Stomach ulcer pain in left side. Peptic Ulcers: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
What are the common symptoms of peptic ulcers. How are peptic ulcers diagnosed and treated. What factors increase the risk of developing peptic ulcers. When should you seek medical attention for potential ulcer complications.
Understanding Peptic Ulcers: A Comprehensive Overview
Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the inner lining of the stomach or the upper portion of the small intestine (duodenum). These painful lesions can cause significant discomfort and, if left untreated, may lead to serious complications. This article delves into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for peptic ulcers, providing valuable insights for those affected by this common digestive condition.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Peptic Ulcers
Identifying the symptoms of peptic ulcers is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. While some individuals may not experience any noticeable signs, others may encounter a range of uncomfortable symptoms.
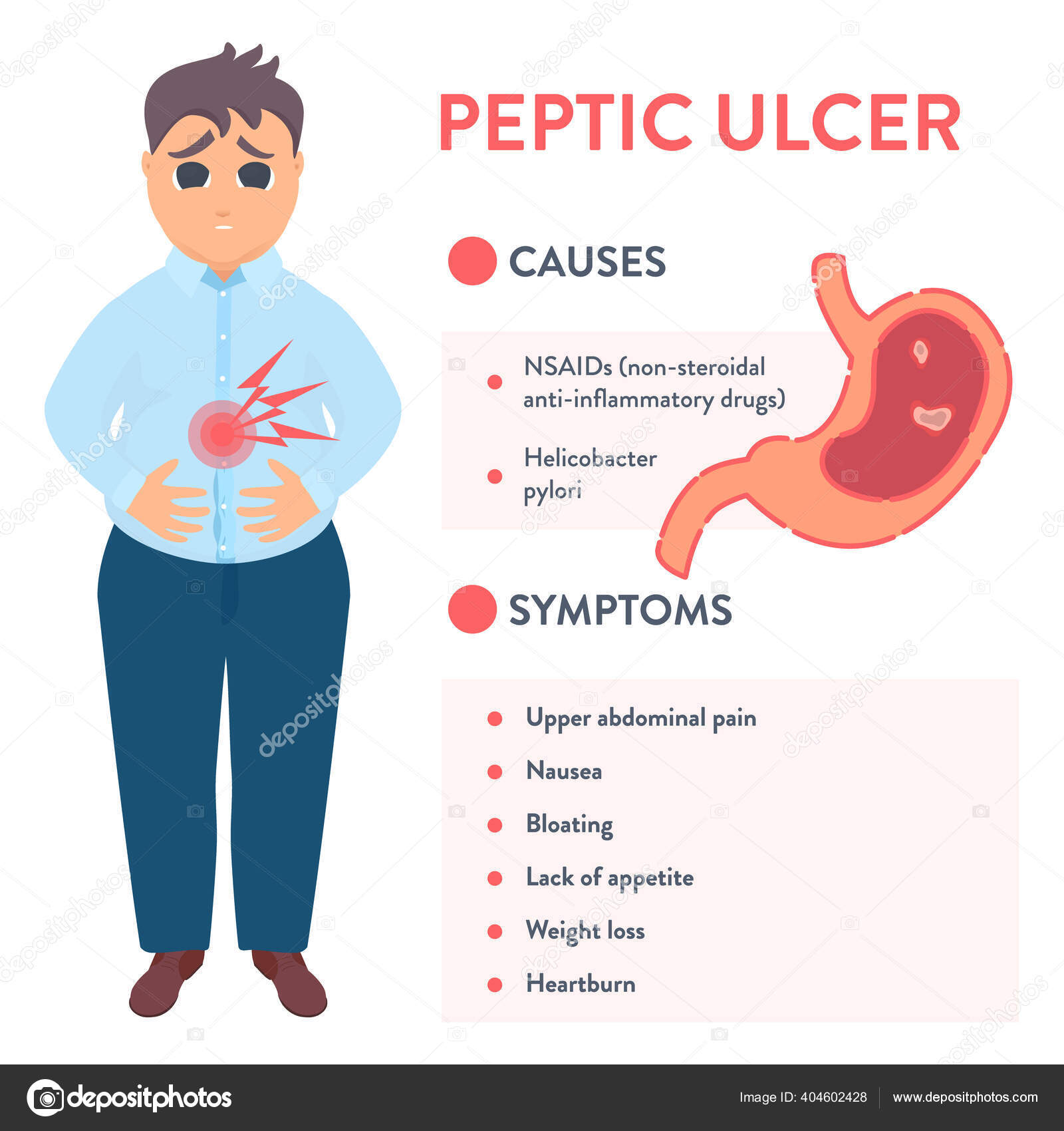
Common Symptoms of Peptic Ulcers
- Abdominal pain or discomfort (typically between the navel and breastbone)
- Feeling full too quickly during meals
- Uncomfortable fullness after eating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloating
- Belching
Is abdominal pain always present in peptic ulcers? Abdominal pain is the most common symptom of peptic ulcers. The pain may be dull or burning and can come and go over time. For some individuals, the discomfort may occur when the stomach is empty or at night, while others may experience relief after eating. It’s important to note that the severity and frequency of symptoms can vary from person to person.
Understanding the Causes of Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers develop when the protective lining of the stomach or duodenum is compromised, allowing digestive acids to damage the underlying tissues. While several factors can contribute to this condition, two primary causes stand out.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) Infection
H. pylori infection is a leading cause of peptic ulcers. This bacteria can weaken the protective mucus layer of the stomach and duodenum, making them more susceptible to damage from stomach acid. How does H. pylori spread? The bacteria may be transmitted through contact with an infected person’s bodily fluids, including vomit, stool, or saliva. Additionally, consuming contaminated food or water can lead to infection.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Regular use of NSAIDs, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, is another common cause of peptic ulcers. These medications can interfere with the stomach’s protective mechanisms, increasing the risk of ulcer formation. Are all NSAIDs equally likely to cause ulcers? Some types of NSAIDs are more likely to cause ulcers than others, and factors such as dosage, duration of use, and combination with other medications can influence the risk.
Risk Factors for Developing Peptic Ulcers
While anyone can develop peptic ulcers, certain factors may increase an individual’s susceptibility to this condition.
- Long-term use of NSAIDs
- H. pylori infection
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Family history of peptic ulcers
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Stress
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., cirrhosis, Crohn’s disease)
Can stress alone cause peptic ulcers? While stress was once believed to be a primary cause of peptic ulcers, current research suggests that it may exacerbate existing ulcers rather than directly cause them. However, stress can influence behaviors that increase ulcer risk, such as smoking or consuming alcohol.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/peptic-ulcer-disease-diagnosis-4707600_final-51498411f53a44d8bc49efda9d31e2fd.jpg)
Diagnosing Peptic Ulcers: Tests and Procedures
Accurate diagnosis of peptic ulcers is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. Healthcare providers may employ various diagnostic tools to confirm the presence of ulcers and identify their underlying causes.
Common Diagnostic Procedures
- Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera is used to examine the stomach and duodenum.
- H. pylori testing: Blood, stool, or breath tests can detect the presence of H. pylori bacteria.
- Upper gastrointestinal series: X-rays of the digestive tract are taken after swallowing a contrast solution.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample is collected during endoscopy for laboratory analysis.
How accurate are these diagnostic tests? While each test has its strengths and limitations, combining multiple diagnostic approaches can significantly improve accuracy. Your healthcare provider will determine the most appropriate tests based on your symptoms and medical history.
Treatment Options for Peptic Ulcers
The treatment of peptic ulcers aims to relieve symptoms, promote healing, and prevent recurrence. The specific approach depends on the underlying cause and severity of the ulcer.

Medications for Peptic Ulcers
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): Reduce stomach acid production
- Histamine blockers (H2 blockers): Decrease acid secretion
- Antacids: Neutralize stomach acid for temporary relief
- Antibiotics: Eradicate H. pylori infection
- Cytoprotective agents: Protect the stomach lining
How long does it take for peptic ulcers to heal with treatment? With appropriate treatment, most peptic ulcers heal within 4 to 8 weeks. However, healing time can vary depending on factors such as ulcer size, location, and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, certain lifestyle changes can support ulcer healing and prevent recurrence:
- Avoiding or limiting NSAID use
- Quitting smoking
- Reducing alcohol consumption
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Complications of Untreated Peptic Ulcers
While many peptic ulcers heal with proper treatment, leaving them untreated can lead to serious complications. Understanding these potential risks underscores the importance of prompt medical attention.
Potential Complications
- Internal bleeding
- Perforation (a hole through the stomach or duodenal wall)
- Obstruction (blockage of the digestive tract)
- Peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity lining)
When should you seek immediate medical attention for potential ulcer complications? If you experience symptoms such as severe, persistent abdominal pain, vomiting blood, or passing black, tarry stools, seek emergency medical care. These signs may indicate a life-threatening complication requiring immediate intervention.
Preventing Peptic Ulcers: Strategies for Reducing Risk
While not all peptic ulcers can be prevented, adopting certain habits and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk of developing this condition.
Preventive Measures
- Practice good hygiene to reduce the risk of H. pylori infection
- Use NSAIDs cautiously and only as directed by a healthcare provider
- Limit alcohol consumption and avoid smoking
- Manage stress through healthy coping mechanisms
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Get regular exercise to support overall digestive health
Can dietary changes prevent peptic ulcers? While no specific diet has been proven to prevent peptic ulcers, consuming a balanced, nutrient-rich diet can support overall digestive health and potentially reduce the risk of ulcer formation. Some studies suggest that foods rich in antioxidants and probiotics may have protective effects against H. pylori infection.

