Gallstones symptoms in men. Gallstones in Men: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
What are the common symptoms of gallstones in men. How are gallstones diagnosed and treated. What factors increase the risk of developing gallstones. What dietary changes can help prevent gallstone formation.
Understanding Gallstones: Formation and Types
Gallstones are crystal-like deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. These stones develop due to an imbalance in the chemical composition of bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. When cholesterol or bilirubin levels in the bile become too high, they can crystallize and form stones.
There are two main types of gallstones:
- Cholesterol gallstones: These account for the majority of gallstones and form when there’s an excess of cholesterol in the bile or insufficient bile salts.
- Pigment gallstones: These are composed of calcium and bilirubin, typically forming in individuals with certain blood or liver disorders.
Gallstones can vary significantly in size, ranging from tiny crystals to large stones measuring several centimeters in diameter. While some individuals may develop a single large stone, others might have hundreds of smaller ones.
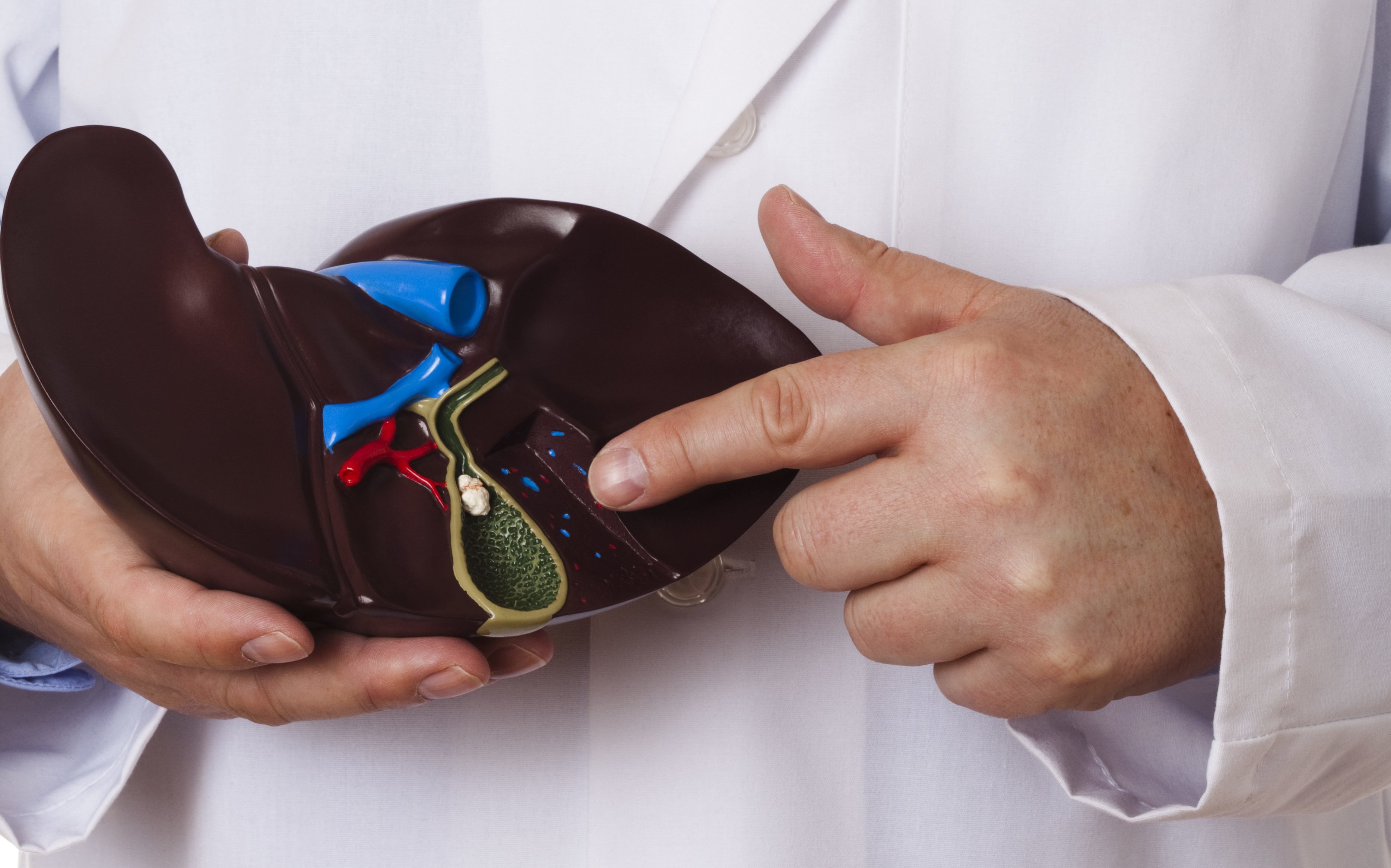
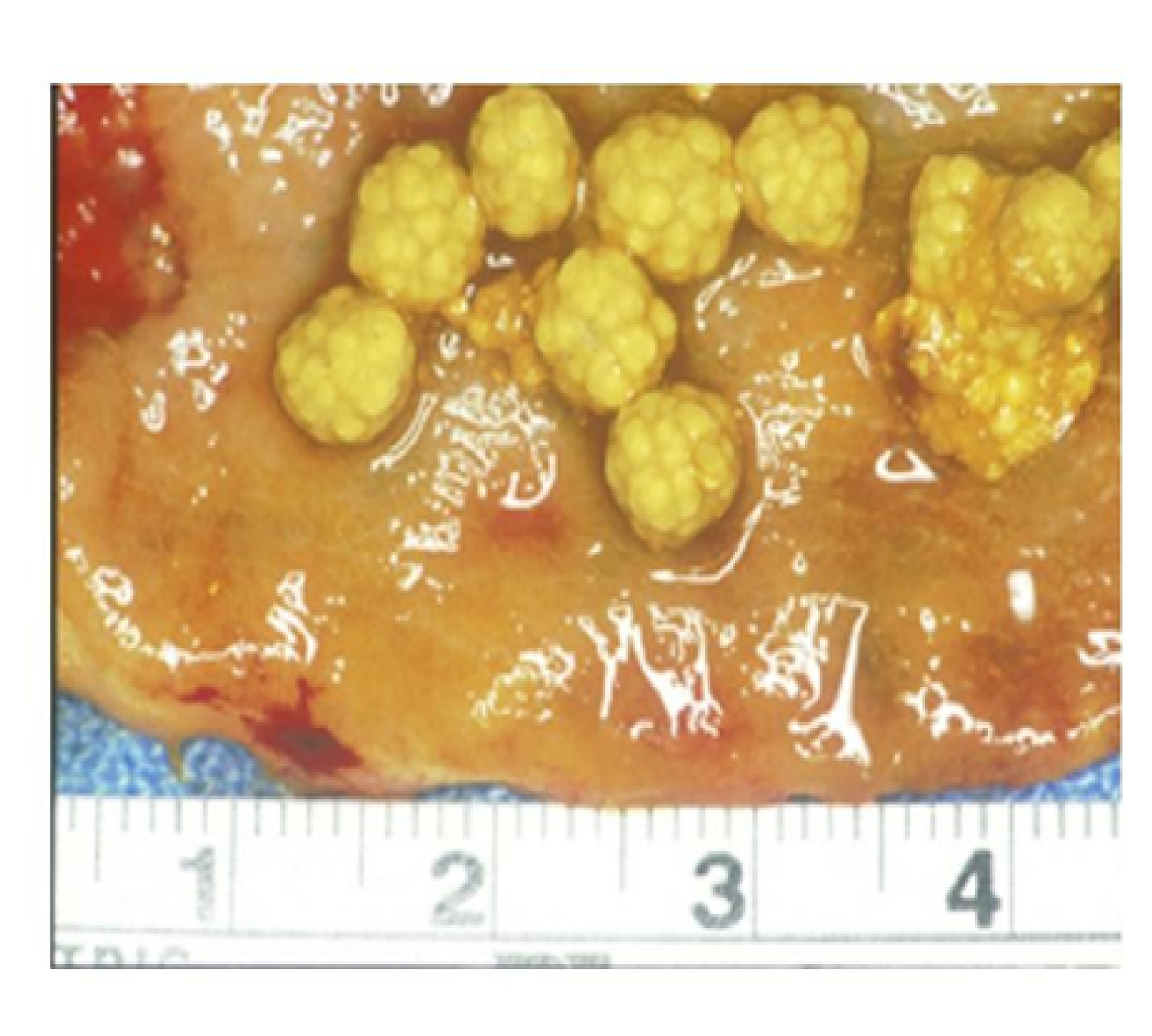
Recognizing Gallstone Symptoms in Men
