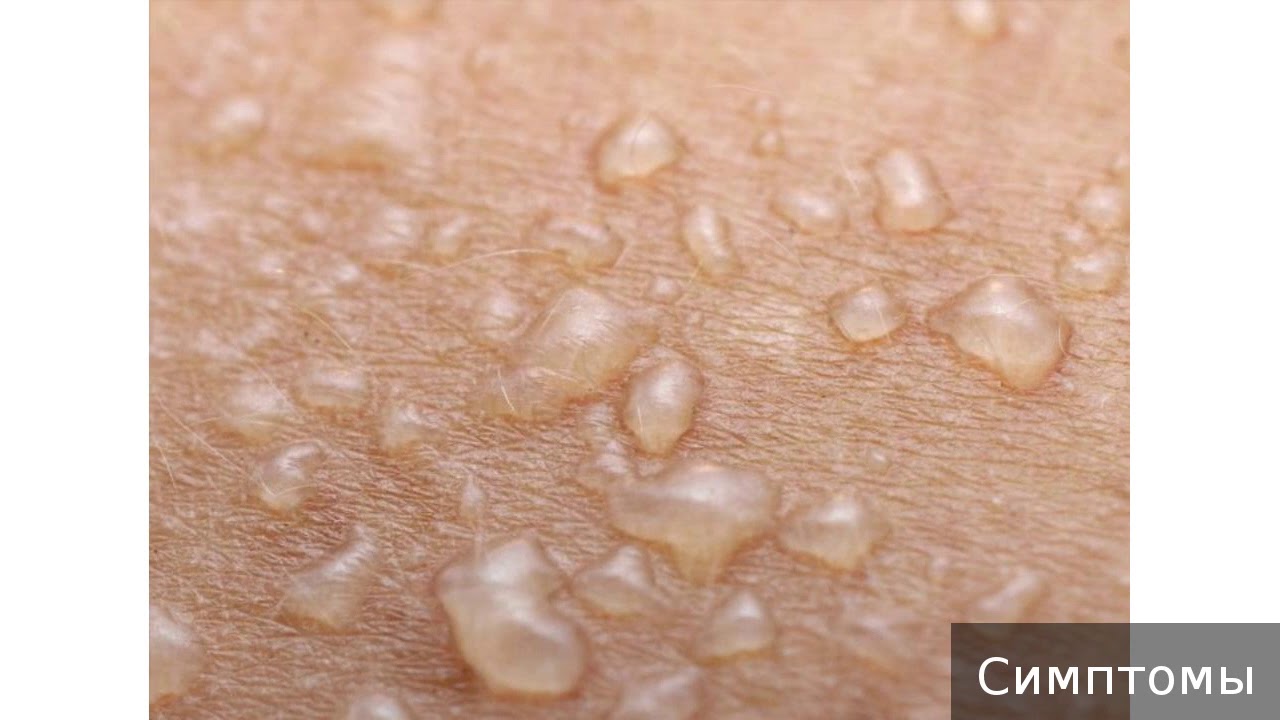
Hives typically cause red, purple, or skin-colored itchy bumps that appear and disappear quickly anywhere on the body. When pressed, these bumps often turn white or temporarily disappear.
Bed Bug Bites: Identifying and Treating the Pesky Culprits
Bed bug bites can easily be mistaken for mosquito bites, but there are some key differences. How can you tell if those itchy bumps are from bed bugs? Look for these signs:
- Bites arranged in a straight line or zigzag pattern
- Other evidence of bed bugs (e.g., bugs on mattress, blood spots on sheets)
- A musty odor in the bedroom
While bed bug bites can appear randomly, a linear pattern is often a telltale sign. Keep in mind that reactions to bed bug bites can take up to two weeks to materialize, making identification challenging.
Contact Dermatitis: When Your Skin Rebels Against Allergens
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen, resulting in an itchy, inflamed rash. This condition can be particularly tricky to diagnose due to the vast number of potential triggers. Did you know there are over 3,700 substances known to cause contact allergies?