Living with Peptic Ulcers: Coping Strategies and Long-Term Management
For individuals diagnosed with peptic ulcers, developing effective coping strategies and adhering to a long-term management plan are crucial for maintaining digestive health and preventing recurrence.
Tips for Managing Peptic Ulcers
- Follow your treatment plan diligently, taking medications as prescribed
- Keep a food diary to identify trigger foods that exacerbate symptoms
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to reduce stomach acid production
- Avoid lying down immediately after meals
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, meditation, or counseling
- Attend regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider
- Join support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges
How often should individuals with a history of peptic ulcers undergo follow-up screenings? The frequency of follow-up screenings depends on various factors, including the severity of the initial ulcer, treatment response, and individual risk factors. Your healthcare provider will recommend an appropriate screening schedule based on your specific situation.
Emerging Research and Future Directions in Peptic Ulcer Treatment
As our understanding of peptic ulcers continues to evolve, researchers are exploring new treatment approaches and preventive strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Promising Areas of Research
- Novel H. pylori eradication therapies
- Development of gastroprotective agents with fewer side effects
- Exploration of probiotics for ulcer prevention and treatment
- Investigation of genetic factors influencing ulcer susceptibility
- Advancements in minimally invasive surgical techniques for complicated ulcers
What potential breakthroughs in peptic ulcer treatment are on the horizon? While it’s difficult to predict specific breakthroughs, ongoing research into targeted therapies, personalized medicine approaches, and innovative drug delivery systems holds promise for more effective and tailored treatments in the future. As our understanding of the complex interactions between genetic, environmental, and microbial factors in ulcer development improves, we may see the emergence of more precise prevention and treatment strategies.
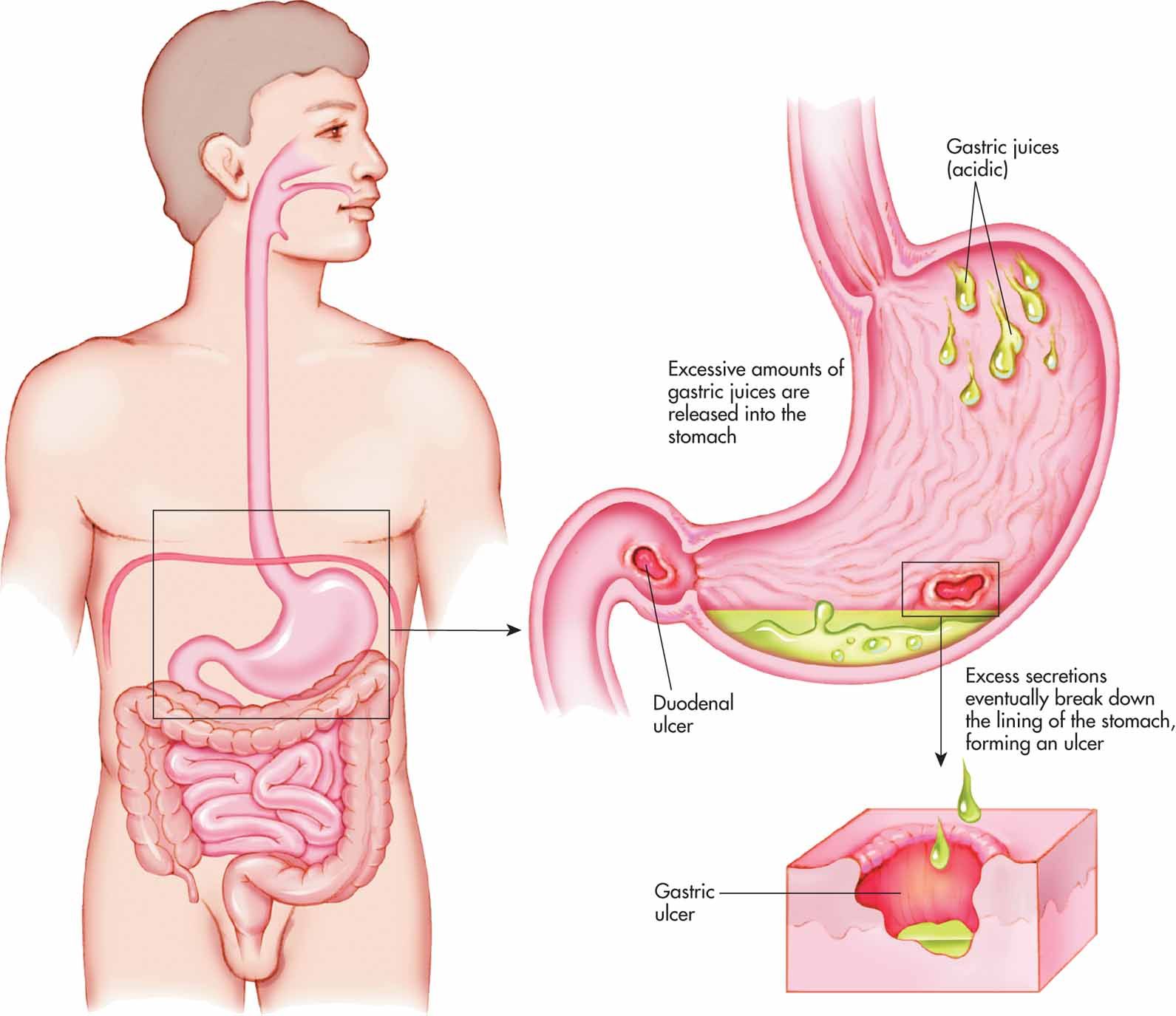
In conclusion, peptic ulcers are a common digestive condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatment options, those affected by peptic ulcers can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively. With proper medical care, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing research advancements, the outlook for individuals with peptic ulcers continues to improve. If you suspect you may have a peptic ulcer or are experiencing persistent digestive symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.
Symptoms & Causes of Peptic Ulcers (Stomach or Duodenal Ulcers)
What are the symptoms of a peptic ulcer?
Peptic ulcers may cause symptoms of indigestion. Common symptoms include
- pain or discomfort in the upper part of your abdomen, anywhere between your belly button and breastbone
- feeling full too soon while eating a meal
- feeling uncomfortably full after eating a meal
- nausea and vomiting
- bloating
- belching
Abdominal pain is the most common symptom of a peptic ulcer.
Abdominal pain is the most common symptom of a peptic ulcer. The pain may be dull or burning and may come and go over time. For some people, the pain may occur when the stomach is empty or at night, and it may go away for a short time after they eat. For other people, eating may make the pain worse.
Many people who have peptic ulcers don’t have any symptoms. They may not develop symptoms until an ulcer leads to complications.
You should call or see your doctor right away if you have symptoms that could be caused by a complication. These symptoms include
- black or tarry stool, or red or maroon blood mixed with your stool
- red blood in your vomit or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- sudden, sharp, or severe abdominal pain that doesn’t go away
- feeling dizzy or fainting
- a rapid pulse or other symptoms of shock
- a change in or worsening of your peptic ulcer symptoms
What causes peptic ulcers?
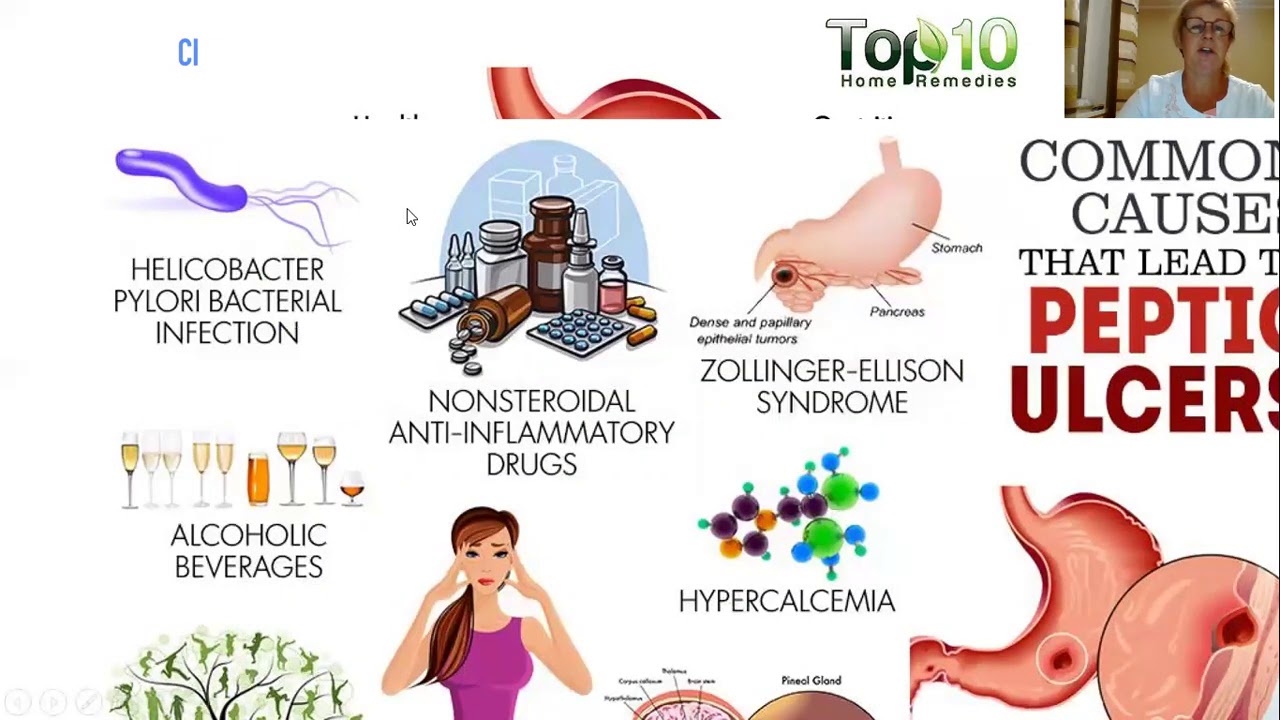
The most common causes of peptic ulcers are Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other causes of peptic ulcers are uncommon or rare.
People with certain risk factors are more likely to develop ulcers.
H. pylori
H. pylori infection is a common cause of peptic ulcers. Researchers are still studying how people become infected with H. pylori bacteria. The bacteria may spread from person to person through contact with an infected person’s vomit, stool, or saliva. Food or water contaminated with an infected person’s vomit, stool, or saliva may also spread the bacteria from person to person.
pylori infection is a common cause of peptic ulcers. Researchers are still studying how people become infected with H. pylori bacteria. The bacteria may spread from person to person through contact with an infected person’s vomit, stool, or saliva. Food or water contaminated with an infected person’s vomit, stool, or saliva may also spread the bacteria from person to person.
NSAIDs
Taking NSAIDs—such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen—is another common cause of peptic ulcers. NSAIDs relieve pain, but they also make the stomach lining more prone to damage and ulcers. Some types of NSAIDs are more likely to cause ulcers than others.
You have a higher chance of developing a peptic ulcer due to NSAIDs if you take
- NSAIDs for a long time
- a type of NSAID that is more likely to cause an ulcer
- high doses of an NSAID or more than one NSAID
- NSAIDs along with other medicines that increase the risk for ulcers
- NSAIDs and you are also infected with H.
 pylori
pylori
Other causes
Less common causes of peptic ulcers include
- infections caused by certain viruses, fungi, or bacteria other than H. pylori
- medicines that increase the risk of developing ulcers, including corticosteroids, medicines used to treat low bone mass, and some antidepressants, especially when you take these medicines with NSAIDs
- surgery or medical procedures that affect the stomach or duodenum
Less common causes of peptic ulcers also include certain diseases and health conditions, such as
- diseases that can affect the stomach, such as cancer or Crohn’s disease
- injury, blockage, or lack of blood flow that affects the stomach or duodenum
- life-threatening health conditions that require critical care
- severe chronic diseases, such as cirrhosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, a condition that occurs when one or more tumors—called gastrinomas—cause your stomach to make too much acid
In rare cases, doctors can’t find the cause of peptic ulcers. Doctors may call ulcers with unknown causes idiopathic peptic ulcers.
Doctors may call ulcers with unknown causes idiopathic peptic ulcers.
Last Reviewed September 2022
Share this page
Facebook
Twitter
Email
WhatsApp
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Previous:
Definition & Facts
Next:
Diagnosis
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
(NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
Upper Left Abdominal Pain | What You Need to Know
Drugs and medications
Many drugs can cause left upper quadrant pain and associated damage with chronic use. A few are listed here:
- Aspirin: High doses can cause stomach bleeding and pain.
- NSAIDs: These are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen.
- Oral antibiotics
- Opioids: Pain may be due to the side effect of chronic constipation.
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Cocaine
Cancer
Cancer is considered a rare cause of pain in the upper left abdomen.
- Localized tumor: A cancerous growth anywhere in the left upper quadrant can cause pain. There may or may not be a lump in the vicinity of the pain.
- Blood cancers: These will affect the entire body and cause symptoms in the organs of the left upper quadrant.

Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas that does not improve, but slowly gets worse over time.
Causes include alcoholism; a blocked pancreatic duct; autoimmune disease, where the body’s natural defenses turn against itself; and possible genetic factors.
Chronic pancreatitis is most common in men from age 30 to 40 with a history of alcoholism and a family history of the disease, but anyone can be affected.
Symptoms include severe pain in the back and abdomen, especially with eating; weight loss; nausea and vomiting; and diarrhea with oily-appearing, pale-colored stools.
The pancreas is vital for blood sugar control and for secreting certain digestive enzymes. If not treated, chronic pancreatitis can lead to permanent pancreatic damage, diabetes, malnutrition, and chronic pain.
Diagnosis is made through patient history, physical examination, and imaging such as x-ray, CT scan, or ultrasound.
Treatment involves pain management through both medication and surgical procedures. Lifestyle improvements through diet, exercise, and stress management can also be very helpful.
Lifestyle improvements through diet, exercise, and stress management can also be very helpful.
Rarity: Rare
Top Symptoms: fatigue, abdominal pain (stomach ache), nausea or vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal pain that comes and goes
Urgency: Primary care doctor
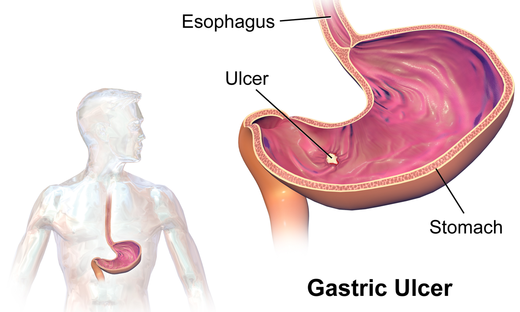
Stomach ulcer
A peptic ulcer or gastric ulcer is an open sore that forms when inflammation occurs in the stomach lining.
This stomach inflammation is caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and by prolonged use of pain relievers such as ibuprofen or aspirin. Chronic inflammation allows acid to damage the stomach lining and an ulcer may form.
Smoking, drinking alcohol, stress, and spicy foods may aggravate ulcers, but do not cause them.
Symptoms include burning pain in the stomach; heartburn; nausea; and bloating.
The pain may be worse between meals or at night. Antacids will only work for a short time. There may be dark red blood in the vomit or stools.
Left untreated, ulcers may bleed and cause anemia. They may perforate the stomach and cause peritonitis (serious infection of the abdominal cavity.)
Diagnosis is made through physical examination and by testing breath and stool for H. pylori. Endoscopy is sometimes used.
Treatment involves a course of antibiotics to kill the bacteria, and medication to block excess acid and heal the stomach.
Rarity: Uncommon
Top Symptoms: fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, moderate abdominal pain, abdominal cramps (stomach cramps)
Symptoms that never occur with stomach ulcer: pain in the lower left abdomen
Urgency: Primary care doctor
Normal abdominal pain
The complaint of abdominal pain and discomfort, with no apparent cause, is one of the most common in medicine. It is a primary reason for patients to visit a medical provider or the emergency room.
The cause of abdominal pain can be difficult to find, because it can just be a completely normal abdominal pain or come from many different sources: the digestive tract, the urinary tract, the pancreas, the gall bladder, or the gynecologic organs.
The pain may simply be caused by overly sensitive nerves in the gut. This hypersensitivity can occur after repeated abdominal injury and/or it may have an emotional cause due to fear of the pain itself.
Diagnosis is made through physical examination, patient history, and simply ruling out any other condition. CT scan is often requested, but can rarely find a specific cause. The benefits must be weighed against the risks of radiation.
Treatment first involves making any needed lifestyle improvements regarding diet, exercise, work, and sleep, in order to reduce stress. In some cases, counseling, hypnosis, mild pain relievers, and antidepressants are helpful.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: abdominal pain (stomach ache), vaginal discharge, fever, nausea
Symptoms that always occur with normal abdominal pain: abdominal pain (stomach ache)
Symptoms that never occur with normal abdominal pain: fever, vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, severe abdominal pain, unintentional weight loss, vaginal discharge
Urgency: Self-treatment
Kidney stone
A kidney stone, also called renal lithiasis or nephrolithiasis, is a solid deposit that forms inside the kidney. Stones may form if the urine becomes too concentrated for any reason, allowing the minerals in it to crystallize.
Stones may form if the urine becomes too concentrated for any reason, allowing the minerals in it to crystallize.
There are several possible causes:
- Not drinking enough water.
- Family or personal history of kidney stones.
- Diets high in protein, salt, or sugar.
- Obesity.
- Digestive diseases and conditions, including gastric bypass surgery.
- Urinary tract infection.
- Metabolic conditions and/or hereditary disorders.
Symptoms include severe pain in the side, back, and abdomen; pain on urination; urine that is pink, red, brown, and/or foul-smelling; nausea and vomiting; and sometimes fever and chills.
Diagnosis is made through blood test, urine test, and imaging.
For smaller stones, the patient may only need to drink extra water and take over-the-counter pain relievers. Medication may be given to help pass the stone. Larger stones may require the patient to be hospitalized for surgical procedures.
Prevention involves drinking more water and restricting certain foods, including animal protein, calcium, and salt. Sometimes prescription medications will be used.
Sometimes prescription medications will be used.
Indigestion (dyspepsia)
Indigestion, also called upset stomach, dyspepsia, or functional dyspepsia, is not a disease but a collection of very common symptoms. Note: Heartburn is a separate condition.
Common causes are eating too much or too rapidly; greasy or spicy foods; overdoing caffeine, alcohol, or carbonated beverages; smoking; and anxiety. Some antibiotics, pain relievers, and vitamin/mineral supplements can cause indigestion.
The most common symptoms are pain, discomfort, and bloating in the upper abdomen soon after eating.
Indigestion that lasts longer than two weeks, and does not respond to simple treatment, may indicate a more serious condition. Upper abdominal pain that radiates to the jaw, neck, or arm is a medical emergency.
Diagnosis is made through patient history and physical examination. If the symptoms began suddenly, laboratory tests on blood, breath, and stool may be ordered. Upper endoscopy or abdominal x-ray may be done.
For functional dyspepsia – “ordinary” indigestion – treatment and prevention are the same. Eating five or six smaller meals per day with lighter, simpler food; managing stress; and finding alternatives for some medications will provide relief.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: nausea, stomach bloating, dyspeptic symptoms, bloating after meals, vomiting
Symptoms that always occur with indigestion (dyspepsia): dyspeptic symptoms
Symptoms that never occur with indigestion (dyspepsia): vomiting (old) blood or passing tarry stools, rectal bleeding, bloody diarrhea, fever
Urgency: Self-treatment
Heart attack in a woman
Most heart attacks happen when a clot in the coronary artery blocks the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart. Often this leads to an irregular heartbeat – called an arrhythmia – that causes a severe decrease in the pumping function of the heart.
Call 911 and seek emergency care immediately
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is the inflammation of the pancreas, which creates and releases insulin and glucagon to keep the sugar levels in your blood stable. It also creates the enzymes that digest your food in the small intestine. When these enzymes accidentally get activated in the pancreas, they digest the pancreas itself, causing pain and inflammation.
It also creates the enzymes that digest your food in the small intestine. When these enzymes accidentally get activated in the pancreas, they digest the pancreas itself, causing pain and inflammation.
You should go to the ER. There, diagnosis is made by physical examination, imaging, and blood tests. Treatment typically involves intravenous (IV) fluids and medicines to control the pain.
Rarity: Rare
Top Symptoms: constant abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting, being severely ill, severe abdominal pain, fever
Symptoms that always occur with acute pancreatitis: constant abdominal pain
Urgency: Hospital emergency room
Acute gastritis
Gastritis means inflammation or irritation of the stomach lining, and is “acute” when it comes on suddenly and severely.
Common causes are infection with H. pylori bacteria in the stomach, which also causes ulcers; regular use of pain relievers; and overuse of alcohol.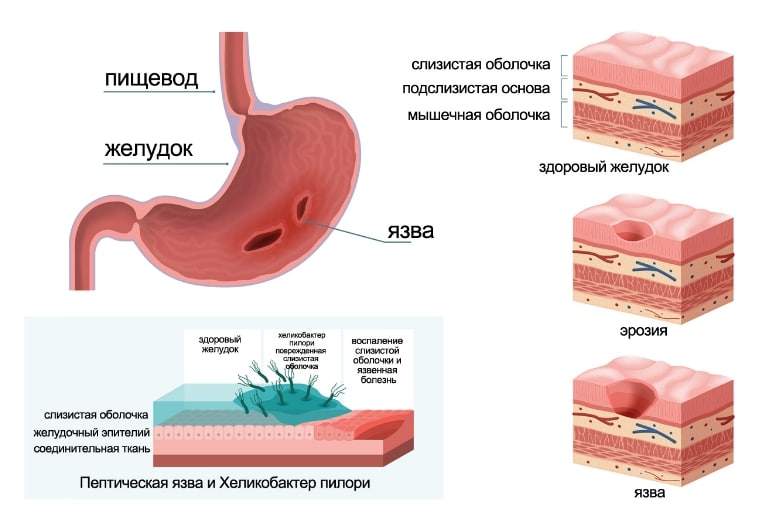 Smoking, stress, and autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease, Hashimoto’s disease, and type 1 diabetes can all contribute to acute gastritis.
Smoking, stress, and autoimmune diseases such as Crohn’s disease, Hashimoto’s disease, and type 1 diabetes can all contribute to acute gastritis.
Symptoms of acute gastritis include sudden fullness and burning pain in the upper abdomen, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. If the symptoms last more than a week, or there are signs of blood in vomit or stool, medical care should be sought.
If not treated, gastritis can lead to stomach ulcers due to the presence of H. pylori.
Diagnosis for H. pylori is made through blood tests, breath tests, and stool sample tests. Upper endoscopy and/or barium swallow x-ray may also be used.
Treatment includes lifestyle changes concerning use of pain relievers, alcohol, and other stomach irritants; antibiotics to treat the H. pylori; and medications to reduce and/or neutralize stomach acid.
- Have you experienced any nausea?
- Any fever today or during the last week?
- Have you been feeling more tired than usual, lethargic or fatigued despite sleeping a normal amount?
- How would you describe the nature of your abdominal pain?
Self-diagnose with our free Buoy Assistant if you answer yes on any of these questions.
Why does pain occur in the left side?
Pain in the left side can be caused by various causes, including problems with the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, back, muscles or bones. The article discusses the main causes of pain in the left side, their symptoms and possible treatments.
Pain in the left side can occur for various reasons. Almost every one of us has experienced an unpleasant sensation in the side area. Pain can manifest itself in a variety of sensations and is characterized by many symptoms.
Sometimes the causes are physical activity or an unhealthy lifestyle, but there are also much more serious causes – heart disease and problems with the digestive system. Pain in the left side can be caused by many factors, and each case requires a separate study.
Although pain can be controlled with painkillers, it is best to know your body and avoid recurrence. If you notice severe pain in your left side or you suspect a disease, be sure to contact a specialist and get qualified medical advice.
Why does my left side hurt?
Pain in the left side can be caused by many factors, ranging from minor problems to serious illnesses. The most common cause of pain in the left side is overeating, which leads to excess stress on the stomach and intestines. However, pain in the left side can also be caused by diseases such as gastritis, stomach ulcers, constipation, colitis, etc. angina or myocardial infarction.
In addition, pregnancy can cause pain in the left side. During pregnancy, the uterus grows in size and puts pressure on the internal organs, which can cause pain in the side and lower back.
If pain persists or gets worse, it is important to seek medical attention. The doctor can identify the cause of the pain and suggest appropriate treatment. In case of serious problems like myocardial infarction or pneumonia, call an ambulance immediately!
- Some main reasons why the left side hurts:
- Overeating
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- Diseases of the respiratory system
- Cardiac problems
- Pregnancy left side
Pain in the left side can be caused by various causes, including diseases of the internal organs or damage to muscles and bones.