Many men with gallstones remain asymptomatic, but when symptoms do occur, they can be quite uncomfortable. The most common early sign of gallstones in men is upper abdominal pain, typically localized in the upper right quadrant. This pain, known as biliary colic, can be sudden and severe, often radiating to the chest, back, or between the shoulders.
Other symptoms that men with gallstones may experience include:
- Indigestion
- Nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Light-colored stools
- Low-grade fever, sweats, and chills (if infection is present)
How can men distinguish gallstone pain from other abdominal discomfort? Gallstone pain often occurs after consuming fatty foods and may wake you up in the middle of the night. The intensity of the pain can be so severe that it prompts immediate medical attention.
Risk Factors for Gallstone Development in Men
While gallstones are more common in women, men are not immune to this condition. Several factors can increase a man’s risk of developing gallstones:
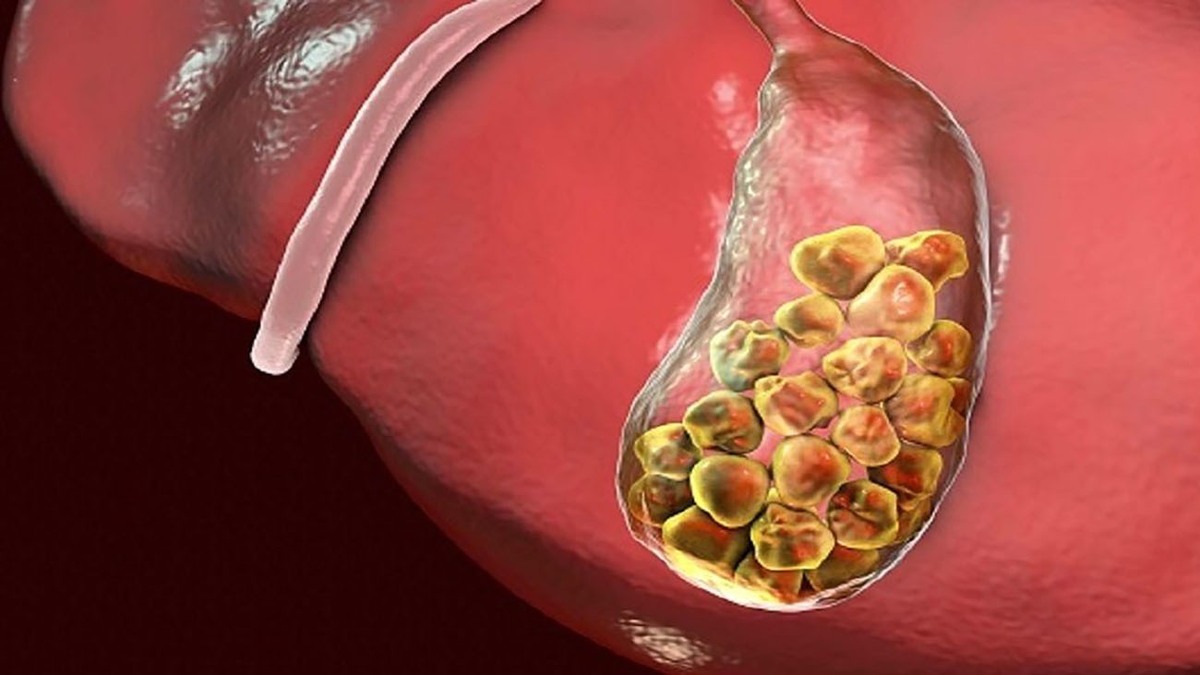
- Age: The risk increases after 40 years
- Ethnicity: Men of European descent are at higher risk compared to Maori, Pacific, or Asian men
- Obesity: Particularly when excess weight is carried around the waist
- Diet: High-fat, low-fiber diets contribute to gallstone formation
- Medical conditions: Diabetes and high blood cholesterol levels increase risk
- Lifestyle factors: Heavy drinking and smoking
- Family history: Genetic predisposition plays a role
Understanding these risk factors can help men take proactive steps to reduce their likelihood of developing gallstones. But how can men effectively mitigate these risks?
