Can you treat pancreatitis at home. Pancreatitis: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Home Remedies for Recovery
What is pancreatitis and how is it diagnosed. What are the treatment options for acute and chronic pancreatitis. How can you support pancreatitis recovery at home. What dietary changes can help manage pancreatitis symptoms.
Understanding Pancreatitis: Types, Symptoms, and Causes
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the pancreas, a vital organ responsible for producing digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin. This inflammation can lead to severe abdominal pain and potentially life-threatening complications if left untreated.
Types of Pancreatitis
There are two main types of pancreatitis:
- Acute Pancreatitis: A sudden onset of inflammation that typically resolves within a few days with proper treatment.
- Chronic Pancreatitis: A long-term condition characterized by ongoing inflammation and progressive damage to the pancreas.
Common Symptoms of Pancreatitis
While symptoms can vary between acute and chronic forms, some common signs include:
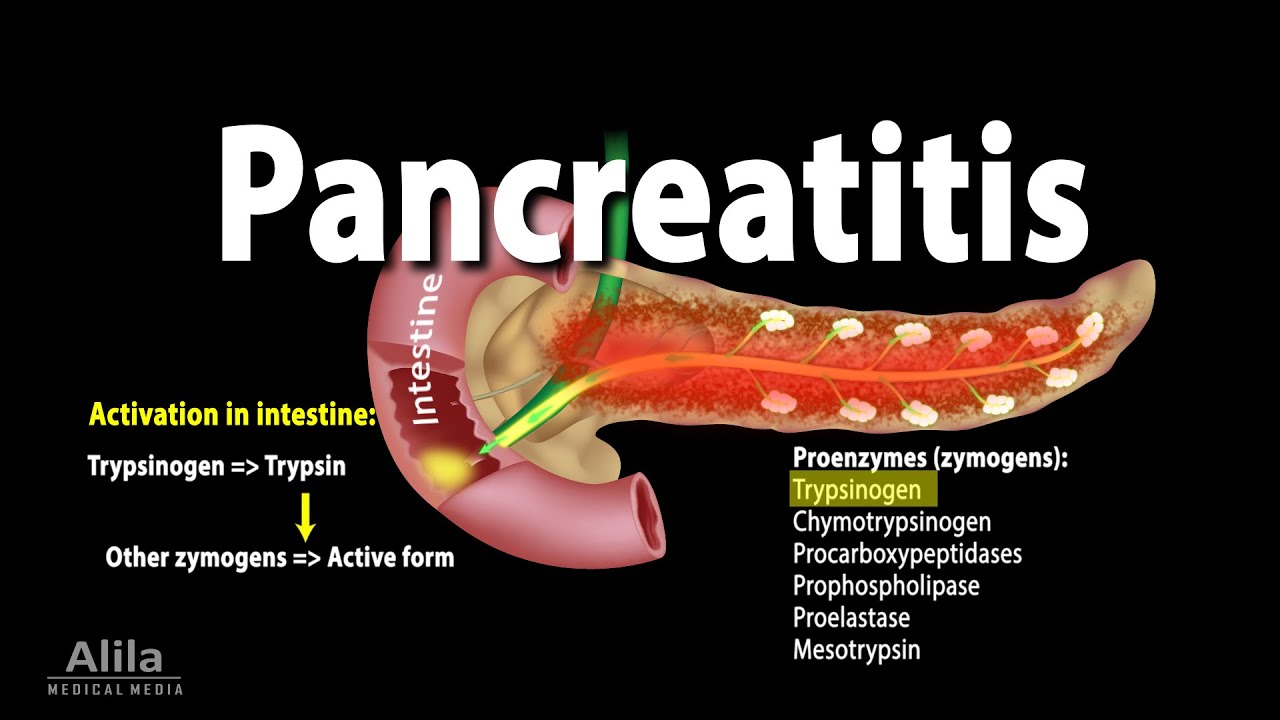
- Severe upper abdominal pain that may radiate to the back
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Rapid pulse
- Tenderness when touching the abdomen
- Unintended weight loss (more common in chronic pancreatitis)
- Oily, smelly stools (steatorrhea)
Causes and Risk Factors
Pancreatitis can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Gallstones
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- High triglyceride levels
- Certain medications
- Abdominal injury or surgery
- Genetic disorders
- Infections
- Pancreatic cancer
Risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing pancreatitis include obesity, smoking, and a family history of pancreatic disorders.
Diagnosing Pancreatitis: From Home Observations to Medical Tests
Can you diagnose pancreatitis at home? While self-diagnosis is not possible or recommended, being aware of potential symptoms can help you seek timely medical attention. The definitive diagnosis of pancreatitis requires professional medical evaluation and specific tests.
Initial Home Observations
If you experience persistent, severe upper abdominal pain, especially if it radiates to your back, it’s crucial to pay attention. Other warning signs include:

- Pain that worsens after eating
- Difficulty finding a comfortable position
- Nausea or vomiting that doesn’t subside
- Fever accompanied by abdominal discomfort
While these symptoms don’t definitively indicate pancreatitis, they warrant prompt medical evaluation.
Professional Diagnostic Procedures
When you visit a healthcare provider with suspected pancreatitis, they may perform several tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- Blood tests: To check for elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase).
- Imaging studies: Such as CT scans or ultrasounds to visualize the pancreas and surrounding tissues.
- Endoscopic ultrasound: A specialized procedure that provides detailed images of the pancreas and bile ducts.
- MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography): A non-invasive imaging technique to examine the pancreatic and bile ducts.
- Stool tests: To check for malabsorption issues in chronic pancreatitis.
These diagnostic tools help healthcare providers determine the severity of pancreatitis and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Treatment Approaches for Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
The treatment of pancreatitis varies depending on whether it’s acute or chronic, as well as the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Acute Pancreatitis Treatment
For acute pancreatitis, treatment typically involves:
- Hospitalization: Most cases require a hospital stay for close monitoring and supportive care.
- Fasting and IV fluids: To rest the pancreas and prevent dehydration.
- Pain management: Using appropriate medications to control severe abdominal pain.
- Treating the underlying cause: For example, removing gallstones if they’re the trigger.
- Antibiotics: If there’s an infection present or at high risk of developing.
- Nutritional support: Once fasting is no longer necessary, a carefully planned diet is introduced.
Chronic Pancreatitis Treatment
For chronic pancreatitis, the focus is on managing symptoms and preventing complications:
- Pain management: Through medications and sometimes nerve blocks.
- Enzyme replacement therapy: To aid digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Dietary modifications: A low-fat diet and abstaining from alcohol are crucial.
- Blood sugar management: As chronic pancreatitis can lead to diabetes.
- Surgery: In severe cases, to relieve pain or remove damaged portions of the pancreas.
In both acute and chronic cases, lifestyle changes play a significant role in recovery and prevention of recurrence.

Supporting Pancreatitis Recovery at Home: Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
While professional medical care is essential for treating pancreatitis, there are several ways to support recovery and manage symptoms at home, particularly for those with chronic pancreatitis or recovering from an acute episode.
Dietary Changes for Pancreatitis
A proper diet is crucial in managing pancreatitis and supporting pancreatic function:
- Low-fat diet: Reduce overall fat intake to ease the workload on the pancreas.
- Small, frequent meals: This approach can help prevent overwhelming the pancreas.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of clear fluids to maintain hydration and support digestion.
- Avoid trigger foods: Identify and eliminate foods that seem to worsen symptoms.
- Increase fiber intake: Gradually add more fiber to your diet to support digestive health.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact pancreatitis management:
- Alcohol abstinence: Completely avoid alcohol to prevent further pancreatic damage.