One common cause of left flank pain is gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), which can cause burning and discomfort in the flank. Belching, heartburn and nausea can also accompany this disease.
Another cause of pain in the left side can be myocarditis, an inflammatory disease of the heart muscle. It can occur due to a viral infection or an autoimmune disease and is often accompanied by weakness, shortness of breath, and palpitations.
Scoliosis and other diseases of the spine can also cause pain in the left side, especially if they have led to displacement of the vertebrae or pressure on the nerves in this area.
Finally, pain in the left side can be caused by damage to the muscles and bones. This can happen as a result of acute injury or repetitive muscle activity such as heavy lifting or high-intensity exercise.
In any case, if you experience severe pain in your left side or other serious symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor for professional advice and treatment.

What diseases can cause pain in the left side?
Pain in the left side can be caused by various diseases, including:
- Intestinal infections . Occurs when the intestines are infected with pathogenic microorganisms. May be accompanied by pain in the abdomen and left side, diarrhea, vomiting and fever.
- Problems with the pancreas . Pancreatic dysfunction can cause pain in the left side, as well as diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.
- Colitis . Inflammation of the large intestine can lead to pain in the abdomen and left side, as well as diarrhea and bloody discharge.
- Abdominal hernia . The appearance of a hernia of the abdomen can cause pain in the left side, as well as a feeling of heaviness and pain after eating.
- Myocardial infarction . Pain in the left side can be a sign of myocardial infarction. In this case, it is usually accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath and sweating.

If you have pain in your left side, see your doctor. Only he can determine the cause of the pain and prescribe treatment.
Cardiac problems
Pain in the left side may be associated with cardiac problems that require immediate medical attention.
One of the most dangerous cardiac conditions that can cause pain in the left side is myocardial infarction. With this disease, there is a violation of the blood supply to the heart, which can lead to a strong and prolonged pain syndrome.
In addition, there may be an early stage of arrhythmia, in which the heartbeat becomes unstable, which can also cause pain in the left side.
To prevent the development of cardiac problems, it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle, refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol, allow yourself good sleep and proper nutrition. However, if the pain in the left side persists or intensifies, you should consult a cardiologist for diagnosis and treatment.

- Symptoms of cardiac problems:
- Pain in the left side
- Feeling of tightness or pressure in the chest
- Brief loss of consciousness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Symptoms of inflammatory lung disease:
- Continuous pain or pressure on the left side of the chest
- Weakness and fatigue
- Cough with or without sputum
- Difficulty breathing
- Symptoms of diaphragm irritation :
- Pain in left side when eating or drinking
- Pain in the left side when moving or exercising
- Pain that subsides with rest
- Gastritis – inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which is often accompanied by pain in the upper abdomen. However, the pain can also spread to the left side. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, belching, heartburn, and loss of appetite.
- Gastric ulcer is the formation of ulcers on the walls of the stomach, often caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori or excessive use of NSAIDs (eg aspirin). Ulcer pain may radiate to the left side and may worsen after eating. There may also be symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and loss of appetite.
- Colitis is an inflammation of the large intestine often caused by chronic diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. The pain may be localized on the left side of the abdomen and may be accompanied by diarrhea, bloody stools, bloating, and loss of appetite.

- Massage. A gentle massage of the muscles of the left side will help reduce pain inside the muscle tissue and improve blood circulation.
- Physiotherapy. A set of exercises aimed at strengthening muscles and stretching will help get rid of pain in the side.
- Antibacterial preparations. Anti-inflammatory drugs will help speed up the healing of damaged tissues.
- Medicines . Drug therapy may include antibiotics, pain relievers, antispasmodics, and others. It is important to strictly follow the recommendations of the doctor and not to exceed the dosage.
- Physiotherapy . Physiotherapy procedures, such as electrophoresis, UHF, laser therapy, and others, help eliminate inflammation and improve blood circulation.
- Diet . If the cause of pain in the left side is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, it is important to follow dietary recommendations and avoid spicy, fatty, salty and smoked foods.

- Surgery . If a tumor, cyst, or other pathology is found that requires surgery, the doctor may recommend surgery.
- Electrotherapy helps stimulate muscles and improve circulation.
- Massage helps to relax muscles and improve blood circulation in tissues.
- Posture correction can help reduce the risk of injury to the back and lateral muscles.
- Basic principles of massage of the left side:
- Start the massage with light kneading;
- Move on to basic massage techniques;
- Use moderate force when massaging with your hands;
- Focus on the diseased part of the body;
- Massage for at least 15 minutes.

- Moderate physical activity. Regular sports or exercise strengthens the muscles of the abdominal wall and improves blood flow in the body. This will help prevent pain.
- Proper nutrition. Eating a diet rich in fiber will normalize the stool and reduce the risk of constipation, which can cause pain in the left side.
 It is also worth limiting the consumption of fatty, spicy and salty foods.
It is also worth limiting the consumption of fatty, spicy and salty foods. - Avoid stress. Psycho-emotional state can cause pain in the left side. Try not to overload yourself with work and make time for rest and hobbies.
- Regular check-ups with a doctor. Annual preventive examinations help to timely identify various diseases that can cause pain in the left side. Also, the treatment of any diseases should be carried out on time to avoid complications and the chronic form of the disease.
- Main symptoms:
- Pain in left side;
- Pain after eating;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Dyspepsia;
- Pain in upper abdomen;
- Intestinal disorders.
- Diet: Avoid spicy, fried, fatty, smoked foods, and foods that trigger heartburn and acid reflux.
- Medications: the doctor may prescribe antisecretory or antibiotic drugs, B vitamins, antidepressants.
- Ways to relieve pain: take anti-point drugs, use a heating pad on the stomach, apply cold to the sore spot.
- Symptoms of pancreatitis: acute pain in the abdomen and left side, fever, nausea and vomiting.
- Treatment of pancreatitis: complex treatment, use of drugs, diet.

