Pictures of ascaris. Ascaris Lumbricoides: Understanding the Parasitic Roundworm and Its Impact on Human Health
What are the key characteristics of Ascaris lumbricoides. How does this parasitic roundworm affect human health. What are the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for ascariasis. How can this common helminthic infection be prevented.
The Biology and Life Cycle of Ascaris Lumbricoides
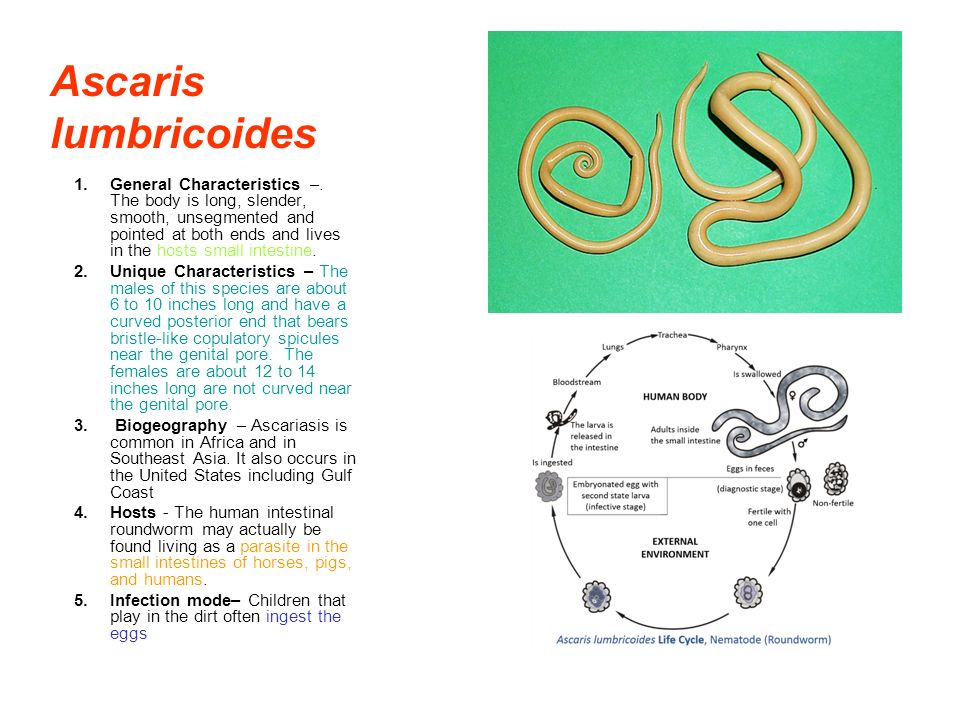
Ascaris lumbricoides, commonly known as the giant roundworm, is a parasitic nematode that infects human intestines. This helminth is responsible for ascariasis, one of the most common parasitic infections worldwide.
The life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides is complex and involves several stages:
- Eggs are passed in human feces and contaminate soil
- Larvae develop within the eggs in favorable conditions
- Humans ingest infective eggs through contaminated food or water
- Larvae hatch in the small intestine and penetrate the intestinal wall
- Larvae migrate through the bloodstream to the lungs
- Larvae ascend the respiratory tract and are swallowed back into the intestines
- Adult worms develop and reproduce in the small intestine
Adult Ascaris worms can grow up to 35 cm in length, making them one of the largest intestinal nematodes affecting humans. The female worm can produce up to 200,000 eggs per day, which are then passed in feces to continue the cycle.
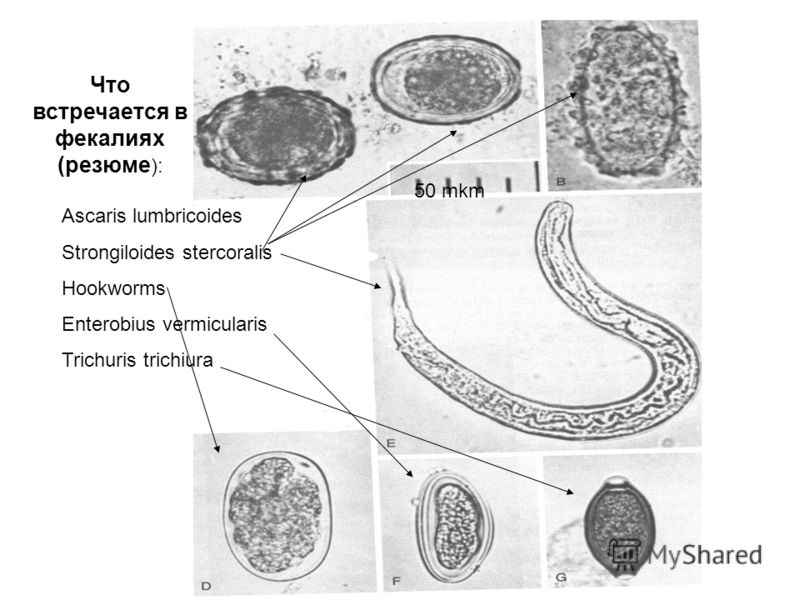
Prevalence and Risk Factors for Ascariasis
Ascariasis is a global health concern, affecting an estimated 1 billion people worldwide. The infection is particularly prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions with poor sanitation and hygiene practices.
Several factors contribute to the high prevalence of ascariasis:
- Inadequate sanitation facilities
- Limited access to clean water
- Poor personal hygiene practices
- Use of human feces as fertilizer (night soil)
- Crowded living conditions
- Lack of health education
Children are particularly vulnerable to ascariasis due to their play habits and less developed immune systems. In endemic areas, repeated infections throughout childhood can lead to chronic health issues and impaired growth and development.