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
While some risk factors, such as age and genetics, cannot be modified, there are several lifestyle changes men can adopt to reduce their risk of gallstone formation:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Gradual weight loss can help prevent gallstone development
- Adopt a balanced diet: Increase fiber intake and reduce consumption of high-fat foods
- Stay hydrated: Adequate water intake helps maintain proper bile consistency
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity can help prevent gallstone formation
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive drinking can increase the risk of gallstones
- Quit smoking: Smoking is associated with a higher risk of gallstone development
Implementing these changes can significantly reduce the risk of gallstone formation in men. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before making drastic lifestyle changes, especially if you have existing health conditions.
Diagnostic Procedures for Gallstones
When gallstones are suspected, accurate diagnosis is crucial for appropriate treatment. Healthcare providers employ various diagnostic tools to confirm the presence of gallstones and assess their impact on the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
Common Diagnostic Tests
- Abdominal Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging technique is the most common method for diagnosing gallstones. It uses sound waves to create pictures of the gallbladder, allowing doctors to identify the presence and size of stones.
- Blood Tests: These help assess liver and pancreas function and rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): This procedure can detect smaller stones that might be missed by an abdominal ultrasound. It involves passing a thin, flexible tube through the mouth and into the digestive tract to provide detailed images of the gallbladder and nearby tissues.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): This test is used when gallstones are suspected to be blocking the ducts. It combines endoscopy with X-ray imaging to examine the bile ducts.
How accurate are these diagnostic procedures? While abdominal ultrasound is highly effective in detecting gallstones, its accuracy can be affected by factors such as obesity or the location of the stones. In such cases, additional tests like EUS or ERCP may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis.

Treatment Options for Gallstones in Men
The treatment approach for gallstones in men depends on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s overall health. Options range from watchful waiting to surgical intervention.
Conservative Management
For men with asymptomatic gallstones or mild symptoms, a wait-and-see approach may be recommended. This involves monitoring the condition and making lifestyle changes to prevent complications.
Medical Treatments
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers can help manage discomfort during gallstone attacks.
- Bile Acid Pills: In some cases, medications that dissolve small cholesterol stones may be prescribed. However, this treatment can take months or years to be effective and is not suitable for all types of gallstones.
Surgical Interventions
For men with recurrent or severe symptoms, surgery is often the recommended treatment:
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: This minimally invasive procedure involves removing the gallbladder through small incisions in the abdomen. It’s the most common and effective treatment for gallstones.
- Open Cholecystectomy: In some cases, a traditional open surgery may be necessary, especially if there are complications or the patient has had previous abdominal surgeries.
What are the potential risks and benefits of gallbladder surgery? While cholecystectomy is generally safe and effective, like any surgery, it carries some risks. These may include infection, bleeding, or injury to nearby organs. However, the benefits of relieving symptoms and preventing future gallstone-related complications often outweigh the risks for most patients.

Living Without a Gallbladder: Post-Surgery Adjustments
After gallbladder removal, most men can lead normal, healthy lives without significant changes. The liver continues to produce bile, which flows directly into the small intestine to aid digestion. However, some individuals may need to make dietary adjustments to manage potential side effects.
Dietary Considerations Post-Cholecystectomy
- Gradual Diet Reintroduction: Start with clear liquids and gradually introduce solid foods as tolerated.
- Low-Fat Diet: Initially, a low-fat diet may help reduce digestive discomfort.
- Fiber Intake: Increasing fiber consumption can help normalize bowel movements.
- Small, Frequent Meals: Eating smaller portions more frequently throughout the day can ease digestion.
How long does it take to adjust to life without a gallbladder? Most men adapt within a few weeks to months after surgery. However, some individuals may experience ongoing digestive changes, such as looser stools or more frequent bowel movements. If these symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
Emerging Research and Future Treatments
As medical science advances, researchers continue to explore new ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat gallstones. Some areas of ongoing research include:
- Genetic Factors: Studies are investigating the genetic components that may predispose individuals to gallstone formation.
- Non-Invasive Treatments: Researchers are exploring less invasive methods to break down or remove gallstones without surgery.
- Preventive Strategies: New approaches to prevent gallstone formation in high-risk individuals are being developed.
- Improved Imaging Techniques: Advancements in imaging technology may lead to earlier and more accurate detection of gallstones.
What promising treatments are on the horizon for gallstone management? While still in experimental stages, techniques such as shock wave lithotripsy (using sound waves to break up stones) and dissolving agents delivered directly to the gallbladder show potential for treating certain types of gallstones without surgery.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Gallstones-symptoms1-5ace3c12ba617700366abe5f.png)
As research progresses, men with gallstones or those at risk may have access to more targeted and less invasive treatment options in the future. However, it’s important to note that these emerging treatments are still under investigation and may not be suitable for all patients.
Gallstones in Special Populations
While this article focuses on gallstones in men, it’s worth noting that certain populations may have unique considerations when it comes to gallstone development and treatment.
Elderly Men
Older men are at increased risk of developing gallstones due to age-related changes in bile composition and gallbladder function. They may also be more likely to experience complications from gallstones.
Men with Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome, characterized by obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, is associated with an increased risk of gallstone formation in men.
Athletes and Physically Active Men
Rapid weight loss, which can occur in athletes or men on extreme diets, may increase the risk of gallstone formation. Conversely, regular physical activity can help prevent gallstones.

How do treatment approaches differ for these special populations? Treatment strategies may need to be tailored based on the individual’s overall health status, age, and specific risk factors. For example, elderly men or those with multiple health conditions may require a more conservative approach to treatment, weighing the risks and benefits of surgery carefully.