- Smoking cessation: Quit smoking, as it’s a risk factor for pancreatitis and its complications.
- Stress management: Practice relaxation techniques to reduce stress, which can exacerbate symptoms.
- Regular exercise: Engage in moderate physical activity as approved by your healthcare provider.
- Medication adherence: Take all prescribed medications as directed by your doctor.
Remember, these home-based strategies should complement, not replace, professional medical treatment.
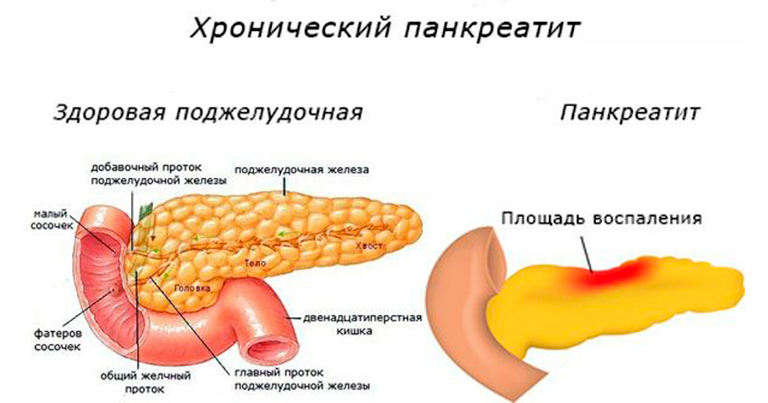
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Pancreatitis Relief
While natural remedies should never replace prescribed medical treatments, some may offer complementary support in managing pancreatitis symptoms. Always consult with your healthcare provider before trying any new supplements or natural remedies.
Potential Beneficial Supplements
- Omega-3 fatty acids: May help reduce inflammation in the body.
- Probiotics: Could support digestive health and immune function.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C and E, along with selenium, may help combat oxidative stress.
- Curcumin: The active compound in turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties.
Herbal Remedies with Potential Benefits
Some herbs have traditionally been used to support pancreatic health, though scientific evidence is often limited:
- Ginger: May help with nausea and have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Dandelion: Traditionally used to support digestive health.
- Licorice root: May have anti-inflammatory properties, but should be used cautiously due to potential side effects.
It’s crucial to approach these natural remedies with caution and always under medical supervision, as some may interact with medications or have contraindications for certain individuals.

Managing Pain and Discomfort in Pancreatitis
Pain management is a crucial aspect of pancreatitis treatment, particularly in chronic cases. While severe pain should always be addressed by a healthcare provider, there are some strategies that can help manage milder discomfort at home.
Non-Pharmacological Pain Management Techniques
- Heat therapy: Applying a heating pad to the abdomen may provide relief.
- Relaxation techniques: Deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress and pain.
- Posture adjustments: Finding comfortable positions, such as sitting up straight or slightly leaning forward, may alleviate pain.
- Gentle exercise: Light physical activity, as approved by your doctor, can help reduce pain and improve overall well-being.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
For mild pain, over-the-counter medications may be helpful, but should only be used under medical guidance:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol): Often preferred over NSAIDs for pancreatitis-related pain.
- NSAIDs: While sometimes used, they should be taken with caution as they may irritate the stomach.
Always consult your healthcare provider before taking any pain medications, as some may be contraindicated in certain cases of pancreatitis.

Preventing Pancreatitis Recurrence: Long-Term Strategies
For those who have experienced pancreatitis, preventing recurrence is a key concern. While some risk factors are beyond control, many preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of future episodes.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a risk factor for pancreatitis, so keeping a healthy BMI is important.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation, so finding effective stress-reduction techniques is crucial.
- Regular check-ups: Stay on top of your health with regular medical check-ups and screenings.
Dietary Considerations for Long-Term Pancreatic Health
A balanced, pancreas-friendly diet can play a significant role in preventing recurrence:
- Limit processed foods: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods instead.
- Moderate fat intake: While some healthy fats are necessary, excessive fat can strain the pancreas.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate hydration supports overall digestive health.
- Consider Mediterranean-style eating: This diet pattern has been associated with reduced inflammation and better overall health.
By incorporating these strategies into daily life, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining pancreatic health and reducing the risk of future pancreatitis episodes.
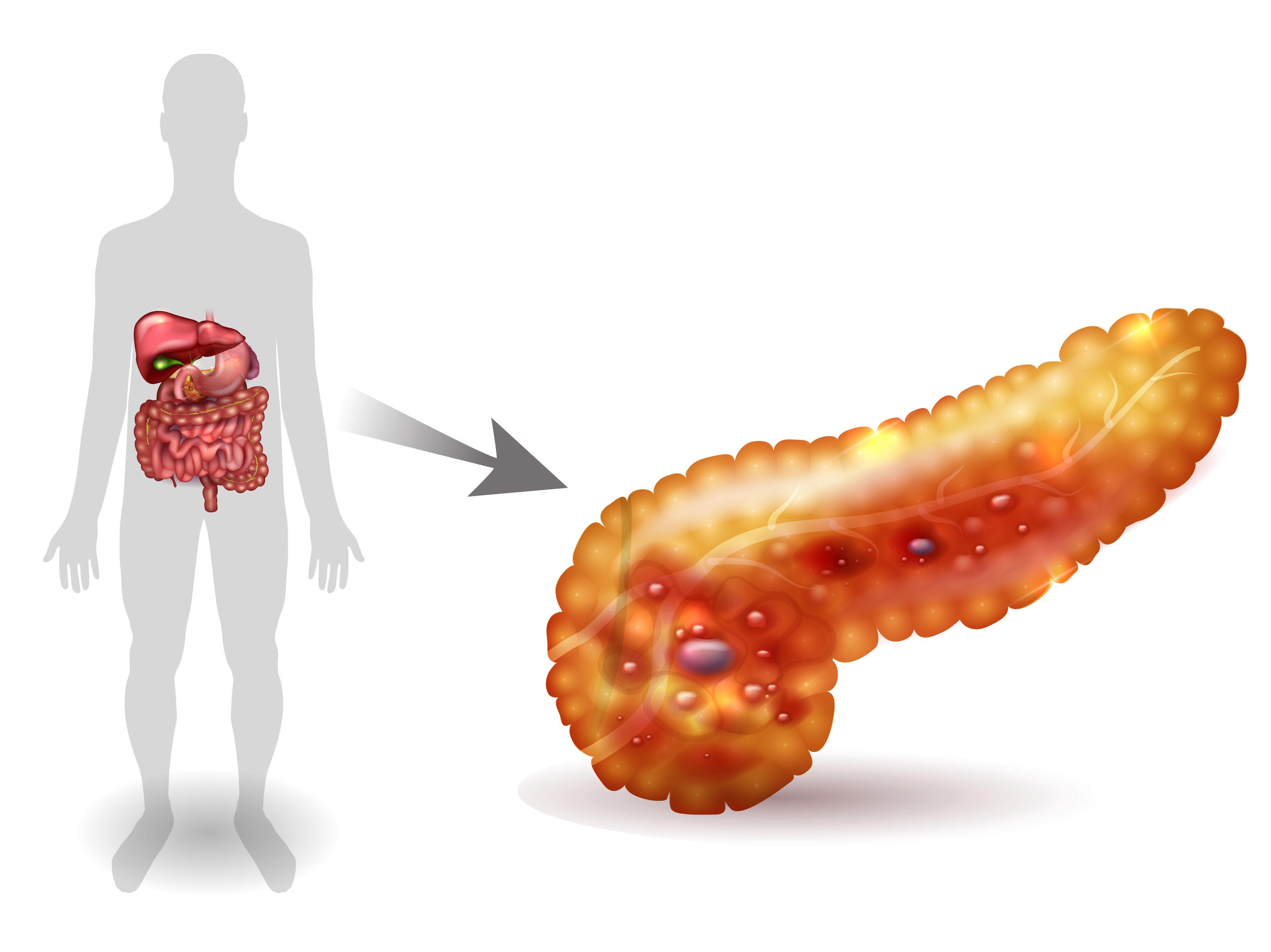
When to Seek Emergency Care for Pancreatitis
While some cases of pancreatitis can be managed at home under medical supervision, there are situations where immediate medical attention is crucial. Recognizing these warning signs can be life-saving.