Geographical Distribution
While ascariasis occurs globally, it is most common in:
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- Southeast Asia
- Central and South America
- Parts of the Middle East
In these regions, prevalence rates can exceed 50% in some communities, highlighting the urgent need for improved sanitation and public health measures.

Clinical Manifestations of Ascariasis
The symptoms of ascariasis vary depending on the stage of infection and worm burden. Many infected individuals may be asymptomatic, especially in cases of light infections.
Pulmonary Phase
During larval migration through the lungs, patients may experience:
- Cough
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Chest discomfort
These symptoms are associated with Löffler’s syndrome, a form of eosinophilic pneumonitis caused by the immune response to migrating larvae.
Intestinal Phase
As adult worms establish in the intestines, patients may develop:
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Malnutrition (in chronic infections)
In heavy infections, intestinal obstruction can occur, leading to severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and constipation. This is a medical emergency requiring prompt intervention.
Complications
Ascariasis can lead to several serious complications:
- Intestinal obstruction
- Biliary tract obstruction
- Pancreatic duct obstruction
- Appendicitis
- Peritonitis (if intestinal perforation occurs)
- Malnutrition and growth stunting in children
In rare cases, adult worms can migrate to unusual locations, causing complications in the respiratory tract, genitourinary system, or central nervous system.

Diagnosis and Treatment of Ascariasis
Accurate diagnosis of ascariasis is crucial for effective treatment and management of the infection.
Diagnostic Methods
Several techniques are used to diagnose ascariasis:
- Stool microscopy: Detection of Ascaris eggs in fecal samples
- Imaging studies: X-rays or ultrasounds to visualize adult worms
- Blood tests: Elevated eosinophil count may indicate infection
- Serological tests: Detection of antibodies against Ascaris antigens
In some cases, adult worms may be visible in stool or vomit, providing a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Anthelmintic medications are the primary treatment for ascariasis. Commonly used drugs include:
- Albendazole
- Mebendazole
- Ivermectin
- Pyrantel pamoate
These medications are generally safe and effective, with cure rates exceeding 90% in most cases. A single dose is often sufficient, but repeat treatment may be necessary in areas of high transmission.
For patients with complications such as intestinal obstruction, surgical intervention may be required. Supportive care, including fluid and electrolyte management, is essential in severe cases.

Prevention Strategies for Ascariasis
Preventing ascariasis requires a multifaceted approach addressing the various risk factors associated with transmission.
Personal Hygiene
Promoting good personal hygiene practices is crucial in preventing ascariasis:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water
- Proper food handling and preparation
- Avoiding consumption of raw or unwashed vegetables
- Using clean water for drinking and cooking
Sanitation Improvements
Improving sanitation infrastructure is essential for long-term prevention:
- Construction and use of proper latrines
- Safe disposal of human waste
- Improved sewage systems in urban areas
- Avoiding the use of untreated human feces as fertilizer
Mass Drug Administration
In endemic areas, preventive chemotherapy through mass drug administration (MDA) programs can significantly reduce the burden of ascariasis. These programs typically target school-age children and other high-risk groups.
Health Education
Raising awareness about ascariasis and its prevention is crucial. Health education programs should focus on:

- Transmission routes of Ascaris
- Importance of personal hygiene
- Proper sanitation practices
- Recognition of symptoms and seeking medical care
The Global Health Impact of Ascariasis
Ascariasis poses a significant public health challenge, particularly in resource-limited settings. The infection contributes to:
- Malnutrition and growth stunting in children
- Reduced cognitive function and educational performance
- Economic burden due to healthcare costs and lost productivity
- Exacerbation of poverty in endemic communities
The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified ascariasis as a neglected tropical disease (NTD) and set targets for its control and elimination. Efforts to address ascariasis are often integrated with programs targeting other soil-transmitted helminths.
Economic Impact
The economic burden of ascariasis is substantial, with estimates suggesting annual productivity losses in the billions of dollars globally. This impact is particularly severe in low-income countries where the infection is most prevalent.
Sustainable Development Goals
Addressing ascariasis is crucial for achieving several Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including:
- SDG 1: No Poverty
- SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
By reducing the burden of ascariasis, communities can improve health outcomes, increase productivity, and break the cycle of poverty associated with neglected tropical diseases.
Research and Future Directions in Ascariasis Control
Ongoing research in ascariasis focuses on several key areas:
Vaccine Development
While no vaccine currently exists for ascariasis, researchers are exploring potential vaccine candidates targeting various stages of the Ascaris life cycle. A successful vaccine could provide long-term protection and complement existing control strategies.
Improved Diagnostics
Developing more sensitive and specific diagnostic tools is crucial for accurate detection of ascariasis, particularly in low-intensity infections. Novel molecular techniques, such as PCR-based methods, show promise in this area.

Drug Resistance Monitoring
As with other parasitic infections, there is concern about the potential development of drug resistance in Ascaris populations. Ongoing surveillance and research into alternative treatment options are essential to maintain effective control strategies.
Environmental Interventions
Exploring innovative approaches to interrupt Ascaris transmission in the environment is an active area of research. This includes studying the impact of improved sanitation technologies and evaluating the effectiveness of soil treatment methods to reduce egg viability.
One Health Approach
Recognizing the zoonotic potential of some Ascaris species, researchers are adopting a One Health approach to understand the complex interactions between human, animal, and environmental health in the context of ascariasis control.
As research progresses, integrating new findings into existing control programs will be crucial for achieving sustainable reductions in ascariasis burden worldwide.