Complementary and Alternative Approaches
While conventional medical treatments remain the primary approach for managing gallstones, some men may be interested in complementary or alternative therapies. It’s important to note that these approaches should not replace medical advice or treatment but may be used in conjunction with conventional care under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Herbal Remedies
Some herbs have been traditionally used to support gallbladder health:
- Milk Thistle: May help protect liver cells and support bile production
- Dandelion Root: Believed to stimulate bile flow
- Artichoke Leaf: May help improve bile production and flow
Acupuncture
Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help relieve gallstone-related pain and improve gallbladder function. However, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness.

Gallbladder Flush
Some alternative health practitioners recommend “gallbladder flushes” or “liver cleanses” to help pass gallstones. These typically involve drinking large quantities of olive oil and citrus juices. However, there is limited scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of these methods, and they may carry risks.
Are these alternative approaches safe and effective for managing gallstones? While some men may find relief from complementary therapies, it’s crucial to approach these methods with caution. Many alternative treatments lack robust scientific evidence, and some may even be harmful. Always consult with a healthcare provider before trying any alternative treatments for gallstones.
The Importance of Early Detection and Management
Early detection and proper management of gallstones can significantly improve outcomes for men affected by this condition. Regular health check-ups, especially for those with known risk factors, can help identify gallstones before they cause severe symptoms or complications.
Benefits of Early Detection
- Prevention of Complications: Early intervention can prevent serious complications such as acute cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) or pancreatitis.
- More Treatment Options: Catching gallstones early may provide a wider range of treatment options, including non-surgical approaches.
- Improved Quality of Life: Addressing gallstone issues promptly can prevent chronic pain and discomfort, improving overall quality of life.
Long-Term Management Strategies
For men diagnosed with gallstones, long-term management may involve:
- Regular Monitoring: Periodic check-ups and imaging studies to track the progression of asymptomatic gallstones.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy diet and weight to prevent the formation of new stones or growth of existing ones.
- Symptom Management: Developing strategies to manage mild symptoms and recognize when medical attention is necessary.
- Ongoing Education: Staying informed about new developments in gallstone treatment and prevention.
How can men take a proactive approach to gallstone prevention and management? By understanding their risk factors, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and maintaining regular communication with their healthcare providers, men can play an active role in preventing gallstone formation and managing existing gallstones effectively.

In conclusion, while gallstones can be a painful and disruptive condition for men, understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options can lead to better outcomes. Whether through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, or surgical procedures, there are numerous ways to address gallstone issues and maintain optimal gallbladder health. As research continues to advance our understanding of this condition, men can look forward to even more effective and personalized approaches to gallstone prevention and treatment in the future.
Gallstones – symptoms, causes and treatment
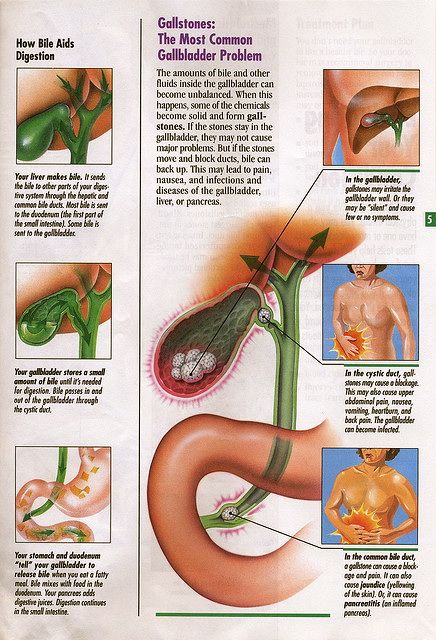
Gallstones are crystal-like deposits that form in the gallbladder – a small organ under the liver that stores bile (a fluid used by the digestive system).
The stones may stay in the gallbladder and cause no symptoms, or they may irritate the gallbladder wall or block gallbladder ducts, resulting in infection, inflammation and upper abdominal pain. It is possible for the infection to spread to the liver or pancreas. Treatment can range from pain relief to surgery.
In New Zealand, the proportion of the population with gallstones may be as high as 20%.
Causes
The gallbladder is part of the digestive system. It is a pear-shaped, sac-like structure approximately 8 cm long and 2.5 cm wide, located alongside the stomach and attached to the lower surface of the liver. The function of the gallbladder is to concentrate, store, and excrete bile ( a fluid that helps in the digestion of fat).
gastrointestinal tract gallbladder
Bile has several components including cholesterol, bile salts, and bile pigments (eg: bilirubin). Gallstones are thought to develop because of an imbalance in the chemical composition of bile inside the gallbladder, such as when the levels of cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile become too high. The excess cholesterol or bile forms crystals, which eventually form stones.
Gallstones are thought to develop because of an imbalance in the chemical composition of bile inside the gallbladder, such as when the levels of cholesterol or bilirubin in the bile become too high. The excess cholesterol or bile forms crystals, which eventually form stones.
The two main types of gallstones are:
- Cholesterol gallstones: The majority of all gallstones are cholesterol stones. The amount of cholesterol that can dissolve in bile depends on how much bile salt it contains. Too much cholesterol, or too little bile salt, tends to cause cholesterol stones to form in the gallbladder.
- Pigment gallstones: These stones are formed by calcium and bilirubin when there is an excess of bilirubin in the gallbladder. Pigment stones tend to form in patients with certain blood or liver disorders.
Risk factors
The risk of developing gallstones tends to increase with age (especially after age 40 years) and they’re more common among people of European ethnicity than Maori, Pacific or Asian New Zealanders.
Women develop gallstones more commonly than men and at a younger age, and there is frequently a family history of the disease.
Other factors that increase the risk of developing gallstones include:
- Being overweight or obese – particularly when the extra weight is carried around the waist
- Eating a high-fat, low-fibre diet
- Having diabetes
- Having high blood cholesterol levels
- Heavy drinking
- Smoking.
As pregnancy and contraceptive pills can slow down gallbladder activity, women who have had multiple pregnancies or long-term contraceptive pill use are at higher risk of developing gallstones.
Signs and symptoms
Gallstones vary greatly in size. Some people may form one large stone, whereas others may have hundreds of tiny stones. Most commonly, gallstones are 5–10 mm in diameter.