Red Flags Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Severe, persistent abdominal pain: Especially if it’s accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Signs of shock: Such as rapid heartbeat, shallow breathing, or clammy skin.
- High fever: A temperature above 101°F (38.3°C) could indicate an infection.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin or eyes may suggest a blockage in the bile duct.
- Severe dehydration: Symptoms include extreme thirst, dark urine, and dizziness.
- Difficulty breathing: This could indicate a serious complication affecting the lungs.
What to Expect in the Emergency Room
If you need to go to the ER for suspected pancreatitis, you can expect:
- Immediate pain management
- Blood tests to check pancreatic enzyme levels
- Imaging studies like CT scans or ultrasounds
- IV fluids to prevent dehydration
- Possible admission for further treatment and monitoring
Remember, pancreatitis can be a serious condition, and timely medical intervention is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring the best possible outcome.

How To Support Your Recovery At Home
Sudden shooting pain across your upper abdomen maybe a worrying sign of pancreatitis. The organ resembling a leaf may not look like much but it does a brilliant task of keeping your digestive process going. If you have pancreatitis, it might mean that this organ is stressed out and needs a break. The home remedies for pancreatitis that you can read here along with a few diet tips, can be useful to restore it back to health as smoothly and safely as possible.
In This Article
What Is Pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. Located in the abdomen, the pancreas is an organ that is responsible for secreting digestive juices. In pancreatitis, not only the pancreas but even the surrounding blood vessels may get inflamed leading to possible bleeding and infection.
There are broadly two types of pancreatitis:
1. Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis begins suddenly and may last for a few days. It maybe life-threatening and needs to be treated right away. It most often presents as severe pain in the upper abdomen area that spreads towards the back. Other symptoms of acute pancreatitis include tenderness on the abdomen, fever, nausea, vomiting, and rapid pulse (1).
It maybe life-threatening and needs to be treated right away. It most often presents as severe pain in the upper abdomen area that spreads towards the back. Other symptoms of acute pancreatitis include tenderness on the abdomen, fever, nausea, vomiting, and rapid pulse (1).
2. Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis on the other hand is a slowly progressing disease that may continue for years and occur intermittently. Untreated chronic pancreatitis may result in serious health conditions like diabetes, pancreatic infection, respiratory problems, kidney failure, and may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Symptoms associated with this form of pancreatitis include unintended weight loss, upper abdominal pain that is worse after eating, and oily and smelly feces (2).
As you can see, the most common symptom of pancreatitis is abdominal pain. If you experience severe pain that does not subside or makes it difficult to sit still or be comfortable, contact your healthcare provider as early as possible.
Is there a way to know that you have pancreatitis before you visit your doctor? Let’s find out.
How To Test For Pancreatitis At Home
Image: Shutterstock
You cannot self-diagnose pancreatitis at home as it requires multiple laboratory tests like a blood test, a CT scan, and sometimes, an ultrasound scan. Your doctor may also prescribe you a stool test to check for chronic pancreatitis.
The best way to be aware of whether your pancreas is inflamed is to touch your abdomen for tenderness on experiencing upper abdominal pain. The next step is to contact your doctor, as untreated pancreatitis can prove to be fatal.
Like similar symptoms, both acute and chronic pancreatitis have some common underlying causes. Let us take a closer look at them.
What Causes Pancreatitis?
There are many probable reasons why you may develop pancreatitis, including (3):
- Excessive drinking of alcohol
- Gallstones
- Certain medications
- Cystic fibrosisi X A rare genetic disorder that causes sticky mucus to build up in organs, including the lungs, pancreas, and digestive tracts.

- Abdominal surgery
- High levels of triglyceridesi XNaturally occurring fat that gives you energy and is stored in the blood, which the body uses in between meals. in the blood
- High levels of calcium in the blood
- Abdominal injury
- Pancreatic cancer
- Infections
- Genetic disorders of the pancreas
The most common reason behind acute pancreatitis is the formation of gallstones, whereas genetics and lifestyle factors play a more important role in the development of chronic pancreatitis. Some of these risk factors include (3):
- Heavy alcohol use
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Genetics
Did You Know?
In the United States, approximately 200,000 hospital admissions annually are due to acute pancreatitis (4).
Acute pancreatitis generally requires hospitalization and depending on what has caused it, its treatment course is decided. Chronic pancreatitis, on the other hand, maybe managed at home if it is recurrent and not severe.
In either case, there are certain home remedies for pancreatitis that may support your recovery and alleviate some of its symptoms. Let us see what they involve.
Natural Remedies For Pancreatitis Relief
Pancreatitis treatment at home typically involves staying hydrated, avoiding fatty foods and alcohol, and fasting. In the case of mild pancreatitis, self-care measures can aid symptom management and support healing, but medical attention may still be necessary for more severe cases. It is always important to consult a doctor before trying any medical or natural remedies.
1. Make Dietary Changes
Image: Shutterstock
Medical professionals recommend that you avoid any food during an episode of pancreatic inflammation. This restriction may last from a few hours to a few days. You should stay hydrated with fluids during that time. In case you are required to go without food for a long period of time, you may have to be intravenously fed to get your supply of essential nutrients. When you are allowed to eat again, you should take several small meals throughout the day. Avoid food with high-fat content. In addition, incorporate plenty of fluids in your diet and limit your caffeine intake (5), (6).
When you are allowed to eat again, you should take several small meals throughout the day. Avoid food with high-fat content. In addition, incorporate plenty of fluids in your diet and limit your caffeine intake (5), (6).
Did You Know?
A clinical description of acute pancreatitis was first presented by the Dutch anatomist Nicholas Tulp in 1652 (7).
2. Make Lifestyle Changes
Smoking, heavy drinking, and lack of an active lifestyle are closely linked to the development and worsening of pancreatitis (8). Completely stop consuming alcohol to lower the risk of triggering inflammation. Adopt a routine for exercise to help you manage your weight. Smoking cigarettes also puts you under oxidative stress and toxin load so quit it as early as possible (9), (10).
3. Lose Weight
Image: Shutterstock
Obesity has been linked to a higher risk of gallstones and pancreatitis. It also makes the severity of symptoms related to pancreatitis worse. Therefore, doctors routinely recommend those with pancreatitis to lose weight and manage it around a healthy BMI. Increased fat deposits in the abdominal area are linked to an increased risk of inflammation (11). To lose weight sustainably, you may need to:
Increased fat deposits in the abdominal area are linked to an increased risk of inflammation (11). To lose weight sustainably, you may need to:
- Control portion sizes
- Substitute simple and processed carbohydrates with complex carbohydrates and whole grains
- Limit added sugar and exclude sweetened carbonated drinks
- Limit fat intake
- Choose healthy snacks like nuts, fruits, and seeds
4. Take Glutamine Supplements
According to research, glutamine supplements may support treatment for pancreatitis by reducing the risk of associated complications and infections (12), (13). Glutamine is an amino acid that helps to break down food and gives a boost to the immune system. However, larger studies are warranted to establish the efficacy of glutamine supplementation for pancreatitis.