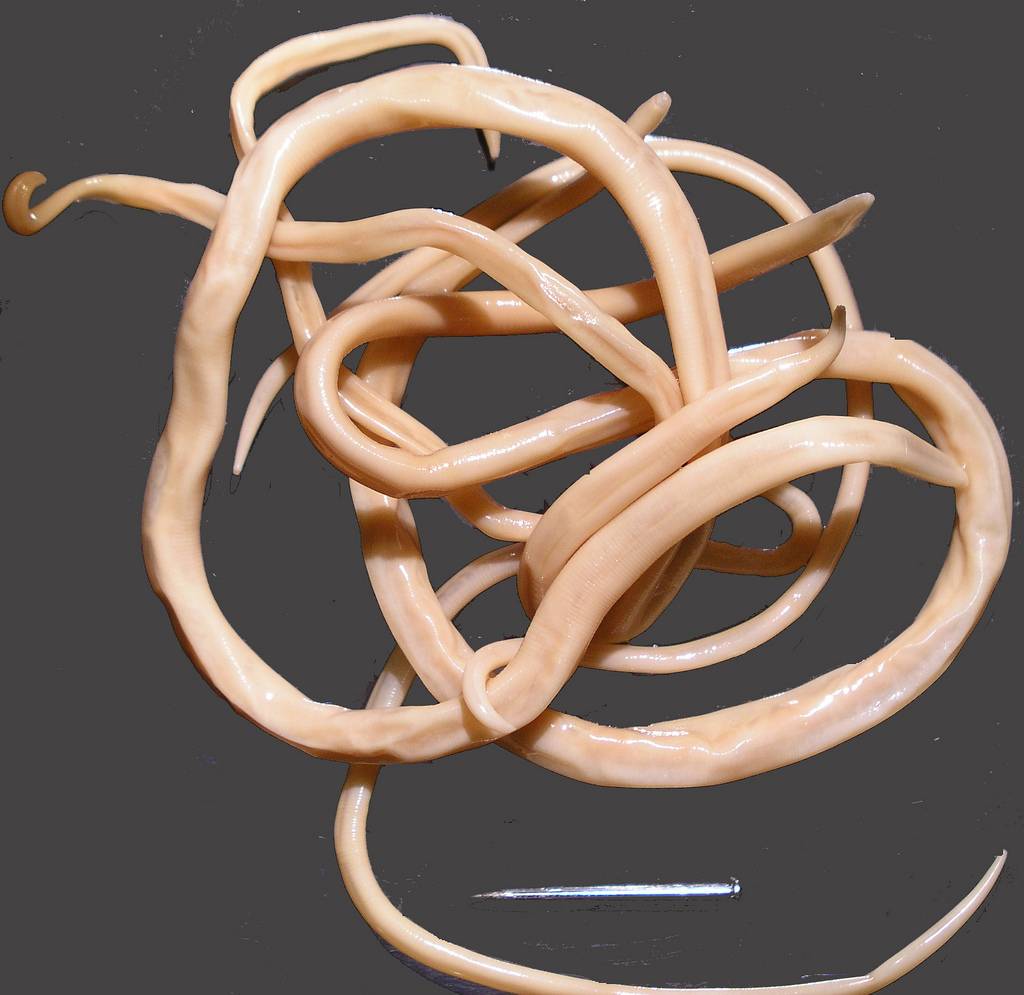
Conclusion
Ascaris lumbricoides remains a significant global health challenge, particularly in resource-limited settings. Understanding the biology, epidemiology, and clinical aspects of this parasitic infection is crucial for effective control and prevention strategies.
While progress has been made in reducing the global burden of ascariasis through improved sanitation, mass drug administration programs, and health education, sustained efforts are needed to achieve long-term control and elimination goals.
By addressing ascariasis and other neglected tropical diseases, we can improve the health and well-being of millions of people worldwide, contributing to broader goals of poverty reduction and sustainable development.
As research continues to advance our understanding of Ascaris lumbricoides and ascariasis, integrating new knowledge into public health interventions will be essential for optimizing control strategies and ultimately reducing the impact of this ancient parasite on human health.
Southwest Journal of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep – Imaging
Wednesday, February 11, 2015 at 8:00AM
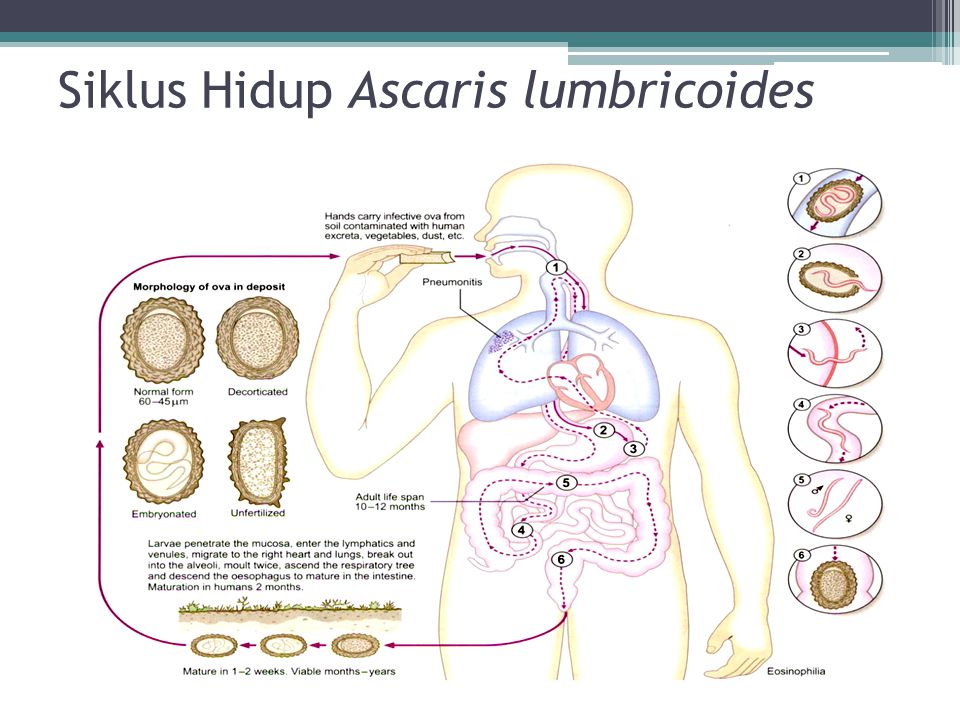
Figure 1. 23 cm adult Ascaris lumbricodes recovered from patient’s feces.