Most people with gallstones do not experience any symptoms. If symptoms are present, the most common early sign of gallstones is upper abdominal pain. This pain usually occurs in the upper right side of the abdomen, is often sudden and severe, and may radiate to the chest, back, or the area between the shoulders. Other symptoms that may occur include:
This pain usually occurs in the upper right side of the abdomen, is often sudden and severe, and may radiate to the chest, back, or the area between the shoulders. Other symptoms that may occur include:
- Indigestion
- Nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice (the yellow appearance of skin and the whites of eyes caused by bilirubin build-up in the blood) when gallstones block the passage of bile
- Light-coloured stools.
The abdominal pain associated with gallstones is referred to as biliary colic. This type of pain is commonly set off by eating fatty foods and often occurs in the middle of the night. The symptoms experienced may be so severe that people need to seek immediate medical attention.
When infection of the gallbladder is present it is possible to also experience low-grade fever, sweats, and chills.
Diagnosis
If gallstones are suspected, it is important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. The doctor will look for signs of jaundice and will assess the abdomen for swelling and pain. Blood tests are usually performed to check the function of the liver and pancreas and to rule out other conditions that may be causing the symptoms.
The doctor will look for signs of jaundice and will assess the abdomen for swelling and pain. Blood tests are usually performed to check the function of the liver and pancreas and to rule out other conditions that may be causing the symptoms.
The most common test used to definitively diagnose gallstones is an abdominal ultrasound scan to create pictures of the gallbladder, which are then analysed to look for signs of gallstones.
An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a procedure that can help identify smaller stones that may be missed by an abdominal ultrasound. A thin, flexible tube (endoscope) is passed through the mouth and into the digestive tract, to provide a precise image of the gallbladder and nearby tissues.
If it is suspected that gallstones are blocking the ducts, then a test called endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) may be performed. This test involves inserting an endoscope with a light and camera at its tip through the mouth into the digestive tract. A special dye is injected through the endoscope into the bile ducts allowing the outline of the ducts to be highlighted. Gallstones found in the ducts can sometimes be removed during the ERCP procedure.
A special dye is injected through the endoscope into the bile ducts allowing the outline of the ducts to be highlighted. Gallstones found in the ducts can sometimes be removed during the ERCP procedure.
Other specialised scans or x-rays are sometimes used to confirm the diagnosis and highlight the location of the gallstones.
Treatment
In general, treatment will depend on the frequency and severity of the symptoms experienced. Because it is possible that people who experience biliary colic will not experience a further episode, your doctor may advise a wait and see approach.
If attacks are occasional and mild, they may be able to be managed with pain-relieving medications, applying heat to the affected area, resting and taking sips of water. Reducing the amount of fat in your diet and maintaining a healthy body weight may also be beneficial. If attacks are frequent or severe surgery is usually recommended.
Surgery
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder and is a common and routine procedure. It may be recommended when the symptoms of gallstones are problematic. If there is infection or acute inflammation of the gallbladder, this may need to be treated with antibiotics before the gallbladder can be removed.
It may be recommended when the symptoms of gallstones are problematic. If there is infection or acute inflammation of the gallbladder, this may need to be treated with antibiotics before the gallbladder can be removed.
The gallbladder is not essential to live or to digest food. When the gallbladder is removed, bile is still produced by the liver and flows directly into the small intestine.
The two cholecystectomy techniques are:
Open cholecystectomy
This is the “traditional” but now-a-days less common surgical technique for removing the gallbladder and is performed under a general anaesthetic. A single incision is made below the rib cage. Through the incision, the surgeon can view the area and remove the gallbladder.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is also performed under general anaesthetic but is less invasive and much more commonly used than the open cholecystectomy technique. It has a faster recovery time and a shorter hospital stay (usually just one night). A telescope-like instrument (a laparoscope) is inserted through one incision (allowing the surgeon to view the inside of the abdominal cavity on a television monitor) and surgical instruments are inserted through other incisions. The gallbladder is located and removed through an incision in the belly button.
A telescope-like instrument (a laparoscope) is inserted through one incision (allowing the surgeon to view the inside of the abdominal cavity on a television monitor) and surgical instruments are inserted through other incisions. The gallbladder is located and removed through an incision in the belly button.
Surgery risks and complications
As with any surgery, there are possible risks and complications which you should discuss with your doctor before surgery. These include:
- Anaesthetic complications
- Bleeding
- Wound infection
- Injury to or leakage from the bile duct
- Discomfort or numbness around the area of incision
- Jaundice.
Medication
For small gallstones that don’t contain calcium, it may be possible to dissolve them by taking ursodeoxycholic acid tablets. However, ursodeoxycholic acid tablets are not often recommended because they are not always effective, need to be taken for a long time (up to 2 years), and gallstones are likely to form again once treatment is stopped. They are usually used for people who are unable to undergo surgery. Occasionally, they may be used to prevent gallstones in people at high risk of developing them.
They are usually used for people who are unable to undergo surgery. Occasionally, they may be used to prevent gallstones in people at high risk of developing them.
References
Chapman, B.A., et al. (2003). Gallstone prevalence in Christchurch: risk factors and clinical significance. N Z Med J. 2000;113(1104):46–8.
Mayo Clinic (2019). Gallstones (Web Page). Rochester, MN: Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/symptoms-causes/syc-20354214 [Accessed: 23/08/19]
NHS (2015). Gallstones (Web Page). Redditch: National Health Service (NHS)
England. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gallstones/ [Accessed: 23/08/19]
O’Toole, M.T. (Ed.) (2017). Cholelithiasis. Mosby’s Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing & Health Professions (10th ed.). St Louis: Elsevier.
O’Toole, M.T. (Ed.) (2017). Choledocholithiasis. Mosby’s Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing & Health Professions (10th ed.). St Louis: Elsevier.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Gallstones-diagnosis1-5ace3c853418c60037cd56c2.png)
Stringer, M.D., et al. (2013). Gallstones in New Zealand: composition, risk factors and ethnic differences. ANZ J Surg. 2013 Jul;83(7-8):575–80.
Last Reviewed – September 2019
Go to our Medical Library Index Page to find information on other medical conditions.
Gallstones symptoms – causes and treatment
Time for an anatomy pop quiz: Do you know where your gallbladder is?