These home remedies for pancreatitis maybe supplemented with foods that can help with the condition. Let’s explore what makes up a pancreatitis diet.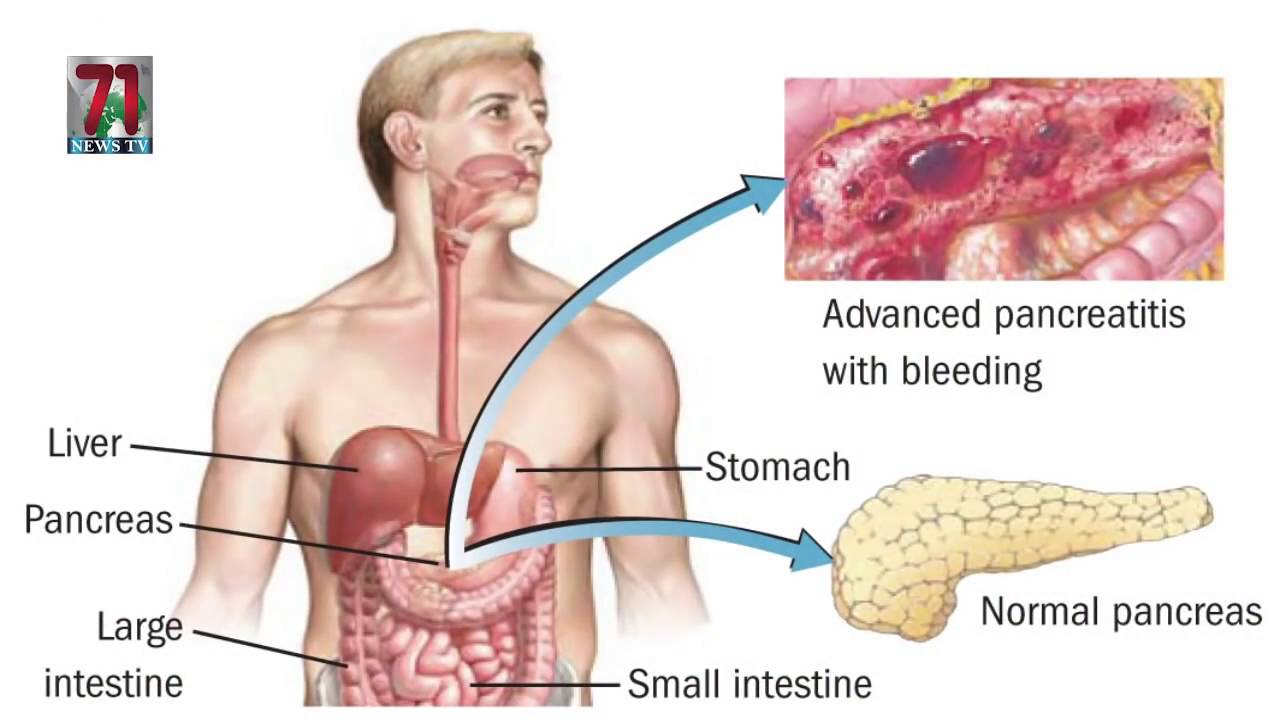
Is There A Specific Diet For Pancreatitis?
Image: Shutterstock
Your healthcare provider may work with you and design a specific diet based on the severity of your condition. As such, there is no one-size-fits-all diet specifically designed for pancreatitis. Having said that, there are definitely certain foods that can benefit you if you are recovering from an attack of acute pancreatitis or living with chronic pancreatitis. There are also a few foods that you are better off without. Some of them are listed below:
- Blueberries
Blueberries are packed with antioxidants which can help reduce the number of free radicals in your body and lower inflammation. Free radicals in the body can aggravate or play a part in the development of pancreatitis (14). Adding blueberries to your diet may help you improve your condition and prevent severe flare-ups (15), (16).
- Tofu
Tofu is a good alternative to meat for people with chronic pancreatitis. Red meat consumption is a risk factor for gallstones that can trigger an inflammation of the pancreas. The high-fat content in red meat may also exacerbate the condition (17). You can incorporate tofu-based meals in your diet to get your source of meaty, low-fat protein.
Red meat consumption is a risk factor for gallstones that can trigger an inflammation of the pancreas. The high-fat content in red meat may also exacerbate the condition (17). You can incorporate tofu-based meals in your diet to get your source of meaty, low-fat protein.
- Yogurt
Yogurt is a probiotic that can help you regulate the microbiomei XThe community or collection of all microorganisms that live on and inside the body, such as fungi and bacteria. in your gut and strengthen your immune system (18). A strong immune system can lower inflammation in and around your pancreas and also reduce the risk of infection, which is one of the most common causes of death associated with acute pancreatitis (19), (1).
Related: 18 Health Benefits Of Turmeric, How To Use It, & Side Effects
- Reishi Mushrooms
Reishi mushrooms have been used in traditional medicine for centuries. It is densely packed with antioxidants and bioactive compounds. Additionally, it has antimicrobial, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties (20). There is some evidence to suggest that reishi mushrooms may protect pancreatic cells from damage when used in the diet for managing pancreatitis (21).
Additionally, it has antimicrobial, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties (20). There is some evidence to suggest that reishi mushrooms may protect pancreatic cells from damage when used in the diet for managing pancreatitis (21).
- Coconut Oil
Doctors often recommend a very low-fat diet for those with acute or chronic pancreatitis. Coconut oil, however, is one of the few cooking fats that maybe added to your diet. Coconut oil has a good balance of omega fatty acidsi XHealthy fat mostly found in fish that reduce inflammation and the risk of heart diseases, and build brain cells. and contains medium-chain-triglycerides or MCTs which may help fight inflammation in the pancreas. Coconut oil may also help in better absorption of nutrients (22).
Related: 25 Benefits Of Coconut Oil, Types, How To Include In Your Diet
- Turmeric
Turmeric, with its active compound curcumin, is a potent anti-inflammatory agent and antioxidant that may have a protective effect on the pancreas. It may also help reduce inflammation in the body (23). You can add turmeric to your diet by adding it to low-fat milk, making turmeric pepper tea, or using it in stir-fries or in one-pot meals as a spice.
It may also help reduce inflammation in the body (23). You can add turmeric to your diet by adding it to low-fat milk, making turmeric pepper tea, or using it in stir-fries or in one-pot meals as a spice.
Related: 11 Greek Yogurt Benefits, Nutrition Profile, & How To Make It
- Spinach
Leafy greens, especially spinach, are a great source of micronutrients (24). Pancreatitis may lead to poor absorption of nutrients. For instance, deficiency in vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and seleniumi XAn essential mineral that helps DNA synthesis and protects cells from oxidative damage and infections. have been linked with worsening conditions in pancreatitis (25), (26). Adding spinach to your diet is a good way of replenishing these nutrients.
The foods and natural ways to manage symptoms of pancreatitis should only be used in a supportive role as you go along with your prescribed treatment and work closely with your healthcare provider. Many of the natural remedies available for managing pancreatitis are aimed at the prevention of further inflammatory attacks on the pancreas. Let’s take a look at some of them.
Many of the natural remedies available for managing pancreatitis are aimed at the prevention of further inflammatory attacks on the pancreas. Let’s take a look at some of them.
Prevention Tips
Image: Shutterstock
You may lower your risk of pancreatitis by taking a few steps for a healthy lifestyle, like:
- Stop drinking alcohol.
- Stop smoking.
- Lose weight.
- Avoid added sugar.
- Engage in physical activities like walking, swimming, cycling, or strength training for 30 minutes at least 3 days a week.
- Certain medications/supplements can also increase your risk, so discuss with your doctor all supplements you are on.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods.