Common allergens include:
- Latex
- Certain metals (e.g., nickel)
- Household products
- Cosmetics and skincare products
Symptoms of contact dermatitis may take 1-2 days to develop and can persist for 2-3 weeks. Unlike simple bug bites, contact dermatitis often causes pain in addition to itching and may present with blisters.
Scabies: The Microscopic Mite Menace
Scabies is caused by the human itch mite, a tiny parasite that burrows into the top layer of skin to lay eggs. This condition leads to intense itching and a rash that can resemble mosquito bites. How does scabies differ from other skin conditions?
- Visible burrow tracks: Raised, crooked, skin-colored lines may be visible on the skin’s surface
- Intense itching: Particularly at night
- Specific affected areas: Common sites include between fingers, under nails, and in skin folds
Scabies is highly contagious and requires prompt medical treatment to prevent spread to others.
Effective Treatments for Itchy Skin Bumps
While the specific treatment depends on the underlying cause, there are some general principles to follow when dealing with itchy skin bumps:
- Avoid scratching: This can lead to skin damage and potential infection
- Use cold compresses: This can help reduce inflammation and itching
- Apply anti-itch creams: Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream can provide relief
- Take antihistamines: These can help reduce itching and inflammation
- Identify and avoid triggers: This is crucial for preventing future outbreaks
Treatment for Hives
For mild cases of hives, over-the-counter antihistamines and anti-itch lotions are often sufficient. However, more severe outbreaks may require prescription-strength medications. In cases of severe allergies, some individuals may need to carry an epinephrine auto-injector (e.g., EpiPen) for emergency use.

Dealing with Bed Bug Bites
Treating bed bug bites primarily involves symptom management and eliminating the infestation. Key steps include:
- Applying antiseptic creams to prevent infection
- Using antihistamines to reduce itching
- Thoroughly cleaning and treating the affected living space
Managing Contact Dermatitis
The primary goal in treating contact dermatitis is to identify and avoid the allergen. Additional treatments may include:
- Cold compresses and soothing baths
- Calamine lotion for itch relief
- Prescription antihistamines or corticosteroids for severe cases
Treating Scabies
Scabies requires medical intervention. Treatment typically involves:
- Prescription scabicide medications
- Thorough cleaning of clothing and bedding
- Treating all household members and close contacts to prevent reinfestation
When to Seek Medical Attention for Skin Rashes
While many skin conditions can be managed at home, certain symptoms warrant professional medical attention. When should you consult a healthcare provider for itchy skin bumps?
- The rash is widespread or rapidly spreading
- You experience symptoms of a severe allergic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat)
- The rash is accompanied by fever or other systemic symptoms
- Home treatments fail to provide relief after several days
- The rash interferes with daily activities or sleep
Remember, early intervention can prevent complications and provide faster relief.
Preventing Itchy Skin Bumps: Proactive Measures
While it’s not always possible to prevent itchy skin bumps, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Identify and avoid known allergens
- Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products
- Keep skin moisturized to maintain its protective barrier
- Wear protective clothing when outdoors to avoid insect bites
- Practice good hygiene to prevent infections
- Manage stress, which can exacerbate some skin conditions
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet
By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can help keep your skin healthy and reduce the likelihood of developing itchy bumps.
The Role of Diet in Skin Health
Can what you eat affect your skin’s tendency to develop itchy bumps? While diet isn’t the sole factor in skin health, it can play a significant role. How does nutrition impact your skin’s condition?
- Hydration: Proper fluid intake helps maintain skin elasticity and function
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in vitamins A, C, and E can help protect skin from damage
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These can help reduce inflammation in the body, including the skin
- Probiotics: A healthy gut microbiome may contribute to better skin health
Conversely, some foods can trigger allergic reactions or exacerbate existing skin conditions in sensitive individuals. Common culprits include:
- Dairy products
- Gluten
- Nightshade vegetables (e.g., tomatoes, peppers)
- Processed foods high in preservatives
If you suspect certain foods may be contributing to your skin issues, consider keeping a food diary and consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.
Environmental Factors and Skin Irritation
Your environment can significantly impact your skin’s health and its susceptibility to developing itchy bumps. What environmental factors should you be aware of?