This small, pear-shaped organ is located beneath your liver on the right side of your abdomen. Its primary function is to hold bile, a fluid produced by the liver that’s released into your small intestines to help you digest fatty foods. Sometimes, hard deposits called gallstones can build up in your gallbladder.
What Are Gallstones?
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive material. They can be as small as a grain of sand, the size of a pebble or even as large as a golf ball. Two main types exist: cholesterol stones, which are made of hardened cholesterol, and pigment stones, which are made of bilirubin (an orange-yellow compound produced during the normal breakdown of red blood cells).
Gallstones are relatively common, affecting about 10 to 15 percent of the U.S. population according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. The medical term for gallstones is cholelithiasis.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Someone can have gallstones and be symptom free, or gallstone symptoms can be similar to that of other problems, so it’s important to consult with a medical doctor to determine if you have gallstones.
The most commonly reported symptoms of gallstones include:
- Sudden, severe pain in the upper right stomach or in the center of your stomach just beneath your breastbone (sternum)
- Pain between the shoulder blades, or your right shoulder
- Indigestion, nausea or vomiting
Common Causes of Gallstones
Our medical and research team at SIU Medicine is on the frontline when it comes to determining what causes gallstones and why certain people develop them. It’s thought that if your bile contains too much cholesterol or bilirubin, or if something prevents your gallbladder from properly emptying, then gallstones are more likely to occur.
It’s thought that if your bile contains too much cholesterol or bilirubin, or if something prevents your gallbladder from properly emptying, then gallstones are more likely to occur.
We also know that certain people may be more likely to develop gallstones, including people who are:
- Overweight
- Older than 40
- Of Native American, Hispanic, or Mexican origin
- Sedentary
- Pregnant
- Taking medications containing estrogen, such as oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy
- Losing weight quickly
Having a family history of gallstones or certain underlying health conditions including diabetes, liver disease or blood disorders may also increase the risk of gallstones. Nutrition may affect gallstone development, too, such as eating a diet high in cholesterol and fat but low in fiber.
Gallstones are diagnosed using a combination of tests and techniques, including blood tests and imaging studies like abdominal ultrasounds.
How to Prevent and Manage Gallstones
Staying active, eating plenty of fiber-rich foods and maintaining a healthy weight are some of the best things you can do to avoid gallstones. But if you already have gallstones, and they are causing uncomfortable symptoms, you might be eligible for gallbladder removal surgery, called cholecystectomy. Cholecystectomy is a simple procedure that can often times be done laparoscopically. Without a gallbladder, your bile will simply flow directly from your liver into your small intestines.
Gallstones can also be treated with medications, although surgery is generally the more effective intervention.
Could Your Symptoms Be Due to Gallstones?
If you have severe pain or vomiting that you feel may be related to gallstones or you’re experiencing symptoms of an infection, please go to your nearest ER or call 911. Signs of a possible infection include:
- Abdominal pain lasting more than a few hours
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever—even a low-grade fever—or chills
- Yellowish color of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Tea-colored urine and light-colored stools
If you have questions or concerns about symptoms of gallstones, call SIU Medicine to connect with a physician who can help.
90,000 symptoms, treatment. What causes stones in the gallbladder?
The disease ranks third in prevalence after cardiovascular and endocrine pathologies. The disease is more often diagnosed in women.
Gallbladder stones: causes and mechanism of disease development
Stones in the gallbladder and bile ducts are formed due to a violation of the process of metabolism of bile components. Pathology develops with the simultaneous presence of the following factors: the production of lithogenic bile (oversaturated with cholesterol), an imbalance between the activity of pronucleating and antinucleating components, and a decrease in the contractile function of the gallbladder.
Among the main causes of gallstone disease are:
- hereditary factor;
- overweight;
- dramatic weight loss;
- eating foods high in cholesterol and low in fiber;
- inflammatory processes and biliary dyskinesia;
- taking oral contraceptives;
- malabsorption syndrome;
- disorders in the work of the endocrine system;
- Crohn’s disease;
- liver diseases.

Also, the disease can develop during pregnancy.
There are 2 main mechanisms for the development of the process of formation of stones in the gallbladder: vesicoinflammatory and hepatometabolic. The first variant develops against the background of an inflammatory process, leading to a violation of the acid-base balance of bile and a decrease in the protection of protein fractions, which causes crystallization of bilirubin. Further, the epithelium and mucus join it, which causes the formation of a calculus. In the second case, the disease develops against the background of a violation of the metabolic processes of the liver, which is often the result of existing liver diseases, unbalanced nutrition, endocrine disorders, hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of cholelithiasis
The disease develops gradually and may not manifest itself in the early stages. The average growth rate of stones is 3-5 mm per year, so the first symptoms often appear only after a few years.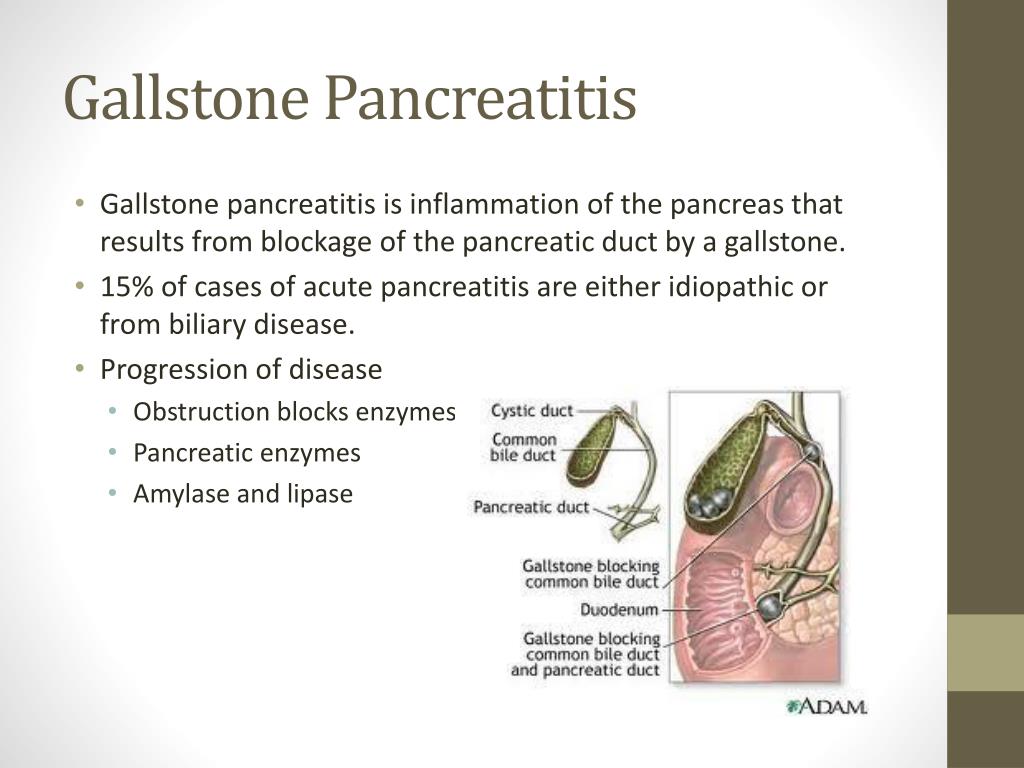
Symptoms of gallstone disease are varied and depend on the location of the stones, their size, etc. You can suspect stones in the gallbladder by the following signs:
- pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- taste of bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea;
- flatulence and other bowel disorders;
- belching of air;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
Many of these symptoms may indicate other diseases, so for an accurate diagnosis, you need to see a doctor. You can contact a general practitioner or go directly to a gastroenterologist. The main method for diagnosing cholelithiasis is ultrasound, it allows not only to confirm the diagnosis, but also to determine the exact localization of stones and their size.