A 25 year-old man was admitted to the ICU with acute renal failure and acute respiratory failure from fluid overload after attempting to cross the border. The patient was successfully extubated after five days of mechanical ventilation and renal replacement therapy. Following extubation, the patient had a bowel movement and passed a 23cm adult Ascaris lumbricoides. He was treated with a single dose of albendazole 400 mg.
Ascariasis is a very common helminthic infection, particularly in pediatric populations, and affects mostly the gastrointestinal tract. When infective eggs are swallowed by the host, larvae hatch in the GI tract. The larvae invade the GI mucosa and then are brought into the lungs via portal circulation. The larvae can then move up the tracheobronchial tree and then are swallowed into the GI tract where the mature worms form (1).
While our patient had a simple gastrointestinal infection, several pulmonary complications of ascariasis have been reported (2). Adult worms can cause largyngospasm as well as mechanical obstruction of the airway which can result in cardiac arrest (3,4). This migration of worms from the stomach to the trachea may be related to the use of anesthetics and the subsequent relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter. Ascaris larvae have been implicated in Loeffler’s syndrome, also described as simple pulmonary eosinophilia, characterized by transient pulmonary infiltrates and eosinophilia with a usually benign course.
Candy Wong1; Aaron Fernandes2, Jennifer Huang2, and Sachin Chaudhary1
1Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, Allergy, and Sleep Medicine.
2 Department of Medicine
University of Arizona
Tucson, AZ
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
 Parasites – Ascariasis. Biology. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/biology.html (accessed 1/13/2015).
Parasites – Ascariasis. Biology. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/biology.html (accessed 1/13/2015).Li QY, Zhao DH, Qu HY, Zhou CN. Life-threatening complications of ascariasis in trauma patients: a review of the literature. World J Emerg Med. 2014;5(3):165-70. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Maletin M, Veselinović I, Stojiljkovic GB, Vapa D, Budakov B. Death due to an unrecognized ascariasis infestation: two medicolegal autopsy cases. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2009;30(3):292-4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Husain SJ, Zubairi AB, Sultan N, Beg MA, Mehraj V. Recurrent episodes of upper airway blockage associated with Ascaris lumbricoides causing cardiopulmonary arrest in a young patient. BMJ Case Rep. 2009;2009. pii: bcr01.2009.1415. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Reference as: Wong C, Fernandes A, Huang J, Chaudhary S. Medical image of the week: ascaris lumbridoies. Souhtwest J Pulm Crit Care. 2015;10(2):81-2. doi: http://dx. doi.org/10.13175/swjpcc008-15 PDF
doi.org/10.13175/swjpcc008-15 PDF
Ascaris Egg Stock Photos and Images
White egg on old wooden backgroundPREMIUM
Chicken eggs on a wooden background. concept photo. close-up. high quality photoPREMIUM
Ugly abnormal crooked egg on the background of burlap, close-up.PREMIUM
A lone egg shell standing upright in a field.PREMIUM
One egg in darkPREMIUM
Egg shell with white background.PREMIUM
Egg balanced on two metal forks, black backgroundPREMIUM
Ostrich egg in straw nestPREMIUM
Brown egg separate and out of the cup filled with white eggs. various light adjustments.PREMIUM
Happy easter card with natural color eggs and feathersPREMIUM
Egg on black backgroundPREMIUM
Easter composition with spring flowers and eggs on white backgroundPREMIUM
Fresh farm eggs, milk and butter on wood table.PREMIUM
Natural egg in nest with feathers, vintage plate, pussy willow branches and napkin on aged wood. rustic easter still life. easter table decoration. moody imagePREMIUM
easter table decoration. moody imagePREMIUM