In short, pancreatitis refers to the inflammation of the pancreas that maybe either acute or chronic. Acute pancreatitis may last up to a few days, after which you need to focus on recovery. Chronic pancreatitis can last over years and is characterized by recurrent inflammations. Management of this condition using home remedies for pancreatitis involves lifestyle modifications and dietary adjustments. To prevent your risk of developing pancreatitis, it is essential to take care of oneself and quit smoking and drinking.
Management of this condition using home remedies for pancreatitis involves lifestyle modifications and dietary adjustments. To prevent your risk of developing pancreatitis, it is essential to take care of oneself and quit smoking and drinking.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is lemon water good for pancreatitis?
Lemon may have an antiinflammatory effect on the body, which can help with pancreatitis (27). However, research is limited in regard to the safety of lemon juice intake in different stages of pancreatitis and hence it should not be consumed without medical guidance.
Is ginger good for pancreatitis?
Ginger may have a protective effect against pancreatic cancer and reduce pancreatic damage (28). However, more research is warranted in this regard and ginger should not be consumed by individuals with pancreatitis without medical guidance.
Which tea is good for pancreas?
Green tea is rich in antioxidants and may help fight inflammation. However, it may also cause dehydration and lead to acute pancreatitis (29), (30). Therefore, individuals with pancreatic damage or pancreatitis are recommended to consult their healthcare provider before consuming green tea or any other tea.
Therefore, individuals with pancreatic damage or pancreatitis are recommended to consult their healthcare provider before consuming green tea or any other tea.
What spices are good for pancreatitis?
Basil, mint, and tarragon are good spices for pancreatitis.
Is Honey OK for pancreatitis?
A little amount of honey is okay for pancreatitis, depending on the body’s ability to manage blood sugar levels.
Key Takeaways
- Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas caused by excessive drinking of alcohol, gallstones, abdominal injury, and pancreatic cancer.
- Making dietary changes, losing weight, taking glutamine supplements may help alleviate symptoms of pancreatitis.
- Upper abdominal pain and tenderness are common symptoms of both acute and chronic pancreatitis.
Sources
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Acute pancreatitis: current perspectives on diagnosis and management
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5849938/ - Chronic pancreatitis: review and update of etiology risk factors and management
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5958317/ - Symptoms & Causes of Pancreatitis
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/pancreatitis/symptoms-causes - Pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538337/ - Nutrition management in acute pancreatitis: Clinical practice consideration
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7211526/ - ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in acute and chronic pancreatitis
https://www.clinicalnutritionjournal.com/article/S0261-5614(20)30009-1/fulltext - Acute pancreatitis: a historical perspective
https://pubmed. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19390402/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19390402/ - Metabolic and lifestyle risk factors for acute pancreatitis in Chinese adults: A prospective cohort study of 0.5 million people
https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1002618 - Impact of Smoking on the Risk of Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0124075 - Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Pancreatitis: Effect of Antioxidant Therapy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4009983/ - Obesity and pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6640854/ - Glutamine supplementation in acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1424390313007606?via%3Dihub - The role of infection in acute pancreatitis
https://gut. bmj.com/content/45/2/311
bmj.com/content/45/2/311 - Role of oxygen free radicals in patients with acute pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4656475/ - Recent Research on the Health Benefits of Blueberries and Their Anthocyanins
https://academic.oup.com/advances/article/11/2/224/5536953 - Experimental and clinical evidence of antioxidant therapy in acute pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3482639/ - Dietary Factors Reduce Risk of Acute Pancreatitis in a Large Multiethnic Cohort
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5241169/ - Immunologic effects of yogurt
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/71/4/861/4729065 - Diet and Immune Function
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6723551/ - Antitumour Antimicrobial Antioxidant and Antiacetylcholinesterase Effect of Ganoderma Lucidum Terpenoids and Polysaccharides: A Review
https://www. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6017764/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6017764/ - In vitro and in vivo protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on alloxan-induced pancreatic islets damage
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12941433/ - The Use of Medium-Chain Triglycerides in Gastrointestinal Disorders
https://med.virginia.edu/ginutrition/wp-content/uploads/sites/199/2014/06/Parrish-February-17.pdf - Effects of curcumin on oxidative stress inflammation and apoptosis in L-arginine induced acute pancreatitis in mice
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844019358827 - Spinach raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168462/nutrients - Nutrition in chronic pancreatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3831208/ - Chronic Pancreatitis and Nutrition Therapy
https://aspenjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ncp. 10379
10379 - Protective effect of citrus lemon on inflammation and adipokine levels in acrylamide-induced oxidative stress in rats
https://www.scielo.br/j/bjps/a/ZwxM39gGjtFB6CXhdZPQ77L/?lang=en - Anticancer Effect of Ginger Extract against Pancreatic Cancer Cells Mainly through Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Autotic Cell Death
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4427290/ - Epicatechin gallate and catechin gallate are superior to epigallocatechin gallate in growth suppression and anti-inflammatory activities in pancreatic tumor cells
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21241417/ - Can Green Tea Extract Become a Cause of Acute Pancreatitis?
https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-2009-1216532
The following two tabs change content below.
- Reviewer
- Author
How To Relieve Pancreatitis Pain: Home Remedies & Treatment
Article Contents
- What Is Pancreatitis?
- What Causes Pancreatitis?
- Where Do You Feel Pancreatitis Pain And What Does It Feel Like?
- 9 Natural Remedies To Relieve Pancreatitis Pain
- Medical Treatments For Pancreatitis
- Conclusion
- Source
If you’ve ever suffered from pancreatitis, you’re already aware of the debilitating pain it can cause.
Rates of acute pancreatitis (short-term) are increasing along with obesity and the prevalence of gallstones.
One of the main concerns people suffering from pancreatitis have is how to relieve pancreatitis pain.
What Is Pancreatitis?
Your pancreas is a vital organ. It’s a long, flat gland resting behind your stomach in your upper abdominal area. It helps secrete enzymes that aid in digestion and also produces insulin, a hormone that helps lower your blood sugar levels.
Your pancreas connects to the start of your small intestine and contains a pancreatic duct that empties digestive enzymes into your small intestine.
The pancreatic enzymes include amylase (breaks down carbohydrates), lipase (breaks down fats), as well as trypsin and chymotrypsin (breaks down proteins).
Pancreatitis is a condition where your pancreas becomes inflamed. Acute pancreatitis usually resolves within a matter of weeks. Chronic pancreatitis can linger for years and increase severity as the pancreas becomes damaged.
Around 80% of patients with acute pancreatitis have mild symptoms which resolve fairly quickly. The other 20% have more complicated bouts of severe acute pancreatitis, which can lead to further health problems.
Symptoms of pancreatitis:
- Upper abdominal pain
- Abdominal pain that radiates to your back
- Tenderness when touching your abdomen
- Fever
- Rapid pulse
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Chronic pancreatitis signs and symptoms:
- Upper abdominal pain
- Abdominal pain that feels worse after eating
- Losing weight without trying
- Oily, smelly stools (steatorrhea) due to lack of pancreatic enzymes that help break down fats
Get Your FREE Diabetes Diet Plan
- 15 foods to naturally lower blood sugar levels
- 3 day sample meal plan
- Designed exclusively by our nutritionist
By clicking “Download Now”, I agree to Ben’s Natural Health Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy.
What Causes Pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis occurs when the digestive enzymes it produces activate before they leave your pancreas. This leads to the pancreas being irritated and causing pain and inflammation.