Treatment of cholelithiasis
If stones are found in the gallbladder, treatment should be started immediately. Otherwise, the disease will progress and lead to complications, including: acute cholecystitis, pancreatitis, perforation of the gallbladder, stones in the intestines and the formation of intestinal obstruction.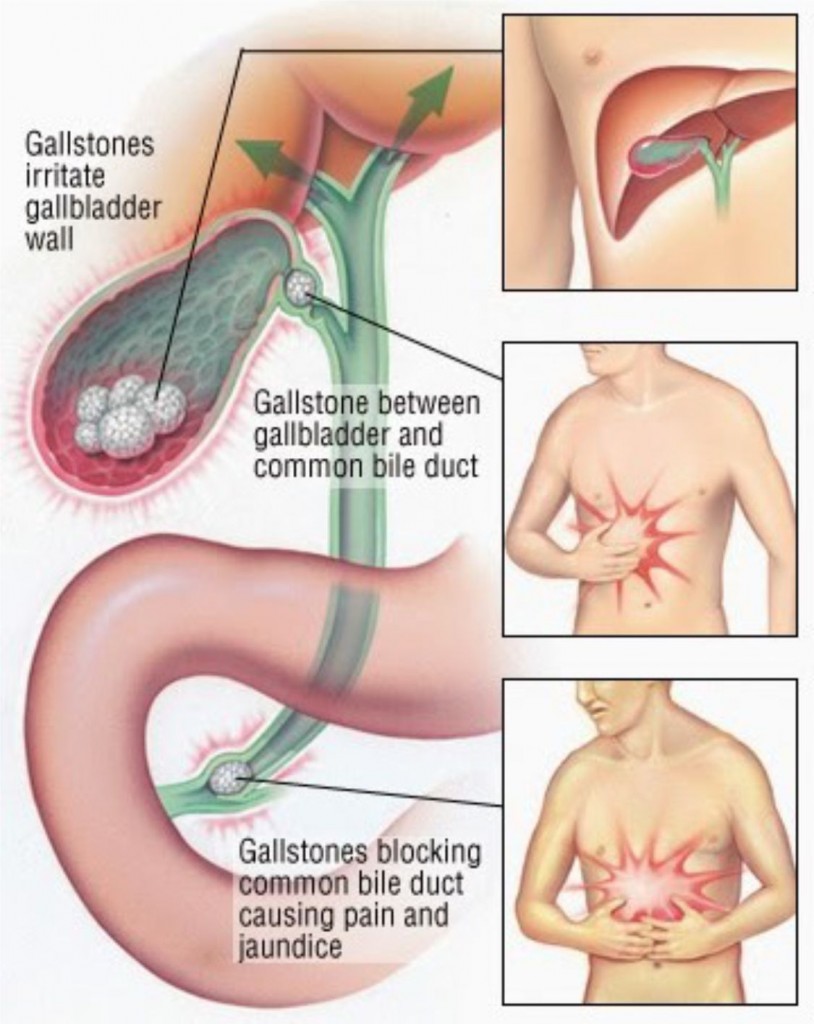 Also, over time, the disease can provoke the development of an oncological process in the gallbladder.
Also, over time, the disease can provoke the development of an oncological process in the gallbladder.
The possibilities of modern medicine make it possible to successfully treat gallstone disease. The main thing is to choose the right tactics. There are 2 main options here:
- conservative treatment;
- surgery.
Conservative treatment is aimed at dissolving stones with the help of special preparations and crushing them with the help of a laser or ultrasound. There are a number of contraindications to these methods of treatment, besides, it does not always completely solve the problem, therefore, an operation is often prescribed for stones in the gallbladder – cholecystectomy, which involves the removal of the gallbladder.
To date, most often the removal of the gallbladder is carried out by the modern laparoscopic method, since the strip operation requires a longer rehabilitation. Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia: the surgeon makes 2-4 punctures of the abdominal wall. A video endoscope with a light source is inserted into one puncture, and manipulators into the others. The whole process usually takes 1-2 hours. After that, the patient is sent to the hospital. In the absence of complications, in most cases, the patient is discharged after one or two days.
A video endoscope with a light source is inserted into one puncture, and manipulators into the others. The whole process usually takes 1-2 hours. After that, the patient is sent to the hospital. In the absence of complications, in most cases, the patient is discharged after one or two days.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy can be done at the DIALINE Surgery Center. The operation is carried out using advanced high-precision equipment, which, combined with the extensive experience of our specialists, allows us to solve the problem quickly and without consequences.