Goose egg close-upPREMIUM
Composition of fresh white easter eggs in carton box and williw catkins isolated on dark background. easter holidays concept. top view. flat layPREMIUM
White egg on a yellow-blue background. easter eggs.PREMIUM
Golden egg on a tablePREMIUM
Egg in hand closeup on black background with space for text. concept of life and health.black and white photography art, soft focus and hard light.PREMIUM
Broken eggs on top of each other on a platePREMIUM
Happy easter. a little girl’s hands are holding a brown easter egg for a holiday on a white background. egg decoration, festive cooking. the christian tradition. greeting card. top view. copyspacePREMIUM
One last white egg in a black carton trayPREMIUM
Cracked eggsPREMIUM
Handmade and decorative easter egg with texture and painting in resin, marble, stone and chocolate. details and volumes.PREMIUM
Organic eggs in trayPREMIUM
Quinoa burger ingredients: quinoa, mangold, dry grain mix, chili pepper, eggs green peas basil on white rustic boardPREMIUM
Egg in the white plate with black background and copy space. PREMIUM
PREMIUM
An old duck egg recipe in ash. salty pickled duck egg in ash on a white background.PREMIUM
White chicken egg on a black background with written text 2022 lies on a yellow straw hat, easter and culture in the new year, foodPREMIUM
Egg on red background in vertical positionPREMIUM
Intact golden egg among broken white eggs. the concept of reliability, resistance to adverse conditions.PREMIUM
Easter card. eggs with marble stone effect painted with natural dye carcade flower on grey sparkling background with blank space for text. top view. flat layPREMIUM
Easter decor on the grey backgroundPREMIUM
Chicken eggs on the table. farm products, natural eggs.PREMIUM
Rustic easter still life. natural egg in nest with feathers, vintage plate, cutlery, pussy willow branches and napkin on aged wood. easter table decorationPREMIUM
Fresh eggs on a white backgroundPREMIUM
The chicken egg is white in color on burlap and on green grass.PREMIUM
Fresh white eggs in a cardboard box on a yellow background.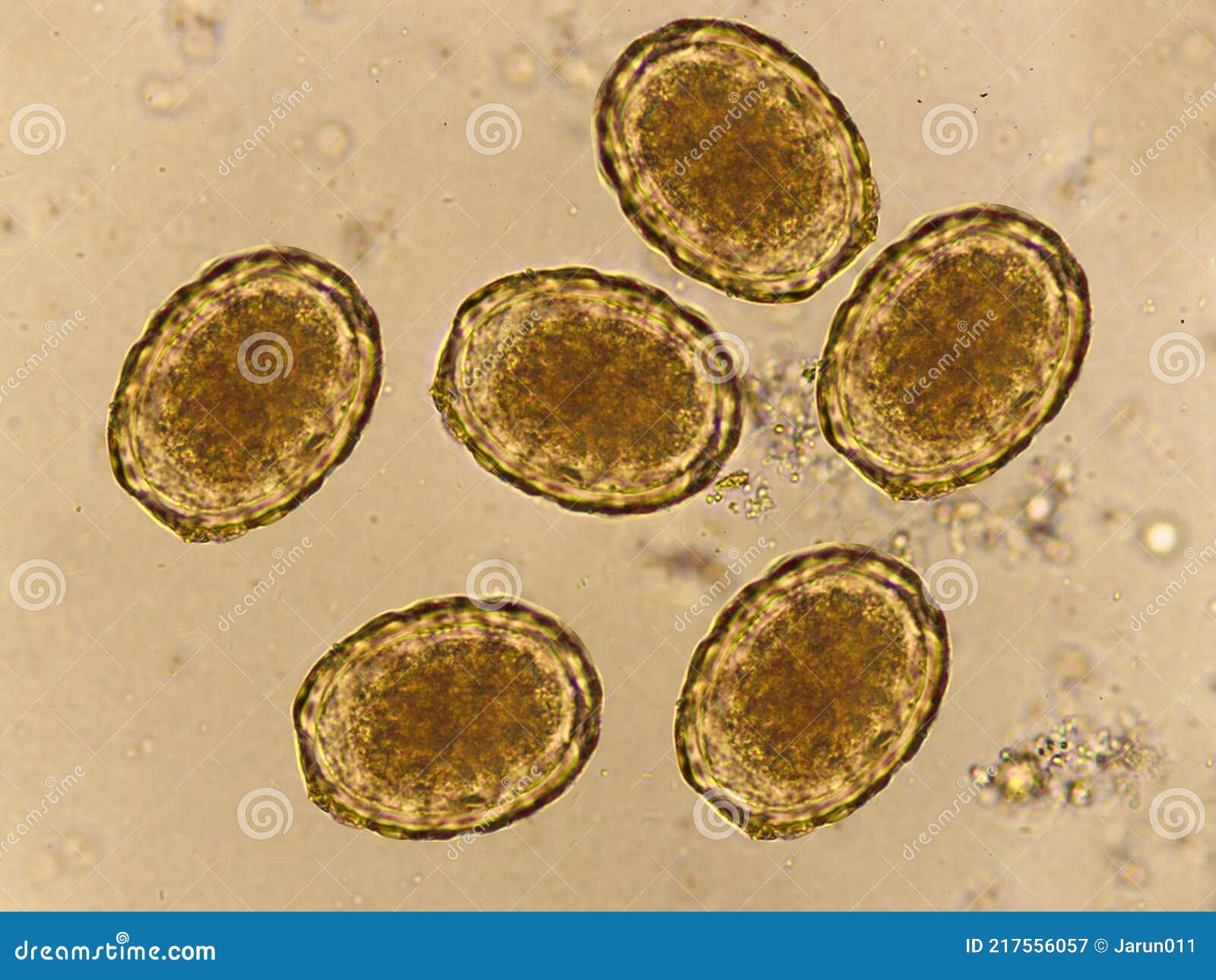 chicken eggs in sustainable packaging made from recycled materials. selective focus. space for textPREMIUM
chicken eggs in sustainable packaging made from recycled materials. selective focus. space for textPREMIUM
White organic egg in a box consisting 50 percent grass fibers and is fully recyclable.PREMIUM
Hand holding a mini bowl with fresh raw egg. directly above shotPREMIUM
Boiled egg for breakfast on the wooden holderPREMIUM
Araucana egg on wooden background. light blue egg from araucana chicken. easter festival concept. easter egg. blue araucana chicken egg very nice colors. space for text.PREMIUM
White egg dripping with drops of white paint on a black background. minimalistic easter concept.PREMIUM
Unpainted easter eggs on a blue backgroundPREMIUM
This is duck egg in black background, soft tonePREMIUM
White eggs in rustic carton on white backgroung. easter holidays conceptPREMIUM
Easter egg cup on white backgroundPREMIUM
Ingredient, branding and diet concept – egg on marble table as minimalistic food flat lay, top view food brand photography flatlay and recipe inspiration for cooking blog, menu or cookbook designPREMIUM
Three beige eggs lie on the granite surface, willow twigs in the corners. PREMIUM
PREMIUM
Broken egg with yolk, protein and shell on leopard skinPREMIUM
Shell boiled egg on back plate backgroundPREMIUM
Close up of painted easter chicken eggsPREMIUM
Hand holding big goose egg, isolated on white backgroundPREMIUM
Brown egg in boxPREMIUM
Catkin easter eggs with white on a blue backgroundPREMIUM
Chicken eggs in a container on a white background. one egg is silver. easter eggs. eggs in a container on a white background with place for text.PREMIUM
Brown eggs in cardboard on pastel pink background. modern concept of minimalismPREMIUM
An upright chicken’s egg (whitened) in small nest on wood plank table.PREMIUM