The most common risk factors for developing pancreatitis are excessive alcohol use, cigarette smoking, obesity, having gallstones, having diabetes, and having a family history of pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis can also be triggered by certain health conditions like:
- Certain medications
- High triglyceride levels in the blood (hypertriglyceridemia)
- Pancreatic cancer
- Abdominal surgery
- Cystic fibrosis
- Infection
- Injury to your abdomen
- Trauma
Chronic alcohol abuse causes your body to make thicker, more viscous secretions which can block the pancreatic ducts and lead to pancreatitis.
One of the more common causes of acute pancreatitis is having gallstones. Gallstones can get caught in a pancreatic duct, blocking the exit of pancreatic enzymes. This type of acute pancreatitis is gallstone pancreatitis.
Gallstones can get caught in a pancreatic duct, blocking the exit of pancreatic enzymes. This type of acute pancreatitis is gallstone pancreatitis.
Where Do You Feel Pancreatitis Pain And What Does It Feel Like?
You’re likely to feel pancreatitis pain near your pancreas which is in your upper abdomen. The pain may also spread to your back.
Pancreatitis pain will likely differ from person to person, but it’s usually severe and disabling. Someone with pancreatitis will quickly look and feel very ill and need immediate medical attention.
If you feel pain in your upper abdomen and it’s accompanied by other symptoms like diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, it’s likely that you’re suffering from pancreatitis and should seek medical help for treatment.
9 Natural Remedies To Relieve Pancreatitis Pain
You might be wondering how to relieve pancreatitis pain at home. If your symptoms aren’t severe enough to land you in the hospital, here are some natural methods of pancreatitis pain relief.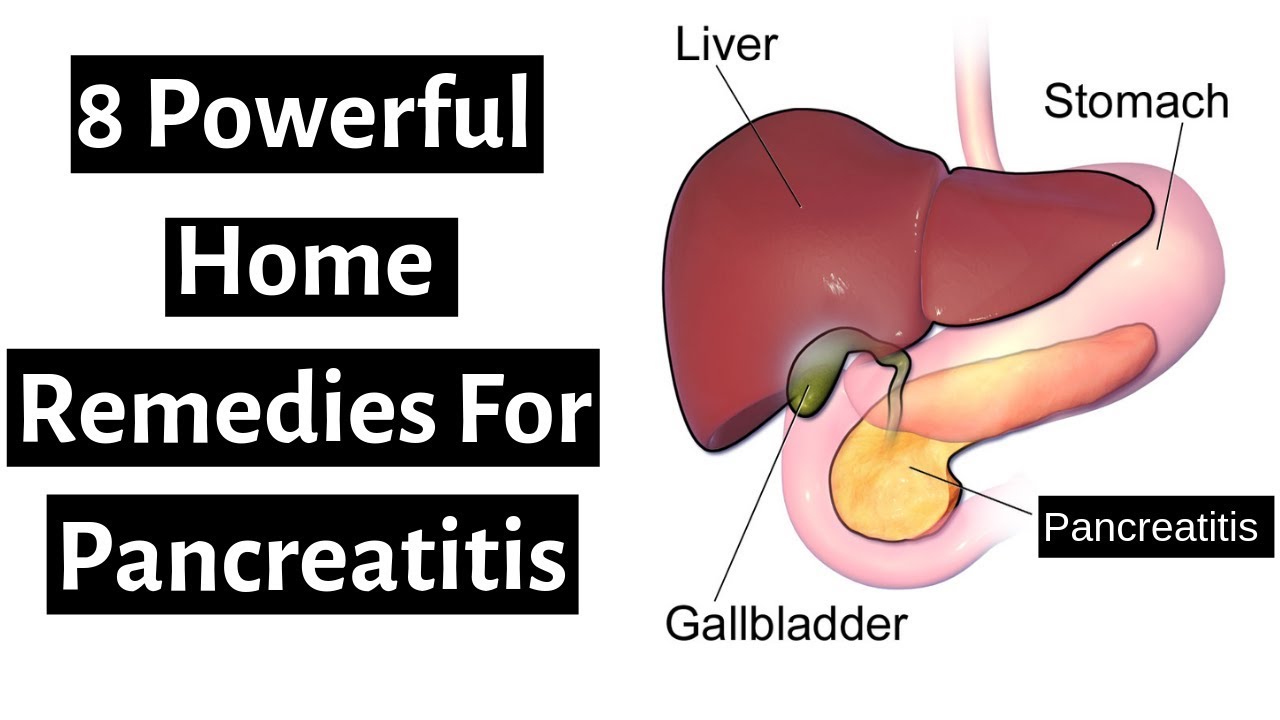
Eat a low-fat diet
High-fat foods stimulate your pancreas to create lipase to digest the fats. A high-fat diet can worsen both acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis symptoms.
Avoid eating high-fat animal foods like whole milk products, butter, and fatty meat. Instead, focus on getting plenty of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and low-fat or nonfat dairy or dairy alternatives like almond milk.
Heat therapy
A hot water bottle can potentially alleviate the discomfort associated with pancreatitis pain. Placing a hot water bottle on the affected area may help to relax the muscles and reduce the intensity of the pain.
Take it easy
Getting adequate rest and avoiding physical activity can potentially help alleviate pancreatitis pain.
Stick to a clear liquid diet if your symptoms are severe
In cases of intense pancreatitis pain, it is recommended to follow a clear liquid diet until your symptoms alleviate.
This includes consuming beverages such as juice, jello, broth, and popsicles, which can provide relief to your pancreas.
Use digestive enzymes
Digestive enzymes are available for over-the-counter purchase. Taking digestive enzymes might alleviate some of the digestive discomfort and pain from pancreatitis.
Choose a digestive enzyme blend containing amylase, protease, and lipase to cover all of the macronutrients.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves the insertion of thin needles into the skin, has been found to alleviate pain and distension in some individuals with pancreatitis.
Mind-body techniques
Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga could help reduce stress and alleviate pancreatitis pain.
Probiotics
Probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that promote gut health, may reduce inflammation and ease pancreatitis pain.
Staying hydrated
Drinking plenty of water can help keep the body hydrated and potentially reduce pancreatitis pain.
Medical Treatments For Pancreatitis
Pain relief
If you’re admitted to the hospital for pancreatitis pain, you’ll likely be given a strong pain medication to help manage and relieve your pain.
Antibiotics
If your pancreatitis is caused by an infection in your pancreas, you’ll be given antibiotics to help treat the infection.
IV fluids
Severe cases of acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis might require IV fluids to help treat dehydration.
Nutrition support
If you can’t eat, you may receive a feeding tube to meet your nutritional needs. In severe cases where your digestive system needs complete rest, IV nutrition in the form of parenteral nutrition will be prescribed.
A meta-analysis concluded that tube feeding (enteral nutrition) is more advantageous than IV nutrition (parenteral nutrition) in people hospitalized for severe acute pancreatitis.
Gallbladder removal
Gallstone pancreatitis is one of the causes of repeat pancreatitis. A cholecystectomy is surgery to remove your gallbladder. Your healthcare provider might recommend this surgery if gallstones are causing recurrent pancreatitis.
A cholecystectomy is surgery to remove your gallbladder. Your healthcare provider might recommend this surgery if gallstones are causing recurrent pancreatitis.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
This procedure is used to scope out issues with your pancreas. A gastroenterologist (doctor specializing in the digestive system) can use ERCP to remove gallstones that might be blocking your pancreatic duct.
Surgery
Your doctor might recommend surgery to remove blockages near your pancreas. If part of your pancreas becomes severely damaged from chronic pancreatitis, then your doctor may recommend removing parts of it.
If parts of your pancreas become permanently damaged from chronic pancreatitis, you might develop diabetes. This type of diabetes is called type 3c diabetes and occurs when the part of your pancreas that produces insulin is damaged.