You can make an appointment with a gastroenterologist either on your own in your DIALINE personal account or by ordering a call back.
Do not delay treatment, see a doctor right now:
Stones in the gallbladder and kidneys, symptoms in men and women
Date of publication: 10/29/2021
Gastroenterologist
All authors
Article contents
- Causes of gallstones
- Types of stones
- Kidney stones: symptoms in men and women
- Therapeutic diet
- Which foods dissolve gallstones
- Gallbladder stones treatment
- Kidney stones: symptoms in women and their treatment
- Sources
- Ask an expert on the topic of the article
Gallstone disease (GSD) is a fairly common pathology. According to WHO, today it is observed in 20% of the population. The disease is manifested by the formation of solid substances in the gallbladder or ducts.
According to WHO, today it is observed in 20% of the population. The disease is manifested by the formation of solid substances in the gallbladder or ducts.
The main treatment for cholelithiasis is surgery. Some proponents of naturopathy believe that using certain foods can dissolve gallstones. Is this really so – we will tell in the article.
Causes of formation of stones in the gallbladder
Formation of calculi is associated with the composition of bile – a product of secretion of liver cells. The substance is produced in the liver, and without it, full digestion is impossible.
During the digestion of food, bile:
- breaks down fats;
- participates in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins by the body;
- disinfects food;
- takes part in enzymatic reactions.
If the digestion process does not occur, the substance accumulates in the bladder.
Bilirubin and cholesterol (Cholesterol) are one of the main components of bile juice. With an increase in cholesterol in the body, an increase in its concentration in bile is simultaneously observed. As a result, it becomes very viscous. Increased viscosity makes it difficult for bile to exit the bladder and causes it to crystallize. This is the stage of formation of “sand”, which eventually turns into stones.
With an increase in cholesterol in the body, an increase in its concentration in bile is simultaneously observed. As a result, it becomes very viscous. Increased viscosity makes it difficult for bile to exit the bladder and causes it to crystallize. This is the stage of formation of “sand”, which eventually turns into stones.
The main causes of cholelithiasis include:
- wrong food;
- treatment with certain drugs;
- alcohol abuse;
- heredity;
- overweight;
- bladder inflammation;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), cirrhosis, diabetes;
- pregnancy, multiple births.
You might be interested: How does Gilbert’s Syndrome manifest itself?
The psychosomatic component is of great importance. It has been established that more often calculous cholecystitis occurs in emotionally labile people and in those who are prone to depressive manifestations.
Types of stones
Depending on the composition, stones are distinguished:
- cholesterol – the most common type.
 They mainly consist of undissolved cholesterol. They are predominantly yellow in color;
They mainly consist of undissolved cholesterol. They are predominantly yellow in color; - bilirubin – formed when there is an excess of bilirubin in bile. Painted in dark colors – brown or black;
- mixed – they contain both cholesterol and bilirubin;
- calcareous – rich in calcium.
Kidney stones: symptoms in men and women
Very often the disease is asymptomatic. And only when the stones reach large sizes or cause blockage of the ducts, the first signs appear. In such cases, the pathology is manifested by an attack of colic.
Its symptoms:
- pain in the right side, pain often radiates under the shoulder blade and in the back;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- nausea, vomiting;
- subfebrile temperature.
When blocking the ducts, in addition to the listed symptoms, there are itching, yellowness of the skin and sclera, discoloration of feces and urine.
If discomfort occurs, lie on your right side and try to relax.:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/1999/om7q3BTtpGVima1fIuwQ_Vesica_biliaris_2.png) Often it is the state of rest that helps to relieve an attack. But even if it was possible to get rid of the pain in this way, it is necessary to consult with a gastroenterologist in the future.
Often it is the state of rest that helps to relieve an attack. But even if it was possible to get rid of the pain in this way, it is necessary to consult with a gastroenterologist in the future.
However, the symptoms are often so complex that the patient cannot independently distinguish biliary colic from a pathological process in the kidneys. In such cases, it is imperative to call an ambulance.
Therapeutic diet
Diet is an important part of the treatment process. Following the recommended menu, you can:
- improve general condition;
- reduce bile stasis;
- reduce the risk of seizures.
Low-fat meat and fish, boiled or baked vegetables, vegetable soups are useful for patients with cholelithiasis.
What Foods Dissolve Gallbladder Stones
Let’s be honest: self-administering a diet of certain foods to break down gallstones is fraught with negative health consequences. However, on many forums on the Internet you can find folk recipes and diets that include the following products:
However, on many forums on the Internet you can find folk recipes and diets that include the following products:
- Apple juice with apple cider vinegar. The acid found in apples is believed to soften stones, while vinegar controls cholesterol levels. However, in order to dissolve the stone, a person will probably have to eat only apples and drink vinegar. From such a diet, the entire gastrointestinal tract can suffer.
- Beetroot decoction. It allegedly increases the outflow of bile and thus reduces the size of the stones. In fact, the effect of it is zero.
- Lemon juice. Traditional medicine gives it the ability to dissolve stones and remove them in the form of sand. However, dietitians forbid to use it for cholelithiasis.
To avoid surgery, many patients use traditional methods. But their uncontrolled use can increase the formation of bile and the migration of formations. This will lead to blockage of the ducts and require urgent hospitalization.
Gallbladder stones treatment
Clinical guidelines for the treatment of gallstones state the following. For colic and calculous cholecystitis, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and/or antispasmodics are recommended as first aid for pain relief.
Subsequent bile acid preparations (ursodeoxycholic acid – UDCA) are recommended. They dissolve gallstones when they accumulate in the ducts. The following conditions are necessary for successful litholytic therapy:
- absence of inflammation in the biliary system;
- the size of the stone should not exceed 10 mm, or the volume of small stones should not exceed ½ the size of the gallbladder;
- treatment should be prolonged from 6 to 12 months;
- diet therapy with the exception of fried, smoked, carbonated;
- follow-up long-term maintenance therapy for prophylaxis.
If medical and dietary therapy is ineffective, patients are prescribed surgical removal of the gallbladder and ducts.

 They mainly consist of undissolved cholesterol. They are predominantly yellow in color;
They mainly consist of undissolved cholesterol. They are predominantly yellow in color;