Happy easter! easter eggs on wooden backgroundPREMIUM
Boiled egg on white background. (selective focus, focus on the front of the shell on the first egg)PREMIUM
White eggs in a white glass bowl. isolated on a dark gray background. top view close up photo.PREMIUM
Wicker basket with easter eggs, pussy willow branch and baby chicken on gray tablePREMIUM
SpicesPREMIUM
Chicken eggs in a cardboard box on a dark backgroundPREMIUM
Oval new egg-shaped sponges for cosmetics and foundationPREMIUM
Fresh village chicken eggs lie on the surface of the table with a wooden spoon, one broke. PREMIUM
PREMIUM
One egg on dark fabric background. easter, spring or eco food concept. top viewPREMIUM
Egg on cement groundPREMIUM
Wooden spoon of organic raw egg on black backgroundPREMIUM
Quail eggs on a black background. stock photo.PREMIUM
Two fresh eggs in eggcup and ground on white backgroundPREMIUM
White egg on a spoon on a white backgroundPREMIUM
Festive easter eggs in a clay plate of willow twigs on a table. light background happy easter concept. flat layoutPREMIUM
Concept of fresh and natural farm product – eggs, top viewPREMIUM
Hen eggs with broken shell on black isolatedPREMIUM
White eggs located in the egg carton greenPREMIUM
Close-up of fresh eggPREMIUM
Soft boiled brown egg in a white ceramic egg cup, on a white ceramic plate with a spoon, on a white cloth tableclothPREMIUM
White chicken egg stands on two fork on a wooden table in the kitchenPREMIUM
White eggs with fabric ribbon on brown paper background, happy easter dayPREMIUM
Brown boiled half-peeled egg and pieces of black bread on a dark wooden background with scattered salt and shellPREMIUM
White egg with golden background. easter concept.PREMIUM
easter concept.PREMIUM
Closeup view of chocolate candy with golden splashes on crumpled paperPREMIUM
Chicken eggs and shell eggs symbol penis. excruciating pain in the groin. the concept of male problems.PREMIUM
Still life. a large white egg lies on two crossed forks on a black background with reflectionPREMIUM
White eggs in green bowl on dark moody black plain minimal background, angle view, happy easter dayPREMIUM
Chocolate egg on white eggs stand holder with copy spacePREMIUM
White egg on a white isolated background with shadow. ingredient.healthy food.easterPREMIUM
Single cracked egg isolated on dark background with reflected base and pieces of shell. business concept for excessive stress.PREMIUM
Eggs on a dark background in different anglesPREMIUM
Easter eggs basket. natural color egg in basket with spring tulips, white feathers on wooden table background in happy easter decoration. traditional decoration in sun lightPREMIUM
The crack white chicken egg. PREMIUM
PREMIUM
Thailand mango on olive board closeupPREMIUM
Easter background with colorful chicken and quail eggs hiding in green grass on gray slate surface. mockup for greeting card to spring holiday, closeup, copy spacePREMIUM
Easter egg in hay nest on white stand. composition with egg ready to eat and spoon on wooden table background. front viewPREMIUM
An egg is on the red backgroundPREMIUM
Wooden eggs on saw cut of a tree with pussy willow. easter basckground with space for text. focus picked.PREMIUM
White background with white eggs and feathers. white background. top viewPREMIUM
One white egg on white background viewed from the sidePREMIUM
Beautiful easter eggs and eucalyptus branches on light background, closeupPREMIUM
Ascaris in children | how to treat roundworm in humans | photo of roundworm
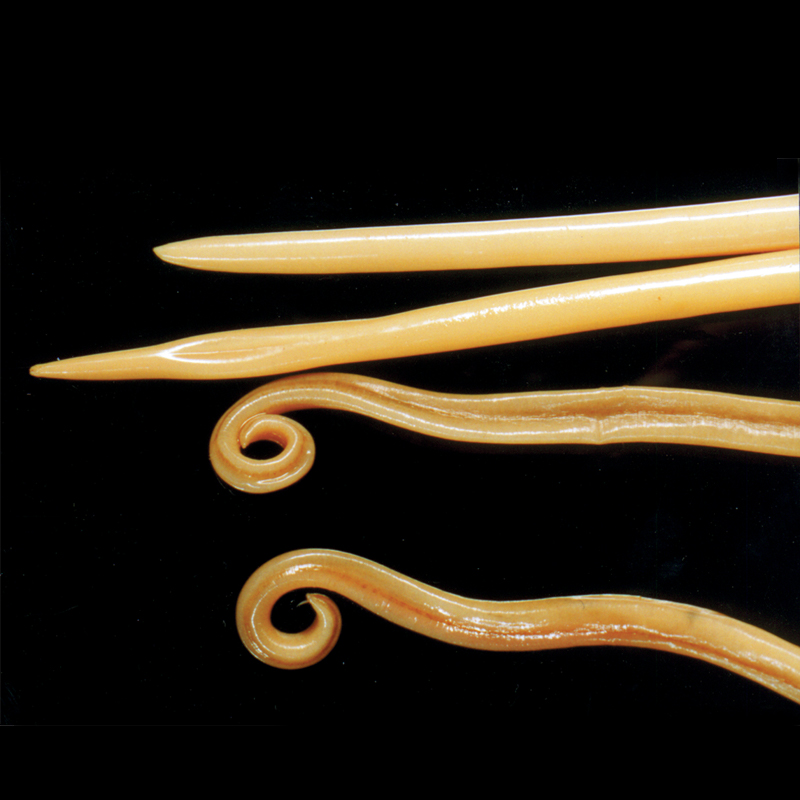
What are roundworms? These are roundworms that parasitize in the human body and cause such a disease as ascariasis . These helminths are bisexual, roundworm length can reach up to 25 cm for males and up to 40 cm for females. Unlike many other parasites, the adult roundworm is not attached to the intestines and can move freely inside the body and penetrate into various organ systems, causing damage to them.