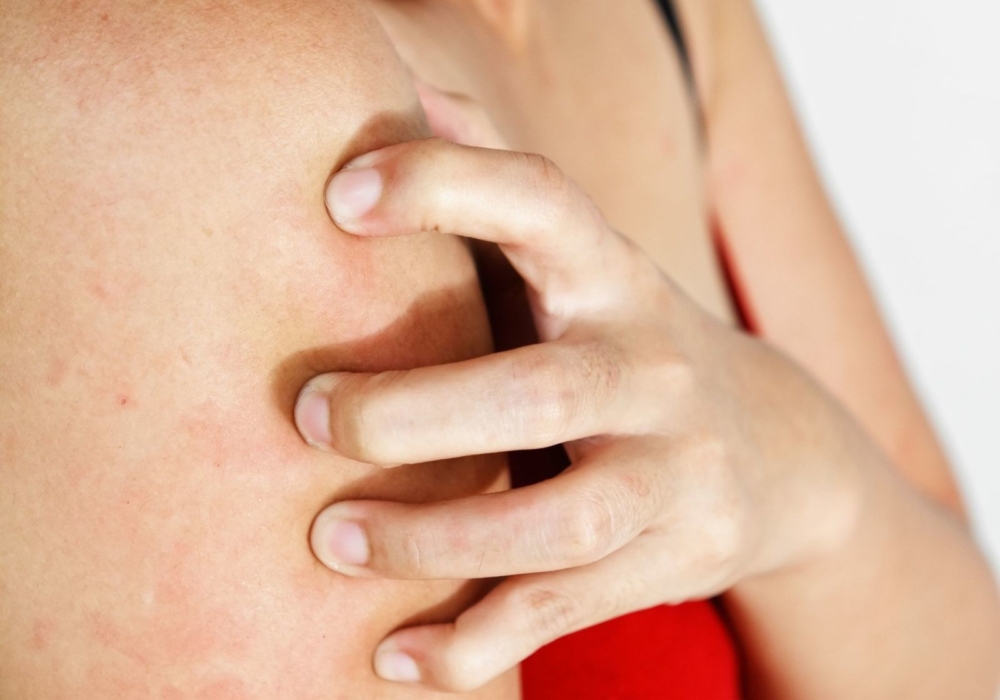
- Temperature and humidity: Extreme heat, cold, or dryness can irritate the skin
- Sun exposure: Sunburn can lead to itchy, peeling skin
- Air pollution: Particulate matter can clog pores and irritate sensitive skin
- Indoor allergens: Dust mites, pet dander, and mold can trigger skin reactions in some people
To minimize the impact of these factors:
- Use a humidifier in dry climates or during winter months
- Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily
- Keep your living space clean and well-ventilated
- Use air purifiers to reduce indoor allergens
- Choose clothing made from natural, breathable fabrics
By being mindful of your environment and taking steps to protect your skin, you can reduce the likelihood of developing irritating skin conditions.
The Psychological Impact of Chronic Skin Conditions
Persistent or recurrent skin issues can have a significant impact on mental health and quality of life. How do chronic skin conditions affect psychological well-being?
- Self-esteem: Visible skin conditions can affect body image and confidence
- Social anxiety: Concern about others’ reactions may lead to social withdrawal
- Depression: Chronic discomfort and the emotional toll of skin issues can contribute to depression
- Stress: Dealing with persistent symptoms can be stressful, which may, in turn, exacerbate skin conditions
If you’re struggling with the psychological impact of a skin condition, consider these strategies:
- Seek support from friends, family, or support groups
- Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga
- Consult a mental health professional if needed
- Focus on overall health and well-being, not just skin appearance
- Educate yourself and others about your condition to reduce stigma
Remember, your worth is not determined by your skin’s appearance. Seeking help for both the physical and emotional aspects of skin conditions is essential for overall well-being.
Emerging Treatments and Research in Dermatology
The field of dermatology is constantly evolving, with new treatments and therapies emerging to address various skin conditions. What are some promising areas of research for itchy skin conditions?