Treatment for malabsorption
Chronic pancreatitis can cause malabsorption of important nutrients from pancreatic damage. Your doctor may advise you to take (or receive an infusion of) vitamins A, D, E, and K (fat-soluble vitamins) as well as vitamin B12 shots.
Your doctor may advise you to take (or receive an infusion of) vitamins A, D, E, and K (fat-soluble vitamins) as well as vitamin B12 shots.
Nerve block procedure
If your pancreatitis is causing severe pain, your doctor might offer you a nerve block procedure. Numbing medication is injected directly into the abdominal nerves that carry the pain signals from your pancreas to your brain.
Doctors usually reserve this procedure (a celiac plexus block) for those suffering from chronic pancreatitis.
Conclusion
Your pancreas makes digestive enzymes that help break down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates that you eat.
Pancreatitis is a painful condition where your pancreas becomes inflamed because these digestive enzymes become activated before they leave your pancreas.
Most people who suffer from pancreatitis have acute pancreatitis, meaning it goes away. You can manage acute pancreatitis pain at home with diet changes.
Chronic pancreatitis is rarer and may require more advanced medical procedures to manage it. These include surgery, nerve blocks, and IV or tube feeding nutrition.
These include surgery, nerve blocks, and IV or tube feeding nutrition.
Explore More
How Long Does Pancreatitis Take To Heal?
How to relieve an attack of pancreatitis at home, treatment at home
Call us right now by phone
+7 (812) 435 55 55
Call a doctor at home
Article content
- Symptoms 9001 1
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Home treatment
- Medical therapy
- Diet
- Vitamin therapy
- Seizure First Aid
- Possible complications
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. This is one of the most common pathologies of the digestive tract. It accounts for about 9% of all gastrointestinal diseases. It is equally found in both men and women.
The pancreas takes an active part in digestion and is also responsible for the production of insulin. Prolonged inflammation of the organ can lead to serious problems with the gastrointestinal tract and the development of diabetes. In addition, untimely treatment of pancreatitis is complicated by a bacterial infection that can spread to other tissues. It is possible to avoid undesirable consequences by contacting a doctor early. This article contains home treatment recommendations for informational purposes only. Therapy should be prescribed by a doctor and take place under close medical supervision.
In addition, untimely treatment of pancreatitis is complicated by a bacterial infection that can spread to other tissues. It is possible to avoid undesirable consequences by contacting a doctor early. This article contains home treatment recommendations for informational purposes only. Therapy should be prescribed by a doctor and take place under close medical supervision.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of the disease directly depend on its form. If pancreatitis is acute, then the person complains of:
- pain in the right hypochondrium – intense, constant, cutting or dull;
- fever, high or low blood pressure;
- general weakness, dizziness;
- pale or yellow complexion;
- nausea and vomiting;
- the appearance of a white coating on the root of the tongue;
- bloating;
- hiccups and eructations;
- diarrhea or constipation – frothy stools, with a fetid odor and remnants of undigested food.

Chronic pancreatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain – girdle character, occurs after eating, often spreads to the back;
- intoxication – malaise, decreased appetite, weight loss, lowering blood pressure;
- endocrine disorders – ketoacidosis, diabetes mellitus;
- dry skin, brittle hair and nails.
Causes
The trigger for the development of pancreatitis is the premature activation of digestive enzymes. Normally, they should be transported to the intestine in an inactive form, but in pathological disorders, these enzymes destroy the pancreas. The most common reasons that lead to the development of this failure are:
- excessive drinking;
- cholelithiasis;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- abdominal injuries, surgeries;
- anomalies in the structure of the pancreas;
- autoimmune diseases;
- uncontrolled medication: antibiotics, glucocorticosteroids, hormonal drugs;
- malnutrition with excessive consumption of spicy and fatty foods.

Diagnosis
Pancreatic pancreatitis is diagnosed and treated by a gastroenterologist. It is to him that you need to turn when you find the first signs of the disease. During the consultation, the doctor interviews the patient, conducts a visual examination of the abdomen and palpates the abdominal cavity. As a rule, the data obtained is already enough to suspect pancreatitis. But for the final confirmation of the diagnosis, an additional examination is prescribed:
- General and biochemical blood test. Markers of the inflammatory process: increased activity of pancreatic enzymes and an increase in the concentration of leukocytes.
- Analysis of feces and urine. In the chronic course of the disease, an excessive concentration of fats in the stool is often found on the coprogram. This indicates a violation of the digestive function.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Needed to assess the structure and size of the pancreas.

- CT or MRI. It allows you to get a detailed picture of the organ, due to which even small foci of inflammation and neoplasms are detected.
Home treatment
Home treatment of pancreatitis should be carried out strictly under medical supervision. Self-treatment and treatment with folk remedies can only aggravate the pathological process. Therefore, it is important to contact a gastroenterologist for qualified medical help as soon as possible. Only a doctor can tell you how to cure the disease and improve your well-being without harm to health.
Medical therapy
It is possible to remove the clinical symptoms of pancreatitis and stop further damage to the pancreas with medication. To do this, the patient is prescribed a course of medications:
- antispasmodics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs – to relieve pain in the acute form of the disease or exacerbation of the chronic;
- proton pump inhibitors – to suppress the secretory function of the pancreas;
- enzymes – to unload the pancreas and maintain a normal digestive process;
- antibiotics – to eliminate and prevent the development of infection;
- saline and physiological solutions – used in violation of water and electrolyte balance.

Diet
This is the most important component of the prevention of recurrence of pancreatitis and the normalization of well-being during its exacerbation. In acute inflammation, you will need to completely refuse to eat for 1-2 days. This will help reduce enzyme production. After that, cereals, mashed potatoes and herbal decoctions must be added to the diet. Gradually, as the state of health improves, the patient returns to a moderate diet.
To prevent a recurrence of pancreatitis, it is recommended to permanently exclude or minimize the consumption of:
- alcoholic beverages from the diet;
- spicy and salty;
- fried foods;
- sodas;
- marinades;
- fresh juices;
- products with a high content of essential oils and extractives: broths, coffee, cocoa, etc.
Vitamin therapy
Gastroenterologists consider taking vitamins essential in the treatment of pancreatitis. During an exacerbation, their use is not recommended to prevent excessive stress on the pancreas. In the remission phase, the intake is indicated:
During an exacerbation, their use is not recommended to prevent excessive stress on the pancreas. In the remission phase, the intake is indicated:
- vitamin A – accelerates tissue regeneration and enhances immune protection;
- vitamins of group B (B1, B2, B3, B6, B12) – improve tissue trophism, increase the elasticity of blood vessels, normalize metabolism;
- vitamin C – protects the pancreas from the negative effects of free radicals;
- vitamin E – restores damaged cells of the body, increases blood flow.
First aid for an attack
Most often, patients with pancreatitis ask themselves: “How to remove an attack?”. During an exacerbation of the pathology, there is a violation of digestion and severe, sometimes unbearable pain. Before the provision of qualified medical care, several manipulations can be carried out that will help improve well-being:
- Apply a cold compress or ice pack to the epigastric region.

- Lie on your side and bring your legs close to your sternum.
- Trying to induce vomiting may provide some relief.
- Do not take any food or drink. Only clean water is allowed to drink.
- Take an antispasmodic.
If the condition does not improve within an hour, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Possible complications
In the absence of treatment and non-compliance with medical recommendations, pancreatitis is complicated by the following severe pathologies:
- purulent inflammation of the pancreas;
- pancreatic necrosis;
- inflammation of the abdomen and peritonitis;
- sepsis;
- anemia;
- diabetes mellitus;
- obstructive jaundice;
- gastroduodenal ulcers;
- chronic duodenal obstruction;
- cardiovascular, renal and respiratory insufficiency;
- pancreatic cancer.