- Untimely treatment of pancreatitis can lead to complications such as pancreatic gangrene and necrosis of internal organs.
- Stop eating spicy food;
- Take medicine for stomach pain;
- Treatment with drugs that protect the stomach wall;
- Follow a diet;
- Stop smoking and reduce alcohol intake;
- Regular use of medicines, vitamin complexes and mineral supplements.
- Rest is the best home treatment for left side pain. It is recommended to lie on your back and elevate your legs to relieve pressure on your stomach.
- Hot water Drinks such as warm tea or soup, or warm water on the abdomen can help relieve pain in the stomach and left side.
- Digestive products – Enzyme based products such as gastric juice can help reduce symptoms after spicy meals.
- Compresses – Applying a warm compress to the abdomen can help reduce the curve area and reduce pain in the left side.
900 37
Lack of movement, fatty and abundant food, chronic stress, physical inactivity affect our health in general, and first of all on the heart, so pay special attention to proper nutrition and physical activity.
Neurological problems
Pain in the left side may be associated with neurological problems, including neuralgia of the intercostal nerves. This condition occurs when the intercostal nerves become compressed or irritated, resulting in sharp or dull pain in the left side.
Intercostal neuralgia can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma, poor posture, or tumor development. Treatment may include analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physical therapy.
In addition, diseases of the central nervous system can also be manifested by pain in the side.
 For example, a stroke or multiple sclerosis can cause pain in the left side, which may be accompanied by other symptoms such as paralysis or numbness.
For example, a stroke or multiple sclerosis can cause pain in the left side, which may be accompanied by other symptoms such as paralysis or numbness.If you are experiencing pain in your left side and suspect a neurological problem, be sure to consult a neurologist or other qualified healthcare professional.
Lung and respiratory problems
Pain in the left side may be due to problems in the respiratory system, including the lungs and diaphragm. One of the most common causes is inflammatory lung disease such as pneumonia or bronchitis.
In pulmonary disease, pain may manifest as continuous heaviness or pressure on the left side of the chest, as well as general weakness and fatigue. If you experience these symptoms, see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Another possible cause of pain in the left side could be irritation of the diaphragm, a muscle that plays an important role in breathing. Irritation can be caused by exercise or sudden movements, especially when eating or drinking.

If you have symptoms related to the respiratory system, such as cough, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, contact your doctor. It is important to receive timely treatment to avoid possible complications.
However, if the pain in the left side is not accompanied by respiratory problems, it may be due to other causes. In any case, if you experience prolonged or intense pain on the left side of your body, see your doctor for an examination and diagnosis.
Problems with the stomach and intestines
Pain in the left side can be associated with problems in the stomach and intestines.
 These organs play an important role in digestion and can be sensitive to stress, poor nutrition, and chronic disease. Here are some common problems that can cause left side pain.
These organs play an important role in digestion and can be sensitive to stress, poor nutrition, and chronic disease. Here are some common problems that can cause left side pain.If you often experience pain in your left side, especially after eating or under stress, contact your doctor. He may recommend an examination of the stomach and intestines to see if you have any diseases that need to be treated.
Back and muscle problems
One of the most common causes of left side pain is back and muscle problems. In this case, the pain may be caused by tension, spasm, or damage to the muscles on the left side of the torso. Also, pain can occur when the nerve endings passing through the muscles are disturbed, for example, when the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracic spine are displaced.
Pathologies of the spine, such as scoliosis, osteochondrosis, herniated disc and others, can also cause pain in the side. In this case, the pain can come from both the back and the left leg, which is associated with the transfer of the load to this side of the body.
If you have a painful symptom on the left side of your body that lasts for several days or gets worse, seek medical attention.
 A qualified specialist will help identify the cause of the pain and prescribe the necessary treatment, including massage, physical therapy, antibiotics, or even surgery.
A qualified specialist will help identify the cause of the pain and prescribe the necessary treatment, including massage, physical therapy, antibiotics, or even surgery.Remember that self-treatment can worsen the condition and complicate the treatment process. Only an experienced specialist will be able to correctly diagnose and cure the disease that caused pain in the left side.
Ways to treat pain in the left side
If you experience pain in the left side, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only a qualified specialist will be able to diagnose the cause of the pain and prescribe the correct treatment.

The causes of pain in the left side can be various diseases of the heart, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, nervous system, and others. Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe medication, physical therapy, diet, or surgery.
In addition, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, exercise regularly and monitor nutrition. To reduce stress levels, you can do yoga or meditation.
In any case, only a timely visit to a doctor and compliance with his recommendations will help get rid of pain in the left side and prevent possible complications.
Drug therapy
Different groups of drugs can be prescribed to relieve pain in the left side, depending on the cause of the pain syndrome. For example, in diseases of the stomach and intestines, drugs are most often prescribed that reduce the acidity of gastric juice, improve intestinal motility and protect the mucous membrane.
If the pain is caused by muscle tension or spasm, muscle relaxants are used to relax the muscles. These preparations can be both in the form of tablets, and in the form of ointments and gels for external use.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as diclofenac, nimesulide and their analogues are often used to relieve inflammation and swelling.
 However, it should be remembered that long-term use of these drugs can adversely affect the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
However, it should be remembered that long-term use of these drugs can adversely affect the functioning of the liver and kidneys.To improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system, a course of treatment with β-blockers may be prescribed. They lower the heart rate and reduce the need for oxygen, which reduces the workload on the heart.
However, it is worth remembering that self-treatment can be harmful to health, so treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor, after the necessary examinations and finding out the causes of pain in the left side.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is widely used in the treatment of pain in the left side. It helps to eliminate the cause of pain and speed up the recovery process of the body. Physiotherapy can be prescribed as the main method of treatment, or in combination with other methods.
One of the most common physiotherapy methods for treating left side pain is electrotherapy. It is based on the use of electrical impulses to stimulate muscles and improve blood circulation.
 This method can be used to treat various diseases such as myositis, neuralgia, etc.
This method can be used to treat various diseases such as myositis, neuralgia, etc.Massage is also an effective method of physiotherapy for the treatment of pain in the left side. It helps to relax the muscles and improve blood circulation in the tissues. The massage procedure can help relieve tension in the muscles and improve their performance.
Posture correction may also be prescribed as part of physical therapy for left side pain. Proper body position can help reduce muscle tension and reduce the risk of injury to the back and lateral muscles.
Depending on the cause of the pain in the left side, another method of physiotherapy may be prescribed. It is important to contact a specialist who will help you choose the right method of treatment and determine the required duration of the course.
 By following the recommendations of a specialist and performing the prescribed procedures, you can speed up the recovery process and return to normal life.
By following the recommendations of a specialist and performing the prescribed procedures, you can speed up the recovery process and return to normal life.Massage
Massage is one of the most effective ways to relieve pain in the left side. When performing a massage, blood flow in the muscles improves, spasms are relieved and the load on the diseased area is reduced.
The main methods of massage for pain in the left side are: circular and linear kneading, skin sliding, stroking, rolling and pulling. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the type of pain and choose the right massage method in each case.
One of the important aspects of massage is the use of oils and creams. They contribute to more effective massage techniques, reduce pain and improve the general condition of the body. In addition, massage with oils can have a relaxing effect.
Before performing a massage, you should consult a specialist doctor. In some cases, massage can be undesirable and even dangerous to health.
Rehabilitation after operations
Operations are a serious stress for the body, so rehabilitation after them is a very important step in restoring health. The purpose of rehabilitation is to restore body functions, reduce pain and prevent complications.
The first days after the operation are called the “early period”. During this period, the main task is to prevent complications and ensure normal wound healing. The doctor prescribes the necessary treatment, draws up a diet and monitors the general condition of the patient.
After the early period, the “middle period” of rehabilitation begins. During this period, the patient gradually increases physical activity, performs exercises aimed at restoring body functions. Also at this stage, physiotherapy, massage, therapeutic exercises can be prescribed.

The final period of rehabilitation is the “late period”. At this stage, the main task is to restore the normal functioning of the patient. He is recommended more intense physical activity, increasing stress and returning to daily activities.
It is important to note that rehabilitation should be individualized and depends on the nature of the operation and the patient’s state of health. With any examinations and procedures, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the doctors and be patient in order to fully recover from the surgical intervention.
Preventive measures
To avoid various diseases that cause pain in the left side, it is necessary to monitor your health. Follow these guidelines:
Following the recommendations will help maintain health and avoid discomfort in the left side. However, if you experience symptoms or pain, you should contact your doctor for professional advice and evaluation.
Related videos:
Q&A:
What causes pain in the left side?
Pain in the left side can occur for various reasons, including problems with the stomach, pancreas, liver, left kidney, spleen, or intercostal muscles.
 In addition, it may be associated with problems in the cardiovascular system, such as tonsillitis and myocardial infarction. Also, pain in the left side can be the result of injuries or damage in this area.
In addition, it may be associated with problems in the cardiovascular system, such as tonsillitis and myocardial infarction. Also, pain in the left side can be the result of injuries or damage in this area.How can you tell if the pain in your left side is due to heart problems?
If pain in the left side is accompanied by a feeling of compression, burning or unpleasant pressure in the chest, then this may be a sign of problems with the cardiovascular system. Loss of consciousness, dizziness, and shortness of breath may also be symptoms. If you develop these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Can pain in the left side be related to pregnancy?
Yes, there may be pain in the left side during pregnancy. This may be due to the increase in the size of the uterus and the growth of the fetus, which can lead to pressure on the left kidney or on the intercostal muscles. In addition, some women experience stretching of the ligaments and muscles in the abdominal cavity during pregnancy, which can also cause pain in the left side.