- Targeted biologics: These drugs specifically target the immune pathways involved in certain skin conditions
- Microbiome therapies: Treatments that aim to balance the skin’s natural microbiome
- Gene therapy: Potential treatments that target genetic factors in skin diseases
- Nanotechnology: Improved delivery systems for topical medications
- Artificial intelligence: AI-assisted diagnosis and treatment planning
While many of these treatments are still in development or early stages of use, they offer hope for more effective and personalized approaches to managing skin conditions in the future.
As research continues to advance our understanding of skin health and disease, new options for treating and preventing itchy skin bumps are likely to emerge. Staying informed about these developments can help you make the best decisions for your skin health in consultation with healthcare professionals.
Itchy bumps on skin like mosquito bites: What are they?
Several skin conditions can cause itchy lumps that resemble bug bites. These include allergic reactions, infections, and chronic conditions.
Most people experience this symptom at some point. Itchy bumps can appear as a result of allergies, infections, insects, and, sometimes, nonidentified factors.
However, there is one general principle that the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology recommend people to follow when their skin itches: Do not scratch it.
Additional general self-care practices for itchy skin include:
- bathing frequently in lukewarm water
- using gentle, hypoallergenic soap
- limiting exposure to the sun
- applying cold compresses
- avoiding tight clothing in areas where itchy bumps appear
Understanding the different conditions that can cause itchy bumps on the skin can help people get appropriate treatment. Depending on the cause, treatment can range from avoiding certain foods to taking prescription medications.
Keep reading to learn more about some common causes of itchy bumps that look like mosquito bites and how to treat them.
The medical term for hives is urticaria, and it describes a condition that produces raised itchy areas on the skin. If a person notices bumps on the skin that resemble mosquito bites but has not had any exposure to mosquitos, the cause is probably acute urticaria. The term “acute” means that the condition does not last longer than 6 weeks.
Hives are very common, affecting about 20% of people at some point in their lives. Certain kinds of foods, such as peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood, cause hives in many people due to an allergic reaction. Latex, pollen, insects, various plants, and some medications, such as sulfa drugs or even aspirin, may also cause hives.
Hives cause characteristic red, purple, or skin colored itchy bumps that appear and disappear quickly anywhere on the body. These bumps typically turn white or disappear when a person presses them.
Treatment
The treatment for hives depends on the severity and cause of the rash, but it includes avoiding known triggers. People who are extremely allergic to a trigger — for example, peanuts or certain insects — may need to carry an epinephrine auto-injector, such as an Epipen. This device can stop a potentially life threatening reaction if a person has accidental contact with a known allergen.
Anti-itching lotions and over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines can provide relief for mild symptoms, while more intense outbreaks may require stronger prescription versions of these drugs or corticosteroids.
Learn more about hives here.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), bed bug bites can resemble bites from other bugs, although they can take as long as 2 weeks to materialize.
People who notice itchy bumps on the skin that resemble mosquito bites should check for:
- other signs of bed bugs
- bed bugs themselves on a mattress or sheet
- dead bed bugs
- blood spots on a mattress or sheet
- the characteristic musty smell associated with bed bugs
If the bites appear in a straight line, they are likely to be due to bed bugs. However, bed bug bugs can also appear in more random formations.
However, bed bug bugs can also appear in more random formations.
Treatment
Unless someone has a severe allergic reaction, experts recommend simple self-care practices to treat any bites. These include not scratching, applying OTC antiseptic ointments, and taking antihistamines.
Learn more about bed bugs here.
Contact dermatitis is essentially an allergic reaction that develops when a person’s skin comes into contact with something to which they are allergic, such as latex or certain metals or household products.
It can take 1–2 days for the reaction to develop and 2–3 weeks for symptoms to disappear. Contact dermatitis may hurt as much as it itches, and it may present with inflammation and blisters.
Treatment
Self-care with cold compresses, calamine lotion, and soothing baths can help provide relief.
Prescription medication, such as antihistamines and cortisone, may be necessary if the reaction is severe.
Working with healthcare professionals can help people identify their triggers, which can be complicated.