Pancreatitis: symptoms, treatment and prevention of inflammation of the pancreas
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. At the first signs of pancreatitis, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
Pancreatitis diagnosis
True (primary) pancreatitis is a very rare diagnosis. Its cause in most cases is alcohol abuse. Frequent alcohol intake causes dysmotility in the sphincter of Oddi, because of this, protein plugs form in the pancreatic ducts, the outflow of enzymes is disturbed and there is pressure of the pancreatic juice on the tissues of the gland itself. This causes pain and inflammation. Long-term use of a large number of drugs is also a fairly common cause of pancreatitis. Systematic malnutrition, alcohol, frequent stress and hormonal disorders can also provoke the disease.
More common is secondary (reactive) pancreatitis, which occurs against the background of disorders in the gastrointestinal tract. The main reason for the development of secondary pancreatitis is problems with the gallbladder (for example, cholecystitis – inflammation of the gallbladder, gallstone disease, postcholecystectomy syndrome, bile duct dyskinesia and chronic gastroduodenitis). Thus, the development of pancreatitis is a consequence of other past diseases of the stomach and gallbladder. In children, the disease may appear after suffering viral infections and influenza. True, this happens quite rarely.
The main reason for the development of secondary pancreatitis is problems with the gallbladder (for example, cholecystitis – inflammation of the gallbladder, gallstone disease, postcholecystectomy syndrome, bile duct dyskinesia and chronic gastroduodenitis). Thus, the development of pancreatitis is a consequence of other past diseases of the stomach and gallbladder. In children, the disease may appear after suffering viral infections and influenza. True, this happens quite rarely.
Forms of pancreatitis
In addition to the above types of pancreatitis, medicine distinguishes between acute and chronic pancreatitis. Acute pancreatitis occurs suddenly. Chronic pancreatitis develops gradually and periodically makes itself felt. The chronic form of pancreatitis is dangerous in its progression and can lead to serious consequences.
Symptoms of pancreatitis
Both forms of pancreatitis are accompanied by pain, disorders of the stomach and intestines, nausea and vomiting (these are the most characteristic symptoms of pancreatitis). However, it is worth considering in more detail the symptoms of the acute and chronic forms of this disease.
However, it is worth considering in more detail the symptoms of the acute and chronic forms of this disease.
Acute pancreatitis
Characterized by a very strong pain syndrome. It is impossible to endure such pain, so the patient is immediately called an ambulance and the patient is taken to the surgical department. Pain in acute pancreatitis, the patient experiences both in the upper abdomen and in the entire circumference of the abdomen (girdle pain). There is nausea, vomiting, bloating. The patient complains of pain when probing the abdomen. Your heart rate increases and your blood pressure may drop.
Chronic pancreatitis
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis appear permanently and periodically worsen after exposure to various stimuli. A person feels a constant dull pain in the epigastrium and both hypochondria, due to a lack of enzymes for digesting food, diarrhea, bloating in the abdomen, and unstable stools may occur. During periods of exacerbation of pancreatitis, the patient should follow the instructions of his doctor or contact the ambulance service.
Constipation in pancreatitis
Reactive inflammation may cause constipation. But its cause is not the disease itself, but a violation of the outflow of bile. You need to treat constipation, but first you need to eliminate the root cause.
Treatment of pancreatitis in adults
In the chronic form, antispasmodics are prescribed that improve the outflow of enzymes, antisecretory drugs that relieve the inflammatory process, and replacement therapy. If 90% of the pancreas does not work, enzyme preparations are prescribed. In the acute form of the disease, treatment can be described in three words: hunger, cold and rest. You need to stick to this regimen for three days. In addition, the patient is given a dropper with antispasmodics and a drug that reduces secretion. In case of necrosis of the pancreas, surgical intervention is necessary.
Can pancreatitis be cured?
Acute pancreatitis can end with only one attack, chronic pancreatitis cannot be completely cured, but remission can be achieved. To do this, it is necessary to take medications on time, take tests (blood, feces for a coprogram, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, CT and MRI), engage in prevention, and follow a diet.
To do this, it is necessary to take medications on time, take tests (blood, feces for a coprogram, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, CT and MRI), engage in prevention, and follow a diet.
Diet for pancreatitis
All patients are concerned about the question: what do they eat with pancreatitis – inflammation of the pancreas?
In the chronic course of the disease, a very strict diet must be observed throughout life, since its violation can provoke an exacerbation. During periods of remission, it expands a little, but you still have to constantly monitor nutrition. The patient’s diet should include a large amount of fruits and vegetables, fatty and spicy foods should be avoided in the diet, it is recommended to take additional enzymes to facilitate digestion, and also monitor blood sugar levels.
Can I drink alcohol?
Prolonged and regular consumption of alcohol is unacceptable. On holidays, you can afford to drink a little.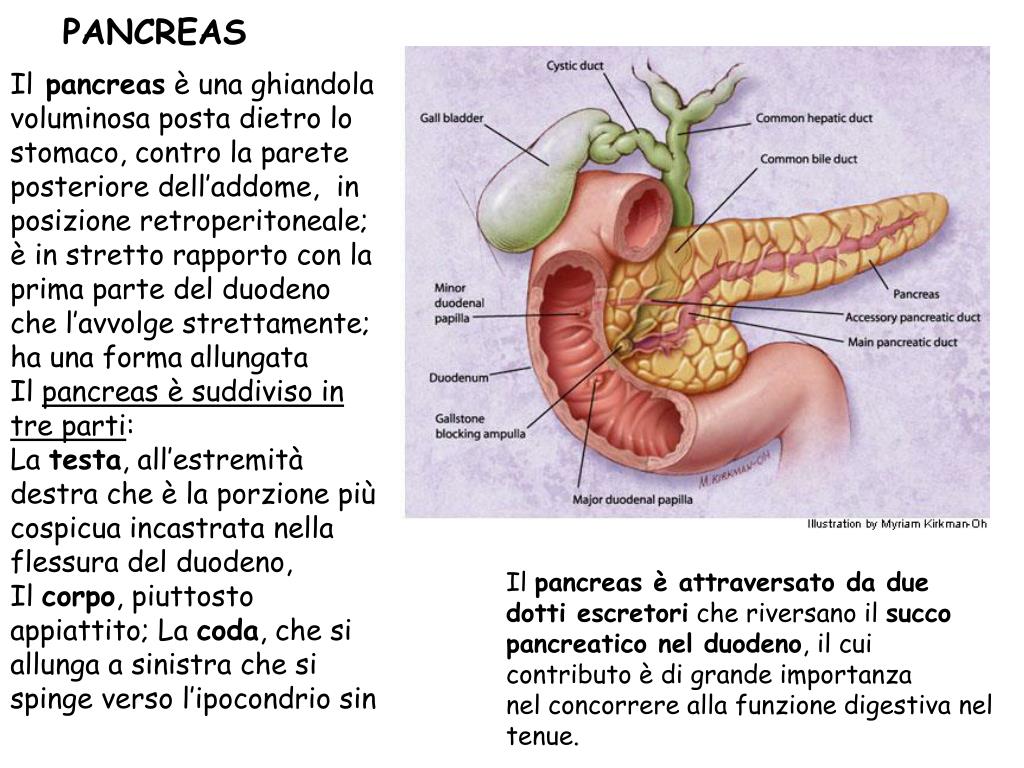


 ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19390402/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19390402/ bmj.com/content/45/2/311
bmj.com/content/45/2/311  ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6017764/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6017764/  10379
10379 