What should I do if I have pain in my left side after eating?
If pain in the left side occurs after eating, it may be due to problems with the stomach or pancreas. In such cases, it is recommended to stop overeating and increase the number of meals per day. It is also necessary to exclude fatty, spicy, smoked and salty foods from the diet. If the pain does not stop or worsens, you should consult a doctor.
What diseases can cause pain in the left side?
Pain in the left side can be associated with various diseases, including gastritis, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, left-sided pulmonary edema, tonsillitis, myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy and coronary heart disease. Also, pain can occur as a result of injuries and injuries. In order to determine the cause of the pain, you need to see a doctor.
How to treat pain in the left side?
The treatment of pain in the left side depends on the cause of the pain. If the pain is caused by a heart problem, your doctor may prescribe medication to regulate your heart rate or dilate blood vessels.
 If the pain is caused by problems with the stomach or pancreas, the patient may be put on diet and medication to control the level of acidity in the stomach. In case of injury or damage, surgery may be required.
If the pain is caused by problems with the stomach or pancreas, the patient may be put on diet and medication to control the level of acidity in the stomach. In case of injury or damage, surgery may be required.What vital organs are in the left side?
In the left side are such vital organs as the left kidney, spleen, stomach, pancreas, left side of the diaphragm and part of the large intestine. However, pain in the left side is not always associated with these organs, so to determine the causes of pain, it is necessary to conduct an examination with a doctor.
Why there is pain in the left side after spicy food: causes and methods of treatment
What to do if after eating spicy or fatty food there is pain in the left side? Causes, diagnosis and treatment. Tips for changing your diet to prevent discomfort.
Pain in the left side after spicy food can occur for various reasons. This may be due to digestive disorders, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as other problems in the body.
 Only a doctor after diagnosis can find out the cause of pain and choose the right method of treatment.
Only a doctor after diagnosis can find out the cause of pain and choose the right method of treatment.One of the most common diseases that can cause pain in the left side after spicy food is a stomach ulcer. This disease is characterized by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. Another cause may be chronic gastritis.
Prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract includes proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, regular intake of drugs to protect the gastric mucosa and strengthen the immune system. In case of pain in the left side after spicy food, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and proper treatment.
Causes of pain in the left side
Pain in the left side after spicy food can be caused by various reasons. For example, a reaction to allergens is possible, which leads to a violation of the digestive processes. Some foods may contain a large amount of fat, which makes it difficult to break down food and leads to pain in the left side.

Another cause of pain in the left side may be an insufficient amount of enzymes or acid, which is responsible for the breakdown of food. This can lead to imbalance and disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
There may also be bowel problems, such as irritation or inflammation, leading to left side pain and abdominal discomfort. This may be due to intoxication, infection or other factors.
It is important to note that if the pain in the left side is constant or lasts for several hours, then it is worth seeking medical help to find out the cause and take effective treatment.
Acute pain after eating: symptoms
Acute pain in the left side after eating is a common symptom that can appear in various diseases. This symptom may be associated with irregular eating habits, eating disorders, indigestion, certain heart or intestinal diseases.
Sharp pain in the left side after eating is usually accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, gas, diarrhea and dyspepsia.
 In addition, there may be pain in the upper abdomen, liver and gallbladder. In some cases, pain may radiate to the lower back, which is associated with kidney and bladder problems.
In addition, there may be pain in the upper abdomen, liver and gallbladder. In some cases, pain may radiate to the lower back, which is associated with kidney and bladder problems.Acute pain may be indicative of a bowel disease, such as a stomach or duodenal ulcer. In addition, it may be associated with heart conditions such as angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. If the pain is systematic, you should consult a doctor to diagnose and prescribe treatment.
If you experience these symptoms after eating, you need to watch your diet and avoid spicy, fatty and heavy foods. In addition, it is necessary to exercise moderately and avoid stressful situations. If the symptoms do not disappear or worsen, you should immediately consult a doctor.

Peptic ulcer
Peptic ulcer is a disease of the stomach or duodenum that can cause pain in the left side after spicy food. At the heart of peptic ulcer is damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestines and the formation of an ulcer.
The main causes of peptic ulcer disease are dietary errors, certain medications, Helicobacter pylori infection, stress and genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of peptic ulcer may include pain in the left side after eating, a feeling of heaviness and fullness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, loss of appetite and weight loss.
The diagnosis of peptic ulcer requires a thorough analysis of symptoms, histological examination of mucosal biopsy specimens, and additional research methods such as fibrogastroscopy or ultrasound.
Treatment of peptic ulcers includes drugs that reduce stomach acid and speed up the healing of the ulcer, as well as diet and lifestyle changes.
Gastritis
Gastritis is a disease that occurs when the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed.
 It can be caused by various factors, including spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, smoking, stress, infection.
It can be caused by various factors, including spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, smoking, stress, infection.Symptoms of gastritis may include: abdominal pain or discomfort, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, acid or bitter taste in the mouth, loss of appetite. If these symptoms do not go away within a few days, you should consult your doctor.
Treatment of gastritis may include changing diet, avoiding certain foods, and taking medications. To prevent gastritis, you should avoid spicy and fatty foods, reduce alcohol and cigarette consumption, and reduce stress levels.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory disease of the pancreas that can present with pain in the left side after eating spicy food.
 With pancreatitis, pancreatic function and metabolism in the body are disrupted, resulting in acute pain in the abdomen and left side, fever, nausea and vomiting. There may also be disturbances in the work of the heart and respiratory system.
With pancreatitis, pancreatic function and metabolism in the body are disrupted, resulting in acute pain in the abdomen and left side, fever, nausea and vomiting. There may also be disturbances in the work of the heart and respiratory system.To cope with pancreatitis, you must immediately consult a doctor and undergo complex treatment. Medications are used, including antibiotics, available only on prescription. It is also important to follow the diet and eat only easily digestible food. Spicy, fatty, spicy and smoked foods should be excluded from the diet.
It is important to remember that pancreatitis is a dangerous disease that can lead to serious complications such as pancreatic gangrene and necrosis of internal organs. Therefore, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor and self-treatment – in this case, only specialists can help.
Colitis
Colitis is an inflammatory disease of the colon that can lead to pain in the left side of the abdomen. The underlying causes of colitis may be due to infectious, autoimmune, or idiopathic causes. In addition, dietary changes or stress can contribute to colitis.
Symptoms of colitis include pain in the left side of the abdomen, diarrhea with blood and mucus, extreme fatigue, and weight loss. Chronic colitis can also lead to a weakened immune system and an increased risk of bowel disease.
Treatment for colitis may include antibiotics, probiotics, rehabilitative therapy, and dietary and stress management. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the affected part of the intestine.
Gallbladder disorder
The gallbladder is an organ located under the liver that stores bile.
 This fluid is essential for the proper digestion of fats in the intestines. A gallbladder disorder can lead to various unpleasant symptoms, including pain in the left side after spicy food.
This fluid is essential for the proper digestion of fats in the intestines. A gallbladder disorder can lead to various unpleasant symptoms, including pain in the left side after spicy food.One of the most common causes of gallbladder disorders is the formation of gallstones. These are tough growths that can clog the bile ducts and lead to painful bile constipation. In addition, diseases of the gallbladder can cause infections, inflammation, or impaired motor activity of the organ.
If you suspect a gallbladder disorder, you should definitely consult a doctor for professional advice. Diagnosis may require an ultrasound of the abdomen or bile duct. Treatment may vary depending on the cause of the disease.
Your healthcare professional may prescribe medications to reduce pain and inflammation, and recommend a diet that is limited in fat and spicy foods. In some cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder or gallstones may be required. In any case, treatment should be prescribed individually and carried out under the constant supervision of a physician.

In general, it should be taken into account that gallbladder disorder can lead to quite serious consequences, so measures must be taken to prevent it. This may include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, moderate fat and alcohol intake, and regular check-ups with a doctor.
Ways to prevent pain after spicy food
1. Moderate consumption of spicy food. It is necessary to limit the amount of spicy food in the diet to avoid overeating. Try to start with a smaller amount and gradually increase the portions, giving your body time to adapt.
2. Avoid eating spicy food late at night. The digestive system works more slowly at night. Eating spicy food before bed can cause stomach pain and discomfort.
3. Drink enough water. Water promotes rapid digestion of food, which can reduce pain after eating spicy food. It is recommended to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day.
4. Prepare spicy food properly.
 Before preparing spicy foods, remove seeds and membranes that contain large amounts of capsaicin, a substance that causes acute pain. It is also useful to fry it with a minimum amount of oil.
Before preparing spicy foods, remove seeds and membranes that contain large amounts of capsaicin, a substance that causes acute pain. It is also useful to fry it with a minimum amount of oil.5. Eat spicy food with other foods. When you eat spicy food in combination with another food, the dish becomes less spicy. It is useful to add vegetables or salads to spicy foods, as they can protect the mucous membrane.
6. Avoid breaking the diet for peptic ulcers. If you suffer from peptic ulcers, spicy food is not recommended. If you do decide to eat spicy food, make sure it is prepared carefully and in moderation.
Treatments for pain in the left side
If you have pain in your left side after spicy food, the first thing to do is stop eating that food. To relieve the condition, you can take medicine for stomach pain, such as antacids or anti-inflammatory drugs. For example, ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
If the disease is caused by irritation of the stomach lining, your doctor may recommend treatment with drugs that help protect the stomach wall.
 These include drugs containing substances that block protons and histamines.
These include drugs containing substances that block protons and histamines.Diet is one of the most effective ways to deal with pain in the left side. Make sure you eat light steamed meals, drink plenty of water, and avoid spicy, fatty or spicy foods. In addition, you should stop smoking and reduce alcohol consumption.
If the disease is chronic, treatment may take a long period of time. In this case, the doctor may recommend regular use of medications, vitamin complexes and mineral supplements to maintain overall health and strengthen immunity.
Medicines to take for left side pain
Painkillers are the most common medicines used for left side pain.
 They help in reducing pain, reduce fever and inflammation. The group of analgesics includes drugs such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen. It is recommended to take them after meals.
They help in reducing pain, reduce fever and inflammation. The group of analgesics includes drugs such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen. It is recommended to take them after meals.Anticonvulsants – These medicines are used to treat neurological conditions that can cause pain in the left side. Anticonvulsants include drugs such as carbamazepine or phenytoin. However, they should only be taken as directed by your doctor.
Heartburn preparations – Left side may hurt due to heartburn or gastritis. In this case, drugs such as Omeprazole or Lantus will help. They reduce the acidity of the stomach, improve the digestion of food and relieve burning sensations and pain in the chest.
Also, in case of pain in the left side, it is recommended to avoid fatty and spicy foods, as well as alcohol. With persistent pain, it is necessary to consult a doctor to determine the cause of the pain syndrome and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Home Treatments for Left Side Pain
If you are experiencing left side pain after spicy food, there are several home treatments that can help relieve symptoms.