According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, there are more than 3,700 substances known to cause contact allergies. Avoiding triggers is a key part of managing contact dermatitis, along with thoroughly washing the affected area with soap and water after exposure happens.
Learn more about contact dermatitis here.
The human itch mite is responsible for scabies. This mite digs its way through the top layer of the skin and lays eggs. Its tunnels can sometimes be visible on the surface of the skin, where they appear as raised, crooked, skin colored lines. However, the most common symptom of scabies is itchy bumps on the skin. These are like mosquito bites, only smaller.
Sites of the body that this very itchy condition commonly affects include the wrists, the elbows, between the fingers, and behind the knees.
Treatment
Only a prescription lotion will treat scabies effectively, and individuals need to follow the application directions exactly. Anyone who has had extensive skin-to-skin contact with someone with scabies should also seek treatment.
Anyone who has had extensive skin-to-skin contact with someone with scabies should also seek treatment.
It is very important that people with scabies thoroughly wash and dry all of their clothes, towels, sheets, bedding, and other household items. Other remedies for scabies may also help.
Learn more about scabies here.
Also known as atopic dermatitis, this common condition causes itchy, red, irritated skin that can sometimes develop bumps. In the long term, it can make the skin thicker, scaly, and flaky, as well as causing it to change color.
Scratching makes eczema worse and increases the risk of infection. Eczema occurs due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, which prompt the immune system to overreact to certain triggers, such as laundry soap or sweating. It typically affects the face, elbows, knees, scalp, and backs of the hands.
Treatment
According to the National Eczema Association, treating eczema calls for a mix of self-care, OTC drugs, and prescription medications. People with eczema can identify and learn to manage or avoid triggers for their outbreaks.
People with eczema can identify and learn to manage or avoid triggers for their outbreaks.
Changing bathing practices and using moisturizer can also help. Prescription lotions, systemic medications, UVB light, and biologics can address more severe symptoms.
Learn more about the different types of eczema here.
Skin problems, such as itchy bumps on the skin similar to mosquito bites, can range from mild to severe.
Some issues, including bed bug bites, can be fleeting, while others, such as allergic reactions to certain foods, are signs of a permanent condition. However, most skin problems generally respond well to treatment.
If the symptoms do not improve with self-care practices, people should see a medical professional to determine what is causing the outbreak and how to treat it.
Itchy bumps on skin like mosquito bites: What are they?
Several skin conditions can cause itchy lumps that resemble bug bites. These include allergic reactions, infections, and chronic conditions.
Most people experience this symptom at some point. Itchy bumps can appear as a result of allergies, infections, insects, and, sometimes, nonidentified factors.
However, there is one general principle that the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology recommend people to follow when their skin itches: Do not scratch it.
Additional general self-care practices for itchy skin include:
- bathing frequently in lukewarm water
- using gentle, hypoallergenic soap
- limiting exposure to the sun
- applying cold compresses
- avoiding tight clothing in areas where itchy bumps appear
Understanding the different conditions that can cause itchy bumps on the skin can help people get appropriate treatment. Depending on the cause, treatment can range from avoiding certain foods to taking prescription medications.
Keep reading to learn more about some common causes of itchy bumps that look like mosquito bites and how to treat them.
The medical term for hives is urticaria, and it describes a condition that produces raised itchy areas on the skin. If a person notices bumps on the skin that resemble mosquito bites but has not had any exposure to mosquitos, the cause is probably acute urticaria. The term “acute” means that the condition does not last longer than 6 weeks.
Hives are very common, affecting about 20% of people at some point in their lives. Certain kinds of foods, such as peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood, cause hives in many people due to an allergic reaction. Latex, pollen, insects, various plants, and some medications, such as sulfa drugs or even aspirin, may also cause hives.
Hives cause characteristic red, purple, or skin colored itchy bumps that appear and disappear quickly anywhere on the body. These bumps typically turn white or disappear when a person presses them.
Treatment
The treatment for hives depends on the severity and cause of the rash, but it includes avoiding known triggers. People who are extremely allergic to a trigger — for example, peanuts or certain insects — may need to carry an epinephrine auto-injector, such as an Epipen. This device can stop a potentially life threatening reaction if a person has accidental contact with a known allergen.