Unlike many other parasites, the adult roundworm is not attached to the intestines and can move freely inside the body and penetrate into various organ systems, causing damage to them.
Where roundworms live: the life cycle of the parasite
Ascaris roundworms are geohelminths: eggs develop in the soil. Under suitable conditions (sufficient humidity and warmth), the egg becomes infective within 10-16 days. If the ambient temperature is below 12ºС, then roundworm eggs do not develop, but remain viable for 2-3 years. This vitality of the egg is provided by the presence of five shells.
Together with particles of the earth, invasive helminth eggs fall on fruits and vegetables, into the water, where they are usually swallowed by a person. Infection can also occur through inhalation of soil particles (for example, while working in the garden).
The swallowed roundworm egg enters the human stomach, and then into the small intestine, where its shell is destroyed and the roundworm larva appears. It pierces the intestinal wall and reaches the circulatory system. Together with the blood flow, roundworms are brought into the bronchi and lungs, where they continue their development. Through the respiratory tract, parasites enter the pharynx and larynx, and, being swallowed again, together with saliva, they again find themselves in the gastrointestinal tract.
It pierces the intestinal wall and reaches the circulatory system. Together with the blood flow, roundworms are brought into the bronchi and lungs, where they continue their development. Through the respiratory tract, parasites enter the pharynx and larynx, and, being swallowed again, together with saliva, they again find themselves in the gastrointestinal tract.
Adult roundworms parasitize in the intestines, but since the worm does not have a device for attaching to its walls, helminths can freely move towards food masses, and also affect the gallbladder, liver, and various organ systems.
After fertilization, the female roundworm produces up to 200,000 eggs per day, which are excreted along with feces. The development of the roundworm worm from an egg to a sexually mature individual after entering the host organism takes 72-76 days, while the life expectancy of a helminth is about a year. After death, the body of the parasite is excreted along with the feces.
Structural features
Like many parasites, roundworms have a fairly simple structure, the most developed reproductive system, which explains the large number of eggs produced by the worm. Roundworm respiration is anaerobic, energy is generated by the breakdown of glycogen. The digestive system is well developed: the roundworm has a mouth opening, thanks to which it swallows food that enters the intestines.
Roundworm respiration is anaerobic, energy is generated by the breakdown of glycogen. The digestive system is well developed: the roundworm has a mouth opening, thanks to which it swallows food that enters the intestines.
The structure of the roundworm allows it to move freely in the gastrointestinal tract and cavities of the human body, while with a slight invasion, the patient may not even be aware of the presence of parasites. There are frequent cases when roundworms in children are found only a year after the invasion: with the natural death of the worm.
Ascaris in children and adults
Unlike other types of worms, roundworms do not change owners throughout their entire life cycle, while both larvae and adults are equally dangerous for humans. Larvae migrating through the bloodstream can be introduced into any organ systems, causing damage to them, but they pose the most serious threat to the respiratory system. Roundworms in the lungs affect the alveoli and disrupt normal gas exchange, cause a choking cough, provoke the development of bronchitis and pneumonia. In the process of life, the larvae release toxins that destroy lung tissue, making the respiratory system vulnerable to other parasites, as well as fungal infections, viruses and bacteria. Larval migration lasts 9-12 days, after which their development continues in the intestine.
In the process of life, the larvae release toxins that destroy lung tissue, making the respiratory system vulnerable to other parasites, as well as fungal infections, viruses and bacteria. Larval migration lasts 9-12 days, after which their development continues in the intestine.
The danger of roundworms for humans also lies in the fact that, with significant invasion, the worms are able to block the intestinal lumens, causing its mechanical obstruction. Ascaris in a child and an adult cause severe intoxication, as well as metabolic disorders due to the fact that most of the micronutrients are absorbed by helminths and not absorbed by the body. All this makes ascariasis one of the most dangerous, and at the same time common, helminthiases. The symptoms of ascaris in adults and children are described in detail in the article about ascariasis posted on this site.
How to remove ascaris from the body?
Due to the wide distribution of these parasites and their danger to humans, doctors face the question of timely diagnosis of helminths and their removal. Classical therapy involves deworming with chemicals, but they can not be taken for long courses. As a result, chemicals affect only adult worms, and ascaris larvae, which are no less dangerous to humans, remain viable.
Classical therapy involves deworming with chemicals, but they can not be taken for long courses. As a result, chemicals affect only adult worms, and ascaris larvae, which are no less dangerous to humans, remain viable.