It is important to remember that these home treatments do not work for everyone and are not a substitute for qualified medical care for continued or worsening pain in the left side after spicy food. If additional symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Important things to know about pain in the left side
Pain in the left side is common among people, but it is not always the result of diseases or pathologies.

Some causes of pain in the left side may include excessive intake of fatty, spicy or fried foods; alcohol abuse; prolonged stay in the supine position on the left side; physical overload and stress.
However, if the pain in the left side occurs regularly, then there may be signs of serious illness.
Pain in the left side can be provoked by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis and diverticulosis. In addition, pain can be associated with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, as well as internal organs such as the heart and lungs.
In any case, if pain in the left side occurs regularly, it is necessary to consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
It is important to remember that pain in the left side can critically affect the quality of life, so it is necessary to take the necessary measures for their prevention and treatment.
How to Diagnose Pain in the Left Side
If you experience pain in the left side after spicy food, this may be an introductory sign of the disease.
 However, to accurately diagnose the condition, you need to see a doctor.
However, to accurately diagnose the condition, you need to see a doctor.First, the doctor will perform a visual examination and ask you questions about your health history. An important role is played in the description of pain: which area of pain occurs, the accompanying symptoms, the time of the day when the pain manifests itself.
Details about your general health will also help your doctor determine if you have underlying conditions such as peptic ulcers, current infections, allergies to certain foods, and other conditions that may be causing side pain. If necessary, laboratory diagnostics is prescribed: blood tests, urine, feces, ultrasound.
A correct diagnosis will help determine the cause and select the appropriate treatment. Do not delay contacting a doctor if pain in the left side occurs regularly and interferes with living a normal life. Take care of your health and be attentive to your body!
When should I see a doctor?
If pain in the left side occurs after spicy food and does not go away within a few hours, you should consult a doctor.
 You should also seek help if the pain is accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fever, loss of appetite, etc. These symptoms may indicate serious illnesses such as pancreatitis or stomach ulcers.
You should also seek help if the pain is accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fever, loss of appetite, etc. These symptoms may indicate serious illnesses such as pancreatitis or stomach ulcers.If you notice the appearance of painful symptoms after eating certain foods, you should consult an allergist. It will help determine if you have allergies to certain foods and tell you which foods to eliminate from your diet.
Some diseases that can cause pain in the left side can be extremely dangerous and even life-threatening. If you have pain in your left side that doesn’t go away within hours or even days, don’t put off seeing your doctor. He will be able to conduct the necessary research and give the correct diagnosis, as well as prescribe effective treatment.
Related videos:
Q&A:
Why does pain appear in the left side after spicy food?
The appearance of pain in the left side after spicy food may be associated with irritation of the gastrointestinal tract.
 Spicy food can cause infections and inflammation, which can lead to pain in the left side.
Spicy food can cause infections and inflammation, which can lead to pain in the left side.How can you prevent pain in your left side after spicy food?
To prevent pain in the left side after spicy food, reduce the amount of spicy food in the diet and increase water intake. Foods that can cause infections and inflammation should also be avoided.
Can pain in the left side after spicy food be a sign of heart failure?
Yes, pain in the left side after spicy food can be a sign of heart failure, as it can signal a violation of the blood supply to the heart. It is necessary to contact a cardiologist to conduct the necessary examinations and find out the causes of pain.
What diseases can lead to pain in the left side after spicy food?
Pain in the left side after spicy food can be a sign of diseases such as gastritis, stomach ulcers, cholecystitis, pancreatitis and other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. To find out the causes of pain, you need to consult a doctor and undergo an examination.

What symptoms may accompany pain in the left side after spicy food?
Symptoms that may accompany pain in the left side after spicy food include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, anorexia, and gastrointestinal dysfunction. In any case, if the pain persists for more than 2 days, you should consult a doctor.
What can be done to relieve pain in the left side after spicy food?
To relieve pain in the left side after spicy food, you can take painkillers, apply heat compresses to the painful area, reduce the consumption of spicy foods and increase water intake. However, if the pain persists, you should consult a doctor for examination and treatment.
What treatments can be used for pain in the left side after spicy food?
The treatment for pain in the left side after spicy food depends on the cause of the pain. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat infectious diseases, and anti-inflammatory therapy and diet may be used to treat inflammatory diseases.


 pylori
pylori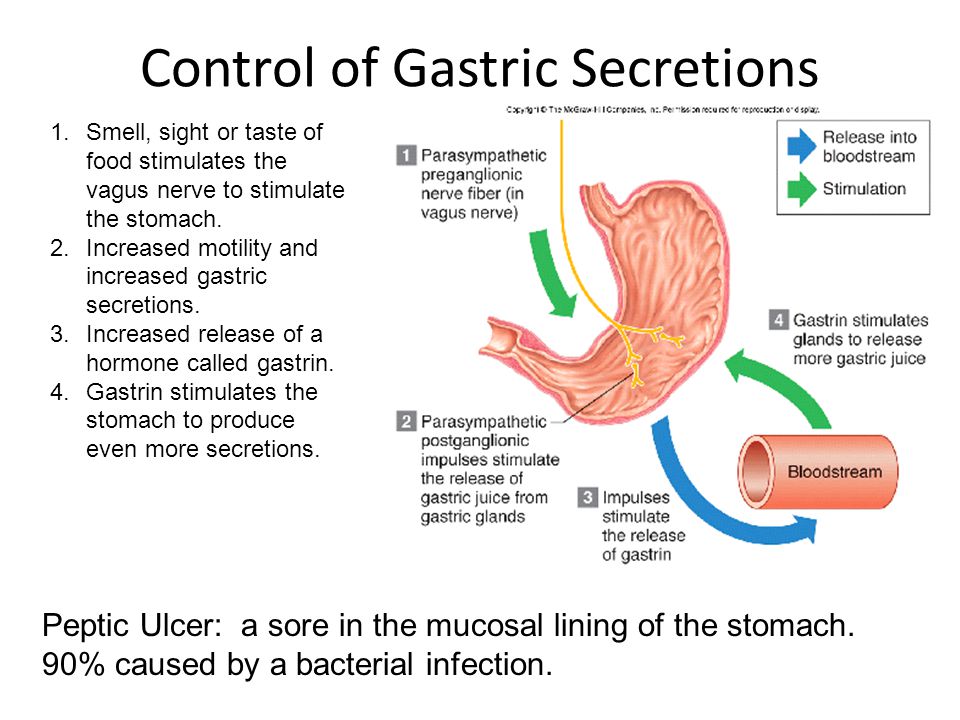




 For example, a stroke or multiple sclerosis can cause pain in the left side, which may be accompanied by other symptoms such as paralysis or numbness.
For example, a stroke or multiple sclerosis can cause pain in the left side, which may be accompanied by other symptoms such as paralysis or numbness.
 These organs play an important role in digestion and can be sensitive to stress, poor nutrition, and chronic disease. Here are some common problems that can cause left side pain.
These organs play an important role in digestion and can be sensitive to stress, poor nutrition, and chronic disease. Here are some common problems that can cause left side pain.
 A qualified specialist will help identify the cause of the pain and prescribe the necessary treatment, including massage, physical therapy, antibiotics, or even surgery.
A qualified specialist will help identify the cause of the pain and prescribe the necessary treatment, including massage, physical therapy, antibiotics, or even surgery.

 However, it should be remembered that long-term use of these drugs can adversely affect the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
However, it should be remembered that long-term use of these drugs can adversely affect the functioning of the liver and kidneys. This method can be used to treat various diseases such as myositis, neuralgia, etc.
This method can be used to treat various diseases such as myositis, neuralgia, etc. By following the recommendations of a specialist and performing the prescribed procedures, you can speed up the recovery process and return to normal life.
By following the recommendations of a specialist and performing the prescribed procedures, you can speed up the recovery process and return to normal life.