People who are extremely allergic to a trigger — for example, peanuts or certain insects — may need to carry an epinephrine auto-injector, such as an Epipen. This device can stop a potentially life threatening reaction if a person has accidental contact with a known allergen.
Anti-itching lotions and over-the-counter (OTC) antihistamines can provide relief for mild symptoms, while more intense outbreaks may require stronger prescription versions of these drugs or corticosteroids.
Learn more about hives here.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), bed bug bites can resemble bites from other bugs, although they can take as long as 2 weeks to materialize.
People who notice itchy bumps on the skin that resemble mosquito bites should check for:
- other signs of bed bugs
- bed bugs themselves on a mattress or sheet
- dead bed bugs
- blood spots on a mattress or sheet
- the characteristic musty smell associated with bed bugs
If the bites appear in a straight line, they are likely to be due to bed bugs. However, bed bug bugs can also appear in more random formations.
However, bed bug bugs can also appear in more random formations.
Treatment
Unless someone has a severe allergic reaction, experts recommend simple self-care practices to treat any bites. These include not scratching, applying OTC antiseptic ointments, and taking antihistamines.
Learn more about bed bugs here.
Contact dermatitis is essentially an allergic reaction that develops when a person’s skin comes into contact with something to which they are allergic, such as latex or certain metals or household products.
It can take 1–2 days for the reaction to develop and 2–3 weeks for symptoms to disappear. Contact dermatitis may hurt as much as it itches, and it may present with inflammation and blisters.
Treatment
Self-care with cold compresses, calamine lotion, and soothing baths can help provide relief.
Prescription medication, such as antihistamines and cortisone, may be necessary if the reaction is severe.
Working with healthcare professionals can help people identify their triggers, which can be complicated.
According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, there are more than 3,700 substances known to cause contact allergies. Avoiding triggers is a key part of managing contact dermatitis, along with thoroughly washing the affected area with soap and water after exposure happens.
Learn more about contact dermatitis here.
The human itch mite is responsible for scabies. This mite digs its way through the top layer of the skin and lays eggs. Its tunnels can sometimes be visible on the surface of the skin, where they appear as raised, crooked, skin colored lines. However, the most common symptom of scabies is itchy bumps on the skin. These are like mosquito bites, only smaller.
Sites of the body that this very itchy condition commonly affects include the wrists, the elbows, between the fingers, and behind the knees.
Treatment
Only a prescription lotion will treat scabies effectively, and individuals need to follow the application directions exactly. Anyone who has had extensive skin-to-skin contact with someone with scabies should also seek treatment.
Anyone who has had extensive skin-to-skin contact with someone with scabies should also seek treatment.
It is very important that people with scabies thoroughly wash and dry all of their clothes, towels, sheets, bedding, and other household items. Other remedies for scabies may also help.
Learn more about scabies here.
Also known as atopic dermatitis, this common condition causes itchy, red, irritated skin that can sometimes develop bumps. In the long term, it can make the skin thicker, scaly, and flaky, as well as causing it to change color.
Scratching makes eczema worse and increases the risk of infection. Eczema occurs due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, which prompt the immune system to overreact to certain triggers, such as laundry soap or sweating. It typically affects the face, elbows, knees, scalp, and backs of the hands.
Treatment
According to the National Eczema Association, treating eczema calls for a mix of self-care, OTC drugs, and prescription medications. People with eczema can identify and learn to manage or avoid triggers for their outbreaks.
People with eczema can identify and learn to manage or avoid triggers for their outbreaks.
Changing bathing practices and using moisturizer can also help. Prescription lotions, systemic medications, UVB light, and biologics can address more severe symptoms.
Learn more about the different types of eczema here.
Skin problems, such as itchy bumps on the skin similar to mosquito bites, can range from mild to severe.
Some issues, including bed bug bites, can be fleeting, while others, such as allergic reactions to certain foods, are signs of a permanent condition. However, most skin problems generally respond well to treatment.
If the symptoms do not improve with self-care practices, people should see a medical professional to determine what is causing the outbreak and how to treat it.