Effective deworming must be comprehensive. Antiparasitic drugs from NPK “Optisalt”, created exclusively from natural ingredients, can be taken in long courses, the duration of which is sufficient to remove not only adult roundworms from the body, but also their larvae, as well as eggs. In addition, the Optisalt complex eliminates the harm caused to the human body by helminthic invasion: it removes the waste products of the worm, improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, replenishes the reserves of trace elements. You can read in detail about how and how to treat roundworms in our article about ascariasis, published on the website.
Ascariasis: treatment, symptoms, diagnosis, classification
Ascariasis is the defeat of the small intestine of the body by helminthic invasions. The causative agent is roundworms – roundworms (hence the name), parasitizing at the expense of human intestinal tissues.
The causative agent is roundworms – roundworms (hence the name), parasitizing at the expense of human intestinal tissues.
Intestinal nematodosis (another name for the disease) occurs in people of all ages and genders everywhere – regardless of climatic conditions.
Main symptoms of disease
Symptoms of ascariasis depend largely on the extent of damage to the small intestine, as well as the age of the patient and the stage of development of the disease.
The primary phase may pass without clinical manifestations, especially in the period of migration of larvae. A person may experience one or more characteristic symptoms:
- an allergic reaction is manifested by numerous rashes on the limbs or torso. They itch intensely, bringing serious discomfort;
- infectious syndrome is expressed by elevated body temperature, excessive sweating, loss of strength;
- a liver factor can be observed – ascariasis is manifested by an increase in the size of the spleen and liver and causes pain under the ribs on the right side.

In most cases, the patient suffers from a wet or dry cough and severe shortness of breath, pain in the chest area. All this can lead to pleurisy.
If ascariasis in children or adults is started, there may be a sharp decrease in appetite, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, bloating, pain in the intestinal area, convulsions, weight loss.
Main causes of infection
The main cause of ascariasis is infection with helminth eggs, which occurs as a result of their getting into the mouth of a person after his bodily contact with an infected person, as well as with unwashed vegetables, fruits, berries, and household items.
Once inside the human body, the larvae hatch from eggs and penetrate the circulatory system, spreading to the capillaries of the lungs. From there they reach the bronchi, trachea and pharyngeal zone. There they mix with saliva, are swallowed by a person and again enter the small intestine, growing in it to full-fledged adults.
Most affected categories
Most often, ascariasis is diagnosed in children with an insufficient level of hygienic education. Also, agricultural workers, gardeners, cleaners, and specialists working at sewage treatment plants are especially susceptible to the disease.
Preventive measures
Prevention of ascariasis is based on the timely detection of the disease and adequate treatment under the supervision of a physician.
Of particular importance in this process is the observance of all hygiene rules: it is necessary not only to keep your hands and children’s hands clean, but also to instill in them proper hygiene habits.
Regular washing of hands after a walk, going to the toilet, before eating, as well as proper sanitization of food that falls on the table, can largely protect the body from infection with roundworms.
Diagnostic features
Having noted one or more symptoms of this disease in yourself or your child, you should seek help from an infectious disease specialist (in the case of a child, a pediatrician or a pediatric infectious disease specialist).
Diagnosis of ascariasis involves the delivery of a general blood test: an increase in ESR and eosinophils, a slight increase in the number of leukocytes and a decrease in hemoglobin will indicate the presence of an ailment.
In addition, an X-ray of the lungs can be prescribed, on which, in the presence of helminths, foci of infiltration are detected.
The presence of ascaris can also be confirmed by microscopic examination of sputum.
It is important to seek help from a center with a really competent specialist and high-quality equipment, since helminths tend to show themselves far from all analyzes. Only an experienced doctor is able to see their presence in the patient’s body.
Treatment
Drug therapy based on the intake of anthelmintic drugs is prescribed. They are selected depending on the stage at which the disease is currently located. In some cases, a single dose for ascariasis may not be enough, and the drug will need to be taken 3 times with a pause between doses set by the doctor.
In the presence of allergic manifestations, the doctor additionally prescribes antihistamines. If the patient has a disorder of the stool, bloating and pain in the abdomen and other disorders of the intestines, then enzymes and probiotics are also selected for him.
At the end of the main treatment for the next 3 months, the patient is at the dispensary with periodic blood and stool tests.
Treatment of disease at home
Treatment of ascariasis should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
Thoughtless taking of drugs can provoke serious toxic poisoning of the body with further use of a dropper and hospitalization.
Answers to common questions
Is it possible to get rid of ascaris with herbs?
Many medicines contain herbal ingredients. Herbs also have a certain effect, but we must not forget about the serious side reactions that their thoughtless use can lead to.
Self-treatment of ascariasis with herbs is categorically not recommended.
Can I get rid of ascaris myself without going to a doctor?
No, this is strictly prohibited, as it is fraught with poisoning of the body and the occurrence of serious complications in the work of internal organs, in particular, the organs of the pulmonary system and intestines.
How is ascariasis transmitted?
The disease can be transmitted by shaking hands, as well as other types of bodily contact.
The most common infection is through contact with poorly washed fruits, vegetables, berries and herbs. You should also remember about hand hygiene after returning from the street and using the toilet.
What foods can cause disease?
Absolutely any, if they are not processed properly.
Why does cough develop in ascariasis?
Cough appears due to the penetration of larvae through the capillary vessels into the region of the lungs and bronchi.
What is the prognosis after treatment of ascariasis?
The prognosis is generally favorable.

 Parasites – Ascariasis. Biology. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/biology.html (accessed 1/13/2015).
Parasites – Ascariasis. Biology. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/biology.html (accessed 1/13/2015).