 It is also worth limiting the consumption of fatty, spicy and salty foods.
It is also worth limiting the consumption of fatty, spicy and salty foods. In addition, it may be associated with problems in the cardiovascular system, such as tonsillitis and myocardial infarction. Also, pain in the left side can be the result of injuries or damage in this area.
In addition, it may be associated with problems in the cardiovascular system, such as tonsillitis and myocardial infarction. Also, pain in the left side can be the result of injuries or damage in this area.
 If the pain is caused by problems with the stomach or pancreas, the patient may be put on diet and medication to control the level of acidity in the stomach. In case of injury or damage, surgery may be required.
If the pain is caused by problems with the stomach or pancreas, the patient may be put on diet and medication to control the level of acidity in the stomach. In case of injury or damage, surgery may be required.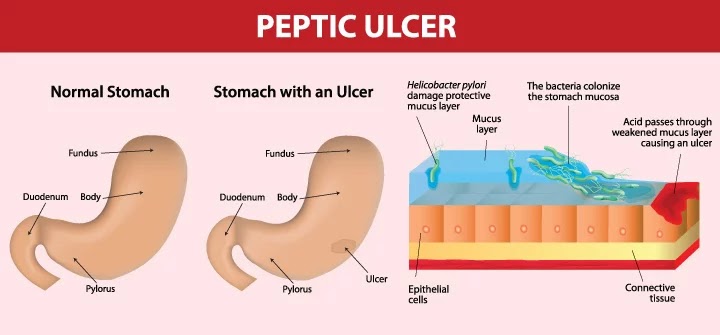 Only a doctor after diagnosis can find out the cause of pain and choose the right method of treatment.
Only a doctor after diagnosis can find out the cause of pain and choose the right method of treatment. In addition, there may be pain in the upper abdomen, liver and gallbladder. In some cases, pain may radiate to the lower back, which is associated with kidney and bladder problems.
In addition, there may be pain in the upper abdomen, liver and gallbladder. In some cases, pain may radiate to the lower back, which is associated with kidney and bladder problems.
 It can be caused by various factors, including spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, smoking, stress, infection.
It can be caused by various factors, including spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, smoking, stress, infection.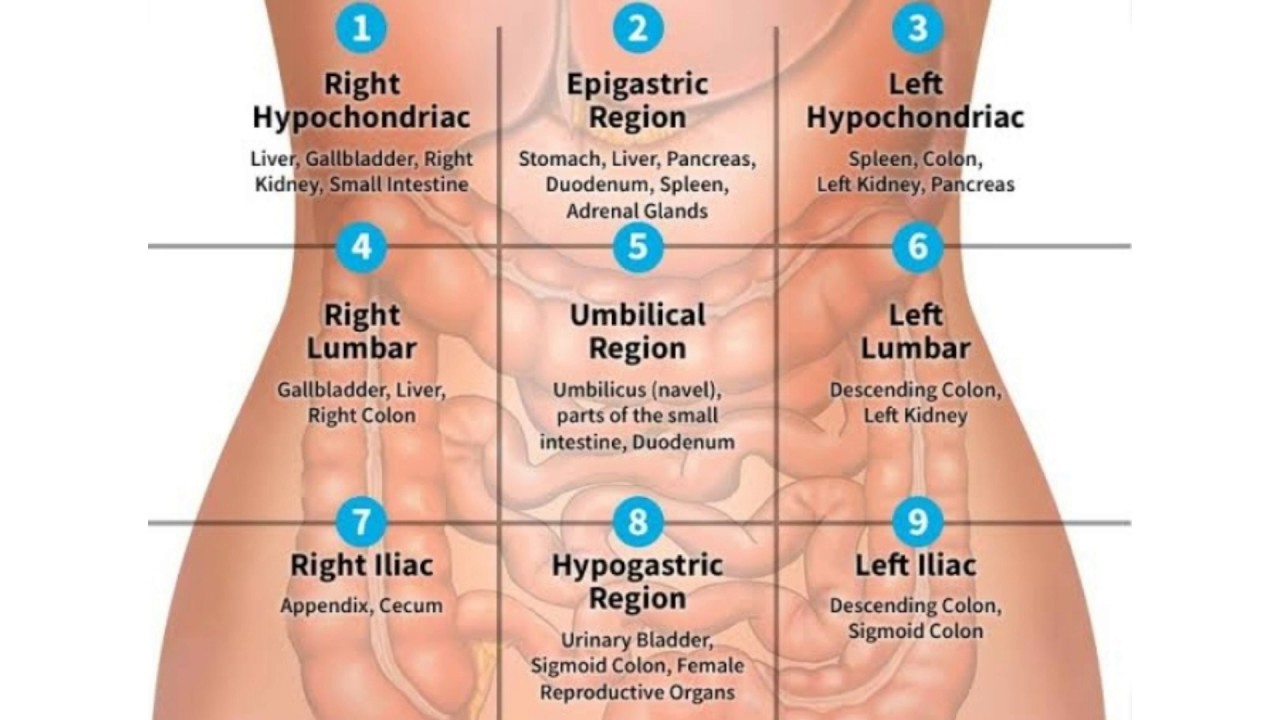 With pancreatitis, pancreatic function and metabolism in the body are disrupted, resulting in acute pain in the abdomen and left side, fever, nausea and vomiting. There may also be disturbances in the work of the heart and respiratory system.
With pancreatitis, pancreatic function and metabolism in the body are disrupted, resulting in acute pain in the abdomen and left side, fever, nausea and vomiting. There may also be disturbances in the work of the heart and respiratory system.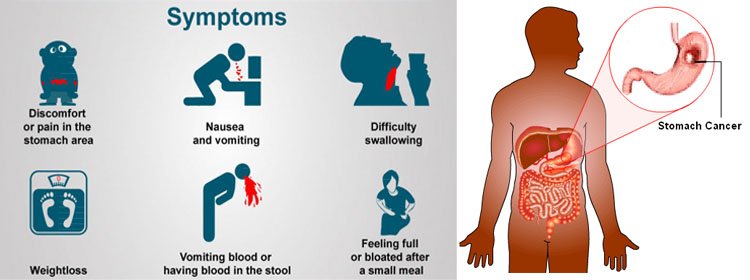
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/severe-stomach-pain-when-to-go-to-the-er-19452821-5c869d9446e0fb00011366d7.png) This fluid is essential for the proper digestion of fats in the intestines. A gallbladder disorder can lead to various unpleasant symptoms, including pain in the left side after spicy food.
This fluid is essential for the proper digestion of fats in the intestines. A gallbladder disorder can lead to various unpleasant symptoms, including pain in the left side after spicy food.
 Before preparing spicy foods, remove seeds and membranes that contain large amounts of capsaicin, a substance that causes acute pain. It is also useful to fry it with a minimum amount of oil.
Before preparing spicy foods, remove seeds and membranes that contain large amounts of capsaicin, a substance that causes acute pain. It is also useful to fry it with a minimum amount of oil. These include drugs containing substances that block protons and histamines.
These include drugs containing substances that block protons and histamines. They help in reducing pain, reduce fever and inflammation. The group of analgesics includes drugs such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen. It is recommended to take them after meals.
They help in reducing pain, reduce fever and inflammation. The group of analgesics includes drugs such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen. It is recommended to take them after meals.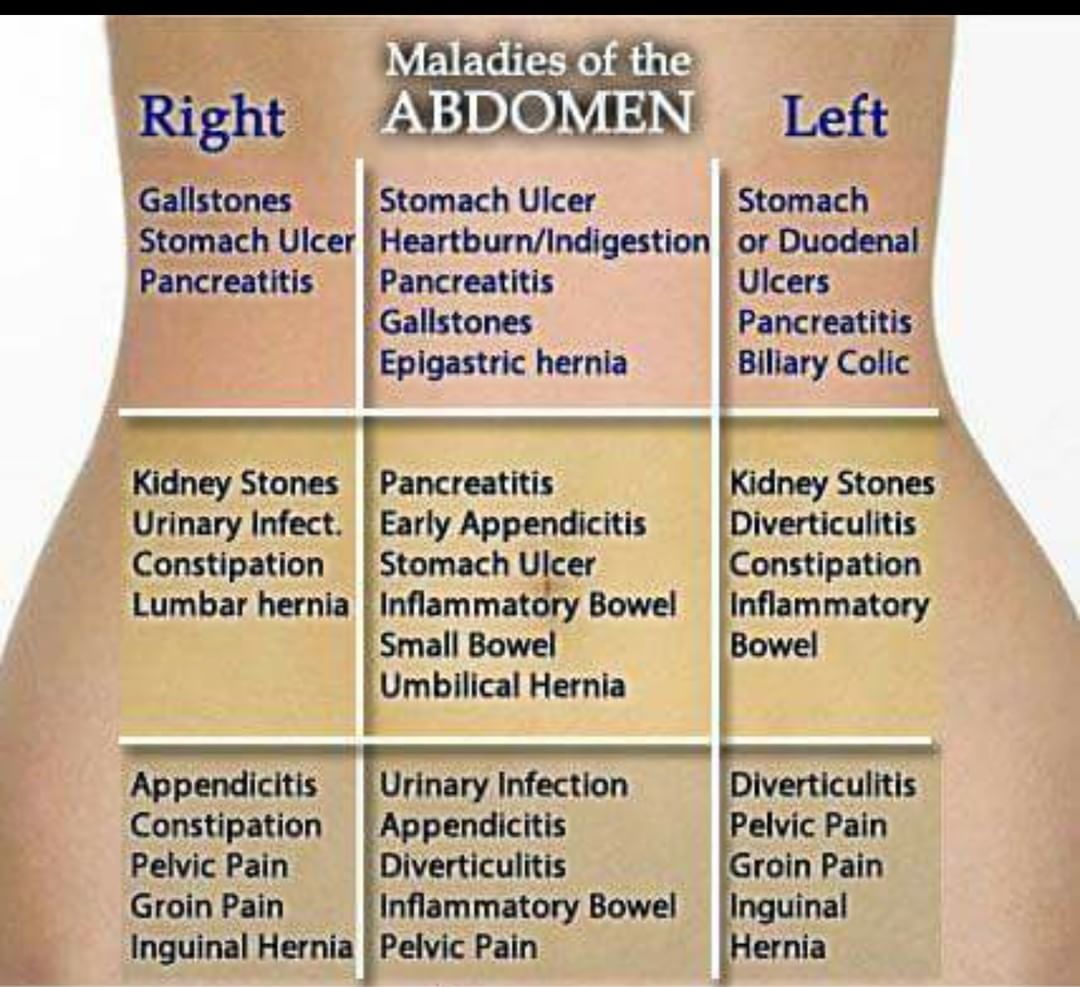

 However, to accurately diagnose the condition, you need to see a doctor.
However, to accurately diagnose the condition, you need to see a doctor. You should also seek help if the pain is accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fever, loss of appetite, etc. These symptoms may indicate serious illnesses such as pancreatitis or stomach ulcers.
You should also seek help if the pain is accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, fever, loss of appetite, etc. These symptoms may indicate serious illnesses such as pancreatitis or stomach ulcers. Spicy food can cause infections and inflammation, which can lead to pain in the left side.
Spicy food can cause infections and inflammation, which can lead to pain in the left side.