What to do if bitten by a mosquito and everything itches and itches
Health
June 27
You don’t have to develop willpower.
Why mosquito bites itch so much
Mosquitoes pierce the skin with a special mouth apparatus and suck blood through it. At this time, their saliva, which contains proteins foreign to humans, enters the skin. The immune system reacts to this and inflammation sets in, which manifests itself as an itchy pink bump.
At this time, their saliva, which contains proteins foreign to humans, enters the skin. The immune system reacts to this and inflammation sets in, which manifests itself as an itchy pink bump.
Most people are slightly sensitive to mosquito saliva, so the reaction does not go beyond the bite. But for some, the immune system is more aggressive, so there is a lot of swelling, redness and soreness around. In this case, the temperature may rise, and the general condition may worsen.
How to relieve itching from mosquito bites
Although mosquito bites are very common, there is very little research on their treatment. The fact is that they heal so well: even if you do nothing, the discomfort from the bite will disappear in a couple of days. So scientists tend to focus on diseases that mosquitoes can carry.
This is why most recommendations are based on expert opinion and clinical experience.
Apply an ice cube
Ice slows down blood flow, which means it reduces the reaction to foreign protein – inflammation, pain, swelling and itching. Therefore, apply an ice pack wrapped in a light towel to the bite for at least 10 minutes. Another option is to rub the bump with an ice cube for 30 seconds.
Therefore, apply an ice pack wrapped in a light towel to the bite for at least 10 minutes. Another option is to rub the bump with an ice cube for 30 seconds.
Wipe the bite with an alcohol wipe
Alcohol causes proteins in mosquito saliva to break down, so the reaction should be less. Of course, this will only help immediately after the bite.
Apply calamine lotion
Calamine lotion reduces itching, so may also be useful against mosquito bites.
Apply OTC steroid
Corticosteroids reduce immune response. Therefore, inflammation, itching and pain at the bite sites become less. Apply a very thin layer of cream, such as a hydrocortisone-based cream, spot on the bite.
Apply Antihistamine Ointment
Histamine is a chemical released by immune system cells when it encounters an allergen. So apply antihistamine ointment on the bites to help reduce itching.
Take an over-the-counter antihistamine
For more severe reactions or more bites, you can take an over-the-counter antihistamine to reduce symptoms.
What folk methods can work
These methods have not been tested by scientists to reduce itching from bites. But some of this is used in other situations, and some of it has been tested by experience. So if they help you, use them.
Attach tea bag
The easiest way to apply to the bite is a tea bag that has been wrung out and cooled. You should not use a new one, so that it does not stain the skin.
In addition to ordinary tea, you can take chamomile, as it contains terpenoids and flavonoids, which have antioxidant and antihistamine properties.
Press the sachet against mosquito bites for 10 minutes and then wipe off any remaining tea with a clean towel. You can then put the bag in the refrigerator to make such compresses during the day.
Apply tea tree oil
Tea tree oil reduces inflammation and is said to help with mosquito bites. Remember that it is better not to abuse it, as it can lead to irritation, an allergic reaction and contact dermatitis.
Apply baking soda paste
Add just a little water to baking soda to make a paste. It must be applied pointwise to the bites so that they do not itch so much.
Wipe the bite with vinegar
This substance can also destroy proteins from mosquito saliva, so you can wipe a completely fresh puncture with it.
Apply Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe Leaf Gel contains salicylic acid to help reduce itching and pain. So try spotting it on the bite.
Brush the bite with honey
Honey contains the catalase enzyme, which breaks down protein. Therefore, it can reduce inflammation slightly. In general, anoint the bites with honey, and cover the top with gauze so that nothing sticks to you.
Apply oatmeal
Gluten is said to soothe the skin. Therefore, you can grind the cereal in a blender, and then mix it with a little water to make a thick paste. It must be applied to the bite.
Apply pressure to the bite
Sounds strange, but pressure on the bite helps reduce itching. Someone generally makes two dents in the shape of a cross with a fingernail and thinks that this is the best way. Try different options, but try not to scratch the skin to the point of bleeding.
Someone generally makes two dents in the shape of a cross with a fingernail and thinks that this is the best way. Try different options, but try not to scratch the skin to the point of bleeding.
Grate the bite with an onion or banana
Not sure if it will help, but you can try. True, it is better not to leave onion juice on sensitive skin for a long time, because it can cause irritation.
Pat the bite
Instead of scratching, pat the bite. There is an opinion that in this way you will deceive the brain: it will think that you have scratched yourself.
Apply a hot spoon
Heat is thought to help break down proteins in saliva, but immunologist Catriona Nguyen-Robertson says it’s more likely that you’re shifting your focus away from itching again.
You should be careful with this method: if you overdo it, you may get burned.
When to see a doctor about mosquito bites
See a doctor if:
- your general condition worsens and flu-like symptoms develop;
- you are concerned about an excessive skin reaction;
- bites do not go away after a few days, but rather increase in size;
- you have damaged the bite, and an infection has developed there – it is red, sore, maybe there is a discharge.

Read also 🧐
- How to get rid of mosquitoes in the area
- 7 reasons why you are attractive to mosquitoes
- How to choose the right mosquito repellent for children
7 signs of skin cancer that no one pays attention to
Everyone knows that if a mole has changed size or color, you need to urgently run to an oncologist. But it happens that the body gives much less obvious signals that may indicate a malignant skin tumor.
16,000 Britons are diagnosed with skin cancer every year, and 2,500 of them eventually die, reports the Mirror. The good news is that 80 to 100 percent of cases found in stage 1 or 2 are easily treatable. How not to overlook the tumor, said dermatologist Ross Perry.
1. Unexplained scars
Basalioma. Photo © Wikimedia Commons
If out of nowhere you have a scar that grows in size, this may be a sign of a basalioma. It occurs on areas of the skin that are exposed to intense sun exposure. The scar may look like a waxy thickening. This is the most common form of skin cancer, but, fortunately, the least dangerous if detected early.
The scar may look like a waxy thickening. This is the most common form of skin cancer, but, fortunately, the least dangerous if detected early.
2. Eruptions on the eyelids
Basalioma on the eyelid. Photo © BOPSS
Eyelid malignancies may be brown, black, red, or flesh-colored. They can be hard to the touch, itchy and painful, or shiny and waxy. It is important to record all the changes that occur to them. To protect your eyelids from ultraviolet light, you need to wear sunglasses or a hat, and use sunscreen.
3. Black spots under nails
Subungual melanoma. Video screenshot: YouTube / The Doctors
Subungual melanoma can easily be confused with a bruise. Most often, it occurs under the thumbnail as a result of regular injury to this area. If left untreated, subungual melanoma can spread to other parts of the body.
4. Itching of the scalp
Squamous cell carcinoma. Photo © Brown University
If your head is constantly itching, take a close look at the skin under your hair. Scalp cancer is more common in men and there are three types. Firstly, it is a basalioma, but it is rare and not so dangerous. The second form is squamous cell carcinoma. It affects fair-skinned people who are often exposed to the sun, and appears as scaly red spots, open sores, rough, thickened, or warty areas of the skin, and raised, dimpled growths. But the most dangerous form is melanoma, and it looks like a normal mole.
Scalp cancer is more common in men and there are three types. Firstly, it is a basalioma, but it is rare and not so dangerous. The second form is squamous cell carcinoma. It affects fair-skinned people who are often exposed to the sun, and appears as scaly red spots, open sores, rough, thickened, or warty areas of the skin, and raised, dimpled growths. But the most dangerous form is melanoma, and it looks like a normal mole.
5. Non-healing ulcers
Basalioma. Photo © Wikimedia Commons
These sores can look lumpy, dry and scaly. They can also itch and bleed. All these signs indicate the risk of developing basalioma.
6. Non-healing “insect bites”
Site of mosquito bite. Photo © Wikimedia Commons
Red bumps, which in the warm season can easily be mistaken for mosquito bites, can actually be something much more serious. If they have not gone away even after a few weeks, you should go to the doctor to rule out the risk of developing skin cancer.

